Association Between Birth Outcomes and Gestational Weight Gain Among Forcibly Displaced Rohingya and Nearby Host Community, in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
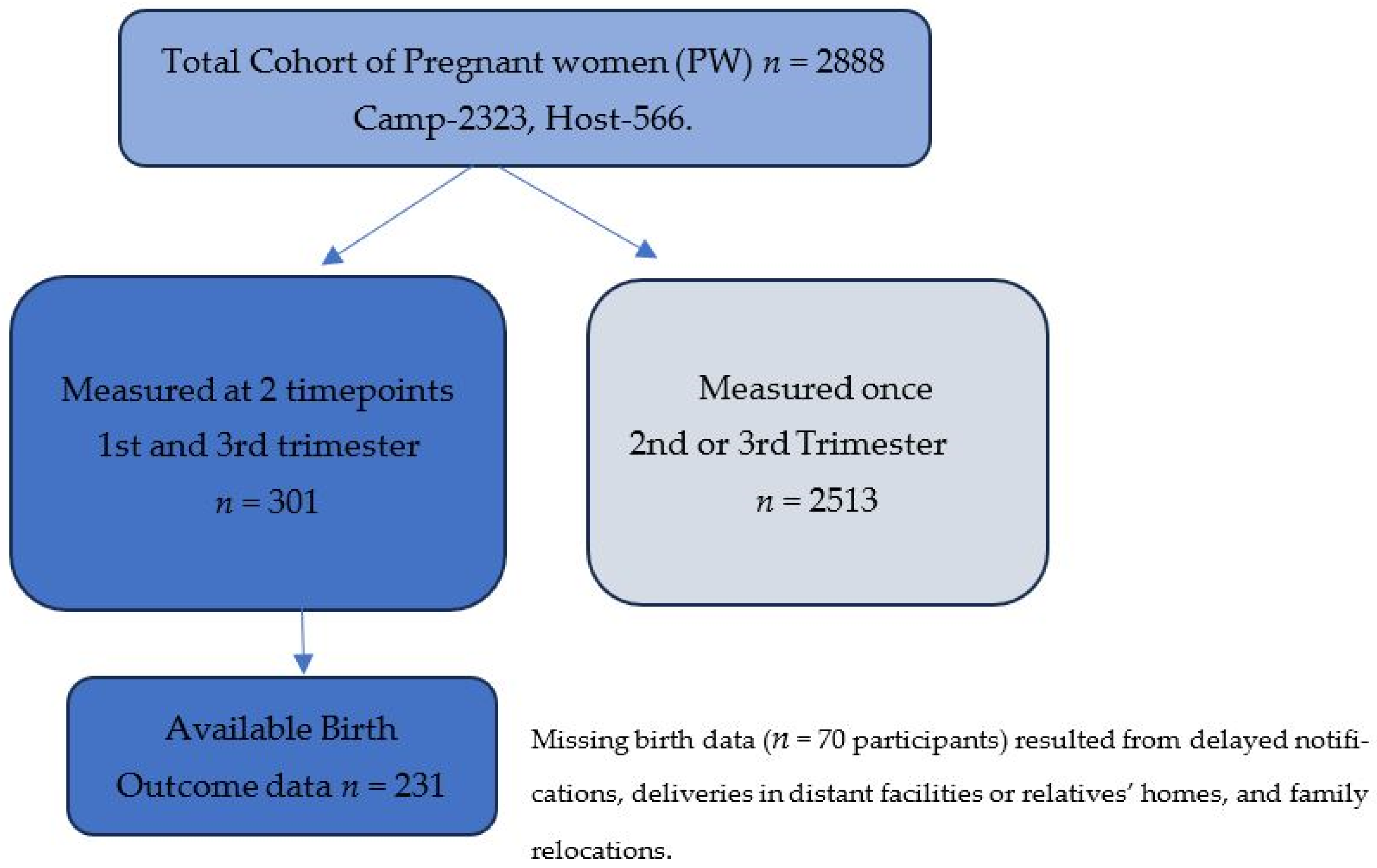
2.2. Sample Selection and Procedure
2.3. Data Collection Procedure and Tools
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OD | Odds Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
Appendix A
| Characteristic | Not Missing at Birth n = 231 1 (%) | Missing at Birth n = 70 1 (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mother Age (Year) | 0.334 2 | ||
| Below 20 | 127 (54.98) | 45 (64.29) | |
| 20–29 | 82 (35.50) | 21 (30.00) | |
| 30–39 | 22 (9.52) | 4 (5.71) | |
| Education | 0.516 3 | ||
| No School (No class) | 18 (7.79) | 2 (2.86) | |
| Madrassa (Religious education) | 74 (32.03) | 23 (32.86) | |
| Reached primary (Preschool to class 3) | 53 (22.94) | 19 (27.14) | |
| More than primary (More than class 3) | 86 (37.23) | 26 (37.14) | |
| Parity | 0.004 2 | ||
| Nulliparous | 78 (33.77) | 38 (54.29) | |
| Primiparous | 61 (26.41) | 17 (24.29) | |
| Multiparous | 92 (39.83) | 15 (21.43) | |
| Pre pregnancy BMI | 0.994 2 | ||
| Underweight (<18.5 kg/m2) | 30 (12.99) | 10 (14.29) | |
| Normal Weight (18.5–22.9 kg/m2) | 130 (56.28) | 39 (55.71) | |
| Overweight (23–24.9 kg/m2) | 34 (14.72) | 10 (14.29) | |
| Obese ≥ 25 kg/m2 | 37 (16.02) | 11 (15.71) | |
| Toilet facility | 203 (87.88) | 67 (95.71) | 0.059 2 |
| Bathing facility | 219 (94.81) | 68 (97.14) | 0.533 3 |
References
- Farpour-Lambert, N.J.; Baker, J.L.; Hassapidou, M.; Holm, J.C.; Nowicka, P.; O’Malley, G.; Weiss, R. Childhood Obesity Is a Chronic Disease Demanding Specific Health Care—A Position Statement from the Childhood Obesity Task Force (COTF) of the European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). Obes. Facts 2015, 8, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.; Voerman, E.; Amiano, P.; Barros, H.; Beilin, L.J.; Bergström, A.; Charles, M.A.; Chatzi, L.; Chevrier, C.; Chrousos, G.P.; et al. Impact of maternal body mass index and gestational weight gain on pregnancy complications: An individual participant data meta-analysis of European, North American and Australian cohorts. BJOG 2019, 126, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heslehurst, N.; Brown, H.; Pemu, A.; Coleman, H.; Rankin, J. Perinatal health outcomes and care among asylum seekers and refugees: A systematic review of systematic reviews. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deputy, N.P.; Sharma, A.