Visual Dysfunctions in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Focus on Accommodative System Impairments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
3.1. Definition
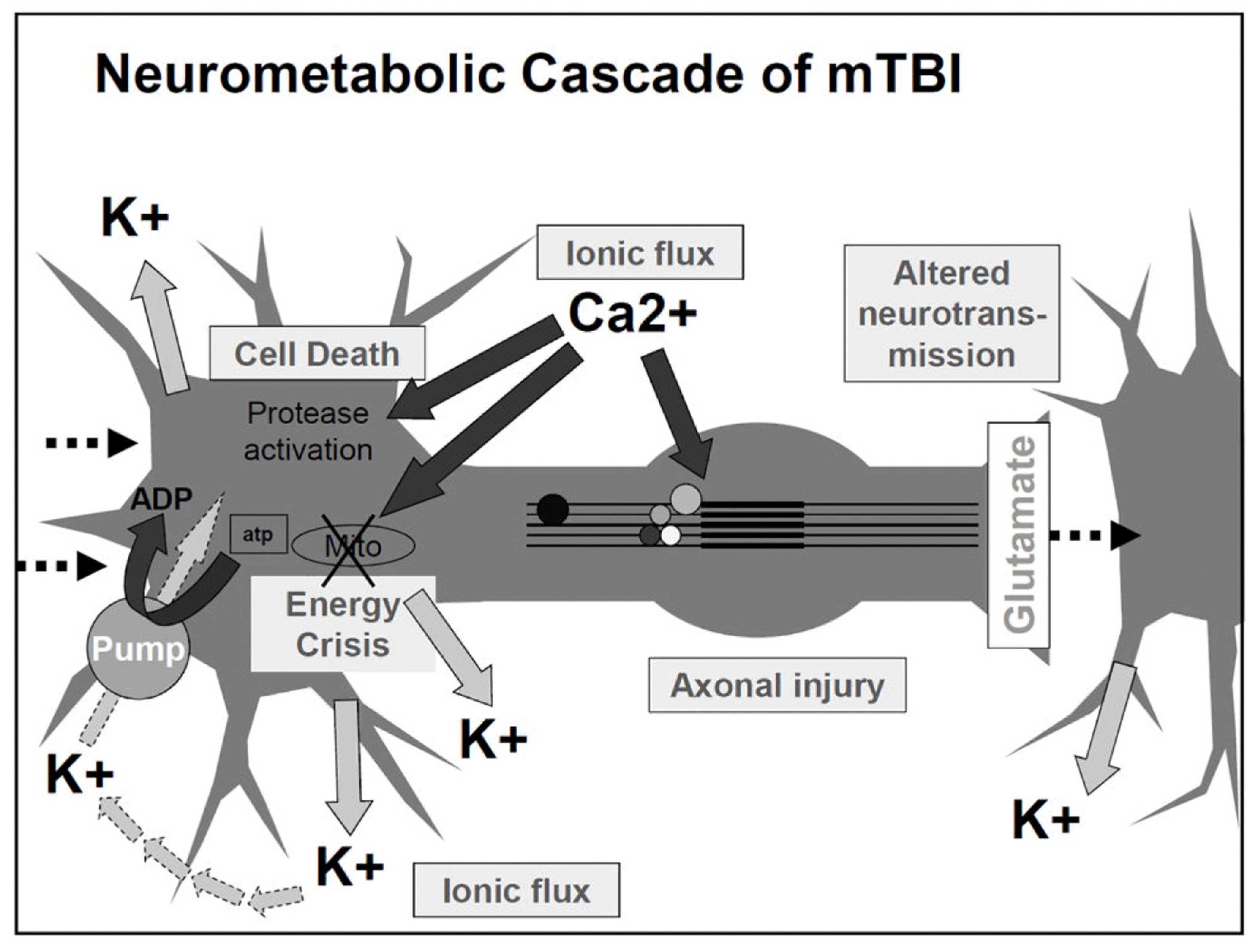
3.2. Mechanism and Neuropathology of mTBI
4. MTBI Impact on Oculomotor and Non-Oculomotor Function
4.1. MTBI General Sequalae
4.2. MTBI Impact on the Non-Oculomotor Visual System
4.3. MTBI Impact on the Oculomotor System
5. Accommodative System Control
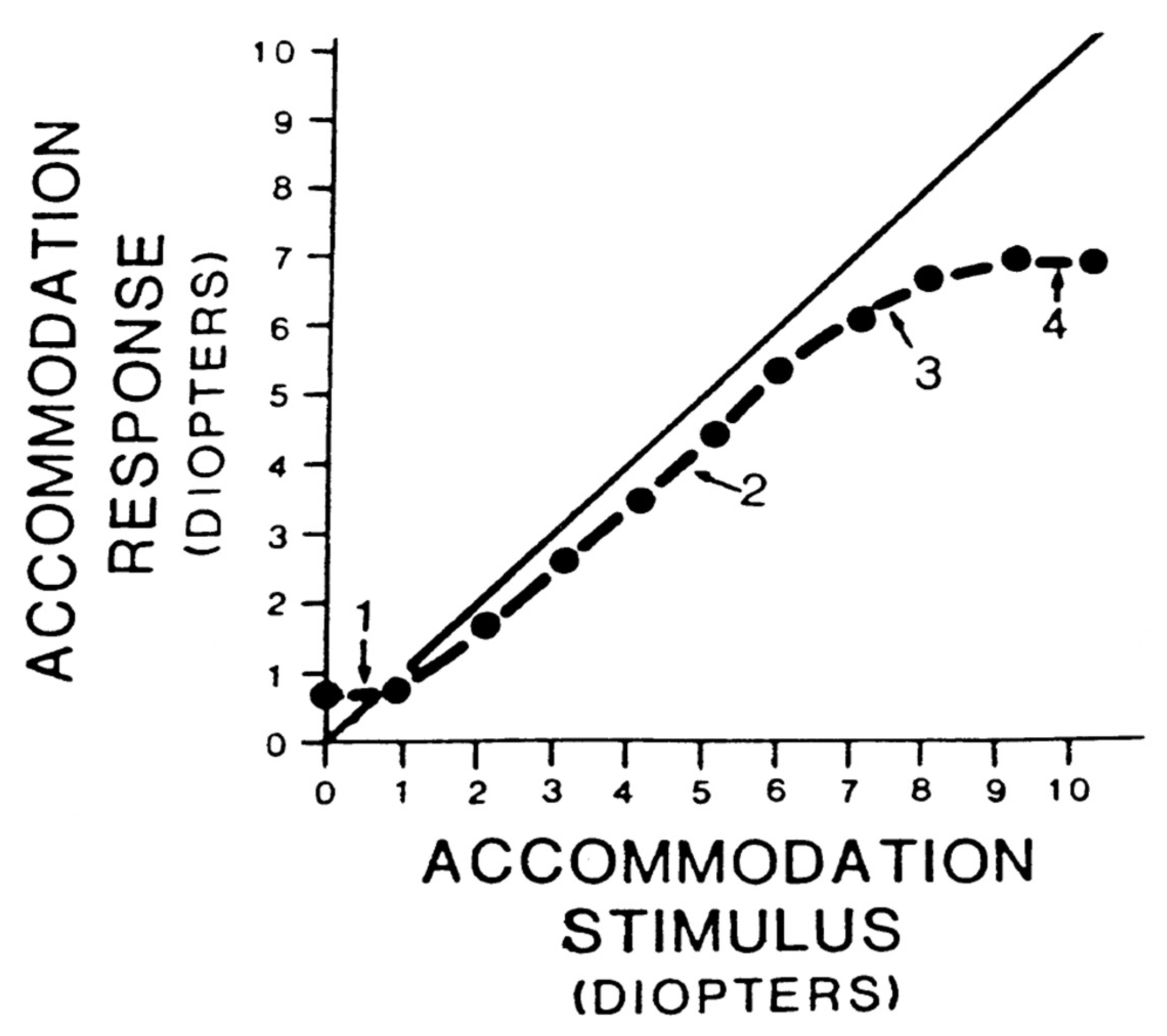
5.1. Static Accommodation
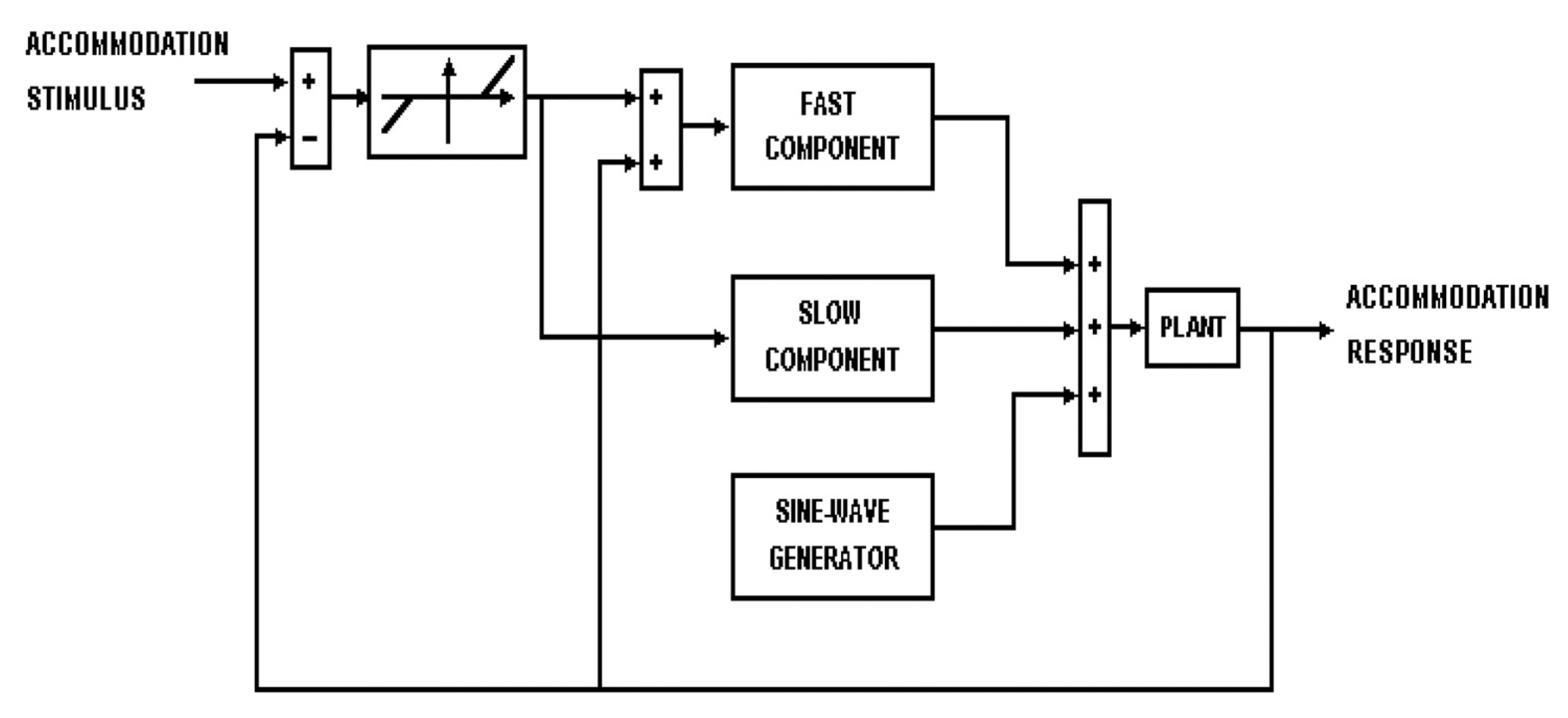
5.2. Dynamic Accommodation
6. MTBI Impact on the Accommodative System
6.1. Accommodation Model and mTBI
6.2. Clinical Implications: Using Accommodation Models to Guide Vision Therapy in mTBI
6.3. Factors Influencing Variability in Visual System Recovery After mTBI
7. Limitations
8. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruns, J., Jr.; Hauser, W.A. The Epidemiology of Traumatic Brain Injury: A Review. Epilepsia 2003, 44, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, J.; McArthur, D.; Silberman, T. Epidemiology of Mild Brain Injury. Semin. Neurol. 1994, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefevre-Dognin, C.; Cogné, M.; Perdrieau, V.; Granger, A.; Heslot, C.; Azouvi, P. Definition and epidemiology of mild traumatic brain injury. Neurochirurgie 2021, 67, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, J.D.; Connolly, J.; Schwab, K.A.; Scher, A.I. Update on the Epidemiology of Concussion/Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2015, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, C.; Geburek, A.J.; Rist, F.; Blumenroth, H.; Fischer, B.; Husstedt, I.; Arolt, V.; Schiffbauer, H.; Lohmann, H. Long-term cognitive and emotional consequences of mild traumatic brain injury. Psychol. Med. 2011, 41, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, L.; Cassidy, J.D.; Holm, L.; Kraus, J.; Coronado, V. Methodological issues and research recommendations for mild traumatic brain injury: The who collaborating centre task force on mild traumatic brain injury. J. Rehabil. Med. 2004, 36, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittl, R.L.; Grossman, R.I.; Hiehle, J.F.; Hurst, R.W.; Kauder, D.R.; Gennarelli, T.A.; Alburger, G.W. Prevalence of MR evidence of diffuse axonal injury in patients with mild head injury and normal head CT findings. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1994, 15, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Meaney, D.F.; Smith, D.H. Biomechanics of Concussion. Clin. Sports Med. 2011, 30, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhoudarian, G.; Hovda, D.A.; Giza, C.C. The Molecular Pathophysiology of Concussive Brain Injury. Clin. Sports Med. 2011, 30, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giza, C.C.; Hovda, D.A. The Neurometabolic Cascade of Concussion. J. Athl. Train. 