Targeting MAPK Signaling: Loureirins A and B from Dracaena Loureiri Inhibit Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.3. Red Blood Cell (RBC) Hemolysis Assay
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Wound-Healing Migration Assay
2.6. Trans-Well Invasion Assay
2.7. Gelatin Zymography Assay
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Loureirin A and Loureirin B on Human NSCLC Cell Viability
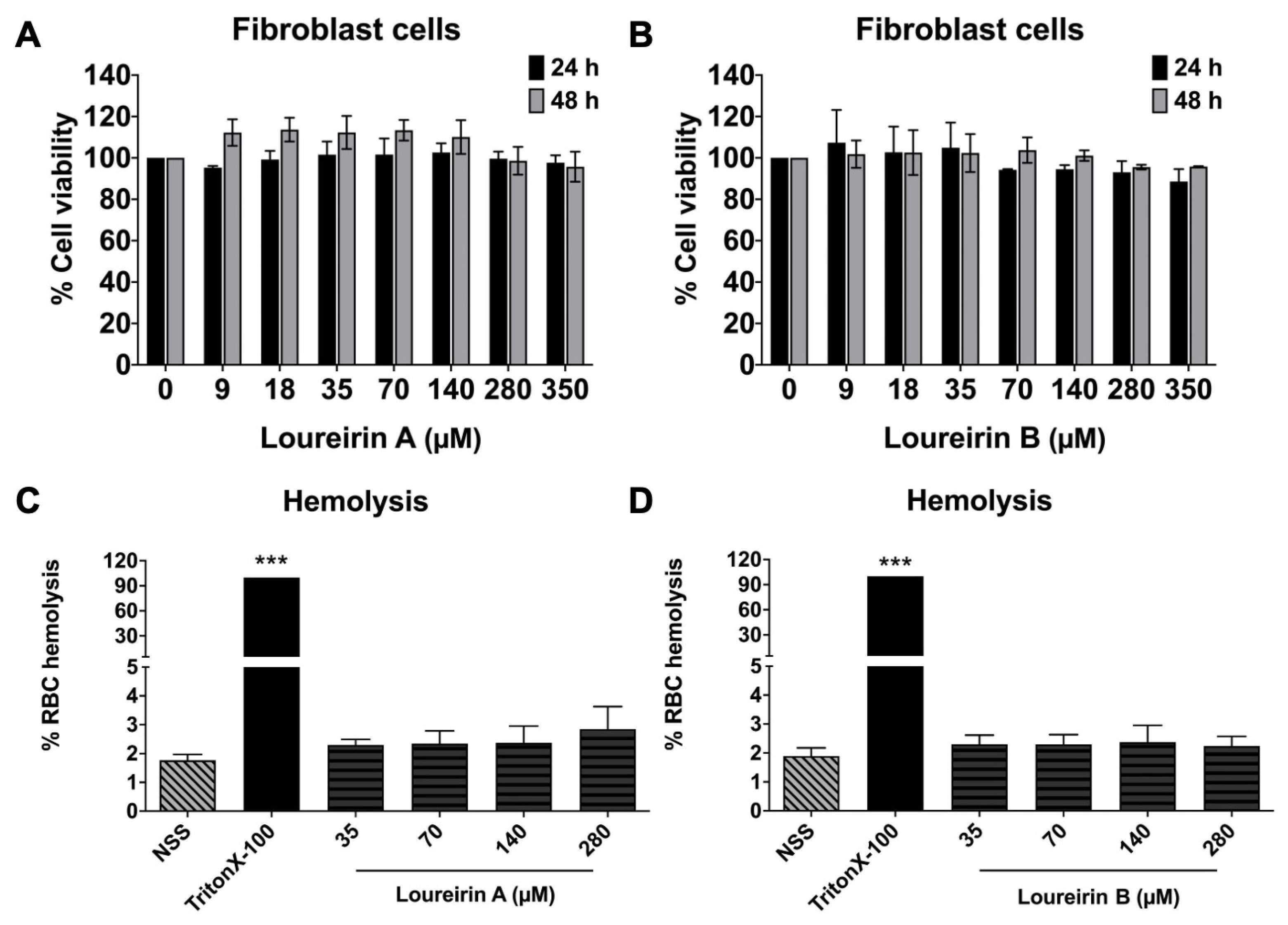
3.2. Evaluation Loureirin A and Loureirin B Induced Toxicity in Normal Cells
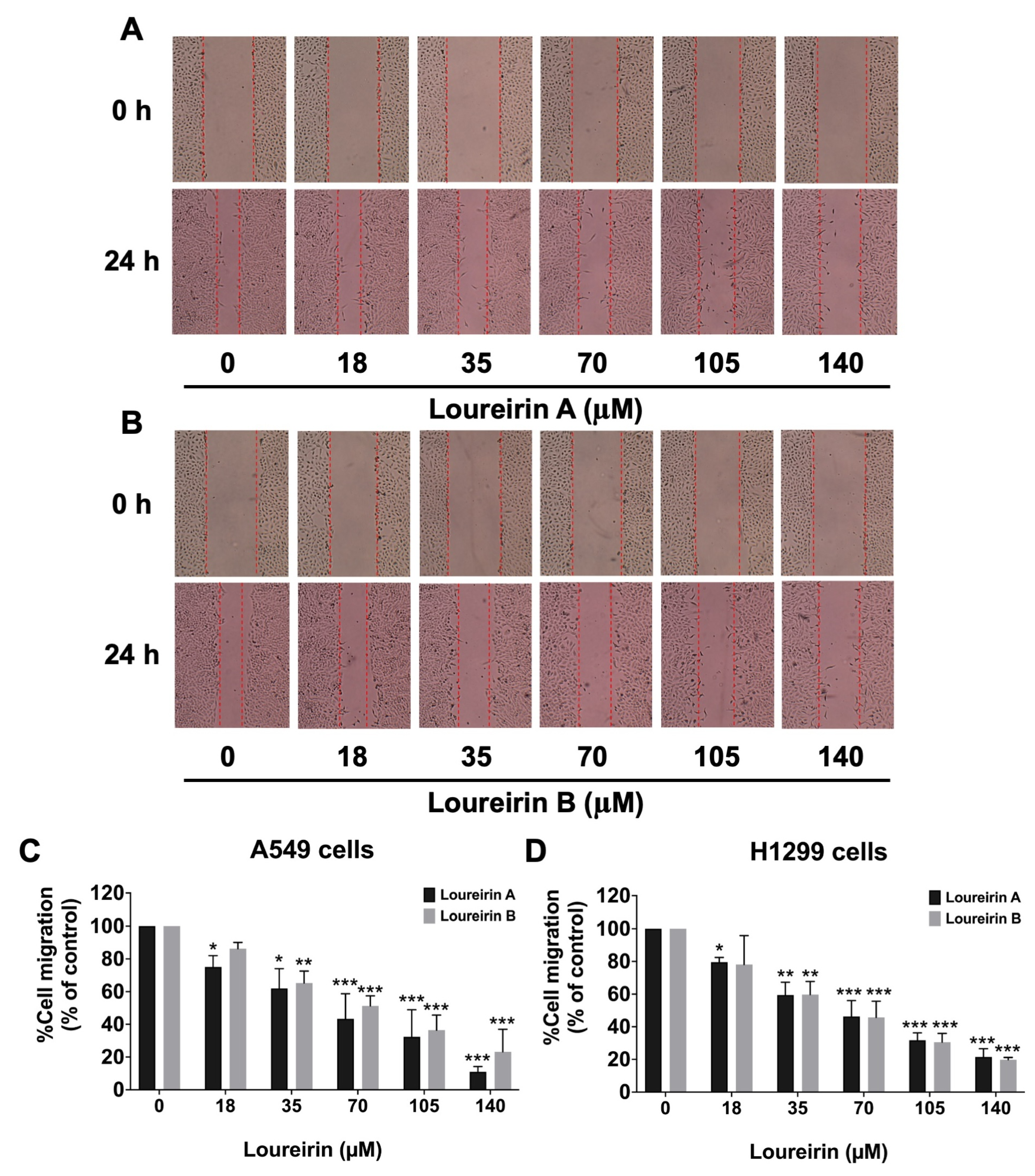
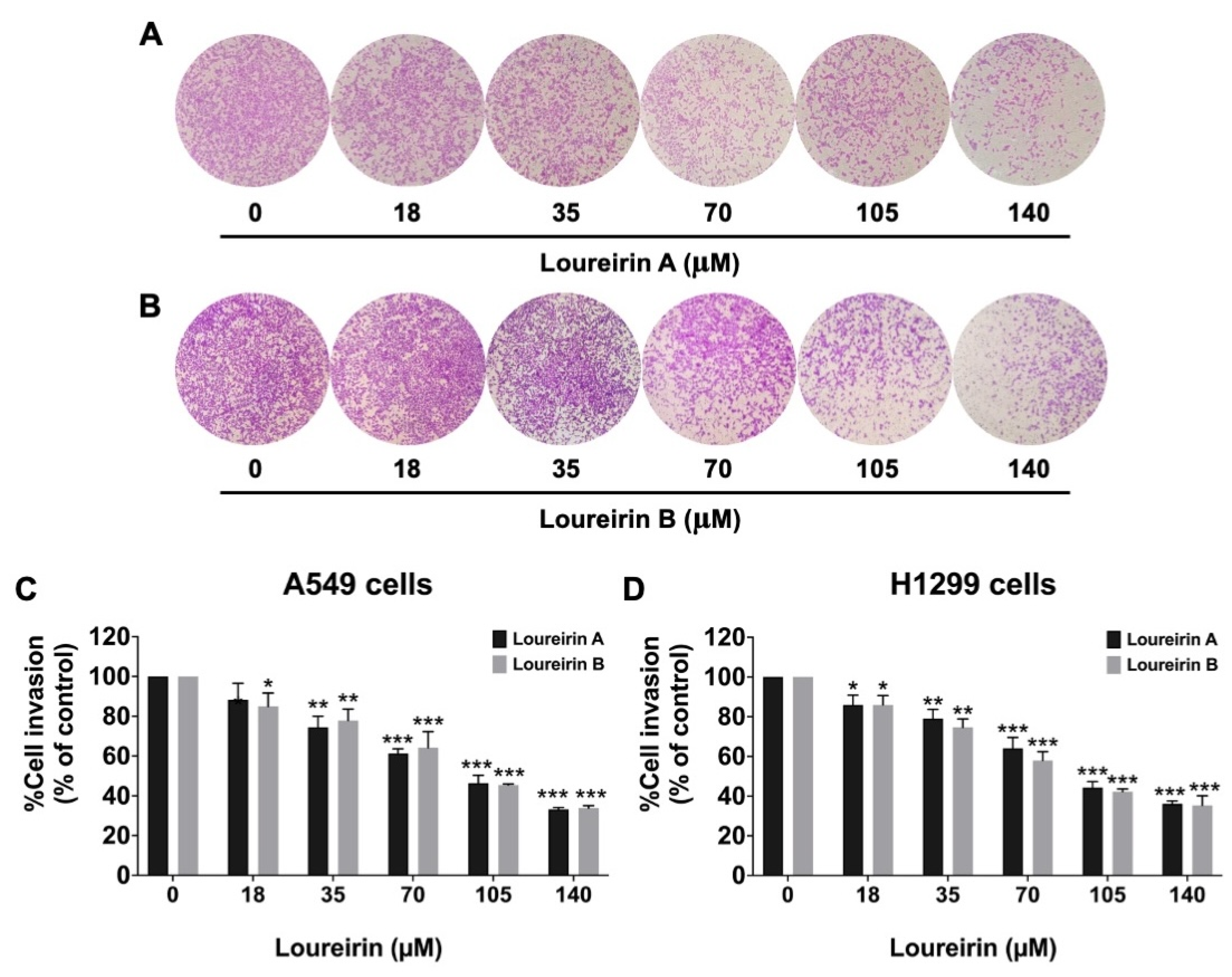
3.3. Loureirin A and Loureirin B Impaired the Migration and Invasion Abilities of Human NSCLC Cells
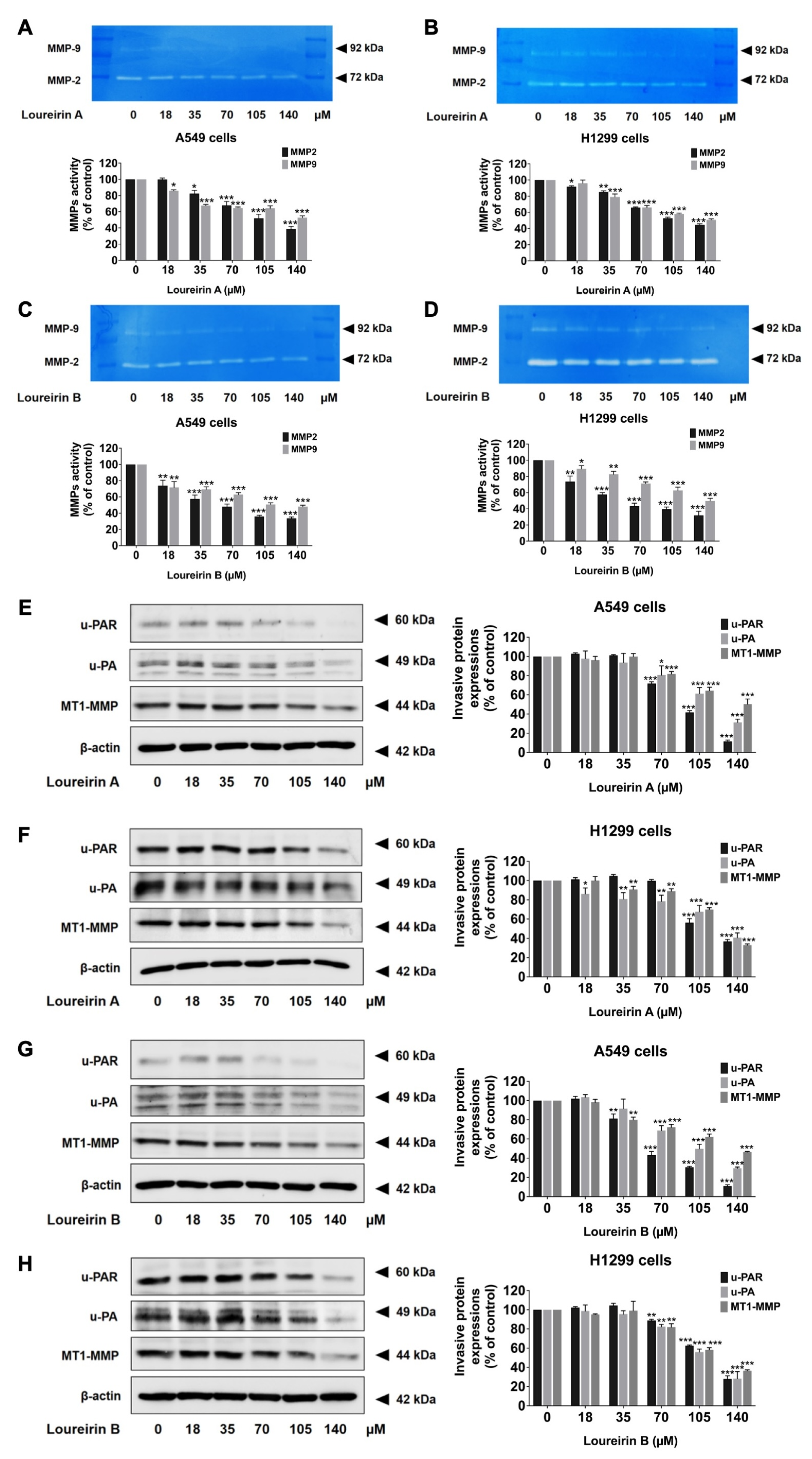
3.4. Loureirin A and Loureirin B Reduce MMP-2 and MMP-9 Activity and Suppress the Expression of Invasive Proteins in Human NSCLC Cells
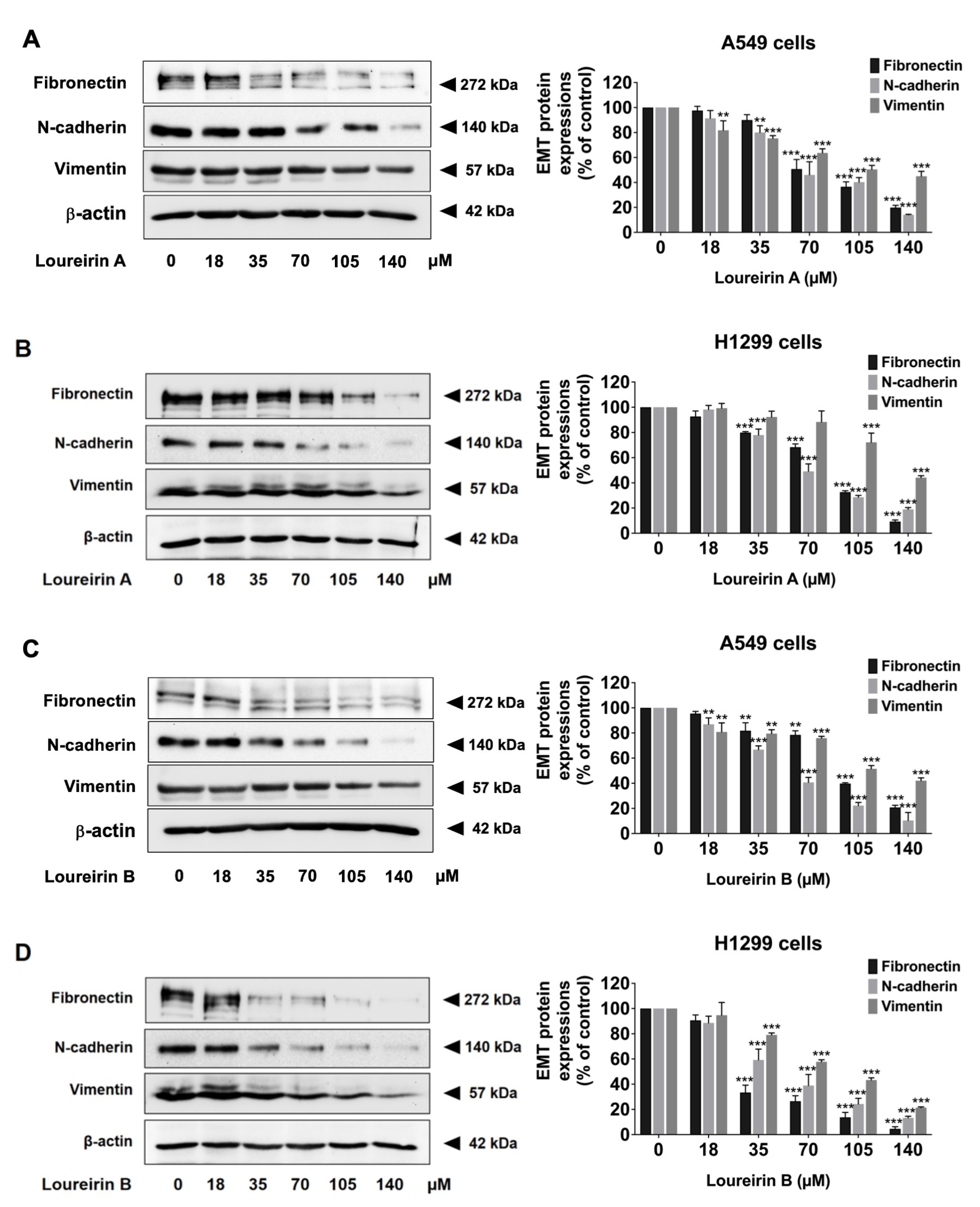
3.5. Loureirin A and Loureirin B Decrease EMT Protein Levels in Human NSCLC Cells
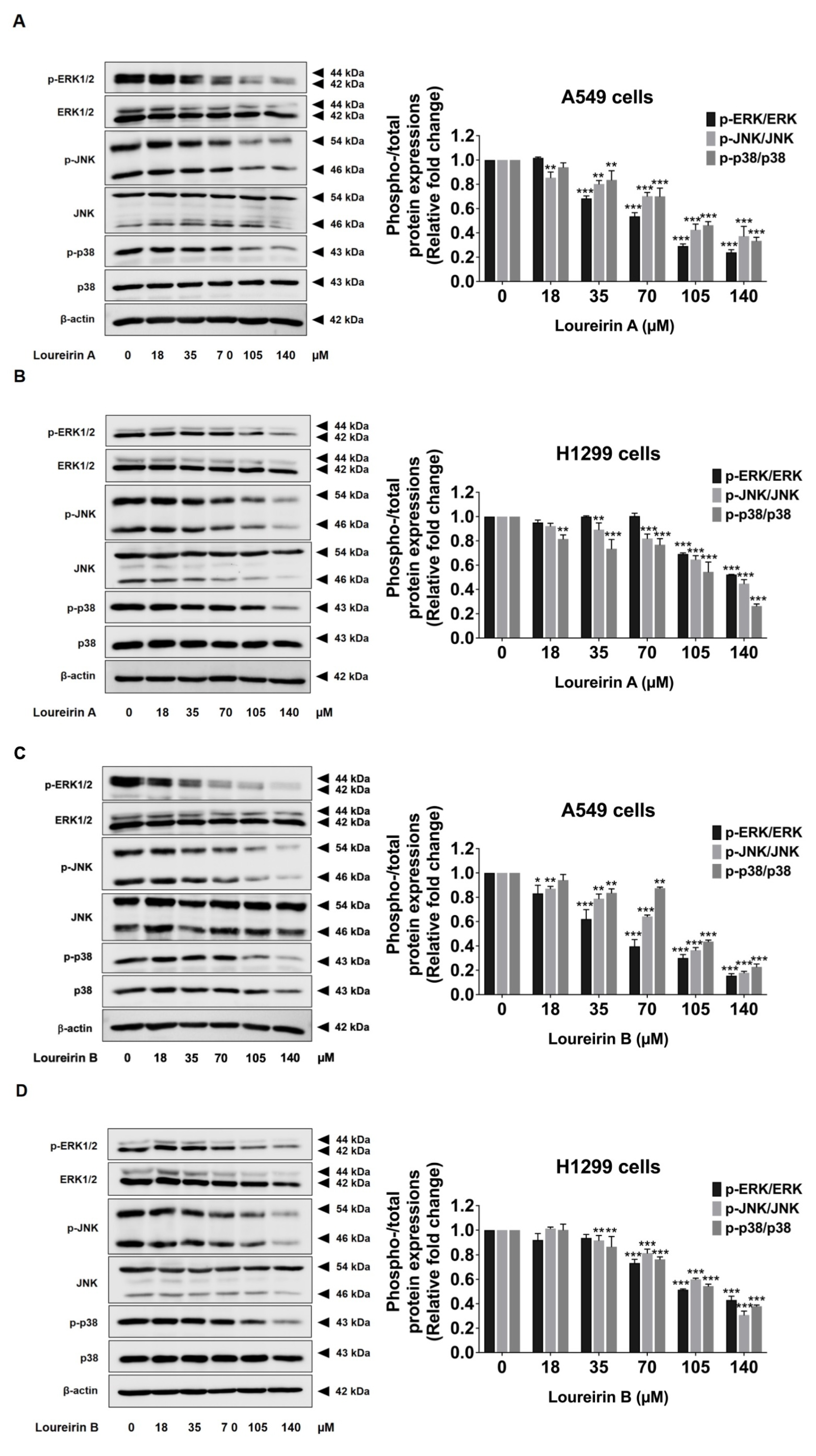
3.6. Loureirin A and Loureirin B Suppress the Activation of the MAPK Signaling Pathway in Human NSCLC Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, T.B.; Bandi, P.; Freedman, N.D.; Smith, R.A.; Travis, W.D.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Lung cancer statistics, 2023. Cancer 2024, 130, 1330–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiter, A.; Veluswamy, R.R.; Wisnivesky, J.P. The global burden of lung cancer: Current status and future trends. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridelli, C.; Rossi, A.; Carbone, D.P.; Guarize, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Mok, T.; Petrella, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Rosell, R. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yan, B.; He, S. Advances and challenges in the treatment of lung cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, J.S.; Cimino-Mathews, A.; Thompson, E.; Provencio, M.; Forde, P.M.; Spicer, J.; Girard, N.; Wang, D.; Anders, R.A.; Gabrielson, E.; et al. Association between pathologic response and survival after neoadjuvant therapy in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popper, H.H. Progression and metastasis of lung cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhu, H.; Wen, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, T.; Fan, M. Metastasis Patterns and Prognosis of Octogenarians with NSCLC: A Population-Based Study. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Nelson, R.A.; Bogardus, A.; Grannis, F.W., Jr. Five-year lung cancer survival: Which advanced stage nonsmall cell lung cancer patients attain long-term survival? Cancer 2010, 116, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kwok, H.F. Current Strategies for Treating NSCLC: From Biological Mechanisms to Clinical Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imyanitov, E.N.; Iyevleva, A.G.; Levchenko, E.V. Molecular testing and targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: Current status and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 157, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; You, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.Z. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): A biological process in the development, stem cell differentiation, and tumorigenesis. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 3261–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastushenko, I.; Blanpain, C. EMT Transition States during Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, C.S.; Van Tubergen, E.A.; Inglehart, R.C.; D’Silva, N.J. Biomarkers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, N.; Nagaraju, G.P.; Rajitha, B.; Lammata, S.; Jella, K.K.; Buchwald, Z.S.; Lakka, S.S.; Ali, A.N. Matrix metalloproteinases: Their functional role in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 766–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, B.; Kwaan, H.C. The plasminogen activator system and cancer. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2008, 36, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Yin, Q.; Snell, A.H.; Wan, L. RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer evolution and treatment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 123–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kciuk, M.; Gielecińska, A.; Budzinska, A.; Mojzych, M.; Kontek, R. Metastasis and MAPK Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuffreda, L.; Incani, U.C.; Steelman, L.S.; Abrams, S.L.; Falcone, I.; Curatolo, A.D.; Chappell, W.H.; Franklin, R.A.; Vari, S.; Cognetti, F.; et al. Signaling intermediates (MAPK and PI3K) as therapeutic targets in NSCLC. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 3944–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tang, G.; Cheng, C.S.; Yeerken, R.; Chan, Y.T.; Fu, Z.; Zheng, Y.C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, N. Traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of cancers of hepatobiliary system: From clinical evidence to drug discovery. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Khan, M.A.; Srivastava, A.N.; Gupta, A.; Srivastava, A.; Jafri, T.R.; Siddiqui, Z.; Chaubey, S.; Khan, T.; Srivastava, A.K. Anticancer Potential of Dietary Natural Products: A Comprehensive Review. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 122–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Qi, B. Natural products targeting the MAPK-signaling pathway in cancer: Overview. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanvorachote, P.; Chamni, S.; Ninsontia, C.; Phiboonchaiyanan, P.P. Potential Anti-Metastasis Natural Compounds for Lung Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 5707–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, M.S.; Zhang, H.J.; Tsang, S.W. Perspectives of Plant Natural Products in Inhibition of Cancer Invasion and Metastasis by Regulating Multiple Signaling Pathways. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 5057–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yao, R.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wei, J.H. Dragon’s Blood from Dracaena Worldwide: Species, Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 1315–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhitwitayawuid, K.; Sawasdee, K.; Kirtikara, K. Flavonoids and stilbenoids with COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitory activity from Dracaena loureiri. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.Z.; He, A.D.; Wang, D.C.