A Pipeline for Phasing and Genotype Imputation on Mixed Human Data (Parents-Offspring Trios and Unrelated Subjects) by Reviewing Current Methods and Software
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
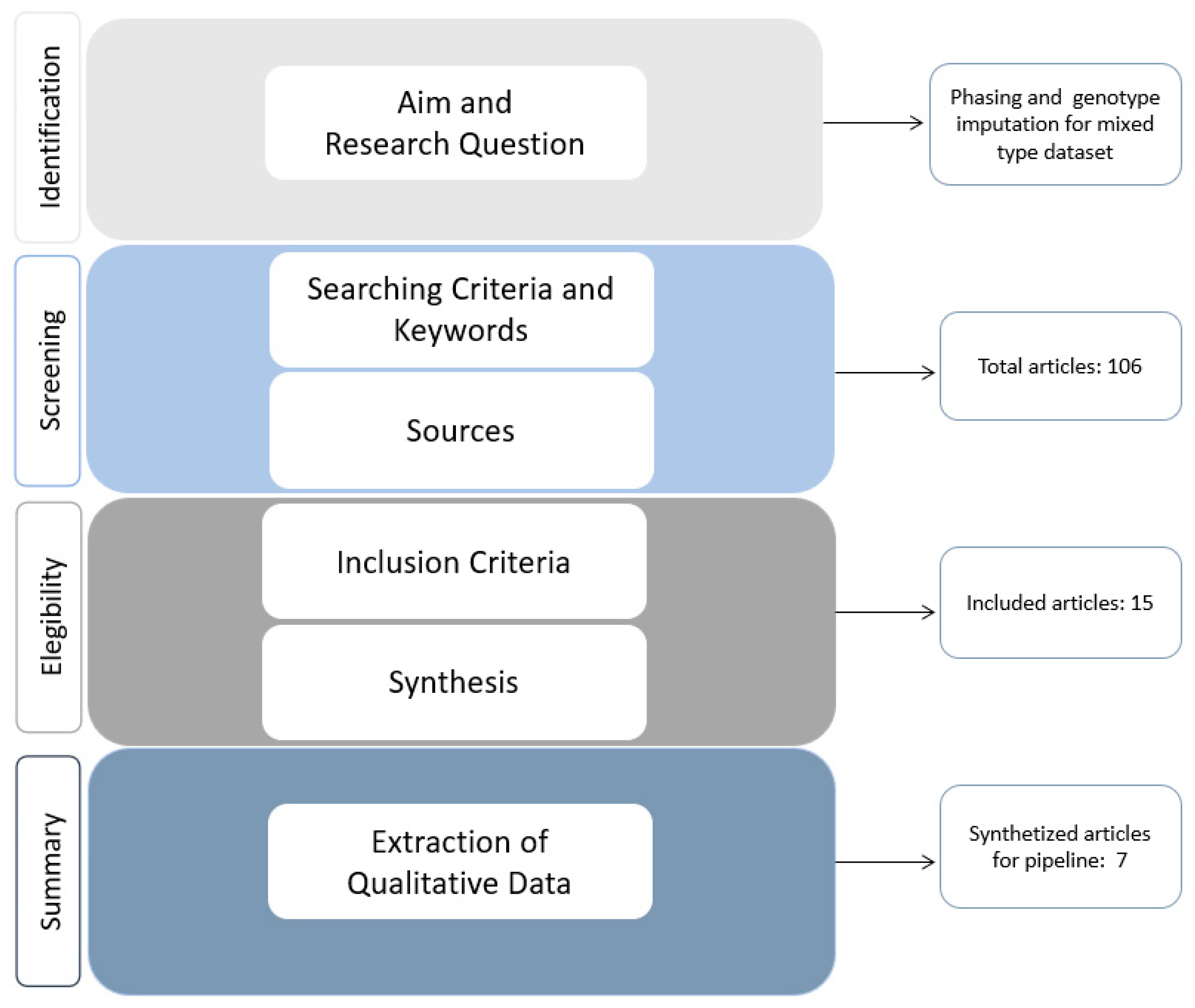
- Definition of the aim and research questionOur main research question was: “To define our feasible pipeline, which is the algorithm, and consequently the software, that can be used for performing genotype imputation and, if required, pre-phasing in the case of mixed type data?”.
- Definition of the searching strategy and keywordsThe search strategy was based on the inclusion of papers which contained the following topics: (i) imputation and phasing methods for genotypic data in trio or nuclear families and/or (ii) imputation and phasing methods in unrelated subjects; papers related to both (i) and (ii) had to contain (iii) free software for imputation and/or phasing from a SNP genotyping platform. The keywords considered were: genotype imputation, haplotype phasing, haplotype estimation, freeware, Hidden Markov Model (HMM), trio, case-control, LD-based method, IBD-based method, nuclear data, family data, related subjects, unrelated subjects, SNP genotyping platform, and SNP array.
- Definition of information sourcesTo retrieve the documents, we used NCBI-PubMed and Google Scholar, selecting both original research articles and reviews. Our literature search was carried out in February 2022.
