Pediatric Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder: Case Series and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Cases
2.1. NMOSDs with AQP4-IgG
2.1.1. Case 1
2.1.2. Case 2
2.1.3. Case 3
2.2. NMOSDs without AQP4-IgG
2.2.1. Case 4
2.2.2. Case 5
2.2.3. Case 6
2.2.4. Case 7
3. Literature Review
3.1. Methods
3.2. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Epidemiology
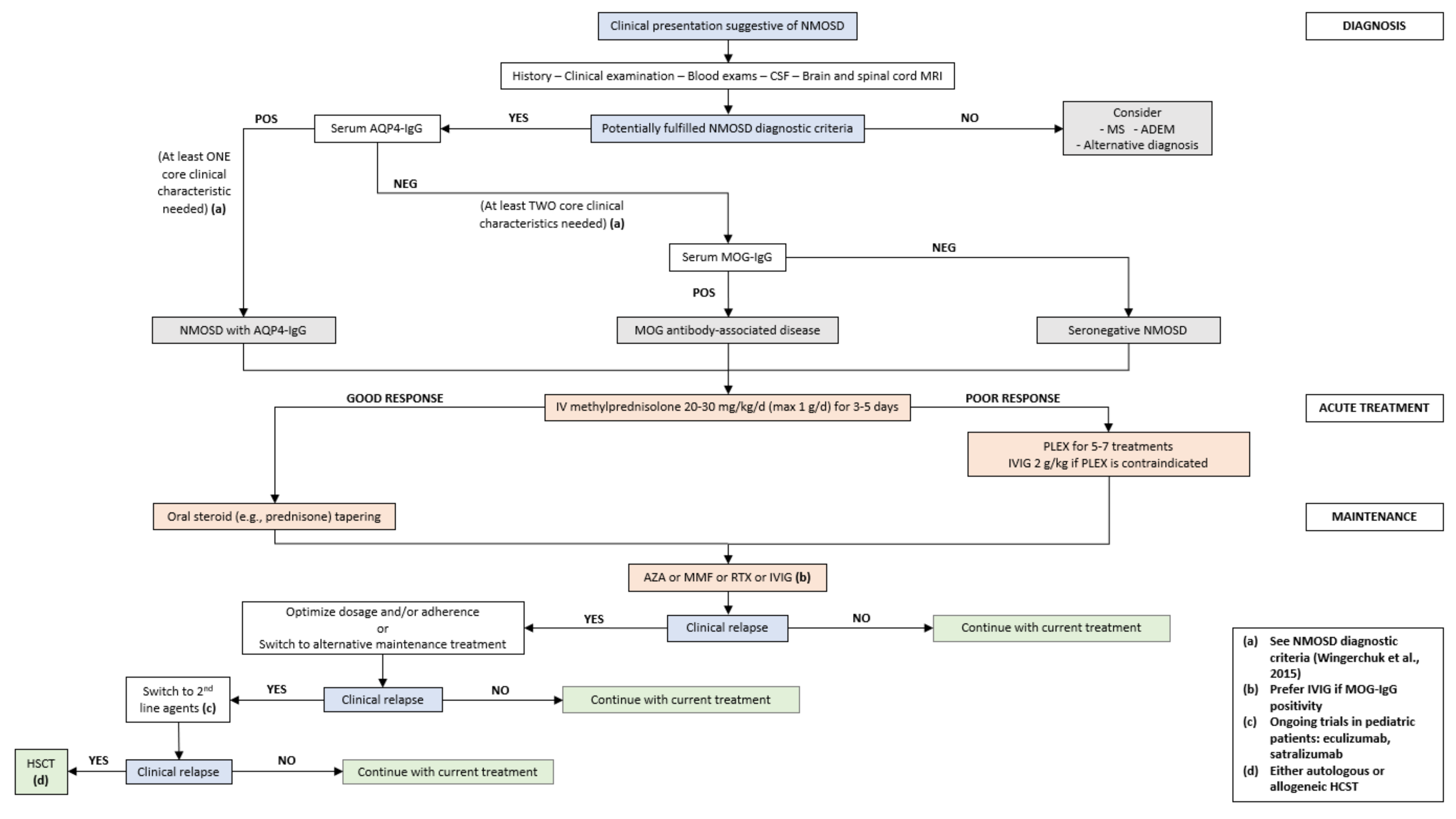
4.2. Diagnostic Criteria
4.3. Clinical Features
4.4. Imaging Findings
4.5. Laboratory Features
4.6. Treatment
4.6.1. Acute Treatment
4.6.2. Preventive Treatment
Intravenous Immunoglobulin
Azathioprine
Mycophenolate Mofetil
Rituximab
Preventive Treatment in MOG-IgG Positive Patients
4.6.3. New Therapeutic Agents
Eculizumab
Tocilizumab
Satralizumab
Inebilizumab
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lennon, V.A.; Kryzer, T.J.; Pittock, S.J.; Verkman, A.S.; Hinson, S.R. IgG marker of optic-spinal multiple sclerosis binds to the aquaporin-4 water channel. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadoun, S.; Waters, P.; MacDonald, C.; Bell, B.A.; Vincent, A.; Verkman, A.S.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Neutrophil protease inhibition reduces neuromyelitis optica-immunoglobulin G-induced damage in mouse brain. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Verkman, A.S. Eosinophil pathogenicity mechanisms and therapeutics in neuromyelitis optica. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasiak-Zatonska, M.; Kalinowska-Lyszczarz, A.; Michalak, S. The Immunology of Neuromyelitis Optica-Current Knowledge, Clinical Implications, Controversies and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Chen, J. What You Need to Know About AQP4, MOG, and NMOSD. Semin. Neurol. 2019, 39, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostasy, K.; Mader, S.; Schanda, K.; Peter, H.; Jutta Gärtner, J.; Kraus, V.; Karenfort, M.; Tibussek, D.; Blaschek, A.; Bajer-Kornek, B.; et al. Anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies in pediatric patients with optic neuritis. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferilli, M.A.N.; Valeriani, M.; Papi, C.; Papetti, L.; Ruscitto, C.; Figà Talamanca, L.; Ursitti, F.; Moavero, R.; Vigevano, F.; Iorio, R. Clinical and neuroimaging characteristics of MOG autoimmunity in children with acquired demyelinating syndromes. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 50, 102837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absoud, M.; Lim, M.J.; Appleton, R.; Jacob, A.; Kitley, J.; Leite, M.I.; Pike, M.G.; Vincent, A.; Wassmer, E.; Waters, P.; et al. Paediatric neuromyelitis optica: Clinical, MRI of the brain and prognostic features. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quek, A.M.L.; McKeon, A.; Lennon, V.A.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Iorio, R.; Jiao, Y.; Costanzi, C.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; et al. Effects of age and sex on aquaporin-4 autoimmunity. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeon, A.; Lennon, V.A.; Lotze, T.; Tenenbaum, S.; Ness, J.M.; Rensel, M.; Kuntz, N.L.; Fryer, J.P.; Homburger, H.; Hunter, J.; et al. CNS aquaporin-4 autoimmunity in children. Neurology 2008, 71, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenembaum, S.; Chitnis, T.; Nakashima, I.; Collongues, N.; McKeon, A.; Levy, M.; Rostasy, K. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders in children and adolescents. Neurology 2016, 87, S59–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palace, J.; Leite, M.I.; Nairne, A.; Vincent, A. Interferon Beta Treatment in Neuromyelitis Optica. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 1016–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Hutchinson, M.; Elsone, L.; Kelly, S.; Ali, R.; Saukans, I.; Tubridy, N.; Boggild, M. Does natalizumab therapy worsen neuromyelitis optica? Neurology 2012, 79, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.-H.; Kim, B.J.; Lee, K.H. Development of extensive brain lesions following fingolimod (FTY720) treatment in a patient with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Mult. Scler. J. 2011, 18, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; De Seze, J.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 2015, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoso, Y.D.; Ferreira, M.L.; Oliveira, E.M.; Domingues, R.; Ribeiro, T.A.; Brooks, J.B.; Claudino, R.; Netto, J.M.; Gomes, S.; Adoni, T.; et al. Neuromyelitis Optica With Onset in Childhood and Adolescence. Pediatr. Neurol. 2014, 50, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolilo, R.B.; Hacohen, Y.; Yazbeck, E.; Armangue, T.; Bruijstens, A.; Lechner, C.; Apostolos-Pereira, S.L.; Martynenko, Y.; Breu, M.; Rimkus, C.D.M.; et al. Treatment and outcome of aquaporin-4 antibody–positive NMOSD. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, T.; Ness, J.; Krupp, L.; Waubant, E.; Hunt, T.; Olsen, C.S.; Rodriguez, M.; Lotze, T.; Gorman, M.; Benson, L.; et al. Clinical features of neuromyelitis optica in children. Neurology 2015, 86, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.R.; Wang, C. Aquaporin-4 neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in a 2-year-old girl: Diagnostic and treatment considerations. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 41, 102030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmuca, S.; Lieberman, S.; Mehta, J. Pediatric Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder and Sjögren Syndrome: More Common Than Previously Thought? J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 959–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraş, H.; Kara, B.; Anık, Y. Seropositive Neuromyelitis Optica: A Pediatric Case Report and 6-Year Follow-Up. Pediatr. Neurol. 2013, 49, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, N.A.; Silver, K.; Onel, K.; Ko, M.; Javed, A. Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in Pediatric Neuromyelitis Optica. J. Child Neurol. 