2001, 36, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giza, C.C.; Hovda, D.A. The New Neurometabolic Cascade of Concussion. Neurosurgery 2014, 75, S24–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakase-Richardson, R.; Yablon, S.A.; Sherer, M. Prospective comparison of acute confusion severity with duration of post-traumatic amnesia in predicting employment outcome after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.A.; Koch, P.F. Disruption of Network Synchrony and Cognitive Dysfunction After Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, A.R.; Levin, H.S. Cognitive Sequelae of Traumatic Brain Injury. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, K.; Friesen, C.L.; MacKenzie, D.E.; Westwood, D.A.; Boe, S.G. Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) and chronic cognitive impairment: A scoping review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croall, I.D.; Cowie, C.J.A.; He, J.; Peel, A.; Wood, J.; Aribisala, B.S.; Mitchell, P.; Mendelow, A.D.; Smith, F.E.; Millar, D.; et al. White matter correlates of cognitive dysfunction after mild traumatic brain injury. Neurology 2014, 83, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinder, S.; Cnossen, M.C.; Real, R.G.L.; Covic, A.; Gorbunova, A.; Voormolen, D.C.; Master, C.L.; Haagsma, J.A.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; von Steinbuechel, N. A Multidimensional Approach to Post-concussion Symptoms in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancelliere, C.; Verville, L.; Stubbs, J.L.; Yu, H.; Hincapié, C.A.; Cassidy, J.D.; Wong, J.J.; Shearer, H.M.; Connell, G.; Southerst, D.; et al. Post-Concussion Symptoms and Disability in Adults With Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Neurotrauma 2023, 40, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuffreda, K.J.; Ludlam, D.P. Conceptual model of optometric vision care in mild traumatic brain injury. J. Behav. Optom. 2011, 22, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Suter, P.S.; Harvey, L.H. Vision Rehabilitation: Multidisciplinary Care of the Patient Following Brain Injury; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, J.Q.; Ciuffreda, K.J.; Han, M.H.E.; Suchoff, I.B. Photosensitivity in mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI): A retrospective analysis. Brain Inj. 2014, 28, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capó-Aponte, J.E.; Urosevich, T.G.; Temme, L.A.; Tarbett, A.K.; Sanghera, N.K. Visual Dysfunctions and Symptoms During the Subacute Stage of Blast-Induced Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Mil. Med. 2012, 177, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digre, K.B.; Brennan, K.C. Shedding Light on Photophobia. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2012, 32, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, P.A.; Taylor, R.H.; Mortimer, M.J. The Use of Tinted Glasses in Childhood Migraine. Headache J. Head Face Pain 1991, 31, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; Hasselfeld, K.; Bigsby, K.; Divine, J. Colored Glasses to Mitigate Photophobia Symptoms Posttraumatic Brain Injury. J. Athl. Train. 2017, 52, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuffreda, K.J.; Kapoor, N.; Rutner, D.; Suchoff, I.B.; Han, M.E.; Craig, S. Occurrence of oculomotor dysfunctions in acquired brain injury: A retrospective analysis. Optom.—J. Am. Optom. Assoc. 2007, 78, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, A.; West, A.L.; Trobe, J.D.; Musch, D.C. Third, fourth, and sixth cranial nerve palsies following closed head injury. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2006, 26, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Master, C.L.; Scheiman, M.; Gallaway, M.; Goodman, A.; Robinson, R.L.; Master, S.R.; Grady, M.F. Vision diagnoses are common after concussion in adolescents. Clin. Pediatr. 2016, 55, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, R.; Asper, L.; Khuu, S.K. Deficits in saccades and smooth-pursuit eye movements in adults with traumatic brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1315–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, R.E.; Balcer, L.J.; Galetta, S.L.; Rucker, J.C. Ocular motor assessment in concussion: Current status and future directions. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 361, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, M.W.; Borsting, E.; Hyman, L.; Hussein, M.; Cotter, S.A.; Flynn, M.; Scheiman, M.; Gallaway, M.; De Land, P.N. Frequency of convergence insufficiency among fifth and sixth graders. The Convergence Insufficiency and Reading Study (CIRS) group. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1999, 76, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcar, E.; Martinez-Palomera, A. Prevalence of General Binocular Dysfunctions in a Population of University Students. Optom. Vis. Sci. Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Optom. 1997, 74, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiman, M.; Talasan, H.; Mitchell, G.L.; Alvarez, T.L. Objective Assessment of Vergence after Treatment of Concussion-Related CI: A Pilot Study. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2017, 94, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capó-Aponte, J.E.; Jorgensen-Wagers, K.L.; Sosa, J.A.; Walsh, D.V.; Goodrich, G.L.; Temme, L.A.; Riggs, D.W. Visual Dysfunctions at Different Stages after Blast and Non-blast Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2017, 94, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cini, M. Models of the Visual System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4419-3377-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, G.K.; Ciuffreda, K.J.; Khosroyani, M.; Jiang, B.