The Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: An Elusive Therapeutic Target
Abstract
1. The IGF Signaling Axis
2. Physiological Functions of the IGF Signaling Pathway
The IGF Signaling Pathway and Normal Breast Biology
3. The IGF Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer
3.1. IGF Signaling Pathway Expression in Breast Cancer
3.2. The IGF Signaling Pathway and Breast Cancer Initiation
3.3. The IGF Signaling Pathway and Breast Cancer Progression
4. Targeting the IGF Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbieri, M.; Bonafe, M.; Franceschi, C.; Paolisso, G. Insulin/IGF-I-signaling pathway: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism of longevity from yeast to humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E1064–E1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Scalia, P.; Sciacca, L.; Mineo, R.; Costantino, A.; Goldfine, I.D.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized, high-affinity insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 3278–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Jones, E.Y.; Forbes, B.E. Keeping IGF-II under control: Lessons from the IGF-II-IGF2R crystal structure. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, A.; Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 586–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornfeld, S. Structure and function of the mannose 6-phosphate/insulinlike growth factor II receptors. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1992, 61, 307–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, R.C. IGF binding proteins in cancer: Mechanistic and clinical insights. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P.; Whittaker, J. Structural biology of insulin and IGF1 receptors: Implications for drug design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.F. IRS proteins and the common path to diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 283, E413–E422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavan, B.E.; Fantin, V.R.; Chang, E.T.; Lane, W.S.; Keller, S.R.; Lienhard, G.E. A novel 160-kDa phosphotyrosine protein in insulin-treated embryonic kidney cells is a new member of the insulin receptor substrate family. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21403–21407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavan, B.E.; Lane, W.S.; Lienhard, G.E. The 60-kDa phosphotyrosine protein in insulin-treated adipocytes is a new member of the insulin receptor substrate family. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 11439–11443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornholm, M.; He, A.R.; Attersand, A.; Lake, S.; Liu, S.C.; Lienhard, G.E.; Taylor, S.; Arner, P.; Zierath, J.R. Absence of functional insulin receptor substrate-3 (IRS-3) gene in humans. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mardilovich, K.; Pankratz, S.L.; Shaw, L.M. Expression and function of the insulin receptor substrate proteins in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2009, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R.; Vella, V.; Lawrence, M.C.; Sciacca, L.; Frasca, F.; Morrione, A.; Vigneri, R. Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Physiology and Disease: An Updated View. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 379–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneri, R.; Goldfine, I.D.; Frittitta, L. Insulin, insulin receptors, and cancer. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2016, 39, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneri, R.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, P. Rethinking the Relationship between Insulin and Cancer. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belardi, V.; Gallagher, E.J.; Novosyadlyy, R.; LeRoith, D. Insulin and IGFs in obesity-related breast cancer. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2013, 18, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laron, Z.; Werner, H. Laron syndrome-A historical perspective. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 22, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Braxton, L.; Hollingshead, P.; Warburton, C.; Dowd, M.; Pitts-Meek, S.; Dalton, D.; Gillett, N.; Stewart, T.A. IGF-I is required for normal embryonic growth in mice. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 2609–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.P.; Baker, J.; Perkins, A.S.; Robertson, E.J.; Efstratiadis, A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 1993, 75, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.; Liu, J.P.; Robertson, E.J.; Efstratiadis, A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell 1993, 75, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, D.L.; Wood, T.L.; Furth, P.A.; Lee, A.V. Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I in the transition from normal mammary development to preneoplastic mammary lesions. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, C. IGF2 and cancer. Endocrine.-related Cancer 2013, 20, R321–R339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeChiara, T.M.; Efstratiadis, A.; Robertson, E.J. A growth-deficiency phenotype in heterozygous mice carrying an insulin-like growth factor II gene disrupted by targeting. Nature 1990, 345, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, E.; Lipes, M.A.; Patti, M.E.; Bruning, J.C.; Haag, B., 3rd; Johnson, R.S.; Kahn, C.R. Alternative pathway of insulin signalling in mice with targeted disruption of the IRS-1 gene. Nature 1994, 372, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamemoto, H.; Kadowaki, T.; Tobe, K.; Yagi, T.; Sakura, H.; Hayakawa, T.; Terauchi, Y.; Ueki, K.; Kaburagi, Y.; Satoh, S.; et al. Insulin resistance and growth retardation in mice lacking insulin receptor substrate-1. Nature 1994, 372, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, D.J.; Gutierrez, J.S.; Towery, H.; Burks, D.J.; Ren, J.M.; Previs, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bernal, D.; Pons, S.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature 1998, 391, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Brazil, D.P.; Burks, D.J.; Kushner, J.A.; Ye, J.; Flint, C.L.; Farhang-Fallah, J.; Dikkes, P.; Warot, X.M.; Rio, C.; et al. Insulin receptor substrate-2 deficiency impairs brain growth and promotes tau phosphorylation. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7084–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantin, V.R.; Wang, Q.; Lienhard, G.E.; Keller, S.R. Mice lacking insulin receptor substrate 4 exhibit mild defects in growth, reproduction, and glucose homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 278, E127–E133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanelli, R.J.; LeBeau, A.P.; Fulmer, C.G.; Lazzarino, D.A.; Hochberg, A.; Wood, T.L. Insulin-like growth factor type-I receptor internalization and recycling mediate the sustained phosphorylation of Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22513–22524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapf, A.; Hsu, D.; Olefsky, J.M. Comparison of the intracellular itineraries of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin and their receptors in Rat-1 fibroblasts. Endocrinology 1994, 134, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C.; Condorelli, G.; Smith, R.J. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor internalization regulates signaling via the Shc/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, but not the insulin receptor substrate-1 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 4672–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gual, P.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Tanti, J.F. Positive and negative regulation of insulin signaling through IRS-1 phosphorylation. Biochimie 2005, 87, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.V.; Gooch, J.L.; Oesterreich, S.; Guler, R.L.; Yee, D. Insulin-like growth factor I-induced degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1 is mediated by the 26S proteasome and blocked by phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase inhibition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, L.; Fisher, T.L.; Thomas, J.; White, M.F. Regulation of insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling by proteasome-mediated degradation of insulin receptor substrate-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 40362–40367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, K.E.; Rojo, F.; She, Q.B.; Solit, D.; Mills, G.B.; Smith, D.; Lane, H.; Hofmann, F.; Hicklin, D.J.; Ludwig, D.L.; et al. mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowzee, A.M.; Lazzarino, D.A.; Rota, L.; Sun, Z.; Wood, T.L. IGF ligand and receptor regulation of mammary development. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2008, 13, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Kleinberg, D.L. Insulin-like growth factor I is essential for terminal end bud formation and ductal morphogenesis during mammary development. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 5075–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoith, D.; Neuenschwander, S.; Wood, T.L.; Hennighausen, L. Insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 inhibit involution of the mammary gland following lactation: Studies in transgenic mice. Prog. Growth Factor Res. 1995, 6, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.S.; Boyle, P.L.; Corl, B.A.; Wong, E.A.; Gwazdauskas, F.C.; Akers, R.M. Expression of ovine insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) stimulates alveolar bud development in mammary glands of transgenic mice. Endocrine 1998, 8, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannata, D.; Lann, D.; Wu, Y.; Elis, S.; Sun, H.; Yakar, S.; Lazzarino, D.A.; Wood, T.L.; Leroith, D. Elevated circulating IGF-I promotes mammary gland development and proliferation. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5751–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisken, C.; Ayyannan, A.; Nguyen, C.; Heineman, A.; Reinhardt, F.; Tan, J.; Dey, S.K.; Dotto, G.P.; Weinberg, R.A. IGF-2 is a mediator of prolactin-induced morphogenesis in the breast. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovey, R.C.; Harris, J.; Hadsell, D.L.; Lee, A.V.; Ormandy, C.J.; Vonderhaar, B.K. Local insulin-like growth factor-II mediates prolactin-induced mammary gland development. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bonnette, S.G.; Hadsell, D.L. Targeted disruption of the IGF-I receptor gene decreases cellular proliferation in mammary terminal end buds. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 4937–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Shushanov, S.; LeRoith, D.; Wood, T.L. Decreased IGF type 1 receptor signaling in mammary epithelium during pregnancy leads to reduced proliferation, alveolar differentiation, and expression of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and IRS-2. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3233–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, N.; Silveyra, P. Estrogen receptor signaling mechanisms. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2019, 116, 135–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, C.K.; Schiff, R. Growth factor receptor cross-talk with estrogen receptor as a mechanism for tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Breast 2003, 12, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, C.K.; Shou, J.; Massarweh, S.; Schiff, R. Crosstalk between estrogen receptor and growth factor receptor pathways as a cause for endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 865s–870s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Norman, M.J. Multihormonal regulation of the progesterone receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: Interrelationships among insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I, serum, and estrogen. Endocrinology 1990, 126, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.V.; Weng, C.N.; Jackson, J.G.; Yee, D. Activation of estrogen receptor-mediated gene transcription by IGF-I in human breast cancer cells. J. Endocrinol. 1997, 152, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.A.; Ibrahim, Y.H.; Cui, X.; Lee, A.V.; Yee, D. The IGF pathway regulates ERalpha through a S6K1-dependent mechanism in breast cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siersbaek, R.; Kumar, S.; Carroll, J.S. Signaling pathways and steroid receptors modulating estrogen receptor alpha function in breast cancer. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.V.; Jackson, J.G.; Gooch, J.L.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Coronado-Heinsohn, E.; Osborne, C.K.; Yee, D. Enhancement of insulin-like growth factor signaling in human breast cancer: Estrogen regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.V.; Darbre, P.; King, R.J. Processing of insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) by human breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1994, 99, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, H.; Nickerson, T.; Pollak, M.; Yang, X. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression by the pure antiestrogen ICI 182780. Clin. Cancer Res. 1996, 2, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, M.; Vignon, F.; Capony, F.; Rochefort, H. Estradiol down-regulates the mannose-6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor-II receptor gene and induces cathepsin-D in breast cancer cells: A receptor saturation mechanism to increase the secretion of lysosomal proenzymes. Mol. Endocrinol. 1991, 5, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, S.; Nuedling, S.; van Eickels, M.; Vetter, H.; Meyer, R.; Grohe, C. Estrogen receptor alpha rapidly activates the IGF-1 receptor pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 18447–18453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Gao, W.; Jiang, E.; Lu, F.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Lv, T. Interaction between IGF-IR and ER Induced by E2 and IGF-I. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perou, C.M.; Sorlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennigs, A.; Riedel, F.; Gondos, A.; Sinn, P.; Schirmacher, P.; Marme, F.; Jager, D.; Kauczor, H.U.; Stieber, A.; Lindel, K.; et al. Prognosis of breast cancer molecular subtypes in routine clinical care: A large prospective cohort study. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabaugh, S.M.; Boone, D.N.; Lee, A.V. Role of IGF1R in Breast Cancer Subtypes, Stemness, and Lineage Differentiation. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2015, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas, N. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, T.O.; Andrews, H.N.; Cheang, M.; Kucab, J.E.; Hsu, F.D.; Ragaz, J.; Gilks, C.B.; Makretsov, N.; Bajdik, C.D.; Brookes, C.; et al. Expression of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor and urokinase plasminogen activator in breast cancer is associated with poor survival: Potential for intervention with 17-allylamino geldanamycin. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, C.; Hasegawa, T.; Tani, Y.; Takahashi, F.; Takeuchi, M.; Watanabe, T.; Ando, M.; Katsumata, N.; Fujiwara, Y. Expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in primary breast cancer: Immunohistochemical analysis. Hum. Pathol. 2004, 35, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerushalmi, R.; Gelmon, K.A.; Leung, S.; Gao, D.; Cheang, M.; Pollak, M.; Turashvili, G.; Gilks, B.C.; Kennecke, H. Insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) in breast cancer subtypes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 132, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, N.; Knuppel, A.; Papadimitriou, N.; Martin, R.M.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Smith-Byrne, K.; Fensom, G.; Perez-Cornago, A.; Travis, R.C.; Key, T.J.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3, and breast cancer risk: Observational and Mendelian randomization analyses with approximately 430,000 women. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, F.; Huo, D. Circulating Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Risk of Total and 19 Site-Specific Cancers: Cohort Study Analyses from the UK Biobank. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 2332–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankinson, S.E.; Willett, W.C.; Colditz, G.A.; Hunter, D.J.; Michaud, D.S.; Deroo, B.; Rosner, B.; Speizer, F.E.; Pollak, M. Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer. Lancet 1998, 351, 1393–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renehan, A.G.; Zwahlen, M.; Minder, C.; O’Dwyer, S.T.; Shalet, S.M.; Egger, M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: Systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Yu, H.; McLarty, J.; Glass, J. IGF-I and breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 111, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla Singh, S.; Tan, Q.W.; Brito, C.; De Leon, M.; Garberoglio, C.; De Leon, D. Differential insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) expression: A potential role for breast cancer survival disparity. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2010, 20, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronbaek, H.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Mellemkjaer, L.; Tjonneland, A.; Christensen, J.; Sorensen, H.T.; Overvad, K. Serum insulin-like growth factors, insulin-like growth factor binding proteins, and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2004, 13, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poloz, Y.; Stambolic, V. Obesity and cancer, a case for insulin signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmons, D.R.; Underwood, L.E. Nutritional regulation of IGF-I and IGF binding proteins. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1991, 11, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.H.; Habibi, G.; Hu, K.; Masoudi, H.; Wang, M.Y.; Stratford, A.L.; Park, E.; Gee, J.M.; Finlay, P.; Jones, H.E.; et al. Phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor-i/insulin receptor is present in all breast cancer subtypes and is related to poor survival. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 10238–10246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, L.; Santos, A.; Campbell, F.; Figueiredo, C.; Hammond, D.; Ellies, L.G.; Weyer-Czernilofsky, U.; Bogenrieder, T.; Schmid, M.; Mielgo, A. Blockade of insulin-like growth factors increases efficacy of paclitaxel in metastatic breast cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2022–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creighton, C.J.; Casa, A.; Lazard, Z.; Huang, S.; Tsimelzon, A.