Utility of RGNEF in the Prediction of Clinical Prognosis in Patients with Rectal Cancer Receiving Preoperative Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Mining of a Rectal Cancer Microarray Dataset
2.2. Patients and Samples
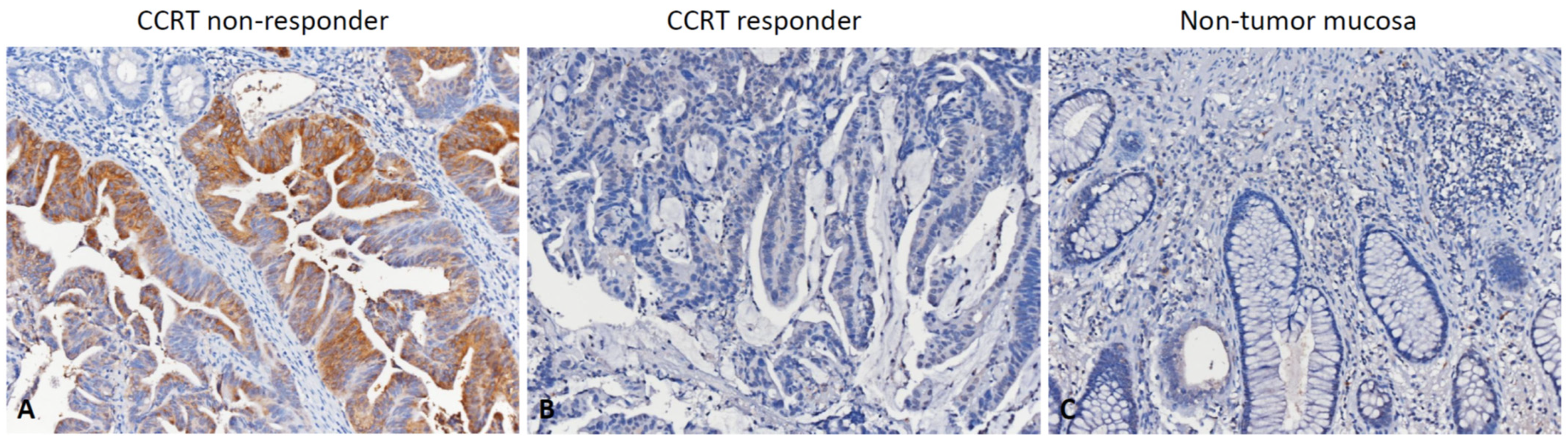
2.3. Histopathological Assessments and Immunohistochemical Scoring
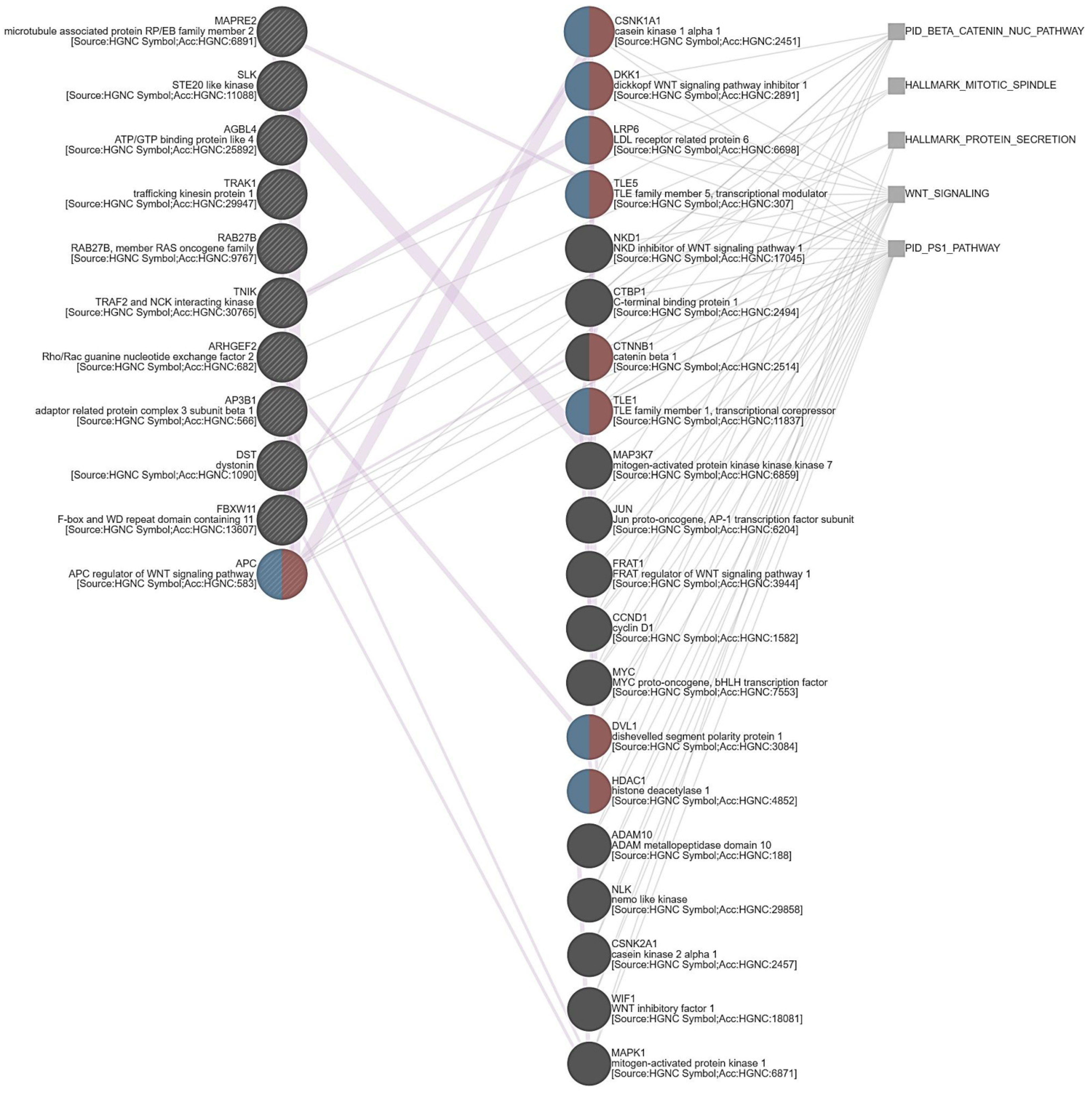
2.4. Gene Ontology Enrichment Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ARHGEF28 Is the Most Upregulated DEG Related to CCRT Resistance in Rectal Cancer Associated with Rho Guanyl-Nucleotide Exchange Factor Activity
3.2. Clinicopathological Features
3.3. Association between RGNEF Expression and Clinicopathological Parameters
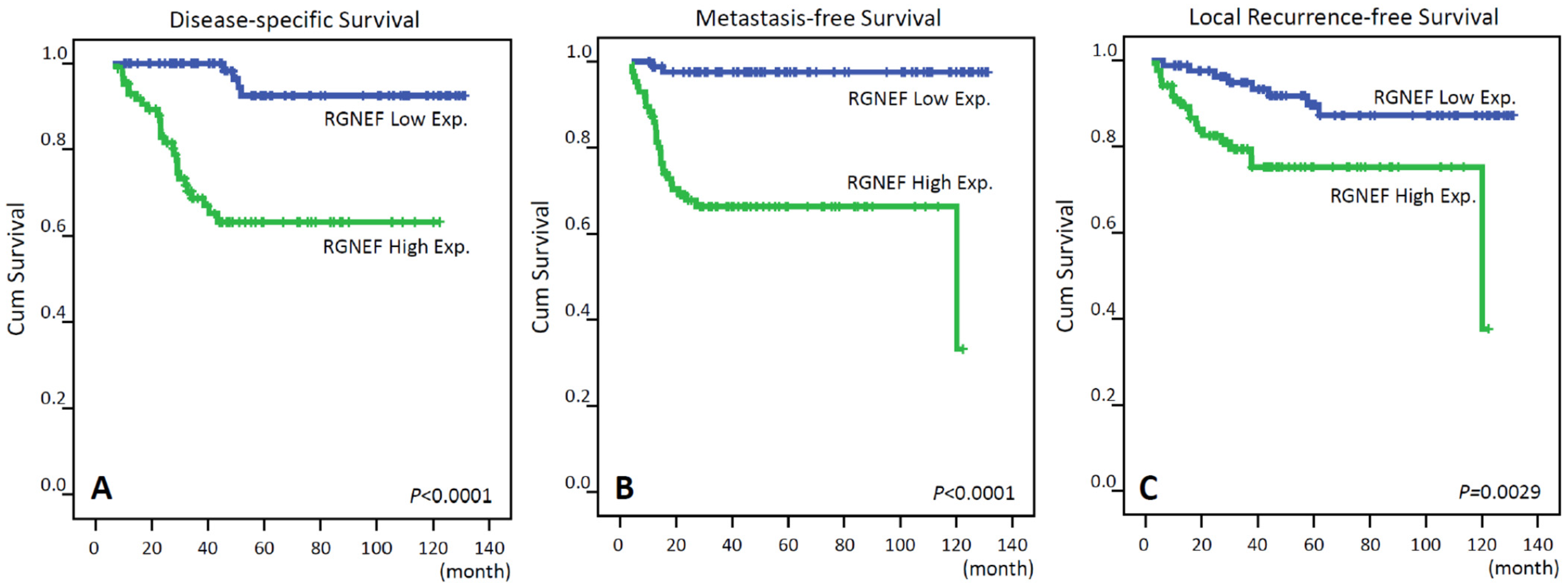
3.4. Survival and Prognostic Significances of RGNEF Expression
3.5. ARHGEF28 Overexpression May Be Linked to Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Rectal Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.E.; Hu, C.Y.; You, Y.N.; Bednarski, B.K.; Rodriguez-Bigas, M.A.; Skibber, J.M.; Cantor, S.B.; Chang, G.J. Increasing disparities in the age-related incidences of colon and rectal cancers in the United States, 1975–2010. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosset, J.F.; Calais, G.; Mineur, L.; Maingon, P.; Stojanovic-Rundic, S.; Bensadoun, R.J.; Bardet, E.; Beny, A.; Ollier, J.C.; Bolla, M.; et al. Fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy after preoperative chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer: Long-term results of the EORTC 22921 randomised study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, J.P.; Conroy, T.; Bonnetain, F.; Bouche, O.; Chapet, O.; Closon-Dejardin, M.T.; Untereiner, M.; Leduc, B.; Francois, E.; Maurel, J.; et al. Preoperative radiotherapy with or without concurrent fluorouracil and leucovorin in T3-4 rectal cancers: Results of FFCD 9203. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4620–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodel, C.; Graeven, U.; Fietkau, R.; Hohenberger, W.; Hothorn, T.; Arnold, D.; Hofheinz, R.D.; Ghadimi, M.; Wolff, H.A.; Lang-Welzenbach, M.; et al. Oxaliplatin added to fluorouracil-based preoperative chemoradiotherapy and postoperative chemotherapy of locally advanced rectal cancer (the German CAO/ARO/AIO-04 study): Final results of the multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsons, J.T.; Horwitz, A.