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, Y.J.; Liu, G.; Liang, M.L.; Da, X.W.; Yao, G.Q.; Xie, W.; et al. Antiplatelet Activity of Loureirin A by Attenuating Akt Phosphorylation: In Vitro Studies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 746, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.L.; Wang, K.; Shi, Y.F.; Shao, Z.X.; Zhang, C.X.; Sheng, K.W.; Ge, Z.D.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, X.Y. Downregulating Akt/NF-κB Signaling and Its Antioxidant Activity with Loureirin A for Alleviating the Progression of Osteoarthritis: In Vitro and Vivo Studies. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 78, 105953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wen, K.; Xu, Z.; He, Z.; Wu, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. Effect of Loureirin B on Crohn’s disease rat model induced by TNBS via IL-6/STAT3/NF-κB signaling pathway. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Qu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Shi, H.; Liu, G. Loureirin B Accelerates Diabetic Wound Healing by Promoting TGFβ/Smad-Dependent Macrophage M2 Polarization: A Concerted Analytical Approach Through Single-Cell RNA Sequencing and Experimental Verification. Phytother. Res. 2024; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Bai, X.; Yang, L.; Fan, L.; Li, Y.; Su, L.; Gao, J.; Han, S.; Hu, D. Loureirin B Inhibits Hypertrophic Scar Formation via Inhibition of the TGF-β1-ERK/JNK Pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; He, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Tao, K.; Shi, J.; Tang, C.; Su, L.; Hu, D. Loureirin B inhibits fibroblast proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition in hypertrophic scar via TGF-β/Smad pathway. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, K.T.; Chin-Sinex, H.; DeLuca, T.; Pomerening, J.R.; Sherer, J.; Watkins, J.B., 3rd; Foley, J.; Jesseph, J.M.; Mendonca, M.S. Dichloroacetate alters Warburg metabolism, inhibits cell growth, and increases the X-ray sensitivity of human A549 and H1299 NSC lung cancer cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapoung, S.; Arjsri, P.; Thippraphan, P.; Semmarath, W.; Yodkeeree, S.; Chiewchanvit, S.; Piyamongkol, W.; Limtrakul, P. Photochemoprotective effects of Spirulina platensis extract against UVB irradiated human skin fibroblasts. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 130, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorteau, J.; Chevalier, F.P.; Bonnet, S.; Barthélemy, T.; Lopez-Gaydon, A.; Martin, L.S.; Bechetoille, N.; Lamartine, J. Maintenance of Chronological Aging Features in Culture of Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts from Old Donors. Cells 2022, 11, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjsri, P.; Srisawad, K.; Mapoung, S.; Semmarath, W.; Thippraphan, P.; Umsumarng, S.; Yodkeeree, S.; Dejkriengkraikul, P. Hesperetin from root extract of Clerodendrum petasites S. Moore inhibits SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 subunit-induced NLRP3 inflammasome in A549 lung cells via modulation of the Akt/MAPK/AP-1 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiesen, L.C.; Baccarin, T.; Fischer-Muller, A.F.; Meyre-Silva, C.; Couto, A.G.; Bresolin, T.M.B.; Santin, J.R. Photochemoprotective effects against UVA and UVB irradiation and photosafety assessment of Litchi chinensis leaves extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 167, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, E.A.; Kasinski, A.L. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay in Cell Culture to Investigate Cell Proliferation. Bio Protoc. 2016, 6, e1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinotti, S.; Ranzato, E. Scratch Wound Healing Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2109, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Arnedo, A.; Torres Figueroa, F.; Clavijo, C.; Arbeláez, P.; Cruz, J.C.; Muñoz-Camargo, C. An image J plugin for the high throughput image analysis of in vitro scratch wound healing assays. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjsri, P.; Phetcharaburanin, J.; Suksawat, M.; Mapoung, S.; Subkamkaew, C.; Semmarath, W.; Yodkeeree, S.; Limtrakul, P. Spirogyra neglecta (Hassall) Kützing attenuates metastasis of castration-resistant human prostate cancer via the blockage of AKT signaling pathway. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 139, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbour, K.C.; Riely, G.J. Systemic Therapy for Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reckamp, K.L. Targeted Therapy for Patients with Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Wu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhu, X. The metastasizing mechanisms of lung cancer: Recent advances and therapeutic challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, R.; Das, C.; Kityania, S.; Nath, D.; Das, S.; Choudhury, M.D.; Patra, J.K.; Talukdar, A.D. Natural Flavonoids in the Prevention and Treatment of Lung Cancer: A Pharmacological Aspect. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2023, 26, 863–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, Ş.; Kaya, S.; Akkol, E.K.; Bardakçı, H. A comprehensive and current review on the role of flavonoids in lung cancer-Experimental and theoretical approaches. Phytomedicine 2022, 98, 153938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, J.N.; Fan, B.; Chen, X.N.; Pang, D.R.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.F.; Xiao, W.; Tu, P.F.; et al. Phenolic constituents, pharmacological activities, quality control, and metabolism of Dracaena species: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 244, 112138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.Y.; Yi, T.; Sze-To, C.M.; Zhu, L.; Peng, W.L.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Chen, H.B. A systematic review of the botanical, phytochemical and pharmacological profile of Dracaena cochinchinensis, a plant source of the ethnomedicine “dragon’s blood”. Molecules 2014, 19, 10650–10669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Arjsri, P.; Srisawad, K.; Yodkeeree, S.; Dejkriengkraikul, P. Exploring the Anticancer Potential of Traditional Thai Medicinal Plants: A Focus on Dracaena loureiri and Its Effects on Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Plants 2024, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonckheere, S.; Adams, J.; De Groote, D.; Campbell, K.; Berx, G.; Goossens, S. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) as a Therapeutic Target. Cells Tissues Organs 2022, 211, 157–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.R.; Moon, J.Y.; Ediriweera, M.K.; Song, Y.W.; Cho, M.; Kasiviswanathan, D.; Cho, S.K. Dietary flavonoid myricetin inhibits invasion and migration of radioresistant lung cancer cells (A549-IR) by suppressing MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions through inhibition of the FAK-ERK signaling pathway. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.E.; Kim, H.J.; Song, I.S.; Park, C.; Jung, J.W.; Park, D.S.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.R. Salinomycin suppresses TGF-β1-induced EMT by down-regulating MMP-2 and MMP-9 via the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, R.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K.; Gupta, G.; Dua, K. MAPK pathway: A potential target for the treatment of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Che, X.; Gao, X.; Liu, H. Rac3 Regulates Cell Invasion, Migration and EMT in Lung Adenocarcinoma Through p38 MAPK Pathway. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cao, X.; Zhao, H.; Guo, M.; Fang, X.; Li, K.; Qin, L.; He, Y.; Liu, X. Hypoxia Activates Notch4 via ERK/JNK/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathways to Promote Lung Adenocarcinoma Progression and Metastasis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 780121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.B.; Nabha, S.M.; Atanaskova, N. Role of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lan, M.; Chen, X.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, T.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Anti-invasion and anti-metastasis effects of Valjatrate E via reduction of matrix metalloproteinases expression and suppression of MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.Y.; Liu, L.; Kuok, C.F.; Wang, X.L.; Shi, D.; Ma, Q.; Cheng, X.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Li, M.J.; Zheng, Q.S.; et al. Loureirin A Promotes Cell Differentiation and Suppresses Migration and Invasion of Melanoma Cells via WNT and AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 47, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Sun, X.; Lu, L. Loureirin B inhibits Cervical Cancer Development by Blocking PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway: Network Pharmacology Analysis and Experimental Validation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 8587–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibino, S.; Kawazoe, T.; Kasahara, H.; Itoh, S.; Ishimoto, T.; Sakata-Yanagimoto, M.; Taniguchi, K. Inflammation-Induced Tumorigenesis and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappavigna, S.; Cossu, A.M.; Grimaldi, A.; Bocchetti, M.; Ferraro, G.A.; Nicoletti, G.F.; Filosa, R.; Caraglia, M. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs as Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| A549 Cells | H1299 Cells | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Loureirin A (µM) | 24 h | 245 ± 22.91 | 280 ± 21.79 |
| 48 h | 133 ± 8.19 | 126 ± 9.07 | |
| Loureirin B (µM) | 24 h | 350 ± 13.23 | 280 ± 20.00 |
| 48 h | 150 ± 15.00 | 136 ± 19.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Arjsri, P.; Srisawad, K.; Umsumarng, S.; Yodkeeree, S.; Dejkriengkraikul, P. Targeting MAPK Signaling: Loureirins A and B from Dracaena Loureiri Inhibit Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Life 2025, 15, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030396
Huang X, Arjsri P, Srisawad K, Umsumarng S, Yodkeeree S, Dejkriengkraikul P. Targeting MAPK Signaling: Loureirins A and B from Dracaena Loureiri Inhibit Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Life. 2025; 15(3):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030396
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiaomin, Punnida Arjsri, Kamonwan Srisawad, Sonthaya Umsumarng, Supachai Yodkeeree, and Pornngarm Dejkriengkraikul. 2025. "Targeting MAPK Signaling: Loureirins A and B from Dracaena Loureiri Inhibit Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines" Life 15, no. 3: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030396
APA StyleHuang, X., Arjsri, P., Srisawad, K., Umsumarng, S., Yodkeeree, S., & Dejkriengkraikul, P. (2025). Targeting MAPK Signaling: Loureirins A and B from Dracaena Loureiri Inhibit Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Life, 15(3), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030396










