Advances in the Multimodal Management of Pediatric Arteriovenous Malformations: A 10-Year Review
Abstract
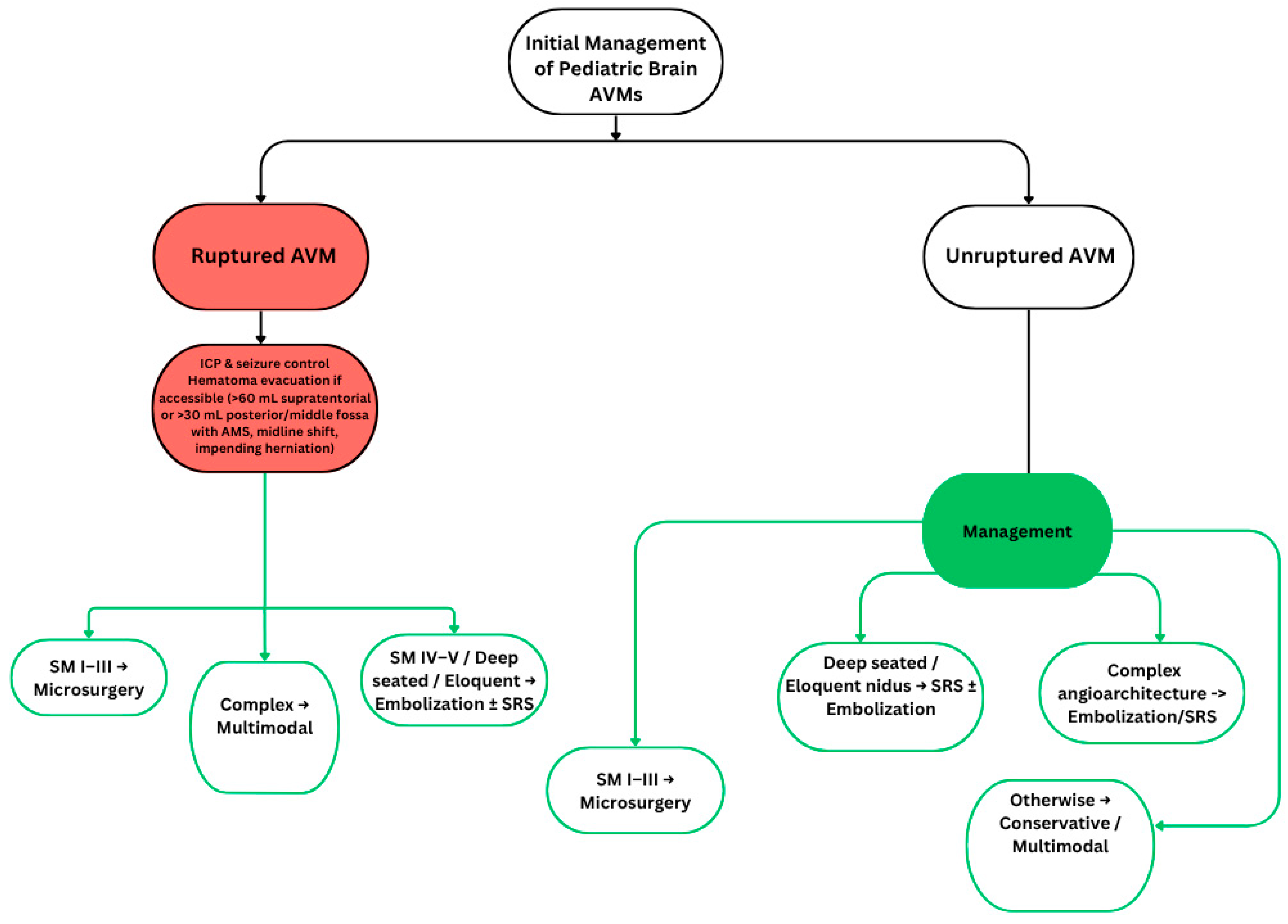
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Microsurgical Resection
3.2. Stereotactic Radiosurgery
3.3. Endovascular Embolization
3.4. Multimodality Approaches
3.5. Recurrence
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| AVM | Arteriovenous Malformation |
| SRS | Stereotactic Radiosurgery |
| GOS | Glasgow Outcome Scale |
| DSA | Digital Subtraction Angiography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| SM | Spetzler–Martin (Grading System) |
| ARE | Adverse Radiation Effect |
| HFSRT | Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy |
| mRS | Modified Rankin Scale |
| RIC | Radiation-Induced Complication |
| CTA | Computed Tomography Angiography |
| GKRS | Gamma Knife Radiosurgery |
| LINAC | Linear Accelerator |
| Onyx | Ethylene–vinyl alcohol copolymer embolic agent |
| ISRS | International Stereotactic Radiosurgery Society |
References
- See, A.P.; Smith, E.R. Management of pediatric intracranial arteriovenous malformations. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2024, 67, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.H.D.; James, G. Natural history and clinical manifestation of Pediatric Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2024, 67, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, L.; Shotar, E.; Blauwblomme, T.; Sourour, N.; Alias, Q.; Stricker, S.; Mathon, B.; Kossorotoff, M.; Gariel, F.; Boddaert, N.; et al. Risk factors for early brain AVM rupture: Cohort study of pediatric and adult patients. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 2358–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, W.R.; Dandapat, S.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S. Hemorrhagic cerebrovascular pathology in the pediatric population. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Ma, Y.; Song, Z.; Ye, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P. Paediatric intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: Clinical characteristics, treatment outcomes and prognosis. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2025, 10, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetts, S.W.; Keenan, K.; Fullerton, H.J.; Young, W.; English, J.; Gupta, N.; Dowd, C.; Higashida, R.; Lawton, M.; Halbach, V. Pediatric intracranial nongalenic pial arteriovenous fistulas: Clinical features, angioarchitecture, and outcomes. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, H.W.; Shanahan, R.M.; Aiyudu, C.; Miller, T.A.; Liu, H.Y.; Greene, S. Current trends, molecular insights, and future directions toward precision medicine in the management of pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2024, 34, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliava, S.S.; Pilipenko, Y.V.; Yakovlev, S.B.; Golanov, A.V.; Maryashev, S.A.; Grebenev, F.V. Arteriovenous malformations of the brain in children: Treatment results for 376 patients. Zhurnal Vopr. Neirokhirurgii Im. NN Burdenko 2020, 84, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copelan, A.; Drocton, G.; Caton, M.T.; Smith, E.R.; Cooke, D.L.; Nelson, J.; Abla, A.A.; Fox, C.; Amans, M.R.; Dowd, C.F.; et al. Brain arteriovenous malformation recurrence after apparent microsurgical cure: Increased risk in children who present with arteriovenous malformation rupture. Stroke 2020, 51, 2990–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtaya, A.; Millar, J.; Sparrow, O. Multimodality management and outcomes of brain arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) in children: Personal experience and review of the literature, with specific emphasis on age at first AVM bleed. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hak, J.F.; Boulouis, G.; Kerleroux, B.; Benichi, S.; Stricker, S.; Gariel, F.; Garzelli, L.; Meyer, P.; Kossorotoff, M.; Boddaert, N.; et al. Pediatric brain arteriovenous malformation recurrence: A cohort study, systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2022, 14, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez-Perdomo, W.A.; Reyes Bello, J.S.; Moscote Salazar, L.R.; Agrawal, A.; Janjua, T.; Chavda, V.; García-Ballestas, E.; Abdulla, E. Gamma knife radio surgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical outcomes. Egypt. J. Neurosurgery 2024, 39, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patibandla, M.R.; Ding, D.; Xu, Z.; Sheehan, J.P. Stereotactic radiosurgery for pediatric high-grade brain arteriovenous malformations: Our experience and review of literature. World Neurosurg. 2017, 102, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.H.; Treechairusame, T.; Chiang, J.; White, Z.; Jackson, S.; Quon, J.L.; Appelboom, G.; Chang, S.D.; Soltys, S.G.; Guzman, R.; et al. Robotic radiosurgery for the treatment of pediatric arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2025, 36, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrash, G.W.; Evans, R.E.; Sun, Y.; Roberts, A.C.; Derryberry, C.; Hale, A.T.; Das, S.; Boudreau, H.; George, J.A.; Atchley, T.J.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery treatment of pediatric arteriovenous malformations: A PRISMA systematic review and meta-analysis. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2025, 41, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.M.; Chen, C.J.; Ding, D.; Buell, T.J.; Sokolowski, J.; A Sheehan, K.; Lee, C.-C.; E Sheehan, D.; Kano, H.; Kearns, K.N.; et al. Effect of prior embolization on outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery for pediatric brain arteriovenous malformations: An international multicenter study. Neurosurgery 2021, 89, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges de Almeida, G.; Pamplona, J.; Baptista, M.; Carvalho, R.; Conceição, C.; da Silva, R.L.; Sagarribay, A.; Reis, J.; Fragata, I. Endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients: A single center experience and review of the literature. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2024, 85, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.; Duddy, J.C.; Saeed, D.; Hennigan, D.; Israni, A.; Puthuran, M.; Chandran, A.; Mallucci, C. Multi-modality treatment approach for paediatric AVMs with quality-of-life outcome measures. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2023, 39, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghanem, M.; Kass-Hout, T.; Kass-Hout, O.; Alderazi, Y.J.; Amuluru, K.; Al-Mufti, F.; Prestigiacomo, C.J.; Gandhi, C.D. Arteriovenous malformations in the pediatric population: Review of the existing literature. Interv. Neurol. 