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Cell adhesion: Integrating cytoskeletal dynamics and cellular tension. Nature reviews. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne-Manneville, S.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 2002, 420, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Cui, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gnosa, S.; Ali, Z.; Jensen, L.; Jonsson, J.I.; Blockhuys, S.; Lam, E.W.; et al. The Critical Role of Dysregulated RhoB Signaling Pathway in Radioresistance of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.F.; Xu, Y.W.; Li, J.; Niu, H.L.; Ma, W.X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, P.R.; Liu, X.; Ye, D.L.; Liu, X.R.; et al. Mir20a/106a-WTX axis regulates RhoGDIa/CDC42 signaling and colon cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, J.; Nie, S.; Tang, Z.; Kang, A.; Fu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liao, Q.; Xiong, W.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Y.; et al. Long noncoding RNA EPB41L4A-AS1 functions as an oncogene by regulating the Rho/ROCK pathway in colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y. Dbl family guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Horck, F.P.; Ahmadian, M.R.; Haeusler, L.C.; Moolenaar, W.H.; Kranenburg, O. Characterization of p190RhoGEF, a RhoA-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor that interacts with microtubules. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 4948–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, Y.; Lim, S.T.; Tomar, A.; Gardel, M.; Bernard-Trifilo, J.A.; Chen, X.L.; Uryu, S.A.; Canete-Soler, R.; Zhai, J.; Lin, H.; et al. PyK2 and FAK connections to p190Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor regulate RhoA activity, focal adhesion formation, and cell motility. J. Cell. Biol. 2008, 180, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, N.L.; Lawson, C.; Chen, X.L.; Lim, S.T.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Rgnef (p190RhoGEF) knockout inhibits RhoA activity, focal adhesion establishment, and cell motility downstream of integrins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.G.; Nam, J.O.; Miller, N.L.; Tanjoni, I.; Walsh, C.; Shi, L.; Kim, L.; Chen, X.L.; Tomar, A.; Lim, S.T.; et al. p190RhoGEF (Rgnef) promotes colon carcinoma tumor progression via interaction with focal adhesion kinase. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleinschmidt, E.G.; Miller, N.L.G.; Ozmadenci, D.; Tancioni, I.; Osterman, C.D.; Barrie, A.M.; Taylor, K.N.; Ye, A.; Jiang, S.; Connolly, D.C.; et al. Rgnef promotes ovarian tumor progression and confers protection from oxidative stress. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6323–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droppelmann, C.A.; Campos-Melo, D.; Volkening, K.; Strong, M.J. The emerging role of guanine nucleotide exchange factors in ALS and other neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Zhai, J.; Lin, H.; Nie, Z.; Ge, W.W.; Garcia-Bermejo, L.; Muschel, R.J.; Schlaepfer, W.W.; Canete-Soler, R. Cytoplasmic retention sites in p190RhoGEF confer anti-apoptotic activity to an EGFP-tagged protein. Brain research. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 117, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, B.; Beggs, H.E.; Schahin-Reed, D.; Kimes, N.; Schmidt, A.; Reichardt, L.F. Control of axonal branching and synapse formation by focal adhesion kinase. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Bareiss, S.; Kim, K.K.; Tatum, R.; Han, J.R.; Jin, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Lu, Q.; Kim, K. Presenilin-1 inhibits delta-catenin-induced cellular branching and promotes delta-catenin processing and turnover. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Oh, M.; Lu, Q.; Kim, K. E-Cadherin negatively modulates delta-catenin-induced morphological changes and RhoA activity reduction by competing with p190RhoGEF for delta-catenin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, T.; Komuro, Y.; Kiyomatsu, T.; Kanazawa, T.; Kazama, Y.; Tanaka, J.; Tanaka, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Shirane, M.; Muto, T.; et al. Prediction of sensitivity of rectal cancer cells in response to preoperative radiotherapy by DNA microarray analysis of gene expression profiles. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3370–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, C.L.; Chen, T.J.; Tian, Y.F.; Chan, T.C.; Yeh, C.F.; Li, W.S.; Tsai, H.H.; Li, C.F.; Lai, H.Y. Upregulated MUC2 Is an Unfavorable Prognostic Indicator for Rectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Preoperative CCRT. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworak, O.; Keilholz, L.; Hoffmann, A. Pathological features of rectal cancer after preoperative radiochemotherapy. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 1997, 12, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Rodriguez, H.; Lopes, C.; Zuberi, K.; Montojo, J.; Bader, G.D.; Morris, Q. GeneMANIA update 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W60–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duff, K.; Eckman, C.; Zehr, C.; Yu, X.; Prada, C.M.; Perez-tur, J.; Hutton, M.; Buee, L.; Harigaya, Y.; Yager, D.; et al. Increased amyloid-beta42(43) in brains of mice expressing mutant presenilin 1. Nature 1996, 383, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschner, B.W.; VanderWalde, N.A.; Grothey, A.; Shibata, D. Evolution and Current Status of the Multidisciplinary Management of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2021, 17, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droppelmann, C.A.; Keller, B.A.; Campos-Melo, D.; Volkening, K.; Strong, M.J. Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor is an NFL mRNA destabilizing factor that forms cytoplasmic inclusions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.; Droppelmann, C.A.; MacLellan, A.; Cameron, I.; Withers, B.; Campos-Melo, D.; Volkening, K.; Strong, M.J. Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (RGNEF) is a prosurvival factor under stress conditions. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 82, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gregorio, S.E.; Volkening, K.; Strong, M.J.; Duennwald, M.L. Inclusion Formation and Toxicity of the ALS Protein RGNEF and Its Association with the Microtubule Network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masia-Balague, M.; Izquierdo, I.; Garrido, G.; Cordomi, A.; Perez-Benito, L.; Miller, N.L.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Gigoux, V.; Aragay, A.M. Gastrin-stimulated Galpha13 Activation of Rgnef Protein (ArhGEF28) in DLD-1 Colon Carcinoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15197–15209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pino, M.S.; Chung, D.C. The chromosomal instability pathway in colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2059–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, T.W.; Neufeld, K.L. APC controls Wnt-induced beta-catenin destruction complex recruitment in human colonocytes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emons, G.; Spitzner, M.; Reineke, S.; Moller, J.; Auslander, N.; Kramer, F.; Hu, Y.; Beissbarth, T.; Wolff, H.A.; Rave-Frank, M.; et al. Chemoradiotherapy Resistance in Colorectal Cancer Cells is Mediated by Wnt/beta-catenin Signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.R.