Managing Anemia: Point of Convergence for Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
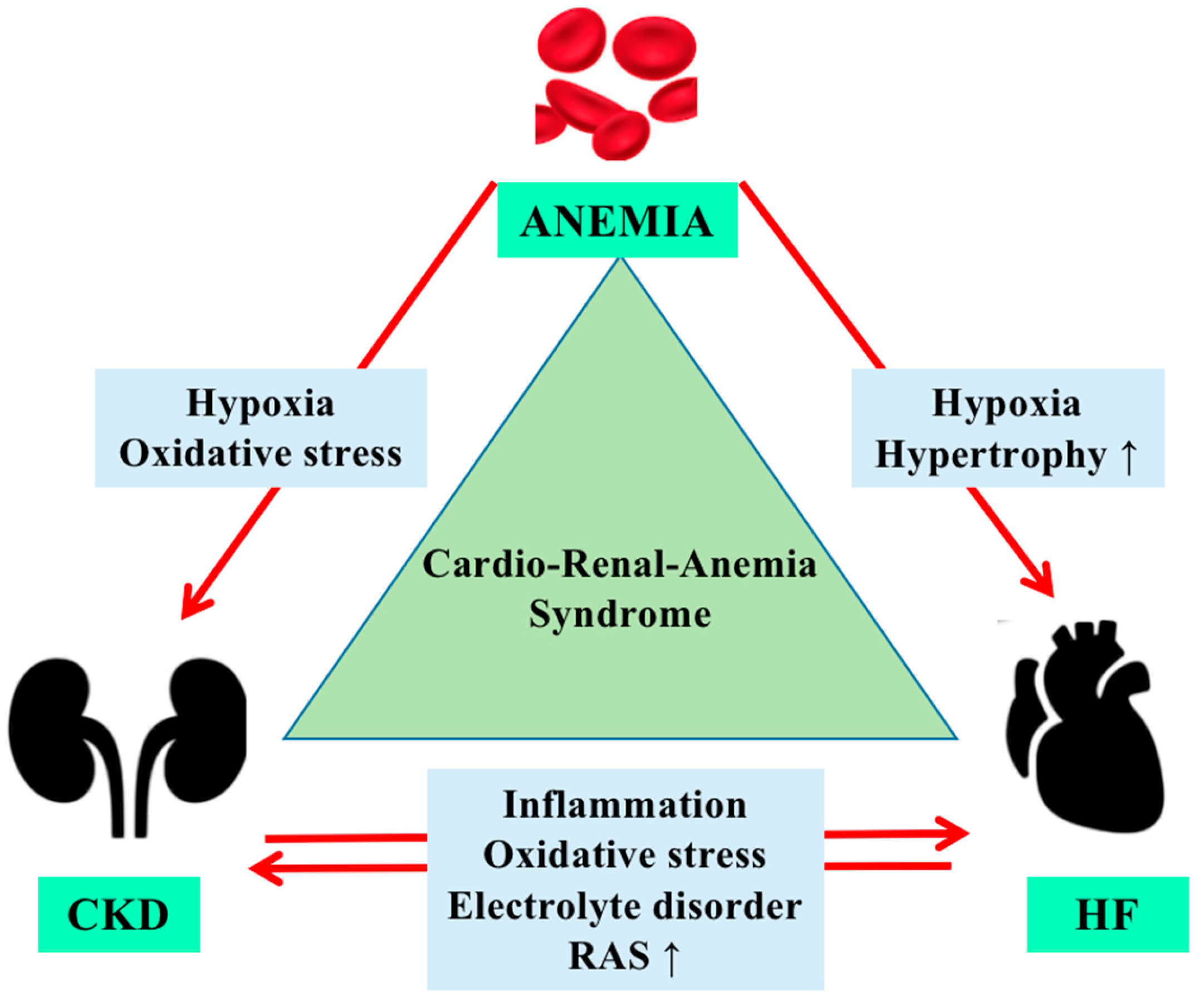
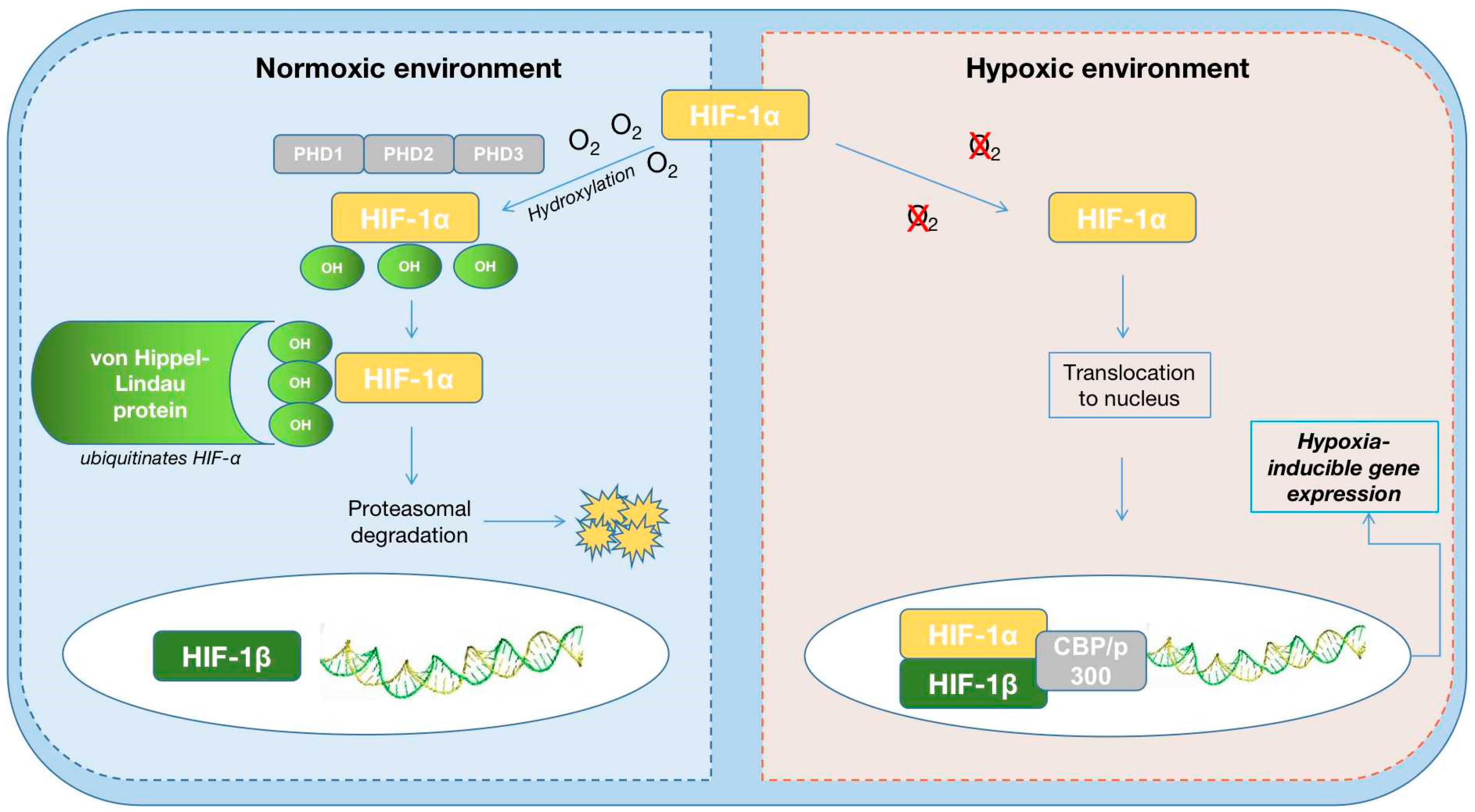
3. Physiopathology of Anemia in Cardiorenal Syndrome
4. Managing Anemia in Cardiorenal Patients
4.1. Intravenous Iron
4.2. Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents
4.3. HIF-PH Inhibitors
| Roxadustat | Daprodustat | Vadadustat | Molidustat | Enarodustat | Desidustat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHD target | all 3 HIF-PHDs | inhibits PHD1 and PHD3 | all three PHDs | mainly inhibits PHD2 | all 3 HIF-PHDs | |
| Benefic Effects |
|
|
|
|
| increased EPO levels and decreased hepcidin and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels, improves EPO-sensitivity by decreasing IL-6, IL-1β, and anti-EPO antibodies [87] |
| Adverse effects |
|
|
|
|
| Pyrexia, vomiting, asthenia, peripheral oedema |
| Half life (h) | 12~15 h | 1.3~2.5 h | 7~9 h | 4~10 h | 15 h | 6–15 h |
| Study population | DD (HD/DP) and NDD | DD (HD/DP) and NDD patients with HF and renal anemia | DD (HD/DP) and NDD | DD (HD/DP) and NDD | DD (HD/DP) and NDD | treatment of anemia associated with CKD (DD and NDD), COVID-2019 infections and chemotherapy induced anemia |
4.4. Hepcidin Antagonist
| Inflammatory status | Hepcidin antagonists anti-IL-6 receptor antibody [91,95] |
| Iron deficiency | Intravenous iron therapy [38,42,43] |
| Hypoxic environment | Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents HIF-PH inhibitors SGLT2 [58,67,88] |
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rangaswami, J.; Bhalla, V.; Blair, J.E.; Chang, T.I.; Costa, S.; Lentine, K.L.; Lerma, E.V.; Mezue, K.; Molitch, M.; Mullens, W.; et al. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Classification, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e840–e878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Costanzo, M.R.; Bellomo, R.; Maisel, A.S. Cardiorenal syndromes: Definition and classification. Contrib. Nephrol. 2010, 164, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Lv, J.; Jia, Q.; Chai, R.; Xue, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction: An Emerging Link in the Pathophysiology of Cardiorenal Syndrome. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 837270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, R.F.; Alibrandi, M.T.S.; Di Lullo, L. The Cardiorenal Anemia Syndrome. Part One: Epidemiology and Clinical Aspects. G. Tec. Nefrol. Dial. 2017, 29, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Farmakis, D.; Filippatos, G. Cardiorenal-anemia syndrome—Definition, epidemiology and management: The Cardiologist’s view. Hippokratia 2011, 15 (Suppl. 2), 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, E.; Cogswell, M.; Egli, I.; Wojdyla, D.; De Benoist, B. Worldwide prevalence of anaemia, WHO Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System, 1993–2005. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Comin Colet, J.; Filippatos, G.; Willenheimer, R.; Dickstein, K.; Drexler, H.; Lüscher, T.M.; Bart, B.; Banasiak, W.; Niegowska, J.; et al. FAIR-HF Trial Investigators. Ferric carboxymaltose in patients with heart failure and iron deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2436–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, O.M. Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia in CKD and End-Stage Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Wettersten, N.; Garimella, P.S. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Pathophysiology. Cardiol. Clin. 2019, 37, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, P.A. Anemia of cardiorenal syndrome. Kidney Int. 2021, 11, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portolés, J.; Martín, L.; Broseta, J.J.; Cases, A. Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology and Current Treatments, to Future Agents. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 642296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertow, G.M.; Pergola, P.E.; Farag, Y.M.; Agarwal, R.; Arnold, S.; Bako, G.; Block, G.A.; Burke, S.; Castillo, F.P.; Jardine, A.G.; et al. Vadadustat in Patients with Anemia and Non–Dialysis-Dependent CKD. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KDIGO Anemia Working Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2012, 2, 279–335. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Weerd, N.C.; Grooteman, M.P.; Nubé, M.J.; Ter Wee, P.M.; Swinkels, D.W.; Gaillard, C.A. Hepcidin in chronic kidney disease: Not an anaemia management tool, but promising as a cardiovascular biomarker. Neth. J. Med. 2015, 73, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deray, G.; Heurtier, A.; Grimaldi, A. Anemia and diabetes. Am. J. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besarab, A.; Hörl, W.H.; Silverberg, D. Iron Metabolism, Iron Deficiency, Thrombocytosis, and the Cardiorenal Anemia Syn-drome. Oncologist 2009, 14, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marecos, C.; Falcao, L.M. Anemia and cardiorenal syndrome in heart failure: Review article. Med. Interna 2010, 17, 236–245. [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama, S.; Maruyama, Y.; Honda, H. A new insight into the treatment of renal anemia with HIF stabilizer. Ren. Replace Therapy 2020, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, D.S.; Wexler, D.; Iaina, A.; Schwartz, D. Correction of Iron Deficiency in the Cardiorenal Syndrome. Int. J. Nephrol. 2011, 2011, 365301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrilho, P. Intravenous iron in heart failure and chronic kidney disease. Nefrologia 2021, 41, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Onuma, S.; Shibagaki, K.; Yuza, T.; Hirao, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Tomosugi, N.; Shibata, T. Associations among Erythroferrone and Biomarkers of Erythropoiesis and Iron Metabolism, and Treatment with Long-Term Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents in Patients on Hemodialysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, T. Erythropoietic regulators of iron metabolism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 133, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazory, A.; Ross, E.A. Anemia: The Point of Convergence or Divergence for Kidney Disease and Heart Failure? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, W.M.; Wiesener, M.S.; Scigalla, P.; Chou, J.; Schmieder, R.E.; Günzler, V.; Eckardt, K.-U. Inhibition of Prolyl Hydroxylases Increases Erythropoietin Production in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 2151–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Physiology and Medicine. Cell 2012, 148, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Wish, J.B. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors: A Potential New Treatment for Anemia in Patients with CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramelo, C.; Justo, S.; Gil, P. Anemia in heart failure: Pathophysiology, pathogenesis, treatment, and incognitae. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2007, 60, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Dor, Y.; Herbert, J.M.; Fukumura, D.; Brusselmans, K.; Dewerchin, M.; Neeman, N.; Bono, F.; Abramovitch, R.; Maxwell, P.; et al. Role of HIF-1 in hypoxia- mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and Tumor angiogenesis. Nature 1998, 394, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. Mutual Antagonism of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Isoforms in Cardiac, Vascular, and Renal Disorders. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelkmann, W. Molecular Biology of Erythropoietin. Intern. Med. 2004, 43, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, K. Anaemia in end-stage renal disease: Pathophysiological considerations. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, J.B. Physiological effects of chronic hypoxia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1965–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, K.-U. The noblesse of kidney physiology. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1250–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Wu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Q.; Fan, J.; Xu, X.; Gu, R.; Hao, H.; Zhang, A.; et al. Clinical Potential of Hypoxia Inducible Factors Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors in Treating Nonanemic Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 837249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Z.-L.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Wen, Y.; Gao, Y.-M.; Liu, B.-C. Hypoxia and chronic kidney disease. EBioMedicine 2022, 77, 103942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, C.E.; Vasile, C.M.; Popescu, M.; Popescu, A.I.S.; Marginean, I.C.; Iacob, G.A.; Popescu, M.D.; Marginean, C.M. Role of Iron Defificiency in Heart Failure—Clinical and Treatment Approach: An Overview. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, M.; Robinson, B.M.; Obrador, G.; Tong, A.; Pisoni, R.L.; Pecoits-Filho, R. Management of Anemia in Nondialysis Chronic Kidney Disease: Current Recommendations, Real-World Practice, and Patient Perspectives. Kidney360 2020, 1, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonko, D.O.; Grzeslo, A.; Witkowski, T.; Mandal, A.K.; Slater, R.M.; Roughton, M.; Foldes, G.; Thum, T.; Majda, J.; Banasiak, W.; et al. Effect of intravenous iron sucrose on exercise tolerance in anemic and non-anemic patients with symptomatic chronic heart failure and iron deficiency FERRIC-HF: A randomized, controlled, observer-blinded trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortman, G.A.M.; Reijnders, D.; Swinkels, D.W. Oral iron supplementation: Potential implications for the gut microbiome and metabolome in patients with CKD. Hemodial. Int. 2017, 21, S28–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigarran Guldris, S.; Gonzalez Parra, E.; Cases Amenos, A. Gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease. Nefrologia 2017, 37, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Assa, E.; Shacham, Y.; Shashar, M.; Leshem-Rubinow, E.; Gal-Oz, A.; Schwartz, I.F.; Schwartz, D.; Silverberg, D.S.; Chernin, G. Target hemoglobin may be achieved with intravenous iron alone in anemic patients with cardiorenal syndrome: An observational study. Cardiorenal Med. 2015, 5, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Lin, V.; Guss, C.; Pratt, R.; Ikizler, T.A.; Besarab, A. Ferric pyrophosphate citrate administered via dialysate reduces erythropoiesis-stimulating agent use and maintains hemoglobin in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbane, S.N.; Singh, A.K.; Cournoyer, S.H.; Jindal, K.K.; Fanti, P.; Guss, C.D.; Lin, V.H.; Pratt, R.D.; Gupta, A. Ferric pyrophosphate citrate (Triferic™) administration via the dialysate maintains hemoglobin and iron balance in chronic hemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdougall, I.C.; Bock, A.H.; Carrera, F.