Sonodynamic Therapy Using 5-Aminolevulinic Acid for Malignant Gliomas: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sonodynamic Therapy for Malignant Gliomas
3. 5-ALA, an Optimal Sonosensitizer for Malignant Gliomas
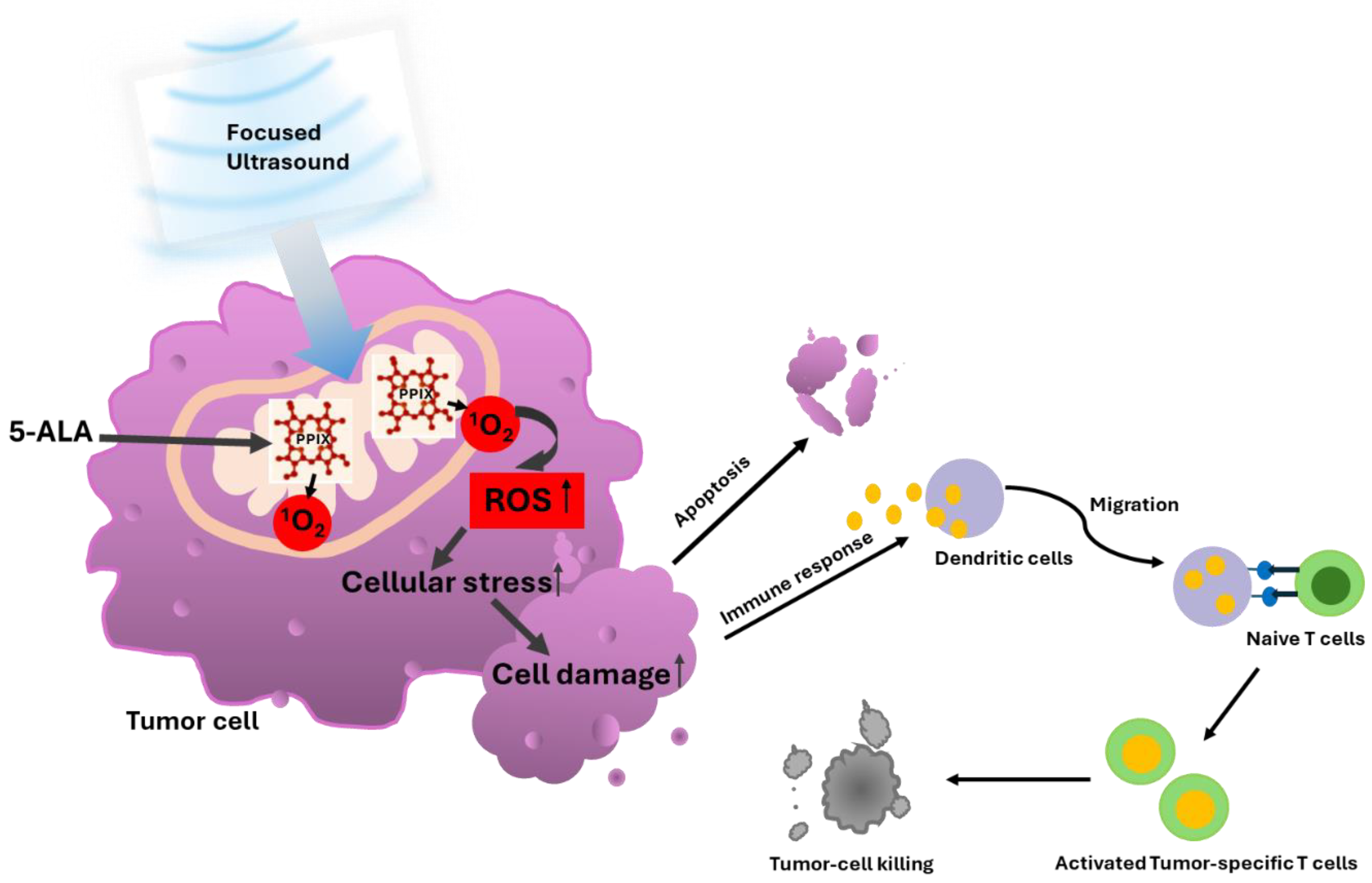
3.1. 5-ALA-SDT Mechanism of Action
3.2. 5-ALA-SDT Evidence of Apoptosis, Anti-Tumor Immune Response and Anti-Angiogenesis
3.3. Preclinical Evidence for the Efficacy of 5-ALA-SDT
3.4. Current SDT Devices
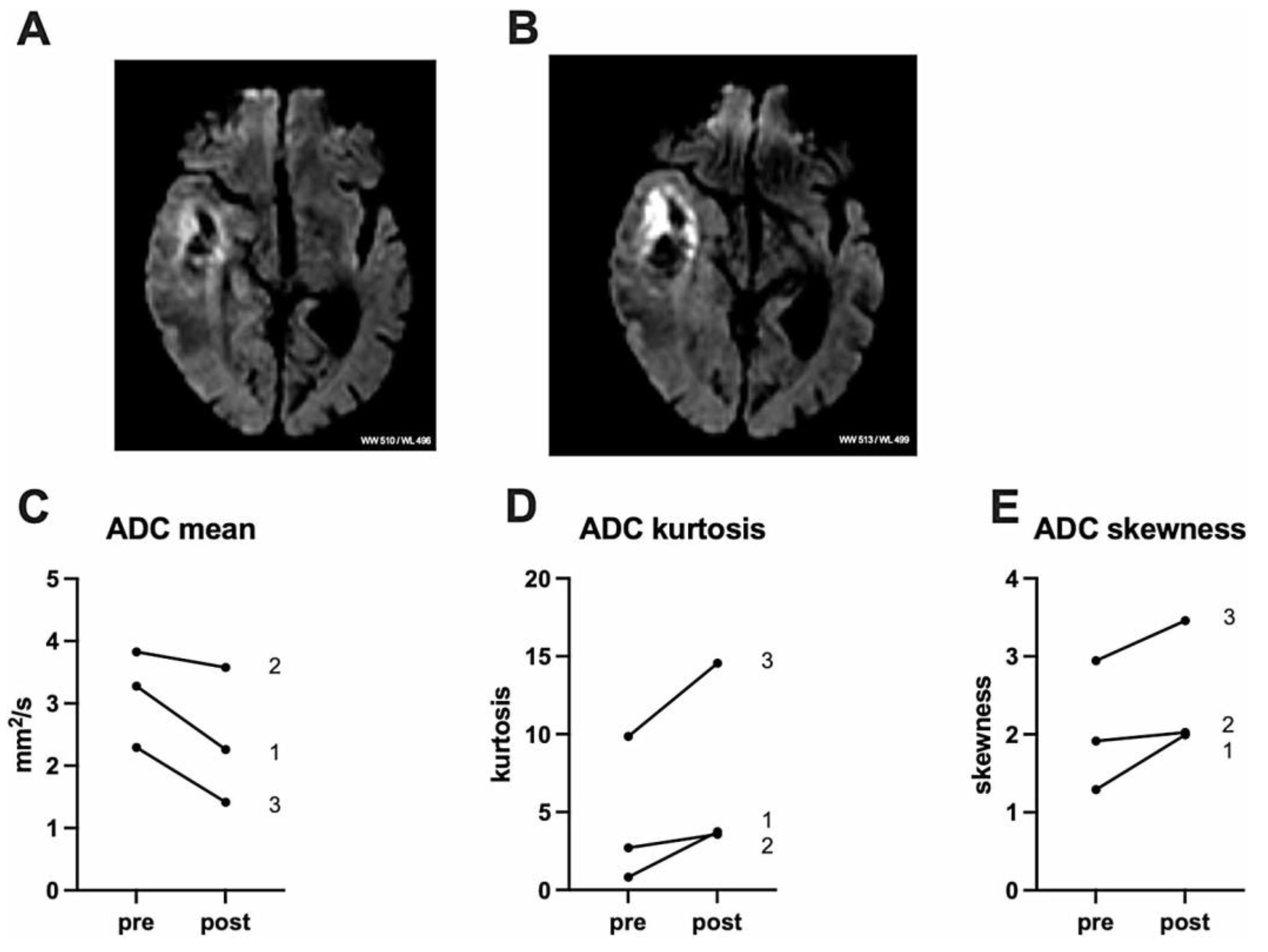
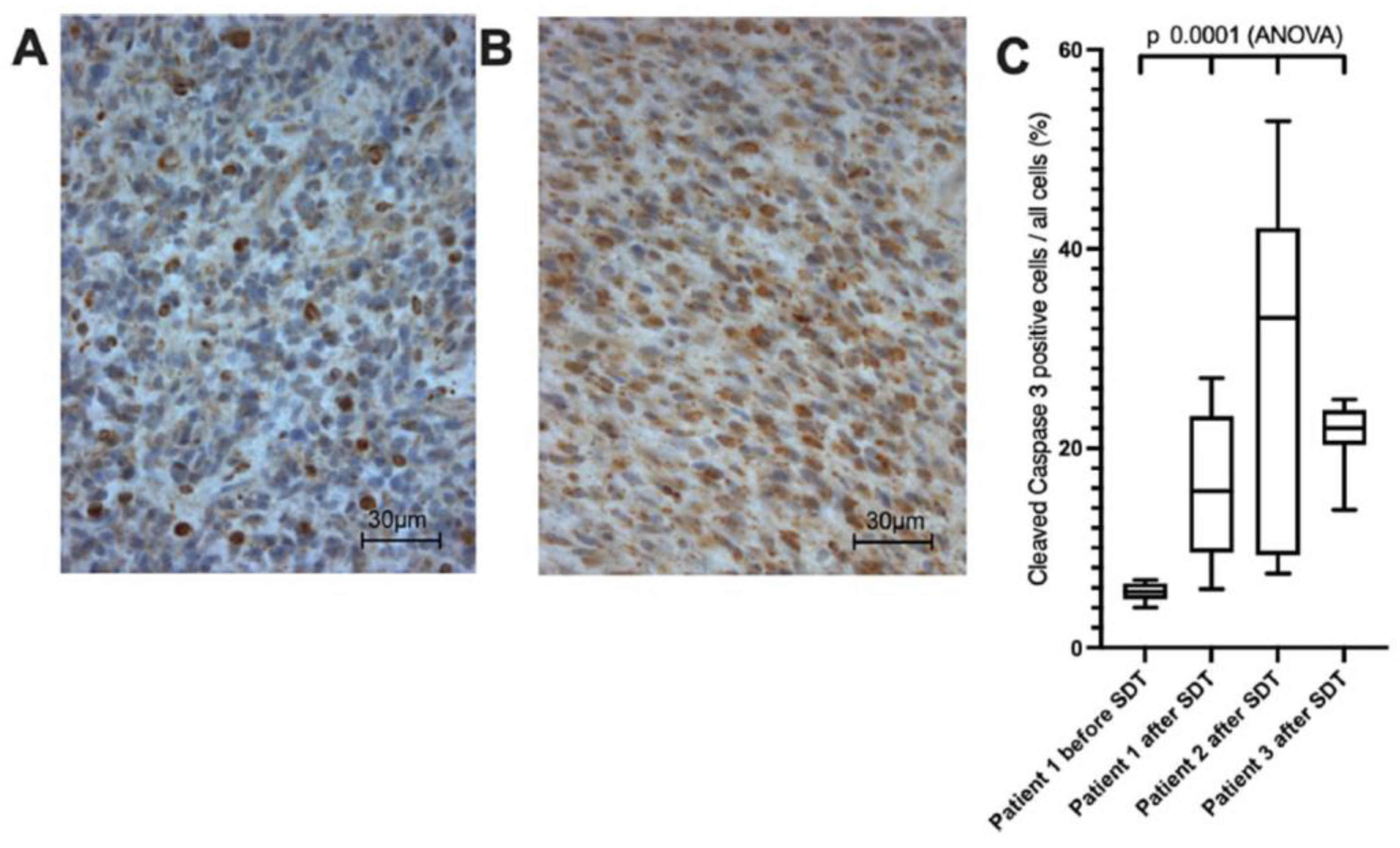
3.5. Clinical Trials and Early Evidence of 5-ALA-SDT
4. Conclusions and Future Direction of the 5-ALA-SDT
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoshida, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Terasaka, S.; Endo, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Motegi, H.; Itay, R.; Suzuki, S.; Brokman, O.; Shapira, Y.; et al. Sonodynamic Therapy for Malignant Glioma Using 220-kHz Transcranial Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Focused Ultrasound and 5-Aminolevulinic acid. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stummer, W.; Pichlmeier, U.; Meinel, T.; Wiestler, O.D.; Zanella, F.; Reulen, H.J. ALA-Glioma Study Group. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: A randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schucht, P.; Beck, J.; Abu-Isa, J.; Andereggen, L.; Murek, M.; Seidel, K.; Stieglitz, L.; Raabe, A. Gross total resection rates in contemporary glioblastoma surgery: Results of an institutional protocol combining 5-aminolevulinic acid intraoperative fluorescence imaging and brain mapping. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 927–935; discussion 935–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, C.; Stummer, W.; Coburger, J.; Scherer, M.; Haas, P.; von der Brelie, C.; Kamp, M.A.; Löhr, M.; Hamisch, C.A.; Skardelly, M.; et al. Intraoperative MRI-Guided Resection Is Not Superior to 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Guidance in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Prospective Controlled Multicenter Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5512–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, P.; Umme, S.; D’Antonio, D.L.; Piattelli, A.; Curia, M.C. Reactive Oxygen Species Produced by 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Photodynamic Therapy in the Treatment of Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, S.; Knap, B.; Przystupski, D.; Saczko, J.; Kedzierska, E.; Knap-Czop, K.; Kotlinska, J.; Michel, O.; Kotowski, K.; Kulbacka, J. photodynamic therapy—Mechanisms, photosensitizers and combinations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz, P.; Yaroslavsky, A.; Kharkwal, G.B.; Hamblin, M.R. Cell death pathways in photodynamic therapy of cancer. Cancers 2011, 3, 2516–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, A.P.; Demidova, T.N.; Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: Part two-cellular signaling, cell metabolism and modes of cell death. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2005, 2, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, A.; Di Venosa, G.; Hasan, T.; Al, B. Mechanisms of resistance to photodynamic therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 2486–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanie, S.; Michael, M.; Louise, S.; Sebastian, Z.; Benjamin, B.; Markus, H.; Oliver, G.; Eric, S.M.; Nils, W.; Walter, S. Combination of ALA-induced fluorescence-guided resection and intraoperative open photodynamic therapy for recurrent glioblastoma: Case series on a promising dual strategy for local tumor control. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 426–436. [Google Scholar]
- Vermandel, M.; Dupont, C.; Lecomte, F.; Leroy, H.A.; Tuleasca, C.; Mordon, S.; Hadjipanayis, C.G.; Reyns, N. Standardized intraoperative 5-ALA photodynamic therapy for newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients: A preliminary analysis of the INDYGO clinical trial. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 152, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lietke, S.; Schmutzer, M.; Schwartz, C.; Weller, J.; Siller, S.; Aumiller, M.; Heckl, C.; Forbrig, R.; Niyazi, M.; Egensperger, R.; et al. Interstitial Photodynamic Therapy Using 5-ALA for Malignant Glioma Recurrences. Cancers 2021, 13, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglar, M.; Aumiller, M.; Bochmann, K.; Buchner, A.; El Fahim, M.; Quach, S.; Sroka, R.; Stepp, H.; Thon, N.; Forbrig, R.; et al. Interstitial Photodynamic Therapy of Glioblastomas: A Long-Term Follow-up Analysis of Survival and Volumetric MRI Data. Cancers 2023, 15, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.J.; Seo, S.J.; Ahn, Y.J.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.K. Sonodynamically induced antitumor effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid and fractionated ultrasound irradiation in an orthotopic rat glioma model. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 2143–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suehiro, S.; Ohnishi, T.; Yamashita, D.; Kohno, S.; Inoue, A.; Nishikawa, M.; Ohue, S.; Tanaka, J.; Kunieda, T. Enhancement of antitumor activity by using 5-ALA-mediated sonodynamic therapy to induce apoptosis in malignant gliomas: Significance of high-intensity focused ultrasound on 5-ALA-SDT in a mouse glioma model. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.K.; Santos, M.A.; Marcus, S.L.; Hynynen, K. MR-guided focused ultrasound facilitates sonodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid in a rat glioma model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Patil, N.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2013–2017. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22 (Suppl. S2), iv1–iv96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, O. Nonsurgical treatment of recurrent glioblastoma. Curr. Oncol. 2015, 22, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karschnia, P.; Young, J.S.; Dono, A.; Häni, L.; Sciortino, T.; Bruno, F.; Juenger, S.T.; Teske, N.; Morshed, R.A.; Haddad, A.F.; et al. Prognostic validation of a new classification system for extent of resection in glioblastoma: A report of the RANO resect group. Neuro Oncol. 