The Role of the Claustrum in Parkinson’s Disease and Vascular Parkinsonism: A Matter of Network?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Anatomical Notes
- -
- Dorsal (insular) claustrum: situated above the rhinal fissure, medial to the insular cortex, this region has been extensively described in the literature [32].
- -
- Ventral (piriform) claustrum or endopiriform nucleus: Located below the rhinal fissure, medial to the piriform cortex, this part is sometimes termed the endopiriform nucleus. Paxinos and Watson [33], after studying rats’ cortexes, subdivided it into the dorsal (DEN) and ventral (VEN) endopiriform nuclei, with the DEN localized rostrally to the pre-endopiriform nucleus [34].
- -
- Projecting neurons, which are characterized by medium-sized to large polymorphic cell bodies and spiny dendrites.
- -
- Interneurons, which are identified by medium-sized to small round or oval cell bodies and aspiny dendrites [37].
3. Vascular Supply
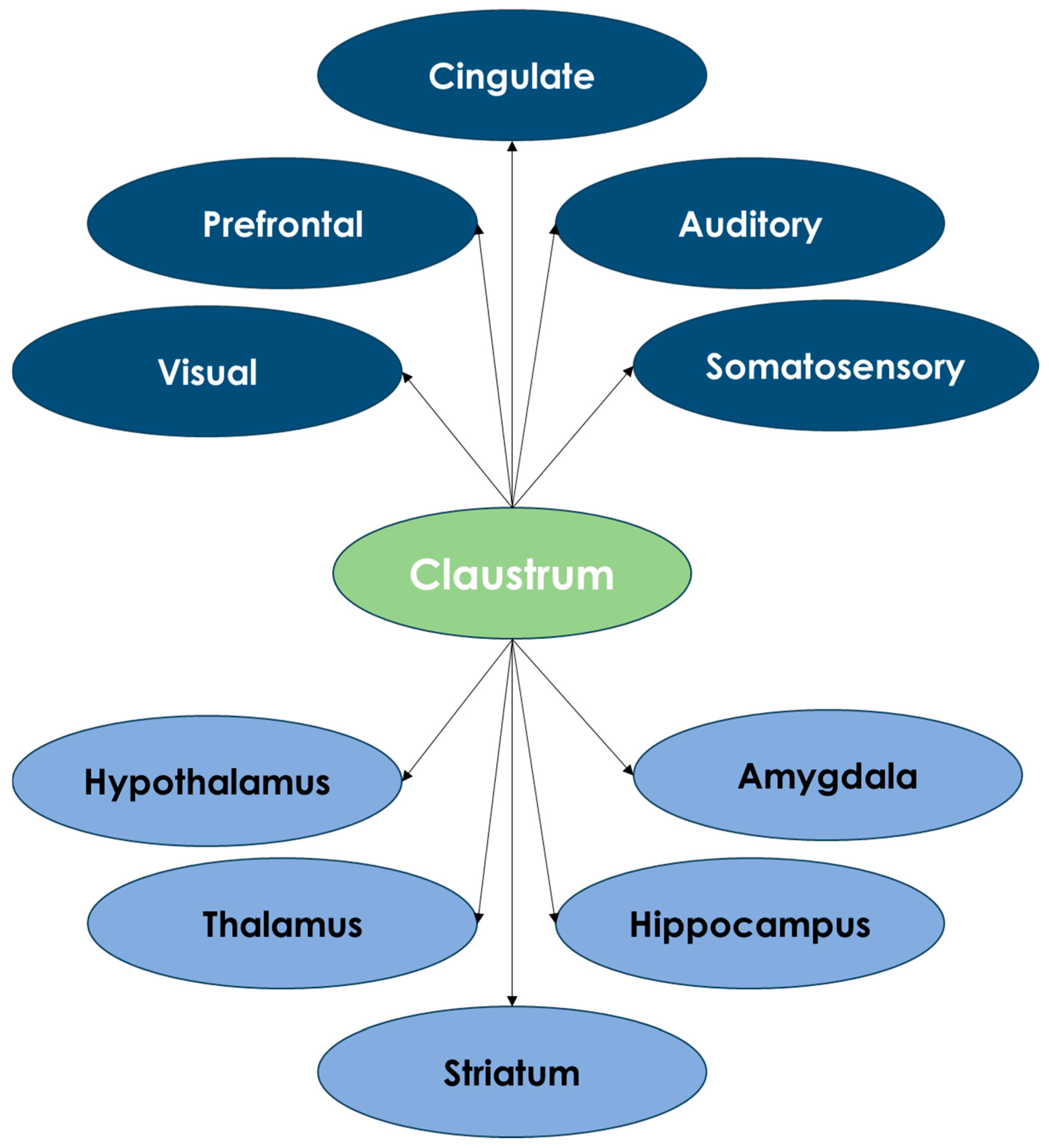
4. Claustrum Connections
5. The Claustrum and Parkinson’s Disease
6. Claustrum Involvement in Vascular Parkinsonism
- -
- Continuous capillary network: In the central nervous system of placental mammals, a continuous capillary network is present, facilitating weak collateral flow between adjacent arteriolar territories.
