Objective Analysis of Reading Ability Using an Eye Tracker in Intermittent Exotropia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Ophthalmic Examination
2.3. Reading Task and Eye-Tracking Protocol
2.4. Fusion Control Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Participants
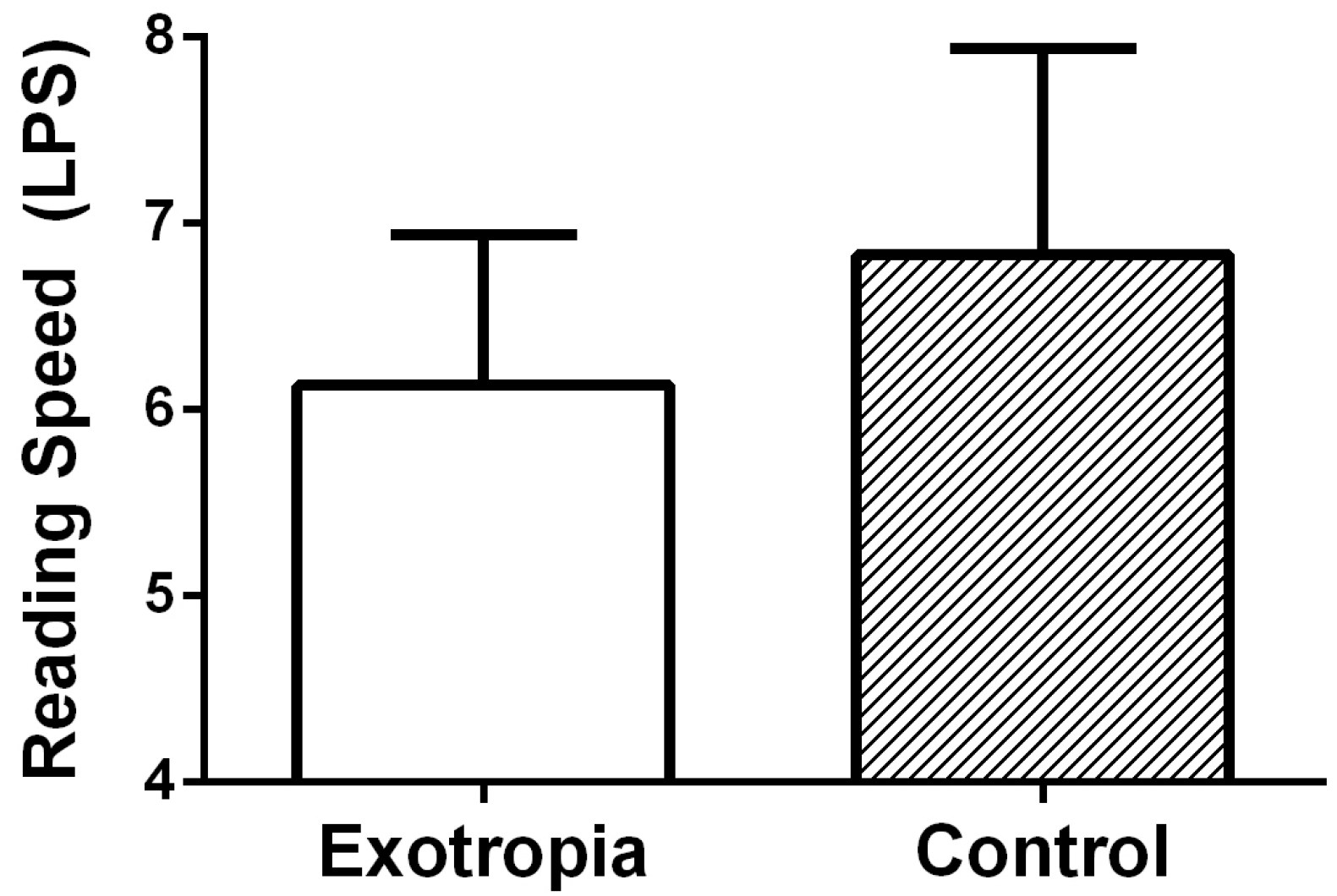
3.2. Reading Speed
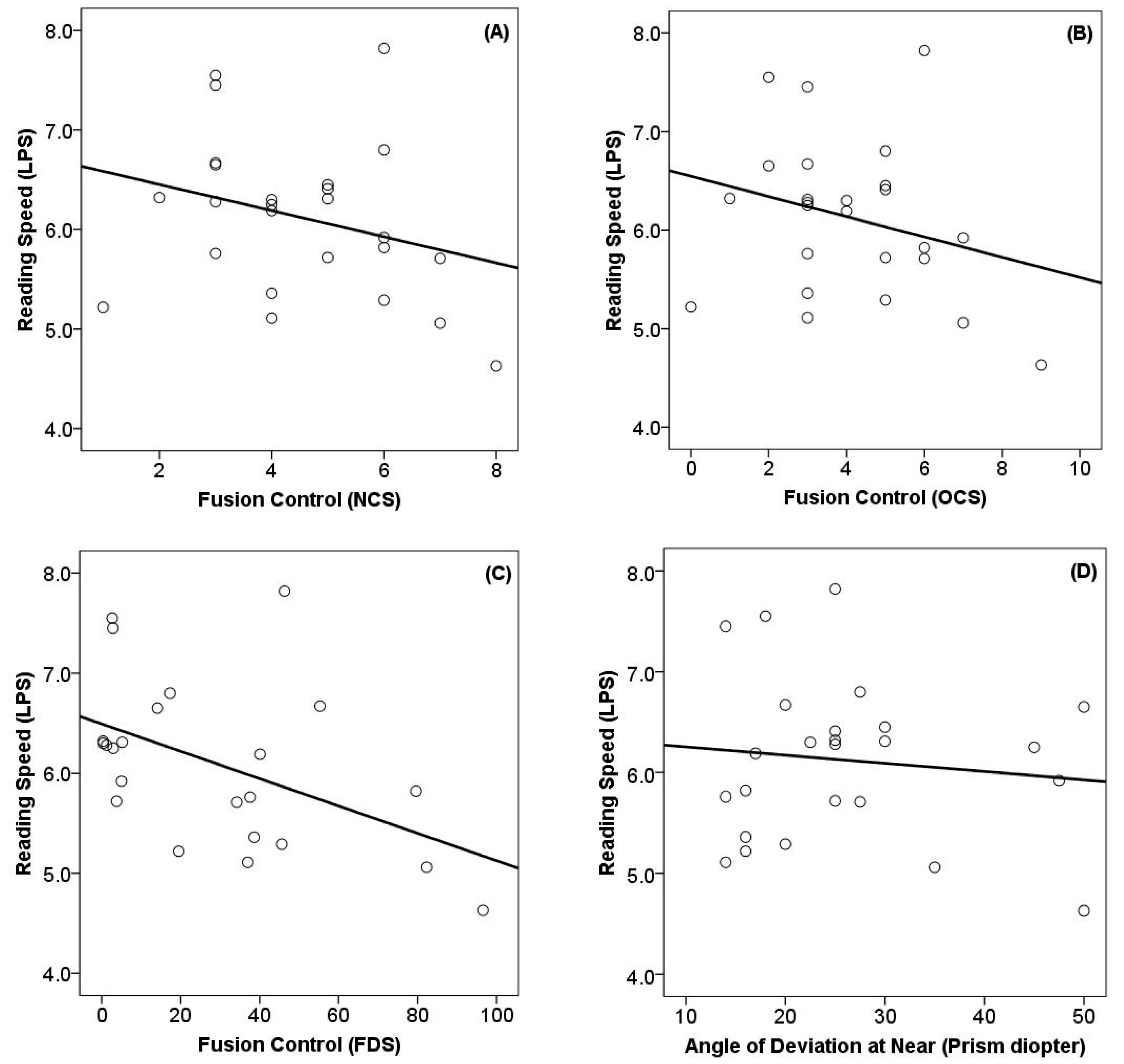
3.3. Relationship Between Reading Speed and Related Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsuo, T.; Matsuo, C. The prevalence of strabismus and amblyopia in Japanese elementary school children. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2005, 12, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.W.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J.J.; Ding, H.; Bai, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, R.B.; Liu, H. Epidemiology of Intermittent Exotropia in Preschool Children in China. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2016, 93, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goseki, T.; Ishikawa, H. The prevalence and types of strabismus, and average of stereopsis in Japanese adults. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 61, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.E.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, K.H.; Epidemiologic Survey Committee of the Korean Ophthalmological Society. Prevalence and risk factors of strabismus in children and adolescents in South Korea: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2008–2011. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.W.; Koo, B.S.; Lee, H.Y. Preschool Vision Screening in Korea: Results in 2003. J. Korean Ophthalmol. Soc. 2006, 47, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.W.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.C. An empirical study of college students’ reading engagement on academic achievement. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1025754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, S.R.; Marsh, H.W.; Sheppard, M.J.; Sheppard, J.L. 7-Year Longitudinal-Study of the Early Prediction of Reading-Achievement. J. Educ. Psychol. 1985, 77, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, H.W.; Newman, R.S. Long-term prediction of achievement and attitudes in mathematics and reading. Child. Dev. 1986, 57, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wu, Y.; Peng, T.; Wang, C.; Lou, J.; Xu, M.; Bao, J.; Chen, C.; Yu, X. Reading speed in school-age children with intermittent exotropia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hou, J.; Huang, H.; Wei, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, T.; Liu, J.; Deng, D.; Ling, S.; Yang, W.; et al. Reading ability in children with intermittent exotropia and its association with binocular visual function and visual information processing capability. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025, 25, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, M.; Kanda, H.; Endo, T.; Lohmann, T.K.; Miyoshi, T.; Morimoto, T.; Fujikado, T. Relationship between reading performance and saccadic disconjugacy in patients with convergence insufficiency type intermittent exotropia. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 60, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, M.; Kanda, H.; Endo, T.; Morimoto, T.; Miyoshi, T.; Fujikado, T. Binocular coordination and reading performance during smartphone reading in intermittent exotropia. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 12, 2069–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H.; Pakbin, M.; Ali, B.; Yekta, A.; Ostadimoghaddam, H.; Asharlous, A.; Aghamirsalim, M.; Khabazkhoob, M. Near Points of Convergence and Accommodation in a Population of University Students in Iran. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2019, 14, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.S.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, Y.S. Korean version of the MNREAD acuity chart. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Yang, H.K.; Han, S.B.; Hwang, J.M. Measurement of Fusion Control with Eye Tracking Device in Intermittent Exotropia. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, D.; Clarke, M.P.; Haggerty, H.; Hrisos, S.; Powell, C.; Sloper, J.; Strong, N.P. Grading the severity of intermittent distance exotropia: The revised Newcastle Control Score. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 92, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggerty, H.; Richardson, S.; Hrisos, S.; Strong, N.P.; Clarke, M.P. The Newcastle Control Score: A new method of grading the severity of intermittent distance exotropia. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohney, B.G.; Holmes, J.M. An office-based scale for assessing control in intermittent exotropia. Strabismus 2006, 14, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, S.R.; Liebermann, L.; Leske, D.A.; Mohney, B.G.; Holmes, J.M. Improved assessment of control in intermittent exotropia using multiple measures. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 152, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, S.R.; Leske, D.A.; Liebermann, L.; Holmes, J.M. Quantifying variability in the measurement of control in intermittent exotropia. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2015, 19, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Yang, H.K.; Hwang, J.M. Binocular visual acuity in intermittent exotropia: Role of accommodative convergence. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 154, 981–986.e983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stifter, E.; Sacu, S.; Weghaupt, H.; Konig, F.; Richter-Muksch, S.; Thaler, A.; Velikay-Parel, M.; Radner, W. Reading performance depending on the type of cataract and its predictability on the visual outcome. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2004, 30, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, F.; Sarac, S.; Erzurum, S.A. Effect of strabismus surgery on the reading ability of school-age children. Clin. Pediatr. 2014, 53, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Choi, M.Y. A Comparison of Reading Speeds of Intermittent Exotropia and Normal Children. J. Korean Ophthalmol. Soc. 2020, 61, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshit, A.; Majhi, D.; Schmid, K.L.; Warkad, V.; Atchison, D.A.; Webber, A.L. Fine Motor Skills, Reading Speed, and Self-Reported Quality of Life in Adults With Amblyopia and/or Strabismus. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2024, 65, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Yang, D.P.; Yang, Y.; Yang, W.H.; Lu, Y.M.; Yu, X.P.; Chang, S. Visual and auditory attention defects in children with intermittent exotropia. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2024, 50, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoureux, D.; Yeo, S.; Bhambhwani, V. Comparison of binocular reading speed in patients with strabismus without amblyopia versus controls. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2025, 60, e281–e285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, A.; Cheong, A.M.; Cheung, S.H.; He, Y.; Kwon, M.; Mansfield, J.S.; Subramanian, A.; Yu, D.; Legge, G.E. Baseline MNREAD Measures for Normally Sighted Subjects From Childhood to Old Age. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 3836–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.H.; Khalid, N.M.; Buari, N.H. Age factor affects reading acuity and reading speed in attaining text information. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 12, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dysli, M.; Vogel, N.; Abegg, M. Reading performance is not affected by a prism induced increase of horizontal and vertical vergence demand. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latvala, M.L.; Korhonen, T.T.; Penttinen, M.; Laippala, P. Ophthalmic findings in dyslexic schoolchildren. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1994, 78, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emam, A.; Youssef, A. Do Females Read Faster than Males? An Empirical Study Using Eye Tracking Systems. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues 2012, 9, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin Fievez, F.; Lions, C.; Bucci, M.P. Preliminary Study: Impact of Strabismus and Surgery on Eye Movements When Children are Reading. Strabismus 2018, 26, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuillade, V.; Bourcier, T.; Gaucher, D.; Speeg, C.; Sauer, A. The effect of strabismus surgery on the learning abilities of school-aged children. Acta Ophthalmol. 2023, 101, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Meng, H.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, S. High-Accuracy Intermittent Strabismus Screening via Wearable Eye-Tracking and AI-Enhanced Ocular Feature Analysis. Biosensors 2025, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, D.M.; Kuchhangi, A.; Tame, J.; Cooper, K.; Hajkazemshirazi, L.; Indaram, M.; Keenan, J.D.; Oatts, J.T. Evaluation of a Novel Virtual Reality Simulated Alternate Cover Test to Assess Strabismus: A Prospective, Masked Study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2025, 269, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugathasan, L.; Partanen, M.; Chu, V.; Lyons, C.; Giaschi, D. Reading ability of children treated for amblyopia. Vis. Res. 2019, 156, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bababekova, Y.; Rosenfield, M.; Hue, J.E.; Huang, R.R. Font size and viewing distance of handheld smart phones. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, 795–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.; Schotter, E.R.; Masson, M.E.J.; Potter, M.C.; Treiman, R. So Much to Read, So Little Time: How Do We Read, and Can Speed Reading Help? Psychol. Sci. Publ. Int. 2016, 17, 4–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Intermittent Exotropia Group (n = 25) | Control Group (n = 25) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Mean ± SD (Min~Max) | Median | IQR | Mean ± SD (Min~Max) | Median | IQR | p Value | Cohen’s D |
| Sex (M:F) | 13:12 | 10:15 | 0.157 * | |||||
| Age at examination (y) | 24.3 ± 6.6 (15.5~40.7) | 24.2 | 19.3~26.0 | 26.8 ± 2.5 (21.4~30.9) | 26.5 | 24.9~29.0 | 0.095 † | 0.5 |
| Distance BCVA (LogMAR) | 0.00 ± 0.01 (0.00~0.02) | 0.00 | 0.00~0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.01 (0.00~0.05) | 0.00 | 0.00~0.00 | 0.428 † | 0.0 |
