Beyond Daily Values: Are Day-to-Day and Albumin-Adjusted Ratios of IL-6, PCT, and CRP Better Predictors of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
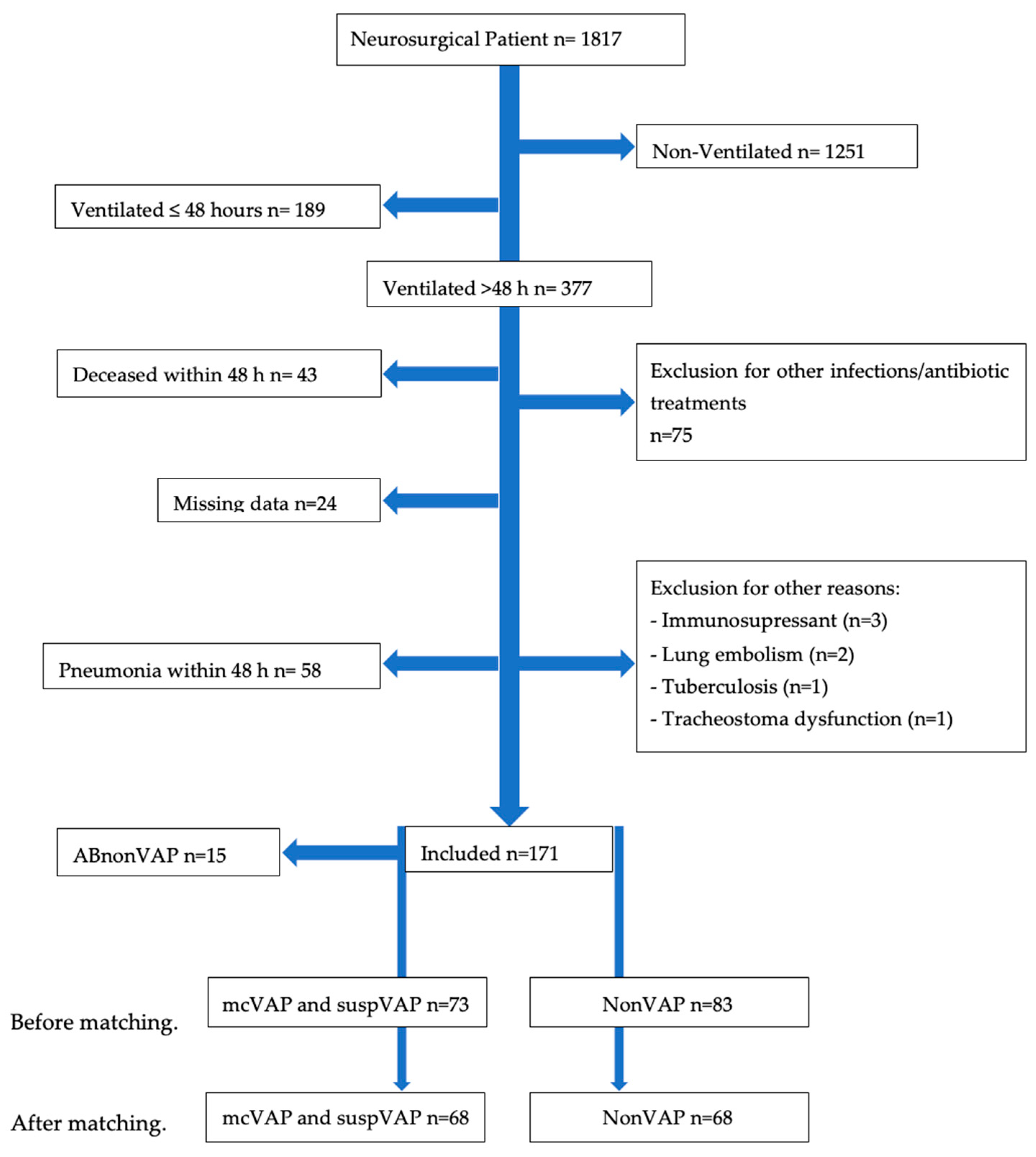
3.1. Population
3.2. Baseline Mcvap/Suspvap vs. Nonvap
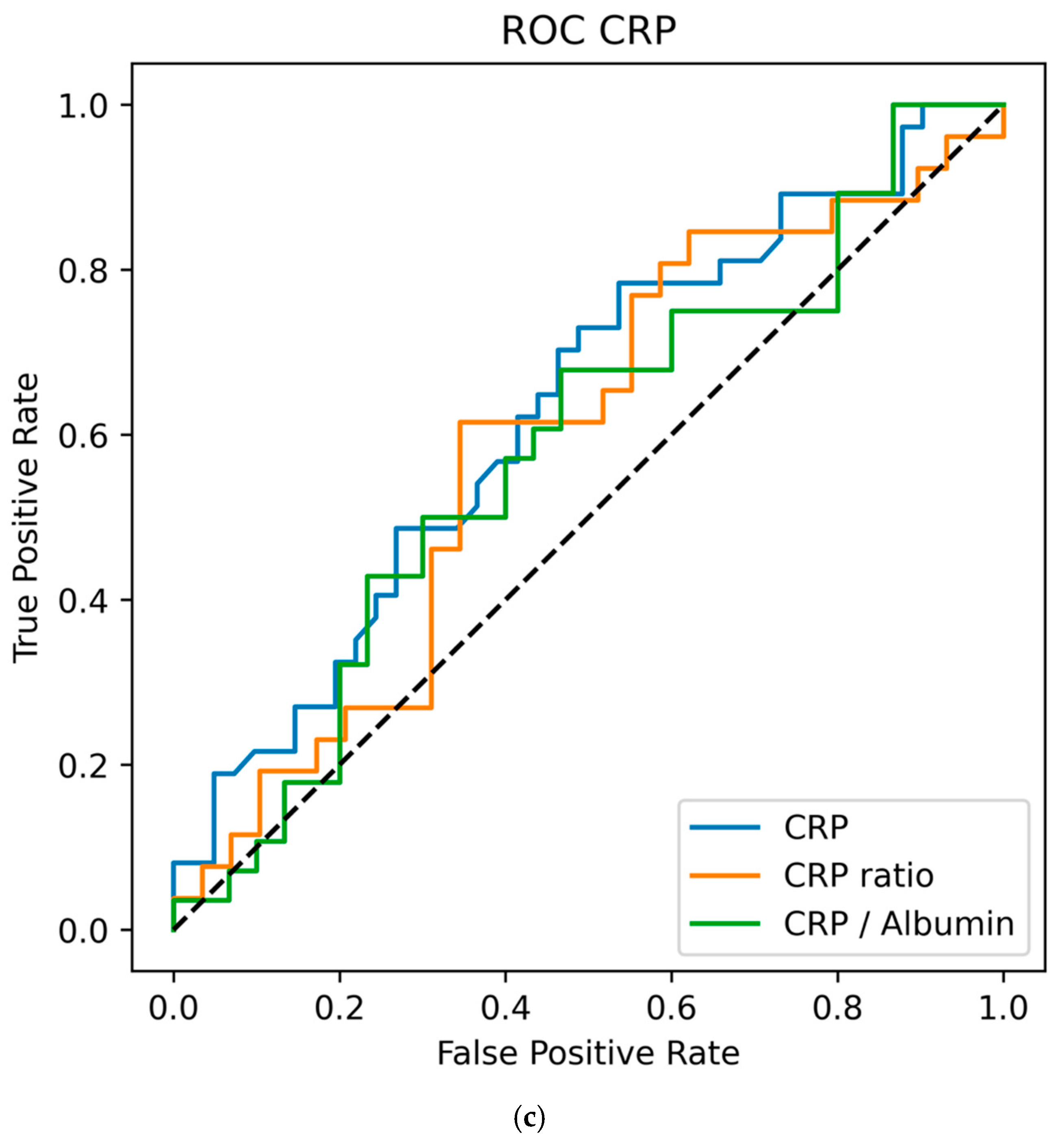
3.3. Biomarker Values vs. Day-To-Day Ratios and Ratios to Albumin to Predict VAP
3.4. Antibiotic Treatment of Patients Who Do Not Meet the Criteria
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABnonVAP | Patients treated with antibiotics for VAP without fulfilling diagnostic criteria |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CRP | C-reactive Protein |
| D0 | Study days relative to VAP diagnosis |
| HRG | Histidine-Rich Glycoprotein |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| IVAC | Infection-Related Ventilator-Associated Complication |
| LR p-value | Logistic Regression p-value |
| mcVAP | Microbiologically confirmed VAP |
| MW p-value | Mann–Whitney U test p-value |
| NonVAP | Patients without VAP (control group) |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PCT | Procalcitonin |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic (curve) |
| SAPS | Simplified Acute Physiology Score |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| suspVAP | Suspected but not microbiologically confirmed VAP |
| Temp | Body Temperature (°C) |
| US | United States |
| VAC | Ventilator-Associated Condition |
| VAE | Ventilator-Associated Event |
| VAP | Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia |
| WBC | White Blood Cell count |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio (P/F ratio) | Ratio of arterial oxygen partial pressure to fraction of inspired oxygen |
Appendix A
| Characteristic | Unmatched mcVAP + suspVAP | Unmatched nonVAP Controls | p-Value | Matched mcVAP + suspVAP | Matched nonVAP Controls | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size (n) | 73 | 83 | 68 | 68 | ||
| SAPS Score (SD) | 41.68 (11.07) | 38.45 (10.78) | 0.079 | 42.55 (10.92) | 38.89 (10.94) | 0.064 |
| Age (SD) | 65.36 (14.01) | 67.36 (13.93) | 0.372 | 65.0 (14.39) | 67.22 (14.30) | 0.368 |