2010, 26, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Kaba, H.; Kaneko, K.; Takahashi, T.; Takeshita, S. MRI findings in pediatric neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with MOG antibody: Four cases and review of the literature. Brain Dev. 2018, 41, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuquilin, M.; Mullaguri, N.; Weinshenker, B. Pediatric familial neuromyelitis optica in two sisters with long term follow-up. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 29, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, T.E.; Northrop, J.L.; Hutton, G.J.; Ross, B.; Schiffman, J.S.; Hunter, J.V. Spectrum of Pediatric Neuromyelitis Optica. Pediatrics 2008, 122, e1039–e1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostásy, K.; Mader, S.; Hennes, E.M.; Schanda, K.; Gredler, V.; Guenther, A.; Blaschek, A.; Korenke, C.; Pritsch, M.; Pohl, D.; et al. Persisting myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies in aquaporin-4 antibody negative pediatric neuromyelitis optica. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 19, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijevic, N.; Bogicevic, D.; Dimitrijevic, A.; Nikolic, D. Early presentation of neuromyelitis optica. Indian Pediatr. 2012, 49, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loma, I.P.; Asato, M.R.; Filipink, R.A.; Alper, G. Neuromyelitis Optica in a Young Child with Positive Serum Autoantibody. Pediatr. Neurol. 2008, 39, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yavuz, H.; Kireşi, D. Unusual Manifestations of Pediatric Neuromyelitis Optica. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 28, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Narula, S.; Lerman, M.A. First Pediatric Patient With Neuromyelitis Optica and Sjögren Syndrome Successfully Treated With Tocilizumab. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 73, e5–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Yu, Y.; Yan, W.; Dai, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chu, L. Individualized Rituximab Treatment for Relapsing Neuromyelitis Optica: A Pediatric Case Report. Pediatr. Neurol. 2014, 51, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elpers, C.; Gross, C.; Fiedler, B.; Meuth, S.G.; Kurlemann, G. A Case Report on Juvenile Neuromyelitis Optica: Early Onset, Long Remission Period, and Atypical Treatment Response. Neuropediatrics 2015, 46, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillart, E.; Renaldo, F.; Papeix, C.; Deiva, K.; Bonheur, J.; Kwon, T.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O.; Germanaud, D.; Marignier, R. Dramatic efficacy of ofatumumab in refractory pediatric-onset AQP4-IgG neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamawal, A.; Hoerning, S.; Galiano, M.; Rompel, O.; Trollmann, R. Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody-Associated Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder in a 6-Year-Old Boy. Klin. Pädiatrie 2019, 231, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, L.A.; Bernard, T.J.; Tseng, B.S.; Miller, B.R.; Corboy, J.R. Neuromyelitis Optica Immunoglobulin G in a Child. Pediatr. Neurol. 2006, 35, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gokce, G.; Ceylan, O.M.; Mutlu, F.M.; I Altinsoy, H.; Koylu, M.T. Relapsing Devic’s disease in a child. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2013, 8, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.R.; Zimmern, V.; Aquino, V.; Wang, C. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in a pediatric patient with aquaporin-4 neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 50, 102852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, T.W.; Myers, G.J. Neuromyelitis optica (Devic syndrome) in a 12-year-old male with complete recovery following steroids. Pediatr. Neurol. 1987, 3, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Thiele, E.; Barnes, P.; Riviello, J.J. Neuromyelitis Optica in Childhood: Case Report With Sequential MRI Findings. J. Child Neurol. 1996, 11, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, J.A.; Ravelo, M.E.; Cruz, E.M.-L.; Montiel-Nava, C. NMO in pediatric patients: Brain involvement and clinical expression. Arq. De Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2011, 69, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Numata, Y.; Uematsu, M.; Suzuki, S.; Miyabayashi, T.; Oyama, T.; Kubota, S.; Itoh, T.; Hino-Fukuyo, N.; Takahashi, T.; Kure, S. Aquaporin-4 autoimmunity in a child without optic neuritis and myelitis. Brain Dev. 2015, 37, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, N.; Zibordi, F.; Erbetta, A.; Pollo, B.; Angelini, L. Neuromyelitis Optica in a Child with Atypical Onset and Severe Outcome. Neuropediatrics 2004, 35, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longoni, G.; Bigi, S.; Branson, H.M.; Hawkins, C.; Rutka, J.T.; Filippi, M.; Yeh, E.A. Multicystic demyelinating myelopathy: Widening spectrum of pediatric aquaporin-4 autoimmunity. Neurology 2014, 82, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, A.; Bartolini, E.; Melani, F.; Guerrini, R.; Mascalchi, M. Isolated recurrent myelitis in a 7-year-old child with serum aquaporin-4 IgG antibodies. J. Neurol. 2016, 264, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabshahi, B. Devic Disease in a Child with Primary Sjögren Syndrome. J. Child Neurol. 2006, 21, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Shu, S.; Fang, F. Identification of the clinical and neuroimaging characteristics in children with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: A case series. Transl. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghbanian, S.M.; Sahraian, M.A.; Moghadasi, A.N.; Asgari, N. Disability and Therapeutic Response in Paediatric Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder: A Case Series from Iran. Iran. J. Child Neurol. 2019, 13, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dembinski, K.; Gieron-Korthals, M.; Martinez, C.R.; Rodriguez, L. Neuromyelitis Optica in Child: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges. Case Rep. Pediatr. 2013, 2013, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, L.; Dara, J.; Duberstein, S.; De, A. Secondary Hypogammaglobulinemia After Rituximab for Neuromyelitis Optica: A Case Report. Drug Saf.