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Osborne, C.K.; Lee, A.V. Insulin-like growth factor-I activates gene transcription programs strongly associated with poor breast cancer prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4078–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litzenburger, B.C.; Creighton, C.J.; Tsimelzon, A.; Chan, B.T.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Wang, T.; Carboni, J.M.; Gottardis, M.M.; Huang, F.; Chang, J.C.; et al. High IGF-IR activity in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines and tumorgrafts correlates with sensitivity to anti-IGF-IR therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2314–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamimi, R.M.; Colditz, G.A.; Wang, Y.; Collins, L.C.; Hu, R.; Rosner, B.; Irie, H.Y.; Connolly, J.L.; Schnitt, S.J. Expression of IGF1R in normal breast tissue and subsequent risk of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 128, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartog, H.; Horlings, H.M.; van der Vegt, B.; Kreike, B.; Ajouaou, A.; van de Vijver, M.J.; Marike Boezen, H.; de Bock, G.H.; van der Graaf, W.T.; Wesseling, J. Divergent effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression on prognosis of estrogen receptor positive versus triple negative invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 129, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Werner, H.; Sarfstein, R.; Laron, Z. The Role of Nuclear Insulin and IGF1 Receptors in Metabolism and Cancer. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Lv, Z.; Cui, C.; Wang, W. IGF-1R Transported to the Cell Nuclei to Regulate the Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon-Zemler, R.; Sarfstein, R.; Werner, H. Nuclear insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) displays proliferative and regulatory activities in non-malignant cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksic, T.; Chitnis, M.M.; Perestenko, O.V.; Gao, S.; Thomas, P.H.; Turner, G.D.; Protheroe, A.S.; Howarth, M.; Macaulay, V.M. Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor translocates to the nucleus of human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6412–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehat, B.; Tofigh, A.; Lin, Y.; Trocme, E.; Liljedahl, U.; Lagergren, J.; Larsson, O. SUMOylation mediates the nuclear translocation and signaling of the IGF-1 receptor. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfstein, R.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Yeheskel, A.; Edry, L.; Shomron, N.; Warman, N.; Wertheimer, E.; Maor, S.; Shochat, L.; Werner, H. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) translocates to nucleus and autoregulates IGF-IR gene expression in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2766–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnarr, B.; Strunz, K.; Ohsam, J.; Benner, A.; Wacker, J.; Mayer, D. Down-regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and insulin receptor substrate-1 expression in advanced human breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 89, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisci, D.; Morelli, C.; Garofalo, C.; Romeo, F.; Morabito, L.; Casaburi, F.; Middea, E.; Cascio, S.; Brunelli, E.; Ando, S.; et al. Expression of nuclear insulin receptor substrate 1 in breast cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, H.A.; Perry, A.; Kingsley, C.; Tran, N.L.; Keegan, A.D. IRS1 is highly expressed in localized breast tumors and regulates the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to chemotherapy, while IRS2 is highly expressed in invasive breast tumors. Cancer Lett. 2013, 338, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.L.; Dresser, K.; Hsieh, C.C.; Sabel, M.; Kleer, C.G.; Khan, A.; Shaw, L.M. Membrane localization of insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) is associated with decreased overall survival in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 130, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, C.; Garofalo, C.; Sisci, D.; del Rincon, S.; Cascio, S.; Tu, X.; Vecchione, A.; Sauter, E.R.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Surmacz, E. Nuclear insulin receptor substrate 1 interacts with estrogen receptor alpha at ERE promoters. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7517–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliaccio, I.; Wu, M.F.; Gutierrez, C.; Malorni, L.; Mohsin, S.K.; Allred, D.C.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Osborne, C.K.; Weiss, H.; Lee, A.V. Nuclear IRS-1 predicts tamoxifen response in patients with early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 123, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, L.M. Identification of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) and IRS-2 as signaling intermediates in the alpha6beta4 integrin-dependent activation of phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and promotion of invasion. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 5082–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Santos, A.; Konganti, K.; Hillhouse, A.; Lambertz, I.U.; Zheng, Y.; Gunaratna, R.T.; Threadgill, D.W.; Fuchs-Young, R.S. Overexpression of IGF-1 During Early Development Expands the Number of Mammary Stem Cells and Primes them for Transformation. Stem Cells 2022, 40, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.; Diaz, E.; Reya, T. Stem cells in cancer initiation and progression. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e201911053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hajj, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Benito-Hernandez, A.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, K.; Shimamura, T.; Kimura, N.; Murayama, T.; Matsubara, D.; Kanauchi, H.; Niida, A.; Shimizu, S.; Nishioka, K.; Tsuji, E.I.; et al. Addiction to the IGF2-ID1-IGF2 circuit for maintenance of the breast cancer stem-like cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.W.; Lin, R.J.; Yu, J.; Chang, W.Y.; Fu, C.H.; Lai, A.; Yu, J.C.; Yu, A.L. The expression and significance of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and its pathway on breast cancer stem/progenitors. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-S.; Lero, M.W.; Mercado-Matos, J.; Zhu, S.; Jo, M.; Tocheny, C.E.; Morgan, J.S.; Shaw, L.M. The insulin and IGF signaling pathway sustains breast cancer stem cells by IRS2/PI3K-mediated regulation of MYC. Cell Rep. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, A.R.; Truong, T.H.; Kerkvliet, C.P.; Paul, K.V.; Kabos, P.; Sartorius, C.A.; Lange, C.A. Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) mediates progesterone receptor-driven stemness and endocrine resistance in oestrogen receptor+ breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, E.S.; Ertel, A.; Davicioni, E.; Kline, J.; Schwartz, G.F.; Witkiewicz, A.K. Progression of ductal carcinoma in situ to invasive breast cancer is associated with gene expression programs of EMT and myoepithelia. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scimeca, M.; Antonacci, C.; Colombo, D.; Bonfiglio, R.; Buonomo, O.C.; Bonanno, E. Emerging prognostic markers related to mesenchymal characteristics of poorly differentiated breast cancers. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 5427–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroni, C.; Broggini, M.; Generali, D.; Damia, G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer: Role, molecular mechanisms and clinical impact. Cancer. Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, L.A.; Damjanovski, S. IGF-1 increases invasive potential of MCF 7 breast cancer cells and induces activation of latent TGF-beta1 resulting in epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2011, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Litzenburger, B.C.; Cui, X.; Delgado, D.A.; Grabiner, B.C.; Lin, X.; Lewis, M.T.; Gottardis, M.M.; Wong, T.W.; Attar, R.M.; et al. Constitutively active type I insulin-like growth factor receptor causes transformation and xenograft growth of immortalized mammary epithelial cells and is accompanied by an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition mediated by NF-kappaB and snail. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felipe Lima, J.; Nofech-Mozes, S.; Bayani, J.; Bartlett, J.M. EMT in Breast Carcinoma—A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lu, P.; Zhang, H.; Luo, M.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, C. Oct-4 and Nanog promote the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer stem cells and are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 10803–10815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taliaferro-Smith, L.; Oberlick, E.; Liu, T.; McGlothen, T.; Alcaide, T.; Tobin, R.; Donnelly, S.; Commander, R.; Kline, E.; Nagaraju, G.P.; et al. FAK activation is required for IGF1R-mediated regulation of EMT, migration, and invasion in mesenchymal triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4757–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Liang, S.; Dang, C. IGF-I Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via the IGF-IR-Src-MicroRNA-30a-E-Cadherin Pathway in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells. Oncol. Res. 2016, 24, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, L.M.; Albanito, L.; Shin, M.E.; Goyeneche, C.L.; Shushanov, S.; Gallagher, E.J.; LeRoith, D.; Lazzarino, D.A.; Wood, T.L. IGF1R inhibition in mammary epithelia promotes canonical Wnt signaling and Wnt1-driven tumors. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5668–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Condeelis, J. Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2007, 1773, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerr, M.E.; Jones, J.I. The roles of integrins and extracellular matrix proteins in the insulin-like growth factor I-stimulated chemotaxis of human breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 2443–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guvakova, M.A.; Adams, J.C.; Boettiger, D. Functional role of alpha-actinin, PI 3-kinase and MEK1/2 in insulin-like growth factor I receptor kinase regulated motility of human breast carcinoma cells. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 4149–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimura, S.; Takahashi, K. Rac1 and Stathmin but Not EB1 Are Required for Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells in Response to IGF-I. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 2011, 615912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mezi, S.; Todi, L.; Orsi, E.; Angeloni, A.; Mancini, P. Involvement of the Src-cortactin pathway in migration induced by IGF-1 and EGF in human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samani, A.A.; Yakar, S.; LeRoith, D.; Brodt, P. The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis: Overview and recent insights. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 20–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, S.E.; Torres, J.V.; Nihei, N.; Barrett, J.C. The insulin-like growth factor-1 elevates urokinase-type plasminogen activator-1 in human breast cancer cells: A new avenue for breast cancer therapy. Mol. Carcinog. 2000, 27, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, S.E.; Torres, J.V.; Oh, J.S.; Cykert, D.M.; Barrett, J.C. Up-regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by insulin-like growth factor-I depends upon phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Mira, E.; Manes, S.; Lacalle, R.A.; Marquez, G.; Martinez, A.C. Insulin-like growth factor I-triggered cell migration and invasion are mediated by matrix metalloproteinase-9. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Manes, S.; Llorente, M.; Lacalle, R.A.; Gomez-Mouton, C.; Kremer, L.; Mira, E.; Martinez, A.C. The matrix metalloproteinase-9 regulates the insulin-like growth factor-triggered autocrine response in DU-145 carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6935–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Yano, K.; Sugimoto, S.; Ishii, G.; Hasebe, T.; Endoh, Y.; Kodama, K.; Goya, M.; Chiba, T.; Ochiai, A. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 facilitates insulin-like growth factor bioavailability through its proteinase activity on insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopoulos, P.F.; Msaouel, P.; Koutsilieris, M. The role of the insulin-like growth factor-1 system in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, K.; Laban, C.; McVittie, C.J.; Ogunkolade, W.; Khalaf, S.; Bustin, S.; Carpenter, R.; Jenkins, P.J. The expression and function of IGFBP-3 in normal and malignant breast tissue. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 3785–3790. [Google Scholar]
