FGFR Pathway Inhibition in Gastric Cancer: The Golden Era of an Old Target?
Abstract
1. Introduction
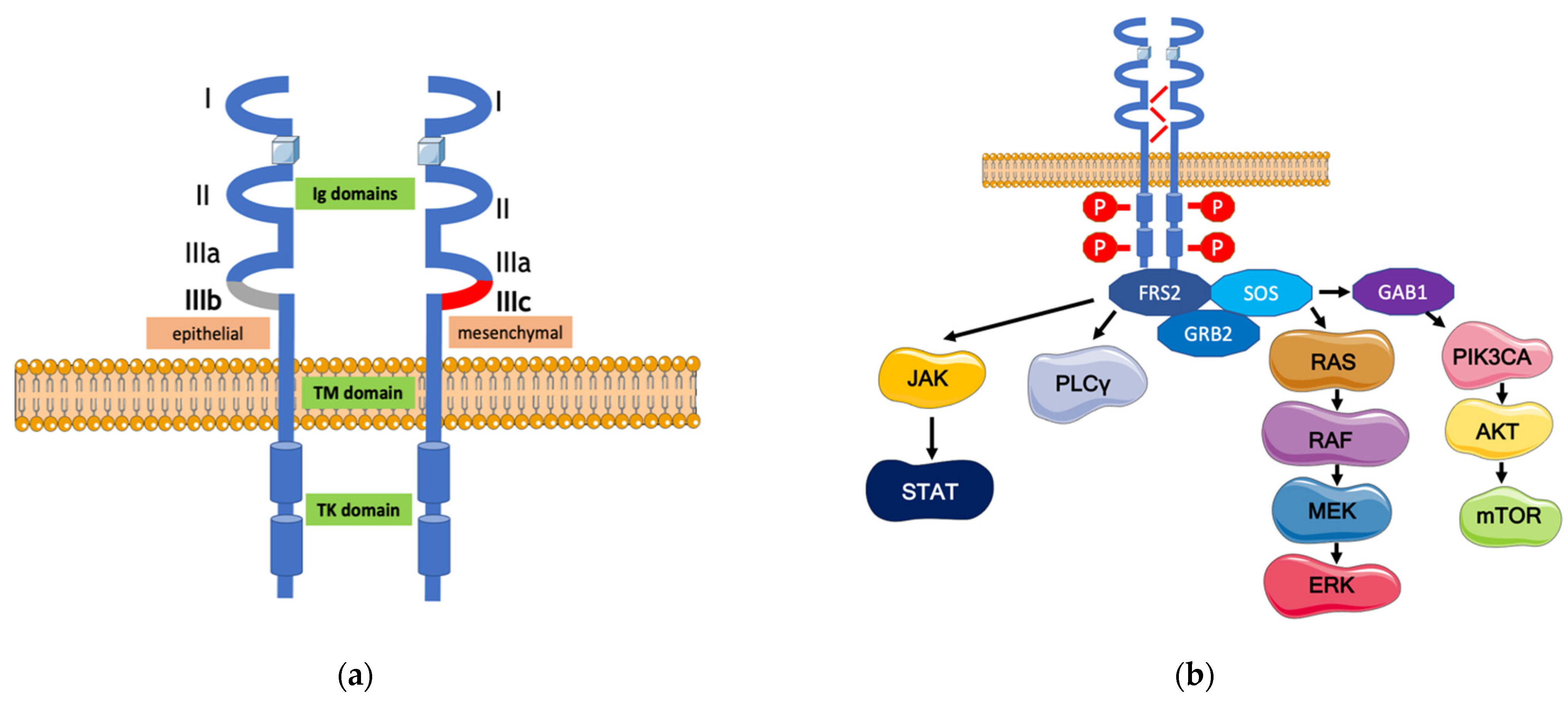
2. The FGFR Signaling Pathway and Its Alterations in Gastric Cancer
3. A Pharmacological Overview on the Anti-FGFR Agents
4. FGFR-Targeted Therapies in Gastric Cancer
4.1. Preclinical Studies and Early Phase Clinical Trials
4.1.1. Multikinase Inhibitors
4.1.2. Pan-FGFR Inhibitors
4.1.3. FGFR1-3 Inhibitors
4.1.4. Selective FGFR Inhibitors
4.1.5. Antibody–Drug Conjugates
4.2. Clinical Trials for FGFR Inhibitors: State of the Art
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, M.; George, R.; Sharma, A.; Graham, D.Y. Changing Trends in Stomach Cancer throughout the World. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 19, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, K. Global patterns and trends in stomach cancer incidence: Age, period and birth cohort analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, A.; Smyth, E.C. 27 years of stomach cancer: Painting a global picture. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 5, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Yeoh, K.-G. Genetics and Molecular Pathogenesis of Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1153–1162.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, R.M., Jr.; Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramacere, I.; Negri, E.; Pelucchi, C.; Bagnardi, V.; Rota, M.; Scotti, L.; Islami, F.; Corrao, G.; La Vecchia, C.; Boffetta, P. A meta-analysis on alcohol drinking and gastric cancer risk. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 23, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, E.C.; Verheij, M.; Allum, W.; Cunningham, D.; Cervantes, A.; Arnold, D.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27 (Suppl. 5), v38–v49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, K.; Van Cutsem, E.; Narita, Y.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Baba, E.; Li, J.; Ryu, M.-H.; Zamaniah, W.I.W.; Yong, W.-P.; Yeh, K.-H.; et al. Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic gastric cancer: A JSMO–ESMO initiative endorsed by CSCO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.D.; Syn, N.L.; Moehler, M.; Grothe, W.; Yong, W.P.; Tai, B.C.; Hol, J.; Unverzagt, S. Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 8, Cd004064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körfer, J.; Lordick, F.; Hacker, U.T. Molecular Targets for Gastric Cancer Treatment and Future Perspectives from a Clinical and Translational Point of View. Cancers 2021, 13, 5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 513, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiu, J.; Baca, Y.; Battaglin, F.; Arai, H.; Kawanishi, N.; Soni, S.; Zhang, W.; Millstein, J.; Salhia, B.; et al. Large-scale analysis of KMT2 mutations defines a distinctive molecular subset with treatment implication in gastric cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4894–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.E.; Puccini, A.; Xiu, J.; Raghavan, D.; Lenz, H.-J.; Korn, W.M.; Shields, A.F.; Philip, P.A.; Marshall, J.L.; Goldberg, R.M. Comparative Molecular Analyses of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Esophageal Adenocarcinoma, and Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Oncology 2018, 23, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Feng-Yi, F.; Xu, J.M.; Lee, K.W.; Jiao, S.C.; Chong, J.L.; López-Sanchez, R.I.; Price, T.; Gladkov, O.; et al. HER2 screening data from ToGA: Targeting HER2 in gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer. Gastric Cancer 2015, 18, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, Y.-J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Feyereislova, A.; Chung, H.C.; Shen, L.; Sawaki, A.; Lordick, F.; Ohtsu, A.; Omuro, Y.; Satoh, T.; et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, A.; Smyth, E.C. Biomarkers for Precision Treatment in Gastric Cancer. Visc. Med. 2020, 36, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Fuchs, C.S.; Shitara, K.; Tabernero, J.; Muro, K.; Van Cutsem, E.; Bang, Y.