—Case Rep. 2018, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosadini, M.; Alper, G.; Riney, C.J.; Benson, L.A.; Mohammad, S.S.; Ramanathan, S.; Nolan, M.; Appleton, R.; Leventer, R.J.; Deiva, K.; et al. Rituximab monitoring and redosing in pediatric neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 3, e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, C.; Baumann, M.; Hennes, E.-M.; Schanda, K.; Marquard, K.; Karenfort, M.; Leiz, S.; Pohl, D.; Venkateswaran, S.; Pritsch, M.; et al. Antibodies to MOG and AQP4 in children with neuromyelitis optica and limited forms of the disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 87, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longoni, G.; Banwell, B.; Filippi, M.; Yeh, E.A. Rituximab as a first-line preventive treatment in pediatric NMOSDs. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 1, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera, V.; Messina, S.; Elhadd, K.T.; Sanpera-Iglesias, J.; Mariano, R.; Hacohen, Y.; Dobson, R.; Meletti, S.; Wassmer, E.; Lim, M.J.; et al. Early predictors of disability of paediatric-onset AQP4-IgG-seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 93, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, M.J.; Vu, N.; Hunley, T.E.; Chitnis, T. Child Neurology: Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 2017, 88, e10–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglie, G.; Papetti, L.; Valeriani, M.; Merli, P. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Neuromyelitis Optica-Spectrum Disorders (NMO-SD): State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillema, J.; McKeon, A. The Spectrum of Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) in Childhood. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 27, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenembaum, S.; Yeh, E.A.; Alroughani, R.; Altintas, A.; Amezcua, L.; Apiwattanakul, M.; Asgari, N.; Banwell, B.; Abboud, H.; The Guthy-Jackson Foundation International Clinical Consortium (GJCF-ICC); et al. Pediatric NMOSD: A Review and Position Statement on Approach to Work-Up and Diagnosis. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, V.A.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Kryzer, T.J.; Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Fujihara, K.; Nakashima, I.; Weinshenker, B.G. A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: Distinction from multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2004, 364, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lennon, V.A.; Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Weinshenker, B.G. Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2006, 66, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenembaum, S.; Chitnis, T.; Ness, J.; Hahn, J.S. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neurology 2007, 68, S23–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, J.F.; Hoffman, B.M.; Tyor, W.R. CNS inflammatory demyelinating disorders: MS, NMOSD and MOG antibody associated disease. J. Investig. Med. 2019, 68, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghbanian, S.M.; Asgari, N.; Sahraian, M.A.; Moghadasi, A.N. A comparison of pediatric and adult neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: A review of clinical manifestation, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 388, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huda, S.; Whittam, D.; Bhojak, M.; Chamberlain, J.; Noonan, C.; Jacob, A.; Kneen, R. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Clin. Med. 2019, 19, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shosha, E.; Dubey, D.; Palace, J.; Nakashima, I.; Jacob, A.; Fujihara, K.; Takahashi, T.; Whittam, D.; Leite, M.I.; Misu, T.; et al. Area postrema syndrome. Neurology 2018, 91, e1642–e1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zantah, M.; Coyle, T.B.; Datta, D. Acute Respiratory Failure due to Neuromyelitis Optica Treated Successfully with Plasmapheresis. Case Rep. Pulmonol. 2016, 2016, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, R.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Lennon, V.A.; Costanzi, C.; Hinson, S.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Pittock, S.J. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis may herald or accompany neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2011, 77, 1644–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, S.; Khan, M.; Pardo, S.; Izbudak, I.; Levy, M. MOG antibody-associated encephalomyelitis/encephalitis. Mult. Scler. 2019, 25, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohammadi, S.; Doosti, R.; Shahmohammadi, A.; Mohamadianinejad, S.E.; Sahraian, M.A.; Azimi, A.R.; Harirchian, M.H.; Asgari, N.; Moghadasi, A.N. Autoimmune diseases associated with Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders: A literature review. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 27, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornitzer, J.M.; Kimura, Y.; Janow, G.L. Primary Sjögren Syndrome in a Child with a Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 1260–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarigecili, E.; Cobanogullari, M.D.; Komur, M.; Okuyaz, C. A rare concurrence: Antibodies against Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor in a child. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 28, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, H.; Guo, D. AQP4-IgG-seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) coexisting with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis: A case report and literature review. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 35, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mealy, M.A.; Whetstone, A.; Orman, G.; Izbudak, I.; Calabresi, P.; Levy, M. Longitudinally extensive optic neuritis as an MRI biomarker distinguishes neuromyelitis optica from multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 355, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupersmith, M.J.; Alban, T.; Zeiffer, B.; Lefton, D. Contrast-enhanced MRI in acute optic neuritis: Relationship to visual performance. Brain 2002, 125, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, N.; Skejoe, H.P.B.; Lillevang, S.T.; Steenstrup, T.; Stenager, E.; Kyvik, K.O. Modifications of longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis and brainstem lesions in the course of neuromyelitis optica (NMO): A population-based, descriptive study. BMC Neurol. 