- Selection process: definition of the inclusion criteriaThe inclusion criteria for the selected papers were the following: (i) documents published in English; (ii) documents that were open access; (iii) documents that clearly described the methods and algorithms used or discussed; and (iv) scientific papers, software manuals, and online tutorials, which refer to published scientific works in which a freeware is used. No limits were set as to year of publication. Two authors (GNB, TF) independently screened the full text for all the papers, as the abstracts did not allow us to obtain the information required.
- Extraction of qualitative dataAll the information gathered was reported in a table containing: (i) the article reference; (ii) the type of study; (iii) the topic covered, i.e., phasing, imputation, or both; (iv) the type of data analyzed; d) the software used; and (v) the algorithm/s on which the software relies/y.
- Reporting synthesis: summary of qualitative dataThe qualitative synthesis was carried out by considering and discussing software features and algorithms most suitable for mixed data (trios, duos, and unrelated subjects) following the PRISMA guidelines [56] and critical review description outlined by Grant and Boot [54]. Our aim was to summarize how to implement software for haplotype phasing and genomic imputation while controlling for bias introduced by imputation on mixed data.
3. Results
3.1. Critical Review
3.2. Pipeline for Genotype Imputation
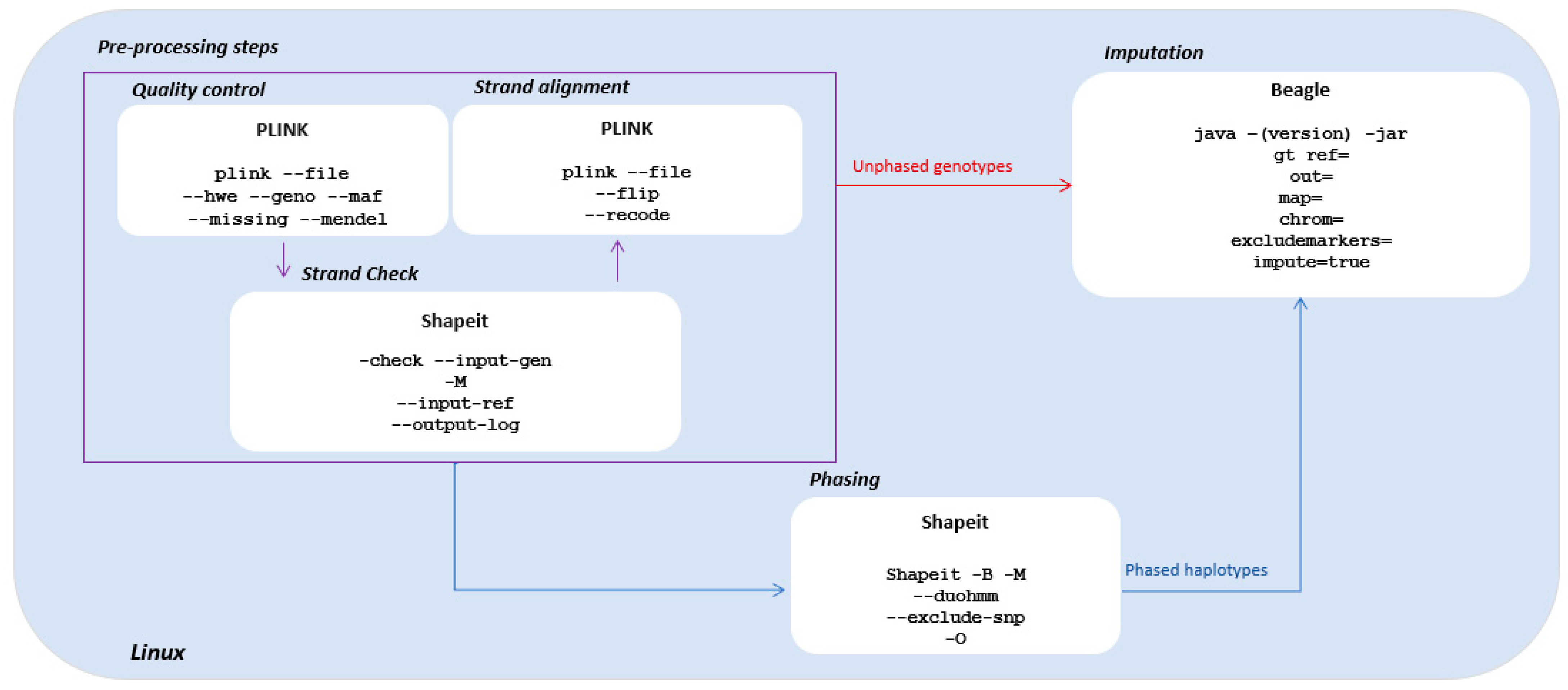
3.2.1. Pre-Processing Steps
3.2.2. Imputation with Pre-Phased Haplotypes
3.2.3. Imputation with Unphased Genotypes
3.2.4. Quality Control Check after Imputation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marchini, J.; Howie, B. Genotype Imputation for Genome-Wide Association Studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daya, M.; der Merwe, L.; Galal, U.; Möller, M.; Salie, M.; Chimusa, E.R.; Galanter, J.M.; van Helden, P.D.; Henn, B.M.; Gignoux, C.R.; et al. A Panel of Ancestry Informative Markers for the Complex Five-Way Admixed South African Coloured Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, N.T.; Freytag, S.; Bickeboeller, H. Coverage and Efficiency in Current SNP Chips. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howie, B.; Marchini, J.; Stephens, M. Genotype Imputation with Thousands of Genomes. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2011, 1, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, K.; Das, S.; LeFaive, J.; Kwong, A.; Pleiness, J.; Forer, L.; Schönherr, S.; Fuchsberger, C.; Smith, A.V.; Abecasis, G.R. Meta-Imputation: An Efficient Method to Combine Genotype Data after Imputation with Multiple Reference Panels. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, D.; Bohra, A.; Thudi, M.; Varshney, R.K. Fine Mapping and Gene Cloning in the Post-NGS Era: Advances and Prospects. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 1791–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhury, O.; Chakrabarty, A.; Emrich, S.J. Highly Accurate and Efficient Data-Driven Methods for Genotype Imputation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2019, 16, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.W.; Hamblin, M.T.; Jannink, J.L. Evaluating Imputation Algorithms for Low-Depth Genotyping-by-Sequencing (GBS) Data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.S.; Khalid, N.; Carlson, C.; Zhao, L.P. Estimating Haplotype Frequencies and Standard Errors for Multiple Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms. Biostatistics 2003, 4, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasaniuc, B.; Rohland, N.; McLaren, P.J.; Garimella, K.; Zaitlen, N.; Li, H.; Gupta, N.; Neale, B.M.; Daly, M.J.; Sklar, P.; et al. Extremely Low-Coverage Sequencing and Imputation Increases Power for Genome-Wide Association Studies. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sidore, C.; Kang, H.M.; Boehnke, M.; Abecasis, G.R. Low-Coverage Sequencing: Implications for Design of Complex Trait Association Studies. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyholt, D.R.; Low, S.K.; Anderson, C.A.; Painter, J.N.; Uno, S.; Morris, A.P.; MacGregor, S.; Gordon, S.D.; Henders, A.K.; Martin, N.G.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Meta-Analysis Identifies New Endometriosis Risk Loci. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marchini, J. Haplotype Estimation and Genotype Imputation. Handb. Stat. Genom. 