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Gaillard, C.; Van Wyck, D.; Roubert, B.; Nolen, J.G.; Roger, S.D. On behalf of the FIND-CKD Study Investigators FIND-CKD: A randomized trial of intravenous ferric carboxymaltose versus oral iron in patients with chronic kidney disease and iron deficiency anaemia. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mursu, J.; Robien, K.; Harnack, L.J.; Park, K.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr. Dietary supplements and mortality rate in older women: The Iowa Women’s Health Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostoker, G.; Griuncelli, M.; Loridon, C.; Magna, T.; Machado, G.; Drahi, G.; Dahan, H.; Janklewicz, P.; Cohen, Y. Reassessment of iron marker for prediction of dialysis iron overload: An MRI study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anraku, M.; Kitamura, K.; Shintomo, R.; Takeuchi, K.; Ikeda, H.; Nagano, J.; Ko, T.; Mera, K.; Tomita, K.; Otagiri, M. Effect of intravenous iron administration frequency on AOPP and inflammatory biomarkers in chronic hemodialysis patients: A pilot study. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdougall, I.C.; White, C.; Anker, S.D.; Bhandari, S.; Farrington, K.; Kalra, P.A.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Murray, H.; Tomson, C.R.V.; Wheeler, D.C.; et al. Intravenous iron in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, Z.; Maali, A.; Shad, J.S.; Farasat, A.; Kouchaki, R.; Moghadami, M.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Azad, M. Updates on Novel Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents: Clinical and Molecular Approach. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2020, 36, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Hamano, T.; Wada, A.; Masakane, I. Types of Erythropoietin-Stimulating Agents and Mortality among Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, P.; Voors, A.A.; Lipsic, E.; Van Gilst, W.H.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J. Erytropoietin in cardiovascular diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2004, 25, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, P.; Lok, D.J.; Januzzi, J.L.; de la Porte, P.W.B.-A.; Lipsic, E.; van Wijngaarden, J.; Voors, A.A.; van Gilst, W.H.; van Veldhuisen, D.J. Adequacy of endogenous erythropoietin levels and mortality in anaemic heart failure patients. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beverborg, N.G.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; van der Meer, P. Anemia in Heart Failure: Still Relevant? JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Barany, P.; Covic, A.; De Francisco, A.; Del Vecchio, L.; Goldsmith, D.; Hörl, W.; London, G.; Vanholder, R.; Van Biesen, W.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes guidelines on anaemia management in chronic kidney disease: A European Renal Best Practice position statement. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1346–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, R.M.; Streja, E.