2013, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Paul, F.; Lana-Peixoto, M.A.; Tenembaum, S.; Asgari, N.; Palace, J.; Klawiter, E.C.; Sato, D.K.; de Seze, J.; Wuerfel, J.; et al. MRI characteristics of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: An international update. Neurology 2015, 84, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banwell, B.; Tenembaum, S.; Lennon, V.A.; Ursell, E.; Kennedy, J.; Bar-Or, A.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Pittock, S.J. Neuromyelitis optica-IgG in childhood inflammatory demyelinating CNS disorders. Neurology 2007, 70, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banwell, B.; Arnold, D.L.; Tillema, J.-M.; Rocca, M.A.; Filippi, M.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Zivadinov, R.; Sormani, M.P. MRI in the evaluation of pediatric multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2016, 87, S88–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittock, S.J.; Lennon, V.A.; Krecke, K.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Weinshenker, B.G. Brain Abnormalities in Neuromyelitis Optica. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Park, M.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Jung, I.J.; Takahashi, T.; Misu, T.; Fujihara, K.; Kim, H.J. Characteristic brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in central nervous system aquaporin-4 autoimmunity. Mult. Scler. J. 2010, 16, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majed, M.; Fryer, J.P.; McKeon, A.; Lennon, V.A.; Pittock, S.J. Clinical utility of testing AQP4-IgG in CSF. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 3, e231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Fryer, J.P.; Lennon, V.A.; Jenkins, S.M.; Quek, A.M.L.; Smith, C.Y.; McKeon, A.; Costanzi, C.; Iorio, R.; Weinshenker, B.G.; et al. Updated estimate of AQP4-IgG serostatus and disability outcome in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2013, 81, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitley, J.; Woodhall, M.; Waters, P.; Leite, M.I.; Devenney, E.; Craig, J.; Palace, J.; Vincent, A. Myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies in adults with a neuromyelitis optica phenotype. Neurology 2012, 79, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarius, S.; Ruprecht, K.; Kleiter, I.; Borisow, N.; Asgari, N.; Pitarokoili, K.; Pache, F.; Stich, O.; Beume, L.-A.; Hümmert, M.W.; et al. MOG-IgG in NMO and related disorders: A multicenter study of 50 patients. Part 2: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, radiological and laboratory features, treatment responses, and long-term outcome. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, P.; Woodhall, M.; O’Connor, K.C.; Reindl, M.; Lang, B.; Sato, D.K.; Juryńczyk, M.; Tackley, G.; Rocha, J.; Takahashi, T.; et al. MOG cell-based assay detects non-MS patients with inflammatory neurologic disease. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 2, e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamaschi, R.; Tonietti, S.; Franciotta, D.; Candeloro, E.; Tavazzi, E.; Piccolo, G.; Romani, A.; Cosi, V. Oligoclonal bands in Devic’s neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis: Differences in repeated cerebrospinal fluid examinations. Mult. Scler. J. 2004, 10, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarius, S.; Paul, F.; Franciotta, D.; Ruprecht, K.; Ringelstein, M.; Bergamaschi, R.; Rommer, P.; Kleiter, I.; Stich, O.; Reuss, R.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid findings in aquaporin-4 antibody positive neuromyelitis optica: Results from 211 lumbar punctures. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 306, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, A.R.; Segal, B. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palace, J.; Leite, I.; Jacob, A. A practical guide to the treatment of neuromyelitis optica. Pract. Neurol. 2012, 12, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellner, J.; Boggild, M.; Clanet, M.; Hintzen, R.Q.; Illes, Z.; Montalban, X.; Du Pasquier, R.; Polman, C.H.; Sorensen, P.S.; Hemmer, B. EFNS guidelines on diagnosis and management of neuromyelitis optica. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinshenker, B.G.; O’Brien, P.C.; Petterson, T.M.; Noseworthy, J.H.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Dodick, D.W.; Pineda, A.A.; Stevens, L.N.; Rodriguez, M. A randomized trial of plasma exchange in acute central nervous system inflammatory demyelinating disease. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abboud, H.; Petrak, A.; Mealy, M.; Sasidharan, S.; Siddique, L.; Levy, M. Treatment of acute relapses in neuromyelitis optica: Steroids alone versus steroids plus plasma exchange. Mult. Scler. J. 2015, 22, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsone, L.; Panicker, J.; Mutch, K.; Boggild, M.; Appleton, R.; Jacob, A. Role of intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of acute relapses of neuromyelitis optica: Experience in 10 patients. Mult. Scler. J. 2013, 20, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebst, C.; Jarius, S.; Berthele, A.; Paul, F.; Schippling, S.; Wildemann, B.; Borisow, N.; Kleiter, I.; Aktas, O.; Kümpfel, T.; et al. Update on the diagnosis and treatment of neuromyelitis optica: Recommendations of the Neuromyelitis Optica Study Group (NEMOS). J. Neurol. 2013, 261, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacohen, Y.; Banwell, B. Treatment Approaches for MOG-Ab-Associated Demyelination in Children. Curr. Treat. Opt. Neurol. 