Novel Circoviruses from Birds Share Common Evolutionary Roots with Fish Origin Circoviruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Circovirus Specific PCR and Complete Genome Amplification
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing
2.4. Software
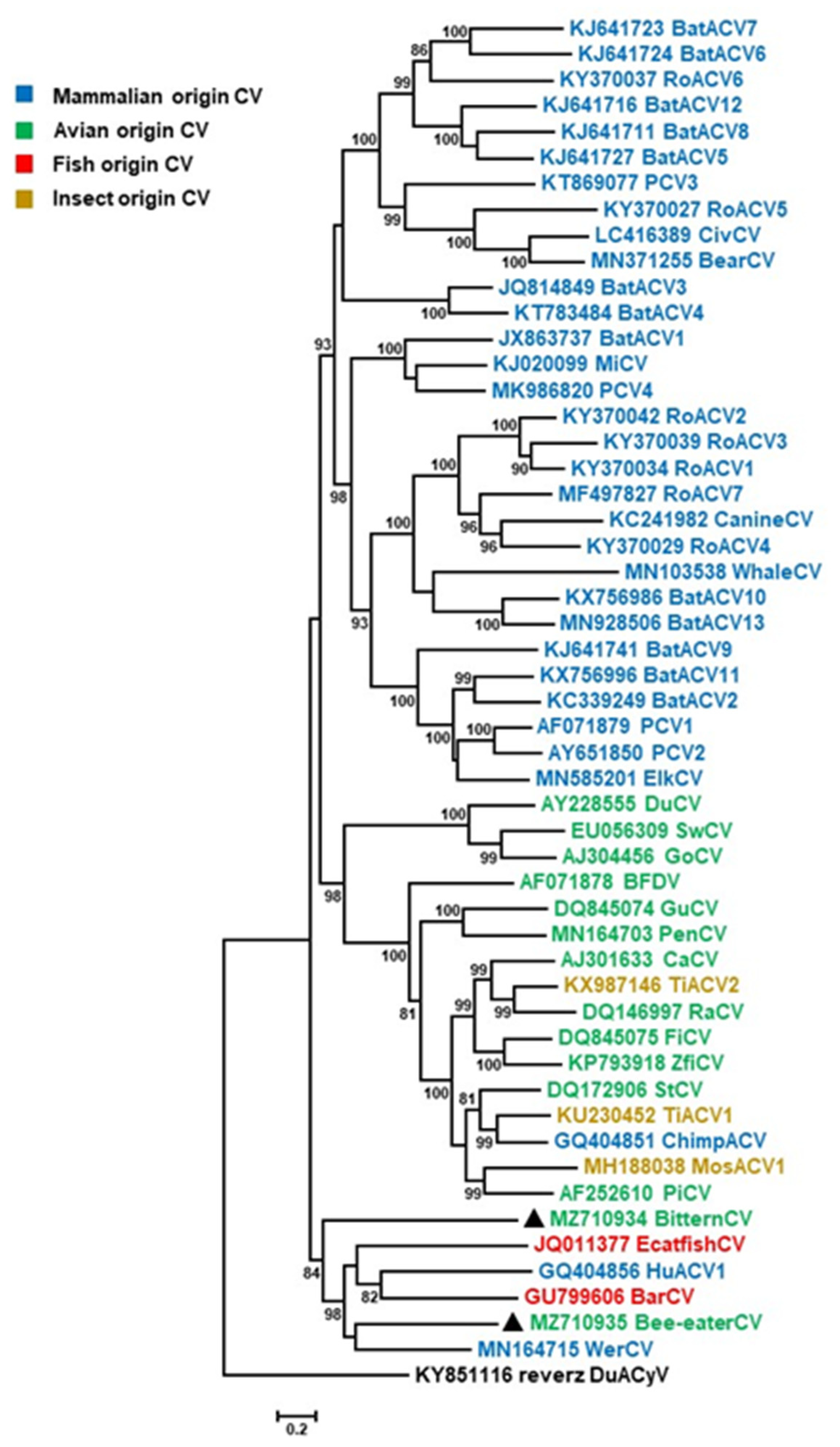
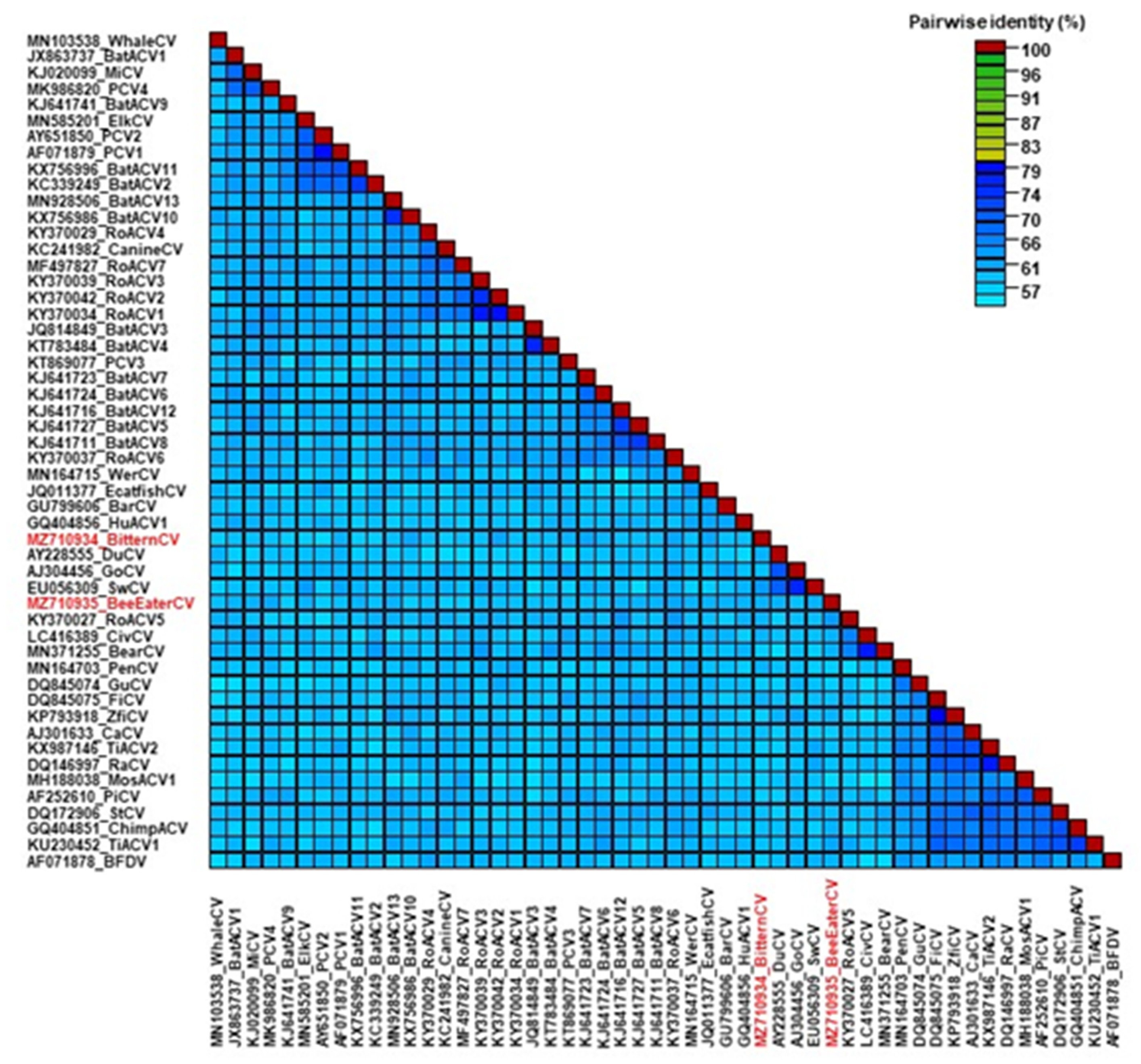
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics approval
References
- Krupovic, M.; Varsani, A.; Kazlauskas, D.; Breitbart, M.; Delwart, E.; Rosario, K.; Yutin, N.; Wolf, Y.I.; Harrach, B.; Zerbini, F.M.; et al. Cressdnaviricota: A virus phylum unifying seven families of Rep-encoding viruses with single-stranded, circular DNA genomes. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00582-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario, K.; Breitbart, M.; Harrach, B.; Segalés, J.; Delwart, E.; Biagini, P.; Varsani, A. Revisiting the taxonomy of the family Circoviridae: Establishment of the genus Cyclovirus and removal of the genus Gyrovirus. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Circella, E.; Legretto, M.; Pugliese, N.; Caroli, A.; Bozzo, G.; Accogli, G.; Lavazza, A.; Camarda, A. Psittacine beak and feather disease-like illness in Gouldian finches (Chloebia gouldiae). Avian Dis. 2014, 58, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Tian, J.; Tan, X.; Yu, H.; Ding, S.; Sun, H.; Yu, X. Pathological observations of an experimental infection of geese with goose circovirus. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, G.P.; Hamel, A.; Lin, L. Detection and characterization of porcine circovirus associated with postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome in pigs. Can. Vet. J. 1997, 38, 385–386. [Google Scholar]
- Raue, R.; Schmidt, V.; Freick, M.; Reinhardt, B.; Johne, R.; Kamphausen, L.; Kaleta, E.; Müller, H.; Krautwald-Junghanns, M.E. A disease complex associated with pigeon circovirus infection, young pigeon disease syndrome. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, B.W.; Niagro, F.D.; Lukert, P.D.; Steffens, W.L.; Latimer, K.S. Characterization of a new virus from cockatoos with psittacine beak and feather disease. Virology 1989, 171, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaprasad, H.L.; Hill, D.; Todd, D.; Smyth, J.A. Circovirus infection in a Gouldian finch (Chloebia gouldiae). Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soike, D.; Kohler, B.; Albrecht, K. A circovirus-like infection of geese related to a runting syndrome. Avian Pathol. 1999, 28, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soike, D.; Albrecht, K.; Hattermann, K.; Schmitt, C.; Mankertz, A. Novel circovirus in mulard ducks with developmental and feathering disorders. Vet. Rec. 2004, 154, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.; Weston, J.; Ball, N.W.; Borghmans, B.J.; Smyth, J.A.; Gelmini, L.; Lavazza, A. Nucleotide sequence-based identification of a novel circovirus of canaries. Avian Pathol. 2001, 30, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, D.; Scott, A.N.; Fringuelli, E.; Shivraprasad, H.L.; Gavier-Widen, D.; Smyth, J.A. Molecular characterization of novel circoviruses from finch and gull. Avian Pathol. 2007, 36, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehér, E.; Kaszab, E.; Forró, B.; Bali, K.; Marton, S.; Lengyel, G.; Bányai, K. Genome sequence of a mallard duck origin cyclovirus, DuACyV-1. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3925–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaszab, E.; Marton, S.; Forró, B.; Bali, K.; Lengyel, G.; Bányai, K.; Fehér, E. Characterization of the genomic sequence of a novel CRESS DNA virus identified in Eurasian jay (Garrulus glandarius). Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaszab, E.; Lengyel, G.; Marton, S.; Dán, Á.; Bányai, K.; Fehér, E. Occurrence and genetic diversity of CRESS DNA viruses in wild birds: A Hungarian study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Kapoor, A.; Slikas, B.; Bamidele, O.S.; Wang, C.; Shaukat, S.; Masroor, M.A.; Wilson, M.L.; Ndjango, J.B.; Peeters, M.; et al. Multiple diverse circoviruses infect farm animals and are commonly found in human and chimpanzee feces. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1674–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A. AliView: A fast and lightweight alignment viewer and editor for large datasets. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhire, B.M.; Varsani, A.; Martin, D.P. SDT: A virus classification tool based on pairwise sequence alignment and identity calculation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario, K.; Duffy, S.; Breitbart, M. A field guide to eukaryotic circular single-stranded DNA viruses: Insights gained from metagenomics. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1851–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecis, R.; Mucedda, M.; Pidinchedda, E.; Zobba, R.; Pittau, M.; Alberti, A. Genomic characterization of a novel bat-associated circovirus detected in European Miniopterus schreibersii bats. Virus Genes 2020, 56, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.; Jiang, T.; Hu, T.; Mi, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Feng, J.; Fan, Q.; He, B.; Tu, C. Molecular characterization of a novel bat-associated circovirus with a poly-T tract in the 3′ intergenic region. Virus Res. 2018, 250, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldován, N.; Balázs, Z.S.; Tombácz, D.; Csabai, Z.; Szűcs, A.; Snyder, M.; Boldogkői, Z. Multi-platform analysis reveals a complex transcriptome architecture of a circovirus. Virus Res. 2017, 237, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tian, B.; Graber, J.H. Signals for pre-mRNA cleavage and polyadenylation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2012, 3, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, E.; Mihalov-Kovács, E.; Kaszab, E.; Malik, Y.S.; Marton, S.; Bányai, K. Genomic diversity of CRESS DNA viruses in the eukaryotic virome of swine feces. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandini, V.; Dugger, K.M.; Ballard, G.; Elrod, M.; Schmidt, A.; Ruoppolo, V.; Lescroël, A.; Jongsomjit, D.; Massaro, M.; Pennycook, J.; et al. Identification of a novel Adelie penguin circovirus at Cape Crozier (Ross Island, Antarctica). Viruses 2019, 11, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.K.; Das, S.; Roby, J.A.; Sarker, S.; Luque, D.; Raidal, S.R.; Forwood, J.K. Structural perspectives of beak and feather disease virus and porcine circovirus proteins. Viral Immunol. 