Biodiversity and Interannual Variation of Harmful Algal Bloom Species in the Coastal Sea of Qinhuangdao, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
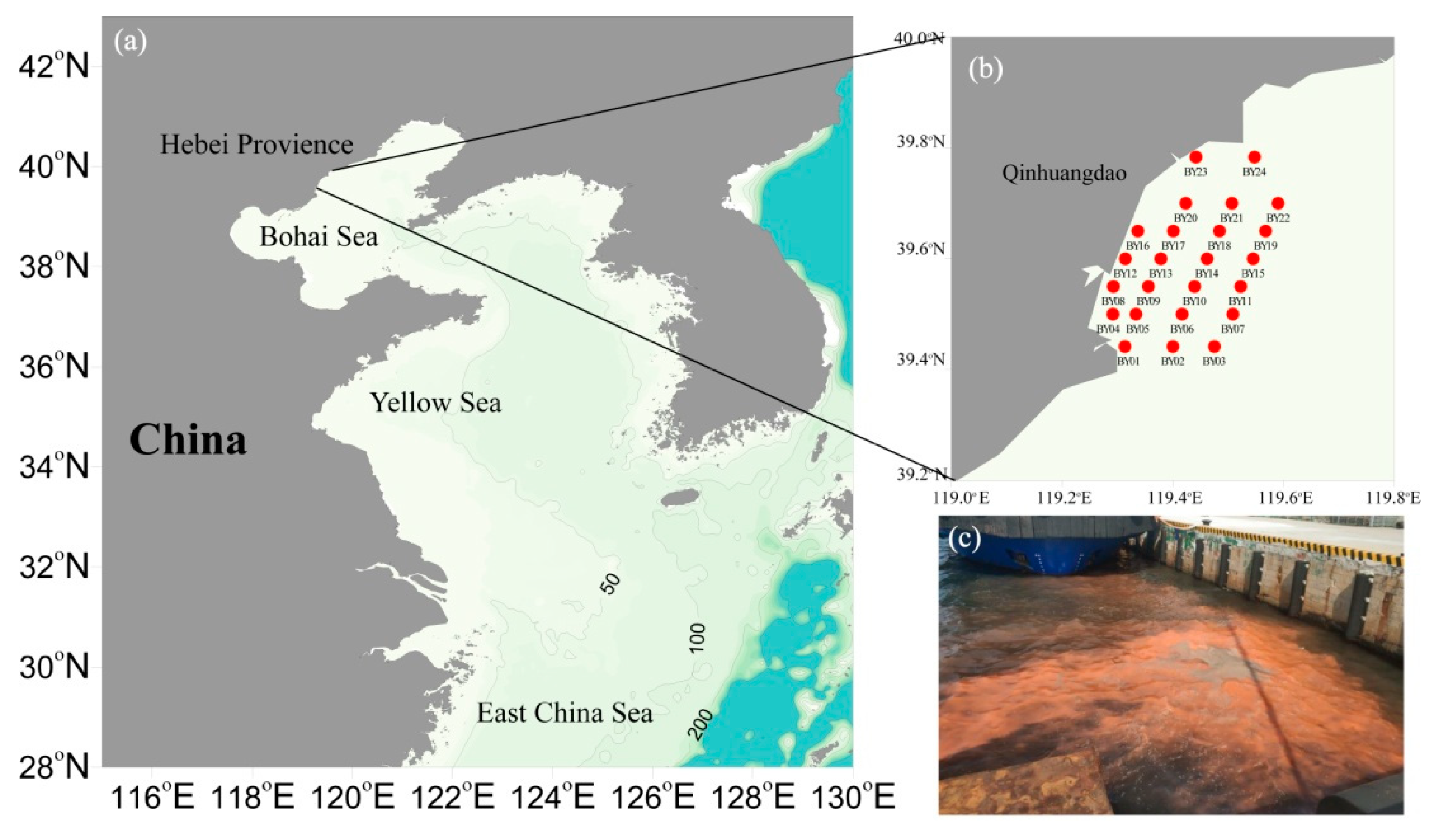
2.1. Sampling Sites and Sample Collection in the Qinhuangdao Coastal Sea Area
2.2. Collection and Determination of Environmental Factors
2.3. Taxonomic Annotation and Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
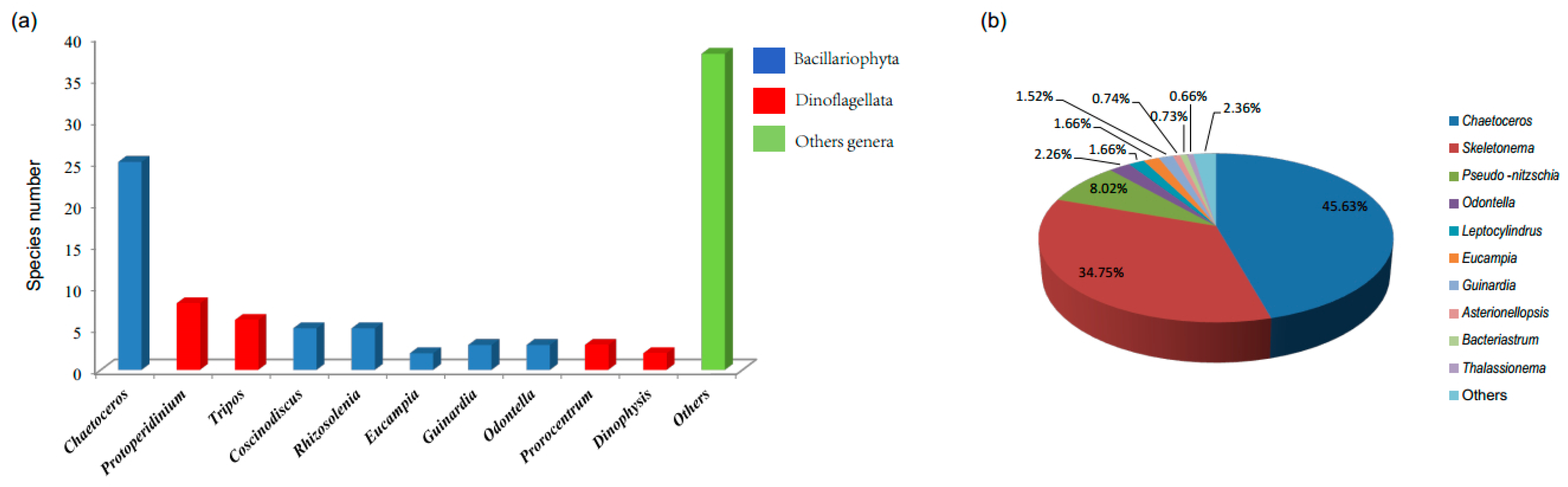
3.1. Composition and Alpha Diversity of Algae in QCS
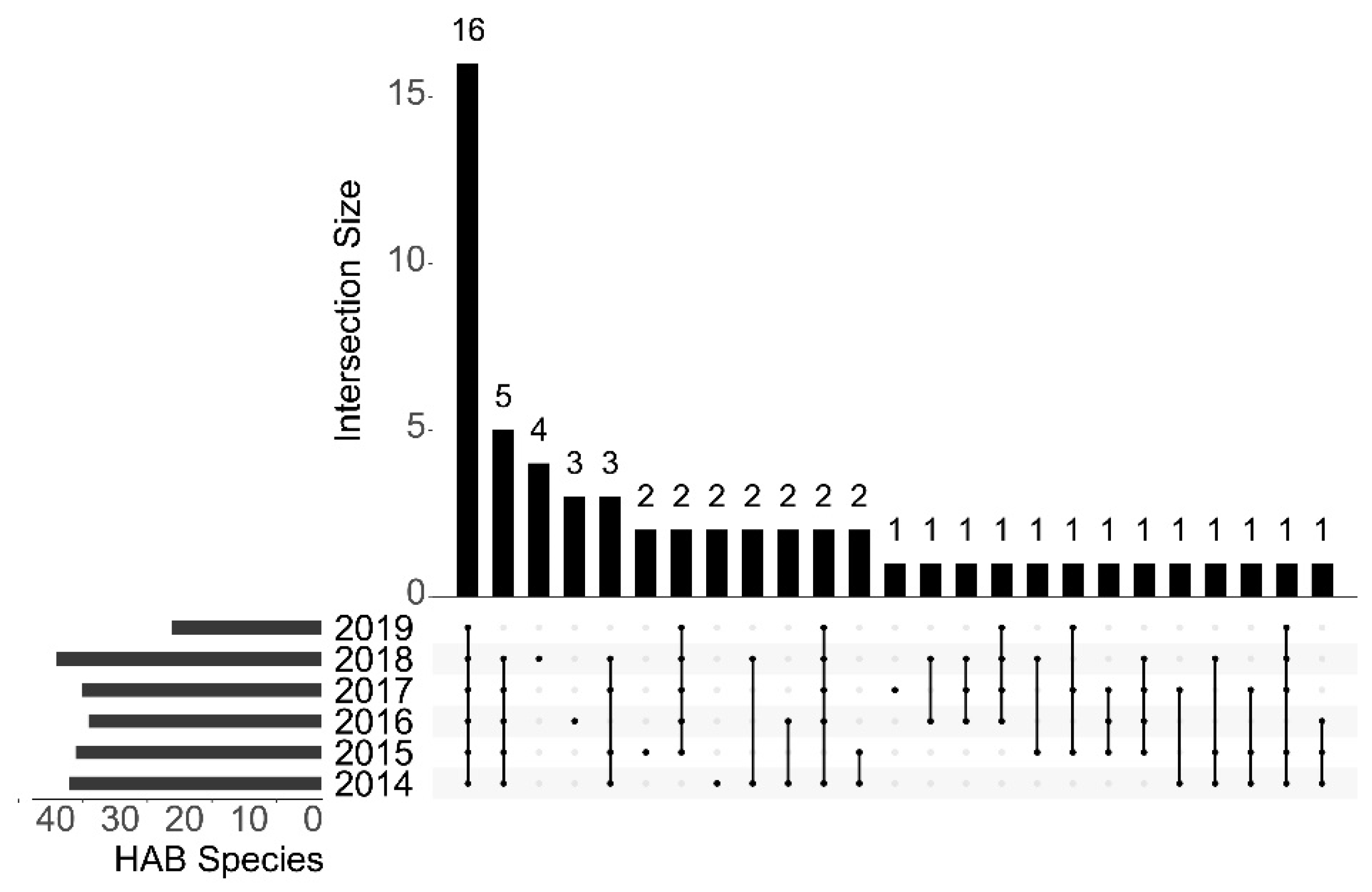
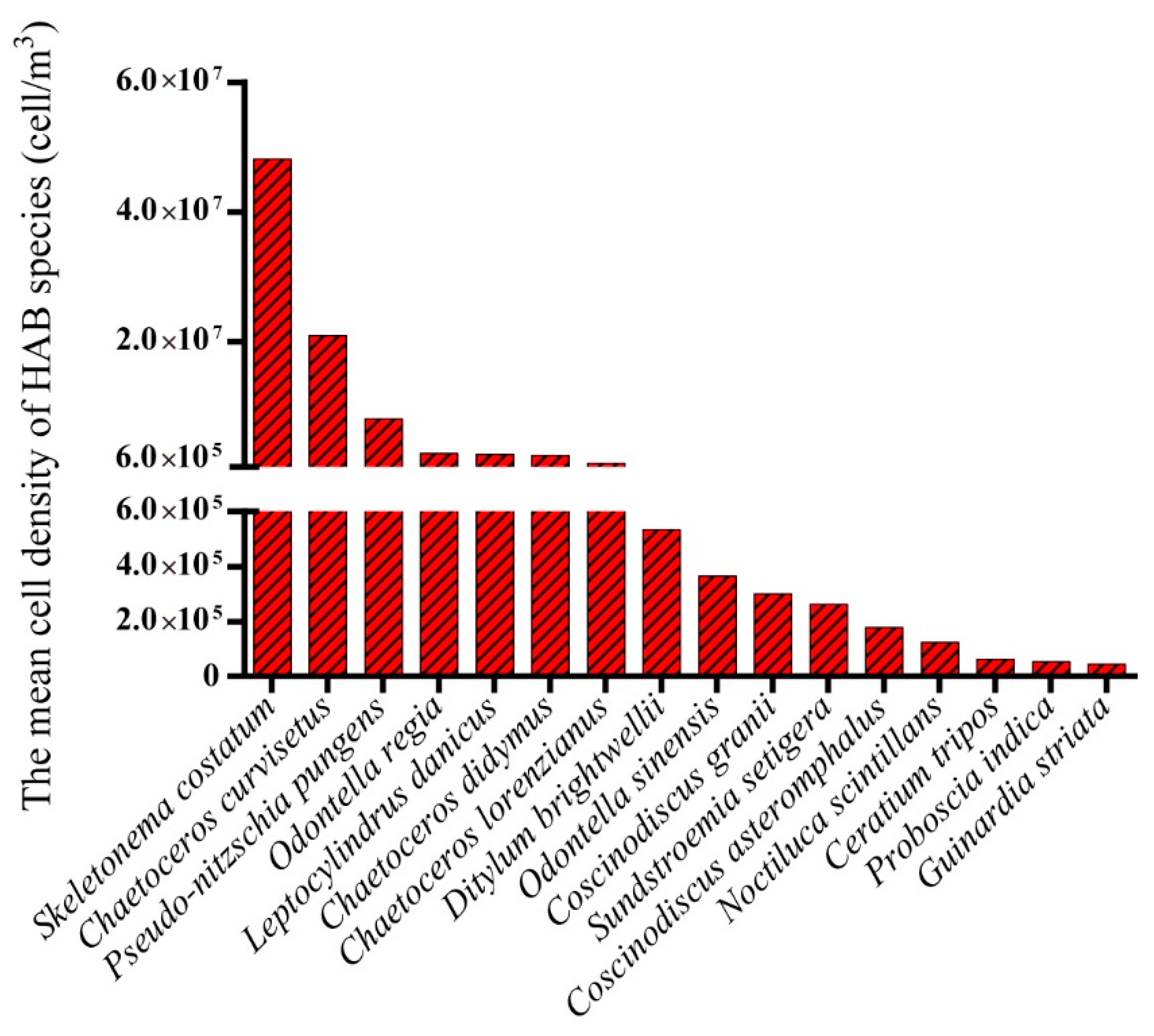
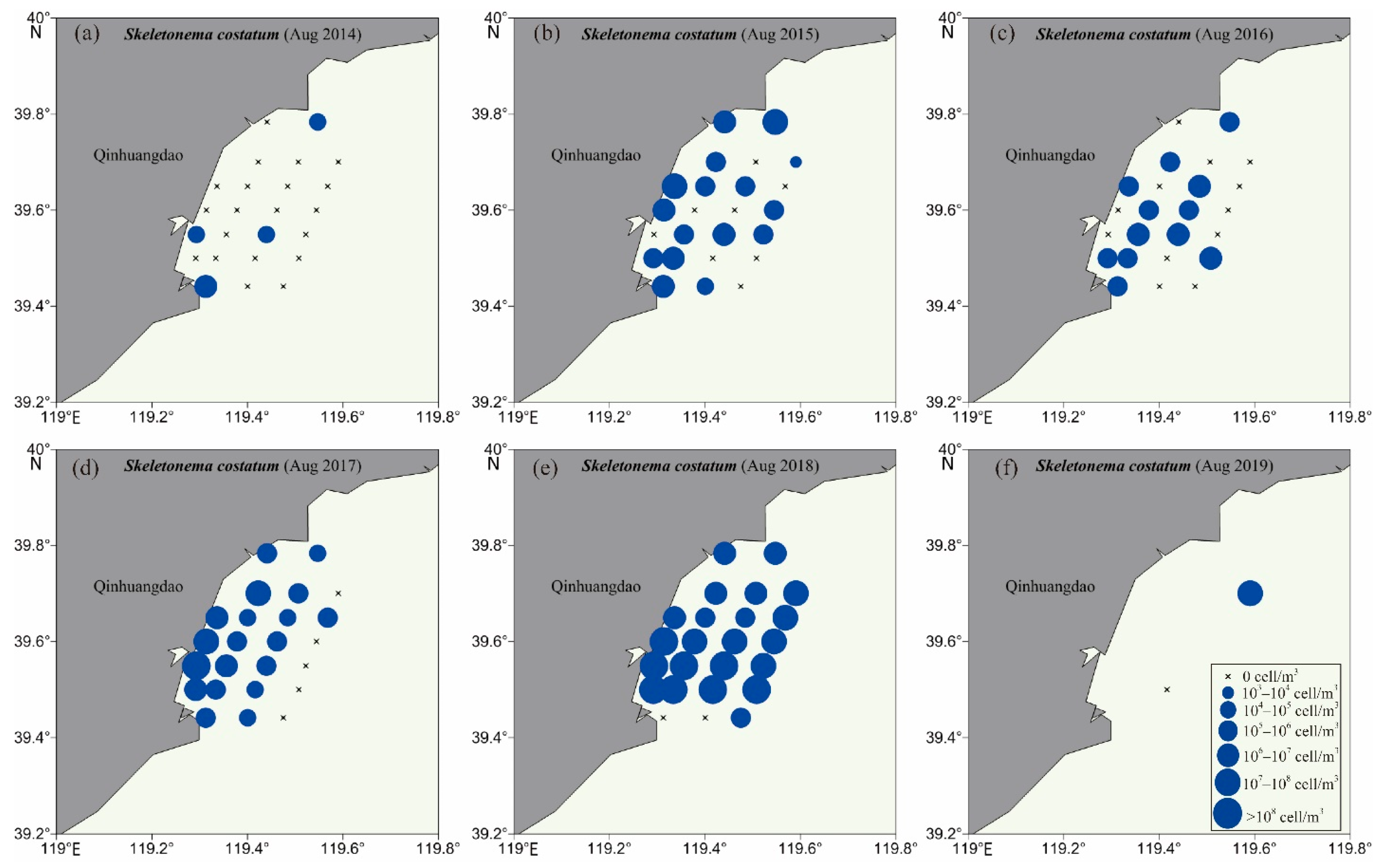
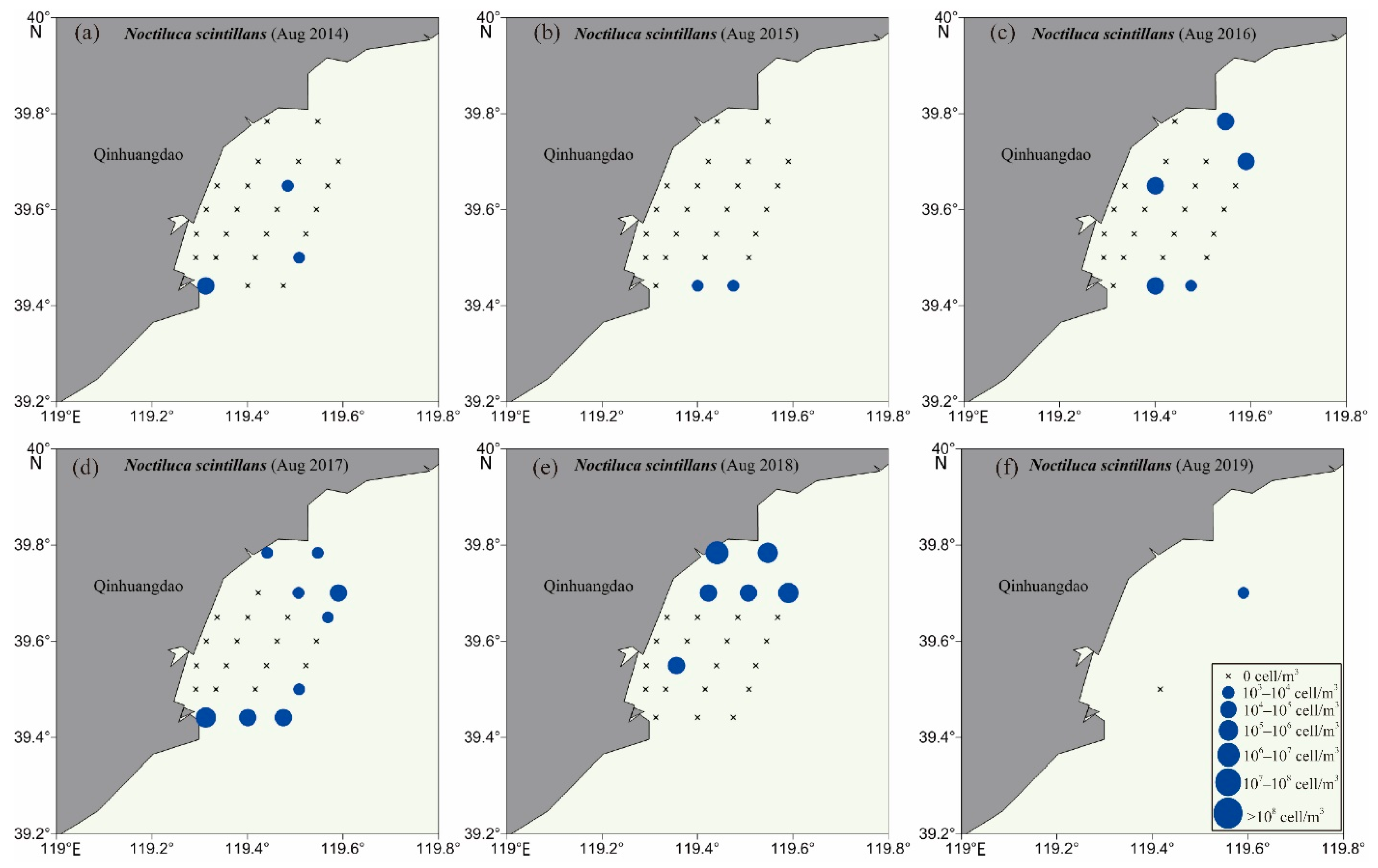
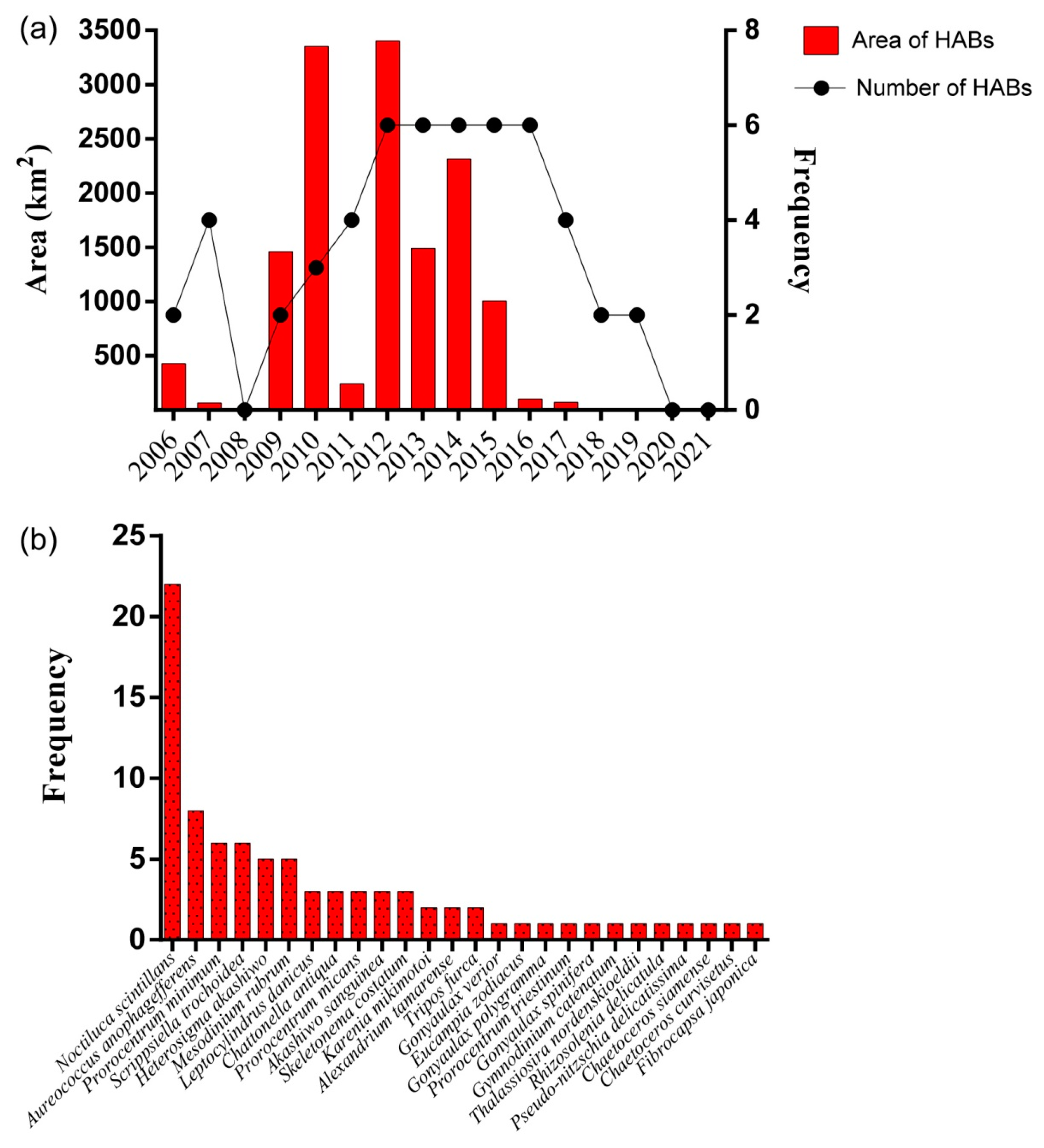
3.2. Biodiversity and Distribution Patterns of HAB Species
3.3. Impact of Environmental Factors on Main HAB Species
4. Discussion
4.1. Interannual Variation of Algae in the Qinhuangdao Coastal Sea
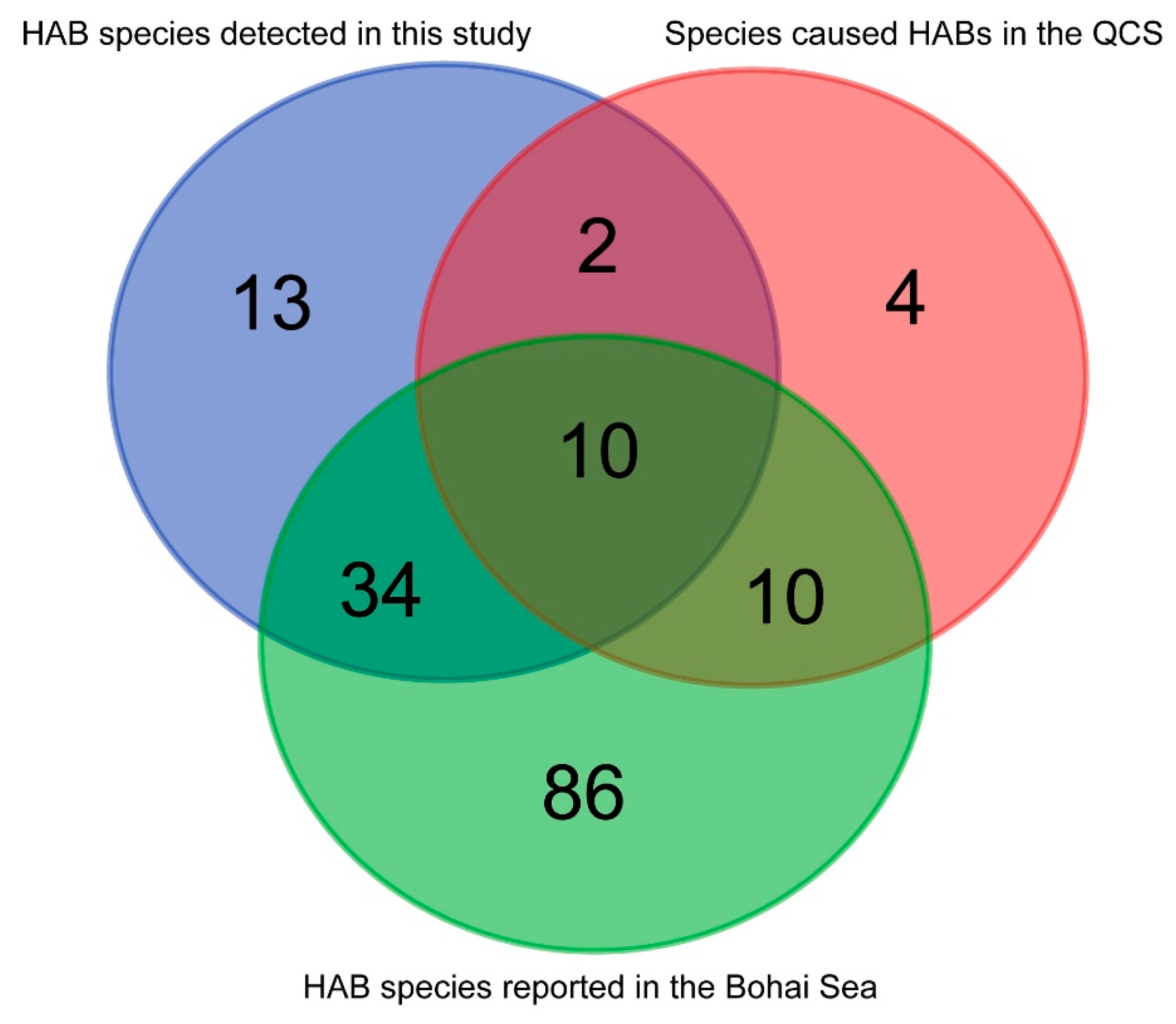
4.2. High Biodiversity of HAB Species in the Qinhuangdao Coastal Sea
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Cembella, A.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Progress in understanding harmful algal blooms: Paradigm shifts and new technologies for research, monitoring, and management. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and golden seaweed tides on the rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.C.; Lü, S.H.; Qi, Y.Z.; Zhou, M.J. Progress and Perspectives of Harmful Algal Bloom Studies in China. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2020, 51, 768–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 1993, 32, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granéli, E.; Weberg, M.; Salomon, P.S. Harmful algal blooms of allelopathic microalgal species: The role of eutrophication. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.M.; Xu, Q.; Gibson, K.; Liu, S.Y.; Chen, N.S. Metabarcoding analysis of harmful algal bloom species in the Changjiang Estuary, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.S.; Huang, H.L. Advances in the study of biodiversity of phytoplankton and red tide species in China (I): The Bohai Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2021, 52, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.Q.; Wang, N.; Wu, N.; Lin, W.N. Temporal and spatial distribution of harmful algal blooms in the Bohai Sea during 1952-2006 based on GIS. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, H.N. The cause of the red tide. Xue Yi 1952, 22, 1–3. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.H.; Huang, J.; Guo, K.M.; Jiang, C.B.; Li, P.S. The analysis of red tide and environmental facotr in Bayuquan, Liaodong Bay. Mar. Forecast. 2005, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Xu, Q.; Gibson, K.; Chen, Y.; Chen, N.S. Molecular characterization of harmful algal blooms in the Bohai Sea using metabarcoding analysis. Harmful Algae 2021, 106, 102066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.F.; Wang, Q.; Guan, C.Y.; Shen, X.X.; Li, R.L. Study on the Occurrence Law of Red Tide and Its Influencing Factors in the Offshore Waters of China from 2001 to 2017. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2020, 56, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.Z.; Yu, R.C.; Zhang, Q.C.; Yan, T.; Zhou, M.J. Pigment characterization for the 2011 bloom in Qinhuangdao implicated “brown tide” events in China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.C.; Qiu, L.M.; Yu, R.C.; Kong, F.Z.; Wang, Y.F.; Yan, T.; Gobler, C.J.; Zhou, M.J. Emergence of brown tides caused by Aureococcus anophagefferens Hargraves et Sieburth in China. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhao, S.L.; Li, J.M. An analysis of red tide characteristics in Qinhuangdao coastal seawater. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MNR. Bulletin of China Marine Disaster; Ministry of Natural Resources: Beijing, China, 1989–2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.Z.; Ma, Z.P.; Hu, Z.X.; Deng, Y.Y.; Yang, A.; Lin, S.H.; Yi, L.; Chai, Z.Y.; Gobler, C.J. 3000 km and 1500-year presence of Aureococcus anophagefferens reveals indigenous origin of brown tides in China. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 4065–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.F.; Tan, L.J.; Wang, J.T. Nutrients structure changes impact the competition and succession between diatom and dinoflagellate in the East China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Han, H.B.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, Y. Molecular identification of the macroalgae that cause green tides in the Bohai Sea, China. Aquat. Bot. 2019, 156, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utermöhl, H. Neue Wege in der quantitativen Erfassung des Plankton. (Mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Ultraplanktons). Mitt. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 1931, 5, 567–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H. Illustrations of Planktons Responsible for the Blooms in Chinese Coastal Waters; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2004. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H.; Zhou, M.J.; Fukuyo, Y.; Matsuda, O.; Lee, S.-G.; Lee, C.-K.; Shulkin, V.; Orlova, T.; Kim, H.-G.; Lu, S.H. Integrated Report on Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs) for the NOWPAP Region; NOWPAP CEARAC: Toyama, Japan, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.Z. Red Tide off the Coast of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1993. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. An Introduction to Mathematical Ecology; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N.; Strobelt, H.; Vuillemot, R.; Pfister, H. UpSet: Visualization of Intersecting Sets. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2014, 20, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Wei, T.Y. ggcor: Extended Tools for Correlation Analysis and Visualization. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/houyunhuang/ggcor (accessed on 27 December 2020).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Oceanic-Adminstration. Bulletin of Marine Ecological Environment of Hebei Province; Department of Natural Resources of Hebei Province: Shijiazhuang, China, 2019–2021. (In Chinese)
- QBEE. Qinhuangdao City Ecological Environment Condition Bulletin; Qinhuangdao Bureau of Ecological Environment: Qinhuangdao, China, 2011–2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bian, M.M.; Song, J.L.; Feng, J.Y.; Liu, Z.L. Occurrence and analysis of red tides in Qinhuangdao sea area. Hebei Fish. 2019, 8, 26–28+48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yu, Z.M.; He, L.Y.; Cheng, F.J.; Cao, X.H.; Song, X.X. Nano- and micro-phytoplankton community characteristics in brown tide bloom-prone waters of the Qinhuangdao coast, Bohai Sea, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Yu, R.C.; Zhou, M.J. Seasonal succession of microalgal blooms from diatoms to dinoflagellates in the East China Sea: A numerical simulation study. Ecol. Model. 2017, 360, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, D.J.; Tang, J.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Liu, Z.G.; Ding, P.X.; He, S.Q. Phytoplankton Distribution and Variation in the Yangtze River Estuary and Its Adjacent Sea. Environ. Sci. 2007, 28, 719–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.C.; Zhang, Q.C.; Kong, F.Z.; Zhou, Z.X.; Chen, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, H.X.; Dai, L.; Yan, T.; Zhou, M.J. Status, impacts and long-term changes of harmful algal blooms in the sea area adjacent to the Changjiang river estuary. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2017, 48, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.Q.; Xiao, W.P.; Liu, X. Spatial-temporal distributions and successional patterns of phytoplankton communities in the Chinese marginal seas. J. Xiamen Univ. 2021, 60, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Liu, X.; Irwin, A.J.; Laws, E.A.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, B. Warming and eutrophication combine to restructure diatoms and dinoflagellates. Water Res. 2018, 128, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Laws, E.A.; Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Huang, B. Responses of marine phytoplankton communities to environmental changes: New insights from a niche classification scheme. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egge, E.S.; Johannessen, T.V.; Andersen, T.; Eikrem, W.; Bittner, L.; Larsen, A.; Sandaa, R.-A.; Edvardsen, B. Seasonal diversity and dynamics of haptophytes in the Skagerrak, Norway, explored by high-throughput sequencing. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 3026–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaulot, D.; Eikrem, W.; Viprey, M.; Moreau, H. The diversity of small eukaryotic phytoplankton (≤3 μm) in marine ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egge, E.S.; Eikrem, W.; Edvardsen, B. Deep-branching Novel Lineages and High Diversity of Haptophytes in the Skagerrak (Norway) Uncovered by 454 Pyrosequencing. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2015, 62, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.J.; Ji, N.J.; Luo, H. Recent Progress in Marine Harmful Algal Bloom Research. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2019, 50, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, U.; Litaker, R.W.; Montresor, M.; Murray, S.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Formal Revision of the Alexandrium tamarense Species Complex (Dinophyceae) Taxonomy: The Introduction of Five Species with Emphasis on Molecular-based (rDNA) Classification. Protist 2014, 165, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilly, E.L.; Halanych, K.M.; Anderson, D.M. Species boundaries and global biogeography of the Alexandrium tamarense complex (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.C.; Niu, Z.; Wang, J.X.; Liu, C.; Kong, F.Z.; Hu, X.K.; Zhao, J.Y.; Yu, R.C. Development of high-resolution chloroplast markers for intraspecific phylogeographic studies of Phaeocystis globosa. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Lan, D.Z.; Huang, Y.H.; Gu, H.F. Effect of Temperature, Salinity and Nutrient on the Growth of Different Strains of Alexandrium tamarense. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2007, 25, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.S. Metabarcoding analysis of harmful algal blooms: Opportunities and challenges. Mar. Sci. 2020, 44, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, F.P.; Min, M.; Pitz, K.; Truelove, N.; Baker, J.; LaScala-Grunewald, D.; Blum, M.; Walz, K.; Nye, C.; Djurhuus, A.; et al. Observing life in the sea using environmental DNA. Oceanography 2021, 34, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Mendez, G.; Faust, K.; Henry, N.; Decelle, J.; Colin, S.; Carcillo, F.; Chaffron, S.; Ignacio-Espinosa, J.C.; Roux, S.; Vincent, F.; et al. Determinants of community structure in the global plankton interactome. Science 2015, 348, 1262073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic units in marker-gene data analysis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Q.; Gibson, K.; Chen, N.S. Metabarcoding dissection of harmful algal bloom species in the East China Sea off Southern Zhejiang Province in late spring. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, F.; He, L.; Cao, X.; Song, X. Molecular diversity and ecological characteristics of the eukaryotic phytoplankton community in the coastal waters of the Bohai Sea, China. Harmful Algae 2017, 61, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Bates, S.S.; Lundholm, N.; Thessen, A.E.; Cochlan, W.P.; Adams, N.G.; Trick, C.G. Pseudo-nitzschia physiological ecology, phylogeny, toxicity, monitoring and impacts on ecosystem health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 271300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Liu, K.Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, N.S. Development of a high-resolution molecular marker for tracking Pseudo-nitzschia pungens genetic diversity through comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 2283–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassus, P.; Chomérat, N.; Hess, P.; Nézan, E. Toxic and Harmful Microalgae of the World Ocean; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae/Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. Ocean climate change, phytoplankton community responses, and harmful algal blooms: A formidable predictive challenge. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smayda, T.J.; Reynolds, C.S. Strategies of marine dinoflagellate survival and some rules of assembly. J. Sea Res. 2003, 49, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| NO | Species | Phylum | Class | Toxicology | Year | HAB Evidence Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Akashiwo sanguinea | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | Ichthyotoxic | 2014/2016/2018 | [22] |
| 2 | Asterionellopsis glacialis | Bacillariophyta | Bacillariophyceae | NO | 2015–2019 | [22] |
| 3 | Bacillaria paxillifera | Bacillariophyta | Bacillariophyceae | NO | 2014–2015 | [22] |
| 4 | Cerataulina pelagica | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2018 | [8] |
| 5 | Ceratium tripos | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [8] |
| 6 | Chaetoceros affinis | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2015/2017–2019 | [8] |
| 7 | Chaetoceros compressus | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2018 | [8] |
| 8 | Chaetoceros curvisetus | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [8] |
| 9 | Chaetoceros debilis | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2015/2018 | [8] |
| 10 | Chaetoceros diadema | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014 | [8] |
| 11 | Chaetoceros didymus | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [8] |
| 12 | Chaetoceros lorenzianus | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [8] |
| 13 | Chaetoceros paradoxus | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2018 | [17] |
| 14 | Chaetoceros peruvianus | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2018 | [22] |
| 15 | Chaetoceros siamense | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2015–2019 | [8] |
| 16 | Chaetoceros socialis | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2015/2018 | [8] |
| 17 | Chattonella marina | Ochrophyta | Raphidophyceae | Ichthyotoxic | 2018 | [8] |
| 18 | Coscinodiscus asteromphalus | Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [8] |
| 19 | Coscinodiscus granii | Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [8] |
| 20 | Coscinodiscus radiatus | Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscophyceae | NO | 2014 | [8] |
| 21 | Coscinodiscus wailesii | Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscophyceae | NO | 2014/2016–2019 | [8] |