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Burden of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: Beyond Erythropoietin. Adv. Ther. 2020, 38, 52–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, L.; Minutolo, R. ESA, Iron Therapy and New Drugs: Are There New Perspectives in the Treatment of Anaemia? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, M.R. Managing Anemia across the Stages of Kidney Disease in Those Hyporesponsive to Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents. Am. J. Nephrol. 2021, 52, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, D.S.; Wexler, D.; Iaina, A. The importance of anemia and its correction in the management of severe congestive heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2002, 4, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayus, J.C.; Go, A.S.; Valderrabano, F.; Verde, E.; de Vinuesa, S.G.; Achinger, S.G.; Lorenzo, V.; Arieff, A.I.; Luao, J. Spanish Group for the study of the anemia and left ventricular hypertrophy in pre-dialysis patients. Effects of erythropoietin on left ventricular hypertrophy in adults with severe chronic renal failure and hemoglobin < 10 g/dL. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaishi, M.; Hiroe, M.; Hada, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Tsubakihara, Y.; Akizawa, T. KRN321 Study Group. Effect of anemia correction on left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with modestly high hemoglobin level and chronic kidney disease. J. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyam, S.; Tomonari, H.; Yoshida, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Sakai, O. Reversal of Anemia by Erythropoietin Therapy Retards the Progression of Chronic Renal Failure, Especially in Nondiabetic Patients. Nephron 1997, 77, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouva, C.; Nikolopoulos, P.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Siamopoulos, K.C. Treating anemia early in renal failure patients slows the decline of renal function: A randomized controlled trial. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- McCullough, P.A.; Barnhart, H.X.; Inrig, J.K.; Reddan, D.; Sapp, S.; Patel, U.D.; Singh, A.K.; Szczech, L.A.; Califf, R.M. Cardiovascular Toxicity of Epoetin-Alfa in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 37, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenga, M.F.; Emans, M.E.; van der Putten, K.; Cramer, M.J.; Diepenbroek, A.; Velthuis, B.K.; Doevendans, P.A.; Verhaar, M.C.; Joles, J.A.; Bakker, S.J.L.; et al. Epoetin Beta and C-Terminal Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackevicius, C.A.; Co, M.J.; Warner, A.L. Predictors of erythropoietin use in patients with cardiorenal anaemia syndrome. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2014, 23, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. Oxygen sensing, homeostasis, and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, V.H. HIF-PH inhibitors for anemia of CKD. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2021, 11, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, R.; Nagao, Y.; Fujioka, M.; Akizawa, T. Treatment of anemia associated with chronic kidney disease with the HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor enarodustat: A review of the evidence. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2022, 26, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallon, V.; Rose, M.; Gerasimova, M.; Satriano, J.; Platt, K.A.; Koepsell, H.; Cunard, R.; Sharma, K.; Thomson, S.C.; Rieg, T.; et al. Knockout of Na-glucose transporter SGLT2 attenuates hyperglycemia and glomerular hyperfiltration but not kidney growth or injury in diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2013, 304, F156–F167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, A.; Fu, Y.; Patel, R.; Darshi, M.; Crespo-Masip, M.; Huang, W.; Song, P.; Freeman, B.; Kim, Y.C.; Soleimani, M.; et al. A role for the tubular Na+-H+-exchanger NHE3 in the natri-uretic effect of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2020, 319, 712–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inzucchi, S.E.; Zinman, B.; Fitchett, D.; Wanner, C.; Ferrannini, E.; Schumacher, M.; Schmoor, C.; Ohneberg, K.; Johansen, O.E.; George, J.T.; et al. How does empagliflozin reduce cardiovascular mortality? Insights from a mediation analysis of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, E.R.; Walmsley, S.R. Inflflammation and hypoxia: HIF and PHD isoform selectivity. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iso, T.; Matsue, Y.; Mizukami, A.; Tokano, T.; Isoda, K.; Suwa, S.; Miyauchi, K.; Yanagisawa, N.; Okumura, Y.; Minamino, T. Daprodustat for anaemia in patients with heart failure and chronic kidney disease: A randomized controlled study. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 4291–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghani, N.S.; Haase, V.H. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Activators in Renal Anemia: Current Clinical Experience. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019, 26, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Xu, J.; Chai, Y. Roxadustat promotes angiogenesis through HIF-1α/VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling and accelerates cutaneous wound healing in diabetic rats. Wound Repair Regen. 2019, 27, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Qian, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, X.; Mei, C.; Hao, C.; Jiang, G.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, L.; et al. Phase 2 studies of oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor FG-4592 for treatment of anemia in China. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbane, S.; El-Shahawy, M.A.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Van, B.P.; Houser, M.T.; Frison, L.; Little, D.J.; Guzman, N.J.; Pergola, P.E. Roxadustat for Treating Anemia in Patients with CKD Not on Dialysis: Results from a Randomized Phase 3 Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 737–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, R.; Shutov, E.; Eremeeva, L.; Korneyeva, S.; Poole, L.; Saha, G.; Bradley, C.; Eyassu, M.; Besarab, A.; Leong, R.; et al. Roxadustat for anemia in patients with end-stage renal disease incident to dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Hao, C.; Liu, B.-C.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Xing, C.; Liang, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Roxadustat Treatment for Anemia in Patients Undergoing Long-Term Dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Xiong, Q.W.; Yao, X.; Liu, F.; Tang, X.; Fu, H.; Tong, T.; Mao, J.; Peng, W.X. Roxadustat: Do we know all the answers? Biomol. Biomed. 2023, 23, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PMDA. Japanese Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency Report on Roxadustat. Available online: https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000234811 (accessed on 22 July 2020).
