The Influence of a Plant-Based Diet on Skin Health: Inflammatory Skin Diseases, Skin Healing, and Plant-Based Sources of Micro- and Macro-Nutrients
Abstract
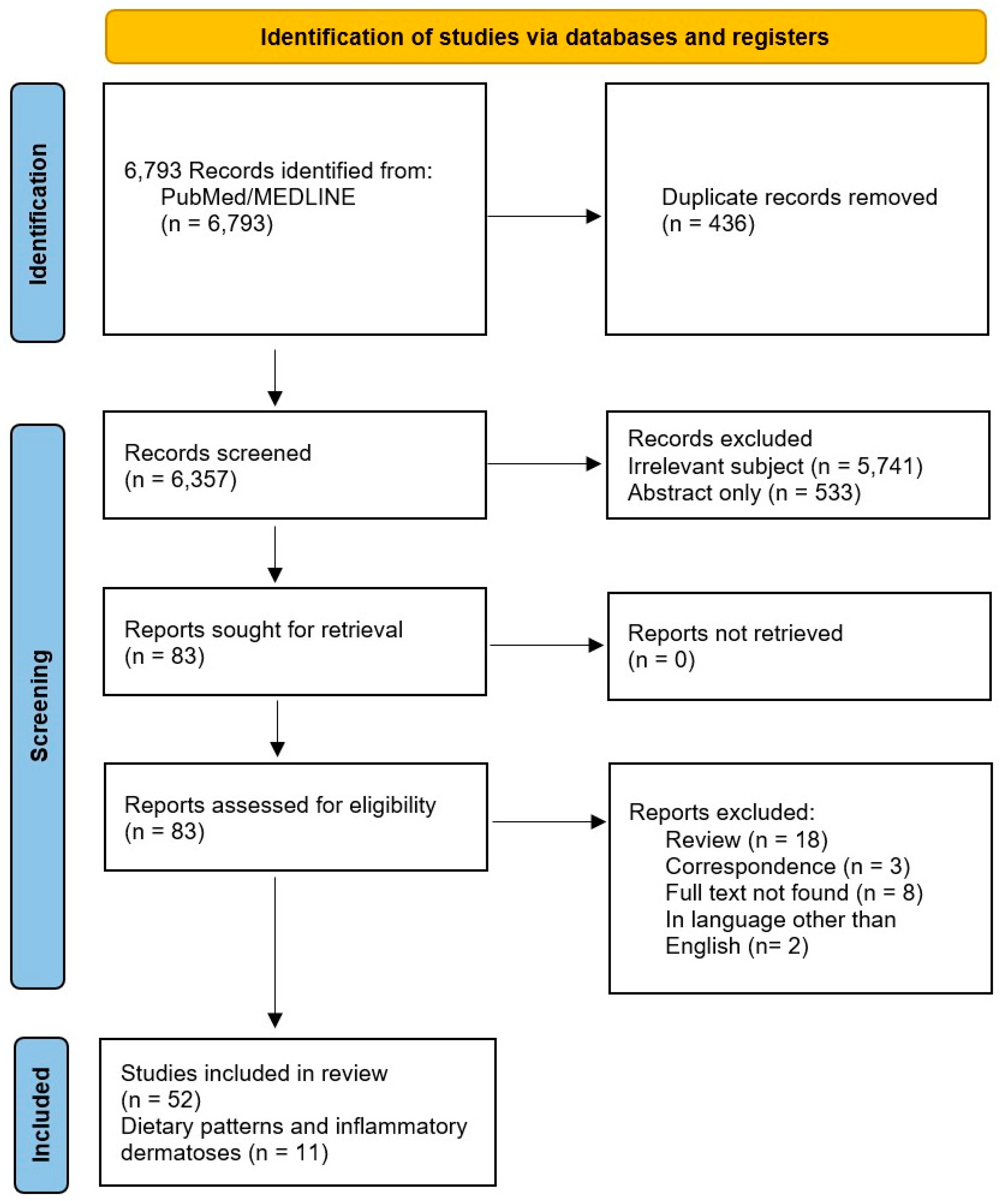
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Psoriasis
3.2. Acne Vulgaris
3.3. Hidradenitis Suppurativa
3.4. Atopic Dermatitis
3.5. Skin and Wound Healing
3.6. Nutritional Deficiencies
3.7. Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
3.8. Protein Intake
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chow, O.; Barbul, A. Immunonutrition: Role in Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, Y.; Kinoshita, M.; Shimada, S.; Kawamura, T. Zinc and Skin Disorders. Nutrients 2018, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBaise, M.; Tarleton, S.M. Hair, Nails, and Skin: Differentiating Cutaneous Manifestations of Micronutrient Deficiency. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotallevi, F.; Campanati, A.; Martina, E.; Radi, G.; Paolinelli, M.; Marani, A.; Molinelli, E.; Candelora, M.; Taus, M.; Galeazzi, T.; et al. The Role of Nutrition in Immune-Mediated, Inflammatory Skin Disease: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.R.; Akter, S.; Tamanna, S.K.; Mazumder, L.; Esti, I.Z.; Banerjee, S.; Akter, S.; Hasan, M.R.; Acharjee, M.; Hossain, M.S.; et al. Impact of gut microbiome on skin health: Gut-skin axis observed through the lenses of therapeutics and skin diseases. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2096995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.; Skov, L. Psoriasis and Obesity. Dermatology 2016, 232, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivanand, A.; Gulliver, W.P.; Josan, C.K.; Alhusayen, R.; Fleming, P.J. Weight Loss and Dietary Interventions for Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2020, 24, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Dulai, A.S.; Ahmad, N.; Sivamani, R.K. Review of Integrative Medical Therapies for Psoriasis: The Microbiome, Probiotics, Diet, and Mindfulness. J. Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis 2024, 9, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, S.R.K.; Kok, C.W.; Kunasegaran, T.; Ramadas, A. Effect of Plant-Based Diets on Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review of Interventional Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, M.B.; Kouris-Blazos, A.; Wattanapenpaiboon, N.; Lukito, W.; Rothenberg, E.M.; Steen, B.C.; Wahlqvist, M.L. Skin wrinkling: Can food make a difference? J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2001, 20, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, C.; Nakamura, K.; Wada, K.; Oba, S.; Hayashi, M.; Takeda, N.; Yasuda, K. Association of dietary fat, vegetables and antioxidant micronutrients with skin ageing in Japanese women. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.Y.; Jeong, J.K.; Lee, Y.E.; Daily, J.W., 3rd. Health benefits of kimchi (Korean fermented vegetables) as a probiotic food. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romo Ventura, E.; Konigorski, S.; Rohrmann, S.; Schneider, H.; Stalla, G.K.; Pischon, T.; Linseisen, J.; Nimptsch, K. Association of dietary intake of milk and dairy products with blood concentrations of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) in Bavarian adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, R.; Heitmann, B.L.; Andersen, K.W.; Nielsen, O.H.; Sorensen, S.B.; Jawhara, M.; Bygum, A.; Hvid, L.; Grauslund, J.; Wied, J.; et al. Impact of red and processed meat and fibre intake on treatment outcomes among patients with chronic inflammatory diseases: Protocol for a prospective cohort study of prognostic factors and personalised medicine. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e018166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afifi, L.; Danesh, M.J.; Lee, K.M.; Beroukhim, K.; Farahnik, B.; Ahn, R.S.; Yan, D.; Singh, R.K.; Nakamura, M.; Koo, J.; et al. Dietary Behaviors in Psoriasis: Patient-Reported Outcomes from a U.S. National Survey. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 7, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingkapairoj, K.; Chularojanamontri, L.; Chaiyabutr, C.; Silpa-Archa, N.; Wongpraparut, C.; Bunyaratavej, S. Dietary habits and perceptions of psoriatic patients: Mediterranean versus Asian diets. J. Dermatolog Treat. 2022, 33, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Balato, N.; Di Somma, C.; Macchia, P.E.; Napolitano, M.; Savanelli, M.C.; Esposito, K.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Nutrition and psoriasis: Is there any association between the severity of the disease and adherence to the Mediterranean diet? J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenska, K.; Moskot, M.; Smolinska-Fijolek, E.; Jakobkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A.; Slominski, B.; Gabig-Ciminska, M. Impact of isoflavone genistein on psoriasis in in vivo and in vitro investigations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberger, S.; Harats, D.; Salameh, F.; Lubish, T.; Harari, A.; Trau, H.; Shaish, A. 9-cis-rich beta-carotene powder of the alga Dunaliella reduces the severity of chronic plaque psoriasis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2012, 31, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guertler, A.; Volsky, A.; Eijkenboom, Q.; Fiedler, T.; French, L.E.; Reinholz, M. Dietary Patterns in Acne and Rosacea Patients—A Controlled Study and Comprehensive Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.M.; Marr, K.D.; Hendricks, A.J.; Price, K.N.; Ludwig, C.M.; Maarouf, M.; Hsiao, J.L.; Shi, V.Y. Alleviating and exacerbating foods in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Fabbrocini, G.; Annunziata, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Donnarumma, M.; Marasca, C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Role of Nutrition and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in the Multidisciplinary Approach of Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Evaluation of Nutritional Status and Its Association with Severity of Disease. Nutrients 2018, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorite-Fuentes, I.; Montero-Vilchez, T.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Molina-Leyva, A. Potential Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity in Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Spanish Population. Nutrients 2022, 14, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velluzzi, F.; Anedda, J.; Pisanu, S.; Dell’Antonia, M.; Deledda, A.; Boi, A.; Ferreli, C.; Atzori, L. Mediterranean diet, lifestyle and quality of life in Sardinian patients affected with Hidradenitis suppurativa. J. Public Health Res. 2021, 11, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danby, F.W. Diet in the prevention of hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa). J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, S52–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwood, P.; Asher, M.I.; Garcia-Marcos, L.; Williams, H.; Keil, U.; Robertson, C.; Nagel, G.; Group, I.P.I.S. Do fast foods cause asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis and eczema? Global findings from the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) phase three. Thorax 2013, 68, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.P.; Wang, L.; Wood, L.G.; Wang, G. Is the consumption of fast foods associated with asthma or other allergic diseases? Respirology 2018, 23, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouda, K.; Tanaka, T.; Kouda, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Takeuchi, A.; Nakamura, H.; Takigawa, M. Low-energy diet in atopic dermatitis patients: Clinical findings and DNA damage. J. Physiol. Anthropol. Appl. Human. Sci. 2000, 19, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehncke, W.H.; Schon, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, M.; Shani, J.; Hristakieva, E.; Stanimirovic, A.; Seidl, W.; Burdo, A. Clinical evaluation of a more rapid and sensitive Psoriasis Assessment Severity Score (PASS), and its comparison with the classic method of Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI), before and after climatotherapy at the Dead-Sea. Int. J. Dermatol. 