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Olson, C.K. Achieving Appropriate Gestational Weight Gain: The Role of Healthcare Provider Advice. J. Womens Health 2018, 27, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray-Davis, B.; Berger, H.; Melamed, N.; Mawjee, K.; Syed, M.; Barrett, J.; Ray, J.G.; Geary, M.; McDonald, S.D. Gestational weight gain counselling practices among different antenatal health care providers: A qualitative grounded theory study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkay, Ü.; Balcı, E.; Çolak, E.; Korkmaz, A.; Arslan, H. Gestational Weight Gain and Perinatal Outcomes in Refugee Women: A Retrospective Study from a Single Center. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 33, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar]
- Reese Masterson, A.; Usta, J.; Gupta, J.; Ettinger, A.S. Assessment of reproductive health and violence against women among displaced Syrians in Lebanon. BMC Womens Health 2014, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, R.L.; Benno, M.T.; Salk, R.H.; Kolko, R.P.; Levine, M.D. Healthcare provider advice on gestational weight gain: Uncovering a need for more effective weight counselling. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 38, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamminpää, R.; Vehviläinen-Julkunen, K.; Selander, T.; Rajapolvi, S.; Schwab, U. Feasibility of a Dietary Intervention to Limit Gestational Weight Gain and Gestational Diabetes in Overweight and Obese Pregnant Women. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 8, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, J.C.; Campbell, K.J.; van der Pligt, P.; Hoban, E.; Pidd, D.; Wilkinson, S. Excess gestational weight gain: An exploration of midwives’ views and practice. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2012, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Fan, D.; Wu, S.; Chen, G.; Li, P.; Ma, H.; Ye, S.; Rao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, M.; et al. The effect of gestational weight gain on perinatal outcomes among Chinese twin gestations based on Institute of Medicine guidelines. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieles, N.C.; Tankink, J.B.; van Midde, M.; Düker, J.; van der Lans, P.; Wessels, C.M.; Bloemenkamp, K.W.M.; Bonsel, G.; van den Akker, T.; Goosen, S.; et al. Maternal and perinatal outcomes of asylum seekers and undocumented migrants in Europe: A systematic review. Eur. J. Public Health 2019, 29, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, S.; Vargas, J.; Foster, A.M. “We need good nutrition but we have no money to buy food”: Sociocultural context, care experiences, and newborn health in two UNHCR-supported camps in South Sudan. BMC Int. Health Hum. Rights 2018, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behboudi-Gandevani, S.; Bidhendi-Yarandi, R.; Panahi, M.H.; Mardani, A.; Paal, P.; Prinds, C.; Vaismoradi, M. Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes and International Immigration Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Glob. Health 2022, 88, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.M.; Moutinho, A.R.; Siciliano, F.; Leite, J.; Caldas, J.P. Maternal Mental Health in Refugees and Migrants: A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Int. Migr. Integr. 2024, 25, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olander, E.K.; Atkinson, L.; Edmunds, J.K.; French, D.P. The views of pre- and post-natal women and health professionals regarding gestational weight gain: An exploratory study. Sex. Reprod. Healthc. 2011, 2, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanigaratne, S.; Ueno, E.; Canizares, K.; Strong, J.; Aguilar, A.; Atkinson, J.; O’Campo, P. Interventions for Healthy Weight and Weight Gain in Pregnancy among Refugee Women: A Scoping Review. Matern. Child Health J. 2018, 22, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar]
- Hijazi, H.H.; Alyahya, M.S.; Abdi, R.M.A.; Alolayyan, M.N.; Sindiani, A.M.; Raffee, L.A.; Marzouqi, A.M.A. The impact of perceived social support during pregnancy on postpartum infant-focused anxieties: A prospective cohort study of mothers in Northern Jordan. Int. J. Womens Health 2021, 13, 973–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganchimeg, T.; Ota, E.; Morisaki, N.; Laopaiboon, M.; Lumbiganon, P.; Zhang, J.; Yamdamsuren, B.; Temmerman, M.; Say, L.; Tunçalp, Ö.; et al. Pregnancy and childbirth outcomes among adolescent mothers: A World Health Organization multicountry study. BJOG 2014, 121 (Suppl. S1), 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuermli, A.; Hiott, C.; Ugarte, E.; Rahman, S.; Elahi, M.; Rahim, A.; Tofail, F. Cohort Profile: A Study of Intergenerational Risk and Resilience after War and Forced Displacement. PsyArXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOM. Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines. In Institute of Medicine (US) and National Research Council (US) and Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutcheon, J.A.; Chapinal, N.; Bodnar, L.M.; Lee, L. The INTERGROWTH-21st Gestational Weight Gain Standard and Interpregnancy Weight Increase: A Population-Based Study of Successive Pregnancies. Obesity 2017, 25, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 2004, 363, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, L.; Huang, X.; Cao, X. Effects of Maternal Prepregnancy Nutritional Status on Pregnancy Outcomes. Emerg. Med. Int. 2025, 2025, 