- Tsubakihara, Y.; Akizawa, T.; Nangaku, M.; Onoue, T.; Yonekawa, T.; Matsushita, H.; Endo, Y.; Cobitz, A. A 24-Week Anemia Correction Study of Daprodustat in Japanese Dialysis Patients. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2019, 24, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akizawa, T.; MacDougall, I.C.; Berns, J.S.; Bernhardt, T.; Staedtler, G.; Taguchi, M.; Iekushi, K.; Krueger, T. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Molidustat for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: DIALOGUE Extension Studies. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 49, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crugliano, G.; Serra, R.; Ielapi, N.; Battaglia, Y.; Coppolino, G.; Bolignano, D.; Bracale, U.M.; Pisani, A.; Faga, T.; Michael, A.; et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Stabilizers in End Stage Kidney Disease: “Can the Promise Be Kept?”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergola, P.E.; Spinowitz, B.S.; Hartman, C.S.; Maroni, B.J.; Haase, V.H. Vadadustat, a novel oral HIF stabilizer, provides effective anemia treatment in nondialysis dependent chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Desidustat: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, R.; Takiyama, Y.; Takiyama, T.; Kitsunai, H.; Takeda, Y.; Sakagami, H.; Ota, T. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is the therapeutic target of the SGLT2 inhibitor for diabetic nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, P.H.; Eckardt, K.U. HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for the treatment of renal anaemia and beyond. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016, 12, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallalio, G.; Law, E.; Means, R.T. Hepcidin inhibits in vitroerythroid colony formation at reduced erythropoietin concentrations. Blood 2006, 107, 2702–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A. Increased hepcidin-25 and erythropoietin responsiveness in patients with cardio-renal anemia syndrome. Future Cardiol. 2010, 6, 769–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, A.; Nai, A.; Silvestri, L.; Camaschella, C. Hepcidin and Anemia: A Tight Relationship. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srai, S.K.; Chung, B.; Marks, J.; Pourvali, K.; Solanky, N.; Rapisarda, C.; Chaston, T.B.; Hanif, R.; Unwin, R.J.; Debnam, E.S.; et al. Erythropoietin regulates intestinal iron absorption in a rat model of chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsic, E.; Van Der Meer, P.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J. Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents and Heart Failure. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2011, 29, e52–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-J.; Jin, H.-M.; Cho, Y.-N.; Kang, J.-H.; Jung, H.-J.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Yim, Y.-R.; Lee, J.-W.; Lee, K.-E.; et al. Clinical and Hematological Effects of Tocilizumab on Serum Hepcidin, Anemia Response and Disease Activity in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 23, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheetz, M.; Barrington, P.; Callies, S.; Berg, P.; McColm, J.; Marbury, T.; Decker, B.; Dyas, G.L.; Truhlar, S.M.; Benschop, R.; et al. Targeting the hepcidin-ferroportin pathway in anaemia of chronic kidney disease. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renders, L.; Budde, K.; Rosenberger, C.; Van Swelm, R.; Swinkels, D.; Dellanna, F.; Feuerer, W.; Wen, M.; Erley, C.; Bader, B.; et al. First-in-human Phase I studies of PRS-080#22, a hepcidin antagonist, in healthy volunteers and patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing hemodialysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buliga-Finis, O.N.; Ouatu, A.; Tanase, D.M.; Gosav, E.M.; Seritean Isac, P.N.; Richter, P.; Rezus, C. Managing Anemia: Point of Convergence for Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease? Life 2023, 13, 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061311
Buliga-Finis ON, Ouatu A, Tanase DM, Gosav EM, Seritean Isac PN, Richter P, Rezus C. Managing Anemia: Point of Convergence for Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease? Life. 2023; 13(6):1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061311
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuliga-Finis, Oana Nicoleta, Anca Ouatu, Daniela Maria Tanase, Evelina Maria Gosav, Petronela Nicoleta Seritean Isac, Patricia Richter, and Ciprian Rezus. 2023. "Managing Anemia: Point of Convergence for Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease?" Life 13, no. 6: 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061311
APA StyleBuliga-Finis, O. N., Ouatu, A., Tanase, D. M., Gosav, E. M., Seritean Isac, P. N., Richter, P., & Rezus, C. (2023). Managing Anemia: Point of Convergence for Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease? Life, 13(6), 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061311