2019, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, W.; Fu, G.; Ma, L.; Richards, J.; Rao, W.; Bythwood, T.; Guo, S.; Song, Q. High-Accuracy Haplotype Imputation Using Unphased Genotype Data as the References. Gene 2015, 572, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delaneau, O.; Zagury, J.F.; Robinson, M.R.; Marchini, J.L.; Dermitzakis, E.T. Accurate, Scalable and Integrative Haplotype Estimation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabe-Bordbar, S.; Emad, A.; Zhao, S.D.; Sinha, S. A Closer Look at Cross-Validation for Assessing the Accuracy of Gene Regulatory Networks and Models. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, L.; Willer, C.; Sanna, S.; Abecasis, G. Genotype Imputation. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 387–406. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.A.; Pettersson, F.H.; Clarke, G.M.; Cardon, L.R.; Morris, A.P.; Zondervan, K.T. Data Quality Control in Genetic Case-Control Association Studies. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- al Bkhetan, Z.; Chana, G.; Ramamohanarao, K.; Verspoor, K.; Goudey, B. Evaluation of Consensus Strategies for Haplotype Phasing. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, S.R.; Browning, B.L. Haplotype Phasing: Existing Methods and New Developments. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Zhi, D.; Zhang, K.; Gao, G.; Limdi, N.A.; Liu, N. Practical Consideration of Genotype Imputation: Sample Size, Window Size, Reference Choice, and Untyped Rate. Stat. Interface 2011, 4, 339–351. [Google Scholar]
- Durbin, R.M.; Burton, J.; Carter, D.M.; Churcher, C.; Coffey, A.; Cox, A.; Palotie, A.; Quail, M.; Skelly, T.; Stalker, J.; et al. A Map of Human Genome Variation from Population-Scale Sequencing The 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. Nature 2011, 467, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmont, J.W.; Boudreau, A.; Leal, S.M.; Hardenbol, P.; Pasternak, S.; Wheeler, D.A.; Willis, T.D.; Yu, F.; Yang, H.; Gao, Y.; et al. A Haplotype Map of the Human Genome. Nature 2005, 437, 1299–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Yuan, N.; Yang, M.; Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Sheng, X.; Wu, J.; Xiao, J. Comprehensive Assessment of Genotype Imputation Performance. Hum. Hered. 2019, 83, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, A.; Masson, G.; Frigge, M.L.; Gylfason, A.; Zusmanovich, P.; Thorleifsson, G.; Olason, P.I.; Ingason, A.; Steinberg, S.; Rafnar, T.; et al. Detection of Sharing by Descent, Long-Range Phasing and Haplotype Imputation. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wood, A.R.; Perry, J.R.B.; Tanaka, T.; Hernandez, D.G.; Zheng, H.-F. Imputation of Variants from the 1000 Genomes Project Modestly Improves Known Associations and Can Identify Low-Frequency Variant-Phenotype Associations Undetected by HapMap Based Imputation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S.; Das, S.; Kretzschmar, W.; Delaneau, O.; Wood, A.R.; Teumer, A.; Kang, H.M.; Fuchsberger, C.; Danecek, P.; Sharp, K.; et al. A Reference Panel of 64,976 Haplotypes for Genotype Imputation. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, T.; Zhang, P.; Garrick, D.; Gao, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, F. Comparison of Genotype Imputation for SNP Array and Low-Coverage Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 704118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.I.; van der Lee, S.J.; Bonnemaijer, P.W.M.; Höhn, R.; Nag, A.; Gharahkhani, P.; Khawaja, A.P.; Broer, L.; International Glaucoma Genetics Consortium (IGGC); Foster, P.J.; et al. Haplotype reference consortium panel: Practical implications of imputations with large reference panels. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charon, C.; Allodji, R.; Meyer, V.; Deleuze, J.F. Impact of Pre- and Post-Variant Filtration Strategies on Imputation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.F.; Rong, J.J.; Liu, M.; Han, F.; Zhang, X.W.; Richards, J.B.; Wang, L. Performance of Genotype Imputation for Low Frequency and Rare Variants from the 1000 Genomes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Bakshi, A.; Zhu, Z.; Hemani, G.; Vinkhuyzen, A.A.E.; Lee, S.H.; Robinson, M.R.; Perry, J.R.B.; Nolte, I.M.; van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, J.V.; et al. Genetic Variance Estimation with Imputed Variants Finds Negligible Missing Heritability for Human Height and Body Mass Index. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deelen, P.; Menelaou, A.; van Leeuwen, E.M.; Kanterakis, A.; van Dijk, F.