Antioxidant Supplementation with ProCloSupp Protects Against Renal Toxicity of Atypical Antipsychotics in Rats: Implications for Safer Treatment Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. Drug Treatment
2.4. Tissue Collection
2.5. Tissue Preparation and Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
2.6. SDS Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and Immunoblotting
2.7. Light Microscopy
- Discrete—when the shape of the tubule lumen was regular (oval or round) in at least 75% of all tubules examined and when round nuclei were present in all cells or poorly visible in less than 50% of all tubules examined.
- Moderate—if the shape of the tubule lumen was stellate in at least 75% of all tubules examined and the nuclei were poorly visible in at least 50% of all cells examined, with focal absence in less than 50% of all tubules.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of APP with or Without PCS on Kidney Morphology
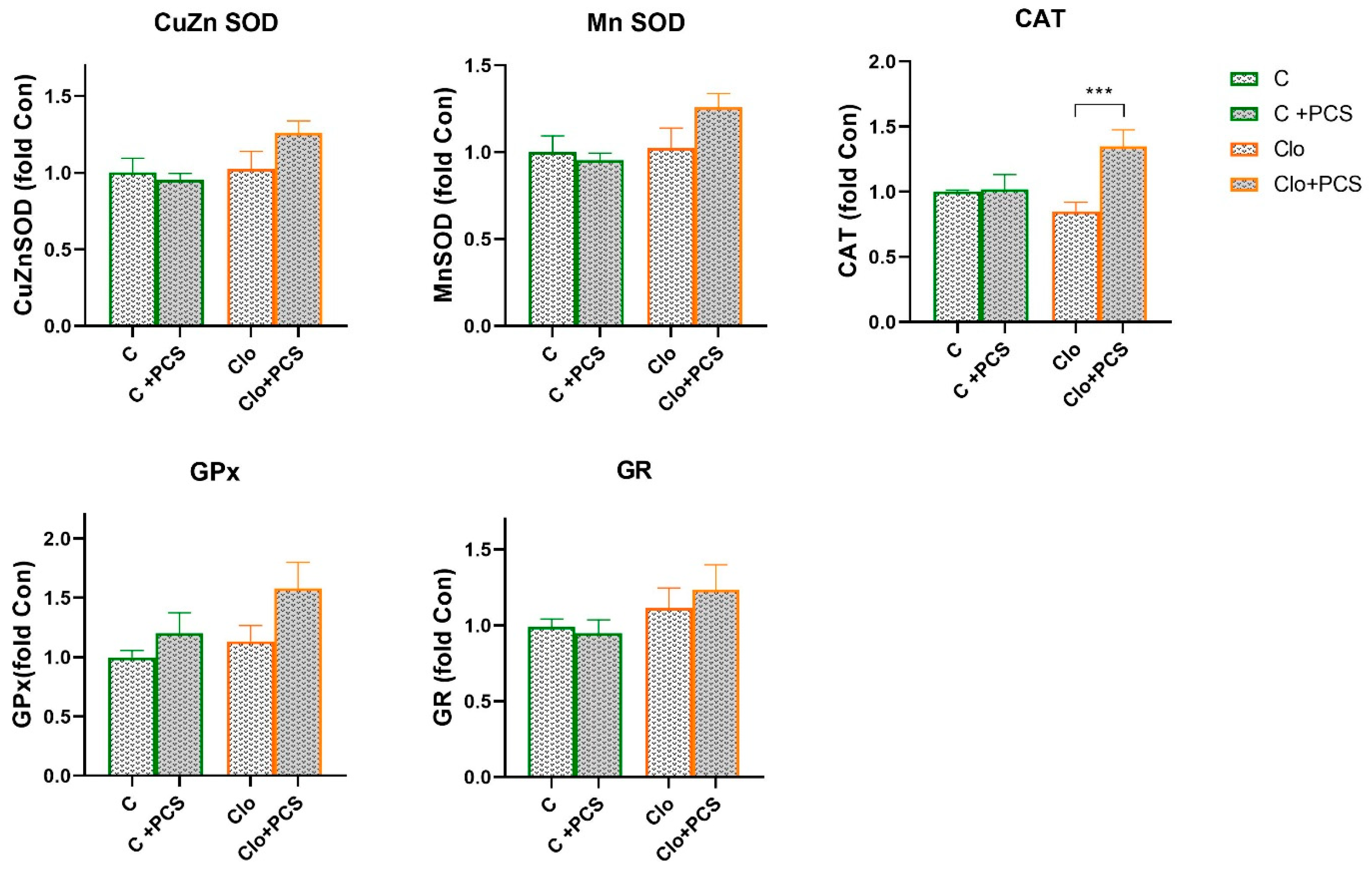
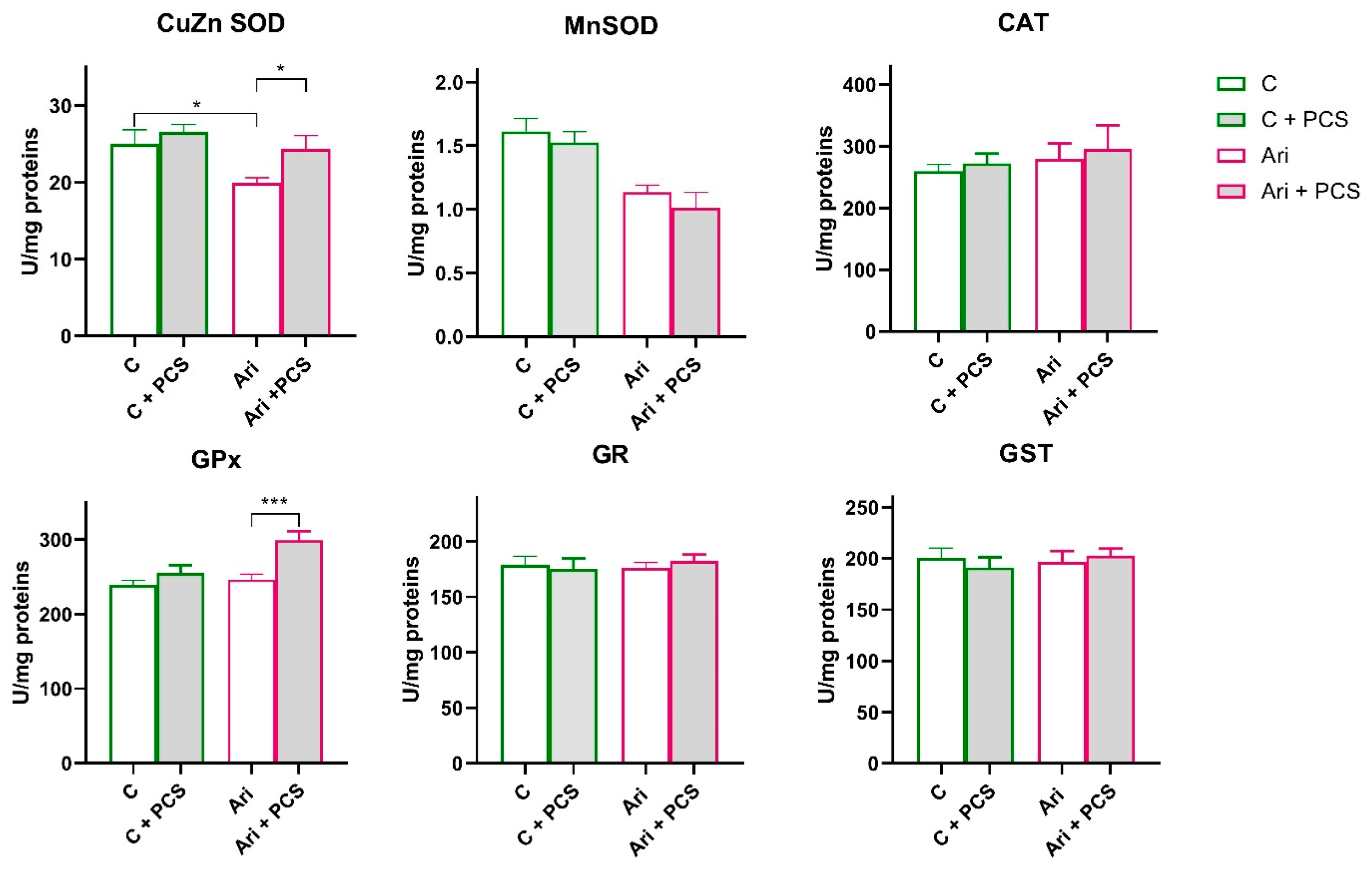
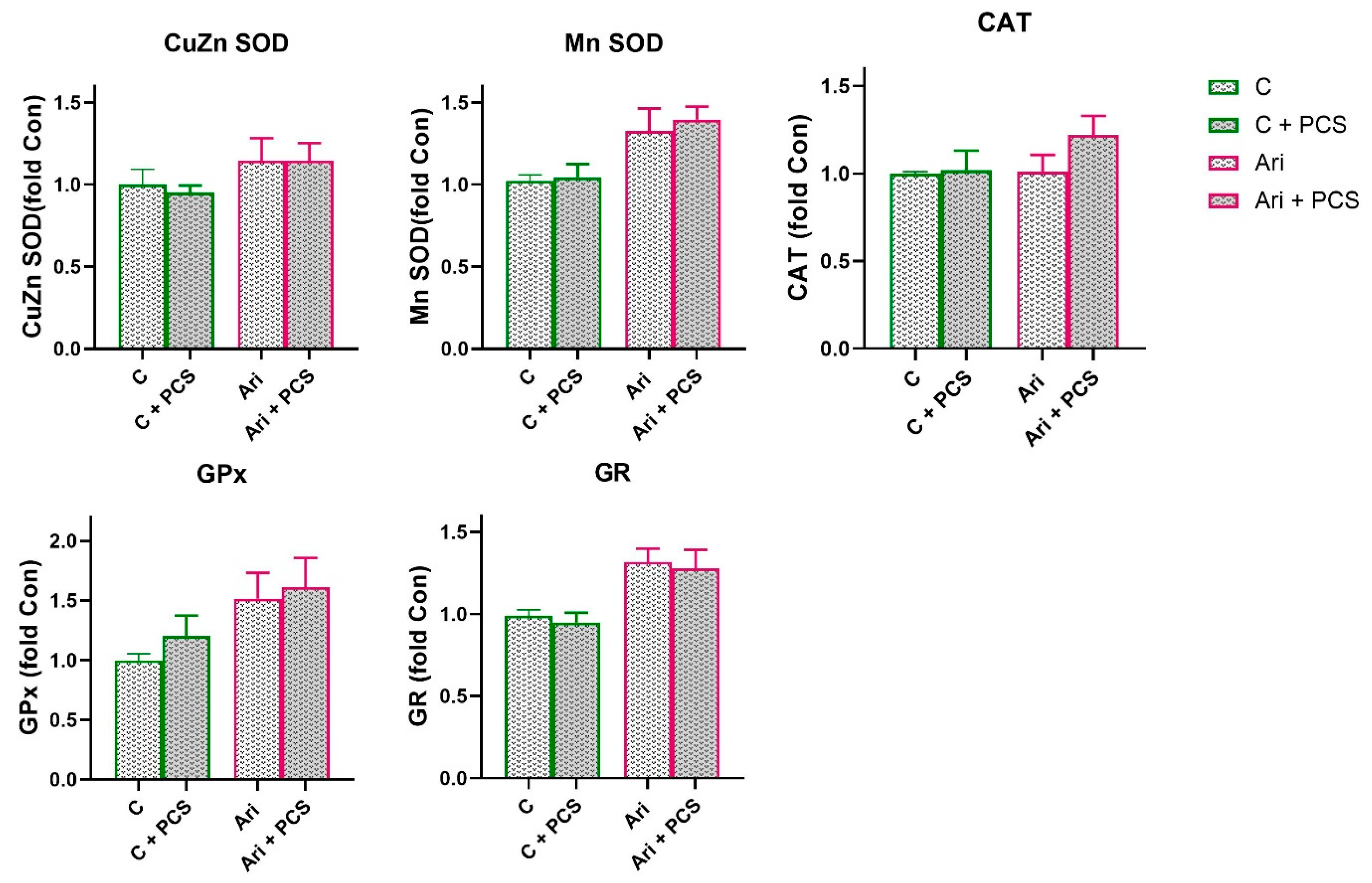
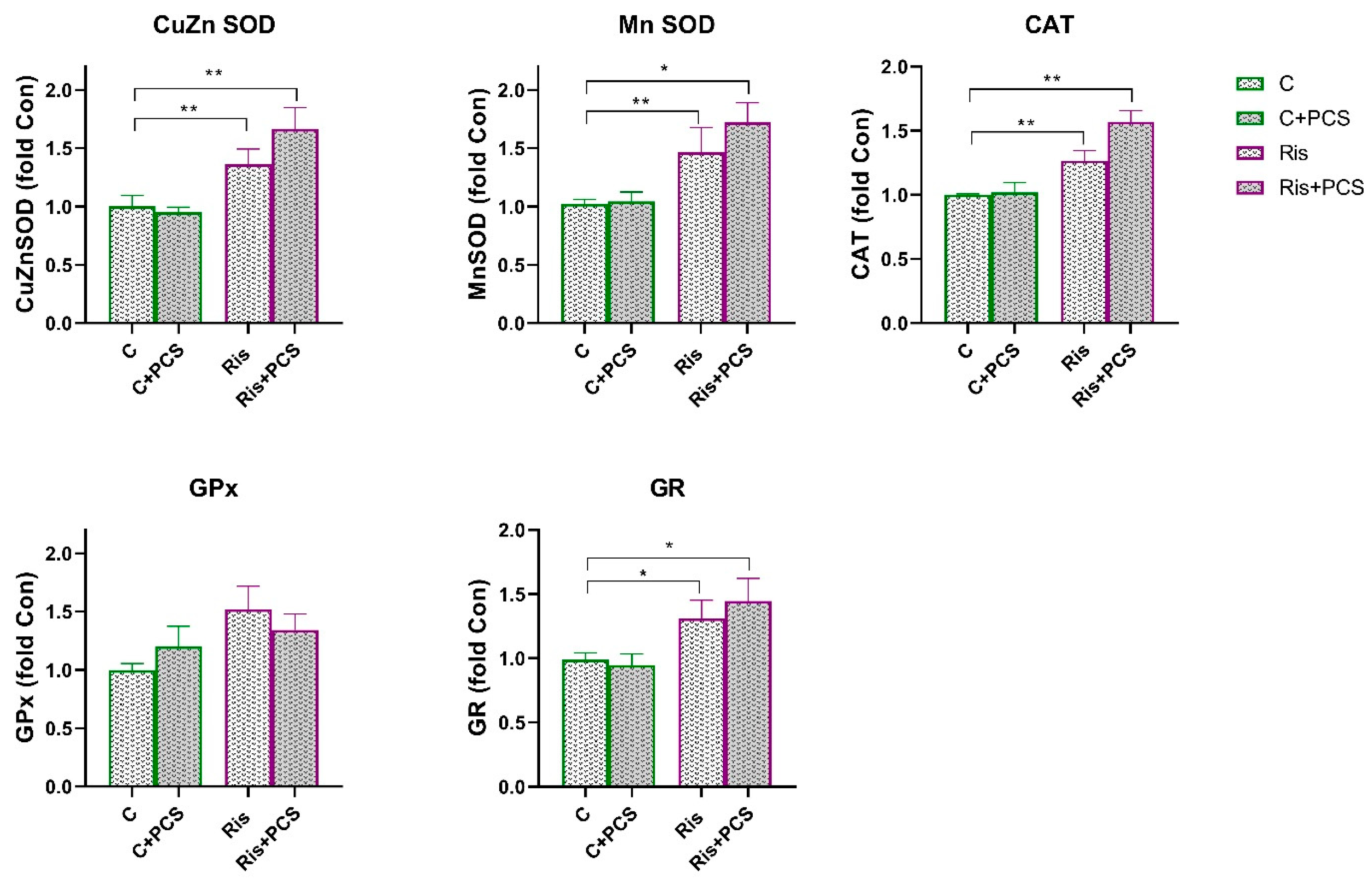
3.2. Effects of AAP Treatment Without and with Supplementation with PCS on Renal Antioxidant Enzymes Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAPs | Atypical antipsychotics |
| PCS | Composite dietary antioxidant supplement “ProCloSupp” |
| Clozapine | Clo |
| Ari | Aripiprazole |
| Ris | Risperidone |
| SeMet | Seleno-methionine |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| GR | Glutathione reductase |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| U | Units |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulphate |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene difluoride |
| ECL | Enhanced chemiluminiscent |
| HE | Haematoxylin–eosin |
References