- -
- Multiple sources of blood supply: Some regions of the brain receive blood from two or three widely separated surface (pial) arterial sources, providing a more robust collateral supply.
- -
- Interdigitation: This refers to the overlapping and interpenetrating territories of adjacent arterioles. Instead of having smooth, distinct boundaries, the perfusion territories in the capillary bed fit together like a jigsaw puzzle.
7. Insights and Prospects for the Claustrum as a Therapeutic Target in Parkinsonism
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smythies, J.R.; Edelstein, L.R.; Ramachandran, V.S. The Claustrum: Structural, Functional, and Clinical Neuroscience; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski, M.M.; O’Mara, S.M. Dynamics of place, boundary and object encoding in rat anterior claustrum. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.B.; Lee, A.K.; Jackson, J. The claustrum. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R1401–R1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.G.; Mu, C.Q.; Qadir, H.; Madden, M.B.; Zeng, H.K.; Mathur, B.N. The mouse claustrum is required for optimal behavioral performance under high cognitive demand. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 88, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rinsveld, A.; Dricot, L.; Guillaume, M.; Rossion, B.; Schiltz, C. Mental arithmetic in the bilingual brain: Language matters. Neuropsychologia 2017, 101, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, B.N. The Claustrum in Review. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goll, Y.; Atlan, G.; Citri, A. Attention: The Claustrum. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crick, F.C.; Koch, C. What Is the Function of the Claustrum? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renouard, L.; Billwiller, F.; Ogawa, K.; Clément, O.; Camargo, N.; Abdelkarim, M.; Gay, N.; Scoté-Blachon, C.; Touré, R.; Libourel, P.-A.; et al. The Supramammillary Nucleus and the Claustrum Activate the Cortex During REM Sleep. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narikiyo, K.; Mizuguchi, R.; Ajima, A.; Shiozaki, M.; Hamanaka, H.; Johansen, J.P.; Mori, K.; Yoshihara, Y. The Claustrum Coordinates Cortical Slow-Wave Activity. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norimoto, H.; Fenk, L.A.; Li, H.-H.; Tosches, M.A.; Gallego-Flores, T.; Hain, D.; Reiter, S.; Kobayashi, R.; Macias, A.; Arends, A.; et al. A Claustrum in Reptiles and Its Role in Slow-Wave Sleep. Nature 2020, 578, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remedios, R.; Logothetis, N.K.; Kayser, C. Unimodal Responses Prevail Within the Multisensory Claustrum. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 12902–12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smythies, J.; Edelstein, L.; Ramachandran, V. Hypotheses Relating to the Function of the Claustrum. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlan, G.; Terem, A.; Peretz-Rivlin, N.; Sehrawat, K.; Gonzales, B.J.; Pozner, G.; Tasaka, G.-I.; Goll, Y.; Refaeli, R.; Zviran, O.; et al. The Claustrum Supports Resilience to Distraction. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2752–2762.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.G.; Mathur, B.N. Claustrum Circuit Components for Top-Down Input Processing and Cortical Broadcast. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 3945–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.; Smith, J.B.; Lee, A.K. The Anatomy and Physiology of Claustrum-Cortex Interactions. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 43, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hannesson, D.K.; Saucier, D.M.; Wallace, A.E.; Howland, J.; Corcoran, M.E. Susceptibility to Kindling and Neuronal Connections of the Anterior Claustrum. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 3674–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.; Tsuji, H.; Tamaoka, A. Mumps Virus Encephalitis with Symmetric Claustrum Lesions. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, E139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascella, N.G.; Gerner, G.J.; Fieldstone, S.C.; Sawa, A.; Schretlen, D.J. The Insula-Claustrum Region and Delusions in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 133, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, A.; Calamuneri, A.; Milardi, D.; Mormina, E.; Gaeta, M.; Corallo, F.; Buono, V.L.; Chillemi, G.; Marino, S.; Cacciola, A.; et al. Claustral Structural Connectivity and Cognitive Impairment in Drug naive Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Imaging Behav. 