Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain via Toll-like Receptor 4 in the Mouse Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. FM Model and Bio-Plex ELISA
2.3. EA Treatments
2.4. Pain Behavior Test
2.5. Western Blotting Analysis
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. Intracerebroventricular Injection
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
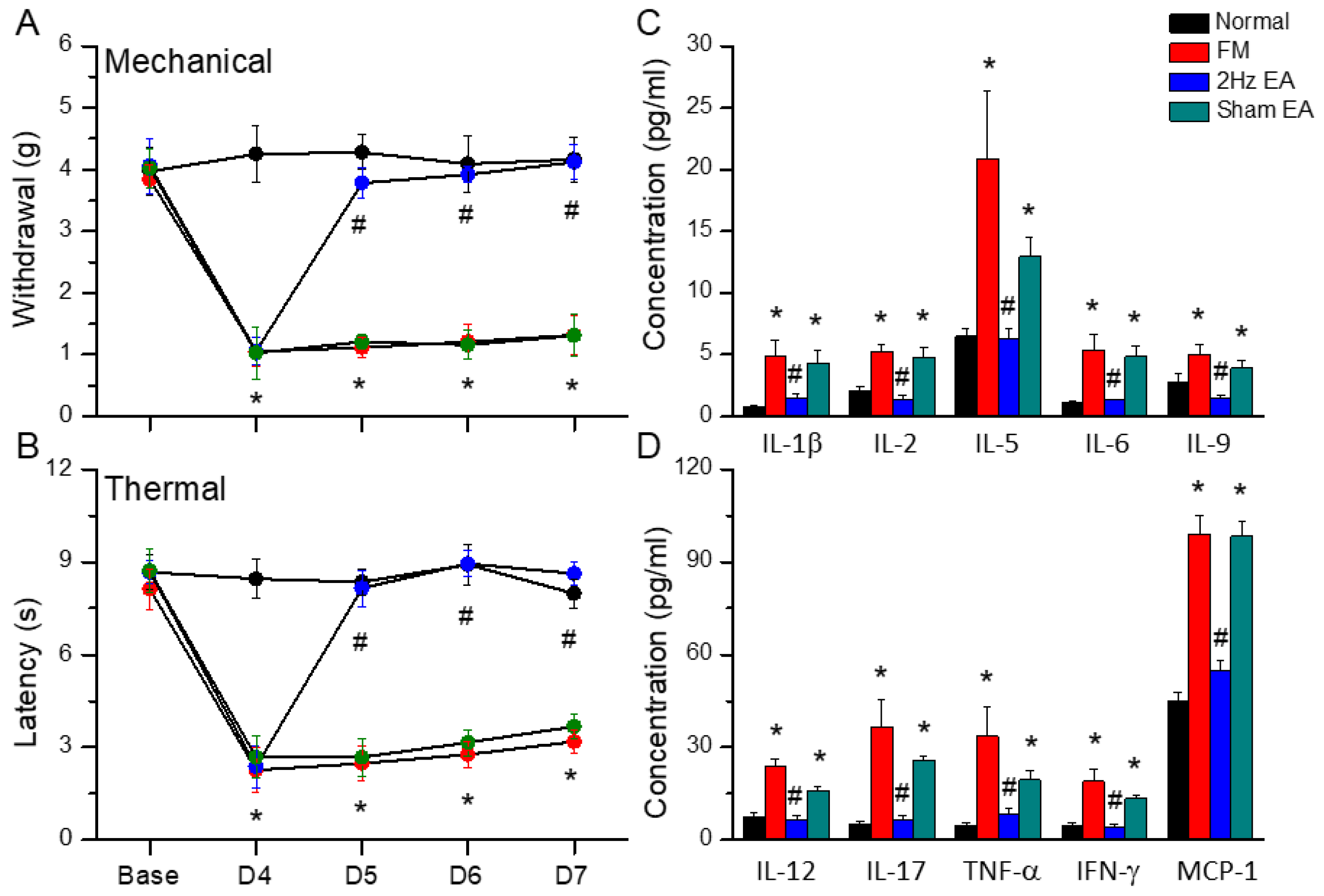
3.1. Electroacupuncture Attenuated Fibromyalgia-like Pain in Mice
3.2. Electroacupuncture Treatment Alleviated the Increase in Inflammatory Cytokines Caused by Cold-Stress-Induced Pain
3.3. Electroacupuncture but Not Sham Electroacupuncture Attenuated Cold-Stress-Induced Pain via TRPV1 Pathways in the Mouse Hypothalamus and Periaqueductal Gray
3.4. TLR4 Signaling in the Cold-Stress-Induced Pain Mouse Cerebellum Was Attenuated by Electroacupuncture but Not Sham Electroacupuncture
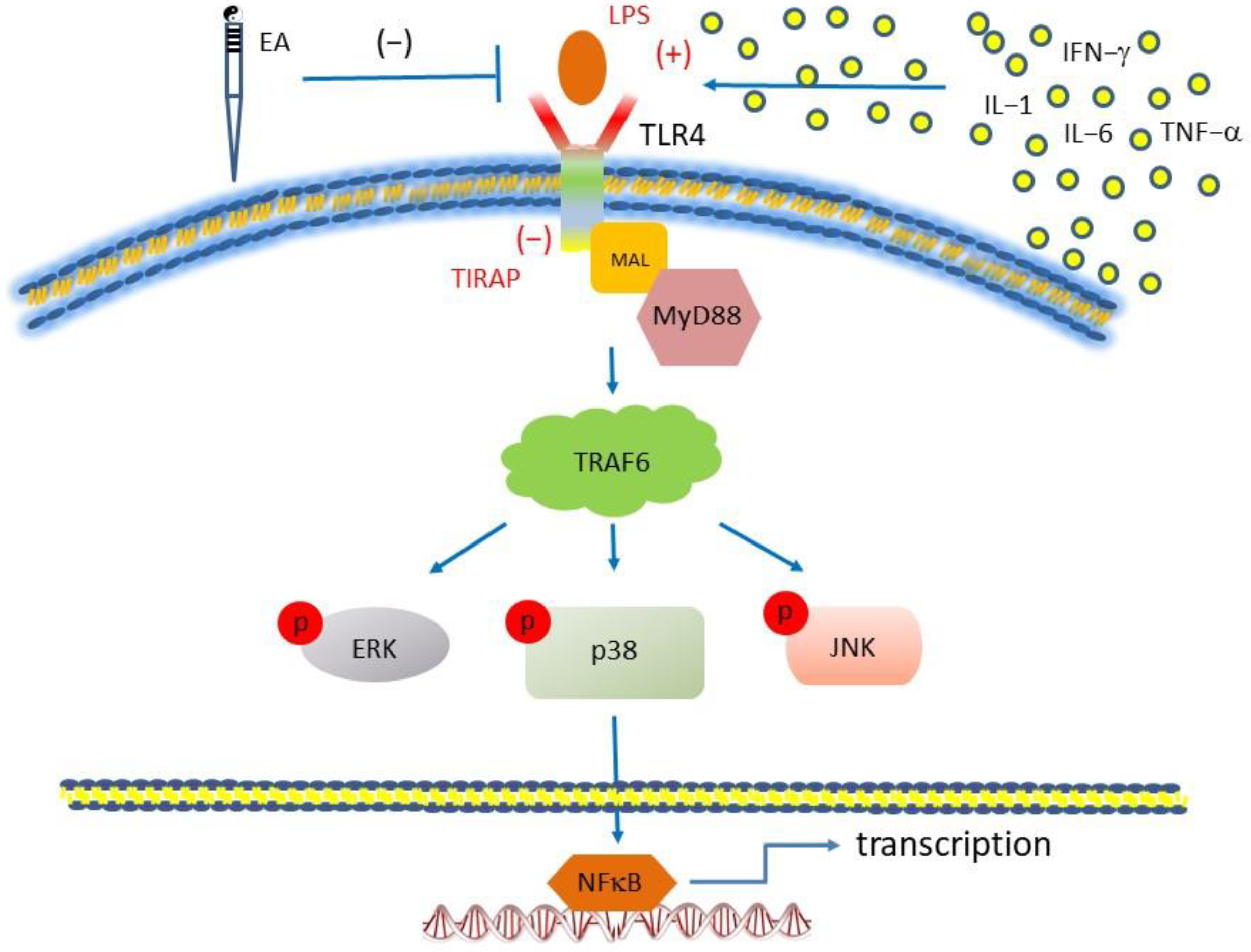
3.5. Activation of TLR4 by LPS Injection Mimics CSP and Further Reversed by TLR4 Antagonist TIRAP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bair, M.J.; Krebs, E.E. Fibromyalgia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, ITC33–ITC48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, F.; Ross, K.; Anderson, J.; Russell, I.J.; Hebert, L. The prevalence and characteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, A.P.; Santo, A.; Berssaneti, A.A.; Matsutani, L.A.; Yuan, S.L.K. Prevalence of fibromyalgia: Literature review update. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. Engl. Ed. 2017, 57, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzcharles, M.A.; Ste-Marie, P.A.; Goldenberg, D.L.; Pereira, J.X.; Abbey, S.; Choinière, M.; Ko, G.; Moulin, D.E.; Panopalis, P.; Proulx, J.; et al. 2012 Canadian Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of fibromyalgia syndrome: Executive summary. Pain. Res. Manag. 2013, 18, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, W.; Ablin, J.; Perrot, S.; Fitzcharles, M.A. Management of fibromyalgia: Practical guides from recent evidence-based guidelines. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2017, 127, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez-López, F.; Maestre-Cascales, C.; Russell, D.; Alvarez-Gallardo, I.C.; Rodriguez-Ayllon, M.; Hughes, C.M.; Davison, G.W.; Sanudo, B.; McVeigh, J.G. Effectiveness of Exercise on Fatigue and Sleep Quality in Fibromyalgia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Trials. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 102, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, K.; Flor, H.; Turk, D.C. Psychological pain treatment in fibromyalgia syndrome: Efficacy of operant behavioural and cognitive behavioural treatments. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. Efficacy of acupuncture on fibromyalgia syndrome: A meta-analysis. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 34, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluka, K.A.; Kalra, A.; and Moore, S.A. Unilateral intramuscular injections of acidic saline produce a bilateral, long-lasting hyperalgesia. Muscle Nerve 2001, 24, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, H.F.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lai, C.L.; Chen, C.C. Activation of acid-sensing ion channel 3 by lysophosphatidylcholine 16:0 mediates psychological stress-induced fibromyalgia-like pain. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1644–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyori, M.; Nagai, J.; Nakazawa, T.; Ueda, H. Absence of morphine analgesia and its underlying descending serotonergic activation in an experimental mouse model of fibromyalgia. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 472, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.W.; Chou, A.I.W.; Su, H.; Su, K.P. Transient receptor potential V1(TRPV1) modulates the therapeutic effects for comorbidity of pain and depression: The common molecular implication for electroacupuncture and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmich, N.N.; Sivak, K.V.; Chubarev, V.N.; Porozov, Y.B.; Savateeva-Lyubimova, T.N.; Peri, F. TLR4 Signaling Pathway Modulators as Potential Therapeutics in Inflammation and Sepsis. Vaccines 2017, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.K.; Huang, T.L.; Huang, K.W.; Huang, Y.L.; Hung, Y.Y. Association between toll-like receptor 4 expression and symptoms of major depressive disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 1853–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, K.K.; Saini, J.; Mahajan, K.; Singh, D.; Jayswal, D.P.; Mishra, S.; Bishayee, A.; Sethi, G.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Therapeutic implications of toll-like receptors in peripheral neuropathic pain. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 115, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tang, J.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhu, T.; Zhao, F.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Qu, Y.; et al. Role of toll-like receptor 4 in the regulation of the cell death pathway and neuroinflammation. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 148, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso-Loeches, S.; Pascual-Lucas, M.; Blanco, A.M.; Sanchez-Vera, I.; Guerri, C. Pivotal role of TLR4 receptors in alcohol-induced neuroinflammation and brain damage. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 8285–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, S.; Herkenham, M. Toll-like receptor 4 on nonhematopoietic cells sustains CNS inflammation during endotoxemia, independent of systemic cytokines. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.Y.; Hsieh, C.L.; Huang, C.P.