- Muench, J.; Hamer, A.M. Adverse effects of antipsychotic medications. Am. Fam. Physician 2010, 81, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ong, L.T.; Chee, N.M.Z.; Loh, A.J.C. Risk of renal impairment in atypical antipsychotics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 80, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Yang, W.C.; Wang, C.M.; Wu, C.F.; Lin, J.W.; Lin, W.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Lin, T.C.; Liao, H.J.; et al. Clozapine worsens glucose intolerance, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, kidney damage, and retinal injury and increases renal reactive oxygen species production and chromium loss in obese mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, M.R.; Navaira, E.; Escamilla, M.A.; Raventos, H.; Walss-Bass, C. Clozapine treatment causes oxidation of proteins involved in energy metabolism in lymphoblastoid cells: A possible mechanism for antipsychotic-induced metabolic alterations. J. Psychiatr. Pract. 2010, 16, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić-Kokic, A.; Tatalović, N.; Nestorov, J.; Miler, M.; Oreščanin-Dušić, Z.; Nikolić, M.; Milošević, V.; Blagojević, D.; Spasić, M.; Miljević, Č. Effects of antipsychotic drug administration on antioxidative defense enzymes in male rat kidney. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2016, 79, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, A.; Ganai, A.A.; Mujeeb, M.; Siddiqui, W.A. Ellagic acid, an NF-κB inhibitor, ameliorates renal function in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 219, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghan Shahreza, F. Oxidative stress, free radicals, kidney disease and plant antioxidants. Immunopathol. Persa. 2017, 3, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocchegiani, E.; Malavolta, M. Role of zinc and selenium in oxidative stress and immunosenescence: Implications for healthy aging and longevity. In Handbook of Immunosenescence; Fulop, T., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 2539–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marreiro, D.D.; Cruz, K.J.; Morais, J.B.; Beserra, J.B.; Severo, J.S.; Oliveira, A.R. Zinc and oxidative stress: Current mechanisms. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, J.M.; Witting, P.K. Protective role for antioxidants in acute kidney disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Du, Y.; He, Y.; Li, S. Selenomethionine alleviates kidney necroptosis and inflammation by restoring lipopolysaccharide-mediated mitochondrial dynamics imbalance via the TLR4/RIPK3/DRP1 signaling pathway in laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanvand, A.; Abbaszadeh, A.; Darabi, S.; Nazari, A.; Gholami, M.; Kharazmkia, A. Evaluation of selenium on kidney function following ischemic injury in rats: Protective effects and antioxidant activity. J. Renal Inj. Prev. 2016, 6, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Bao, J.; Xing, H. Selenomethionine protects against ammonia-induced apoptosis through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress in pig kidneys. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 223, 112596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammadova-Bach, E.; Braun, A. Zinc homeostasis in platelet-related diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Loutsidou, A.C.; Spiliopoulou, C.A.; Stefanidou, M.E. Zinc and human health: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanon, R.S.; Minakshi, N.; Nihal, A. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2007, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, H.; Fridovich, I. The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 3170–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, E. Red Cell Metabolism: A Manual of Biochemical Methods, 3rd ed.; Grune and Stratton: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, D.; Valentine, W. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1967, 70, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glatzle, D.; Vuilleumier, J.; Weber, F.; Decker, K. Glutathione reductase test with whole blood, a convenient procedure for the assessment of the riboflavin status in humans. Experientia 1974, 30, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habig, N.; Pabst, M.; Jakoby, N. GST: 1st enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, A.; Randall, R. Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, S.; Villar, V.A.; Jose, P.A.; Armando, I. Renal dopamine receptors, oxidative stress and hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17553–17572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Hernández, A.; Figuero-Pérez, L.; Cruz-Hernandez, J.J.; González Sarmiento, R.; Usategui-Martin, R.; Miramontes-González, J.P. Dopamine receptors and the kidney: An overview of health- and pharmacological-targeted implications. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.C.; Uetrecht, J.P. Clozapine is oxidized by activated human neutrophils to a reactive nitrenium ion that irreversibly binds to the cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 275, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobach, A.R.; Uetrecht, J. Involvement of myeloperoxidase and NADPH oxidase in the covalent binding of amodiaquine and Clozapine to neutrophils: Implications for drug-induced agranulocytosis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, D.; Sloss, G.; Piatkov, I. Clozapine-induced acute renal failure and cytochrome P450 genotype. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2016, 50, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woesner, M.E.; Kanofsky, J.D.; Harris, A.Z.; Kelleher, P.J.; Gittens, K.; Jerschow, E. A case of acute renal failure in a patient recently treated with Clozapine and a review of previously reported cases. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2011, 13, 10br01091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, S.; Siskind, D.; Spivak, V.; Wysoczanski, D.; Halangoda, P. Fever, confusion, acute kidney injury: Is this atypical neuroleptic malignant syndrome following polypharmacy with Clozapine and risperidone? Australas. Psychiatry 2016, 6, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-P.; Chang, C.