-C. Models of Accommodation. In Models of the Visual System; Hung, G.K., Ciuffreda, K.J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 287–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, G.K.; Semmlow, J.L. Static behavior of accommodation and vergence: Computer simulation of an interactive dual-feedback system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1980, BME-27, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.A. Effects of luminance and stimulus distance on accommodation and visual resolution. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1976, 66, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.A. A comparison of accommodative responsiveness and contrast sensitivity for sinusoidal gratings. Vis. Res. 1980, 20, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuffreda, K.J.; Hokoda, S.C. Spatial frequency dependence of accommodative responses in amblyopic eyes. Vis. Res. 1983, 23, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.-C. Integration of a sensory component into the accommodation model reveals differences between emmetropia and late-onset myopia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.-C. A modified control model for steady-state accommodation. In Accommodation and Vergence Mechanisms in the Visual System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, G.K. Dynamic model of the vergence eye movement system: Simulations using matlab/simulink. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 1998, 55, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroyani, M.; Hung, G.K. A dual-mode dynamic model of the human accommodation system. Bull. Math. Biol. 2002, 64, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, W.; Ciuffreda, K.J.; Thiagarajan, P.; Szymanowicz, D.; Ludlam, D.P.; Kapoor, N. Accommodation in mild traumatic brain injury. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2010, 47, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiagarajan, P.; Ciuffreda, K.J. Effect of oculomotor rehabilitation on accommodative responsivity in mild traumatic brain injury. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2014, 51, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Atiya, A.; Vittal, S.; Ambika, S.; Hussaindeen, J.R. Pupillary dynamics and accommodative response in mild traumatic brain injury. Taiwan J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 14, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Liao, M.; Yang, C.; Liu, L. Accommodation and stereopsis in adults with traumatic brain injury. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2020, 103, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiecek, E.K.; Roberts, T.L.; Shah, A.S.; Raghuram, A. Vergence, accommodation, and visual tracking in children and adolescents evaluated in a multidisciplinary concussion clinic. Vis. Res. 2021, 184, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haensel, J.X.; Marusic, S.; Slinger, K.E.; Wu, C.H.; Vyas, N.; Ameyaw Baah, C.A.; Hu, A.; Leonen, J.; Lew, C.Y.; Srinivasan, G.; et al. Accommodative and Vergence Responses to a Moving Stimulus in Concussion. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2024, 65, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, N.M.; Hayes, J.; Hampson, K.M.; Liu, C. Accommodation microfluctuation in individuals with mTBI and the potential effect of chromatic filter on this parameter. Vis. Res. 2025, 227, 108545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, P.; Ciuffreda, K.J. Accommodative and pupillary dysfunctions in concussion/mild traumatic brain injury: A Review. NeuroRehabilitation 2022, 50, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, G.; Ciuffreda, K.; Semmlow, J.; Hokoda, S. Model of Static Accommodative Behavior in Human Amblyopia. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1983, 30, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuffreda, K.J.; Hokoda, S.C.; Hung, G.K.; Semmlow, J.L.; Selenow, A. Static aspects of accommodation in human amblyopia. Am. J. Optom. Physiol. Opt. 1983, 60, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labhishetty, V.; Chakraborty, A.; Bobier, W.R. Is blur sensitivity altered in children with progressive myopia? Vision. Res. 2019, 154, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiman, M.; Kulp, M.T.; Cotter, S.A.; Lawrenson, J.G.; Wang, L.; Li, T. Interventions for convergence insufficiency: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, CD006768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiman, M.; Mitchell, G.L.; Cotter, S.; Cooper, J.; Kulp, M.; Rouse, M.; Borsting, E.; London, R.; Wensveen, J. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Treatments for Convergence Insufficiency in Children. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2005, 123, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiman, M.; Mitchell, G.L.; Cotter, S.; Kulp, M.T.; Cooper, J.; Rouse, M.; Borsting, E.; London, R.; Wensveen, J. A randomized clinical trial of vision therapy/orthoptics versus pencil pushups for the treatment of convergence insufficiency in young adults. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2005, 82, E583–E595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convergence Insufficiency Treatment Trial Study Group. Long-term effectiveness of treatments for symptomatic convergence insufficiency in children. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2009, 86, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Vicci, V.R.; Alkan, Y.; Kim, E.H.; Gohel, S.; Barrett, A.M.; Chiaravalloti, N.; Biswal, B.B. Vision Therapy in Adults with Convergence Insufficiency: Clinical and Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measures. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, E985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, T.; Jaswal, R.; Gohel, S.; Biswal, B.B. Functional activity significantly correlates to symmetrical vergence peak velocity: An fMRI study of vision therapy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2661. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Scheiman, M.; Santos, E.M.; Morales, C.; Yaramothu, C.; d’Antonio-Bertagnolli, J.V.; Gohel, S.; Biswal, B.B.; Li, X. Clinical and functional imaging changes induced from vision therapy in patients with convergence insufficiency. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 104–109. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8857163/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Ciuffreda, K.J. The scientific basis for and efficacy of optometric vision therapy in nonstrabismic accommodative and vergence disorders. Optometry 2002, 73, 735–762. [Google Scholar]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Health Care Services; Board on Health Sciences Policy; Committee on Accelerating Progress in Traumatic Brain Injury Research and Care. Understanding Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. In Traumatic Brain Injury: A Roadmap for Accelerating Progress; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK580077/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Merezhinskaya, N.; Mallia, R.K.; Park, D.; Bryden, D.W.; Mathur, K.; Barker, F.M.I. Visual Deficits and Dysfunctions Associated with Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2019, 96, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Population-Based Study of Pre-Existing Health Conditions in Traumatic Brain Injury|Neurotrauma Reports. Available online: https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/neur.2020.0065 (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Biscardi, M.; Grossinger, Z.; Colantonio, A.; Bayley, M.; Mollayeva, T. Efficacy of restitutive interventions for oculomotor deficits in adults with mild traumatic brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Inj. 2024, 38, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author (Year) | Sample Size (mTBI/Control) | Age Range/Mean | Type of TBI | Duration Since Injury | Accommodation Type (Static/Dynamic) | Parameters Tested | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green et al. (2010) [45] | 12/10 | 18–40 years | mTBI | Varied (not specified) | Static and Dynamic | AA, accommodative interactions, peak velocity, fatigue | Reduced AA, abnormal interactions, slowed dynamics with fatigue; both static and dynamic deficits noted |