-J.; De Vita, F.; Landers, G.; Yen, C.-J.; et al. Assessment of Pembrolizumab Therapy for the Treatment of Microsatellite Instability-High Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer Among Patients in the KEYNOTE-059, KEYNOTE-061, and KEYNOTE-062 Clinical Trials. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambardella, V.; Fleitas, T.; Tarazona, N.; Papaccio, F.; Huerta, M.; Roselló, S.; Gimeno-Valiente, F.; Roda, D.; Cervantes, A. Precision Medicine to Treat Advanced Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Work in Progress. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.-T.; Li, N.-G.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Xie, W.-C.; Yang, S.-P.; Lu, T.; Shi, Z.-H. Recent advance in the development of novel, selective and potent FGFR inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 186, 111884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. The role of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of cancers including those of the urinary bladder. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 151, 104567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy Burman, D.; Das, S.; Das, C.; Bhattacharya, R. Alternative splicing modulates cancer aggressiveness: Role in EMT/metastasis and chemoresistance. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzmann, K.; Grunt, T.; Heinzle, C.; Sampl, S.; Steinhoff, H.; Reichmann, N.; Kleiter, M.; Hauck, M.; Marian, B. Alternative Splicing of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor IgIII Loops in Cancer. J. Nucleic Acids 2011, 2012, 950508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, R.; Palapetta, S.M.; Sandhya, V.K.; Sahu, A.; Alipoor, A.; Balakrishnan, L.; Advani, J.; George, B.; Kini, K.R.; Geetha, N.P.; et al. A Network Map of FGF-1/FGFR Signaling System. J. Signal Transduct. 2014, 2014, 962962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, N.; Ornitz, D.M. Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Piccolo, N.; Sarabipour, S.; Hristova, K. A New Method to Study Heterodimerization of Membrane Proteins and Its Application to Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, H.R.; Smith, M.P.; Francavilla, C. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors (FGFRs) and Noncanonical Partners in Cancer Signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.H.; Guy, G.R.; Hadari, Y.R.; Laks, S.; Gotoh, N.; Schlessinger, J.; Lax, I. FRS2 Proteins Recruit Intracellular Signaling Pathways by Binding to Diverse Targets on Fibroblast Growth Factor and Nerve Growth Factor Receptors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkun, Y.; Yasemi, M. Dynamics and control of the ERK signaling pathway: Sensitivity, bistability, and oscillations. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossahebi-Mohammadi, M.; Quan, M.; Zhang, J.-S.; Li, X. FGF Signaling Pathway: A Key Regulator of Stem Cell Pluripotency. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Tyagi, K.; Roy, A. Recent advances in understanding the molecular role of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C gamma 1 as an emerging onco-driver and novel therapeutic target in human carcinogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer. 2021, 1876, 188619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsten, T.; Schwaederle, M.; Kurzrock, R. Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling in hereditary and neoplastic disease: Biologic and clinical implications. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Du, F.; Hu, X.; Guo, H.; Song, C.; Tao, R.; et al. Comprehensive identification of FGFR1-4 alterations in 5 557 Chinese patients with solid tumors by next-generation sequencing. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 3893–3906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Zhu, W.; He, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, J.; Han-Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; et al. A comprehensive pan-cancer study of fibroblast growth factor receptor aberrations in Chinese cancer patients. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristescu, R.; Lee, J.; Nebozhyn, M.; Kim, K.-M.; Ting, J.C.; Wong, S.S.; Liu, J.; Yue, Y.G.; Wang, J.; Yu, K.; et al. Molecular analysis of gastric cancer identifies subtypes associated with distinct clinical outcomes. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuboki, Y.; Schatz, C.A.; Koechert, K.; Schubert, S.; Feng, J.; Wittemer-Rump, S.; Ziegelbauer, K.; Krahn, T.; Nagatsuma, A.K.; Ochiai, A. In situ analysis of FGFR2 mRNA and comparison with FGFR2 gene copy number by dual-color in situ hybridization in a large cohort of gastric cancer patients. Gastric Cancer 2017, 21, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Arao, T.; Hamaguchi, T.; Shimada, Y.; Kato, K.; Oda, I.; Taniguchi, H.; Koizumi, F.; Yanagihara, K.; Sasaki, H.; et al. FGFR2 gene amplification and clinicopathological features in gastric cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, K.; Kim, K.-M.; Kang, S.Y.; Lee, T.; Kim, S.T.; Park, S.H.; Park, Y.S.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Detection of Fusion Genes Using a Targeted RNA Sequencing Panel in Gastrointestinal and Rare Cancers. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 4659062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Carneiro, B.A.; Taxter, T.; Tavora, F.A.; Kalyan, A.; Pai, S.A.; Chae, Y.K.; Giles, F.J. FGFR3-TACC3 fusion in solid tumors: Mini review. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55924–55938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Ahn, T.; Bang, H.; Ham, J.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.T.; Jang, J.; Shim, M.; Kang, S.Y.; Park, S.H.; et al. Acquired resistance to LY2874455 in FGFR2-amplified gastric cancer through an emergence of novel FGFR2-ACSL5 fusion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15014–15022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, C.; Lu, G.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Du, X. FGF/FGFR signaling pathway involved resistance in various cancer types. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 2000–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienhüser, H.; Schmidt, T. Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touat, M.; Ileana, E.; Postel-Vinay, S.; André, F.; Soria, J.-C. Targeting FGFR Signaling in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2684–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinetti, F.; Hollebecque, A.; Bahleda, R.; Loriot, Y.; Olaussen, K.A.; Massard, C.; Friboulet, L. Facts and New Hopes on Selective FGFR Inhibitors in Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 26, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Carvalho, L.M.; de Oliveira Sapori Avelar, S.; Haslam, A.; Gill, J.; Prasad, V. Estimation of Percentage of Patients with Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Alterations Eligible for Off-label Use of Erdafitinib. JAMA Netw. Open. 2019, 2, e1916091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, A.; Bossaer, J.B. Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitors: A review of a novel therapeutic class. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 27, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, T.P.; Jovcheva, E.; Mevellec, L.; Vialard, J.; De Lange, D.; Verhulst, T.; Paulussen, C.; Van De Ven, K.; King, P.; Freyne, E.; et al. Discovery and Pharmacological Characterization of JNJ-42756493 (Erdafitinib), a Functionally Selective Small-Molecule FGFR Family Inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loriot, Y.; Necchi, A.; Park, S.H.; Garcia-Donas, J.; Huddart, R.; Burgess, E.; Fleming, M.; Rezazadeh, A.; Mellado, B.; Varlamov, S.; et al. Erdafitinib in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.C.C.; Koblish, H.; Wu, L.; Bowman, K.; Diamond, S.; DiMatteo, D.; Zhang, Y.; Hansbury, M.; Rupar, M.; Wen, X.; et al. INCB054828 (pemigatinib), a potent and selective inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptors 1, 2, and 3, displays activity against genetically defined tumor models. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A.; Sahai, V.; Hollebecque, A.; Vaccaro, G.; Melisi, D.; Al-Rajabi, R.; Paulson, A.S.; Borad, M.J.; Gallinson, D.; Murphy, A.G.; et al. LBA40—FIGHT-202: A phase II study of pemigatinib in patients (pts) with previously treated locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Chan, A.G.; Ahene, A.; Bellovin, D.I.; Deng, R.; Hsu, A.W.; Jeffry, U.; Palencia, S.; Powers, J.; Zanghi, J.; et al. Preclinical characterization of bemarituzumab, an anti-FGFR2b antibody for the treatment of cancer. mAbs 2021, 13, 1981202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, P.; Shi, R. Anlotinib as a molecular targeted therapy for tumors (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Zhu, Z.; Mao, W.; Wang, H.; Qian, H.; Wu, J.; Guo, X.; Xu, Q. Anlotinib Combined with Anti-PD-1 Antibodies Therapy in Patients with Advanced Refractory Solid Tumors: A Single-Center, Observational, Prospective Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 683502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, N.; Goh, L.K.; Wang, H.; Das, K.; Tao, J.; Tan, I.; Zhang, S.; Lee, M.; Wu, J.; Lim, K.H.; et al. A comprehensive survey of genomic alterations in gastric cancer reveals systematic patterns of molecular exclusivity and co-occurrence among distinct therapeutic targets. Gut 2012, 61, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Matsui, J.; Matsushima, T.; Obaishi, H.; Miyazaki, K.; Nakamura, K.; Tohyama, O.; Semba, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Hoshi, S.S.; et al. Lenvatinib, an angiogenesis inhibitor targeting VEGFR/FGFR, shows broad antitumor activity in human tumor xenograft models associated with microvessel density and pericyte coverage. Vasc. Cell 2014, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Lv, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Camrelizumab combined with lenvatinib in the treatment of gastric cancer with liver metastasis: A case report. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, D.-C.; Luo, P.-H.; Huang, S.-X.; Wang, H.-L.; Huang, J.-F. Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib versus pembrolizumab and lenvatinib monotherapies in cancers: A systematic review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 91, 107281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilberg, F.; Tontsch-Grunt, U.; Baum, A.; Le, A.T.; Doebele, R.C.; Lieb, S.; Gianni, D.; Voss, T.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Haslinger, C.; et al. Triple Angiokinase Inhibitor Nintedanib Directly Inhibits Tumor Cell Growth and Induces Tumor Shrinkage via Blocking Oncogenic Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 364, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Jang, H.-L.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.-L.; Kim, K.-M.; Cho, J.; Park, S.H.; Park, Y.S.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Pazopanib, a Novel Multitargeted Kinase Inhibitor, Shows Potent In Vitro Antitumor Activity in Gastric Cancer Cell Lines with FGFR2 Amplification. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limaye, S.; Patil, D.; Akolkar, D.; Srivastava, N.; Patil, R.; Apurwa, S.; Patil, S.; John, J.; Gosavi, R.; Nesargikar, P.; et al. Response to pazopanib-based combination regimen in a case of FGFR3 amplified gastric adenocarcinoma. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e04986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozgit, J.M.; Wongchenko, M.; Moran, L.; Wardwell, S.; Mohemmad, Q.K.; Narasimhan, N.I.; Shakespeare, W.C.; Wang, F.; Clackson, T.; Rivera, V.M. Ponatinib (AP24534), a Multitargeted Pan-FGFR Inhibitor with Activity in Multiple FGFR-Amplified or Mutated Cancer Models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Bahleda, R.; Hierro, C.; Sanson, M.; Bridgewater, J.; Arkenau, H.