| Cohort | Controls | mcVAP | suspVAP | ABnonVAP | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 (%) | 52 (31.1) | 32 (19.2) | 20 (12.0) | 5 (3.0) | 109 (65.3) |
| PCT/CRP (%) | 16 (9.6) | 13 (7.8) | 3 (1.8) | 10 (6.0) | 42 (25.1) |
| Total | 68 (40.7) | 45 (26.9) | 23 (13.8) | 15 (9.0) | 151 (100.0) |
| Variable | MW_p | LR_p | MW_p_adj | LR_p_adj |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP Day −1 | 0.177 | 0.835 | 0.212 | 0.835 |
| Day −1/−2 Ratio | 0.648 | 0.372 | 0.686 | 0.5904 |
| CRP-Albumin-Ratio Day −1 | 0.648 | 0.372 | 0.686 | 0.5904 |
| CRP Day 0 | 0.015 | 0.012 | 0.039 | 0.0432 |
| Day 0/−1 Ratio | 0.138 | 0.654 | 0.207 | 0.692470588 |
| CRP to Albumin Day 0 | 0.112 | 0.199 | 0.202 | 0.44775 |
| PCT Day −1 | 0.151 | 0.355 | 0.209 | 0.5904 |
| PCT Day −1/−2 Ratio | 0.177 | 0.065 | 0.212 | 0.167142857 |
| PCT-Albumin-Ratio Day −1 | 0.775 | 0.463 | 0.775 | 0.5904 |
| PCT Day 0 | 0.004 | 0.436 | 0.014 | 0.5904 |
| PCT Day 0/−1 Ratio | 0.126 | 0.492 | 0.206 | 0.5904 |
| PCT to Albumin Day 0 | 0.005 | 0.018 | 0.014 | 0.036 |
| IL-6 Day −1 | 0.040 | 0.545 | 0.090 | 0.613125 |
| IL6 Day −1/−2 Ratio | 0.013 | 0.059 | 0.039 | 0.167142857 |
| IL-6-Albumin-Ratio Day −1 | 0.054 | 0.415 | 0.108 | 0.5904 |
| IL-6 Day 0 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| IL-6 Day 0/−1 Ratio | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| IL-6 to Albumin Day 0 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.006 | 0.006 |
References
- American Thoracic Society; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Hospital-acquired, Ventilator-associated, and Healthcare-associated Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 388–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.K.S.; Fong, C.; Walters, A.M.; Lele, A.V. Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics, and Outcomes Related to Ventilator-Associated Events in Neurocritically Ill Patients. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 33, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melsen, W.G.; Rovers, M.M.; Groenwold, R.; Bergmans, D.C.; Camus, C.; Bauer, T.T.; Hanisch, E.; Klarin, B.; Koeman, M.; Krueger, W.A.; et al. Attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised prevention studies. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimlichman, E.; Henderson, D.; Tamir, O.; Fralnz, C.; Song, P.; Yamin, C.K.; Keohane, C.; Denham, C.R.; Bates, D.W. Health Care–Associated Infections. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; Gauvin, F.; Amre, D.K.; Saint-Louis, P.; Lacroix, J. Serum Procalcitonin and C-Reactive Protein Levels as Markers of Bacterial Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraunberger, P.; Wang, Y.; Holler, E.; Parhofer, K.G.; Nagel, D.; Walli, A.K.; Seidel, D. Prognostic value of interleukin 6, procalcitonin, and C-reactive protein levels in intensive care unit patients during first increase of fever. Shock 2006, 26, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boenisch, S.; Fae, P.; Drexel, H.; Walli, A.K.; Fraunberger, P. Are circulating levels of CRP compared to IL-6 and PCT still relevant in intensive care unit patients? J. Lab. Med. 2013, 37, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmit, X.; Vincent, J.L. The time course of blood C-reactive protein concentrations in relation to the response to initial antimicrobial therapy in patients with sepsis. Infection 2008, 36, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettig, T.C.D.; Verwijmeren, L.; Dijkstra, I.M.; Boerma, D.; Van De Garde, E.M.W.; Noordzij, P.G. Postoperative Interleukin-6 Level and Early Detection of Complications After Elective Major Abdominal Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2016, 263, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Il-6 in inflammation, Immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Póvoa, P.; Coelho, L.; Almeida, E.; Fernandes, A.; Mealha, R.; Moreira, P.; Sabino, H. C-reactive protein as a marker of infection in critically ill patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.; Rabello, L.; Salluh, J.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Rodriguez, A.; Nseir, S.; Gomes, J.A.; Povoa, P. C-reactive protein and procalcitonin profile in ventilator-associated lower respiratory infections. J. Crit. Care 2018, 48, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.; Albrich, W.; Mueller, B. Procalcitonin for diagnosis of infection and guide to antibiotic decisions: Past, present and future. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.G.; Zhou, H.F.; Diao, M.Y.; Xu, Y.; Pan, Q.M.; Shen, X.H. A novel biomarker of serum Histidine-Rich Glycoprotein (HRG) for diagnosing and predicting prognosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP): A pilot study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7920–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Barassi, A.; Severgnini, P.; Gomiero, B.; Finazzi, S.; Merlini, G.; d’Eril, G.M.; Chiaranda, M.; Niederman, M.S. Prognostic role of clinical and laboratory criteria to identify early ventilator-associated pneumonia in brain injury. Chest 2008, 134, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bexten, T.; Wiebe, S.; Brink, M.; Hinzmann, D.; Haarmeyer, G.-S. Early Detection of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in a Neurosurgical Patient: Do Biomarkers Help Us? Cureus 2025, 17, e78567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, P.; Ferrer, M.; Gimeno, R.; Tormo, S.; Valencia, M.; Piñer, R.; Menendez, R.; Torres, A. Systemic inflammatory response and increased risk for ventilator-associated pneumonia: A preliminary study. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Lee, K.H.; Song, Y.G.; Han, S.H. Discrepancy of C-Reactive Protein, Procalcitonin and Interleukin-6 at Hospitalization: Infection in Patients with Normal C-Reactive Protein, Procalcitonin and High Interleukin-6 Values. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Póvoa, P.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Ramirez, P.; Bos, L.D.; Esperatti, M.; Silvestre, J.; Gili, G.; Goma, G.; Berlanga, E.; Espasa, M.; et al. Biomarker kinetics in the prediction of VAP diagnosis: Results from the BioVAP study. Ann. Intensive Care 2016, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wu, X.; Qin, H.; Zhu, H. The PCT to Albumin Ratio Predicts Mortality in Patients with Acute Kidney Injury Caused by Abdominal Infection-Evoked Sepsis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 584461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranzani, O.T.; Zampieri, F.G.; Forte, D.N.