2023, 25, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.W.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhang, N. Recent advances of sonodynamic therapy in cancer treatment. Cancer Biol. Med. 2016, 13, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, W.J.; Huss, D.; Voss, T.; Loomba, J.; Khaled, M.; Zadicario, E.; Frysinger, R.C.; Sperling, S.A.; Wylie, S.; Monteith, S.J.; et al. A pilot study of focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, R.C.; Messmann, H.; Rauch, J.; Seeger, S.; Knuechel, R. Metabolic characterization of tumor cell-specific protoporphyrin IX accumulation after exposure to 5-aminolevulinic acid in human colonic cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 76, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stummer, W.; Novotny, A.; Stepp, H.; Goetz, C.; Bise, K.; Reulen, H.J. Fluorescence-guided resection of glioblastoma multiforme by using 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced porphyrins: A prospective study in 52 consecutive patients. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stummer, W.; Tonn, J.C.; Goetz, C.; Ullrich, W.; Stepp, H.; Bink, A.; Pietsch, T.; Pichlmeier, U. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-derived tumor fluorescence: The diagnostic accuracy of visible fluorescence qualities as corroborated by spectrometry and histology and postoperative imaging. Neurosurgery 2014, 74, 310–319; discussion 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, S.; Yumita, N.; Nishigaki, R.; Umemura, K. Mechanism of cell damage by ultrasound in combination with hematoporphyrin. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1990, 81, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, I.; Sostaric, J.Z.; Riesz, P. Sonodynamic therapy—A review of the synergistic effects of drugs and ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2004, 11, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilmin, K.; Kujawska, T.; Secomski, W.; Nowicki, A.; Grieb, P. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-mediated sonosensitization of rat RG2 glioma cells in vitro. Folia Neuropathol. 2016, 54, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedre, M.; Patterson, M.S.; Wilson, B.C. Direct near-infrared luminescence detection of singlet oxygen generated by photodynamic therapy in cells in vitro and tissues in vivo. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 75, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Sun, X.; Guo, S.; Cao, W.; Chen, H.; Jin, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated sonodynamic therapy on macrophages. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 669–676. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Q.; Jia, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, N.; Zhao, H.; Ji, H.; Li, B.; Cao, W. Antiproliferative and Apoptosis-inducing Effect of exo-Protoporphyrin IX based Sonodynamic Therapy on Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, K.; Su, X.; Hou, J.; Liu, Q. Initiation of autophagy and apoptosis by sonodynamic therapy in murine leukemia L1210 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 2013, 27, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovey, R.; Diaz, R. A bench-top model for the optimization of ultrasound parameters for sonodynamic therapy of glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol. Off. J. Soc. Neuro-Oncol. 