2019, 13, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedderich, D.M.; Menegaux, A.; Li, H.; Schmitz-Koep, B.; Stämpfli, P.; Bäuml, J.G.; Berndt, M.T.; Bäuerlein, F.J.B.; Grothe, M.J.; Dyrba, M.; et al. Aberrant Claustrum Microstructure in Humans After Premature Birth. Cereb. Cortex 2021, 31, 5549–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, A.; Menegaux, A.; Wendt, J.; Li, H.B.; Schmitz-Koep, B.; Ruzok, T.; Thalhammer, M.; Schinz, D.; Bartmann, P.; Wolke, D.; et al. Aberrant Claustrum Structure in Preterm-Born Neonates: An MRI Study. NeuroImage Clin. 2023, 37, 103286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thal, D.R.; Rub, U.; Orantes, M.; Braak, H. Phases of a beta-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology 2002, 58, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloyannis, S.J.; Mavroudis, I.; Baloyannis, I.S.; Costa, V.G. Synaptic alterations in the claustrum in Alzheimer’/INS;s disease: A Golgi and electron microscope study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 333, e356–e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morys, J.; Bobinski, M.; Wegiel, J.; Wisniewski, H.M.; Narkiewicz, O. Alzheimer’s disease severely affects areas of the claustrum connected with the entorhinal cortex. J. Hirnforsch. 1996, 37, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Bruguier, H.; Suarez, R.; Manger, P.; Hoerder-Suabedissen, A.; Shelton, A.M.; Oliver, D.K.; Packer, A.M.; Ferran, J.L.; García-Moreno, F.; Puelles, L.; et al. In Search of Common Developmental and Evolutionary Origin of the Claustrum and Subplate. J. Comp. Neurol. 2020, 528, 2956–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowiański, P.; Dziewiatkowski, J.; Kowiańska, J.; Moryś, J. Comparative Anatomy of the Claustrum in Selected Species: A Morphometric Analysis. Brain Behav. Evol. 1999, 53, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.; Puelles, L. Developmental Gene Expression in the Mouse Clarifies the Organization of the Claustrum and Related Endopiriform Nuclei. J. Comp. Neurol. 2017, 525, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.B.; Alloway, K.D.; Hof, P.R.; Orman, R.; Reser, D.H.; Watakabe, A.; Watson, G.D.R. The Relationship Between the Claustrum and Endopiriform Nucleus: A Perspective Towards Consensus on Cross-Species Homology. J. Comp. Neurol. 2019, 527, 476–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, C.M.; Irimia, A.; Goh, S.Y.M.; van Horn, J.D. The DTI Connectivity of the Human Claustrum. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, K.J.; Johnson, J.I. Diversity of spatial relationships of the claustrum and insula in branches of the mammalian radiation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1225, 30–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Academic Press: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ekstrand, J.J.; Domroese, M.E.; Johnson, D.M.; Feig, S.L.; Knodel, S.M.; Behan, M.; Haberly, L.B. A new subdivision of anterior piriform cortex and associated deep nucleus with novel features of interest for olfaction and epilepsy. J. Comp. Neurol. 2001, 434, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, L.; Legaz, I.; Gonzalez, G.; De Castro, F.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Puelles, L. Expression of Dbx1, Neurogenin 2, Semaphorin 5A, Cadherin 8, and Emx1 distinguish ventral and lateral pallial histogenetic divisions in the developing mouse claustroamygdaloid complex. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 474, 504–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puelles, L.; Kuwana, E.; Puelles, E.; Bulfone, A.; Shimamura, K.; Rubenstein, J.L. Pallial and subpallial derivatives in the embryonic chick and mouse telencephalon, traced by the expression of the genes Dlx-2, Emx-1, Nkx-2.1, Pax-6, and Tbr-1. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 424, 409–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuronal types in the claustrum of man. Anat. Embryol. 1982, 163, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Miranda, J.; Rhoton, A.L., Jr.; Kakizawa, Y.; Choi, C.; Álvarez-Linera, J. The claustrum and its projection system in the human brain: A microsurgical and tractographic anatomical study. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 108, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Miranda, J.; Rhoton, A.L., Jr.; Álvarez-Linera, J.; Kakizawa, Y.; Choi, C.; de Oliveira, E.P. Three-dimensional microsurgical and tractographic anatomy of the white matter of the human brain. Neurosurgery 2008, 62 (Suppl. S3), 989–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türe, U.; Yaşargil, M.G.; Friedman, A.H.; Al-Mefty, O. Fiber dissection technique: Lateral aspect of the brain. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Escartín, F.; García-Catalán, G.; Holanda, V.M.; Muftah Lahirish, I.A.; Quintero, R.B.; Neto, M.R.; Quilis-Quesada, V.; Ibaoc, K.B.; González Darder, J.M.; de Oliveira, E. Microsurgical Anatomy of the Insular Region and Operculoinsular Association Fibers and its Neurosurgical Application. World Neurosurg. 