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; Park, M. C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio Predicts 90-Day Mortality of Septic Patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.K.; Song, I.A.; Lee, J.H. Clinical usefulness of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in predicting 30-day mortality in critically ill patients: A retrospective analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K. Introduction Alternatives to P value: Confidence interval and effect size KJA. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2016, 69, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howroyd, F.; Chacko, C.; MacDuff, A.; Gautam, N.; Pouchet, B.; Tunnicliffe, B.; Weblin, J.; Gao-Smith, F.; Ahmed, Z.; Duggal, N.A.; et al. Ventilator-associated pneumonia: Pathobiological heterogeneity and diagnostic challenges. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccato, A.; Camprubí-Rimblas, M.; Bos, L.D.J.; Povoa, P.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Forné, C.; Areny-Balagueró, A.; Campaña-Duel, E.; Morales-Quinteros, L.; Quero, S.; et al. Evaluation of the Kinetics of Pancreatic Stone Protein as a Predictor of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Huang, Q.D.; Tang, T.Y.; Qin, G.Y. Diagnostic value of pentraxin 3 in respiratory tract infections: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e19532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion. Ventilator-Associated Event (VAE); CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2024.
- Chen, C.Y.; Lin, W.C.; Yang, H.Y. Diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia using electronic nose sensor array signals: Solutions to improve the application of machine learning in respiratory research. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, J. The Current State of Nanopore Sequencing. In Nanopore Sequencing; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirz, Y.; Meier, M.A.; Bouadma, L.; Luyt, C.E.; Wolff, M.; Chastre, J.; Tubach, F.; Schroeder, S.; Nobre, V.; Annane, D.; et al. Effect of procalcitonin-guided antibiotic treatment on clinical outcomes in intensive care unit patients with infection and sepsis patients: A patient-level meta-analysis of randomized trials. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