2021, 34, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, L.; Martin, D.P.; Warburton, L.; Perrin, M.; Horsfield, W.; Kingsley, C.; Rybicki, E.P.; Williamson, A.L. Evidence of unique genotypes of beak and feather disease virus in southern Africa. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9277–9284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.M.; Hon, C.C.; Lam, T.Y.; Li, V.Y.; Wong, C.K.; de Oliveira, T.; Leung, F.C. Evidence for recombination in natural populations of porcine circovirus type 2 in Hong Kong and mainland China. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olvera, A.; Cortey, M.; Segalés, J. Molecular evolution of porcine circovirus type 2 genomes: Phylogeny and clonality. Virology 2007, 357, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piewbang, C.; Jo, W.K.; Puff, C.; van der Vries, E.; Kesdangsakonwut, S.; Rungsipipat, A.; Kruppa, J.; Jung, K.; Baumgärtner, W.; Techangamsuwan, S.; et al. Novel canine circovirus strains from Thailand: Evidence for genetic recombination. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lőrincz, M.; Cságola, A.; Farkas, S.L.; Székely, C.; Tuboly, T. First detection and analysis of a fish circovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lőrincz, M.; Dán, Á.; Láng, M.; Csaba, G.; Tóth, A.G.; Székely, C.; Cságola, A.; Tuboly, T. Novel circovirus in European catfish (Silurus glanis). Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patterson, Q.M.; Kraberger, S.; Martin, D.P.; Shero, M.R.; Beltran, R.S.; Kirkham, A.L.; Aleamotu’a, M.; Ainley, D.G.; Kim, S.; Burns, J.M.; et al. Circoviruses and cycloviruses identified in Weddell seal fecal samples from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 95, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D. Circoviruses: Immunosuppressive threats to avian species: A review. Avian Pathol. 