2024, 26 (Suppl. S8), 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, Z.; Wang, X.; Gu, C.; Gao, Z.; Cao, W.; Zheng, J. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-mediated sonodynamic therapy reverses macrophage and dendritic cell passivity in murine melanoma xenografts. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, K.; Sheehan, D.; Sulaiman, M.; Padilla, F.; Moore, D.; Sheehan, J.; Xu, Z. Investigation of the tumoricidal effects of sonodynamic therapy in malignant glioblastoma brain tumors. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 148, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Sun, L.; Xu, F.; Liu, L.; Hu, F.; Song, D.; Hou, Z.; Wu, W.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; et al. M2 Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Promote Cell Migration and Invasion in Colon Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Marchesi, F.; Malesci, A.; Laghi, L.; Allavena, P. Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, J.; Mlecnik, B.; Bindea, G.; Angell, H.K.; Berger, A.; Lagorce, C.; Lugli, A.; Zlobec, I.; Hartmann, A.; Bifulco, C.; et al. Towards the introduction of the ‘Immunoscore’ in the classification of malignant tumours. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, S.; Cao, W.; Zheng, J. Sonodynamic therapy improves anti-tumor immune effect by increasing the infiltration of CD8+ T cells and altering tumor blood vessels in murine B16F10 melanoma xenograft. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zheng, J.; Yang, B.; Wang, Z.; Fan, H.; Lv, Y.; Li, H.; Jia, L.; Cao, W. Sonodynamic therapy inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenlyside, A.; Marples, T.; Gao, Z.; Hu, H.; Nicely, L.G.; Nogales, J.; Li, H.; Landgraf, L.; Solth, A.; Melzer, A.; et al. Development and optimisation of in vitro sonodynamic therapy for glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmura, T.; Fukushima, T.; Shibaguchi, H.; Yoshizawa, S.; Inoue, T.; Kuroki, M.; Sasaki, K.; Umemura, S. Sonodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid and focused ultrasound for deep-seated intracranial glioma in rat. Anticancer. Res. 2011, 31, 2527–2533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, F.; Asakura, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kitamura, T.; Teramoto, A. Low frequency ultrasonication induced antitumor effect in 5-aminolevulinic acid treated malignant glioma. J. Cancer Ther. 2013, 04, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kong, C.; Shin, J.; Park, J.Y.; Na, Y.C.; Han, S.H.; Chang, J.W.; Song, S.H.; Chang, W.S. Combined Effects of Focused Ultrasound and Photodynamic Treatment for Malignant Brain Tumors Using C6 Glioma Rat Model. Yonsei Med. J. 2023, 64, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raspagliesi, L.; D’Ammando, A.; Gionso, M.; Sheybani, N.D.; Lopes, M.B.; Moore, D.; Allen, S.; Gatesman, J.; Porto, E.; Timbie, K.; et al. Intracranial Sonodynamic Therapy With 5-Aminolevulinic Acid and Sodium Fluorescein: Safety Study in a Porcine Model. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 679989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluhar, G.E.; Arnold, S.; Ling, J.; Hunt, M.; Agarwal, V. Safety and efficacy data from a clinical trial of sonodynamic therapy with 5-Ala HCL oral solution and cv-01 delivered whole hemispheric low intensity non-ablative ultrasound in pet french bulldogs with de novo naturally occurring high grade glioma. Neuro-Oncol. Off. J. Soc. Neuro-Oncol. 2024, 26 (Suppl. S8), 04. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.Y.; Li, J.C.; Chen, K.T.; Lin, Y.J.; Feng, L.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Wei, K.C. Evaluation the Effect of Sonodynamic Therapy with 5-Aminolevulinic Acid and Sodium Fluorescein by Preclinical Animal Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.K.; Tsai, C.L.; Mir, A.; Marcus, S.L.; Hynynen, K. Repeated 5-aminolevulinic acid mediated sonodynamic therapy using magnetic resonance guided focused ultrasound in rat brain tumour models. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, A.M.; Bhimreddy, M.; Weber-Levine, C.; Jiang, K.; Alomari, S.; Theodore, N.; Manbachi, A.; Tyler, B.M. Applications of focused Ultrasound for the Treatment of Glioblastoma: A New Frontier. Cancers 2022, 14, 4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stummer, W.; Gerwing, M.; Bilgin, S.S.; Thomas, C.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.; Agarwal, V.; Stögbauer, L.; Schroeteler, J.; Müther, M. Sonodynamic therapy with a single neoadjuvant, diffuse delivery of low-intensity ultrasound with 5-ALA in treatment naïve glioblastoma results in tumor-specific cytotoxic edema and increased apoptosis. J. Neurooncol. 2025, 172, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, A.; Stupp, R.; Sonabend, A.M.; Dufour, H.; Chinot, O.; Mathon, B.; Ducray, F.; Guyotat, J.; Baize, N.; Menei, P.; et al. Repeated blood-brain barrier opening with a nine-emitter implantable ultrasound device in combination with carboplatin in recurrent glioblastoma: A phase I/II clinical trial. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanai, N.; Tien, A.C.; Tovmasyan, A.; Chang, Y.W.; Margaryan, T.; Hendrickson, K.; Eschbacher, J.; Yoo, W.; Harmon, J.; Hong, A.; et al. CTNI-13. A first-inhuman phase 0/1 trial of 5-aminolevulinic acid sonodynamic therapy (5-ALA SDT) in recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24 (Suppl. S7), vii72–vii73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placantonakis, D.; Grabowski, M.; Burns, T.; Butowski, N.; Clanton, R.; Henry, L.; Potter, W.; Marcus, S.; Benaim, E. A Phase 1/2 Dose Escalation and Expansion Study of Sonodynamic Therapy with sonala-001 in Combination with Non-ablative MR-guided Focused Ultrasound in Subjects with Progressive or Recurrent Glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol. Off. J. Soc. Neuro-Oncol. 