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Francioli, L.C.; Hottenga, J.J.; Karssen, L.C.; Estrada, K.; et al. Improved Imputation Quality of Low-Frequency and Rare Variants in European Samples Using the “Genome of the Netherlands”. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Haritunians, T.; Marjoram, P.; Mckean-Cowdin, R.; Torres, M.; Taylor, K.D.; Rotter, J.I.; Gauderman, W.J.; Varma, R. Genotype Imputation for Latinos Using the HapMap and 1000 Genomes Project Reference Panels. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.F.; Ladouceur, M.; Greenwood, C.M.T.; Richards, J.B. Effect of Genome-Wide Genotyping and Reference Panels on Rare Variants Imputation. J. Genet. Genom. 2012, 39, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitt, M.; Kals, M.; Pärn, K.; Gabriel, S.B.; Lander, E.S.; Palotie, A.; Ripatti, S.; Morris, A.P.; Metspalu, A.; Esko, T.; et al. Improved Imputation Accuracy of Rare and Low-Frequency Variants Using Population-Specific High-Coverage WGS-Based Imputation Reference Panel. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 25, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinacci, S.; Ribeiro, D.M.; Hofmeister, R.J.; Delaneau, O. Publisher Correction: Efficient phasing and imputation of low-coverage sequencing data using large reference panels. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 412, Erratum in Nat Genet. 2021, 53, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargolzaei, M.; Chesnais, J.P.; Schenkel, F.S. A New Approach for Efficient Genotype Imputation Using Information from Relatives. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Qian, Q.; Yu, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zeng, J.; Du, Z.; Xiao, J. RefRGim: An Intelligent Reference Panel Reconstruction Method for Genotype Imputation with Convolutional Neural Networks. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistis, G.; Porcu, E.; Vrieze, S.I.; Sidore, C.; Steri, M.; Danjou, F.; Busonero, F.; Mulas, A.; Zoledziewska, M.; Maschio, A.; et al. Rare Variant Genotype Imputation with Thousands of Study-Specific Whole-Genome Sequences: Implications for Cost-Effective Study Designs. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Helgason, H.; Gudjonsson, S.A.; Zink, F.; Oddson, A.; Gylfason, A.; Besenbacher, S.; Magnusson, G.; Halldorsson, B.V.; Hjartarson, E.; et al. Large-Scale Whole-Genome Sequencing of the Icelandic Population. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidore, C.; Busonero, F.; Maschio, A.; Porcu, E.; Naitza, S.; Zoledziewska, M.; Mulas, A.; Pistis, G.; Steri, M.; Danjou, F.; et al. Genome Sequencing Elucidates Sardinian Genetic Architecture and Augments Association Analyses for Lipid and Blood Inflammatory Markers. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, K.; Min, J.L.; Huang, J.; Crooks, L.; Memari, Y.; McCarthy, S.; Perry, J.R.B.; Xu, C.; Futema, M.; Lawson, D.; et al. The UK10K Project Identifies Rare Variants in Health and Disease. Nature 2015, 526, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schönherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-Generation Genotype Imputation Service and Methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schurz, H.; Müller, S.J.; van Helden, P.D.; Tromp, G.; Hoal, E.G.; Kinnear, C.J.; Möller, M. Evaluating the Accuracy of Imputation Methods in a Five-Way Admixed Population. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshyara, N.R.; Horn, K.; Kirsten, H.; Ahnert, P.; Scholz, M. Comparing Performance of Modern Genotype Imputation Methods in Different Ethnicities. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.D. The Nonlinear Structure of Linkage Disequilibrium. Theor. Popul. Biol. 2020, 134, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabisch, M.; Hamann, U.; Lorenzo Bermejo, J. Imputation of Missing Genotypes within LD-Blocks Relying on the Basic Coalescent and beyond: Consideration of Population Growth and Structure. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schunk, D. A Markov Chain Monte Carlo Algorithm for Multiple Imputation in Large Surveys. AStA Adv. Stat. Anal. 2008, 92, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Ravenzwaaij, D.; Cassey, P.; Brown, S.D. A Simple Introduction to Markov Chain Monte-Carlo Sampling. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2018, 25, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, D.C.; Cortessis, V. A Gibbs Sampling Approach to Linkage Analysis. Hum. Hered. 1992, 42, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, B.L.