2016, 5, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulasvirta, E.; Koroknay-Pál, P.; Numminen, J.; Hafez, A.; Raj, R.; Jahromi, B.R.; Niemelä, M.; Laakso, A. Recurrence of brain arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients: A long-term follow-up study. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järvelin, P.; Pekonen, H.; Koivisto, T.; Frösen, J. Recurrence of arteriovenous malformations of the brain after complete surgical resection: Kuopio University Hospital experience and systematic review of the literature. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 46, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.S.; Sahgal, A.; Regis, J.; Levivier, M.; Fariselli, L.; Gorgulho, A.; Ma, L.; Pollock, B.; Yomo, S.; Sheehan, J.; et al. Pediatric cranial stereotactic radiosurgery: Meta-analysis and international stereotactic radiosurgery society practice guidelines. Neuro. Oncol. 2025, 27, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starke, R.M.; Ding, D.; Kano, H.; Mathieu, D.; Huang, P.P.; Feliciano, C.; Rodriguez-Mercado, R.; Almodovar, L.; Grills, I.S.; Silva, D.; et al. International multicenter cohort study of pediatric brain arteriovenous malformations. Part 2: Outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 19, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, E.A.; Lu, A.; Morshed, R.A.; Yue, J.K.; Rutledge, W.C.; Burkhardt, J.-K.; Patel, A.B.; Ammanuel, S.G.; Braunstein, S.; Fox, C.K.; et al. Bringing high-grade arteriovenous malformations under control: Clinical outcomes following multimodality treatment in children. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2020, 26, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, D.J.; Nordström, H.; Lundin, A.; Xu, Z.; Sheehan, J.P. Dosimetric effects of Onyx embolization on Gamma Knife arteriovenous malformation dose distributions. J Neurosurg. 2016, 125 (Suppl. 1), 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.X.; Cheong, T.M.; Ng, L.P.; Seow, W.T.; Chua, F.H.Z.; Kirollos, R.W.; Low, D.C.Y.; Low, S.Y.Y. Paediatric Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation: Outcomes from a Singapore Children’s Hospital. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.; Slomovic, A.; Ibrahim, G.; Radovanovic, I.; Tymianski, M. Microsurgery for ARUBA trial–eligible unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 2017, 48, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, J.P.; Parides, M.K.; Stapf, C.; Moquete, E.; Moy, C.S.; Overbey, J.R.; Salman, R.A.-S.; Vicaut, E.; Young, W.L.; Houdart, E.; et al. Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): A multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stricker, S.; Boulouis, G.; Benichi, S.; Bourgeois, M.; Gariel, F.; Garzelli, L.; Hak, J.-F.; Alias, Q.; Kerleroux, B.; Beccaria, K.; et al. Acute surgical management of children with ruptured brain arteriovenous malformation. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2021, 27, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Qiu, H.; Jiang, W. Multimodality treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations with one-staged hybrid operation: Clinical characteristics and long-term prognosis. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 2559004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Smadi, A.S.; Ansari, S.A.; Shokuhfar, T.; Malani, A.; Sattar, S.; Hurley, M.C.; Potts, M.B.; Jahromi, B.S.; Alden, T.D.; Dipatri, A.J.; et al. Safety and outcome of combined endovascular and surgical management of low grade cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children compared to surgery alone. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 116, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author (Year) | Country/Setting | N (Patients) | Modality | Key Findings | Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eliava et al. (2020) [8] | Russia (single-center) | 376 | Microsurgery/Embolization | Microsurgical cure 97.8%; embolization cure ~30%; perioperative mortality 0% | 5–10 yrs |
| Copelan et al. (2020) [9] | USA | 115 (<25 yrs) | Surgery | Recurrence 21.4% at 5 yrs; rupture at presentation risk | 5 yrs |
| Shtaya et al. (2017) [10] | UK (single-center) | 52 | Surgery | Cure 96.6%; favorable outcomes improved from 38.3% to 89.4% | 3–5 yrs |
| Hak et al. (2022) [11] | USA (systematic review + cohort) | 70 + 267 | Multimodality/Recurrence | Pooled recurrence 10.9%; higher risk with embolization-only | Up to 10 yrs |
| Florez-Perdomo et al. (2024) [12] | Meta-analysis | 2000+ | SRS | Obliteration 71.6%; hemorrhage 2.5%; neuro deficit 2.6%; mortality <1% | ≥3 yrs |
| Patibandla et al. (2017) [13] | USA | 100+ | SRS (SM IV–V) | Cure 35% at 10 yrs; hemorrhage risk 3.2%/yr | 10 yrs |
| Kim et al. (2025) [14] | South Korea | ~80 | CyberKnife SRS | Obliteration 79%; 31.6% radiation effects | 5 yrs |
| Thrash et al. (2025) [15] | Systematic review | 3400+ | SRS | Obliteration 63%; no GK vs. LINAC difference; hemorrhage cure | ≥1 yr |
| Burke et al. (2021) [16] | Multicenter registry | 539 | Embolization + SRS | 10 yr cure 77.4% (SRS only) vs. 48.7% (embolization + SRS); more radiation changes | 10 yrs |
| Borges de Almeida et al. (2024) [17] | Portugal | 26 | Embolization | Cure 42%; recurrence 17%; complications 17%; all good mRS | 3–5 yrs |
| Aziz et al. (2023) [18] | UK | 52 | Multimodality | Overall cure 88%; no mortality; QoL worse in ruptured/infratentorial cases | 5–10 yrs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saloum, A.; Al-Nuaimy, Y.; Baloi, D.; Karsy, M.; Pahlevani, M.; Lucke-Wold, B. Advances in the Multimodal Management of Pediatric Arteriovenous Malformations: A 10-Year Review. Life 2025, 15, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101620
Saloum A, Al-Nuaimy Y, Baloi D, Karsy M, Pahlevani M, Lucke-Wold B. Advances in the Multimodal Management of Pediatric Arteriovenous Malformations: A 10-Year Review. Life. 2025; 15(10):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101620
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaloum, Ammar, Yusor Al-Nuaimy, Denise Baloi, Michael Karsy, Mehrdad Pahlevani, and Brandon Lucke-Wold. 2025. "Advances in the Multimodal Management of Pediatric Arteriovenous Malformations: A 10-Year Review" Life 15, no. 10: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101620
APA StyleSaloum, A., Al-Nuaimy, Y., Baloi, D., Karsy, M., Pahlevani, M., & Lucke-Wold, B. (2025). Advances in the Multimodal Management of Pediatric Arteriovenous Malformations: A 10-Year Review. Life, 15(10), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101620