2019, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitley, J.; Leite, M.I.; Nakashima, I.; Waters, P.; McNeillis, B.; Brown, R.; Takai, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Misu, T.; Elsone, L.; et al. Prognostic factors and disease course in aquaporin-4 antibody-positive patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder from the United Kingdom and Japan. Brain 2012, 135, 1834–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montcuquet, A.; Collongues, N.; Papeix, C.; Zephir, H.; Audoin, B.; Laplaud, D.; Bourre, B.; Brochet, B.; Camdessanche, J.-P.; Labauge, P.; et al. Effectiveness of mycophenolate mofetil as first-line therapy in AQP4-IgG, MOG-IgG, and seronegative neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Mult. Scler. J. 2016, 23, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M. Neuromyelitis Optica: Potential Roles for Intravenous Immunoglobulin. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 33, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.; Wong, A.H.; Quek, A.M.; Yuki, N. Intravenous immunoglobulin may reduce relapse frequency in neuromyelitis optica. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 282, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magraner, M.; Coret, F.; Casanova, B. The effect of intravenous immunoglobulin on neuromyelitis optica. Neurologia 2013, 28, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzi, C.; Matiello, M.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Pittock, S.J.; Mandrekar, J.; Thapa, P.; McKeon, A. Azathioprine: Tolerability, efficacy, and predictors of benefit in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2011, 77, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsone, L.; Kitley, J.; Luppe, S.; Lythgoe, D.; Mutch, K.; Jacob, S.; Brown, R.; Moss, K.; McNeillis, B.; Goh, Y.Y.; et al. Long-term efficacy, tolerability and retention rate of azathioprine in 103 aquaporin-4 antibody-positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder patients: A multicentre retrospective observational study from the UK. Mult. Scler. J. 2014, 20, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, D.; Carrey, E.A.; Edbury, S.; Smolenski, R.; Jagodzinski, P.; Simmonds, H.A. Mycophenolate mofetil, an inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, causes a paradoxical elevation of GTP in erythrocytes of renal transplant patients. Clin. Sci. 2004, 107, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, S.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Hyun, J.-W.; Joung, A.-R.; Park, M.S.; Kim, B.-J.; Kim, H.J. Mycophenolate Mofetil in the Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Matiello, M.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lucchinetti, C.; Shuster, E.; Carter, J.; Keegan, B.M.; Kantarci, O.H.; Pittock, S.J. Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica With Mycophenolate Mofetil. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosadini, M.; Gadian, J.; Lim, M.; Sartori, S.; Thomas, T.; Dale, R.C. Mycophenolate mofetil in paediatric autoimmune or immune-mediated diseases of the central nervous system: Clinical experience and recommendations. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 61, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, R.C.; Brilot, F.; Duffy, L.V.; Twilt, M.; Waldman, A.T.; Narula, S.; Muscal, E.; Deiva, K.; Andersen, E.; Eyre, M.R.; et al. Utility and safety of rituximab in pediatric autoimmune and inflammatory CNS disease. Neurology 2014, 83, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimbrough, D.; Fujihara, K.; Jacob, A.; Lana-Peixoto, M.A.; Leite, M.I.; Levy, M.; Marignier, R.; Nakashima, I.; Palace, J.; de Seze, J.; et al. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica: Review and recommendations. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2012, 1, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürcan, H.M.; Keskin, D.B.; Stern, J.N.; Nitzberg, M.A.; Shekhani, H.; Ahmed, A.R. A review of the current use of rituximab in autoimmune diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinnò, A.; Marnetto, F.; Valentino, P.; Martire, S.; Balbo, A.; Drago, A.; Leto, M.; Capobianco, M.; Panzica, G.; Bertolotto, A. Rituximab-induced hypogammaglobulinemia in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurol.—Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 5, e498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacohen, Y.; Wong, Y.Y.; Lechner, C.; Jurynczyk, M.; Wright, S.; Konuskan, B.; Kalser, J.; Poulat, A.L.; Maurey, H.; Ganelin-Cohen, E.; et al. Disease Course and Treatment Responses in Children With Relapsing Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody–Associated Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittock, S.J.; Berthele, A.; Fujihara, K.; Kim, H.J.; Levy, M.; Palace, J.; Nakashima, I.; Terzi, M.; Totolyan, N.; Viswanathan, S.; et al. Eculizumab in Aquaporin-4–Positive Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, L.A.; Topaz, N.; Wang, X.; Hariri, S.; Fox, L.; MacNeil, J.R. High Risk for Invasive Meningococcal Disease Among Patients Receiving Eculizumab (Soliris) Despite Receipt of Meningococcal Vaccine. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexion Pharmaceuticals. A Phase 2/3 Open-Label, Single-Arm Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Activity of Eculizumab in Pediatric Patients with Relapsing Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04155424 (accessed on 27 June 2021).
- Araki, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Kusunoki, S.; Okamoto, T.; Murata, M.; Miyake, S.; Aranami, T.; Yamamura, T. Efficacy of the anti-IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab in neuromyelitis optica: A pilot study. Neurology 2014, 82, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, T.; Kleiter, I.; Fujihara, K.; Palace, J.; Greenberg, B.; Zakrzewska-Pniewska, B.; Patti, F.; Tsai, C.-P.; Saiz, A.; Yamazaki, H.; et al. Trial of Satralizumab in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann-La Roche. A Multicenter, Single Arm, Open-Label Study to Evaluate the Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Satralizumab in Patients with Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04660539 (accessed on 22 July 2021).