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates CFA-induced Inflammatory Pain by suppressing Nav1.8 through S100B, TRPV1, Opioid, and Adenosine Pathways in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.M.; Venkatesh, D.; Ravindra, S. Electromyography changes in assessment of functional status of muscles in subjects with knee-osteoarthritis undergoing low level laser therapy. Biomedicine 2021, 41, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, C.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Shao, X.; Liang, Y.; Du, J.; Fang, J.; et al. Electroacupuncture Alleviates Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in Rats via Suppressing TLR4 Signaling and TRPV1 Upregulation in Sensory Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.S. Acupuncture: Neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Rosas, R.; Yehia, G.; Peña, G.; Mishra, P.; del Rocio Thompson-Bonilla, M.; Moreno-Eutimio, M.A.; Arriaga-Pizano, L.A.; Isibasi, A.; Ulloa, L. Dopamine mediates vagal modulation of the immune system by electroacupuncture. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, N.; Chen, M.; Fujita, T.; Xu, Q.; Peng, W.; Liu, W.; Jensen, T.K.; Pei, Y.; Wang, F.; Han, X.; et al. Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Su, Y.; Qi, L.; Yang, W.; Fu, M.; Jing, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Q. A neuroanatomical basis for electroacupuncture to drive the vagal-adrenal axis. Nature 2021, 598, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K.; Krebs, E.E.; Bair, M.J. Pharmacotherapy of chronic pain: A synthesis of recommendations from systematic reviews. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2009, 31, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vas, J.; Santos-Rey, K.; Navarro-Pablo, R.; Modesto, M.; Aguilar, I.; Campos, M.Á.; Aguilar-Velasco, J.F.; Romero, M.; Párraga, P.; Hervás, V.; et al. Acupuncture for fibromyalgia in primary care: A randomised controlled trial. Acupunct. Med. 2016, 34, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorst, J.; Klose, P.; Musial, F.; Irnich, D.; Hauser, W. Efficacy of acupuncture in fibromyalgia syndrome--a systematic review with a meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lottering, B.; Lin, Y.W. TRPV1 Responses in the Cerebellum Lobules VI, VII, VIII Using Electroacupuncture Treatment for Chronic Pain and Depression Comorbidity in a Murine Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zeng, H.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Wu, J.; Feng, Y.; Deng, P.; Zhang, H. Glycyrrhizin ameliorates inflammatory pain by inhibiting microglial activation-mediated inflammatory response via blockage of the HMGB1-TLR4-NF-kB pathway. Exp. Cell. Res. 2018, 369, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Li, F.; Zhao, L.X.; Dong, Y.L.; Gao, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.J. Ligustilide Ameliorates Inflammatory Pain and Inhibits TLR4 Upregulation in Spinal Astrocytes Following Complete Freund’s Adjuvant Peripheral Injection. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Q.; Zhang, Z.L.; Tan, W.F.; Sun, X.J.; Ma, H. Down-Regulation of CXCL12/CXCR4 Expression Alleviates Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Inflammatory Pain via Inhibiting Glial TLR4 Activation in the Spinal Cord. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.Y.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture reduces cold stress-induced pain through microglial inactivation and transient receptor potential V1 in mice. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Mi, W.; Jiang, Y. Analgesic effects of TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway inhibition on chronic neuropathic pain in rats following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurga, A.M.; Rojewska, E.; Piotrowska, A.; Makuch, W.; Pilat, D.; Przewlocka, B.; Mika, J. Blockade of Toll-Like Receptors (TLR2, TLR4) Attenuates Pain and Potentiates Buprenorphine Analgesia in a Rat Neuropathic Pain Model. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 5238730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanga, F.Y.; Nutile-McMenemy, N.; DeLeo, J.A. The CNS role of Toll-like receptor 4 in innate neuroimmunity and painful neuropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5856–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Huang, Y.; Gu, H.F.; Zu, X.Y.; Zou, W.Y.; Song, Z.B.; Guo, Q.L. Effects of intrathecal epigallocatechin gallate, an inhibitor of Toll-like receptor 4, on chronic neuropathic pain in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 676, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risbud, M.V.; Shapiro, I.M. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc content. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, P.-C.; Yen, C.-M.; Lin, M.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Liao, H.-Y.; Huang, Y.-W.; Lin, Y.-W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain via Toll-like Receptor 4 in the Mouse Brain. Life 2023, 13, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051160
Lai P-C, Yen C-M, Lin M-C, Chen Y-H, Liao H-Y, Huang Y-W, Lin Y-W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain via Toll-like Receptor 4 in the Mouse Brain. Life. 2023; 13(5):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051160
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Po-Chih, Chia-Ming Yen, Ming-Chia Lin, Yung-Hsiang Chen, Hsien-Yin Liao, Yu-Wei Huang, and Yi-Wen Lin. 2023. "Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain via Toll-like Receptor 4 in the Mouse Brain" Life 13, no. 5: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051160
APA StyleLai, P.-C., Yen, C.-M., Lin, M.-C., Chen, Y.-H., Liao, H.-Y., Huang, Y.-W., & Lin, Y.-W. (2023). Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain via Toll-like Receptor 4 in the Mouse Brain. Life, 13(5), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051160







