On the Effect of Heterophilic Antibodies on Serum Levels of Cardiac Troponins: A Brief Descriptive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Influence of Heterophile Antibodies on the Concentrations of cTnT and cTnI: Clinical Data
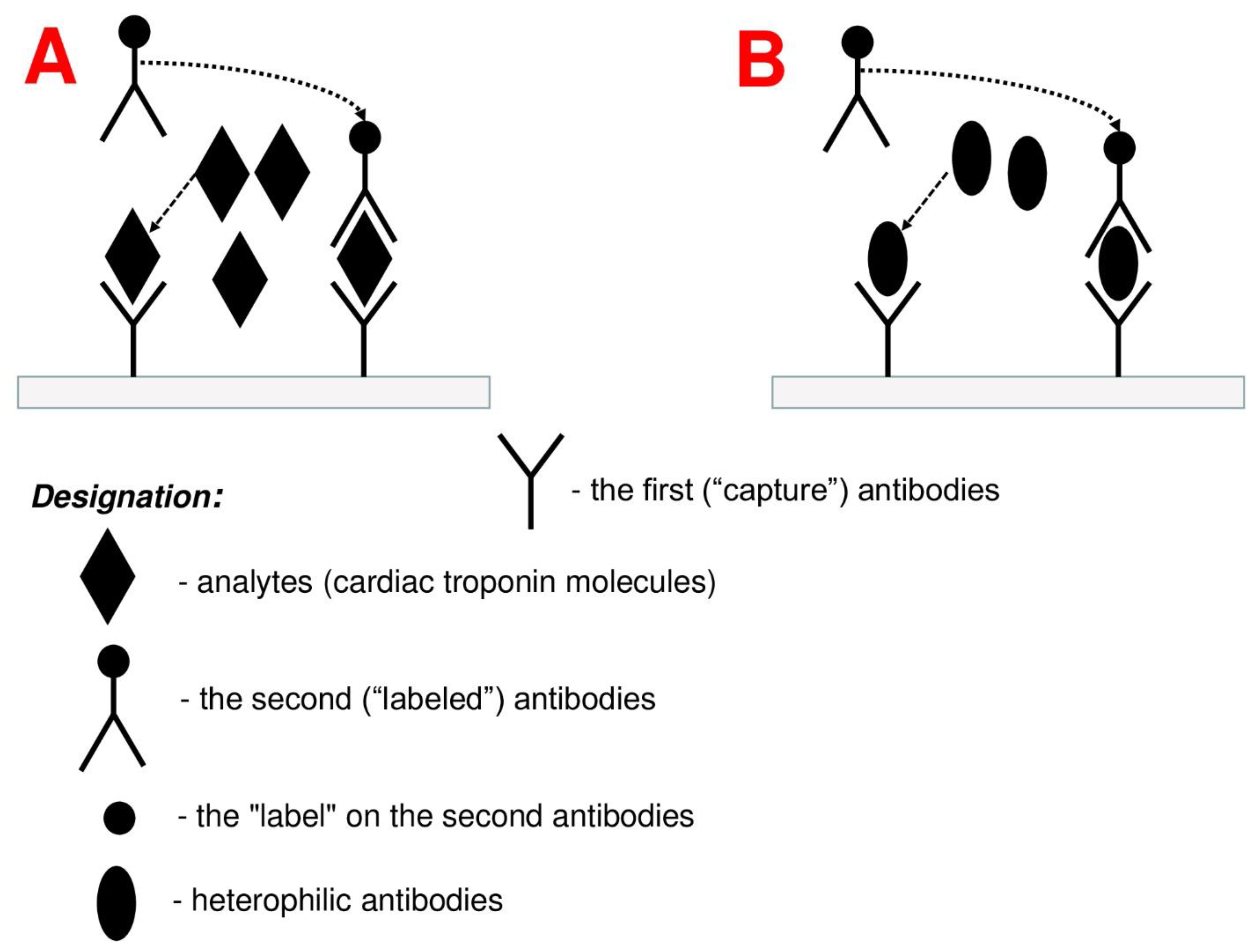
3. Methods for Detection and Control of Heterophile Antibodies
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collet, J.P.; Thiele, H.; Barbato, E.; Barthélémy, O.; Bauersachs, J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Dendale, P.; Dorobantu, M.; Edvardsen, T.; Folliguet, T.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1289–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D.; ESC Scientific Document Group. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 237–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaulin, A. Cardiac Troponins: Contemporary Biological Data and New Methods of Determination. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2021, 17, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Grigorieva, Y.V.; Pavlova, T.V.; Duplyakov, D.V. Diagnostic significance of complete blood count in cardiovascular patients. Russ. J. Cardiol. 2020, 25, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, G.S.; Survant, L.; Voss, E.M.; Smith, S.; Porterfield, D.; Apple, F.S. Cardiac troponin T composition in normal and regenerating human skeletal muscle. Clin. Chem. 1997, 43, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wens, S.C.; Schaaf, G.J.; Michels, M.; Kruijshaar, M.E.; van Gestel, T.J.; Groen, S.I.; Pijnenburg, J.; Dekkers, D.H.; Demmers, J.A.; Verdijk, L.B.; et al. Elevated plasma cardiac troponin T levels caused by skeletal muscle damage in Pompe disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2016, 9, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rusakov, D.Y.; Vologdina, N.N.; Tulayeva, O.N. The development of striated cardiac muscle tissue in the walls of the caval and pulmonary veins. J. Anat. Histopathol. 2015, 4, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, H.; Ushiki, T.; Abe, K. A histological study of the cardiac muscle of the human superior and inferior venae cavae. Arch Histol. Cytol. 1995, 58, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apple, F.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Collinson, P.; Mockel, M.; Ordonez-Llanos, J.; Lindahl, B.; Hollander, J.; Plebani, M.; Than, M.; Chan, M.H.; International Federation of Clinical Chemistry (IFCC) Task Force on Clinical Applications of Cardiac Bio-Markers. IFCC educational materials on selected analytical and clinical applications of high sensitivity cardiac troponin assays. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Abashina, O.E.; Duplyakov, D.V. High-sensitivity cardiac troponins: Detection and central analytical characteristics. Cardiovasc. Ther. Prev. 2021, 20, 2590. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Osuna, A.; Gaze, D.; Grau-Agramunt, M.; Morris, T.; Telha, C.; Bartolome, A.; Bishop, J.J.; Monsalve, L.; Livingston, R.; Estis, J.; et al. Ultrasensitive quantification of cardiac troponin I by a Single Molecule Counting method: Analytical validation and biological features. Clin. Chim Acta 2018, 486, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, D.R.; Lazar, F.L.; Homorodean, C.; Cainap, C.; Focsan, M.; Cainap, S.; Olinic, D.M. High-Sensitivity Troponin: A Review on Characteristics, Assessment, and Clinical Implications. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 9713326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaulin, A.M. Biology of Cardiac Troponins: Emphasis on Metabolism. Biology (Basel) 2022, 11, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervan, P.; Svaguša, T.; Prkačin, I.; Savuk, A.; Bakos, M.; Perkov, S. Urine high sensitive Troponin I measuring in patients with hypertension. Signa Vitae-J. Intensive Care Emerg. Med. 2017, 13 (Suppl. 