- Frampton, J.E. Inebilizumab: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cree, B.A.C.; Bennett, J.L.; Kim, H.J.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Pittock, S.J.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Fujihara, K.; Paul, F.; Cutter, G.R.; Marignier, R.; et al. Inebilizumab for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (N-MOmentum): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled phase 2/3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Bondanza, A.; Oliveira, M.C.; Badoglio, M.; Burman, J.; Piehl, F.; Hagglund, H.; Krasulová, E.; Simoes, B.; Carlson, K.; et al. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in neuromyelitis optica: A registry study of the EBMT Autoimmune Diseases Working Party. Mult. Scler. J. 2014, 21, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
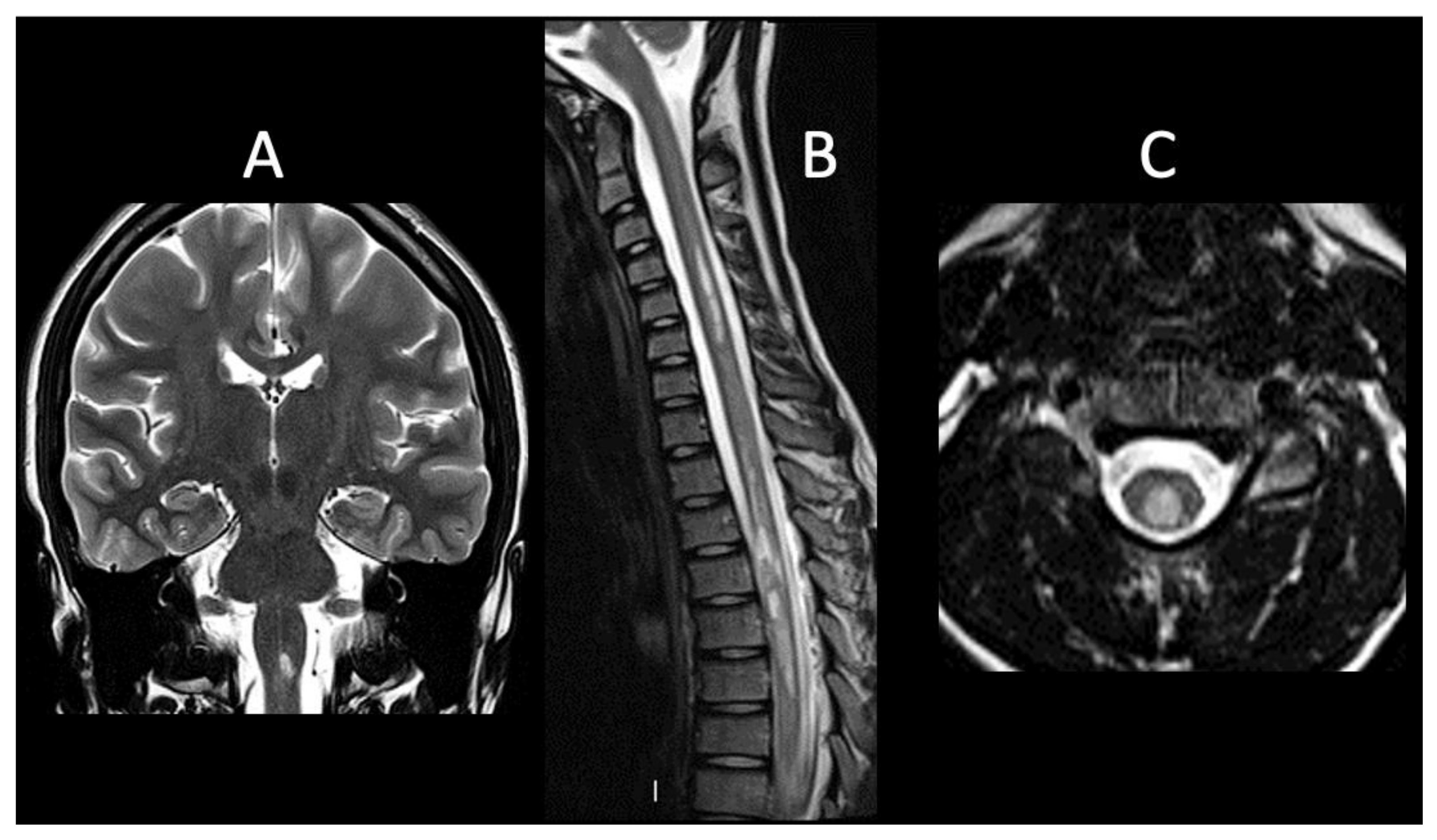

| Pt | Gen, Age (y) | Symptoms/Signs | MRI T2-Hyperintense Lesions | Gd Enhancement | Antibody Status | CSF OCBs | Evoked Potentials | EDSS at the Onset | Acute Attack Therapy | Clinical Course | Long-Term Therapy | EDSS at Last Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F, 16 | Headache, vomiting, vertigo | Right centrum semiovale, near the trigone and the temporal horn of the right ventricle, pons, medulla oblongata, dorsal spine | Yes | AQP4-IgG positive | No | Normal VEPs, SEPs and MEPs | 3 | IVMP | Monophasic | Oral CS, HCQ, MMF | 0 |
| 2 | F, 9 | Bilateral ON, progressive bilateral lower limb hyposthenia | Right frontal subcortical region, corpus callosum, cervical and dorsal spine | Yes | AQP4-IgG positive | Yes | Abnormal VEPs and SEPs (MEPs not available) | 4 | IVMP | Relapsing | Oral CS, RTX, AZA | 5 |
| 3 | F, 8 | Bilateral ON | Bilateral optic nerves | Yes, left optic nerve | AQP4-IgG positive | No | Abnormal VEPs, normal SEPs and MEPs | 4 | IVMP, PE | Monophasic | RTX | 0 |
| 4 | M, 15 | Progressive right lower limb paresis | From cervical spine to the conus medullaris | No | AQP4-IgG and MOG-IgG negative | No | Abnormal VEPs, SEPs and MEPs | 8.5 | IVMP | Relapsing | RTX, MMF | 0 |
| 5 | M, 10 | Right lower limb paresis, sensory level at T10-T11 | Diffuse bilateral cerebral involvement, cervical spine | Yes | AQP4-IgG and MOG-IgG negative | No | Abnormal VEPs, SEPs and MEPs | 9 | IVMP, PE | Relapsing | RTX | 7.5 |
| 6 | M, 13 | Gait ataxia, bilateral lower limb paresthesia, pyramidal signs, sensory level at T10 | Dorsal spine | Yes | AQP4-IgG and MOG-IgG negative | No | Abnormal VEPs (SEPs and MEPs not available) | 6 | IVMP | Monophasic | Oral CS | 0 |
| 7 | M, 11 | Unilateral ON | Left optic nerve and cervical spine | Yes | AQP4-IgG and MOG-IgG negative | No | Abnormal VEPs, normal SEPs and MEPs | 2 | IVMP | Relapsing | IVIG | 1 |
| Reference | Study Type | N | Age Range (years) | Diagnosis | AQP4 + | MOG + | Seronegative NMOSD | Diagnostic Criteria | Symptoms at Onset | Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fragoso YD et al., 2014 [16] | Case series | n = 29 | 13 ± 3.4 (5–17) | NMO | n = 22 | NA | Negative (n = 5), not performed (n = 2) | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | Myelitis (n = 12), ON (n = 8), myelitis and ON (n = 9) | AZA (n = 29), AZA + PDN (n = 4), AZA + GA (n = 3), IVIG (n = 6), PLEX (n = 2), MTX + PDN (n = 1) | NA |
| Paolilo RB et al., 2020 [17] | Retrospective study | n = 67 | 10.2 ± 3.6 | NMOSD | n = 67 | NA | NA | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | ON (n = 20), TM (n = 15), area postrema syndrome (n = 11), simultaneous ON and TM (n = 6), ADEM (n = 6), isolated diencephalic syndrome (n = 1), isolated brainstem syndrome (n = 3), multifocal syndromes (n = 5) | 1 DMT (n = 41), 2 DMTs (n = 12), 3 DMTs (n = 7), 4 DMTs (n = 2), 5 DMTs (n = 1), untreated (n = 4) | EDSS ≥ 3 (n = 29), visual impairment (n = 32), motor deficits (n = 14), cognitive impairment (n = 17) |
| Absoud M et al., 2015 [8] | Retrospective study | n = 20 | 10.5 (2.9–16.8) | NMO | n = 8 | NA | n = 12 | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | ON (n = 12), TM (n = 3), ON + TM (n = 3), ADEM (n = 2) | Oral PDN, AZA, RTX, IVIG, MMF, mitoxantrone, ofatumumab | Visual impairment (n = 10), wheelchair-dependent (n = 3) |
| Chitnis T et al., 2016 [18] | Prospective multicenter database | n = 38 | 10.2 ± 4.7 | NMO NMOSD | n = 24 | NA | n = 14 | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | Visual (n = 21), motor (n = 17), constitutional (n = 23) symptoms | RTX (47%), MMF (39%), AZA (24%), PLEX (39%) | Number of attacks in first two years (1.84 ± 1.44) |
| Khan TR et al., 2020 [19] | Case report | n = 1 | 2 | NMOSD | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | TM (progressive left-hand weakness, gait instability) | IVMP, PLEX, RTX, MMF | Several exacerbations |
| Gmuca S et al., 2017 [20] | Case series | n = 4 | 11–15 | NMOSD + SS | n = 4 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | TM + ON (n = 1), ON (n = 2), intractable emesis and hiccups (n = 1) | IVMP, RTX, CP, PLEX, HCQ, MMF | NA |
| Maraş H et al., 2013 [21] | Case report | n = 1 | 5.67 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Krupp et al., 2007 | ON | IVMP, oral CS, AZA | Several relapses with vision loss |