| 22 | Dictyocha fibula | Ochrophyta | Dictyochophyceae | NO | 2014–2015/2017–2018 | [22] |
| 23 | Dinophysis acuminata | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | Okadaic acid (OA) and Dinophysis toxin (DTX) | 2014/2018 | [8] |
| 24 | Ditylum brightwellii | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [22] |
| 25 | Eucampia cornuta | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2016–2018 | [8] |
| 26 | Eucampia zodiacus | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2016 | [8] |
| 27 | Guinardia delicatula | Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscophyceae | NO | 2016/2018 | [8] |
| 28 | Guinardia flaccida | Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscophyceae | NO | 2015–2017 | [8] |
| 29 | Guinardia striata | Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [22] |
| 30 | Gymnodinium catenatum | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | Paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs) | 2016 | [17] |
| 31 | Gyrodinium spirale | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2014–2015/2017–2018 | [22] |
| 32 | Leptocylindrus danicus | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [17] |
| 33 | Leptocylindrus minimus | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2016 | [23] |
| 34 | Nitzschia closterium | Bacillariophyta | Bacillariophyceae | NO | 2014–2015/2017–2018 | [8] |
| 35 | Noctiluca scintillans | Dinoflagellata | Noctilucaceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [22] |
| 36 | Odontella mobiliensis | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2018 | [8] |
| 37 | Odontella regia | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [8] |
| 38 | Odontella sinensis | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [22] |
| 39 | Proboscia alata | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2015/2017/2019 | [22] |
| 40 | Proboscia indica | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [22] |
| 41 | Prorocentrum micans | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2018 | [8] |
| 42 | Prorocentrum minimum | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | Tetrodotoxins (TTXs) | 2014/2016 | [8] |
| 43 | Prorocentrum triestinum | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2014–2015/2017 | [22] |
| 44 | Protoperidinium bipes | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2014/2016 | [24] |
| 45 | Protoperidinium conicum | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2016–2019 | [22] |
| 46 | Protoperidinium elegans | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2014–2015 | [22] |