2024, 26 (Suppl. S8), 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulder, M.; Johans, T.; Mechtler, L.; Agarwal, V. Results from a phase 1 study of sonodynamic therapy with whole hemispheric low intensity nonablative ultrasound in patients with recurrent high grade glioma. Neuro-Oncol. Off. J. Soc. Neuro-Oncol. 2024, 26 (Suppl. S8), 18. [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn, L.; Keating, R.; Patel, N.; Fonseca, A.; Donoho, D.; Oluigbo, C.; Myseros, J.; Narsinh, K.; Mueller, S.; Ho, W.; et al. Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) using intravenous 5-aminolevulinic acid with non-ablative focused ultrasound for the treatment of diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas in pediatrics: Initial safety and outcomes the multicenter sdt-201. Neuro-Oncol. Off. J. Soc. Neuro-Oncol. 2024, 26 (Suppl. S8), 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, H.R.; Kilburn, L.; Fonseca, A.; Nazarian, J.; Oluigbo, C.; Myseros, J.S.; Packer, R.J.; Keating, R.F. First-in-human sonodynamic therapy with ALA for pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: A phase 1/2 study using low-intensity focused ultrasound: Technical communication. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 162, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBain, C.; Lawrie, T.A.; Rogozińska, E.; Kernohan, A.; Robinson, T.; Jefferies, S. Treatment options for progression or recurrence of glioblastoma: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 5, CD013579. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Bao, C.; Cai, X.; Jin, L.; Sun, L.; Lang, Y.; Li, L. Sonodynamic therapy-assisted immunotherapy: A novel modality for cancer treatment. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1330–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, E.; Shaffer, K.V.; Lin, C.; Byvaltsev, V.A.; Preul, M.C.; Chen, L. Blood-Brain Barrier, Blood-Brain Tumor Barrier, and Fluorescence-Guided Neurosurgical Oncology: Delivering Optical Labels to Brain Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadis, P.; Gandhi, D.; Guo, Y.; Ahmed, A.K.; Bentzen, S.M.; Arvanitis, C.; Woodworth, G.F. Localized blood-brain barrier opening in infiltrating gliomas with MRI-guided acoustic emissions-controlled focused ultrasound. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2103280118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seas, A.A.; Malla, A.P.; Sharifai, N.; Winkles, J.A.; Woodworth, G.F.; Anastasiadis, P. Microbubble-Enhanced Focused Ultrasound for Infiltrating Gliomas. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spille, D.C.; Bunk, E.C.; Thomas, C.; Özdemir, Z.; Wagner, A.; Akkurt, B.H.; Mannil, M.; Paulus, W.; Grauer, O.M.; Stummer, W.; et al. Protoporphyrin IX (PpIX) Fluorescence during Meningioma Surgery: Correlations with Histological Findings and Expression of Heme Pathway Molecules. Cancers 2023, 15, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, P.A.; Millesi, M.; Widhalm, G.; Roberts, D.W. 5-aminolevulinic acid induced protoporphyrin IX (ALA-PpIX) fluorescence guidance in meningioma surgery. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 141, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stummer, W.; Beck, T.; Beyer, W.; Mehrkens, J.H.; Obermeier, A.; Etminan, N.; Stepp, H.; Tonn, J.C.; Baumgartner, R.; Herms, J.; et al. Long-sustaining response in a patient with non-resectable, distant recurrence of glioblastoma multiforme treated by interstitial photodynamic therapy using 5-ALA: Case report. J. Neurooncol. 2008, 87, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, S.L.; de Souza, M.P. Theranostic uses of the heme pathway in neurooncology: Protoporphyrin IX (PpIX) and its journey from photodynamic therapy (PDT) through photodynamic diagnosis (PDD) to sonodynamic therapy (SDT). Cancers 2024, 16, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Bao, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Lai, J.; Yi, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Multi-scale brain attributes contribute to the distribution of diffuse glioma subtypes. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 155, 1670–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, B.; Hu, X.; Kim, H.; Squatrito, M.; Scarpace, L.; deCarvalho, A.C.; Lyu, S.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; et al. Tumor Evolution of Glioma-Intrinsic Gene Expression Subtypes Associates with Immunological Changes in the Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 42–56.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglietta, F.; Gola, G.; Biasibetti, E.; Capucchio, M.T.; Bruni, I.; Francovich, A.; Durando, G.; Serpe, L.; Canaparo, R. 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Triggered by Ultrasound Halts Tumor Proliferation in a Syngeneic Model of Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xu, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, C.; Hu, J.; Liu, P.; Fang, T.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xie, R. 5-Aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride loaded microbubbles-mediated sonodynamic therapy in pancreatic cancer cells. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Feng, X.; Huang, M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q. Sonodynamic Therapy Combined to 2-Deoxyglucose Potentiate Cell Metastasis Inhibition of Breast Cancer. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 2984–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaki, T.; Ono, M.; Uto, Y.; Ishizuka, M.; Tanaka, T.; Yamanaka, N.; Kurahashi, T.; Azuma, K.; Murahata, Y.; Tsuka, T.; et al. Sonodynamic therapy using 5-aminolevulinic acid enhances the efficacy of bleomycin. Ultrasonics 2016, 67, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Xu, L.; Wen, B.; Song, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tong, X.; Yan, H. Ultrasound-excited temozolomide sonosensitization induces necroptosis in glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2023, 554, 216033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiao, J.; Yang, R.; Wen, B.; Wu, Q.; Xu, L.; Tong, X.; Yan, H. Temozolomide-based sonodynamic therapy induces immunogenic cell death in glioma. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 256, 109772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Q.; Yang, S. Functionalized holmium-doped hollow silica nanospheres for combined sonodynamic and hypoxia-activated therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1805764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Chen, L.; Yu, L.; Zhou, B.; Yin, H.; Ren, W.; Liu, C.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; et al. Checkpoint blockade and nanosonosensitizer-augmented noninvasive sonodynamic therapy combination reduces tumour growth and metastases in mice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; He, S.; Jia, L.; Zhu, Y.; Pu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X. Transformable Nanosensitizer with Tumor Microenvironment-Activated Sonodynamic Process and Calcium Release for Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 14051–14059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Yoon, B.; Song, S.H.; Um, W.; Song, Y.; Lee, J.; You, D.G.; An, J.Y.; Park, J.H. Chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer-based immunostimulatory nanoparticles for sonoimmunotherapy. Biomaterials 2022, 283, 121466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Phase Trial Name | Identifier | Device | Status/ Published |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–1 Study of SDT Therapy in Participants with Recurrent High-Grade Glioma (HGG) | NCT04559685 | Exablate 4000 Type-2 Device (220 kHz) | Ongoing [53,54] |
| 1–2 A Study of Sonodynamic Therapy Using SONALA-001 and Exablate 4000 Type 2.0 in Subjects With Recurrent GBM | NCT05370508 | Exablate 4000 Type-2 Device (220 kHz) | Study is terminated due to funding challenges and not due to safety concerns [54] |
| 1 Sonodynamic Therapy in Patients With Recurrent GBM (GBM 001) | NCT06039709 | NaviFUS | Ongoing N/A |
| 1 Study to Evaluate 5-ALA Combined With CV01 Delivery of Ultrasound in Recurrent High- Grade Glioma | NCT05362409 | Alpheus | Complete [55] |
| 2 Sonodynamic Therapy with ExAblate System in Glioblastoma Patients (Sonic ALA) | NCT04845919 | Exablate 4000 Type-2 Device (220 kHz) | Complete N/A |
| 1–2 A Phase 2 Study of Sonodynamic Therapy (SDT) Using SONALA-001 and ExAblate 4000 Type 2.0 in Patients with Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma (DIPG) | NCT05123534 | Exablate 4000 Type-2 Device (220 kHz) | Suspended due to lack of funding but not due to safety concerns [56] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebeling, A.; Prada, F. Sonodynamic Therapy Using 5-Aminolevulinic Acid for Malignant Gliomas: A Review. Life 2025, 15, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050718
Ebeling A, Prada F. Sonodynamic Therapy Using 5-Aminolevulinic Acid for Malignant Gliomas: A Review. Life. 2025; 15(5):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050718
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbeling, Andrea, and Francesco Prada. 2025. "Sonodynamic Therapy Using 5-Aminolevulinic Acid for Malignant Gliomas: A Review" Life 15, no. 5: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050718
APA StyleEbeling, A., & Prada, F. (2025). Sonodynamic Therapy Using 5-Aminolevulinic Acid for Malignant Gliomas: A Review. Life, 15(5), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050718