2019, 129, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoton, A.L. The supratentorial arteries. Neurosurgery 2002, 51 (Suppl. S4), S53–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnavas, G.G.; Grand, W. The insular cortex: Morphological and vascular anatomic characteristics. Neurosurgery 1999, 44, 127–136; discussion 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanriover, N.; Rhoton, A.L., Jr.; Kawashima, M.; Ulm, A.J.; Yasuda, A. Microsurgical anatomy of the insula and the sylvian fissure. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 891–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, J.; De Witt Hamer, P.C.; Berger, M.S.; Lawton, M.T.; Arnold, C.M.; de Lucas, E.M.; Duffau, H. Analysis of the subcomponents and cortical terminations of the perisylvian superior longitudinal fasciculus: A fiber dissection and DTI tractography study. Brain Struct. Funct. 2013, 218, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catani, M.; Jones, D.K.; Ffytche, D.H. Perisylvian language networks of the human brain. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delion, M.; Mercier, P. Microanatomical study of the insular perforating arteries. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 1991–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ture, U.; Yasargil, M.G.; Al-Mefty, O.; Yasargil, D.C. Arteries of the insula. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 92, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delion, M.; Mercier, P.; Brassier, G. Arteries and veins of the sylvian fissure and insula: Microsurgical anatomy. Adv. Tech. Stand. Neurosurg. 2016, 43, 185–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirone, A.; Cozzi, B.; Edelstein, L.; Peruffo, A.; Lenzi, C.; Quilici, F.; Antonini, R.; Castagna, M. Topography of Gng2- and NetrinG2-expression suggests an insular origin of the human claustrum. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilewska, B.; Najdzion, J. Types of neurons of the claustrum in the rabbit-Nissl, Klüver-Barrera and Golgi studies. Folia Morphol. 2001, 60, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, F.E.; Baizer, J.S. Neurochemically defined cell types in the claustrum of the cat. Brain Res. 2007, 1159, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.B.; Watson, G.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Alloway, K. A role for the claustrum in salience processing? Front. Neuroanat. 2019, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krimmel, S.R.; White, M.G.; Panicker, M.H.; Barrett, F.S.; Mathur, B.N.; Seminowicz, D.A. Resting state functional connectivity and cognitive task-related activation of the human claustrum. Neuroimage 2019, 196, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milardi, D.; Bramanti, P.; Milazzo, C.; Finocchio, G.; Arrigo, A.; Santoro, G.; Trimarchi, F.; Quartarone, A.; Anastasi, G.; Gaeta, M. Cortical and subcortical connections of the human claustrum revealed in vivo by constrained spherical deconvolution tractography. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillingham, C.M.; Jankowski, M.M.; Chandra, R.; Frost, B.E.; O’Mara, S.M. The claustrum: Considerations regarding its anatomy, functions and a programme for research. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 2017, 1, 2398212817718962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherk, H. The claustrum and the cerebral cortex. In Sensory-Motor Areas and Aspects of Cortical Connectivity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 467–499. [Google Scholar]
- Smythies, J.; Edelstein, L.; Ramachandran, V. The functional anatomy of the claustrum: The net that binds. Neurosciences 2012, 3, WMC003182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patru, C.M.; Reser, D. A new perspective on delusional states: Evidence for claustrum involvement. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitte, H.H.; Pifl, C.; Rajput, A.H.; Hörtnagl, H.; Tong, J.; Lloyd, G.K.; Kish, S.J.; Hornykiewicz, O. Dopamine and noradrenaline, but not serotonin, in the human claustrum are greatly reduced in patients with Parkinson’s disease: Possible functional implications. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 45, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, H.; Mathur, B.N. Identifying SUM projections to claustrum is about knowing your limits. Claustrum 2019, 4, 1609865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, B.; Dong, H.W.; Tao, H.W.; Zhang, L.I. Input–output organization of the mouse claustrum. J. Comp. Neurol. 2018, 526, 2428–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlan, G.; Terem, A.; Peretz-Rivlin, N.; Groysman, M.; Citri, A. Mapping synaptic cortico-claustral connectivity in the mouse. J. Comp. Neurol. 