-K.; Hayes, R.D.; Harrison, S.; Lee, W.; Broadbent, M.; Taylor, D.; Stewart, R. Retrospective chart review on exposure to psychotropic medications associated with neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2014, 130, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Højlund, M.; Lund, L.C.; Herping, J.L.E.; Haastrup, M.B.; Damkier, P.; Henriksen, D.P. Second-generation antipsychotics and the risk of chronic kidney disease: A population-based case-control study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sernoskie, S.C.; Jee, A.; Uetrecht, J. The role of myeloperoxidase in Clozapine-induced inflammation: A mechanistic update for idiosyncratic drug-induced agranulocytosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmei, P.; Kasna, S.; Probin Roy, K.; Kumar, S. A Review on Pharmacological Advancement of Ellagic Acid. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2024, 15, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, N.S.; Hsu, Y.H.; Ho, S.Y.; Kuo, Y.C.; Lee, H.C.; Yin, Y.J.; Huang, H.L. Is schizophrenia associated with an increased risk of chronic kidney disease? A nationwide matched-cohort study. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehsel, K.; Loeffler, S.; Krieger, K.; Henning, U.; Agelink, M.; Kolb-Bachofen, V.; Klimke, A. Clozapine induces oxidative stress and proapoptotic gene expression in neutrophils of schizophrenic patients. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 25, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, M. Effects of antioxidants on immune system ageing. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.C.; Maggini, S. Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintergerst, E.S.; Maggini, S.; Hornig, D.H. Immune-enhancing role of vitamin C and zinc and effect on clinical conditions. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2006, 50, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancaktutar, A.A.; Bodakci, M.N.; Hatipoglu, N.K.; Soylemez, H.; Basarılı, K.; Turkcu, G. The protective effects of pomegranate extracts against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in male rats. Urol. Ann. 2014, 6, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makled, M.N.; El-Awady, M.S.; Abdel-Aziz, R.R.; Shehab El-Din, A.B.; Ammar, E.M.; Gameil, N.M. Pomegranate extract ameliorates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via suppressing NF-κB pathway. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clément, M.V.; Ponton, A.; Pervaiz, S. Apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide is mediated by decreased superoxide anion concentration and reduction of intracellular milieu. FEBS Lett. 1998, 440, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, R.; Wang, N.; Deng, Y.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y.; Qi, M.; Wang, J. Ellagic Acid Alleviates Oxidative Stress by Mediating Nrf2 Signaling Pathways and Protects against Paraquat-Induced Intestinal Injury in Piglets. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld-Klatta, K.; Jiers, W.; Rzepczyk, S.; Nowicki, F.; Łukasik-Głębocka, M.; Świderski, P.; Zielińska-Psuja, B.; Żaba, Z.; Żaba, C. The effect of neuropsychiatric drugs on the oxidation-reduction balance in therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholampour, H.; Moezi, L.; Shafaroodi, H. Aripiprazole prevents renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats, probably through nitric oxide involvement. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 813, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.F.; Schafer, F.Q.; Buettner, G.R.; Rodgers, V.G. The rate of cellular hydrogen peroxide removal shows dependency on GSH: Mathematical insight into in vivo H2O2 and GPx concentrations. Free. Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raitasuo, V.; Vataja, R.; Elomaa, E. Risperidone-induced neuroleptic malignant syndrome in a young patient. Lancet 1994, 344, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.W.; Lee, Y.; Lee, C.Y.; Lin, P.Y. Neurotoxicity and nephrotoxicity caused by combined use of lithium and risperidone: A case report and literature review. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgiç, S.; Korkmaz, D.T.; Azirak, S.; Güvenç, A.N.; Kocaman, N.; Özer, M.K. Risperidone-induced renal damage and metabolic side effects: The protective effect of resveratrol. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8709521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| AAP Treated | % | AAP + ProCloSupp | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clo | Discrete (8/8) | 100D | Discrete (8/8) | 100D |