1502902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laopaiboon, M.; Lumbiganon, P.; Intarut, N.; Mori, R.; Ganchimeg, T.; Vogel, J.P.; Souza, J.P.; Gülmezoglu, A.M.; WHO Multicountry Survey on Maternal Newborn Health Research Network. Advanced maternal age and pregnancy outcomes: A multicountry assessment. BJOG 2014, 121 (Suppl. S1), 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, K.; Aoki, S.; Toma, R.; Fujiwara, K.; Sakamaki, K.; Hirahara, F. Pregnancy outcomes based on pre-pregnancy body mass index in Japanese women. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, J.M.; Deussen, A.R.; Mitchell, M.; Poprzeczny, A.J.; Louise, J. Maternal overweight and obesity during pregnancy: Strategies to improve outcomes for women, babies, and children. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 17, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemert, A.; Lezius, S.; Pagenkemper, M.; Hansen, G.; Drozdowska, A.; Hecher, K.; Arck, P.; Zyriax, B.C. Maternal nutrition, inadequate gestational weight gain and birth weight: Results from a prospective birth cohort. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2016, 16, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, L.; Younge, N.; Freemark, M. Hormonal determinants of growth and weight gain in the human fetus and preterm infant. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Gisholt, A.C.; Rivas-Ruiz, R.; Clark, P. Maternal diet and vitamin D during pregnancy and association with bone health during childhood. Review of the literature. Bol. Med. Hosp. Infant. Mex. 2012, 69, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, N.E.; Abrams, B.; Barbour, L.A.; Catalano, P.; Christian, P.; Friedman, J.E.; Hay, W.W., Jr.; Hernandez, T.L.; Krebs, N.F.; Oken, E.; et al. The importance of nutrition in pregnancy and lactation: Lifelong consequences. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, 607–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, R.; Cohen, P. The role of the insulin-like growth factor system in prenatal growth. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2005, 86, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.F.; Abell, S.K.; Ranasinha, S.; Misso, M.; Boyle, J.A.; Black, M.H.; Li, N.; Hu, G.; Corrado, F.; Rode, L.; et al. Association of Gestational Weight Gain with Maternal and Infant Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2017, 317, 2207–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, W.A.; Finaret, A.B.; Block, S.A. The economics of malnutrition: Dietary transition and food system transformation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.02579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
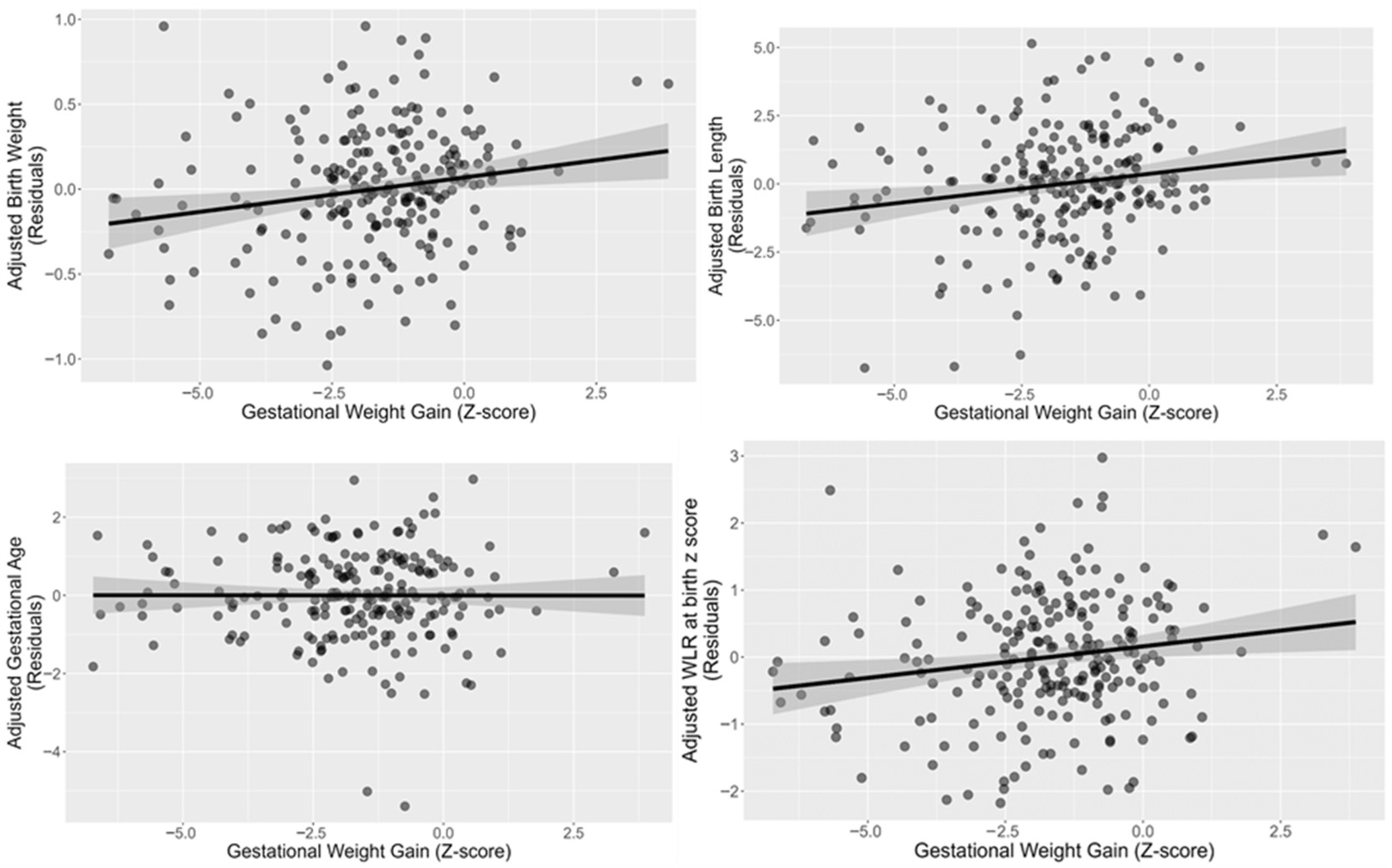