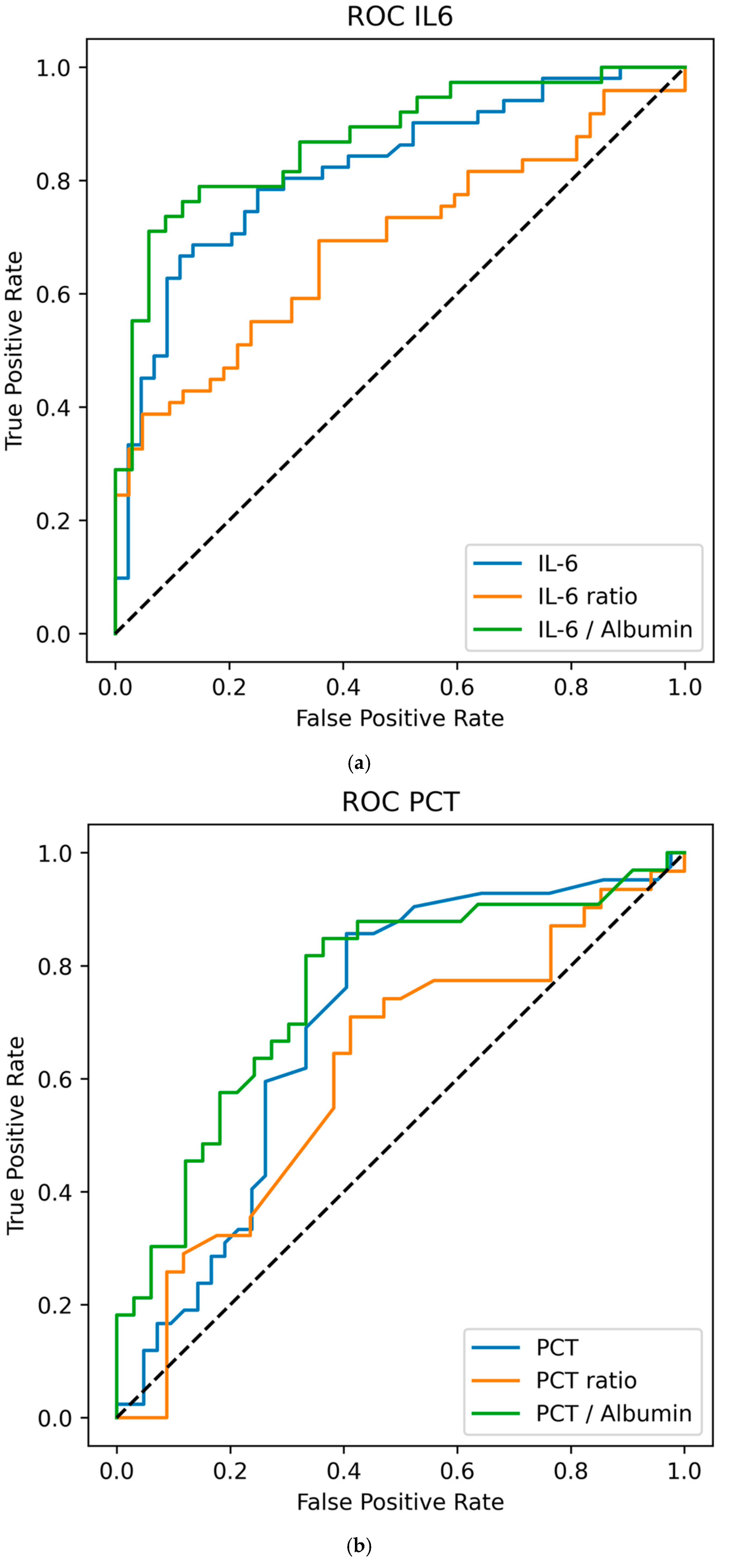
| Variable | nonVAP Median (IQR) | mcVAP and suspVAP Median (IQR) | MW p-Value (W; r-Effect Size) | AUC | OR (95% CI) | LR p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day −1 | ||||||
| PCT in ng/mL | n = 39 | n = 44 | ||||
| Day −1 | 0.16 (0.32) | 0.24 (0.47) | 0.151 (616.00; 0.189) | 0.595 | 1.017 (0.969–1.068) | 0.355 |
| Day −1/−2 Ratio | 0.96 (0.38) | 1.00 (1.42) | 0.177 (321.00; 0.209) | 0.605 | 1.231 (0.823–1.842) | 0.065 |
| PCT to Albumin Ratio | 17.00 (29.30) | 22.77 (37.36) | 0.775 (491.00; 0.043) | 0.521 | 1.033 (0.924–1.155) | 0.463 |
| Day 0 | ||||||
| PCT in ng/mL | n = 31 | n = 42 | ||||
| Day 0 | 0.11 (0.19) | 0.24 (0.34) | 0.004 * (616.00; 0.414) | 0.707 | 1.010 (0.978–1.043) | 0.461 |
| Day 0/−1 Ratio | 0.757 (0.28) | 1.00 (0.44) | 0.126 (241.00; 0.252) | 0.626 | 1.428 (0.516–3.952) | 0.492 |
| PCT to Albumin | 0.04 (0.05) | 0.08 (0.15) | 0.005 (192.50; 0.474) | 0.746 | 1.062(0.116–15.688) | 0.016 |
| Baseline | nonVAP n = 68 | mcVAP/suspVAP n = 68 | ABnonVAP n = 15 | Total n = 171 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) (SD) | 67.22 (14.23) | 65.0 (14.39) | 60.0 (9.43) | 66.4 (13.93) |
| Sex F/M (% of total) | 36/32 (26/15) | 21/47 (14/32) | 14/11 (7/6) | 92/101 (48/52) |
| Length of stay in hours (SD) | 399.81 (360.13) | 599.46 (335.57) | 532.89 (424.82) | 502.29 (367.60) |
| Hours of ventilation in hours (SD) | 198.49 (165.23) | 380.10 (225.32) | 366.20(370.93) | 297.59 (236.05) |
| SAPS on admission [SD] | 38.71 (10.94) | 42.55 (10.02) | 41.22 (17.32) | 40.30 (11.11) |
| Diagnosis (% of Total) | ||||
| Intracerebral bleeding | 55 (36.4) | 58 (38.3) | 15 (9.9) | 128 (84.8) |
| Traumatic head injury | 4 (2.6) | 3 (2.0) | 0 (0) | 7 (4.6) |
| Cerebral tumor | 3 (2.0) | 0 (0.5) | 0 (0) | 3 (2.0) |
| Malignant infarction | 6 (4.0) | 7 (4.6) | 0 (0) | 13 (8.6) |
| Comorbidity (% of Total) | ||||
| Cardiovascular disease | 44 (29.1) | 45 (29.8) | 9 (6.0) | 98 (64.9) |
| Respiratory disease | 4 (2.4) | 3 (2.0) | 3 (2.0) | 10 (6.6) |
| Kidney disease | 1 (0.7) | 3 (2.0) | 2 (1.3) | 6 (4.0) |
| Substance abuse | 5 (3.3) | 9(6.0) | 2 (1.3) | 16 (10.6) |
| Other | 3(2.0) | 11 (7.3) | 3 (2.0) | 17 (11.3) |
