In Situ Harvesting and Molecular Identification for the Germinating Species Diversity of Dinoflagellate Resting Cysts in Jiaozhou Bay, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
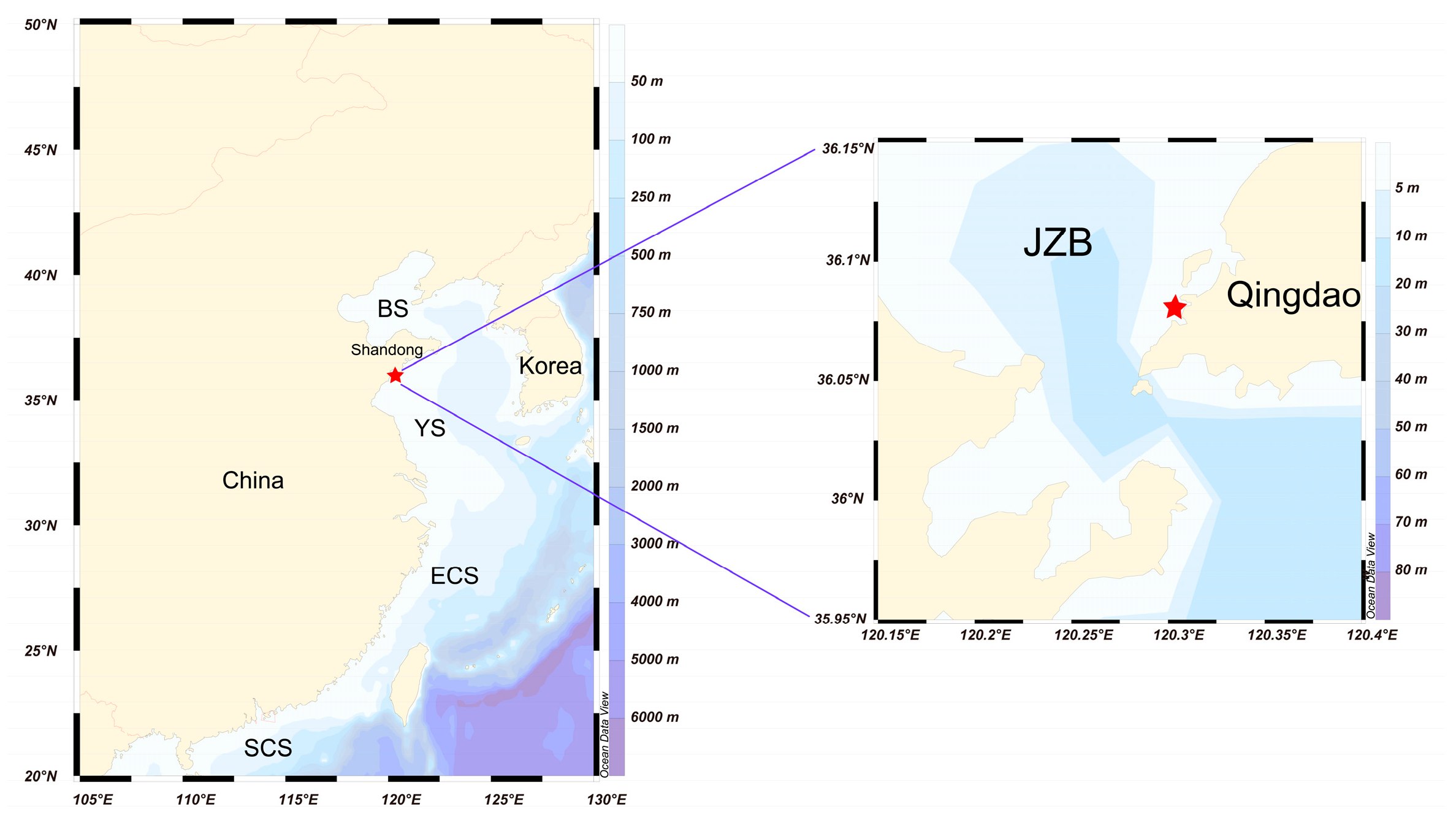
2.1. Sampling Site
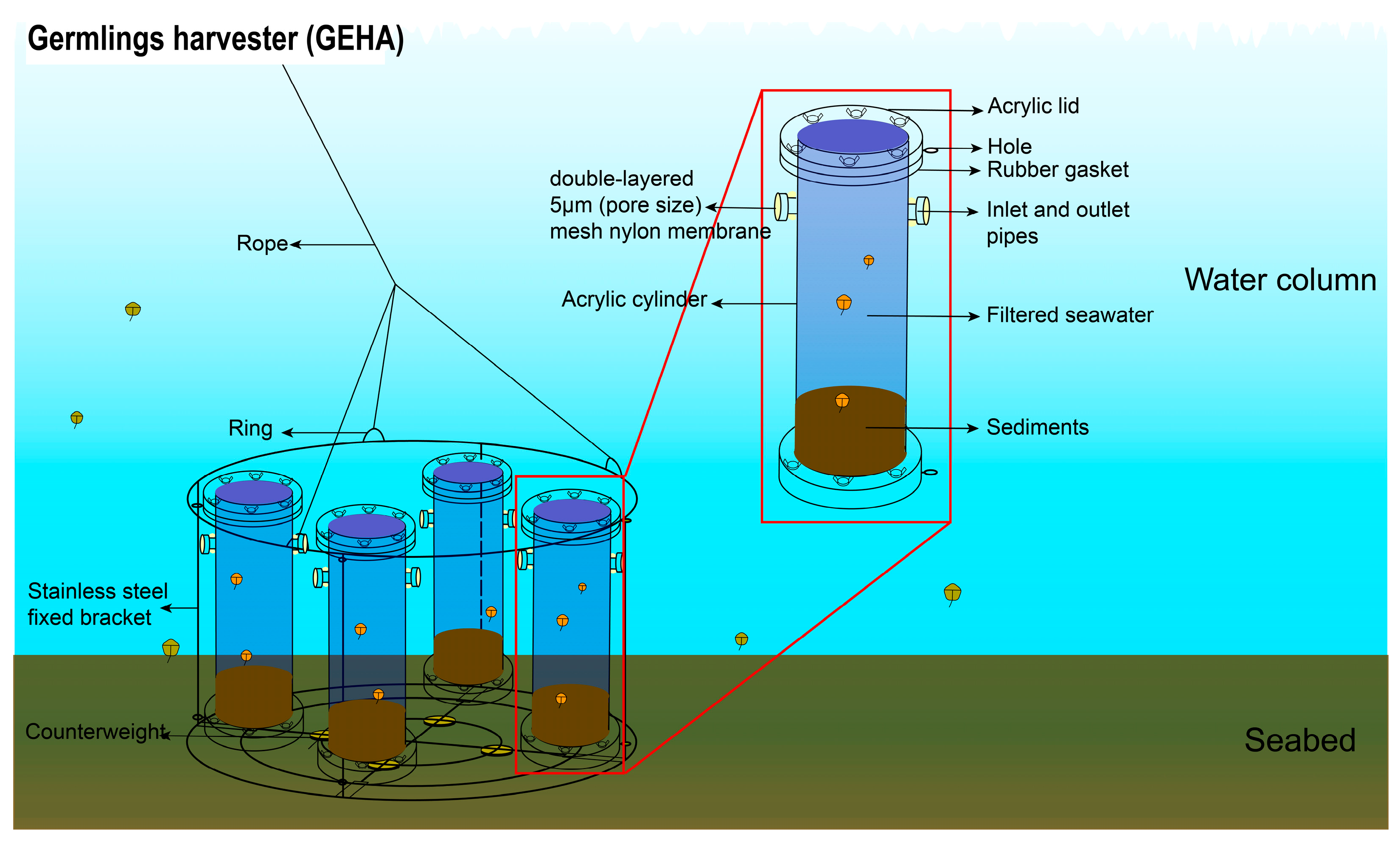
2.2. In Situ Sampling for the Germinated Dinoflagellate Cysts with GEHA
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Metabarcoding Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
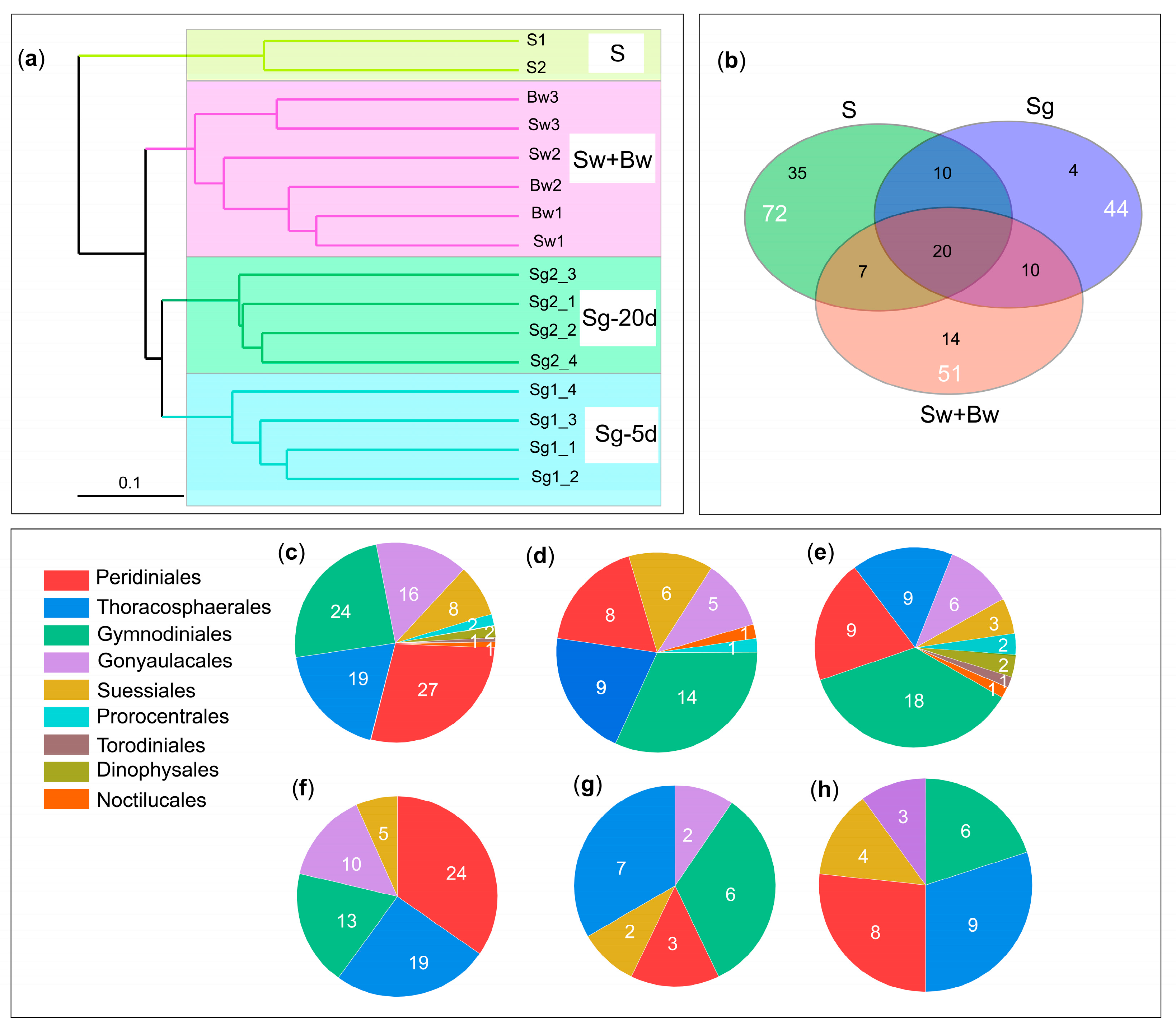
3.1. Overview for the Metabarcoding Sequencing
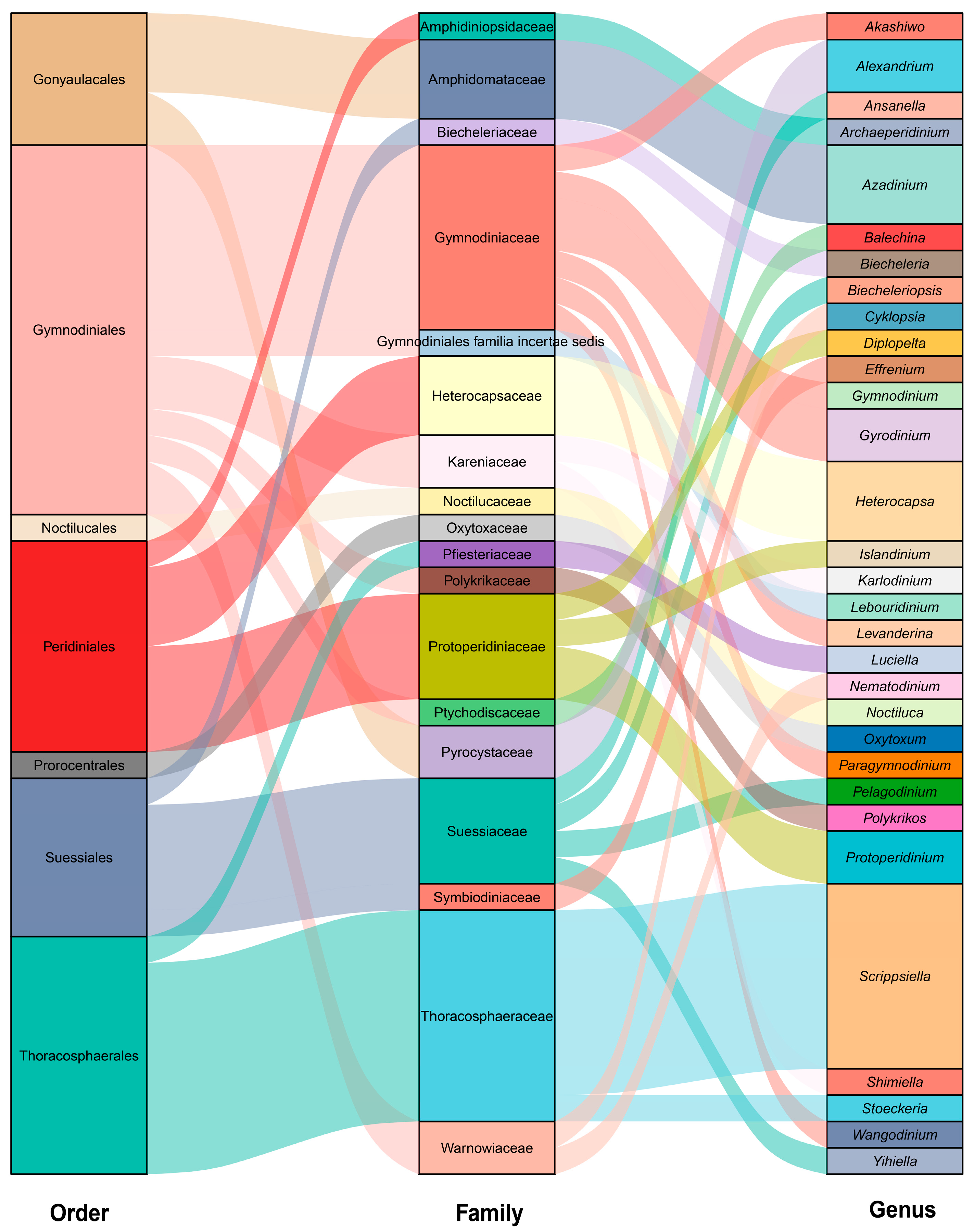
3.2. Species Diversity of In Situ Germinated Dinoflagellate Cysts
3.3. Species of Particular Importance from In Situ Germinated Dinoflagellate Cysts
4. Discussion
4.1. GEHA Combined with Metabarcoding Analysis Detected High Dinoflagellate Diversity from In Situ Germination
4.2. Many Dinoflagellates of Particular Ecological Importance Germinated In Situ from Marine Sediments
4.3. Species Diversity of In Situ Germinated Dinoflagellate Cysts with Germination Duration Extended
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smayda, T.J. Harmful algal blooms: Their ecophysiology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1137–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Kang, H.C.; Lim, A.S.; Jang, S.H.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.Y.; Ok, J.H.; You, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Feeding diverse prey as an excellent strategy of mixotrophic dinoflagellates for global dominance. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Gobler, C.J. Harmful algal blooms in China: History, recent expansion, current status, and future prospects. Harmful Algae 2023, 129, 102499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minstry of Natural Resources Bulletin of China Marine Disaster 1989–2022. Available online: https://www.mnr.gov.cn (accessed on 18 October 2024). (In Chinese)
- Bravo, I.; Figueroa, R.I. Towards an ecological understanding of dinoflagellate cyst functions. Microorganisms 2014, 2, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, M.D. How many species of algae are there? A reprise. Four kingdoms, 14 phyla, 63 classes and still growing. J. Phycol. 2024, 60, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Deng, Y. Characteristical life history (resting cyst) provides a mechanism for recurrence and geographic expansion of harmful algal blooms of dinoflagellates: A Review. Stud. Mar. Sin. 2016, 51, 132–154. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.Z.; Gu, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, D.; Hu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Shang, L.; Qi, Y. Exploration of resting cysts (stages) and their relevance for possibly HABs-causing species in China. Harmful Algae 2021, 107, 102050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Wall, D. Potential importance of benthic cysts of Gonyaulax tamarensis and Gonyaulax excavata in initiating toxic dinoflagellate blooms. J. Phycol. 1978, 14, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnahan, M.L.; Ralston, D.K.; Fischer, A.D.; Solow, A.R.; Anderson, D.M. Bloom termination of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella: Vertical migration behavior, sediment infiltration, and benthic cyst yield. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 2829–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.; Bolch, C. Transport of toxic dinoflagellate cysts via ships ballast water. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 22, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G. A review of Harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 1993, 32, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Hu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, X.; Chai, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhan, Z.; Dobbs, F.C.; Tang, Y.Z. Metagenomic sequencing identifies highly diverse assemblages of dinoflagellate cysts in sediments from ships’ ballast tanks. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.; Morel, F. Seeding of 2 red tide blooms by the germination of benthic Gonyaulax tamarensis hypnocysts. Estuarine Coastal Mar. Sci. 1979, 8, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Hattori, M.; Imai, I. Development of the “plankton emergence trap/chamber (PET Chamber)”, a new sampling device to collect in situ germinating cells from cysts of microalgae in surface sediments of coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Hattori, M.; Ishii, K.-I.; Kulis, D.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Imai, I. In situ dynamics of cyst and vegetative cell populations of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella in Ago Bay, central Japan. J. Plankton Res. 2014, 36, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsuike, M.; Yokoyama, K.; Nishitani, G.; Yamada, Y.; Yoshinaga, I.; Ishikawa, A. Germination fluctuation of toxic Alexandrium fundyense and A. pacificum cysts and the relationship with bloom occurrences in Kesennuma Bay, Japan. Harmful Algae 2017, 62, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Fujita, N.; Taniguchi, A. A sampling device to measure in situ germination rates of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments. J. Plankton Res. 1995, 17, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengefors, K.; Gustafsson, S.; Ståhl-Delbanco, A. Factors regulating the recruitment of cyanobacterial and eukaryotic phytoplankton from littoral and profundal sediments. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Taniguchi, A. In situ germination patterns of cysts, and bloom formation of some armored dinoflagellates in Onagawa Bay, north-east Japan. J. Plankton Res. 1997, 19, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Takei, Y.; Ishii, K.-I.; Yamaguchi, M. Population dynamics of Chattonella (Raphidophyceae), causative flagellates of noxious red tides in Ago Bay, central Japan, with an emphasis on cyst germination. Plankton Benthos Res. 2022, 17, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.-I.; Matsuoka, K.; Imai, I.; Ishikawa, A. Life cycle strategies of the centric diatoms in a shallow embayment revealed by the plankton emergence trap/chamber (PET chamber) experiments. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 889633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Taniguchi, A. Contribution of benthic cysts to the population dynamics of Scrippsiella spp. (Dinophyceae) in Onagawa bay, northeast Japan. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 1996, 140, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglès, S.; Garcés, E.; Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Gobler, C.J. In situ life-cycle stages of Alexandrium fundyense during bloom development in Northport Harbor (New York, USA). Harmful Algae 2012, 16, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglès, S.; Garcés, E.; Reñé, A.; Sampedro, N. Life-cycle alternations in Alexandrium minutum natural populations from the NW Mediterranean Sea. Harmful Algae 2012, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cui, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, N. Composition and spatial-temporal dynamics of phytoplankton community shaped by environmental selection and interactions in the Jiaozhou bay. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Song, J.; Yuan, H. Evolution of marine environmental health in Jiaozhou Bay in recent 40 years based on the ‘DualCore’ assessment framework. Ocean Dev. Manag. 2023, 40, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, N. Advances in biodiversity analysis of phytoplankton and harmful algal bloom species in the Jiaozhou Bay. Mar. Sci. 2021, 45, 170–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F.; Pu, X. Annual variation of primary productivity in Jiaozhou bay. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2005, 36, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.Z. The morphological and phylogenetic characterization for the dinoflagellate Margalefidinium fulvescens (=Cochlodinium fulvescens) isolated from the Jiaozhou Bay, China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Hu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Shang, L.; Gobler, C.J.; Tang, Y.Z. An assessment on the intrapopulational and intraindividual genetic diversity in LSU rDNA in the harmful algal blooms-forming dinoflagellate Margalefidinium (=Cochlodinium) fulvescens based on clonal cultures and bloom samples from Jiaozhou Bay, China. Harmful Algae 2020, 96, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chai, Z.; Hu, Z.; Tang, Y.Z. A combined approach detected novel species diversity and distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in the Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, M.; Ji, S.; Chen, J.; Zheng, H.; Tang, Y.; Hu, R. Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments from the Qingdao coast, the Yellow sea, China: The potential risk of harmful algal blooms. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 910327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, M. Relationship between dinoflagellate cyst and environmental factors in surface sediment of the Jiaozhou Bay. J. Yantai Univ. Nat. Sci. Eng. Ed. 2021, 34, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Shen, P.; Gu, H.; Tan, Y. Distribution of dinoflagellate resting cysts in surface sediment of Jiaozhou bay, China. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2017, 48, 760–766. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Du, J.; Sun, X. Spatial-temporal variation of phytoplankton community structure in Jiaozhou Bay, China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Tao, Z.; Yang, W.; Li, F.; Wei, B.; Yue, C.; Pan, S.; Deng, Y.; Shang, L.; Chai, Z.; et al. A newly developed germlings harvester (GEHA) in combination with metabarcoding analysis detected numerous plankton species, particularly HABs-causing species, from in-situ germination of resting stage cells. Harmful Algae 2025, 150, 103002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Shi, X. Phytoplankton community of the Jiaozhou bay in spring 2009. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2014, 45, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Sun, P.; Xia, B. A preliminary study on phytoplankton community structure and its changes in the Jiaozhou Bay. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2005, 23, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Bolch, C.J.S. The use of sodium polytungstate for the separation and concentration of living dinoflagellate cysts from marine sediments. Phycologia 1997, 36, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, K.A.A.; Wolff, B.; Varuzza, L.; Green, S.J.J.; Barb, J.J.J. Multi-amplicon microbiome data analysis pipelines for mixed orientation sequences using QIIME2: Assessing reference database, variable region and pre-processing bias in classification of mock bacterial community samples. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahe, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Z.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Hu, Z.; Tang, Y.Z. Harmful algal blooms significantly reduce the resource use efficiency in a coastal plankton community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, D.; Dickey, R.; Carlson, R.; Moreygaines, G. Ciguatoxigenic dinoflagellates from the Caribbean Sea. ACS Symp. Ser. 1984, 262, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, P.; Xu, N. Toxic characteristics and action mode of the mixotrophic dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea on co-occurring phytoplankton and zooplankton. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Yang, W.; Leaw, C.P.; Pospelova, V.; Bilien, G.; Liow, G.R.; Lim, P.T.; Gu, H. Cryptic diversity within the harmful dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea in coastal Chinese waters is related to differentiated ecological niches. Harmful Algae 2017, 66, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Z.; Gobler, C.J. Sexual resting cyst production by the dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea: A potential mechanism contributing toward the ubiquitous distribution of a harmful alga. J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Yoo, Y.; Park, J.; Song, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Yih, W. Feeding by phototrophic red-tide dinoflagellates: Five species newly revealed and six species previously known to be mixotrophic. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 40, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zeng, N.; Liu, T.; Yang, W.; Mueller, A.; Krock, B. Morphology, toxicity, and phylogeny of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species along the coast of China. Harmful Algae 2013, 27, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikata, T.; Taniguchi, E.; Sakamoto, S.; Kitatsuji, S.; Yamasaki, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Oikawa, H. Phylogeny, growth and toxicity of the noxious red-tide dinoflagellate Alexandrium leei in Japan. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 36, 101265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Geng, H.-X.; Yu, R.-C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Zhang, Q.-C.; Kong, F.-Z.; Zhou, M.-J. Distribution of Alexandrium pacificum cysts in the area adjacent to the Changjiang River estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, U.; Litaker, R.W.; Montresor, M.; Murray, S.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Formal revision of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex (Dinophyceae) taxonomy: The introduction of five species with emphasis on molecular-based (rDNA) classification. Protist 2014, 165, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Jeong, H.J.; Jang, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kang, N.S.; Lee, M.J.; Potvin, E. Mixotrophy in the newly described dinoflagellate Ansanella granifera: Feeding mechanism, prey species, and effect of prey concentration. Algae 2014, 29, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, K.N.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kawami, H.; Ribeiro, S.; Leander, B.S.; Price, A.M.; Pospelova, V.; Ellegaard, M.; Matsuoka, K. Archaeperidinium saanichi sp. nov.: A new species based on morphological variation of cyst and theca within the Archaeperidinium minutum jörgensen 1912 species complex. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2012, 96–97, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Gottschling, M.; Nezan, E.; Krock, B.; Bilien, G. Morphological and molecular characterization of three new Azadinium species (Amphidomataceae, Dinophyceae) from the Irminger Sea. Protist 2014, 165, 417–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Sanchez-Ramirez, S.; Krock, B.; Bernales-Jimenez, A. A bloom of Azadinium polongum in coastal waters off Peru. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2017, 52, 591–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Soehner, S.; Nézan, E.; Krock, B. First record of the genus Azadinium (Dinophyceae) from the shetland islands, including the description of Azadinium polongum sp. nov. Harmful Algae 2012, 20, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Luo, Z.; Krock, B.; Witt, M.; Tillmann, U. Morphology, phylogeny and azaspiracid profile of Azadinium poporum (Dinophyceae) from the China sea. Harmful Algae 2013, 21–22, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, F.; Artigas, L.F.; Gast, R.J. Molecular phylogeny and synonymy of Balechina gracilis comb. nov. (=Gymnodinium gracile), a widespread polymorphic unarmored dinoflagellate (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2021, 57, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, J.; Tao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Shang, L.; Chai, Z.; et al. Reviving and characterizing three species of dinoflagellate cysts dormant for about 70 years in the East China Sea: Biecheleria brevisulcata, Biecheleriopsis adriatica, and Scrippsiella donghaienis. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 2292–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, E.C.; Holt, C.C.; Jacko-Reynolds, V.K.L.; Leander, B.S.; Keeling, P.J. Photosystems in the eye-like organelles of heterotrophic warnowiid dinoflagellates. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 4252–4260.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Mertens, K.N.; Gu, H. Cyst-theca relationship and phylogenetic positions of the diplopsalioideans (Peridiniales, Dinophyceae), with description of Niea and Qia gen. nov. Phycologia 2015, 54, 210–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Deng, Y.; Shang, L.; Liu, Y.; Tao, Z.; Chai, Z.; Tang, Y.Z. Evidence for the production of asexual resting cysts in a free-living species of Symbiodiniaceae (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2024, 137, 102658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Jang, T.Y.; Lim, A.S.; Kang, N.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, K.Y.; Park, K.-T.; Lee, K. Feeding by the newly described mixotrophic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium smaydae: Feeding mechanism, prey species, and effect of prey concentration. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 459, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Yoo, Y.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoon, E.Y.; Kang, N.S.; Lim, A.S.; Lee, K.H.; Jang, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, H.S. Feeding by heterotrophic protists on the toxic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rene, A.; Camp, J.; Garces, E. Diversity and phylogeny of Gymnodiniales (Dinophyceae) from the NW Mediterranean Sea revealed by a morphological and molecular approach. Protist 2015, 166, 234–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwataki, M.; Hansen, G.; Sawaguchi, T.; Hiroishi, S.; Fukuyo, Y. Investigations of body scales in twelve Heterocapsa species (Peridiniales, Dinophyceae), including a new species H. pseudotriquetra sp. nov. Phycologia 2004, 43, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Huang, S.; Mertens, K.N.; Pospelova, V.; Shen, X.; Gu, H. High-resolution DNA metabarcoding of modern surface sediments uncovers a diverse assemblage of dinoflagellate cysts in the Pacific and Arctic oceans. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 215, 117899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millette, N.C.; Pierson, J.J.; Aceves, A.; Stoecker, D.K. Mixotrophy in Heterocapsa rotundata: A mechanism for dominating the winter phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Gu, H.; Mertens, K.N.; Lan, D. New dinoflagellate species Protoperidinium haizhouense sp. nov. (Peridiniales, Dinophyceae), its cyst-theca relationship and phylogenetic position within the Monovela group. Phycol. Res. 2014, 62, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Tang, Y.Z. Evidence for resting cyst production in the cosmopolitan toxic dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum and the cyst distribution in the China seas. Harmful Algae 2020, 93, 101788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachvaroff, T.R.; Adolf, J.E.; Squier, A.H.; Harvey, H.R.; Place, A.R. Characterization and quantification of karlotoxins by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, A.R.; Bowers, H.A.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Adolf, J.E.; Deeds, J.R.; Sheng, J. Karlodinium veneficum—The little dinoflagellate with a big bite. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Chen, N. Molecular analysis of a polyphasic red tide in Rongcheng Offshore, Shandong Peninsula in 2021~2022. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2023, 54, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, R. Ecological Factors Related to Gyrodinium instriatum Bloom in the Inner Estuary of the Gulf of Guayaquil. In Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea, Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Toxic Marine Phytoplankton, Newport, RI, USA, 28 October–1 November 1991; Smayda, T.J., Shimizu, Y., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publisher B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; Volume 3, pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Shikata, T.; Nagasoe, S.; Matsubara, T.; Yamasaki, Y.; Shimasaki, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Uchida, T.; Jenkinson, I.R.; Honjo, T. Encystment and excystment of Gyrodinium instriatum Freudenthal et Lee. J. Oceanogr. 2008, 64, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, P.L.; Litaker, R.W.; Jeong, H.J.; Ha, J.H.; Reece, K.S.; Stokes, N.A.; Park, J.Y.; Steidinger, K.A.; Vandersea, M.W.; Kibler, S.; et al. Description of a new genus of Pfesteria-like dinoflagellate, Luciella gen. nov (Dinophyceae), including two new species: Luciella masanensis sp. nov and Luciella atlantis sp. nov. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, E.J.; Khoo, L.; Stevens, J.B.; Fan, Z.; Burkholder, J.M. Novel toxic dinoflagellate causes epidemic disease in estuarine fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1996, 32, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Liu, X.; Song, X.; Deng, Y.; Shang, L.; Chai, Z.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.Z. Species and genetic diversity of notorious dinoflagellates Pfiesteria piscicida, Luciella masanensis, and relatives in marine sediments of China. Harmful Algae 2024, 140, 102746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Portela, M.; Moestrup, Ø.; Daugbjerg, N.; Altenburger, A.; Lundholm, N. Studies on the complex Warnowiaceae (Dinophyceae) I. Lohmann’s Pouchetia parva refound and renamed Nematodinium parvum comb. nov. (=Warnowia parva). Phycologia 2023, 62, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, W.; Jiang, F.; Chen, Z.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yan, T.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, X. The dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans in China: A review of its distribution and role in harmful algal blooms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschling, M.; Wietkamp, S.; Bantle, A.; Tillmann, U. Oxytoxaceae are prorocentralean rather than peridinialean dinophytes and taxonomic clarification of heterotrophic Oxytoxum lohmannii (≡“Amphidinium” crassum) by epitypification. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokouchi, K.; Takahashi, K.; Nguyen, V.N.; Iwataki, M.; Horiguchi, T. Ultrastructure and systematics of two new species of dinoflagellate, Paragymnodinium asymmetricum sp. nov. and Paragymnodinium inerme sp. nov. (Gymnodiniales, Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 730–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siano, R.; Montresor, M.; Probert, I.; Not, F.; de Vargas, C. Pelagodinium gen. nov and P. beii comb. nov., a dinoflagellate symbiont of planktonic foraminifera. Protist 2010, 161, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Kawami, H.; Nagai, S.; Iwataki, M.; Takayama, H. Re-examination of cyst-motile relationships of Polykrikos kofoidii Chatton and Polykrikos schwartzii Butschli (Gymnodiniales, Dinophyceae). Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2009, 154, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Sun, J.; Kooistra, W.H.C.F.; Zeng, R. Phylogenetic position and morphology of thecae and cysts of Scrippsiella (Dinophyceae) species in the East China Sea. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lü, S. The relationship between Scrippsiella trochoidea red tide and cysts in the Daya Bay. Mar. Sci. 2001, 25, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.H.; Ok, J.H.; Kang, H.C.; Park, S.A.; Eom, S.H.; Jeong, H.J. Five phototrophic Scrippsiella species lacking mixotrophic ability and the extended prey spectrum of Scrippsiella acuminata (Thoracosphaerales, Dinophyceae). Algae 2023, 38, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yue, C.; Song, X.; Hu, Z.; Shi, S.; Li, R.; Deng, Y.; Shang, L.; et al. Single-cyst morpho-molecular identification detected an unexpected high species diversity of dinoflagellate resting cysts from the coastal seas of China. Harmful Algae 2025, 149, 102941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinssmeister, C.; Soehner, S.; Kirsch, M.; Facher, E.; Meier, K.J.S.; Keupp, H.; Gottschling, M. Same but different: Two novel bicarinate species of extant calcareous dinophytes (Thoracosphaeraceae, Peridiniales) from the Mediterranean Sea. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmann, J.; Zinssmeister, C.; Gottschling, M. Taxonomic clarification of the dinophyte Rhabdosphaera erinaceus KAMPTNER, Scrippsiella erinaceus comb. nov (Thoracosphaeraceae, Peridiniales). Syst. Biodivers. 2014, 12, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J. Cyst-theca relationships in Scrippsiella (Dinophyceae) and related Orthoperidinioid genera. Bot. Mar. 1991, 34, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, J.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.A.; Noh, J.H. Shimiella gen. nov. and Shimiella gracilenta sp. nov. (Dinophyceae, Kareniaceae), a kleptoplastidic dinoflagellate from Korean waters and its survival under starvation. J. Phycol. 2021, 57, 70–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, I.; Lee, S.H.; Ha, J.H.; Yih, W.H. Stoeckeria algicida n. gen., n. sp. (Dinophyceae) from the coastal waters off southern Korea: Morphology and small subunit ribosomal DNA gene sequence. J. Eukaryotic Microbiol. 2005, 52, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Yue, C.; Liu, Y.; Shi, S.; Li, R.; Chai, Z.; Deng, Y.; Shang, L.; Hu, Z.; Gu, H.; et al. A new ribo-type of Wangodinium sinense from germination of resting cysts isolated from ballast tank sediments of incoming ships to China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Moestrup, O.; Kang, N.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Seong, K.A. Yihiella yeosuensis gen. Et sp. nov. (Suessiaceae, Dinophyceae), a novel dinoflagellate isolated from the coastal waters of Korea. J. Phycol. 2017, 53, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhong, Y.; You, X.; Weng, Y.; Zhuang, H. Research on the germination and proliferation of dinoflagellate cysts in the sediments of Xipi Reservoir in Jiulongjiang River. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2015, 35, 2875–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lin, L.; Xue, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, H. Study on the diversity and germination of dinoflagellate cysts in the sediments of foreign ships in Shanghai port. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 205, 116566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Gu, X. Seasonal fluctuation of Scrippsiella trochoidea cyst population in Daya Bay, South China Sea. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2007, 15, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.; Wilson, J.B. A consumer’s guide to evenness indices. Oikos 1996, 76, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, H.; Bennett, D.M.; Cadotte, M.W. Consequences of dominance: A review of evenness effects on local and regional ecosystem processes. Ecology 2008, 89, 1510–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millette, N.C.; Stoecker, D.K.; Pierson, J.J. Top-down control by micro- and mesozooplankton on winter dinoflagellate blooms of Heterocapsa rotundata. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 76, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, K. Interview with Barrie Dale. Harmful Algae News 2025, 80, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder, J.; Glasgow, H. Interactions of a toxic estuarine dinoflagellate with microbial predators and prey. Arch. Protistenkd. 1995, 145, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, E.B.; Sherr, B.F. Significance of predation by protists in aquatic microbial food webs. Antonie Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 81, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Yoo, Y.D.; Kang, N.S.; Rho, J.R.; Seong, K.A.; Park, J.W.; Nam, G.S.; Yih, W. Ecology of Gymnodinium aureolum. I. Feeding in western Korean waters. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.S.; Stoecker, D.K.; Adolf, J.E. Feeding, pigmentation, photosynthesis and growth of the mixotrophic dinoflagellate Gyrodinium galatheanum. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 19, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Hu, Z.; Song, X.; Gobler, C.J.; Tang, Y.Z. Vitamin B12-auxotrophy in dinoflagellates caused by incomplete or absent cobalamin-independent methionine synthase genes (metE). Fundam. Res. 2022, 2, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Tejedor, M.; Soubrier-Pedreno, M.A.; Furones, M.D. Mitigation of lethal effects of Karlodinium veneficum and K. armiger on Sparus aurata: Changes in haematocrit and plasma osmolality. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 77, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanos-Rivera, A.; Alvarez-Munoz, K.; Astuya-Villalon, A.; Lopez-Rosales, L.; Garcia-Camacho, F.; Sanchez-Miron, A.; Krock, B.; Jose Gallardo-Rodriguez, J. Sublethal effect of the toxic dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum on early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 27113–27124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeds, J.R.; Terlizzi, D.E.; Adolf, J.E.; Stoecker, D.K.; Place, A.R. Toxic activity from cultures of Karlodinium micrum (=Gyrodinium galatheanum) (Dinophyceae)—A dinoflagellate associated with fish mortalities in an estuarine aquaculture facility. Harmful Algae 2002, 1, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway, S.E. A review of the effects of algal blooms on shellfish and aquaculture. J. World Aquacult Soc. 1990, 21, 65–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahru, M.; Michell, B.G.; Diaz, A.; Miura, M. MODIS detects a devastating algal bloom in Paracas Bay, Peru. EOS Trans. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2004, 85, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessup, D.A.; Miller, M.A.; Ryan, J.P.; Nevins, H.M.; Kerkering, H.A.; Mekebri, A.; Crane, D.B.; Johnson, T.A.; Kudela, R.M. Mass stranding of marine birds caused by a surfactant-producing red tide. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Pu, X.; Li, W. Evolution and causes of formation of Gymnodinium sanguineum bloom in Yantai Sishili Bay. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2001, 32, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Song, G.; Song, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, N. Distribution of the toxic dinoflagellate Stoeckeria algicida in Liaodong Bay. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.T.; Seong, K.A.; Kim, T.H.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Feeding and grazing impact of the newly described heterotrophic dinoflagellate Stoeckeria algicida on the harmful alga Heterosigma akashiwo. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 295, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.J.; Furuya, K.; Glibert, P.M.; Xu, J.; Liu, H.B.; Yin, K.; Lee, J.H.W.; Anderson, D.M.; Gowen, R.; Al-Azri, A.R.; et al. Geographical distribution of red and green Noctiluca scintillans. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 807–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lin, H.; Peng, C.; Sun, L.; Gao, Y.; Chen, B. Long-term changes in Noctiluca scintillans blooms along the Chinese coast from 1933 to 2020. Global Change Biol. 2023, 29, 5099–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefi, M.A.; Attaran-Fariman, G. Harmful blooming of Noctiluca scintillans in the southeast coastal waters of Iran, Oman sea. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2023, 22, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.D.; Mathews, G.; Obura, D.O.; Laju, R.L.; Bharath, M.S.; Kumar, P.D.; Arasamuthu, A.; Kumar, T.K.A.; Edward, J.K.P. Low oxygen levels caused by Noctiluca scintillans bloom kills corals in Gulf of Mannar, India. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremp, A.; Anderson, D.M. Factors regulating germination of resting cysts of the spring bloom dinoflagellate Scrippsiella hangoei from the northern Baltic Sea. J. Plankton Res. 2000, 22, 1311–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accoroni, S.; Glibert, P.M.; Pichierri, S.; Romagnoli, T.; Marini, M.; Totti, C. A conceptual model of annual Ostreopsis cf. ovata blooms in the northern Adriatic Sea based on the synergic effects of hydrodynamics, temperature, and the N:P ratio of water column nutrients. Harmful Algae 2015, 45, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Taylor, C.; Armbrust, E. The effects of darkness and anaerobiosis on dinoflagellate cyst germination. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1987, 32, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Lan, D.; Fang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cai, F. Distribution and germination of Alexandrium sp. cysts in coastal areas of Southeast China Sea. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 14, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y. Laboratory studies on germination of Scrippsiella trochoidea resting cyst in different environmental conditions. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2010, 29, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Delebecq, G.; Schmidt, S.; Ehrhold, A.; Latimier, M.; Siano, R. Revival of ancient marine dinoflagellates using molecular biostimulation. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Hu, Z.; Shang, L.; Peng, Q.; Tang, Y.Z. Transcriptomic analyses of Scrippsiella trochoidea reveals processes regulating encystment and dormancy in the life cycle of a dinoflagellate, with a particular attention to the role of abscisic acid. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koening, M.L.; Flores Montes, M.J.; Eskinazi Leca, E.; Tiburcio, A.S.X.S. New record of Akashiwo sanguinea (Dinophyta) in the tropical estuarine waters of Northeastern Brazil (Western Atlantic). Braz. J. Biol. 2014, 74, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Larsen, J. Unarmoured dinoflagellates from Australian waters II. Genus Gyrodinium (Gymnodiniales, Dinophyceae). Phycologia 1996, 35, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, S.; Matsuyama, Y.; Takayama, H.; Kotani, Y. Morphology of Polykrikos kofoidii and P. schwartzii (Dinophyceae, Polykrikaceae) cysts obtained in culture. Phycologia 2002, 41, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moestrup, O.; Hakanen, P.; Hansen, G.; Daugbjerg, N.; Ellegaard, M. On Levanderina fissa gen. & comb. nov. (Dinophyceae) (syn. Gymnodinium fissum, Gyrodinium instriatum, Gyr. uncatenum), a dinoflagellate with a very unusual sulcus. Phycologia 2014, 53, 265–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, E.C.; Jacobson, D.M.; Wolfe, G.V.; Bright, K.J.; Saldarriaga, J.F.; Keeling, P.J.; Leander, B.S.; Strom, S.L. Morphology, behavior, and phylogenomics of Oxytoxum lohmannii, dinoflagellata. J. Eukaryotic Microbiol. 2024, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretschmann, J.; Elbraezchter, M.; Zinssmeister, C.; Soehner, S.; Kirsch, M.; Kusber, W.H.; Gottschling, M. Taxonomic clarification of the dinophyte Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenb., Scrippsiella acuminata, comb. nov. (Thoracosphaeraceae, Peridiniales). Phytotaxa 2015, 220, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, F.; Takayama, H.; Moreira, D.; Lopez-Garcia, P. Unarmoured dinoflagellates with a small hyposome: Torodinium and Lebouridinium gen. nov for Katodinium glaucum (Gymnodiniales, Dinophyceae). Eur. J. Phycol. 2016, 51, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillmann, U.; Hoppenrath, M.; Gottschling, M.; Kusber, W.H.; Elbraechter, M. Platepattern clarification of the marine dinophyte Heterocapsa triquetra sensu Stein (Dinophyceae) collected at the Kiel Fjord (Germany). J. Phycol. 2017, 53, 1305–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.C.d.S.; da Silva, D.M.L.; Affe, H.M.d.J.; Nunes, J.M.d.C. Occurrence and distribution of Scrippsiella cf. acuminata (Dinophyta, Thoracospharaceae) in a tropical estuarine gradient. Rodriguésia 2022, 73, e02162020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G. Analysis of the thecal plate pattern in the dinoflagellate Heterocapsa rotundata (Lohmann) comb. nov. (=Katodinium rotundatum (Lohmann) Loeblich). Phycologia 1995, 34, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Jang, S.H.; Moestrup, O.; Kang, N.