2000, 39, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, T.C.F.; Corrente, J.E.; Miot, L.D.B.; Papini, S.J.; Miot, H.A. Dietary patterns of patients with psoriasis at a public healthcare institution in Brazil. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2020, 95, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowska, M.; Dunbar, K.; Kassam, S. Managing Psoriatic Arthritis with a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet: A Case Study. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2021, 15, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonjour, M.; Gabriel, S.; Valencia, A.; Goldhamer, A.C.; Myers, T.R. Challenging Case in Clinical Practice: Prolonged Water-Only Fasting Followed by an Exclusively Whole-Plant-Food Diet in the Management of Severe Plaque Psoriasis. Integr. Complement. Ther. 2022, 28, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbaneh, M.; Millsop, J.W.; Bhatia, B.K.; Koo, J.; Liao, W. Diet and psoriasis, part I: Impact of weight loss interventions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahleova, H.; Rembert, E.; Alwarith, J.; Yonas, W.N.; Tura, A.; Holubkov, R.; Agnello, M.; Chutkan, R.; Barnard, N.D. Effects of a Low-Fat Vegan Diet on Gut Microbiota in Overweight Individuals and Relationships with Body Weight, Body Composition, and Insulin Sensitivity. A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogero, M.M.; Calder, P.C. Obesity, Inflammation, Toll-Like Receptor 4 and Fatty Acids. Nutrients 2018, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, J.; Min, M.; Adnan, S.; Afzal, N.; Maloh, J.; Chambers, C.J.; Fam, V.; Sivamani, R.K. Soy Protein Containing Isoflavones Improves Facial Signs of Photoaging and Skin Hydration in Postmenopausal Women: Results of a Prospective Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, E.C.; Callender, V.D. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: A review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2010, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Varshney, N.; Sahi, A.K.; Poddar, S.; Vishwakarma, N.K.; Kavimandan, G.; Prakash, A.; Mahto, S.K. Freeze-Thaw-Induced Physically Cross-linked Superabsorbent Polyvinyl Alcohol/Soy Protein Isolate Hydrogels for Skin Wound Dressing: In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 14033–14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbualakan, K.; Tajul Urus, N.Q.; Makpol, S.; Jamil, A.; Mohd Ramli, E.S.; Md Pauzi, S.H.; Muhammad, N. A Scoping Review on the Effects of Carotenoids and Flavonoids on Skin Damage Due to Ultraviolet Radiation. Nutrients 2022, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.A.; Lin, T.C. Interacting influence of potassium and polychlorinated biphenyl on cortisol and aldosterone biosynthesis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 220, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutsen-Larson, S.; Dawson, A.L.; Dunnick, C.A.; Dellavalle, R.P. Acne vulgaris: Pathogenesis, treatment, and needs assessment. Dermatol. Clin. 2012, 30, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, T.T.; Feldman, S.R.; Fleischer, A.B., Jr. Only 33% of visits for skin disease in the US in 1995 were to dermatologists: Is decreasing the number of dermatologists the appropriate response? Dermatol. Online J. 1998, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J.; Sinclair, R.D. Perceptions of acne vulgaris in final year medical student written examination answers. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2001, 42, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, A.; Chon, S.Y.; Kimball, A.B. The response of skin disease to stress: Changes in the severity of acne vulgaris as affected by examination stress. Arch. Dermatol. 