| Baseline on day of ICU Admission | ||||
| WBC (IQR) | 11.51 (6.280) | 10.34 (8.29) | 11.45 (7.29) | 10.8 (6.74) |
| IL-6 (IQR) | 40.80 (53.40) | 34.05 (97.73) | 34.85 (22.05) | 40.80 (69.30) |
| PCT (IQR) | 0.3 (0.35) | 0.11 (0.06) | 0.07 (0.05) | 0.11 (0.17) |
| CRP (IQR) | 0.20 (0.95) | 0.30 (2.15) | 0.45 (1.05) | 0.20 (1.55) |
| Variable | nonVAP Median (IQR) | mcVAP and suspVAP Median (IQR) | MW p-Value (W; r-Effect Size) | AUC | OR (95% CI) | LR p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day −1 | ||||||
| IL-6 in pg/mL | n = 40 | n = 52 | ||||
| Day −1 | 46.35 (63.10) | 63.10 (71.00) | p = 0.040 * (739.50; 0.255) | 0.627 | 1.001 (0.998–1.004) | 0.545 |
| Day −1/−2 Ratio | 0.93 (1.42) | 1.84 (1.92) | p = 0.013 * (627.00; 0.313) | 0.656 | 1.289 (0.970–1.713) | 0.059 |
| IL-6-Albumin Ratio | 17.00 (29.30) | 22.77 (37.36) | p = 0.054 (551.50; 0.257) | 0.629 | 1.004 (0.995–1.013) | 0.415 |
| Day 0 | ||||||
| IL-6 in pg/mL | n = 39 | n = 53 | ||||
| Day 0 | 35.40 (35.80) | 109 (180.25) | p < 0.001 * (359.50; 0.631) | 0.816 | 1.012 (1.004–1.020) | p < 0.001 * |
| Day 0/−1 Ratio | 0.74 (0.81) | 1.42 (1.85) | p < 0.001 * (500.00; 0.452) | 0.726 | 2.660 (1.390–5.091) | p < 0.001 * |
| IL-6 to Albumin Ratio | 12.09 (14.72) | 41.48 (65.07) | p < 0.001 * (151.50; 0.257) | 0.864 | 1.065 (1.024–1.109) | p < 0.001 * |
| Variable | nonVAP Median (IQR) | mcVAP and suspVAP Median (IQR) | MW p Value (W; r-Effect Size) | AUC | OR (95% CI) | LR p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day −1 | ||||||
| CRP in mg/L | n = 34 | n = 41 | ||||
| Day −1 | 7.60 (7.50) | 9.65 (12.38) | 0.207 (517.00; 0.175) | 0.588 | 1.058 (0.989–1.132) | 0.084 |
| Day −1/−2 Ratio | 1.09 (1.12) | 1.42 (2.58) | 0.177 (242.00; 0.224) | 0.612 | 1.005 (0.956–1.058) | 0.835 |
| CRP to Albumin Ratio | 3.02 (3.38) | 3.07 (5.52) | 0.648 (435.50; 0.069) | 0.535 | 0.982 (0.936–1.030) | 0.372 |
| Day 0 | ||||||
| CRP in mg/L | n = 32 | n = 37 | ||||
| Day 0 | 7.40 (7.95) | 12.85 (8.55) | 0.015 * (342.00; 0.351) | 0.676 | 1.093 (1.009–1.183) | 0.012 * |
| Day 0/−1 Ratio | 0.94 (0.76) | 1.07 (0.78) | 0.138 (184.50; 0.262) | 0.631 | 1.028 (0.909–1.162) | 0.654 |