- Mercado-Matos, J.; Janusis, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, S.S.; Shaw, L.M. Identification of a novel invasion-promoting region in Insulin Receptor Substrate 2 (IRS2). Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 38, e00590-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.G.; Zhang, X.; Yoneda, T.; Yee, D. Regulation of breast cancer cell motility by insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) in metastatic variants of human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7318–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madu, C.O.; Wang, S.; Madu, C.O.; Lu, Y. Angiogenesis in Breast Cancer Progression, Diagnosis, and Treatment. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 4474–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardilovich, K.; Shaw, L.M. Hypoxia regulates insulin receptor substrate-2 expression to promote breast carcinoma cell survival and invasion. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8894–8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moromisato, D.Y.; Moromisato, M.Y.; Zanconato, S.; Roberts, C.T., Jr. Effect of hypoxia on lung, heart, and liver insulin-like growth factor-I gene and receptor expression in the newborn rat. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 24, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, E.M.; Sims, A.H.; Maggiolini, M.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P.; Clarke, R.B. GPER mediates the angiocrine actions induced by IGF1 through the HIF-1alpha/VEGF pathway in the breast tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.H.; Bae, S.K.; Bae, M.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Moon, E.J.; Cha, H.J.; Kwon, Y.G.; Kim, K.W. Identification of angiogenic properties of insulin-like growth factor II in in vitro angiogenesis models. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Nakajima, K.; Iijima, S.; Aizawa, T.; Hashizume, K. IGF-1 regulates migration and angiogenesis of human endothelial cells. Endocr. J. 1999, 46, S59–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skobe, M.; Hawighorst, T.; Jackson, D.G.; Prevo, R.; Janes, L.; Velasco, P.; Riccardi, L.; Alitalo, K.; Claffey, K.; Detmar, M. Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Fallavollita, L.; Brodt, P. Vascular endothelial growth factor C expression and lymph node metastasis are regulated by the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Bjorndahl, M.; Cao, R.; Nissen, L.J.; Clasper, S.; Johnson, L.A.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Jackson, D.; Hansen, A.J.; Cao, Y. Insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 induce lymphangiogenesis in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15593–15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraga, T.; Myoui, A.; Hashimoto, N.; Sasaki, A.; Hata, K.; Morita, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Rosen, C.J.; Mundy, G.R.; Yoneda, T. Bone-derived IGF mediates crosstalk between bone and breast cancer cells in bony metastases. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4238–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBedis, C.; Chen, K.; Fallavollita, L.; Boutros, T.; Brodt, P. Peripheral lymph node stromal cells can promote growth and tumorigenicity of breast carcinoma cells through the release of IGF-I and EGF. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 100, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, K.; Meszaros, A.; Fazakas, C.; Kozma, M.; Gyori, F.; Reisz, Z.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Farkas, A.E.; Nyul-Toth, A.; Hasko, J.; et al. Pericyte-secreted IGF2 promotes breast cancer brain metastasis formation. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 2040–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Cuadrado, L.; Bullock, E.; Mabruk, Z.; Zhao, H.; Souleimanova, M.; Noer, P.R.; Turnbull, A.K.; Oxvig, C.; Bertos, N.; Byron, A.; et al. Characterisation of the Stromal Microenvironment in Lobular Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Moerkens, M.; Ramaiahgari, S.; de Bont, H.; Price, L.; Meerman, J.; van de Water, B. Elevated insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling induces antiestrogen resistance through the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling routes. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarweh, S.; Osborne, C.K.; Creighton, C.J.; Qin, L.; Tsimelzon, A.; Huang, S.; Weiss, H.; Rimawi, M.; Schiff, R. Tamoxifen resistance in breast tumors is driven by growth factor receptor signaling with repression of classic estrogen receptor genomic function. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, C.; Ramos, P.; Cornille, K.; Bonenfant, D.; Fritsch, C.; Voshol, H.; Bentires-Alj, M. Activation of IGF1R/p110beta/AKT/mTOR confers resistance to alpha-specific PI3K inhibition. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Mascarenhas, D.; Pollak, M. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling and resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin). J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, B.C.; Haffty, B.G.; Narayanan, L.; Yuan, J.; Havre, P.A.; Gumbs, A.A.; Kaplan, L.; Burgaud, J.L.; Carter, D.; Baserga, R.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor overexpression mediates cellular radioresistance and local breast cancer recurrence after lumpectomy and radiation. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 3079–3083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hua, H.; Kong, Q.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y. Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in tumorigenesis and drug resistance: A challenge for cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Yin, Z.; Tao, K.; Wang, G.; Gao, J. Function of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer resistance to chemotherapy. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtrum, D.