2003, 139, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebamowo, C.A.; Spiegelman, D.; Danby, F.W.; Frazier, A.L.; Willett, W.C.; Holmes, M.D. High school dietary dairy intake and teenage acne. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 52, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebamowo, C.A.; Spiegelman, D.; Berkey, C.S.; Danby, F.W.; Rockett, H.H.; Colditz, G.A.; Willett, W.C.; Holmes, M.D. Milk consumption and acne in teenaged boys. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordain, L.; Lindeberg, S.; Hurtado, M.; Hill, K.; Eaton, S.B.; Brand-Miller, J. Acne vulgaris: A disease of Western civilization. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, J. Resolution of hidradenitis suppurativa after weight loss by dietary measures, especially on frictional locations. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 895–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, E.; Dale, H.F.; Jensen, C.; Lied, G.A. Effects of Plant-Based Diets on Weight Status: A Systematic Review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 3433–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner-McGrievy, G.; Mandes, T.; Crimarco, A. A plant-based diet for overweight and obesity prevention and treatment. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silfvast-Kaiser, A.; Youssef, R.; Paek, S.Y. Diet in hidradenitis suppurativa: A review of published and lay literature. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach-Faig, A.; Berry, E.M.; Lairon, D.; Reguant, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Dernini, S.; Medina, F.X.; Battino, M.; Belahsen, R.; Miranda, G.; et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, J.G.; Filion, K.B.; Atallah, R.; Eisenberg, M.J. Systematic Review of the Mediterranean Diet for Long-Term Weight Loss. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millman, J.F.; Okamoto, S.; Teruya, T.; Uema, T.; Ikematsu, S.; Shimabukuro, M.; Masuzaki, H. Extra-virgin olive oil and the gut-brain axis: Influence on gut microbiota, mucosal immunity, and cardiometabolic and cognitive health. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S.; Barrett, M.; Kirthi, S.; Pellanda, P.; Vlckova, K.; Tobin, A.M.; Murphy, M.; Shanahan, F.; O’Toole, P.W. Altered Skin and Gut Microbiome in Hidradenitis Suppurativa. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, S.R.; Walker, W.A. Immune factors in breast milk and the development of atopic disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohmann, N.; Munthe, L.; Schlicht, K.; Geisler, C.; Demetrowitsch, T.J.; Bang, C.; Jensen-Kroll, J.; Türk, K.; Bacher, P.; Franke, A.; et al. Differential Effects of Obesity, Hyperlipidaemia, Dietary Intake and Physical Inactivity on Type I versus Type IV Allergies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, K.L. The science of fatty acids and inflammation. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 293s–301s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carucci, L.; Nocerino, R.; Paparo, L.; De Filippis, F.; Coppola, S.; Giglio, V.; Cozzolino, T.; Valentino, V.; Sequino, G.; Bedogni, G.; et al. Therapeutic effects elicited by the probiotic Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG in children with atopic dermatitis. The results of the ProPAD trial. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 33, e13836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukrowska, B.; Ceregra, A.; Maciorkowska, E.; Surowska, B.; Zegadlo-Mylik, M.A.; Konopka, E.; Trojanowska, I.; Zakrzewska, M.; Bierla, J.B.; Zakrzewski, M.; et al. The Effectiveness of Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus casei Strains in Children with Atopic Dermatitis and Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Lopez, V.; Ramirez-Bosca, A.; Ramon-Vidal, D.; Ruzafa-Costas, B.; Genoves-Martinez, S.; Chenoll-Cuadros, E.; Carrion-Gutierrez, M.; Horga de la Parte, J.