| Characteristic | Inadequate Weight Gain (z Score ≤ −1) n = 201 1 (66.77%) | Adequate Weight Gain (z Score > −1) n = 100 1 (33.22%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mother Age (Year) | 0.018 2 | ||
| below 20 | 106 (52.74) | 66 (66.00) | |
| 20–29 | 72 (35.82) | 31 (31.00) | |
| 30–39 | 23 (11.44) | 3 (3.00) | |
| Education | 0.522 2 | ||
| No School (No class) | 11 (5.47) | 9 (9.00) | |
| Madrassa (Religious education) | 62 (30.85) | 35 (35.00) | |
| Reached primary (Preschool to class 3) | 50 (24.88) | 22 (22.00) | |
| More than primary (More than class 3) | 78 (38.81) | 34 (34.00) | |
| Parity | 0.507 2 | ||
| Nulliparous | 75 (37.31) | 41 (41.00) | |
| Primiparous | 50 (24.88) | 28 (28.00) | |
| Multiparous | 76 (37.81) | 31 (31.00) | |
| First trimester (Early Pregnancy) BMI | |||
| Underweight (<18.5 kg/m2) | 18 (8.96) | 22 (22.00) | 0.007 2 |
| Normal Weight (18.5–22.9 kg/m2) | 114 (56.72) | 55 (55.00) | |
| Overweight (23–27.4 kg/m2) | 31 (15.42) | 13 (13.00) | |
| Obese ≥ 27.5 kg/m2 | 38 (18.91) | 10 (10.00) | |
| Pregnancy Complications and diseases | 14(06.97) | 3(3.00) | 0.160 2 |
| Toilet facility | 181 (90.05) | 89 (89.00) | 0.778 2 |
| Bathing facility | 192 (95.52) | 95 (95.00) | >0.999 3 |
| Characteristic | AOR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Mother Age (Year) | ||
| below 20 | — | |
| 20–29 | 1.33 (0.65, 2.78) | 0.436 |
| 30–39 | 3.96 (1.03, 19.9) | 0.061 |
| Education | ||
| No School (No class) | — | |
| Madrassa (Religious education) | 1.44 (0.50, 4.07) | 0.494 |
| Reached primary (Preschool to class 3) | 1.93 (0.64, 5.70) | 0.235 |
| More than primary (More than class 3) | 1.96 (0.67, 5.65) | 0.212 |
| Parity | ||
| Nulliparous | — | |
| Primiparous | 0.92 (0.47, 1.78) | 0.799 |
| Multiparous | 0.89 (0.38, 2.07) | 0.780 |
| Early pregnancy BMI | ||
| Normal Weight (18.5–22.9 kg/m2) | — | |
| Underweight (<18.5 kg/m2) | 0.40 (0.19, 0.81) | 0.012 * |
| Overweight (23–27.4 kg/m2) | 1.01 (0.48, 2.19) | 0.983 |
| Obese ≥ 27.5 kg/m2 | 1.39 (0.63, 3.26) | 0.434 |
| Pregnancy complications and diseases | ||
| No | — | |
| Yes | 1.89 (0.55, 8.79) | 0.356 |
| Toilet facility | ||
| No | — | |
| Yes | 1.14 (0.48, 2.61) | 0.754 |
| Bathing facility | ||
| No | — | |
| Yes | 1.05 (0.30, 3.33) | 0.937 |
| Characteristic | n = 231 1 (100%) |
|---|---|
| Birth condition | |
| Healthy | 214 (92.64) |
| Ill | 9 (3.90) |
| Died | 8 (3.46) |
| Birth place | |
| Home | 100 (43.29) |
| Hospital | 131 (56.71) |
| Birth born type (n = 230) | |
| Normal | 199 (86.52) |
| Cesarean | 8 (3.48) |
| Mechanical support delivery | 23 (10.00) |
| Unknown | 1 |
| Birth complication | |
| No complication | 111 (48.05) |
| Complication | 120 (51.95) |
| Gestational age | |
| Preterm (<37 week) | 6 (2.60) |