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Potvin, E.; Noh, J.H. Ansanella granifera gen. et sp. nov (Dinophyceae), a new dinoflagellate from the coastal waters of Korea. Algae 2014, 29, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergholtz, T.; Daugbjerg, N.; Moestrup, O.; Fernández-Tejedor, M. On the identity of Karlodinium veneficum and description of Karlodinium armiger sp. nov (Dinophyceae), based on light and electron microscopy, nuclear-encoded LSU rDNA, and pigment composition. J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 170–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.S.; Kim, E.S.; Lee, J.A.; Kim, K.M.; Kwak, M.S.; Yoon, M.; Hong, J.W. First report of the dinoflagellate genus Effrenium in the east sea of Korea: Morphological, genetic, and fatty acid characteristics. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.S.; Jeong, H.J.; Moestrup, O.; Lee, S.Y.; Lim, A.S.; Jang, T.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Jang, S.H.; Potvin, E.; et al. Gymnodinium smaydae n. sp., a new planktonic phototrophic dinoflagellate from the coastal waters of western Korea: Morphology and molecular characterization. J. Eukaryotic Microbiol. 2014, 61, 182–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Species | Synonyms | HAB Effects | Was It the Resting Cyst Formation Reported Before? | Was Germination of Resting Cysts Collected from the Marine Sediment Reported Before? | Is It Heterotrophic? | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akashiwo sanguinea | Gymnodinium sanguineum | B/T | Y | Y | [47,48,49,50,51] | |
| Alexandrium leei | Protogonyaulax leei | B/T | Y | Y | [52,53] | |
| Alexandrium pacificum | B/T | Y | Y | [17,54,55] | ||
| Ansanella granifera | Y | Y | [32,37,56] | |||
| Archaeperidinium saanichi | Y | Y | Y | [57] | ||
| Azadinium cuneatum | Y | Y | [58] | |||
| Azadinium polongum | B | Y | Y | [37,59,60] | ||
| Azadinium poporum | B/T | Y | Y | [61] | ||
| Balechina gracilis | Gymnodinium gracile | Y | [62] | |||
| Biecheleria brevisulcata | Y | Y | [63] | |||
| Biecheleriopsis adriatica | Y | Y | [63] | |||
| Cyklopsia gemma | Y | [64] | ||||
| Diplopelta pusilla | Lebouraia pusilla | Y | Y | Y | [65] | |
| Effrenium voratum | Symbiodinium voratum | Y | [66] | |||
| Gymnodinium smaydae | Y | Y | [37,67] | |||
| Gyrodinium cf. spirale | Y | [68,69] | ||||
| Gyrodinium heterogrammum | Y | Y | Y | [13,37,69] | ||
| Heterocapsa pseudotriquetra | Y | Y | [37,70] | |||
| Heterocapsa rotundata | Y | Y | [71,72] | |||
| Heterocapsa steinii | Y | Y | [71] | |||
| Islandinium tricingulatum | Protoperidinium tricingulatum | Y | Y | Y | [73] | |
| Karlodinium veneficum | B/T | Y | Y | [74,75,76] | ||
| Lebouridinium glaucum | Katodinium glaucum | B | Y | Y | Y | [37,77] |
| Levanderina fissa | Gyrodinium instriatum | B | Y | Y | [78,79] | |
| Luciella masanensis | B | Y | Y | Y | [37,80,81,82] | |
| Nematodinium parvum | Warnowia parva | [83] | ||||
| Noctiluca scintillans | Noctiluca pacifica | B | Y | [84] | ||
| Oxytoxum lohmannii | Amphidinium crissum; Oxytoxum longum | Y | Y | Y | [37,85] | |
| Paragymnodinium asymmetricum | Y | Y | [37,86] | |||
| Pelagodinium beii | Gymnodinium bei | Y | Y | [37,87] | ||
| Polykrikos kofoidii | Y | Y | Y | [68,88] | ||
| Protoperidinium americanum | Peridinium americanum | Y | Y | Y | [73] | |
| Protoperidinium parthenopes | Y | Y | Y | [73] | ||
| Scrippsiella acuminata | Scrippsiella trochoidea | B | Y | Y | [89,90,91] | |
| Scrippsiella aff. acuminata | Y | [92] | ||||
| Scrippsiella bicarinata | Y | Y | [32,93] | |||
| Scrippsiella cf. acuminata | Y | Y | [32] | |||
| Scrippsiella cf. erinaceus | Y | Y | [94] | |||
| Scrippsiella donghaiensis | Y | Y | [63] | |||
| Scrippsiella lachrymosa | Y | [95] | ||||
| Shimiella gracilenta | Y | Y | Y | [37,96] | ||
| Stoeckeria algicida | B/T | Y | Y | [97] | ||
| Wangodinium sinense | Y | Y | [98] | |||
| Yihiella yeosuensis | Y | [99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, S.; Yang, W.; Tao, Z.; Li, F.; Wei, B.; Yue, C.; Deng, Y.; Shang, L.; Chai, Z.; Tang, Y.-Z. In Situ Harvesting and Molecular Identification for the Germinating Species Diversity of Dinoflagellate Resting Cysts in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Life 2025, 15, 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111670
Shi S, Yang W, Tao Z, Li F, Wei B, Yue C, Deng Y, Shang L, Chai Z, Tang Y-Z. In Situ Harvesting and Molecular Identification for the Germinating Species Diversity of Dinoflagellate Resting Cysts in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Life. 2025; 15(11):1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111670
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Shuo, Wanli Yang, Zhe Tao, Fengting Li, Ben Wei, Caixia Yue, Yunyan Deng, Lixia Shang, Zhaoyang Chai, and Ying-Zhong Tang. 2025. "In Situ Harvesting and Molecular Identification for the Germinating Species Diversity of Dinoflagellate Resting Cysts in Jiaozhou Bay, China" Life 15, no. 11: 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111670
APA StyleShi, S., Yang, W., Tao, Z., Li, F., Wei, B., Yue, C., Deng, Y., Shang, L., Chai, Z., & Tang, Y.-Z. (2025). In Situ Harvesting and Molecular Identification for the Germinating Species Diversity of Dinoflagellate Resting Cysts in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Life, 15(11), 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111670