2000, 29, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, T.; Dziewulska, D.; Tykałowski, B.; Śmiałek, M.; Kowalczyk, J.; Koncicki, A. Immunogenicity of pigeon circovirus recombinant capsid protein in pigeons. Viruses. 2018, 31, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Shang, H.; Zhou, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Gao, P.; Guo, P.; Zhu, R.; Sun, Z.; et al. Effects of duck circovirus on immune function and secondary infection of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Bird Species | Sample | Data about the Rescued Bird |
|---|---|---|
| Common blackbird, Turdus merula | B,K,L,T | Leg injury |
| K,L | Traumatic injuries, internal bleeding | |
| K,L,S | Hemorrhagic fluid in the thoracoabdominal cavity | |
| Common buzzard, Buteo buteo | K,L,S | Caseonecrotic granulomas in lung, liver, and gizzard; mycobacteriosis |
| K,L | Electric shock, necrotizing leg | |
| Common crane, Grus grus | Lesion | Signs of pox virus infection |
| Common house martin, Delichon urbicum | K,L | NA |
| L | Eye lesions, small, pale kidneys | |
| Common kestrel, Falco tinnunculus | K,L | Traumatic injuries |
| K,L | Wing injury | |
| B,K,L | NA | |
| K,L | Electric shock | |
| K,L | Electric shock | |
| Common kingfisher, Alcedo atthis | K,L | NA |
| Common pheasant, Phasianus colchicus | K,L,S | NA |
| Eurasian woodcock, Scolopax rusticola | K,L | Shot injury of the breast |
| European bee-eater, Merops apiaster | K,L | Wing injury, weight loss, degenerated kidneys |
| European Green Woodpecker, Picus viridis | B,K,L,S | Head injury |
| European honey buzzard, Pernis apivorus | K,L | Traumatic injuries |
| Eurasian sparrowhawk, Accipiter nisus | B,K,L | Wing injury |
| K,L | Weight loss, bleeding in the stomach | |
| Great cormorant, Phalacrocorax carbo | K,L | Traumatic injuries, tested positive for polyomavirus |
| Great spotted woodpecker, Dendrocopos major | K,L | Traumatic injuries |
| Grey heron, Ardea cinerea | K,L | Necrotizing wing, visceral gout |
| Little bittern, Ixobrychus minutus | B,K,L | Wing injury, poor body condition, weight loss, enlarged liver with lesions |