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Prewett, M.; Pereira, D.S.; Bassi, R.; Abdullah, R.; Hooper, A.T.; Koo, H.; et al. A fully human monoclonal antibody to the insulin-like growth factor I receptor blocks ligand-dependent signaling and inhibits human tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8912–8921. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, B.D.; Baker, D.A.; Soderstrom, C.; Tkalcevic, G.; Rossi, A.M.; Miller, P.E.; Tengowski, M.W.; Wang, F.; Gualberto, A.; Beebe, J.S.; et al. Combination therapy enhances the inhibition of tumor growth with the fully human anti-type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haluska, P.; Carboni, J.M.; Loegering, D.A.; Lee, F.Y.; Wittman, M.; Saulnier, M.G.; Frennesson, D.B.; Kalli, K.R.; Conover, C.A.; Attar, R.M.; et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of the dual insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin receptor inhibitor, BMS-554417. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, D.; Zhang, X.; Matise, I.; Gaillard-Kelly, M.; Yee, D. The type I insulin-like growth factor receptor regulates cancer metastasis independently of primary tumor growth by promoting invasion and survival. Oncogene 2010, 29, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cosimo, S.; Sathyanarayanan, S.; Bendell, J.C.; Cervantes, A.; Stein, M.N.; Brana, I.; Roda, D.; Haines, B.B.; Zhang, T.; Winter, C.G.; et al. Combination of the mTOR inhibitor ridaforolimus and the anti-IGF1R monoclonal antibody dalotuzumab: Preclinical characterization and phase I clinical trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, T.C.; He, J.; O’Sullivan, C.C.; Chen, B.; Northfelt, D.; Dueck, A.C.; Ballman, K.V.; Tenner, K.S.; Linden, H.; Sparano, J.A.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Capecitabine and Lapatinib with or without IMC-A12 (Cituxumumab) in Patients with HER2-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer Previously Treated with Trastuzumab and Chemotherapy: NCCTG N0733 (Alliance). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 188, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, J.F.; Ferrero, J.M.; Bourgeois, H.; Kennecke, H.; de Boer, R.H.; Jacot, W.; McGreivy, J.; Suzuki, S.; Zhu, M.; McCaffery, I.; et al. Ganitumab with either exemestane or fulvestrant for postmenopausal women with advanced, hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer: A randomised, controlled, double-blind, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugo, H.S.; Tredan, O.; Ro, J.; Morales, S.M.; Campone, M.; Musolino, A.; Afonso, N.; Ferreira, M.; Park, K.H.; Cortes, J.; et al. A randomized phase II trial of ridaforolimus, dalotuzumab, and exemestane compared with ridaforolimus and exemestane in patients with advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 165, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, T.; Shen, H.; Cao, H.; Du, J. The adverse events profile of anti-IGF-1R monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 77, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.D.; Neven, P.; Blackwell, K.L.; Dirix, L.Y.; Barrios, C.H.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Fein, L.E.; Fenton, D.; Benner, R.J.; Meech, S.J.; et al. P1-17-01: Figitumumab Plus Exemestane Versus Exemestane as First-Line Treatment of Postmenopausal Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer: A Randomized, Open-Label Phase II Trial. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, P1-17-01–P11-17-01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekyalongo, R.C.; Yee, D. Revisiting the IGF-1R as a breast cancer target. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lero, M.W.; Shaw, L.M. Diversity of insulin and IGF signaling in breast cancer: Implications for therapy. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 527, 111213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osher, E.; Macaulay, V.M. Therapeutic Targeting of the IGF Axis. Cells 2019, 8, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Ge, Z.; Taylor, N.S.; Xu, S.; Horwitz, B.H.; Erdman, S.E. Gastroenteritis in NF-kappaB-deficient mice is produced with wild-type Camplyobacter jejuni but not with C. jejuni lacking cytolethal distending toxin despite persistent colonization with both strains. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Huang, F.; Macedo, L.F.; Harrington, S.C.; Reeves, K.A.; Greer, A.; Finckenstein, F.G.; Brodie, A.; Gottardis, M.M.; Carboni, J.M.; et al. Dual IGF-1R/InsR inhibitor BMS-754807 synergizes with hormonal agents in treatment of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7597–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, J.M.; Wittman, M.; Yang, Z.; Lee, F.; Greer, A.; Hurlburt, W.; Hillerman, S.; Cao, C.; Cantor, G.H.; Dell-John, J.; et al. BMS-754807, a small molecule inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor-1R/IR. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 3341–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaulay, V.M.; Middleton, M.R.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Rudin, C.M.; Juergens, R.A.; Gedrich, R.; Gogov, S.; McCarthy, S.; Poondru, S.; Stephens, A.W.; et al. Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of Linsitinib (OSI-906) and Erlotinib in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puzanov, I.; Lindsay, C.R.; Goff, L.; Sosman, J.; Gilbert, J.; Berlin, J.; Poondru, S.; Simantov, R.; Gedrich, R.; Stephens, A.; et al. A phase I study of continuous oral dosing of OSI-906, a dual inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin receptors, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, J.; Solomon, B.J.; Davis, I.D.; Lipton, L.R.; Hicks, R.; Scott, A.M.; Park, J.; Clemens, P.L.; Gestone, T.A.; Finckenstein, F.G. Phase I dose-escalation study of daily BMS-754807, an oral, dual IGF-1R/insulin receptor (IR) inhibitor in subjects with solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chesebrough, J.W.; Cartlidge, S.A.; Ricketts, S.A.; Incognito, L.; Veldman-Jones, M.; Blakey, D.C.; Tabrizi, M.; Jallal, B.; Trail, P.A.; et al. Dual IGF-I/II-neutralizing antibody MEDI-573 potently inhibits IGF signaling and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haluska, P.; Menefee, M.; Plimack, E.R.; Rosenberg, J.; Northfelt, D.; LaVallee, T.; Shi, L.; Yu, X.Q.; Burke, P.; Huang, J.