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Codoner-Cortes, F.M. Effect of Oral Administration of a Mixture of Probiotic Strains on SCORAD Index and Use of Topical Steroids in Young Patients with Moderate Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayatan, D.; Nouri, K.; Momtaz, S.; Roufogalis, B.D.; Alidadi, M.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Abdolghaffari, A.H.; Sahebkar, A. Plant-Derived Fermented Products: An Interesting Concept for Human Health. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2024, 8, 102162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Dipietro, L.A. Factors affecting wound healing. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusano, M.; Zane, C.; Calzavara-Pinton, P.; Bencini, P.L. Photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis in vegan and omnivore patients: The role of diet on skin healing. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2021, 32, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusano, M.; Fusano, I.; Galimberti, M.G.; Bencini, M.; Bencini, P.L. Comparison of Postsurgical Scars Between Vegan and Omnivore Patients. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpolat, N.D.; Unlu, S. The effect of a restricted diet on the results of fractional microneedle radiofrequency therapy: A comparison of vegan and omnivorous participants in terms of the antiaging effect of radiofrequency therapy. Lasers Surg. Med. 2022, 54, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Sim, N.; Fotouhi, A.; Daveluy, S. Vegan Diet in Dermatology: A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanBuren, C.A.; Everts, H.B. Vitamin A in Skin and Hair: An Update. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosewicz, J.; Spaccarelli, N.; Roberts, K.M.; Hart, P.A.; Kaffenberger, J.A.; Trinidad, J.C.; Kaffenberger, B.H. The epidemiology, impact, and diagnosis of micronutrient nutritional dermatoses part 1: Zinc, selenium, copper, vitamin A, and vitamin C. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melina, V.; Craig, W.; Levin, S. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Vegetarian Diets. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 1970–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahabadi, N.; Bhusal, A.; Banks, S.W. Riboflavin Deficiency. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, B.; Corpeleijn, W.; Dijsselhof, M.; Goorden, S.; Haverkamp, J.; Langeveld, M.; Waterham, H.; Westerbeek, E.; Bosch, A.M. Mind the B2: Life-Threatening Neonatal Complications of a Strict Vegan Diet during Pregnancy. Neonatology 2022, 119, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brescoll, J.; Daveluy, S. A review of vitamin B12 in dermatology. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F. Vitamin B12 sources and bioavailability. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 232, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.X. The importance of omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio in cell function. The gene transfer of omega-3 fatty acid desaturase. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2003, 92, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, J.K.; Calder, P.C. Omega-6 fatty acids and inflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 132, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the Risk for Obesity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; O’Keefe, J. The Importance of Maintaining a Low Omega-6/Omega-3 Ratio for Reducing the Risk of Autoimmune Diseases, Asthma, and Allergies. Mo. Med. 2021, 118, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Balbas, G.M.; Regana, M.S.; Millet, P.U. Study on the use of omega-3 fatty acids as a therapeutic supplement in treatment of psoriasis. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 4, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hong, S.; Sun, X.; Xu, W.; Li, H.; Ma, T.