| B,K,L | Traumatic injuries of the left body site, kidney injury | |
| B,K,L | Poor body condition, broken lower mandible, visceral gout | |
| Little owl, Athene noctua | K,L | Poor body condition and weight loss |
| Mute swan, Cygnus olor | K,L | Weight loss, diarrhea |
| Tawny owl, Strix aluco | K | NA |
| K,L | Enlarged liver, liver failure, pale kidneys | |
| Water rail, Rallus aquaticus | K,L | Pale kidneys |
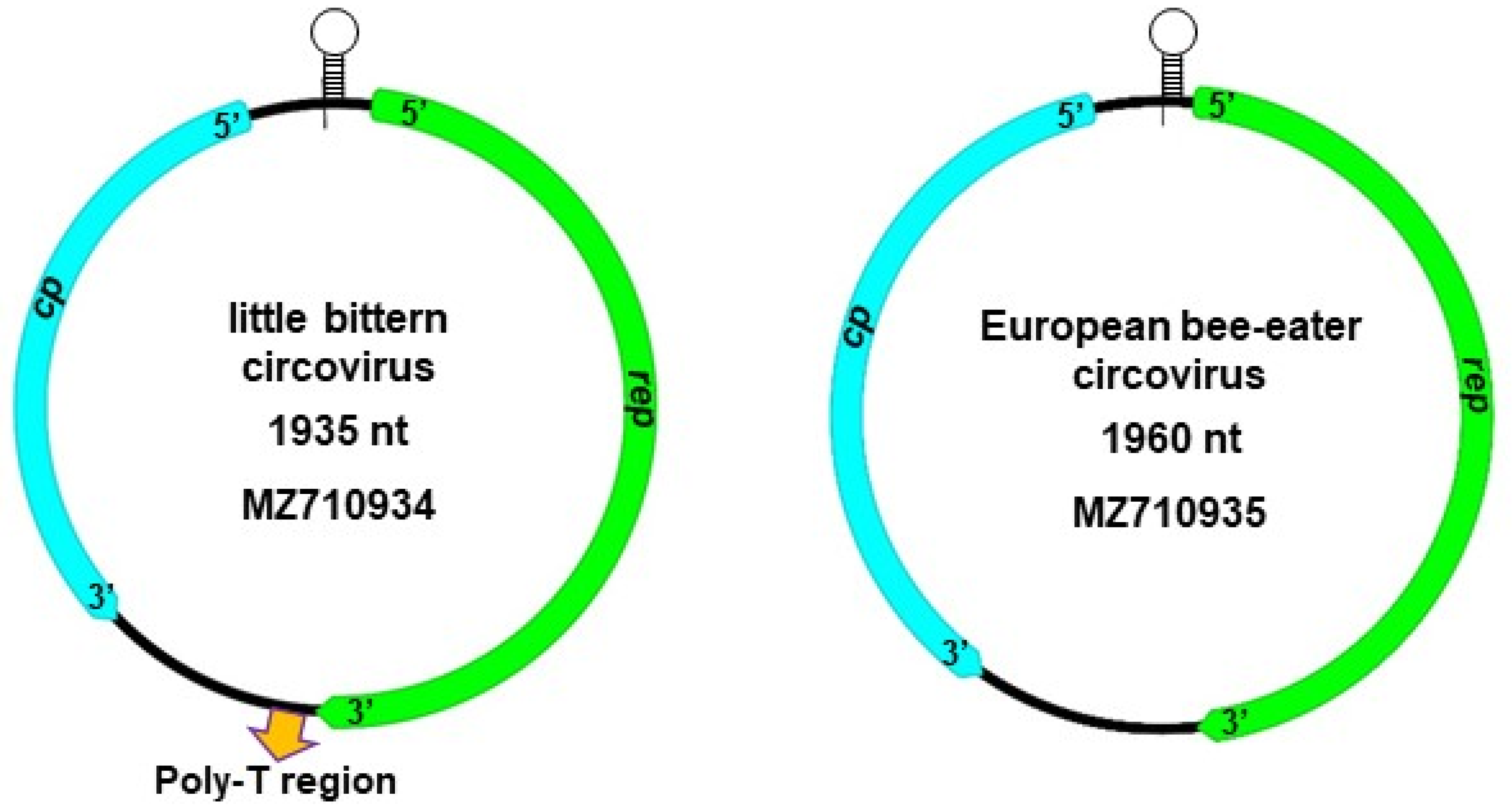
| Little Bittern Circovirus | European Bee-Eater Circovirus | |
|---|---|---|
| Genome | 1935 nt | 1960 nt |
| 5′ intergenic region | nt 1859–51 | nt 1894–33 |
| Nonanucleotide | TAGTATTAC | TAGTATTAC |
| Stem-loop inverted repeat | CACAGGCGCCGG | GCCGAGGTGGCCG |
| rep | nt 52–999 (315 aa) | nt 34–945 (303 aa) |
| RCR motif I | MTLNN | FTLNN |
| RCR motif II | PHLQG | PHLQG |
| RCR motif III | YCSK | YCSK |
| Walker-A motif | GPPGCGKT | GPPGCGKS |
| Walker-B motif | VIDDF | IVDDF |
| Motif C | ITSN | ITSN |
| cp | nt 1858–1229 (209 aa) | nt 1893–1171 (240 aa) |
| 3′ intergenic region | nt 1000–1228 | nt 946–1170 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fehér, E.; Kaszab, E.; Bali, K.; Hoitsy, M.; Sós, E.; Bányai, K. Novel Circoviruses from Birds Share Common Evolutionary Roots with Fish Origin Circoviruses. Life 2022, 12, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030368
Fehér E, Kaszab E, Bali K, Hoitsy M, Sós E, Bányai K. Novel Circoviruses from Birds Share Common Evolutionary Roots with Fish Origin Circoviruses. Life. 2022; 12(3):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030368
Chicago/Turabian StyleFehér, Enikő, Eszter Kaszab, Krisztina Bali, Márton Hoitsy, Endre Sós, and Krisztián Bányai. 2022. "Novel Circoviruses from Birds Share Common Evolutionary Roots with Fish Origin Circoviruses" Life 12, no. 3: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030368
APA StyleFehér, E., Kaszab, E., Bali, K., Hoitsy, M., Sós, E., & Bányai, K. (2022). Novel Circoviruses from Birds Share Common Evolutionary Roots with Fish Origin Circoviruses. Life, 12(3), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12030368