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, F.C.; Zheng, C.H.; Xie, J.W.; Wang, J.B.; Huang, C.M. The expression of presenilin 1 enhances carcinogenesis and metastasis in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10650–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
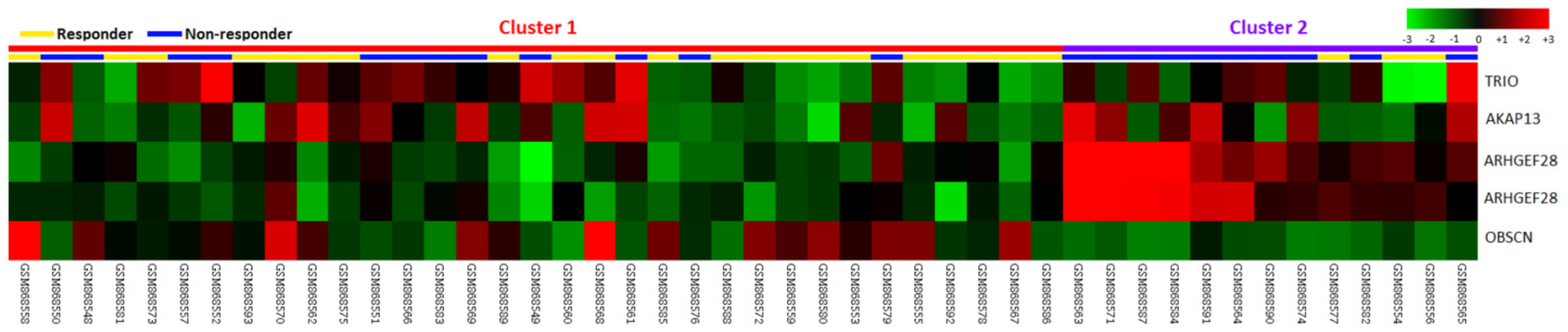

| Probe | Comparison Log Ratio | Comparison p-Value | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Biological Process | Molecular Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1554004_a_at | 0.4167 | 0.0028 | ARHGEF28 | Rho-guanine nucleotide exchange factor 28 | Intracellular signaling cascade, regulation of Rho protein signal transduction | Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity |
| 216697_at | 0.2424 | 0.0002 | TRIO | Triple functional domain (PTPRF interacting) | protein amino acid phosphorylation, regulation of Rho protein signal transduction, transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase signaling pathway | ATP binding, Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity, guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity, kinase activity, nucleotide binding, protein kinase activity, protein serine/threonine kinase activity, transferase activity |
| 222023_at | 0.1782 | 0.0099 | AKAP13 | A kinase (PRKA) anchor protein 13 | Intracellular signaling cascade, regulation of Rho protein signal transduction | Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity, diacylglycerol binding, guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity, metal ion binding, receptor activity, signal transducer activity, zinc ion binding |
| 232994_s_at | 0.4723 | 0.0037 | ARHGEF28 | Rho-guanine nucleotide exchange factor 28 | Intracellular signaling cascade, regulation of Rho protein signal transduction | Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity |
| 233029_at | −0.3843 | 0.0097 | OBSCN | Obscurin; cytoskeletal calmodulin and titin-interacting RhoGEF | Cell differentiation, multicellular organismal development, protein amino acid phosphorylation, regulation of Rho protein signal transduction | ATP binding, Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity, kinase activity, magnesium ion binding, metal ion binding, nucleotide binding, protein binding, protein kinase activity, protein serine/threonine kinase activity, protein-tyrosine kinase activity, transferase activity |
| Parameter | No. | RGNEF Expression | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Exp | High Exp. | ||||
| Gender | Male | 108 | 50 | 58 | 0.207 |
| Female | 64 | 36 | 28 | ||
| Age | <70 | 106 | 49 | 57 | 0.210 |
| ≥70 | 66 | 37 | 29 | ||
| Pre-Tx Tumor Status (cT) | T1-T2 | 81 | 43 | 38 | 0.445 |
| T3-T4 | 91 | 43 | 48 | ||
| Pre-Tx Nodal Status (cN) | N0 | 125 | 71 | 54 | 0.004 * |
| N1-N2 | 47 | 15 | 32 | ||
| Post-Tx Tumor Status (ypT) | T1-T2 | 86 | 46 | 40 | 0.360 |
| T3-T4 | 86 | 40 | 46 | ||
| Post-Tx Nodal Status (ypN) | N0 | 123 | 61 | 62 | 0.866 |
| N1-N2 | 49 | 25 | 24 | ||
| Vascular Invasion | Absent | 157 | 85 | 72 | <0.001 * |
| Present | 15 | 1 | 14 | ||
| Perineural Invasion | Absent | 167 | 84 | 83 | 0.650 |
| Present | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Tumor Regression Grade | Grade 0–1 | 37 | 13 | 24 | 0.018 * |
| Grade 2–3 | 118 | 60 | 58 | ||
| Grade 4 | 17 | 13 | 4 | ||
| Parameter | No. of Case | DSS | LRFS | MeFS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Event | p-Value | No. of Event | p-Value | No. of Event | p-Value | |||
| Gender | Male | 108 | 20 | 0.9026 | 7 | 0.2250 | 17 | 0.3520 |
| Female | 64 | 11 | 20 | 14 | ||||
| Age | <70 | 106 | 19 | 0.8540 | 18 | 0.6615 | 20 | 0.7427 |
| ≥70 | 66 | 12 | 9 | 11 | ||||
| Pre-Tx tumor status (cT) | T1-T2 | 81 | 10 | 0.0776 | 10 | 0.2261 | 11 | 0.1745 |
| T3-T4 | 91 | 21 | 17 | 20 | ||||
| Pre-Tx nodal status (cN) | N0 | 125 | 19 | 0.0711 | 15 | 0.0070 * | 19 | 0.0973 |
| N1-N2 | 47 | 21 | 12 | 12 | ||||
| Post-Tx tumor status (ypT) | T1-T2 | 86 | 7 | 0.0006 * | 7 | 0.0040 * | 8 | 0.0033 * |
| T3-T4 | 86 | 24 | 20 | 23 | ||||
| Post-Tx nodal status (ypN) | N0 | 123 | 21 | 0.5998 | 16 | 0.1320 | 20 | 0.4634 |
| N1-N2 | 49 | 10 | 11 | 11 | ||||
| Vascular invasion | Absent | 157 | 25 | 0.0184 * | 21 | 0.0028 * | 27 | 0.4470 |
| Present | 15 | 6 | 6 | 4 | ||||
| Perineural invasion | Absent | 167 | 29 | 0.2559 | 25 | 0.0940 | 30 | 0.9083 |
| Present | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| Tumor regression grade | Grade 0–1 | 37 | 13 | 0.0038 * | 10 | 0.0090 * | 14 | 0.0006 * |