3), 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Duplyakova, P.D.; Bikbaeva, G.R.; Tukhbatova, A.A.; Grigorieva, E.V.; Duplyakov, D.V. Concentration of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I in the oral fluid in patients with acute myocardial infarction: A pilot study. Russ. J. Cardiol. 2020, 25, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Karslyan, L.S.; Bazyuk, E.V.; Nurbaltaeva, D.A.; Duplyakov, D.V. Clinical and Diagnostic Value of Cardiac Markers in Human Biological Fluids. Kardiologiia 2019, 59, 66–75. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.K.; Bin Mohamad Fathil, M.F.; Gopinath, S.C.; Ruslinda, A.R.; Md Nor, M.N.; Lam, H.Y.; Hashim, U. Cardiac Biomarkers: Invasive to Non-invasive Assessments. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 4270–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M. Possible pathophysiological mechanisms of cardiac troponin level elevations in blood serum and urine in arterial hypertension. Kazan Med. J. 2022, 103, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaii-Dizgah, I.; Riahi, E. Salivary troponin I as an indicator of myocardial infarction. Indian J. Med. Res. 2013, 138, 861–865. [Google Scholar]
- Special Issue "Research on Cardiac Troponins: Past, Present, and Future". Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/life/special_issues/Cardiac_Troponins (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Chaulin, A. Clinical and Diagnostic Value of Highly Sensitive Cardiac Troponins in Arterial Hypertension. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2021, 17, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Duplyakov, D.V. Environmental factors and cardiovascular diseases. Hyg. Sanit. 2021, 100, 223–228. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, K.M.; Lindahl, B. Application of Cardiac Troponin in Cardiovascular Diseases Other Than Acute Coronary Syndrome. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaulin, A.M. Elevation Mechanisms and Diagnostic Consideration of Cardiac Troponins under Conditions Not Associated with Myocardial Infarction. Part 1. Life (Basel) 2021, 11, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Duplyakov, D.V. Comorbidity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Ther. Prev. 2021, 20, 2539. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarino, A.I.; Hamer, M.; Gaze, D.; Collinson, P.; Steptoe, A. The association between cortisol response to mental stress and high sensitivity cardiac troponin T plasma concentration in healthy adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Abashina, O.E.; Duplyakov, D.V. Pathophysiological mechanisms of cardiotoxicity in chemotherapeutic agents. Russ. Open Med. J. 2020, 9, e0305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Duplyakov, D.V. Arrhythmogenic effects of doxorubicin. Complex Issues Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 9, 69–80. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Duplyakov, D.V. Cardioprotective Strategies for Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity: Present and Future. Ration Pharmacother. Cardiol. 2022, 18, 103–112. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Duplyakova, P.D.; Duplyakov, D.V. Circadian rhythms of cardiac troponins: Mechanisms and clinical significance. Russ. J. Cardiol. 2020, 25, 4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, K.; Bissonnette, S.; Inzitari, R.; Schulz, K.; Apple, F.S.; Kavsak, P.A.; Gunsolus, I.L. Independent and combined effects of biotin and hemolysis on high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assays. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 59, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, J.; Beach, L.; Clark, L.; Kavsak, P.A. Matrix and bilirubin interference for high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 442, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, D.S.; Ranjitkar, P.; Yamaguchi, D.; Grenache, D.G.; Greene, D.N. Endogenous alkaline phosphatase interference in cardiac troponin I and other sensitive chemiluminescence immunoassays that use alkaline phosphatase activity for signal amplification. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaulin, A.M. Cardiac troponins: Current information on the main analytical characteristics of determination methods and new diagnostic possibilities. Medwave 2021, 21, e8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, A.; Tsui, A.K.Y.; Alhulaimi, N. Persistent Troponin Elevation in the Setting of an Elevated Rheumatoid Factor: When It Pays to Double Check. CJC Open 2021, 3, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, F.; Rus, H.G.; Maican, A.; Petcovici, M. Anticorpii heterofili [Heterophile antibodies]. Rev. Ig Bacteriol. Virusol. Parazitol. Epidemiol. Pneumoftiziol. Bacteriol. Virusol. Parazitol. Epidemiol. 1989, 34, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Chaulin, A.M. False-Positive Causes in Serum Cardiac Troponin Levels. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2022, 14, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, S.S.; Miller, J.J. Towards a better understanding of heterophile (and the like) antibody interference with modern immunoassays. Clin. Chim Acta 2002, 325, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça Santos, L.; Ribeiro Carvalho, R.; Montenegro Sá, F.; Soares, F.; Pernencar, S.; Castro, R.; Morais, J. Circulating heterophile antibodies causing cardiac troponin elevation: An unusual differential diagnosis of myocardial disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. Case Rep. 2020, 2, 456–460. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, A. When lab tests lie … heterophile antibodies. Aust. Fam. Physician 2014, 43, 391–393. [Google Scholar]
- Bolstad, N.; Warren, D.J.; Nustad, K. Heterophilic antibody interference in immunometric assays. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 27, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzmaurice, T.F.; Brown, C.; Rifai, N.; Wu, A.H.; Yeo, K.T. False increase of cardiac troponin I with heterophilic antibodies. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 2212–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kazmierczak, S.C.; Catrou, P.G.; Briley, K.P. Transient nature of interference effects from heterophile antibodies: Examples of interference with cardiac marker measurements. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2000, 38, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, K.-T.J.; A Storm, C.; Li, Y.; E Jayne, J.; Brough, T.; Quinn-Hall, K.S.; Fitzmaurice, T.F. Performance of the enhanced Abbott AxSYM cardiac troponin I reagent in patients with heterophilic antibodies. Clin. Chim Acta 2000, 292, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uettwiller-Geiger, D.; Wu, A.H.; Apple, F.S.; Jevans, A.W.; Venge, P.; Olson, M.D.; Darte, C.; Woodrum, D.L.; Roberts, S.; Chan, S. Multicenter evaluation of an automated assay for troponin I. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48 Pt 1, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, G.H.; Tideman, P.A. Heterophilic antibody interference with CARDIAC T Quantitative Rapid Assay. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 201–203. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11751561/ (accessed on 10 June 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullova, I.S.; Chaulin, A.M.; Svechkov, A.I.; Pavlova, T.V.; Limareva, L.V.; Duplyakov, D.V. Experimental models of pulmonary embolism. Russ. J. Cardiol. 2022, 27, 4887. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauin, A. The Main Causes and Mechanisms of Increase in Cardiac Troponin Concentrations Other Than Acute Myocardial Infarction (Part 1): Physical Exertion, Inflammatory Heart Disease, Pulmonary Embolism, Renal Failure, Sepsis. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2021, 17, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassin, M.; Cappelletti, P.; Rubin, D.; Zaninotto, M.; Macor, F.; Nicolosi, G.L. Due casi di incremento spurio di troponina I in pazienti con anticorpi eterofili [Two cases of false troponin I increase in patients with heterophile antibodies]. Ital. Heart J. Suppl. 2002, 3, 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Knoblock, R.J.; Lehman, C.M.; Smith, R.A.; Apple, F.S.; Roberts, W.L. False-positive AxSYM cardiac troponin I results in a 53-year-old woman. Arch Pathol. Lab. Med. 2002, 126, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Laterza, O.F.; Hock, K.G.; Pierson-Perry, J.F.; Kaminski, D.M.; Mesguich, M.; Braconnier, F.; Zimmermann, R.; Zaninotto, M.; Plebani, M.; et al. Performance of a revised cardiac troponin method that minimizes interferences from heterophilic antibodies. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaninotto, M.; Mion, M.; Altinier, S.; Forni, M.; Plebani, M. Quality specifications for biochemical markers of myocardial injury. Clin. Chim Acta 2004, 346, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, S.M.; O’Byrne, L.; Finn, J.; Grimes, H.; Daly, K.M. False-positive cardiac troponin I in a routine clinical population. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 89, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mancebo, M.L.; Agulló-Ortuño, M.T.; Gimeno, J.R.; Navarro-Martínez, M.D.; Ruíz-Gómez, J.; Noguera-Velasco, J.A. Heterophile antibodies produce spuriously elevated concentrations of cardiac Troponin I in patients with Legionella pneumophila. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bionda, C.; Rousson, R.; Collin-Chavagnac, D.; Manchon, M.; Chikh, K.; Charrié, A. Unnecessary coronary angiography due to false positive troponin I results in a 51-year-old man. Clin. Chim Acta 2007, 378, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jenkins, M.M.; Brass, D.A.; Ravago, P.G.; Horne, B.D.; Dean, S.B.; Drayton, N. Heterophilic antibody interference in an ultra-sensitive 3-site sandwich troponin I immunoassay. Clin. Chim Acta 2008, 395, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, S.; Lewis, K.; Kazan, V.; Altorok, N.; Taji, J.; Taleb, M.; Lanka, K.; Assaly, R. Fluctuation of spuriously elevated troponin I: A case report. Case Rep. Crit Care 2012, 2012, 585879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nørlund, H.; Bovin, A. False positive troponin I due to heterophile antibodies. Ugeskr. Laeger. 2017, 179, V05170412. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29212594/ (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Nguyen, J.; Thachil, R.; Vyas, N.; Marino, T. Falsely elevated troponin: Rare occurrence or future problem. J. Community Hosp. Intern Med. Perspect. 2016, 6, 32952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manjunath, L.; Yeluru, A.; Rodriguez, F. 27-Year-Old Man with a Positive Troponin: A Case Report. Cardiol. Ther. 2018, 7, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Dupliakov, D.V. Physical Activity And Cardiac Markers: Part 1. Human. Sport Med. 2022, 22, 15–28. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M. Cardiac Troponins Metabolism: From Biochemical Mechanisms to Clinical Practice (Literature Review). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroni, S.; Troiani, E.; Santonocito, C.; Moretti, G.; De Luca, C.; Antenucci, M.; Urbani, A. A false positive case of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin in a patient with acute chest pain: Analytical study of the interference. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 66, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaulin, A.M.; Duplyakov, D.V. Cardiac troponins: Current data on the diagnostic value and analytical characteristics of new determination methods. Cor Vasa 2021, 63, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulin, A.M. Elevation Mechanisms and Diagnostic Consideration of Cardiac Troponins under Conditions Not Associated with Myocardial Infarction. Part 2. Life (Basel) 2021, 11, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaulin, A.M. Main analytical characteristics of laboratory methods for the determination of cardiac troponins: A review from the historical and modern points of view. Orv Hetil. 2022, 163, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavsak, P.A.; Ainsworth, C. A heterophile antibody affecting a contemporary but not a high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assay. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 71, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakusic, N.; Sopek Merkas, I.; Lucinger, D.; Mahovic, D. Heterophile antibodies, false-positive troponin, and acute coronary syndrome: A case report indicating a pitfall in clinical practice. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2021, 5, ytab018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, D.S.; Kavsak, P.A.; Greene, D.N. Variability and Error in Cardiac Troponin Testing: An ACLPS Critical Review. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 148, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Increase in cTnT and cTnI Level Associated with the Myocardial Injury in Primary Cardiac Disease | Increase in cTnT and cTnI Associated with Myocardial Injury in Non-Cardiac Diseases | Increase in cTnT and cTnI Associated with Preanalytical and Analytical Factors |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| Number of Samples, Diagnosis | Frequency of False-Positive break/Troponins Associated with Heterophilic Antibodies, % | Source |
|---|---|---|
| n = 200, healthy people | 2 | [44] |
| n = 101, healthy people | 2 | [45] |
| n = 767, healthy people | 3.1 | [53] |
| n = 60, legionellosis | 47 | [54] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaulin, A.M. On the Effect of Heterophilic Antibodies on Serum Levels of Cardiac Troponins: A Brief Descriptive Review. Life 2022, 12, 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081114
Chaulin AM. On the Effect of Heterophilic Antibodies on Serum Levels of Cardiac Troponins: A Brief Descriptive Review. Life. 2022; 12(8):1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081114
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaulin, Aleksey Michailovich. 2022. "On the Effect of Heterophilic Antibodies on Serum Levels of Cardiac Troponins: A Brief Descriptive Review" Life 12, no. 8: 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081114
APA StyleChaulin, A. M. (2022). On the Effect of Heterophilic Antibodies on Serum Levels of Cardiac Troponins: A Brief Descriptive Review. Life, 12(8), 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081114






