Circulation of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens Species in Mosquitoes in the Southeastern Part of Romania, Under the Influence of Climate Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- (a)
- Biological material
- (b)
- Molecular screening
- (c)
- Estimation infection rate method
- (d)
- Climatic model
- (e)
- Heartworm Development Unit
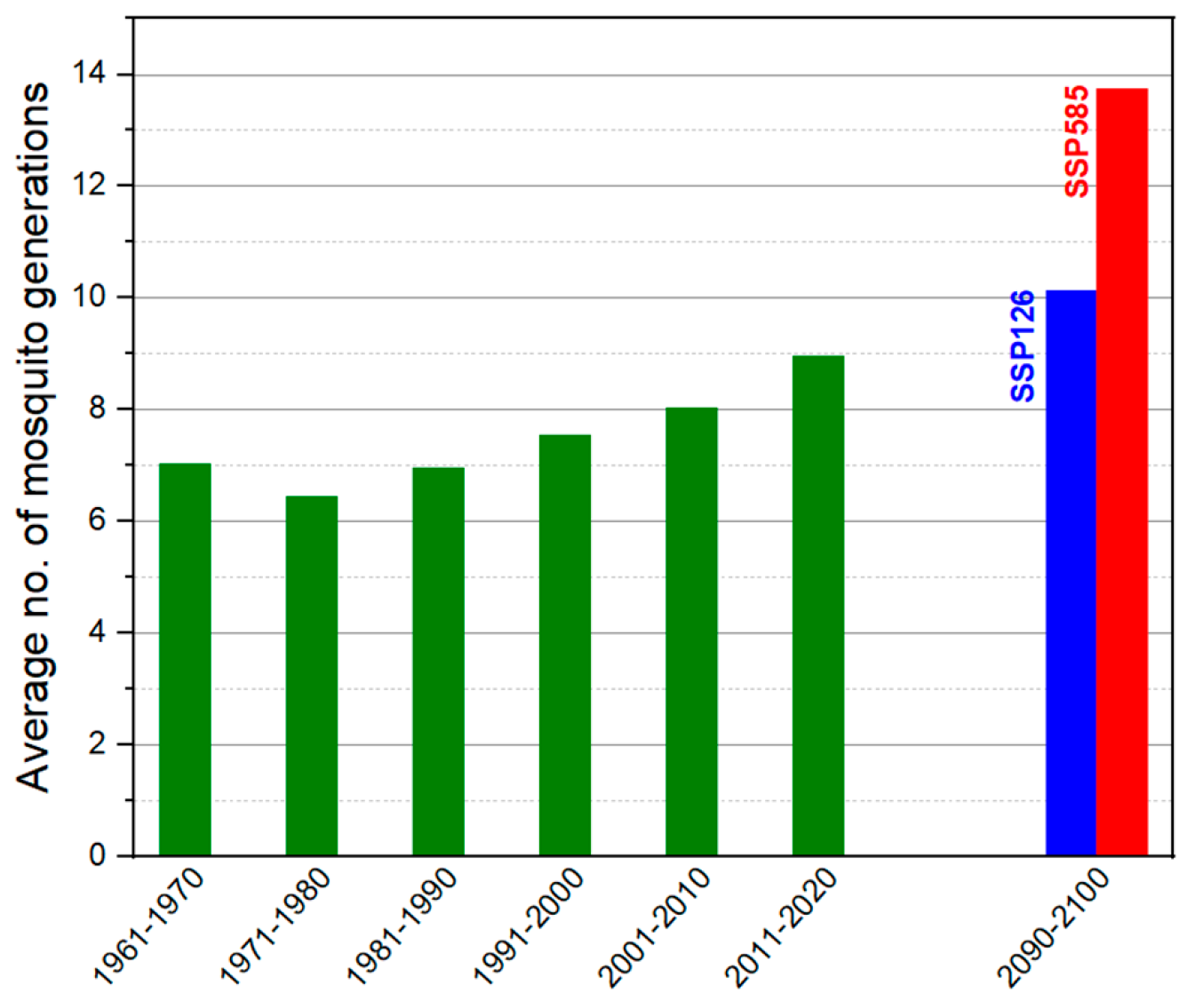
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H. The prevalence of Dirofilaria immitis and D. repens in the Old World. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 280, 108995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, C.; Mortarino, M.; Rinaldi, L.; Cringoli, G.; Traldi, G.; Genchi, M. Changing climate and changing vector-borne disease distribution: The example of Dirofilaria in Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 176, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, B.; Rossi, L.; Meneguz, P.G.; Orusa, R.; Zoppi, S.; Robetto, S.; Marucco, F.; Tizzani, P. Dirofilaria immitis in wolves recolonizing northern Italy: Are wolves competent hosts? Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medkour, H.; Laidoudi, Y.; Marié, J.L.; Fenollar, F.; Davoust, B.; Mediannikov, O. Molecular investigation of vector-borne pathogens in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from southern France. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markakis, G.; Sioutas, G.; Bitchava, D.; Komnenou, A.; Ganoti, M.; Papadopoulos, E. Is the European badger a new host for Dirofilaria immitis? The first records in Greece. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsarraf, M.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D.; Hildebrand, J.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Kloch, A.; Kot, K.; Kurek, K.; Nowak, S.; Mysłajek, R.W.; Myśliwy, I.; et al. Occurrence of Dirofilaria repens in wild carnivores in Poland. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 122, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionică, A.M.; Deak, G.; Boncea, R.; Gherman, C.M.; Mihalca, A.D. The European badger as a new host for Dirofilaria immitis and an update on the distribution of the heartworm in wild carnivores from Romania. Pathogens 2022, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otranto, D.; Deplazes, P. Zoonotic nematodes of wild carnivores. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraf, M.; Levytska, V.; Mierzejewska, J.; Poliukhovych, V.; Rodo, A.; Alsarraf, M.; Kavalevich, D.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D.; Behnke, J.M.; Bajer, A. Emerging risk of Dirofilaria spp. infection in Northeastern Europe: High prevalence of Dirofilaria repens in sled dog kennels from the Baltic countries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrity, S.; Lee-Fowler, T.; Reinero, C. Feline asthma and heartworm disease: Clinical features, diagnostics and therapeutics. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuna, A.; Poblocki, P.; Baranowicz, K.; Grzybek, M. Lesion on the right testicle of 21-year-old patient. One Health 2024, 19, 100863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procop, G.W.; Neafie, R.C. Human parasitic pulmonary infections. In Pulmonary Pathology, 2nd ed.; Zander, D.S., Farver, C.F., Eds.; Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 289–314. [Google Scholar]
- Fontes-Sousa, A.P.; Silvestre-Ferreira, A.C.; Carretón, E.; Esteves-Guimarães, J.; Maia-Rocha, C.; Oliveira, P.; Lobo, L.; Morchón, R.; Araújo, F.; Simón, F.; et al. Exposure of humans to the zoonotic nematode Dirofilaria immitis in Northern Portugal. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, G.; Genchi, C.; Baneth, G.; Bourdeau, P.; Brianti, E.; Cardoso, L.; Danesi, P.; Fuehrer, H.-P.; Giannelli, A.; Ionică, A.M.; et al. Recent advances on Dirofilaria repens in dogs and humans in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momčilović, S.; Gabrielli, S.; Đenić, N.; Živković, N.; Stevanović, G.; Krstić, M.; Ranđelović, M.; Tasić-Otašević, S. New cases of human dirofilariosis on the Balkan Peninsula—“Masked intruders” uncovered by a surgeon. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 86, 102482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.V. Human dirofilariasis: An emerging zoonosis. Trop. Parasitol. 2013, 3, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perles, L.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Krücken, J.; Morchón, R.; Walochnik, J.; Otranto, D. Zoonotic dirofilariases: One, no one, or more than one parasite. Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Fritzenwanker, M.; Pantchev, N.; Lendner, M.; Wongkamchai, S.; Otranto, D.; Kroidl, I.; Dennebaum, M.; Le, T.H.; Le, T.A.; et al. The mitochondrial genomes of the zoonotic canine filarial parasites Dirofilaria (Nochtiella) repens and Candidatus Dirofilaria (Nochtiella) hongkongensis provide evidence for presence of cryptic species. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldis, V.; Ondriska, F.; Bošák, V.; Hajdúk, O.; Antolová, D.; Miterpáková, M. Pseudotumor of the epididymis, a rare clinical presentation of human Dirofilaria repens infection: A report of autochthonous case of dirofilariasis in southwestern Slovakia. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattendorf, C.; Lühken, R. Dirofilaria immitis and D. repens in Europe: A systematic literature review on vectors, host range, and the spatial distribution in the 20th and 21st century. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masny, A.; Gołąb, E.; Cielecka, D.; Sałamatin, R. Vector-borne helminths of dogs and humans—Focus on central and eastern parts of Europe. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Széll, Z.; Bacsadi, Á.; Szeredi, L.; Nemes, C.; Fézer, B.; Bakcsa, E.; Kalla, H.; Tolnai, Z.; Sréter, T. Rapid spread and emergence of heartworm resulting from climate and climate-driven ecological changes in Hungary. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 280, 109067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pampiglione, S.; Rivasi, F.; Angeli, G.; Boldorini, R.; Incensati, R.M.; Pastormerlo, M.; Pavesi, M.; Ramponi, A. Dirofilariasis due to Dirofilaria repens in Italy, an emergent zoonosis: Report of 60 new cases. Histopathology 2001, 38, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, C.; Bowman, D.; Drake, J. Canine Heartworm Disease (Dirofilaria immitis) in Western Europe: Survey of Veterinary Awareness and Perceptions. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrin, B.H.; Peregrine, A.S.; Goring, J.; Beall, M.J.; Little, S.E. Canine Infection with Borrelia burgdorferi, Dirofilaria immitis, Anaplasma spp. and Ehrlichia spp. in Canada, 2013–2014. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, I.; Volkmann, M.; Beelitz, P.; Merle, R.; Müller, E.; Kohn, B. Retrospective Analysis of Vector-Borne Infections in Dogs after Travelling to Endemic Areas (2007–2018). Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 276, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, S.; Băcescu, B.; Coman, T. Epidemiological and paraclinical aspects of canine dirofilariosis. Lucr. Stiinł. Med. Vet. 2007, 40, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ciocan, R.; Dărăbuș, G.; Igna, V. Morphometric study of microfilariae of Dirofilaria spp. on dogs. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. Cluj-Napoca. Vet. Med. 2010, 67, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ciocan, R.; Mederle, N.; Jacsó, O.; Tánczos, B.; Fok, É. Autochthonous cases of Dirofilaria in dogs from Timiș county (western part) Romania. Glob. J. Med. Res. 2013, 13, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mircean, V.; Dumitrache, M.O.; Györke, A.; Pantchev, N.; Jodies, R.; Mihalca, A.D.; Cozma, V. Seroprevalence and geographic distribution of Dirofilaria immitis and tick-borne infections (Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, and Ehrlichia canis) in dogs from Romania. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionică, A.M.; Matei, I.A.; Mircean, V.; Dumitrache, M.O.; D’aMico, G.; Győrke, A.; Pantchev, N.; Annoscia, G.; Albrechtová, K.; Otranto, D.; et al. Current surveys on the prevalence and distribution of Dirofilaria spp. and Acanthocheilonema reconditum infections in dogs in Romania. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionică, A.M.; Matei, I.A.; D’aMico, G.; Daskalaki, A.A.; Juránková, J.; Ionescu, D.T.; Mihalca, A.D.; Modrý, D.; Gherman, C.M. Role of golden jackals (Canis aureus) as natural reservoirs of Dirofilaria spp. in Romania. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomazatos, A.; Cadar, D.; Török, E.; Maranda, I.; Horváth, C.; Keresztes, L.; Spinu, M.; Jansen, S.; Jöst, H.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; et al. Circulation of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens in the Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve, Romania. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morchón, R.; Montoya-Alonso, J.; Rodríguez-Escolar, I.; Carretón, E. What has happened to heartworm disease in Europe in the last 10 years? Pathogens 2022, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, F.; Diosdado, A.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Kartashev, V.; González-Miguel, J. Human dirofilariosis in the 21st century: A scoping review of clinical cases reported in the literature. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2424–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Escolar, I.; Hernández-Lambraño, R.E.; Sánchez-Agudo, J.A.; Collado-Cuadrado, M.; Savić, S.; Stosic, Z.M.; Marcic, D.; Morchón, R. Prediction and validation of potential transmission risk of Dirofilaria spp. infection in Serbia and its projection to 2080. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1352236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Mackay, A.; Stone, C.M. Dynamics of invasive mosquitoes: Introduction pathways, limiting factors, and their potential role in vector-borne pathogen transmission. Front. Trop. Dis. 2024, 5, 1503120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, M.K.; Atkins, C.E. Treatment of dogs with severe heartworm disease. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 283, 109131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, C.J.; Labarthe, N.V.; Paiva, J.P.; Reifur, L.; Mendes-de-Almeida, F.; Merlo, A.; Juliani, P.J.; Ornelas de Almeida, M.A.; Alves, L.C. Updated canine infection rates for Dirofilaria immitis in areas of Brazil previously identified as having a high incidence of heartworm-infected dogs. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 493. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, B.K.; Bonnier, A.; Chong, W.H.; Chieng, H.; Austin, A.; Hu, K.; Shkolnik, B. Human pulmonary dirofilariasis: A review for the clinicians. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 363, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miterpáková, M.; Antolová, D.; Rampalová, J.; Undesser, M.; Krajčovič, T.; Víchová, B. Dirofilaria immitis pulmonary dirofilariasis, Slovakia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.J.; Costa, A.R.; Calvinho, P. Human pulmonary dirofilariasis: A pitfall in solitary pulmonary nodule. Pulmonology 2022, 28, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakou, A.; Prichard, R.K. Concern for Dirofilaria immitis and macrocyclic lactone loss of efficacy: Current situation in the USA and Europe, and future scenarios. Pathogens 2021, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykur, M.; Yağcı, A.; Simşek, S.; Palamar, M.; Yaman, B.; Korkmaz, M.; Dagci, H. First time identification of subconjunctival Dirofilaria immitis in Turkey: Giant episcleral granuloma mimicking scleritis. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 3909–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cope, E.D.; Gupta, N.; Koehler, A.V.; Gasser, R.B.; Crowe, A. Ocular dirofilariasis in migrant from Sri Lanka, Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 829–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahesh, M.; Pauly, M.; Krishna, S.M.; Raman, M.; Biswas, J. Clinicopathological study of parasitic lesions of the eye and ocular adnexa in a tertiary care ophthalmic center in South India. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 70, 1713–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, M.; Antonietti, M.; Sayegh, Y.; Colson, J.D.; Kunkler, A.L.; Clauss, K.D.; Muniz-Castro, H.; Lee, W.W.; Yoo, S.H.; Johnson, T.E.; et al. Ocular dirofilariasis: A clinicopathologic case series and literature review. Ocul. Oncol. Pathol. 2024, 10, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redón-Soriano, M.; Blasco, A.; Gomila, B.; González-Sánchez, M.; Simón, F.; Esteban, J.G. Subconjunctival human dirofilariasis by Dirofilaria repens in the Mediterranean Basin. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2022, 26, 101570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, Z.; Kar, P.; Mohanty, S.; Dey, M.; Kumar Samal, D. Ocular dirofilariasis: A report from Odisha. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 45, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliakova, S.I.; Karliuga, I.A.; Moloda, A.L.; Linchevska, O.G. Dirofilariasis of eyelid and orbit (clinic, diagnosis, treatment). J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 1, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Potters, I.; Vanfraechem, G.; Bottieau, E. Dirofilaria repens nematode infection with microfilaremia in traveler returning to Belgium from Senegal. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupić-Bakrač, A.; Pupić-Bakrač, J.; Beck, A.; Jurković, D.; Polkinghorne, A.; Beck, R. Dirofilaria repens microfilaremia in humans: Case description and literature review. One Health 2021, 13, 2352–7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, S.; Harrington, J.; Carithers, D.S.; Kaminsky, R.; Selzer, P.M. Heartworm disease–Overview, intervention, and industry perspective. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2021, 16, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otranto, D.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Brianti, E.; Traversa, D.; Petrić, D.; Genchi, C.; Capelli, G. Vector-borne helminths of dogs and humans in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancrini, G.; Gabrielli, S. Dirofilariosis in humans: A review of world literature. Parassitologia 2007, 49, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H. Subcutaneous dirofilariosis (Dirofilaria repens): An infection spreading throughout the old world. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șuleșco, T.; von Thien, H.; Toderaș, L.; Toderaș, I.; Lühken, R.; Tannich, E. Circulation of Dirofilaria repens and Dirofilaria immitis in Moldova. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, L.; Genchi, C.; Cascone, C.; Oliva, G.; Musella, V. Canine and feline dirofilariosis in Italy: An update. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Morchón, R.; Carretón, E.; González-Miguel, J.; Mellado-Hernández, I. Heartworm disease (Dirofilaria immitis) and their vectors in Europe–new distribution trends. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Petric, D.; Zgomba, M.; Boase, C.; Madon, M.B.; Dahl, C.; Kaiser, A. Mosquitoes and Their Control; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcitu, M.A. Universal workflow for pathogen detection using real time (RT) PCR. Rom. J. Vet. Med. Pharmacol. 2024, 49, 276–287. [Google Scholar]