| Normal term (37 to 41 week) | 221 (95.67) |
| Post term (>41 week) | 4 (1.73) |
| Birth weight (n = 223) | |
| Low birth weight | 42 (18.83) |
| Normal | 181 (81.17) |
| Unknown | 8 |
| Gestational weight gain | |
| Inadequate weight gain (z score ≤ −1) | 151 (65.37) |
| Adequate weight gain (z score > −1) | 80 (34.63) |
| Mean (±SD) | |
| Birth weight (n = 223) | 2.8 (±0.38) |
| Unknown | 8 |
| Birth length (n = 223) | 48.6 (±2.04) |
| Unknown | 8 |
| Gestational age at birth | 38.8 (±3.12) |
| Birth WLR z score (n = 223) | −1.4 (±0.96) |
| Characteristic | Inadequate Weight Gain (z Score ≤ −1), n = 151 1 | Adequate Weight Gain (z Score > −1), n = 80 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birth weight | 2.8 (±0.40) | 2.8 (±0.33) | 0.128 2 |
| Unknown | 6 | 2 | |
| Birth length | 48.4 (±2.16) | 49.1 (±1.72) | 0.016 2 |
| Unknown | 6 | 2 | |
| Gestational age at birth | 38.6 (±3.73) | 39.2 (±1.26) | 0.172 2 |
| Birth Z score | −1.5 (±0.94) | −1.3 (±0.98) | 0.217 2 |
| Unknown | 6 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahamed, S.; Ugarte, E.; Elahi, M.; Hossain, E.; Rahman, S.; Sanin, K.I.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, G.K.; Wuermli, A.J.; Tofail, F. Association Between Birth Outcomes and Gestational Weight Gain Among Forcibly Displaced Rohingya and Nearby Host Community, in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Life 2025, 15, 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111773
Ahamed S, Ugarte E, Elahi M, Hossain E, Rahman S, Sanin KI, Dutta A, Dutta GK, Wuermli AJ, Tofail F. Association Between Birth Outcomes and Gestational Weight Gain Among Forcibly Displaced Rohingya and Nearby Host Community, in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Life. 2025; 15(11):1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111773
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhamed, Shakil, Elisa Ugarte, Mahbub Elahi, Eamam Hossain, Sajjadur Rahman, Kazi Istiaque Sanin, Abir Dutta, Goutam Kumar Dutta, Alice J. Wuermli, and Fahmida Tofail. 2025. "Association Between Birth Outcomes and Gestational Weight Gain Among Forcibly Displaced Rohingya and Nearby Host Community, in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh" Life 15, no. 11: 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111773
APA StyleAhamed, S., Ugarte, E., Elahi, M., Hossain, E., Rahman, S., Sanin, K. I., Dutta, A., Dutta, G. K., Wuermli, A. J., & Tofail, F. (2025). Association Between Birth Outcomes and Gestational Weight Gain Among Forcibly Displaced Rohingya and Nearby Host Community, in Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh. Life, 15(11), 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111773