| Grade 2–3 | 118 | 17 | 17 | 16 | ||||
| Grade 4 | 17 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
| Down stage after CCRT | Non-Sig. | 150 | 29 | 0.1651 | 24 | 0.5961 | 30 | 0.0853 |
| Sig. (≥2) | 22 | 2 | 3 | 1 | ||||
| RGNEF expression | Low Exp. | 86 | 4 | <0.0001 * | 8 | 0.0029 * | 2 | <0.0001 * |
| High Exp. | 86 | 27 | 19 | 29 | ||||
| Parameter | DSS | LRFS | MeFS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H.R | 95% CI | p-Value | H.R | 95% CI | p-Value | H.R | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Tumor regression grade | 1.721 | 0.840–3.533 | 0.138 | 2.132 | 1.020–4.785 | 0.044 * | 2.049 | 1.022–4.115 | 0.044 * |
| RGNEF expression | 7.985 | 2.708–23.547 | <0.001 * | 2.235 | 0.899–5.558 | 0.084 | 17.011 | 3.986–72.602 | <0.001 * |
| Vascular invasion | 1.278 | 0.496–3.294 | 0.612 | 1.924 | 0.691–5.361 | 0.211 | - | - | - |
| Post-Tx tumor status (ypT) | 3.197 | 1.313–7.784 | 0.010 * | 2.233 | 0.901–5.534 | 0.083 | 2.418 | 1.053–5.551 | 0.037 * |
| Pre-Tx nodal status (cN) | - | - | - | 1.791 | 0.768–4.172 | 0.177 | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-I.; Chen, H.-P.; Liu, K.-W.; Chien, C.-C.; Wei, Y.-C. Utility of RGNEF in the Prediction of Clinical Prognosis in Patients with Rectal Cancer Receiving Preoperative Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy. Life 2022, 12, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010018
Chen C-I, Chen H-P, Liu K-W, Chien C-C, Wei Y-C. Utility of RGNEF in the Prediction of Clinical Prognosis in Patients with Rectal Cancer Receiving Preoperative Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy. Life. 2022; 12(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chih-I., Hsin-Pao Chen, Kuang-Wen Liu, Chu-Chun Chien, and Yu-Ching Wei. 2022. "Utility of RGNEF in the Prediction of Clinical Prognosis in Patients with Rectal Cancer Receiving Preoperative Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy" Life 12, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010018
APA StyleChen, C.-I., Chen, H.-P., Liu, K.-W., Chien, C.-C., & Wei, Y.-C. (2022). Utility of RGNEF in the Prediction of Clinical Prognosis in Patients with Rectal Cancer Receiving Preoperative Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy. Life, 12(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010018