| CRP to Albumin | 3.19 (2.93) | 4.25 (2.96) | 0.112 (200.00; 0.273) | 0.636 | 1.131 (0.926–1.382) | 0.199 |
| Variable | nonVAP (Median, IQR) | ABnonVAP (Median, IQR) | p-Value (W-Value, r-Effect Size) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | n = 68 | n = 15 | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 35.40 (35.80) | 42.80 (42.40) | p = 0.941 (W = 95.00, r = 0.026) |
| PCT (ng/mL) | 0.11 (0.19) | 0.11 (0.15) | p = 0.738 (W = 167.50, r = 0.069) |
| CRP (mg/L) | 7.40 (7.95) | 12.75 (6.03) | p = 0.071 (W = 95.00, r = 0.387) |
| WBC (×109/L) | 9.30 (4.56) | 10.10 (4.15) | p = 0.569 (W = 358.50, r = 0.098) |
| Temp (°C) | 37.20 (0.80) | 37.50 (0.45) | p = 0.412 (W = 414.50, r = 0.136) |
| PaO2/FiO2 | 347.00 (128.00) | 308.00 (147.00) | p = 0.633 (W = 366.00, r = 0.084) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bexten, T.; Haarmeier, G.-S.; Klein, J.; Lindner, H.A.; Rahali, C.; Schneider-Lindner, V. Beyond Daily Values: Are Day-to-Day and Albumin-Adjusted Ratios of IL-6, PCT, and CRP Better Predictors of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia? Life 2025, 15, 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111697
Bexten T, Haarmeier G-S, Klein J, Lindner HA, Rahali C, Schneider-Lindner V. Beyond Daily Values: Are Day-to-Day and Albumin-Adjusted Ratios of IL-6, PCT, and CRP Better Predictors of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia? Life. 2025; 15(11):1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111697
Chicago/Turabian StyleBexten, Tobias, Golo-Sung Haarmeier, Johann Klein, Holger A. Lindner, Chaimae Rahali, and Verena Schneider-Lindner. 2025. "Beyond Daily Values: Are Day-to-Day and Albumin-Adjusted Ratios of IL-6, PCT, and CRP Better Predictors of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia?" Life 15, no. 11: 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111697
APA StyleBexten, T., Haarmeier, G.-S., Klein, J., Lindner, H. A., Rahali, C., & Schneider-Lindner, V. (2025). Beyond Daily Values: Are Day-to-Day and Albumin-Adjusted Ratios of IL-6, PCT, and CRP Better Predictors of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia? Life, 15(11), 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111697