2017, 525, 1381–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.B.; Alloway, K.D. Functional specificity of claustrum connections in the rat: Interhemispheric communication between specific parts of motor cortex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 16832–16844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.G.; Mathur, B.N. Frontal cortical control of posterior sensory and association cortices through the claustrum. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 2999–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, S.; Schurr, R.; Atlan, G.; Citri, A.; Mezer, A.A. Automatic segmentation of the dorsal claustrum in humans using in vivo high-resolution MRI. Cereb. Cortex Commun. 2020, 1, tgaa062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, M.B.; Stewart, B.W.; White, M.G.; Krimmel, S.R.; Qadir, H.; Barrett, F.S.; Seminowicz, D.A.; Mathur, B.N. A role for the claustrum in cognitive control. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2022, 26, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, E.; Ballestrazzi, G.; Biancheri, D.; Caminiti, R.; Luppino, G. Involvement of the claustrum in the cortico-basal ganglia circuitry: Connectional study in the non-human primate. Brain Struct. Funct. 2024, 229, 1143–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzakis, M.E.; Pearce, R.K. The morbid anatomy of dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Pathology of Parkinson’s disease. Changes other than the nigrostriatal pathway. Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 1991, 14, 153–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Morphological substrates of dementia in parkinsonism. A critical update. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1997, 51, 57–82. [Google Scholar]
- Jellinger, K.A. Morphological substrates of mental dysfunction in Lewy body disease: An update. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 2000, 59, 185–212. [Google Scholar]
- Fearnley, J.M.; Lees, A.J. Ageing and Parkinson’s disease: Substantia nigra regional selectivity. Brain 1991, 114, 2283–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.M.; Marner, L.; Pakkenberg, H.; Pakkenberg, B. No global loss of neocortical neurons in Parkinson’s disease: A quantitative stereological study. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, R.; Kuhn, W.; Muller, T.; Woitalla, D.; Graeber, M.; Kosel, S.; Przuntek, H.; Epplen, J.T.; Schöls, L.; Riess, O. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, E.; Lechowicz, W.; Szpak, G.M.; Lewandowska, E.; Dymecki, J.; Wierzba-Bobrowicz, T. Limbic neuropathology in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease with concomitant dementia. Folia Neuropathol. 2004, 42, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Braak, H.; Sastre, M.; Del Tredici, K. Development of alpha-synuclein immunoreactive astrocytes in the forebrain parallels stages of intraneuronal pathology in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rub, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Jansen Steur, E.N.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attems, J.; Jellinger, K.A. The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus is not an obligatory trigger site of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2008, 34, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasson, B.I.; Forman, M.S.; Higuchi, M.; Golbe, L.I.; Graves, C.L.; Kotzbauer, P.T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Initiation and synergistic fibrillization of tau and alpha-synuclein. Science 2003, 300, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masliah, E.; Rockenstein, E.; Veinbergs, I.; Sagara, Y.; Mallory, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Mucke, L. Beta-amyloid peptides enhance alpha-synuclein accumulation and neuronal deficits in a transgenic mouse model linking Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12245–12250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Sandmann-Kiel, D.; Rub, U.; Schultz, C. Nerve cells expressing heat-shock proteins in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2001, 102, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Sastre, M.; Bohl, J.R.; de Vos, R.A.; Del Tredici, K. Parkinson’s disease: Lesions in dorsal horn layer I, involvement of parasympathetic and sympathetic pre-and postganglionic neurons. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 113, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaitzakis, M.E.; Pearce, R.K.; Gentleman, S.M. Clinical correlates of pathology in the claustrum in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 461, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, A.; Komatsuzaki, Y.; Shoji, S. Association of Lewy bodies and glial cytoplasmic inclusions in the brain of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2002, 104, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, S.; Wenning, G.K.; Low, P.A.; Brooks, D.J.; Mathias, C.