| Aripiprazole | Discrete (D) (1/8); moderate (M) (7/8) | 12.5D; 87.5M | Discrete (7/8); moderate (1/8) | 87.5D; 12.5M |
| Risperidone | Discrete (4/4); moderate (4/4) | 50D; 50M | Discrete (7/8); moderate (1/8) | 87.5D; 12.5M |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grahovac, T.; Vidonja Uzelac, T.; Oreščanin Dušić, Z.; Spasić, D.; Mijović, M.; Nikolić-Kokić, A.; Miljević, Č.; Blagojević, D. Antioxidant Supplementation with ProCloSupp Protects Against Renal Toxicity of Atypical Antipsychotics in Rats: Implications for Safer Treatment Strategies. Life 2025, 15, 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111679
Grahovac T, Vidonja Uzelac T, Oreščanin Dušić Z, Spasić D, Mijović M, Nikolić-Kokić A, Miljević Č, Blagojević D. Antioxidant Supplementation with ProCloSupp Protects Against Renal Toxicity of Atypical Antipsychotics in Rats: Implications for Safer Treatment Strategies. Life. 2025; 15(11):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111679
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrahovac, Tanja, Teodora Vidonja Uzelac, Zorana Oreščanin Dušić, Dušan Spasić, Milica Mijović, Aleksandra Nikolić-Kokić, Čedo Miljević, and Duško Blagojević. 2025. "Antioxidant Supplementation with ProCloSupp Protects Against Renal Toxicity of Atypical Antipsychotics in Rats: Implications for Safer Treatment Strategies" Life 15, no. 11: 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111679
APA StyleGrahovac, T., Vidonja Uzelac, T., Oreščanin Dušić, Z., Spasić, D., Mijović, M., Nikolić-Kokić, A., Miljević, Č., & Blagojević, D. (2025). Antioxidant Supplementation with ProCloSupp Protects Against Renal Toxicity of Atypical Antipsychotics in Rats: Implications for Safer Treatment Strategies. Life, 15(11), 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111679