| 47 | Protoperidinium pellucidum | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2014/2017 | [22] |
| 48 | Protoperidinium pentagonum | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2017 | [22] |
| 49 | Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima | Bacillariophyta | Bacillariophyceae | Domoic acid (DA) | 2014–2018 | [8] |
| 50 | Pseudo-nitzschia pungens | Bacillariophyta | Bacillariophyceae | Domoic acid (DA) | 2014–2019 | [22] |
| 51 | Pyrophacus steinii | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2015–2018 | [22] |
| 52 | Rhizosolenia styliformis | Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscophyceae | NO | 2015 | [22] |
| 53 | Skeletonema costatum | Bacillariophyta | Mediophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [22] |
| 54 | Stephanopyxis palmeriana | Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscophyceae | NO | 2014/2016–2019 | [22] |
| 55 | Sundstroemia setigera | Bacillariophyta | Coscinodiscophyceae | NO | 2014–2019 | [8] |
| 56 | Thalassionema nitzschioides | Bacillariophyta | Bacillariophyceae | NO | 2014/2018 | [22] |
| 57 | Tripos breve | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2016 | [22] |
| 58 | Tripos fusus | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2014–2018 | [8] |
| 59 | Tripos massiliensis | Dinoflagellata | Dinophyceae | NO | 2015 | [22] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Su, D.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Y. Biodiversity and Interannual Variation of Harmful Algal Bloom Species in the Coastal Sea of Qinhuangdao, China. Life 2023, 13, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010192
Chen Y, Wang L, Liu Z, Su D, Wang Y, Qi Y. Biodiversity and Interannual Variation of Harmful Algal Bloom Species in the Coastal Sea of Qinhuangdao, China. Life. 2023; 13(1):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010192
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yang, Lu Wang, Zhiliang Liu, Du Su, Yibo Wang, and Yanping Qi. 2023. "Biodiversity and Interannual Variation of Harmful Algal Bloom Species in the Coastal Sea of Qinhuangdao, China" Life 13, no. 1: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010192
APA StyleChen, Y., Wang, L., Liu, Z., Su, D., Wang, Y., & Qi, Y. (2023). Biodiversity and Interannual Variation of Harmful Algal Bloom Species in the Coastal Sea of Qinhuangdao, China. Life, 13(1), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010192