-T.; Tran, B.; Kelley, R.K.; Park, J.O.; Javle, M.; et al. Futibatinib, an Irreversible FGFR1–4 Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors Harboring FGF/FGFR Aberrations: A Phase I Dose-Expansion Study. Cancer Discov. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Han, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Wen, J.; Kan, Q. Silencing of FGFR4 could influence the biological features of gastric cancer cells and its therapeutic value in gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 37, 3185–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, W.-Y.; Chen, D.; Henry, J.R.; Li, H.-Y.; Chen, Z.; Zia-Ebrahimi, M.; Bloem, L.; Zhai, Y.; Huss, K.; et al. A Novel, Selective Inhibitor of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors That Shows a Potent Broad Spectrum of Antitumor Activity in Several Tumor Xenograft Models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2200–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, M.; Bang, Y.-J.; Park, Y.S.; Kang, Y.-K.; Kim, T.M.; Hamid, O.; Thornton, N.; Tate, S.C.; Raddad, E.; Tie, J. A Phase 1 Study of LY2874455, an Oral Selective pan-FGFR Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, K.; Zeng, J.; Wan, G.; He, X.; Feng, Z.; Xiang, W.; Wei, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, N.; Liu, Z.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluations of a series of Pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidinone derivatives as novel selective FGFR inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 220, 113499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.K.; Shen, R.; Berger, M.F.; Ferry, D.; Soria, J.-C.; Mathewson, A.; Rooney, C.; Smith, N.R.; Cullberg, M.; Kilgour, E.; et al. A Phase Ib Open-Label Multicenter Study of AZD4547 in Patients with Advanced Squamous Cell Lung Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5366–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitowska, K.; Gorska-Arcisz, M.; Antoun, D.; Zarczynska, I.; Czaplinska, D.; Szczepaniak, A.; Skladanowski, A.C.; Wieczorek, M.; Stanczak, A.; Skupinska, M.; et al. MET-Pyk2 Axis Mediates Acquired Resistance to FGFR Inhibition in Cancer Cells. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 633410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, I.; Goyal, L.; Cleary, J.; Voss, M.; Oh, D.; Bernstam, F.M.; Ng, C.; Iyer, G.; Ishii, N.; Hu, Y.; et al. SO-003-Debio 1347 in patients with gastrointestinal cancers harboring an FGFR gene fusion: Preliminary results. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, iv122–iv123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Moser, C.; Hellerbrand, C.; Zieker, D.; Wagner, C.; Redekopf, J.; Schlitt, H.J.; Geissler, E.K.; Lang, S.A. Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR) with BGJ398 in a Gastric Cancer Model. Anticancer. Res. 2015, 35, 6655–6665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grygielewicz, P.; Dymek, B.; Bujak, A.; Gunerka, P.; Stanczak, A.; Lamparska-Przybysz, M.; Wieczorek, M.; Dzwonek, K.; Zdżalik-Bielecka, D. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition confers resistance to selective FGFR inhibitors in SNU-16 gastric cancer cells. Gastric Cancer 2014, 19, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Deng, X.; Feng, G.; Chen, Y. Knockdown of Bcl-2-Associated Athanogene-3 Can Enhance the Efficacy of BGJ398 via Suppressing Migration and Inducing Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 66, 3036–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimafeyeu, I.; Ludes-Meyers, J.; Stepanova, E.; Daeyaert, F.; Khochenkov, D.; Joose, J.-B.; Solomko, E.; Van Akene, K.; Peretolchina, N.; Yin, W.; et al. Targeting FGFR2 with alofanib (RPT835) shows potent activity in tumour models. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 61, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, Y.; Wang, M.; Lu, L.; Han, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; et al. The over-expression of FGFR4 could influence the features of gastric cancer cells and inhibit the efficacy of PD173074 and 5-fluorouracil towards gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 37, 6881–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Kalyan, A.; Babich, A.; Liu, R.; Tanigawa, T.; Sommer, A.; Osada, M.; Reetz, F.; Laurent, D.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Study of Aprutumab Ixadotin, a Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 Antibody-Drug Conjugate (BAY 1187982) in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Target Oncol. 2019, 14, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, F.; Di Martino, N.; Fabozzi, A.; Laterza, M.M.; Ventriglia, J.; Savastano, B.; Petrillo, A.; Gambardella, V.; Sforza, V.; Marano, L.; et al. Clinical management of advanced gastric cancer: The role of new molecular drugs. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14537–14558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Mansoor, W.; Petty, R.D.; Chao, Y.; Cunningham, D.; Ferry, D.R.; Smith, N.R.; Frewer, P.; Ratnayake, J.; et al. A randomized, open-label study of the efficacy and safety of AZD4547 monotherapy versus paclitaxel for the treatment of advanced gastric adenocarcinoma with FGFR2 polysomy or gene amplification. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, D.X.; Meng, L.; Ji, G. Anlotinib combined with SOX regimen (S1 (tegafur, gimeracil and oteracil porassium capsules) + oxaliplatin) in treating stage IV gastric cancer: Study protocol for a single-armed and single-centred clinical trial. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e034685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainberg, Z.A.; Enzinger, P.C.; Kang, Y.-K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Qin, S.; Lee, K.-W.; Oh, S.C.; Li, J.; Turk, H.M.; Teixeira, A.C.; et al. Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled phase 2 study of bemarituzumab combined with modified FOLFOX6 (mFOLFOX6) in first-line (1L) treatment of advanced gastric/gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (FIGHT). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenacci, D.V.; Kang, Y.-K.; Saeed, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Qin, S.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, I.-H.; Oh, S.C.; Li, J.; Turk, H.M.; et al. FIGHT: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II study of bemarituzumab (bema) combined with modified FOLFOX6 in 1L FGFR2b+ advanced gastric/gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (GC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, P.M.K.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, A.S.L.; Yu, J.; Kang, W.; To, K.F. Targeting the Oncogenic FGF-FGFR Axis in Gastric Carcinogenesis. Cells 2019, 8, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.K.; Luk, I.Y.; Jenkins, L.J.; Martin, A.; Williams, D.S.; Schoffer, K.L.; Chionh, F.; Buchert, M.; Sjoquist, K.; Boussioutas, A.; et al. Rapid Resistance of FGFR-driven Gastric Cancers to Regorafenib and Targeted FGFR Inhibitors can be Overcome by Parallel Inhibition of MEK. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Dierichs, L.; Gu, J.-N.; Trajkovic-Arsic, M.; Hilger, R.A.; Savvatakis, K.; Vega-Rubin-De-Celis, S.; Liffers, S.-T.; Peña-Llopis, S.; Behrens, D.; et al. TFEB-mediated lysosomal biogenesis and lysosomal drug sequestration confer resistance to MEK inhibition in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englinger, B.; Kallus, S.; Senkiv, J.; Heilos, D.; Gabler, L.; Van Schoonhoven, S.; Terenzi, A.; Moser, P.; Pirker, C.; Timelthaler, G.; et al. Intrinsic fluorescence of the clinically approved multikinase inhibitor nintedanib reveals lysosomal sequestration as resistance mechanism in FGFR-driven lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Klerk, D.J.; Honeywell, R.J.; Jansen, G.; Peters, G.J. Transporter and Lysosomal Mediated (Multi)drug Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Potential Strategies to Overcome Resistance. Cancers 2018, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settembre, C.; Di Malta, C.; Polito, V.A.; Garcia Arencibia, M.; Vetrini, F.; Erdin, S.; Erdin, S.U.; Huynh, T.; Medina, D.; Colella, P.; et al. TFEB Links Autophagy to Lysosomal Biogenesis. Science 2011, 332, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, D.L.; Di Paola, S.; Peluso, I.; Armani, A.; De Stefani, D.; Venditti, R.; Montefusco, S.; Rosato, A.S.; Prezioso, C.; Forrester, A.; et al. Lysosomal calcium signalling regulates autophagy through calcineurin and TFEB. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Panse, M.; Radunski, U.; Koch, R.; Wenzel, D.; Inagaki, N.; Haase, D.; Truemper, L.; Wulf, G.G. ABC transporter A3 facilitates lysosomal sequestration of imatinib and modulates susceptibility of chronic myeloid leukemia cell lines to this drug. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palakurthi, S.; Kuraguchi, M.; Zacharek, S.J.; Zudaire, E.; Huang, W.; Bonal, D.M.; Liu, J.; Dhaneshwar, A.; Depeaux, K.; Gowaski, M.R.; et al. The Combined Effect of FGFR Inhibition and PD-1 Blockade Promotes Tumor-Intrinsic Induction of Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1457–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhand, S.S.; Liu, Z.; Purdy, S.C.; Abdullah, A.; Lin, H.; Cresswell, G.M.; Ratliff, T.L.; Wendt, M.K. Pharmacologic Inhibition of FGFR Modulates the Metastatic Immune Microenvironment and Promotes Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1542–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name of Drug, Intervention | Tumor Type, Setting, Patient Inclusion/Stratification by Molecular Status | Phase | Study Name, Trial ID | Primary Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multikinase Inhibitors | ||||
| Anlotinib | Advanced stomach cancer patients, subsequent line of treatment, no molecular stratification | II/III | ALTER0503, NCT02461407 | OS |
| Anlotinib | Advanced stomach cancer patients, subsequent line of treatment, no molecular stratification | II | THALIA, NCT05029102 | PFS |
| TQB2450 /Anlotinib hydrochloride/ Oxaliplatin/Capecitabine | HER2/Neu negative, advanced or metastatic gastric, second-line treatment | N/A | NCT04891900 | ORR |
| TISLELIZUMAB, Anlotinib plus XELOX | Metastatic gastric cancer, first-line, no molecular stratification | III | NCT04963088 | MTD, ORR |
| Tislelizumab + anlotinib | Metastatic gastric cancer, first-line, no molecular stratification | II | NCT04777162 | ORR |
| Anlotinib Plus Toripalimab | Metastatic gastric cancer, subsequent line, no molecular stratification | II | NCT04278222 | ORR |
| Anlotinib | High grade (3), second-line | II | NCT03457844 | PFS |
| Anlotinib Hydrochloride with Nivolumab | Metastatic gastric cancer, second-line, no molecular stratification | II | NCT04503967 | ORR |
| Dovitinib | Advanced gastric cancer, FGFR2 amplification required, subsequent line | II | NCT01719549, GASDOVI-1 | RR |
| Dovitinib Plus Docetaxel | Advanced gastric cancer, first-line, no molecular stratification | I/II | NCT01921673 | MTD, PFS |
| TKI258 | Advanced gastric cancer, subsequent line, no molecular stratification | II | NCT01576380 | DCR |
| Lenvatinib + Pembrolizumab | Non-metastatic, fist-line, no molecular classification | II | NCT04745988 | MPR rate |
| Lenvatinib + Pembrolizumab | Advanced gastric cancer, subsequent line, no molecular stratification | II | NCT03321630 | ORR, OS |
| Lenvatinib + Pembrolizumab | Female, advanced ovarian and gastric neoplasms, subsequent line | II | NCT04519151 | PFS |
| Lenvatinib + Pembrolizumab | PD-L1 positive, subsequent line | II | NCT03797326 | ORR |
| Lenvatinib | Advanced gastric cancer, subsequent to prior imatinib or sunitinib | II | NCT04193553 | PFS |
| Pazopanib Hydrochloride | Low- or intermediate-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma, advanced, second-line | II | NCT01841736 | PFS |
| Pan FGFR inhibitors | ||||
| Erdafitinib | Advanced gastric cancer, Mandatory FGFR testing, beyond first-line | II | NCT02699606 | ORR |