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Y.; Browning, S.R. Fast Two-Stage Phasing of Large-Scale Sequence Data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howie, B.N.; Donnelly, P.; Marchini, J. A Flexible and Accurate Genotype Imputation Method for the next Generation of Genome-Wide Association Studies. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grant, M.J.; Booth, A. A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2009, 26, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, J.; Gurdasani, D.; Delaneau, O.; Pirastu, N.; Ulivi, S.; Cocca, M.; Traglia, M.; Huang, J.; Huffman, J.E.; Rudan, I.; et al. A General Approach for Haplotype Phasing across the Full Spectrum of Relatedness. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRiSMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Healthcare Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abney, M.; Elsherbiny, A. Kinpute: Using Identity by Descent to Improve Genotype Imputation. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4321–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaneau, O.; Coulonges, C.; Zagury, J.F. Shape-IT: New Rapid and Accurate Algorithm for Haplotype Inference. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Money, D.; Gardner, K.; Migicovsky, Z.; Schwaninger, H.; Zhong, G.Y.; Myles, S. LinkImpute: Fast and Accurate Genotype Imputation for Nonmodel Organisms. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2015, 5, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delaneau, O.; Zagury, J.F.; Marchini, J. Improved Whole-Chromosome Phasing for Disease and Population Genetic Studies. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, S.R.; Browning, B.L. Rapid and Accurate Haplotype Phasing and Missing-Data Inference for Whole-Genome Association Studies by Use of Localized Haplotype Clustering. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khankhanian, P.; Din, L.; Caillier, S.J.; Gourraud, P.A.; Baranzini, S.E. SNP Imputation Bias Reduces Effect Size Determination. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, J.M.; Kinghorn, B.P.; Tier, B.; van der Werf, J.H.; Cleveland, M.A. A phasing and imputation method for pedigreed populations that results in a single-stage genomic evaluation. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2012, 44, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheet, P.; Stephens, M. A fast and flexible statistical model for large-scale population genotype data: Applications to inferring missing genotypes and haplotypic phase. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, M.; Smith, N.J.; Donnelly, P. A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 68, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchini, J.; Howie, B.; Myers, S.; McVean, G.; Donnelly, P. A New Multipoint Method for Genome-Wide Association Studies by Imputation of Genotypes. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Abecasis, G.R.; Browning, B.L. Genotype Imputation from Large Reference Panels. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2018, 19, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, B.L.; Browning, S.R. A Unified Approach to Genotype Imputation and Haplotype-Phase Inference for Large Data Sets of Trios and Unrelated Individuals. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 84, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, D.; Manning, C.D. A* Parsing: Fast Exact Viterbi Parse Selection. In Proceedings of the 2003 Human Language Technology Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, HLT-NAACL 2003, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 27 May–1 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, T.K. The Expectation-Maximization Algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1996, 13, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesia, M.; Sabatti, C.; Candès, E.J. Gene Hunting with Hidden Markov Model Knockoffs. Biometrika 2019, 106, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, S.M.; Wishingrad, V.; Thomson, R.C. Properties of Markov Chain Monte Carlo Performance across Many Empirical Alignments. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 38, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.-J. Hidden Markov Models and Their Applications in Biological Sequence Analysis. Curr. Genom. 2009, 10, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesia, M.; Katsevich, E.; Bates, S.; Candès, E.; Sabatti, C. Multi-Resolution Localization of Causal Variants across the Genome. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.Y. Gibbs Sampler and Coordinate Ascent Variational Inference: A Set-Theoretical Review. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2022, 51, 1549–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.B.; Sobel, E.M.; Wasiolek, R.; Ko, S.; Sinsheimer, J.S.; Zhou, H.; Lange, K. A Fast Data-Driven Method for Genotype Imputation, Phasing and Local Ancestry Inference: MendelImpute.Jl. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 4756–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, S.R.; Browning, B.L. High-Resolution Detection of Identity by Descent in Unrelated Individuals. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moltke, I.; Albrechtsen, A.; Hansen, T.V.O.; Nielsen, F.C.; Nielsen, R. A Method for Detecting IBD Regions Simultaneously in Multiple Individuals-with Applications to Disease Genetics. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1168–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidman, D.N.; Shenoy, S.A.; Kim, M.; Babu, R.; Woods, I.G.; Dyer, T.D.; Lehman, D.M.; Curran, J.E.; Duggirala, R.; Blangero, J.; et al. Rapid, Phase-Free Detection of Long Identity-by-Descent Segments Enables Effective Relationship Classification. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 106, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.-F.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Papasian, C.J.; Deng, H.-W. Analyses and Comparison of Accuracy of Different Genotype Imputation Methods. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.B. Estimating Heritability of Complex Traits from Genome-Wide Association Studies Using IBS-Based Haseman-Elston Regression. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alter, O.; Brown, P.O.; Botstein, D. Singular Value Decomposition for Genome-Wide Expression Data Processing and Modeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10101–10106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niu, T.; Qin, Z.S.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.S. Bayesian Haplotype Inference for Multiple Linked Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troyanskaya, O.; Cantor, M.; Sherlock, G.; Brown, P.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Botstein, D.; Altman, R.B. Missing Value Estim. Methods DNA Microarrays 2001, 17, 520–525. [Google Scholar]
- Tjarnberg, A.; Mahmood, O.; Jackson, C.A.; Saldi, G.A.; Cho, K.; Christiaen, L.A.; Bonneau, R.A. Optimal Tuning of Weighted KNN- And Diffusion-Based Methods for Denoising Single Cell Genomics Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, T. Algorithms for Inferring Haplotypes. Genet. Epidemiol. 2004, 27, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liao, R.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y. A New Genotype Imputation Method with Tolerance to High Missing Rate and Rare Variants. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnston, J.; Kistemaker, G.; Sullivan, P.G. Comparison of Different Imputation Methods. Interbull Bull. 2011, 44, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Singleton, A.B.; Hardy, J.A.; Abecasis, G.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Scheet, P. Genotype-Imputation Accuracy across Worldwide Human Populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 84, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panoutsopoulou, K.; Walter, K. Chapter 3 Quality Control of Common and Rare Variants. Genet. Epidemiol. 2018, 1793, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogatko, A.; Slifker, M.J.; Babb, J.S. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Diagnostics. Theor. Popul. Biol. 2002, 62, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.W.; Fu, Y.X. Conditions for Positive and Negative Correlations between Fitness and Heterozygosity in Equilibrium Populations. Genetics 1998, 148, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, R.D.; Uricchio, L.H.; Hartman, K.; Ye, C.; Dahl, A.; Zaitlen, N. Ultra-rare variants drive substantial cis-heritability of human gene expression. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blue, E.M.; Sun, L.; Tintle, N.L.; Wijsman, E.M. Value of Mendelian Laws of Segregation in Families: Data Quality Control, Imputation, and Beyond. Genet. Epidemiol. 2014, 38, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaneau, O.; Marchini, J.; Zagury, J.F. A Linear Complexity Phasing Method for Thousands of Genomes. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1000 Genomes Project Consortium; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Garrison, E.P.; Kang, H.M.; Korbel, J.O.; Marchini, J.L.; McCarthy, S.; McVean, G.A.