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Wood, N.; Colosimo, C.; Durr, A.; Fowler, C.J.; et al. Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2008, 71, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hely, M.A.; Morris, J.G.; Reid, W.G.; Trafficante, R. Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: Non-L-dopa-responsive problems dominate at 15 years. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederich, N.J.; Goetz, C.G.; Stebbins, G.T. Repeated visual hallucinations in Parkinson’s disease as disturbed external/internal perceptions: Focused review and a new integrative model. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.G.; Dickson, D.W.; Lowe, J.; Emre, M.; O’Brien, J.T.; Feldman, H.; Cummings, J.; Duda, J.E.; Lippa, C.; Perry, E.K.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Third report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2005, 65, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.; Mintzer, J.; Aarsland, D.; Burn, D.; Chiu, H.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Duda, J.E.; Feldman, H.; et al. Dementia with Lewy bodies. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, R.; Iseki, E.; Murayama, N.; Minegishi, M.; Marui, W.; Togo, T.; Katsuse, O.; Kosaka, K.; Kato, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. Correlation in Lewy pathology between the claustrum and visual areas in brains of dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 415, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeVay, S.; Sherk, H. The visual claustrum of the cat. I. Structure and connections. J. Neurosci. 1981, 1, 956–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeVay, S.; Sherk, H. The visual claustrum of the cat. II. The visual field map. J. Neurosci. 1981, 1, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, D.G.; Insausti, R. Retrograde transport of D-[3H]-aspartate injected into the monkey amygdaloid complex. Exp. Brain Res. 1992, 88, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, D.G.; Cowan, W.M. Subcortical afferents to the hippocampal formation in the monkey. J. Comp. Neurol. 1980, 189, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.M.; Baird, A.A. Anatomical changes in the emerging adult brain: A voxel-based morphometry study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2006, 27, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, N.H.; Rudrauf, D.; Damasio, H.; Bechara, A. Damage to the insula disrupts addiction to cigarette smoking. Science 2007, 315, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, A.J.; Broe, G.A.; Halliday, G.M. Visual hallucinations in Lewy body disease relate to Lewy bodies in the temporal lobe. Brain 2002, 125 Pt 2, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzakis, M.E.; Christian, L.M.; Moran, L.B.; Graeber, M.B.; Pearce, R.K.; Gentleman, S.M. Dementia and visual hallucinations associated with limbic pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2009, 15, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I.; Lopez-Gonzalez, I.; Carmona, M.; Dalfo, E.; Pujol, A.; Martinez, A. Neurochemistry and the non-motor aspects of PD. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 508–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qurrat-ul-Ain; Abidi, T.S. Unraveling the function of claustrum. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2005, 55, 123–125. [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan, V.; Healy, D.G.; Pal, S.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Sleep-related problems of Parkinson’s disease. Age Ageing 2006, 35, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perico, C.A.; Skaf, C.R.; Yamada, A.; Duran, F.; Buchpiguel, C.A.; Castro, C.C.; Soares, J.C.; Busatto, G.F. Relationship between regional cerebral blood flow and separate symptom clusters of major depression: A single photon emission computed tomography study using statistical parametric mapping. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 384, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandberg, E.; Larsen, J.P.; Aarsland, D.; Cummings, J.L. The occurrence of depression in Parkinson’s disease. A community-based study. Arch. Neurol. 1996, 53, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, R.T.; Kimbrell, T.A.; Ketter, T.A.; Frye, M.A.; Willis, M.W.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Post, R.M. Principal components of the Beck Depression Inventory and regional cerebral metabolism in unipolar and bipolar depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 51, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyildiz, S.; Velioglu, H.A.; Ayyildiz, B.; Sutcubasi, B.; Hanoglu, L.; Bayraktaroglu, Z.; Yildirim, S.; Atasever, A.; Yulug, B. Differentiation of claustrum resting-state functional connectivity in healthy aging, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2023, 44, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, D.M.; Bell, M.A.; Challa, V.R. Features of the cerebral vascular pattern that predict vulnerability to perfusion or oxygenation deficiency: An anatomic study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1990, 11, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vizcarra, J.A.; Lang, A.E.; Sethi, K.D.; Espay, A.J. Vascular Parkinsonism: Deconstructing a syndrome. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reuck, J.L.; Deramecourt, V.; Auger, F.; Durieux, N.; Cordonnier, C.; Devos, D.; Defebvre, L.; Moreau, C.; Caparros-Lefebvre, D.; Leys, D.; et al. Iron deposits in post-mortem brains of patients with neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular diseases: A semi-quantitative 7.0 T magnetic resonance imaging study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galantucci, S.; Agosta, F.; Stefanova, E.; Basaia, S.; Van Den Heuvel, M.P.; Stojković, T.; Canu, E.; Stanković, I.; Spica, V.; Copetti, M.; et al. Structural brain connectome and cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Radiology 2017, 283, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Yang, J.; Shang, H. Voxelwise meta-analysis of gray matter anomalies in Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy and Parkinson’s disease using anatomic likelihood estimation. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 587, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hafycz, J.; Keenan, B.T.; Guo, X.; Pack, A.; Naidoo, N. Acute sleep loss upregulates the synaptic scaffolding protein, homer1a, in noncanonical sleep/wake brain regions, claustrum, piriform and cingulate cortices. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 4, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunga, N.; Curtis, K.; Tomcik, C.B.; Lizarraga, K.J. Right putamen and claustrum infarction mimicking normal pressure hydrocephalus. BMJ Case Rep. 2024, 17, e259957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramanandam, V.; Lizarraga, K.J.; Soh, D.; Algarni, M.; Rohani, M.; Fasano, A. Unusual gait disorders: A phenomenological approach and classification. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximov, G.K.; Hinova-Palova, D.V.; Iliev, A.A.; Kotov, G.N.; Kirkov, V.K.; Landzhov, B.V.; Maksimov, K.G. Ischemic stroke of the left claustrum in a 55-year-old female: A case report. Claustrum 2018, 3, 1528135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vidal, L.; Alcauter, S.; Barrios, F.A. The functional connectivity of the human claustrum, according to the Human Connectome Project database. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, J.; Neubauer, A.; Hedderich, D.M.; Schmitz-Koep, B.; Ayyildiz, S.; Schinz, D.; Hippen, R.; Daamen, M.; Boecker, H.; Zimmer, C.; et al. Human Claustrum Connections: Robust In Vivo Detection by DWI-Based Tractography in Two Large Samples. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2024, 45, e70042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruen, P.D.; McGeown, W.J.; Shanks, M.F.; Venneri, A. Neuroanatomical correlates of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2008, 131 Pt 9, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koubeissi, M.Z.; Bartolomei, F.; Beltagy, A.; Picard, F. Electrical stimulation of a small brain area reversibly disrupts consciousness. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 37, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolenko, V.N.; Rizaeva, N.A.; Beeraka, N.M.; Oganesyan, M.V.; Kudryashova, V.A.; Dubovets, A.A.; Borminskaya, I.D.; Bulygin, K.V.; Sinelnikov, M.Y.; Aliev, G. The mystery of claustral neural circuits and recent updates on its role in neurodegenerative pathology. Behav. Brain Funct. 2021, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banati, R.B.; Goerres, G.W.; Tjoa, C.; Aggleton, J.P.; Grasby, P. The functional anatomy of visual-tactile integration in man: A study using positron emission tomography. Neuropsychologia 2000, 38, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjikhani, N.; Roland, P.E. Cross-modal transfer of information between the tactile and the visual representations in the human brain: A positron emission tomographic study. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghavi, H.R.; Eriksson, J.; Larsson, A.; Nyberg, L. The claustrum/insula region integrates conceptually related sounds and pictures. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 422, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, P.; Ren, M.; Phan, T.G.; Callisaya, M.; Ly, J.V.; Beare, R.; Chong, W.; Srikanth, V. Silent infarcts and cerebral microbleeds modify the associations of white matter lesions with gait and postural stability: Population-based study. Stroke 2012, 43, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, M.D.; Buckner, R.L.; Liu, H.