- Sandu, I.; Deak, G.; Turcitu, M.; O’Brien, P.J.; Mircean, V. A severe clinical case of Ehrlichia canis and Toxoplasma gondii in a dog (with the first morphological detection of tachyzoites in peripheral blood). Vet. Med. Sci. 2025, 11, e70380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pękacz, M.; Basałaj, K.; Kalinowska, A.; Klockiewicz, M.; Stopka, D.; Bąska, P.; Długosz, E.; Karabowicz, J.; Młocicki, D.; Wiśniewski, M.; et al. Selection of new diagnostic markers for Dirofilaria repens infections with the use of phage display technology. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negron, V.; Saleh, M.N.; Sobotyk, C.; Luksovsky, J.L.; Harvey, T.V.; Verocai, G.G. Probe-based qPCR as an alternative to modified Knott’s test when screening dogs for heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) infection in combination with antigen detection tests. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Peng, J. Some properties of the exact and score methods for binomial proportion and sample size calculation. Commun. Stat.—Simul. Comput. 2007, 36, 1171–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Bilder, C.; Biggerstaff, B.; Schaarschmidt, F.; Hitt, B. binGroup: Evaluation and Experimental Design for Binomial Group Testing, Version 2.2-3; The R Foundation: Kaysville, UT, USA, 2025. [CrossRef]
- Boucher, O.; Denvil, S.; Levavasseur, G.; Cozic, A.; Caubel, A.; Foujols, M.A.; Meurdesoif, Y.; Devilliers, M.; Flavoni, S.; Gastineau, G.; et al. IPSL IPSL-CM6A-LR Model Output Prepared for CMIP6 DCPP dcppC-amv-pos, Version VLR; Earth System Grid Federation: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019.
- Genchi, C.; Rinaldi, L.; Mortarino, M.; Genchi, M.; Cringoli, G. Climate and Dirofilaria infection in Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivănescu, L.M.; Bodale, I.; Grigore-Hristodorescu, S.; Martinescu, G.; Andronic, B.; Matiut, S.; Azoicai, D.; Miron, L. The risk of emerging of dengue fever in Romania, in the context of global warming. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciucă, L.; Musella, V.; Miron, L.D.; Maurelli, M.P.; Cringoli, G.; Bosco, A.; Rinaldi, L. Geographic distribution of canine heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) infection in stray dogs of eastern Romania. Geospat. Health 2016, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matfei, A.; Ivănescu, L.; Mîndru, R.; Martinescu, G.; Lazăr, A.H.; Miron, L. Molecular detection of canine dirofilariosis (D. immitis, D. repens) in Danube Delta region. Rev. Rom. Med. Vet. 2025, 35, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, L.; Davoust, B.; Varloud, M.; Niang, E.A.; Fenollar, F.; Medianniko, O. Development of a multiplex qPCR-based approach for the diagnosis of Dirofilaria immitis, D. repens and Acanthocheilonema reconditum. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, L.; Barré-Cardi, H.; Bedjaoui, S.; Ayhan, N.; Varloud, M.; Mediannikov, O. Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens in mosquitoes from Corsica Island, France. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariuki, F.M.; Wanyonyi, R.W.; Islam, A.S. Analysis of a two-stage negative binomial group testing model for estimating the prevalence of a rare trait. Open Access Libr. J. 2023, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoleriu, L.; Bodale, I.; Apetrei, A.; Stancu, A. Realistic reversible magnetization component in Preisach-type models. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2341–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.H.; Tung, K.C.; Ooi, H.K.; Wang, J.S. Competence of Aedes albopictus and Culex quinquefasciatus as vector of Dirofilaria immitis after blood meal with different microfilarial density. Vet. Parasitol. 2000, 90, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, G. Nature limits filarial transmission. Parasites Vectors 2008, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledesma, N.; Harrington, L. Mosquito vectors of dog heartworm in the United States: Vector status and factors influencing transmission efficiency. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2011, 26, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Principle | Primer/Probe | Sequence 5–3′ | Gene Target | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dirofilaria repens | SYBR Green | For_s16 | GTG TGC TGC GCT ACA TCG ATG TT | 16S rRNA | [62] |