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roshyara, N.R.; Kirsten, H.; Horn, K.; Ahnert, P.; Scholz, M. Impact of Pre-Imputation SNP-Filtering on Genotype Imputation Results. BMC Genet. 2014, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, F.C.; Joshi, P.K.; Clark, D.W.; Ramsay, M.; Wilson, J.F. Runs of Homozygosity: Windows into Population History and Trait Architecture. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Samuels, D.C.; Shyr, Y.; Guo, Y. StrandScript: Evaluation of Illumina genotyping array design and strand correction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2399–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Kocher, J.-P.; Wang, L. Genome Analysis CrossMap: A Versatile Tool for Coordinate Conversion between Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1006–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Browning, B.L.; Browning, S.R. Genotype Error Biases Trio-Based Estimates of Haplotype Phase Accuracy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Stephens, M. Modeling linkage disequilibrium and identifying recombination hotspots using single-nucleotide polymorphism data. Genetics 2003, 165, 2213–2233, Erratum in Genetics 2004, 167, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, K.; Fuerst, R. Haplotyping and Estimation of Haplotype Frequencies for Closely Linked Biallelic Multilocus Genetic Phenotypes Including Nuclear Family Information. Hum. Mutat. 2001, 17, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragsdale, A.P.; Gravel, S. Unbiased Estimation of Linkage Disequilibrium from Unphased Data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 37, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.L.; Peng, X.; Zhang, S.X.; Zhan, H.W.; Lu, J.H.; Xie, S.S.; Zhao, S.H.; Li, X.Y.; Ma, Y.L. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Pig Genotype Imputation Using a Single or Multi-Breed Reference Population. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.; Antolín, R.; Edwards, S.M.; Sánchez-Molano, E.; Haskell, M.J.; Hickey, J.M.; Wiener, P. Accuracy of Genotype Imputation in Labrador Retrievers. Anim. Genet. 2018, 49, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.; Hartz, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Saccone, S.F.; Wang, J.; Tischfield, J.A.; Edenberg, H.J.; Kramer, J.R.; Goate, A.M.; Bierut, L.J.; et al. A New Statistic to Evaluate Imputation Reliability. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshyara, N.R.; Scholz, M. Impact of Genetic Similarity on Imputation Accuracy. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kostem, E.; Eskin, E. Efficiently identifying significant associations in genome-wide association studies. J. Comput. Biol. 2013, 20, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Wu, X.L.; Weigel, K.A.; Rosa, G.J.M.; Bauck, S.; Woodward, B.W.; Schnabel, R.D.; Taylor, J.F.; Gianola, D. An Ensemble-Based Approach to Imputation of Moderate-Density Genotypes for Genomic Selection with Application to Angus Cattle. Genet. Res. 2012, 94, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, W.; He, S.; Ding, X. Comparison of Different Imputation Methods from Low- to High-Density Panels Using Chinese Holstein Cattle. Animal 2013, 7, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krause, R.W.; Huisman, M.; Steglich, C.; Sniiders, T.A.B. Missing network data a comparison of different imputation methods. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, ASONAM, Barcelona, Spain, 28–31 August 2018; pp. 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, S.; Surakka, I.; Taskinen, M.-R.; Salomaa, V.; Palotie, A.; Wessman, M.; Tukiainen, T.; Pirinen, M.; Palta, P.; Ripatti, S. High-resolution population-specific recombination rates and their effect on phasing and genotype imputation. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 29, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, E.C.G.; Edel, C.; Emmerling, R.; Götz, K.U. How Imputation Errors Bias Genomic Predictions. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 4131–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.P.; Tehranchi, A.; Hie, B.; Dacre, M.; Kaplow, I.; Pettie, K.; Combs, P.; Fraser, H.B. Fine-Mapping Cis-Regulatory Variants in Diverse Human Populations. Elife 2019, 8, e39595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.T.; Shetty, A.; O’Connor, E.; Bell, C.; Pomerantz, M.M.; Freedman, M.L.; Gusev, A. Allele-Specific QTL Fine Mapping with PLASMA. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 106, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgul, A.; Szmatoła, T.; Topolski, P.; Jasielczuk, I.; Żukowski, K.; Bugno-Poniewierska, M. The Use of Runs of Homozygosity for Estimation of Recent Inbreeding in Holstein Cattle. J. Appl. Genet. 2016, 57, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.L.; Sandle, J.; Jones, A.A.; Sofronis, A.; Patani, N.R.; Lakhani, S.R. Mapping Loss of Heterozygosity in Normal Human Breast Cells from BRCA1/2 Carriers. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herzig, A.F.; Nutile, T.; Babron, M.C.; Ciullo, M.; Bellenguez, C.; Leutenegger, A.L. Strategies for Phasing and Imputation in a Population Isolate. Genet. Epidemiol. 2018, 42, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
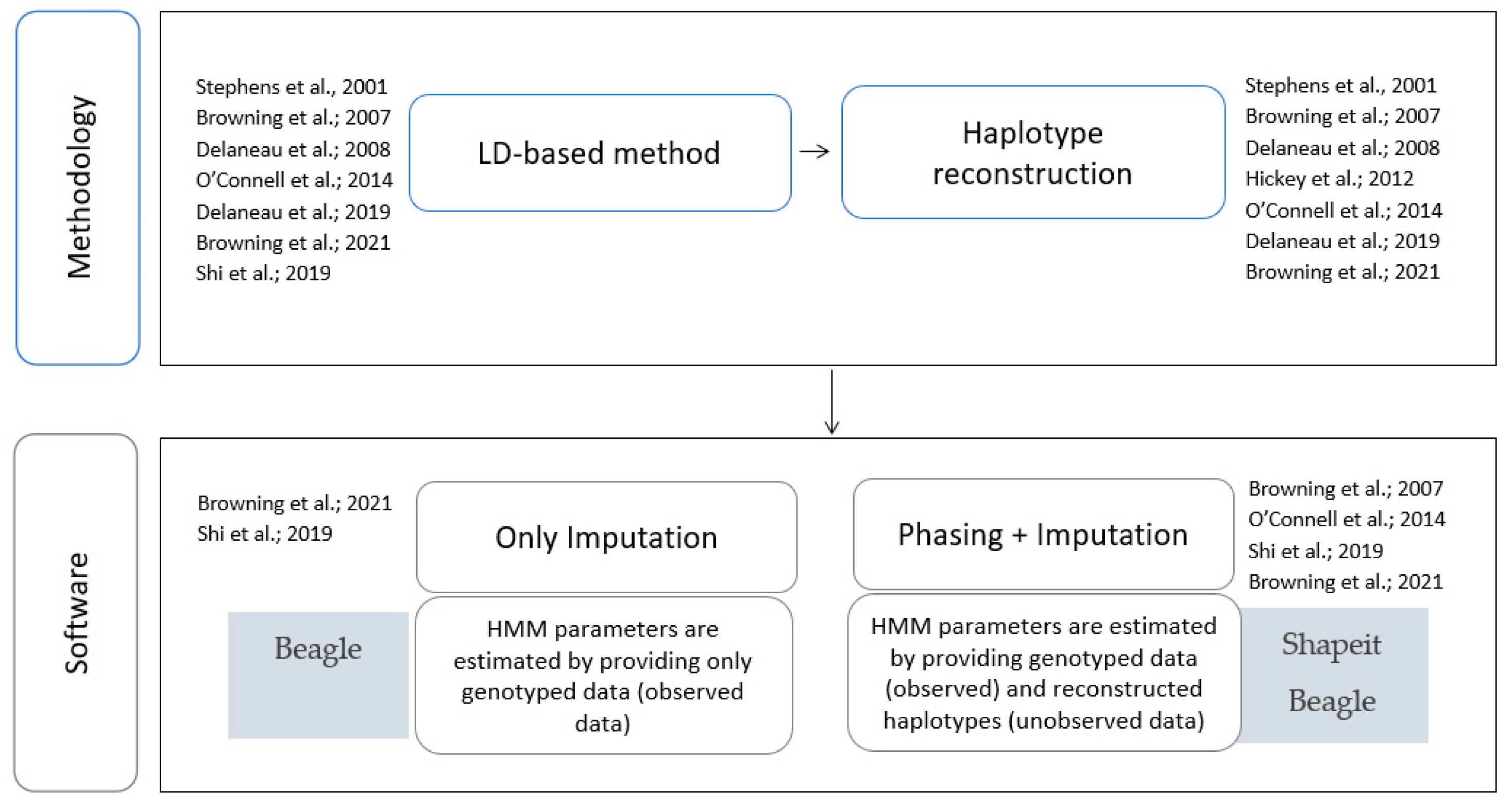
| Article | Setting of Scientific Work | Phasing/ Imputation | Data Type | Software | Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stephens et al., 2001 [65] | Comparison between algorithms | Phasing | Unrelated/ Extended families/Trios | Algorithms’ description | Expectation Maximization alg./Clarck’s alg./HMM |
| Browning et al., 2007 [61] | Software and/or algorithm description | Both | Unrelated/ Extended families/ Trios/Duos | Beagle | LD-based Viterbi’s alg. HMM |
| Delaneau et al., 2008 [58] | Software and/or algorithm description | Phasing | Unrelated/ Extended families/ Trios | Shapeit | LD-based Gibbs’s sampling HMM |
| Kong et al., 2008 [25] | Comparison between algorithms | Phasing | Unrelated/ Extended families | Algorithms’ description | IBD-based |
| Yun et al., 2009 [17] | Review of imputation methods | Imputation | Unrelated/ Extended families | Many methods comparison | IBD-based imputation methods |
| Scheet and Stephens, 2008 [64] | Software documentation | Both | Unrelated/ Extended families/Trios/Duos | FastPHASE | LD-based EM-MC sampling |
| Hickey et al., 2012 [63] | Software and/or algorithm description | Both | Extended families/ Unrelated | AlphaImpute | IBD-based Long-Range Phasing |
| Delaneau et al., 2013 [60] | Software and/or algorithm description | Both | Case-control (GWAS) Unrelated | Shapeit1/Shapeit2 Impute2 | LD-based Gibbs’s sampling HMM |
| O’Connell et al., 2014 [55] | Software and/or algorithm description | Both | Unrelated/ Extended Families/Trios | Shapeit | LD-based Gibbs’s sampling HMM |
| Khankhanian et al., 2015 [62] | Software and/or algorithm description | Imputation | Unrelated | MACH | LD-based HMM |
| Money et al., 2015 [59] | Software and/or algorithm description | Imputation | Unrelated (GWAS) | LinkImpute | LD-based kNN |
| Abney and ElSherbiny, 2019 [57] | Software and/or algorithm description | Imputation | Extended families | Kinpute | IBD-based |
| Delaneau et al., 2019 [15] | Software and/or algorithm description | Phasing | Unrelated/ Extended families/Trios | Shapeit | LD-based Gibbs’s sampling HMM |
| Shi et al., 2019 [24] | Review of imputation methods | Both | Unrelated/ Extended families/Trios | Many software comparison | Comprehensive assessment of LD-based imputation quality |
| Browning et al., 2021 [52] | Software documentation | Both | Unrelated/ Extended families/Trios | Beagle | LD-based Gibbs’s sampling HMM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldrighi, G.N.; Nova, A.; Bernardinelli, L.; Fazia, T. A Pipeline for Phasing and Genotype Imputation on Mixed Human Data (Parents-Offspring Trios and Unrelated Subjects) by Reviewing Current Methods and Software. Life 2022, 12, 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122030
Baldrighi GN, Nova A, Bernardinelli L, Fazia T. A Pipeline for Phasing and Genotype Imputation on Mixed Human Data (Parents-Offspring Trios and Unrelated Subjects) by Reviewing Current Methods and Software. Life. 2022; 12(12):2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122030
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldrighi, Giulia Nicole, Andrea Nova, Luisa Bernardinelli, and Teresa Fazia. 2022. "A Pipeline for Phasing and Genotype Imputation on Mixed Human Data (Parents-Offspring Trios and Unrelated Subjects) by Reviewing Current Methods and Software" Life 12, no. 12: 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122030
APA StyleBaldrighi, G. N., Nova, A., Bernardinelli, L., & Fazia, T. (2022). A Pipeline for Phasing and Genotype Imputation on Mixed Human Data (Parents-Offspring Trios and Unrelated Subjects) by Reviewing Current Methods and Software. Life, 12(12), 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122030