| Mahmood NA et al., 2011 [22] | Case series | n = 2 | 10–15 | NMO | n = 2 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | TM (n = 2) | IVMP, oral CS, IVIG, AZA, RTX | Relapses (ON, bowel and bladder retention, leg weakness) |
| Ikeda A et al., 2019 [23] | Retrospective study | n = 4 | 8 (3–12) | NMOSD | n = 0 | n = 4 | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | ON (n = 2), extremity weakness/paresthesia (n = 2) | IVMP, oral CS, PLEX, AZA, tacrolimus | Several relapses, but no sequelae |
| Chuquilin M et al., 2016 [24] | Case report | n = 2 | 3–3.5 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | NA | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | Blindness (n = 2) | GA, AZA, CS, IFN-beta1a, RTX, PLEX | Several relapses |
| Lotze TE et al., 2018 [25] | Retrospective study | n = 9 | 14 (1.9–16) | NMOSD | n = 7 | NA | NA | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | Visual, motor, and mixed symptoms | IVMP, IVIG, PLEX, CP, MMF, RTX, AZA, GA | Relapsing-remitting course in all patients |
| Rostásy K et al., 2013 [26] | Retrospective study | n = 8 | 10.5 (3–15) | NMO | n = 2 | n = 3 | n = 3 | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | Various | RTX, AZA, oral CS, IVIG | Monophasic (n = 1), relapses (n = 7) |
| Dimitrijevic N et al., 2012 [27] | Case report | n = 1 | 3 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | NA | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | Isolated ON (sudden visual loss) | IVMP, oral CS, IVIG | Several relapses leading to blindness, paraplegia, urinary and bowel incontinence, short stature |
| Loma IP et al., 2008 [28] | Case report | n = 1 | 3.9 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | Bilateral leg weakness, urinary and bowel incontinence (LETM) | IVMP, oral CS, IVIG, AZA | Several relapses, but no sequelae |
| Yavuz H et al., 2013 [29] | Case report | n = 1 | 13 | NMO | NA | NA | NA | Sellner et al., 2010 | Visual loss, behavioral changes | CS, IVIG, PLEX, AZA | Several relapses with vision impairment |
| Marino A et al., 2017 [30] | Case report | n = 1 | 1.9 | NMO + SS | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | Central pontine myelinolysis, unilateral ON, ON + TM | IVIG, IVMP, PLEX, HCQ, CP, RTX, MMF, TCZ | Several relapses before TCZ introduction |
| He D et al., 2014 [31] | Case report | n = 1 | 5 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Krupp et al., 2007 | Bilateral ON | IVMP, oral CS, IVIG, RTX | Several relapses before RTX introduction |
| Elpers C et al., 2015 [32] | Case report | n = 1 | 12 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | Left arm paresis, left leg progressive paresis, dizziness, neck pain (LETM) | IVMP, oral CS, PLEX, AZA, RTX | Relapses before RTX introduction |
| Maillart E et al., 2020 [33] | Case report | n = 1 | 8 | NMOSD | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | Bilateral ON + LETM | IVMP, oral CS, PLEX, MMF, RTX, ofatumumab | Several relapses with permanent visual disability |
| Kamawal A et al., 2019 [34] | Case report | n = 1 | 6 | NMOSD | n = 0 | n = 1 | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | Progressive headache, meningism | IVMP, PLEX, MMF | Neurological restitutio ad integrum within two months |
| Hudson LA et al., 2006 [35] | Case report | n = 1 | 8 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | Bilateral upper extremity paresthesia | IVMP, oral CS | One relapse |
| Gokce G et al., 2013 [36] | Case report | n = 1 | 10 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | Sudden visual loss | IVMP, oral CS, AZA | Significant bilateral optic atrophy |
| Khan TR et al., 2021 [37] | Case report | n = 1 | 2 | NMOSD | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | Left-hand weakness and abnormal gait (LETM) | PLEX, RTX, MMF, TCZ, autologous HSCT | Highly active disease with several hospitalizations |
| Arnold TW et al., 1987 [38] | Case report | n = 1 | 12 | NMO | NA | NA | NA | NA | Decreased vision in the right eye, paraparesis, bilateral leg pain | PDN | Normal neurologic examination eight months after discharge |
| Davis R et al., 1996 [39] | Case report | n = 1 | 4 | NMO | NA | NA | NA | NA | TM | IV and oral dexamethasone | One relapse (ON); unremarkable neurologic examination after 18 months |
| Peña JA et al., 2011 [40] | Cohort study | n = 6 | 11 (5–13) | NMO | n = 4 | NA | Negative (n = 1), not performed (n = 1) | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | ON (n = 3), TM (n = 1), ON + TM (n = 2) | IVMP, IVIG, PDN, AZA, IFN-beta1a | Relapsing-remitting course with bilateral vision loss and paraparesis in all patients |
| Numata Y et al., 2015 [41] | Case report | n = 1 | 9 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | Nausea, vomiting, intractable hiccups | IVMP, IVIG, oral PDN | Recurrence-free for 10 months after discharge |
| Milani N. et al., 2004 [42] | Case report | n = 1 | 7 | NMO | NA | NA | NA | Wingerchuk et al., 1999 | Fever and vomiting, followed by headache, neck stiffness and visual impairment | IVMP, IVIG, PDN, CP, AZA | Relapsing-remitting course: paraparesis with normal brain MRI |
| Longoni G et al., 2014 [43] | Case report | n = 1 | 10 | NMOSD | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | NA | Subacute lower limb weakness, gait ataxia | Targeted immunotherapy | Partial lesion resolution |