| Near BCVA (LogMAR) | 0.00 ± 0.01 (0.00~0.05) | 0.00 | 0.00~0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 (0.00~0.00) | 0.00 | 0.00~0.00 | 0.317 † | 0.0 |
| Refractive errors, SEQ (D) | −3.19 ± 2.74 (−9.88~+1.81) | −2.50 | −5.10~−1.34 | −3.00 ± 2.89 (−8.94~+0.69) | −2.98 | −4.69~−0.47 | 0.720 † | 0.1 |
| Stereopsis (LogArcsec) | 1.95 ± 0.29 (1.51~2.60) | 2.00 | 1.70~2.00 | 1.58 ± 0.30 (1.10~2.00) | 1.58 | 1.35~1.80 | <0.001 † | 1.3 |
| NPC (cm) | 8.7 ± 3.0 (3.5~26.0) | 7.0 | 6.0~10.8 | 7.9 ± 2.0 (5.0~13.0) | 7.0 | 6.0~9.3 | 0.564 † | 0.3 |
| NPA (cm) | 9.8 ± 3.7 (4.8~19.0) | 10.0 | 6.4~11.6 | 9.1 ± 2.0 (5.5~14.5) | 9.5 | 7.3~10.5 | 0.655 † | 0.2 |
| Distance deviation (PD) | 21.1± 13.0 (4~50) | 20.0 | 7.0~28.8 | 0.2 ± 0.9 (0~4) | 0.0 | 0.0~0.0 | <0.001 † | 2.3 |
| Near deviation (PD) | 27.1 ± 10.0 (14~50) | 25.0 | 16.5~30.0 | 0.8 ± 1.4 (0~4) | 0.0 | 0.0~0.0 | <0.001 † | 3.7 |
| Male | Female | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (Min~Max) | Median (IQR) | Mean ± SD (Min~Max) | Median (IQR) | p Value | |
| LPS_IXT group | 6.1 ± 1.0 (4.6~8.4) | 6.0 (5.5~6.6) | 6.2 ± 0.6 (5.6~7.4) | 6.2 (5.6~6.5) | 0.856 |
| LPS_Control group | 7.3 ± 1.0 (5.5~9.0) | 7.2 (6.8~7.9) | 6.5 ± 1.1 (4.7~9.0) | 6.5 (6.1~6.7) | 0.104 |
| FD score_IXT group | 36.4 ± 29.9 (2.9~96.6) | 34.2 (14.1~46.3) | 22.4 ± 27.4 (0.4~82.3) | 26.5 (14.4~39.5) | 0.257 |
| Predictor | B (Estimate) | SE | 95% CI | Wald χ2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | −0.04 | 0.02 | −0.08 to 0.00 | 3.29 | 0.070 |
| Stereopsis (LogArcsec) | −0.05 | 0.06 | −0.17 to 0.06 | 0.83 | 0.361 |
| Refractive errors (D) | −0.37 | 0.45 | −1.25 to 0.51 | 0.68 | 0.409 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.H.; Hwang, J.-M.; Yang, H.K. Objective Analysis of Reading Ability Using an Eye Tracker in Intermittent Exotropia. Life 2025, 15, 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111778
Kim DH, Hwang J-M, Yang HK. Objective Analysis of Reading Ability Using an Eye Tracker in Intermittent Exotropia. Life. 2025; 15(11):1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111778
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dong Hyun, Jeong-Min Hwang, and Hee Kyung Yang. 2025. "Objective Analysis of Reading Ability Using an Eye Tracker in Intermittent Exotropia" Life 15, no. 11: 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111778
APA StyleKim, D. H., Hwang, J.-M., & Yang, H. K. (2025). Objective Analysis of Reading Ability Using an Eye Tracker in Intermittent Exotropia. Life, 15(11), 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111778