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Lozano, A.M.; Pascual-Leone, A. Resting-state networks link invasive and noninvasive brain stimulation across diverse psychiatric and neurological diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4367–E4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Z.; Bailey, S.K.; Zhou, J.; Cutting, L.E.; Gore, J.C.; Ding, Z. Functional connectivity and activity of white matter in somatosensory pathways under tactile stimulations. Neuroimage 2017, 152, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Huang, Y.; Bailey, S.K.; Gao, Y.; Cutting, L.E.; Rogers, B.P.; Newton, A.T.; Gore, J.C. Detection of synchronous brain activity in white matter tracts at rest and under functional loading. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boes, A.D.; Prasad, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Caviness, V.S.; Fox, M.D. Network localization of neurological symptoms from focal brain lesions. Brain 2015, 138 Pt 10, 3061–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, D.B.; Boes, A.D.; Demertzi, A.; Evrard, H.C.; Laureys, S.; Edlow, B.L.; Liu, H.; Saper, C.B.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Fox, M.D.; et al. A human brain network derived from coma-causing brainstem lesions. Neurology 2016, 87, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganiere, S.; Boes, A.D.; Fox, M.D. Network localization of hemichorea-hemiballismus. Neurology 2016, 86, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutterer, M.J.; Bruss, J.; Boes, A.D.; Voss, M.W.; Bechara, A.; Tranel, D. Canceled connections: Lesion-derived network mapping helps explain differences in performance on a complex decision-making task. Cortex 2016, 78, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, R.R.; Horn, A.; Cushman, F.; Fox, M.D. Lesion network localization of criminal behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, R.R.; Laganiere, S.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Prasad, S.; Fox, M.D. Finding the imposter: Brain connectivity of lesions causing delusional misidentifications. Brain 2017, 140 Pt 2, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A.; Laganiere, S.E.; Lam, S.; Fox, M.D. Lesions causing freezing of gait localize to a cerebellar functional network. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joutsa, J.; Horn, A.; Hsu, J.; Fox, M.D. Localizing parkinsonism based on focal brain lesions. Brain 2018, 141, 2445–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Segment | Features |
|---|---|
| Dorsal Claustrum (Insular Claustrum) | A continuous, irregular lamina of gray matter situated between the putamen (separated by the external capsule) and the insular cortex (separated by the extreme capsule). It has a triangular cross-sectional shape, narrowing superiorly and widening inferiorly. The external capsule, in contrast, widens superiorly and becomes thinner or absent near the lower dorsal claustrum. |
| Ventral Claustrum (Fragmented Claustrum) | It is composed of diffuse, island-like gray matter fragmented by the uncinate and inferior occipitofrontal fascicles. It has superior and inferior parts: The superior ventral claustrum connects to the anteroinferior pole of the dorsal claustrum and extends toward the base of the frontal lobe near the prepiriform cortex. The inferior ventral claustrum connects to the posteroinferior pole of the dorsal claustrum and extends toward the amygdalar region, with which it shares a close anatomical relationship, and it is often difficult to delineate. |
| Pathological Changes | Details |
|---|---|
| Lewy Body (LB) and Lewy Neurite (LN) Pathology |
|
| Astrocytic αSyn Inclusions |
|
| Proteinopathies |
|
| Functional Connectivity Changes |
|
| Clinical Correlations |
|
| Behavioral and Psychiatric Symptoms |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zedde, M.; Quatrale, R.; Cossu, G.; Sette, M.D.; Pascarella, R. The Role of the Claustrum in Parkinson’s Disease and Vascular Parkinsonism: A Matter of Network? Life 2025, 15, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020180
Zedde M, Quatrale R, Cossu G, Sette MD, Pascarella R. The Role of the Claustrum in Parkinson’s Disease and Vascular Parkinsonism: A Matter of Network? Life. 2025; 15(2):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020180
Chicago/Turabian StyleZedde, Marialuisa, Rocco Quatrale, Gianni Cossu, Massimo Del Sette, and Rosario Pascarella. 2025. "The Role of the Claustrum in Parkinson’s Disease and Vascular Parkinsonism: A Matter of Network?" Life 15, no. 2: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020180
APA StyleZedde, M., Quatrale, R., Cossu, G., Sette, M. D., & Pascarella, R. (2025). The Role of the Claustrum in Parkinson’s Disease and Vascular Parkinsonism: A Matter of Network? Life, 15(2), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020180