| Erdafitinib | Advanced Solid tumor, second-line or beyond, FGFR testing | II | NCT02465060 | ORR |
| Futibatinib | Advanced gastric cancer, FGFR testing, beyond first-line | II | NCT04189445 | ORR |
| FGFR1-3 inhibitors | ||||
| AZD 4547 | Advanced, second line or third line, Mandatory confirmation of FGFR gene amplification | II | NCT01795768 | Molecular change as correlated with tumor size change |
| AZD 4547 | Advanced solid tumor, second-line or beyond, based on molecular stratification | NCT02465060, MATCH | ORR | |
| Debio1347 | Advanced solid tumor, second-line or beyond, based on molecular stratification | II | NCT03834220 | ORR |
| Infigratinib | Advanced gastric cancer, second-line or beyond, based on FGFR status | II | NCT05019794 | ORR |
| Derazantinib + paclitaxel-ramucirumab/ atezolizumab | Advanced gastric cancer, second-line or beyond, based on FGFR status | I/II | NCT04604132, FIDES-03 | ORR |
| Selective FGFR2-inhibitor | ||||
| mFOLFOX6 ± bemarituzumab | Advanced gastric cancer, first-line, based on FGFR status | III | NCT05052801, FORTITUDE-101 | OS |
| Pan FGFR inhibitors | ||||
| Erdafitinib | Advanced gastric cancer, Mandatory FGFR testing, beyond first-line | II | NCT02699606 | ORR |
| Erdafitinib | Advanced Solid tumor, second line or beyond, FGFR testing | II | NCT02465060 | ORR |
| Futibatinib | Advanced gastric cancer, FGFR testing, beyond first-line | II | NCT04189445 | ORR |
| FGFR1-3 inhibitors | ||||
| AZD 4547 | Advanced, second-line or third-line, Mandatory confirmation of FGFR gene amplification | II | NCT01795768 | Molecular change as correlated with tumor size change |
| AZD 4547 | Advanced solid tumor, second-line or beyond, based on molecular stratification | NCT02465060, MATCH | ORR | |
| Debio1347 | Advanced solid tumor, second-line or beyond, based on molecular stratification | II | NCT03834220 | ORR |
| Infigratinib | Advanced gastric cancer, second-line or beyond, based on FGFR status | II | NCT05019794 | ORR |
| Derazantinib + paclitaxel-ramucirumab/ atezolizumab | Advanced gastric cancer, second-line or beyond, based on FGFR status | I/II | NCT04604132, FIDES-03 | ORR |
| Potential Target | Mechanism of Resistance |
|---|---|
| SHP2 | Downstream mediator of the FGFR-response |
| MET | Overexpression is associated with anti-FGFR resistance |
| Pyk2 | Overexpression is associated with anti-FGFR resistance |
| MET | Secondary activation associated with resistance to anti-FGFR |
| YAP1 | Downstream modulator of the FGFR2 signalling |
| TAK1 | Regulator of the lysosome biogenesis and mediated resistance to anti-FGFR agents |
| mTORC1 | Regulator of the lysosome biogenesis and mediated resistance to anti-FGFR agents |
| FGF18 | Oncogenic stimulation of cancer cells |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lengyel, C.G.; Hussain, S.; Seeber, A.; Jamil Nidhamalddin, S.; Trapani, D.; Habeeb, B.S.; Elfaham, E.; Mazher, S.A.; Seid, F.; Khan, S.Z.; et al. FGFR Pathway Inhibition in Gastric Cancer: The Golden Era of an Old Target? Life 2022, 12, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010081
Lengyel CG, Hussain S, Seeber A, Jamil Nidhamalddin S, Trapani D, Habeeb BS, Elfaham E, Mazher SA, Seid F, Khan SZ, et al. FGFR Pathway Inhibition in Gastric Cancer: The Golden Era of an Old Target? Life. 2022; 12(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleLengyel, Csongor G., Sadaqat Hussain, Andreas Seeber, Sara Jamil Nidhamalddin, Dario Trapani, Baker S. Habeeb, Essam Elfaham, Syed Ayub Mazher, Fahmi Seid, Shah Z. Khan, and et al. 2022. "FGFR Pathway Inhibition in Gastric Cancer: The Golden Era of an Old Target?" Life 12, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010081
APA StyleLengyel, C. G., Hussain, S., Seeber, A., Jamil Nidhamalddin, S., Trapani, D., Habeeb, B. S., Elfaham, E., Mazher, S. A., Seid, F., Khan, S. Z., El Bairi, K., Odhiambo, A., Altuna, S. C., & Petrillo, A. (2022). FGFR Pathway Inhibition in Gastric Cancer: The Golden Era of an Old Target? Life, 12(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010081