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of MEDI-573, a bispecific, antiligand monoclonal antibody against IGFI and IGFII, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4747–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, H.; Nishina, T.; Nogami, N.; Kozuki, T.; Yamagiwa, Y.; Yagawa, K. Phase I dose-escalation study evaluating safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of MEDI-573, a dual IGF-I/II neutralizing antibody, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumours. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedbichler, K.; Hofmann, M.H.; Kroez, M.; Ostermann, E.; Lamche, H.R.; Koessl, C.; Borges, E.; Pollak, M.N.; Adolf, G.; Adam, P.J. Pharmacodynamic and antineoplastic activity of BI 836845, a fully human IGF ligand-neutralizing antibody, and mechanistic rationale for combination with rapamycin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Sablin, M.P.; Bergh, J.; Im, S.A.; Lu, Y.S.; Martinez, N.; Neven, P.; Lee, K.S.; Morales, S.; Perez-Fidalgo, J.A.; et al. A phase Ib/II study of xentuzumab, an IGF-neutralising antibody, combined with exemestane and everolimus in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Raffaghello, L.; Brandhorst, S.; Safdie, F.M.; Bianchi, G.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; Pistoia, V.; Wei, M.; Hwang, S.; Merlino, A.; et al. Fasting cycles retard growth of tumors and sensitize a range of cancer cell types to chemotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 124ra27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffa, I.; Spagnolo, V.; Vernieri, C.; Valdemarin, F.; Becherini, P.; Wei, M.; Brandhorst, S.; Zucal, C.; Driehuis, E.; Ferrando, L.; et al. Fasting-mimicking diet and hormone therapy induce breast cancer regression. Nature 2020, 583, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, S.; Lugtenberg, R.T.; Cohen, D.; Welters, M.J.P.; Ehsan, I.; Vreeswijk, M.P.G.; Smit, V.; de Graaf, H.; Heijns, J.B.; Portielje, J.E.A.; et al. Fasting mimicking diet as an adjunct to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer in the multicentre randomized phase 2 DIRECT trial. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byron, S.A.; Horwitz, K.B.; Richer, J.K.; Lange, C.A.; Zhang, X.; Yee, D. Insulin receptor substrates mediate distinct biological responses to insulin-like growth factor receptor activation in breast cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 1220–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
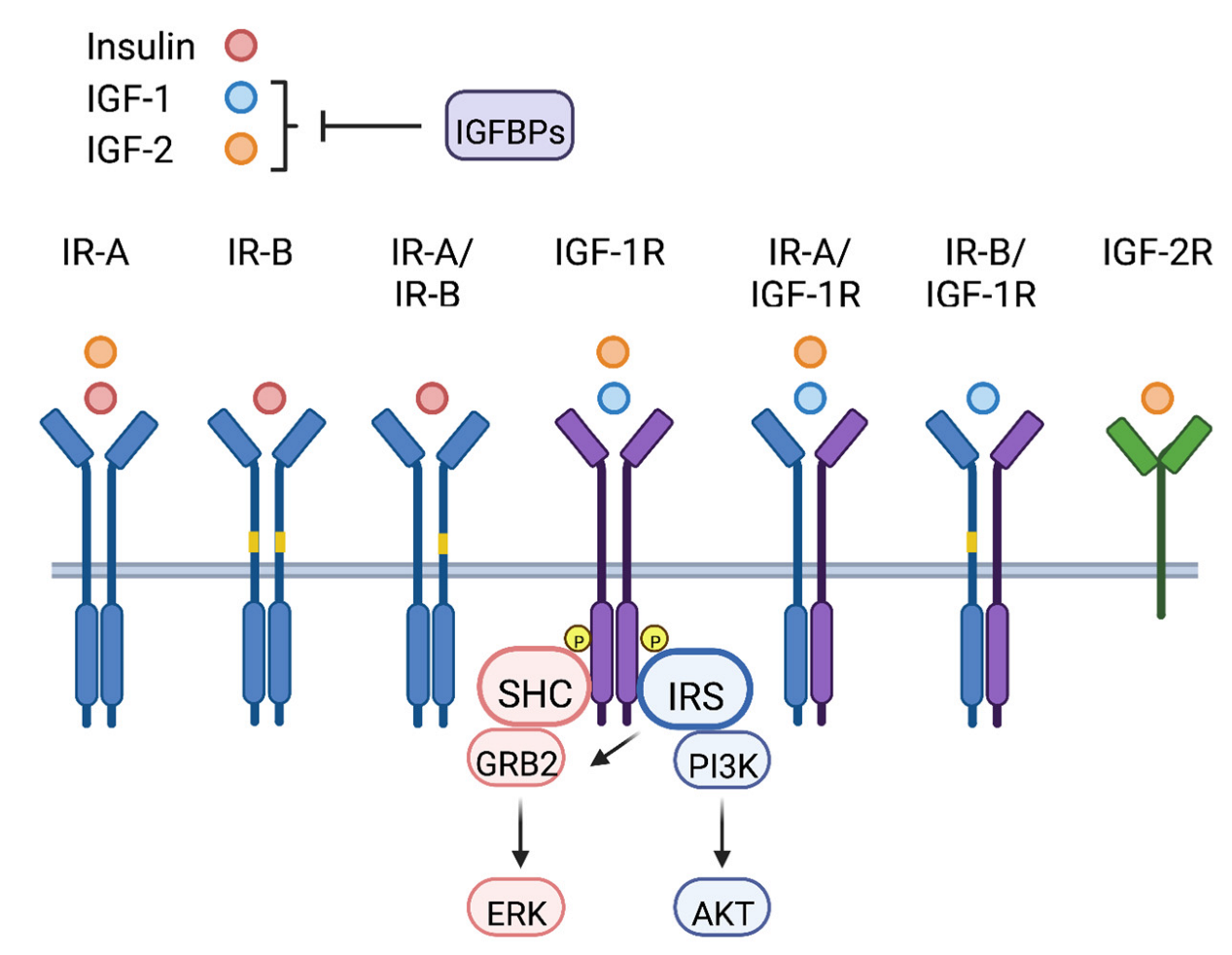

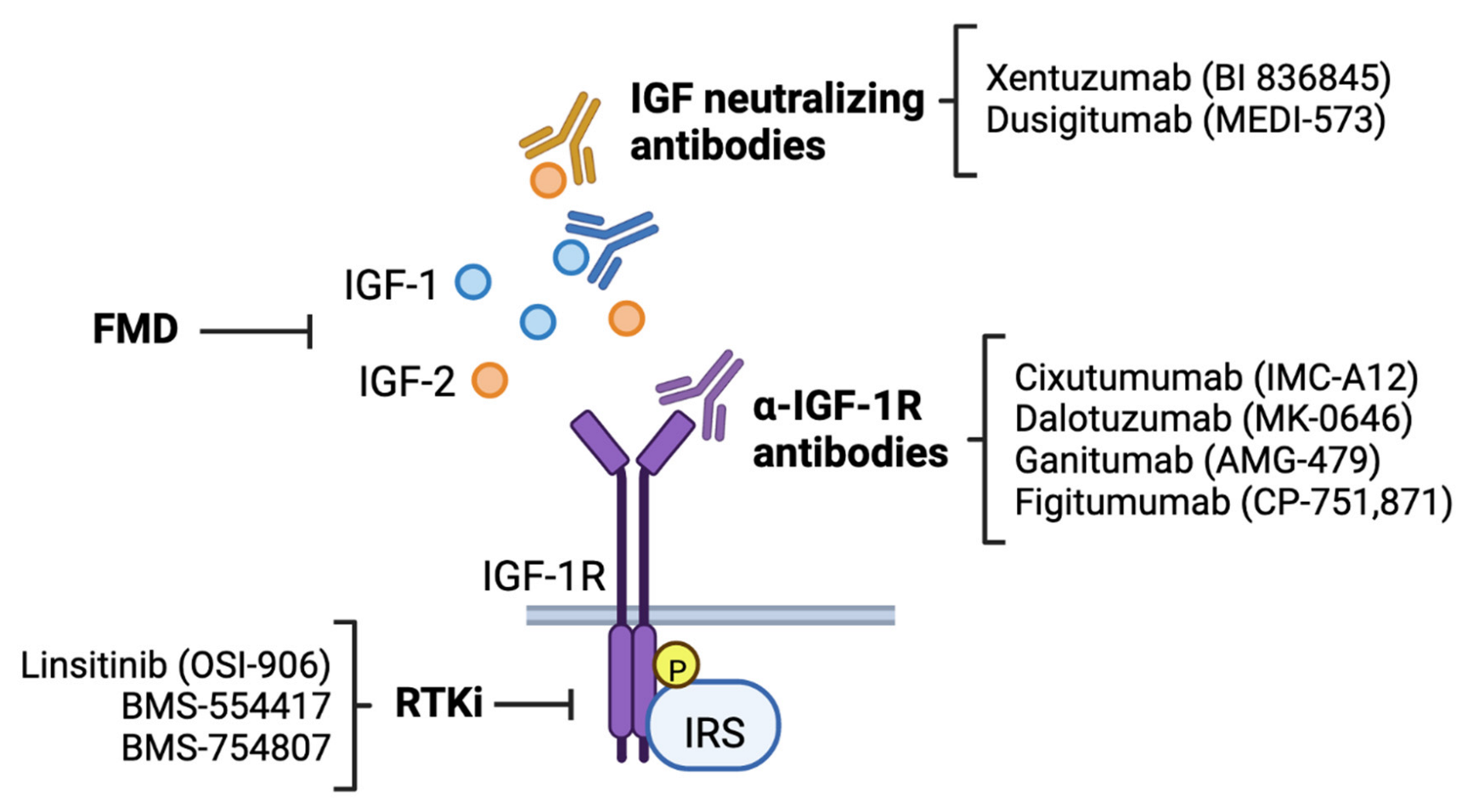
| Therapeutic Class | Clinical Trial NCT Number | Phase | Treatment | Malignancy Type | Status | Reported Outcome(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGF-1R monoclonal antibody | NCT00684983 | II | cixutumumab (IMC-A12) + lapatinib + capecitabine | HER2+ Stage IIIB/VI breast cancer | Completed | no improvement in PFS, ORR, or OS |
| NCT00699491 | I/II | cixutumumab (IMC-A12) + temsirolimus | Male breast cancer; Recurrent breast cancer; Stage IV breast bancer | Completed | ||
| NCT01605396 | II | dalotuzumab (MK-0646) + ridaforolimus + exemestane | High proliferation, ER+ breast cancer | Completed | no improvement in PFS | |
| NCT00903006 | I/II | dalotuzumab (MK-0646) + fulvestrant + dasatinib | Metastatic HR+, HER2− breast cancer | Terminated (low accrual) | ||
| NCT00626106 | II | ganitumab (AMG-479) with and without exemestane or fulvestrant | HR+ locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer previously treated with endocrine therapy | Completed | no improvement in PFS; worse OS | |
| NCT00372996 | II | figitumumab (CP-751,871) + exemestane | HR+ advanced breast cancer | Terminated (business reasons) | ||
| NCT00976508 | I | figitumumab (CP-751, 871) + pegvisomant | Advanced solid tumors (colorectal, lung, breast, prostate, sarcomas) | Terminated (business reasons/low accrual) | ||
| Dual IGF-1R/IR RTKi | NCT01225172 | II | BMS-754807 with or without letrozole | HR+ breast cancer resistant to non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors | Terminated (business reasons) | |
| NCT01205685 | II | linsitinib (OSI-906) + letrozole with or without erlotinib | Hormone-sensitive metastatic breast cancer | Terminated (therapy toxicities) | ||
| IGF-1/2 neutralizing antibody | NCT02123823 | Ib/II | xentuzumab (BI 836845) + everolimus + exemestane | ER+ metastatic breast cancer | Completed | no improvement in PFS in overall population; evidence of benefit in patients without visceral metastases |
| NCT03659136 | II | xentuzumab (BI 836845) + everolimus + exemestane | HR+, HER2− metastatic breast cancer without visceral disease | Completed | ||
| NCT01446159 | Ib/II | dusigitumab (MEDI-573) with or without aromatase inhibitors | HR+, HER2− metastatic breast cancer | Completed | ||
| Fasting Mimicking Diet (FMD) | NCT02126449 | II/III | neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without FMD | HER2- breast cancer | Completed | complete or partial response to radiation occurred more frequently with FMD |
| NCT05503108 | III | neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without FMD | HR+, HER2- metastatic breast cancer | Not yet recruiting | TBD | |
| NCT04248998 | II | preoperative chemotherapy + FMD with or without metformin | TN breast cancer | Recruiting | TBD |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-S.; Tocheny, C.E.; Shaw, L.M. The Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: An Elusive Therapeutic Target. Life 2022, 12, 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121992
Lee J-S, Tocheny CE, Shaw LM. The Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: An Elusive Therapeutic Target. Life. 2022; 12(12):1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121992
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji-Sun, Claire E. Tocheny, and Leslie M. Shaw. 2022. "The Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: An Elusive Therapeutic Target" Life 12, no. 12: 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121992
APA StyleLee, J.-S., Tocheny, C. E., & Shaw, L. M. (2022). The Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: An Elusive Therapeutic Target. Life, 12(12), 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121992