| Thiagarajan and Ciuffreda (2014) [46] | 12/10 | 23–33 years (mean 29) | mTBI | >1 year | Static and Dynamic | Amplitude of Accommodation(AA), PRA/NRA, peak velocity, time constant | Reduced AA (~1.5D), reduced PRA/NRA, decreased peak velocity, prolonged response time; improved post-training |
| Chen et al. (2020) [48] | 22/22 | 18–38 years (mean ≈ 27.2) | TBI (Mild and Severe) | 0.17–84 months | Static | Accommodative amplitude, accommodative facility, accommodative lag (2–5 D), variability, stereopsis | Significantly reduced AA and facility; greater accommodative lag and variability across stimulus levels; 32% showed accommodative insufficiency; strong correlation with symptom severity |
| Wiecek et al. (2021) [49] | 116/— | 5–21 years (median 15) | Concussion (mTBI) | ≥21 days | Static | Accommodative amplitude, near point of convergence | 63/116 showed reduced accommodative amplitude; correlated with convergence and tracking deficits |
| Dutta et al. (2024) [47] | 63/90 | 18–35 years | mTBI | ≥6 months | Static (response magnitude) | Accommodative response (diopters), pupillary dynamics | Reduced accommodative response (~−1.12 vs. −1.39 D); also reduced pupillary constriction velocities |
| Haensel et al. (2024) [50] | 32/32 | 14.4 ± 2.6 (mTBI), 12.7 ± 2.1 (controls) | Concussion (mTBI) | 36–273 days (mean 107) | Dynamic | Amplitude of accommodative response to moving target (0.1 Hz) | Reduced monocular accommodative response in mTBI; no vergence differences; disparity-driven response |
| Almutairi et al. (2025) [51] | 30/54 | 18–33 (mTBI), 20–30 (controls) | mTBI | Up to 5 years | Static (Steady-State) | Accommodation Microfluctuations (LFC, HFC), Tonic Accommodation (TA) | Lower MFs (LFC and HFC) in mTBI, especially at high stimulus levels; strong AE–LFC negative correlation suggests impaired motor control |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almutairi, N.M. Visual Dysfunctions in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Focus on Accommodative System Impairments. Life 2025, 15, 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050744
Almutairi NM. Visual Dysfunctions in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Focus on Accommodative System Impairments. Life. 2025; 15(5):744. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050744
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmutairi, Nawaf M. 2025. "Visual Dysfunctions in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Focus on Accommodative System Impairments" Life 15, no. 5: 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050744
APA StyleAlmutairi, N. M. (2025). Visual Dysfunctions in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Focus on Accommodative System Impairments. Life, 15(5), 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050744