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qiang, Y.; et al. Efficacy of fish oil and its components in the management of psoriasis: A systematic review of 18 randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.S. Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Dietary sources, metabolism, and significance—A review. Life Sci. 2018, 203, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, G.C.G.; Roschel, G.G.; Ferrari, R.A.; Alencar, S.M.; Ota, H.C.; da Silveira, T.F.F.; Castro, I.A. Chemical characterization of Echium plantagineum seed oil obtained by three methods of extraction. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 5307–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zenary, A.S.A.; Elkin, R.G.; Harvatine, K.J. Comparison of Ahiflower oil containing stearidonic acid to a high-alpha-linolenic acid flaxseed oil at two dietary levels on omega-3 enrichment of egg yolk and tissues in laying hens. Lipids 2023, 58, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, N.; LeBlanc, R.; Surette, M.E. Dietary Buglossoides Arvensis Oil Increases Circulating n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in a Dose-Dependent Manner and Enhances Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Whole Blood Interleukin-10-A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2017, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doughman, S.D.; Krupanidhi, S.; Sanjeevi, C.B. Omega-3 fatty acids for nutrition and medicine: Considering microalgae oil as a vegetarian source of EPA and DHA. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2007, 3, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Metherel, A.H.; Fiabane, L.; Buddenbaum, N.; Bazinet, R.P.; Shaikh, S.R. Do Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid Have the Potential to Compete against Each Other? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcieri, S.T.; Cheung, S.; Belkin, A.; Pillai, A.; Gupta, R. Kwashiorkor on the south shore. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2021, 11, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, M.C. The dermatosis of kwashiorkor in young children. Semin. Dermatol. 1991, 10, 270–272. [Google Scholar]
- Fooddata Central. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/ (accessed on 15 August 2024).


| Skin Condition | Exacerbating | Alleviating |
|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis | ||
| Acne Vulgaris | ||
| Hidradenitis Suppurativa |
| |
| Atopic Dermatitis |
|
|
| Food | Protein Content per 100 g |
|---|---|
| Soybeans | 18.2 g |
| Firm tofu | 10.9 g |
| Black beans | 8.86 g |
| Lentils | 9.02 g |
| Chickpeas | 8.86 g |
| Quinoa | 4.4 g |
| Almonds | 21.2 g |
| Oats (non-fortified) | 13.2 g |
| Raw spinach | 2.86 g |
| Raw spirulina | 5.92 g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, M.; Tarmaster, A.; Bodemer, A.; Sivamani, R.K. The Influence of a Plant-Based Diet on Skin Health: Inflammatory Skin Diseases, Skin Healing, and Plant-Based Sources of Micro- and Macro-Nutrients. Life 2024, 14, 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111439
Min M, Tarmaster A, Bodemer A, Sivamani RK. The Influence of a Plant-Based Diet on Skin Health: Inflammatory Skin Diseases, Skin Healing, and Plant-Based Sources of Micro- and Macro-Nutrients. Life. 2024; 14(11):1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111439
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Mildred, Anurag Tarmaster, Apple Bodemer, and Raja K. Sivamani. 2024. "The Influence of a Plant-Based Diet on Skin Health: Inflammatory Skin Diseases, Skin Healing, and Plant-Based Sources of Micro- and Macro-Nutrients" Life 14, no. 11: 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111439
APA StyleMin, M., Tarmaster, A., Bodemer, A., & Sivamani, R. K. (2024). The Influence of a Plant-Based Diet on Skin Health: Inflammatory Skin Diseases, Skin Healing, and Plant-Based Sources of Micro- and Macro-Nutrients. Life, 14(11), 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111439