| Rev_s16 | ATA AAC CGC TCT GTC TCA CGA CG | ||||
| Dirofilaria immitis | TaqMan | Fil.COI.749-F | CAT CCT GAG GTT TAT GTT ATT ATT TT | Cox-1 | [63] |
| Fil.COI.914-R | CWG TAT ACA TAT GAT GRC CYC A | ||||
| Probe | 6FAM-CGG TGT TTG GGA TTG TTA GTG-MGB |
| Mosquito Species | Total Pools Tested (20 Mosquitoes/Pool) D. immitis and D. repens | D. immitis (Positive Pools) | D. repens (Positive Pools) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ur. unguiculata | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Ae. albopictus | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Ae. vexans | 16 | 8 | 0 |
| An. hyrcanus | 8 | 3 | 0 |
| An. maculipennis | 12 | 9 | 2 |
| Cx. pipiens complex | 29 | 12 | 0 |
| Ae. caspius | 7 | 2 | 0 |
| Total | 76 | 36 | 2 |
| Mosquito Species | No. of Mosquitoes | No. of Total Pools | No. of Pools Positive Tested for D. immitis | PTP (%) | EIR | CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for Confidence Level by 95% | ||||||
| Ur. unguiculata * | 60 | 3 | 1 | 33% | 0.02007 | 0.00317–0.07558 |
| Ae. albopictus ** | 7 | 1 | 1 | 100% | 1 | 0.03251–1 |
| Ae. vexans * | 320 | 16 | 8 | 50% | 0.03406 | 0.01629–0.06167 |
| An. hyrcanus * | 160 | 8 | 3 | 38% | 0.01033 | 0.00341–0.02772 |
| An. maculipennis * | 240 | 12 | 9 | 75% | 0.06697 | 0.03104–0.11400 |
| Cx pipiens complex * | 580 | 29 | 12 | 41% | 0.02635 | 0.01462–0.04391 |
| Ae. caspius * | 140 | 7 | 2 | 29% | 0.01668 | 0.00428–0.04994 |
| Total * | 1507 | 75 | 36 | 48% | 0.03217 | 0.02289–0.04375 |
| Mosquito Species | No. of Mosquitoes | No. of Total Pools | No. of Pools Positive Tested for D. repens | PTP (%) | EIR | CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for Confidence Level by 95% | ||||||
| Ur. unguiculata * | 60 | 3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0–0.04038 |
| Ae. albopictus ** | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0–0.20170 |
| Ae. vexans * | 320 | 16 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0–0.01070 |
| An. hyrcanus * | 160 | 8 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0–0.01942 |
| An. maculipennis * | 240 | 12 | 2 | 16.67 | 0.00079 | 0.00022–0.00283 |
| Cx pipiens complex * | 580 | 29 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0–0.00620 |
| Ae. caspius * | 140 | 7 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0–0.02164 |
| Total * | 1507 | 75 | 2 | 2.67 | 0.00135 | 0.00037–0.00482 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivănescu, L.; Mîndru, R.; Bodale, I.; Apopei, G.-V.; Andronic, L.; Hristodorescu, S.; Azoicăi, D.; Miron, L. Circulation of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens Species in Mosquitoes in the Southeastern Part of Romania, Under the Influence of Climate Change. Life 2025, 15, 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101612
Ivănescu L, Mîndru R, Bodale I, Apopei G-V, Andronic L, Hristodorescu S, Azoicăi D, Miron L. Circulation of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens Species in Mosquitoes in the Southeastern Part of Romania, Under the Influence of Climate Change. Life. 2025; 15(10):1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101612
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvănescu, Larisa, Raluca Mîndru, Ilie Bodale, Gabriela-Victoria Apopei, Lavinia Andronic, Smaranda Hristodorescu, Doina Azoicăi, and Liviu Miron. 2025. "Circulation of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens Species in Mosquitoes in the Southeastern Part of Romania, Under the Influence of Climate Change" Life 15, no. 10: 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101612
APA StyleIvănescu, L., Mîndru, R., Bodale, I., Apopei, G.-V., Andronic, L., Hristodorescu, S., Azoicăi, D., & Miron, L. (2025). Circulation of Dirofilaria immitis and Dirofilaria repens Species in Mosquitoes in the Southeastern Part of Romania, Under the Influence of Climate Change. Life, 15(10), 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101612