| Bianchi A et al., 2017 [44] | Case report | n = 1 | 7 | NMOSD | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | Cervical back pain, paraparesis | IVMP, oral CS, AZA, RTX | Three episodes of isolated recurrent myelitis with no further relapses after RTX introduction |
| Arabshahi B et al., 2006 [45] | Case report | n = 1 | 11 | NMO + SS | NA | NA | NA | NA | Bilateral ON | CS, PLEX, CP | Visual impairment |
| Zhang Z et al., 2021 [46] | Case series | n = 11 | 7 (5–13) | NMOSD | n = 2 (n = 1: both AQP4 and MOG) | n = 2 (n = 1: both AQP4 and MOG) | Negative (n = 5), not performed (n = 3) | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | ON (n = 4), ON + encephalopathy (n = 5), myelitis + encephalopathy (n = 2) | NA | NA |
| Baghbanian SM et al., 2019 [47] | Case series | n = 10 | 13 (8–17) | NMOSD | n = 7 | NA | NA | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | ON (n = 4), ON + TM (n = 1), LETM (n = 3), APS (n = 2) | IVMP, PLEX (n = 5), AZA, RTX (n = 5) | Favorable: EDSS before preventive therapy was 3 (range 0–5) and decreased to 2.5 (range 0–5) after preventive therapy |
| Dembinski K et al., 2013 [48] | Case report | n = 1 | 13 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2006 | Encephalopathy with waxing and waning mental status, flat affect, ophthalmoparesis, with decreased visual acuity and color agnosia | IVIG, IVMP, RTX | Favorable |
| Farhat L et al., 2018 [49] | Case report | n = 1 | 17 | NMO | NA | NA | NA | NA | Acute vision loss in the left eye | AZA, CS, RTX, IGRT | Secondary hypogammaglobulinemia following RTX administration |
| Nosadini M et al., 2016 [50] | Multicenter retrospective study | n = 16 | 1.8–15.3 | NMO NMOSD | NA | NA | NA | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | ON (n = 4), TM (n = 4), ON+TM (n = 2), BD (n = 3), TM + BD (n = 2), ON + BD (n = 1) | Before RTX, 62.5% had received AZT, MMF, or CP. Then all 16 patients had ≥ 2 RTX courses | 6 patients were relapse-free, although 21 relapses occurred in 10 patients |
| Lechner C et al., 2020 [51] | Multicenter pro- and retrospective study | n = 24 | 11 (3–17) | NMOSD | n = 16 | n = 4 | n = 3 | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | LETM (n = 5), BS (n = 3), bilateral ON (n = 1), APS (n = 1), LETM + bilateral ON (n = 4), LETM + BS (n = 2), LETM + unilateral ON (n = 1), LETM + BS + bilateral ON (n = 1) | Acute: IVM, IVIG (n = 7), PLEX (n = 7), RTX (n = 2). Long-term: RTX (n = 8), AZA (n = 4), TCZ (n = 2), MMF (n = 1), IVIG (n = 1), CP (n = 1) | NA |
| Longoni G et al., 2014 [52] | Retrospective observational cohort study | n = 5 | 10.9–17 | NMO NMOSD | n = 5 | NA | n = 0 | NA | ON (n = 1), hiccups with nausea and vomiting (n = 2), gait disturbances (n = 1), hiccups with nausea and vomiting and progressive encephalopathy (n = 1) | Acute: IVMP, IVIG (n = 3), RTX (at 6 months and 12 months) | Favorable: EDSS score in the 5 patients decreased from 3.0 at initiation of RTX to 2.0 at 6 months from onset and 0.8 at 12 months from onset |
| Camera V et al., 2021 [53] | Retrospective multicenter cohort study | n = 49 | 12 ± 4.1 | NMOSD | n = 49 | NA | n = 0 | NA | Multifocal onset presentation (26.5%), optic nerve (47%), area postrema/brainstem (48.9%), encephalon (28.6%) | NA | NA |
| Bradshaw MJ et al., 2017 [54] | Case report | n = 1 | 3 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | Wingerchuk et al., 2015 | Progressive bilateral vision loss, left Babinski sign | 5 sessions of PLEX/IVMP, RTX | Favorable: vision improvement after IVMP and after first cycle of RTX |
| Ceglie G et al., 2019 [55] | Case report | n = 1 | 9 | NMO | n = 1 | NA | n = 0 | NA | Bilateral ON and progressive hyposthenia at the lower limbs | High-dose CS, AZA, cyclosporine, RTX, allogeneic HSCT | Favorable: no re-exacerbation, with long-term stabilization |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferilli, M.A.N.; Paparella, R.; Morandini, I.; Papetti, L.; Figà Talamanca, L.; Ruscitto, C.; Ursitti, F.; Moavero, R.; Sforza, G.; Tarantino, S.; et al. Pediatric Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder: Case Series and Literature Review. Life 2022, 12, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010019
Ferilli MAN, Paparella R, Morandini I, Papetti L, Figà Talamanca L, Ruscitto C, Ursitti F, Moavero R, Sforza G, Tarantino S, et al. Pediatric Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder: Case Series and Literature Review. Life. 2022; 12(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerilli, Michela Ada Noris, Roberto Paparella, Ilaria Morandini, Laura Papetti, Lorenzo Figà Talamanca, Claudia Ruscitto, Fabiana Ursitti, Romina Moavero, Giorgia Sforza, Samuela Tarantino, and et al. 2022. "Pediatric Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder: Case Series and Literature Review" Life 12, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010019
APA StyleFerilli, M. A. N., Paparella, R., Morandini, I., Papetti, L., Figà Talamanca, L., Ruscitto, C., Ursitti, F., Moavero, R., Sforza, G., Tarantino, S., Proietti Checchi, M., Vigevano, F., & Valeriani, M. (2022). Pediatric Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder: Case Series and Literature Review. Life, 12(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010019







