Botulinum Toxin Injection for Painful Adductor Pollicis Contracture after Thumb Carpometacarpal Resection Arthroplasty
Abstract
:1. Introduction
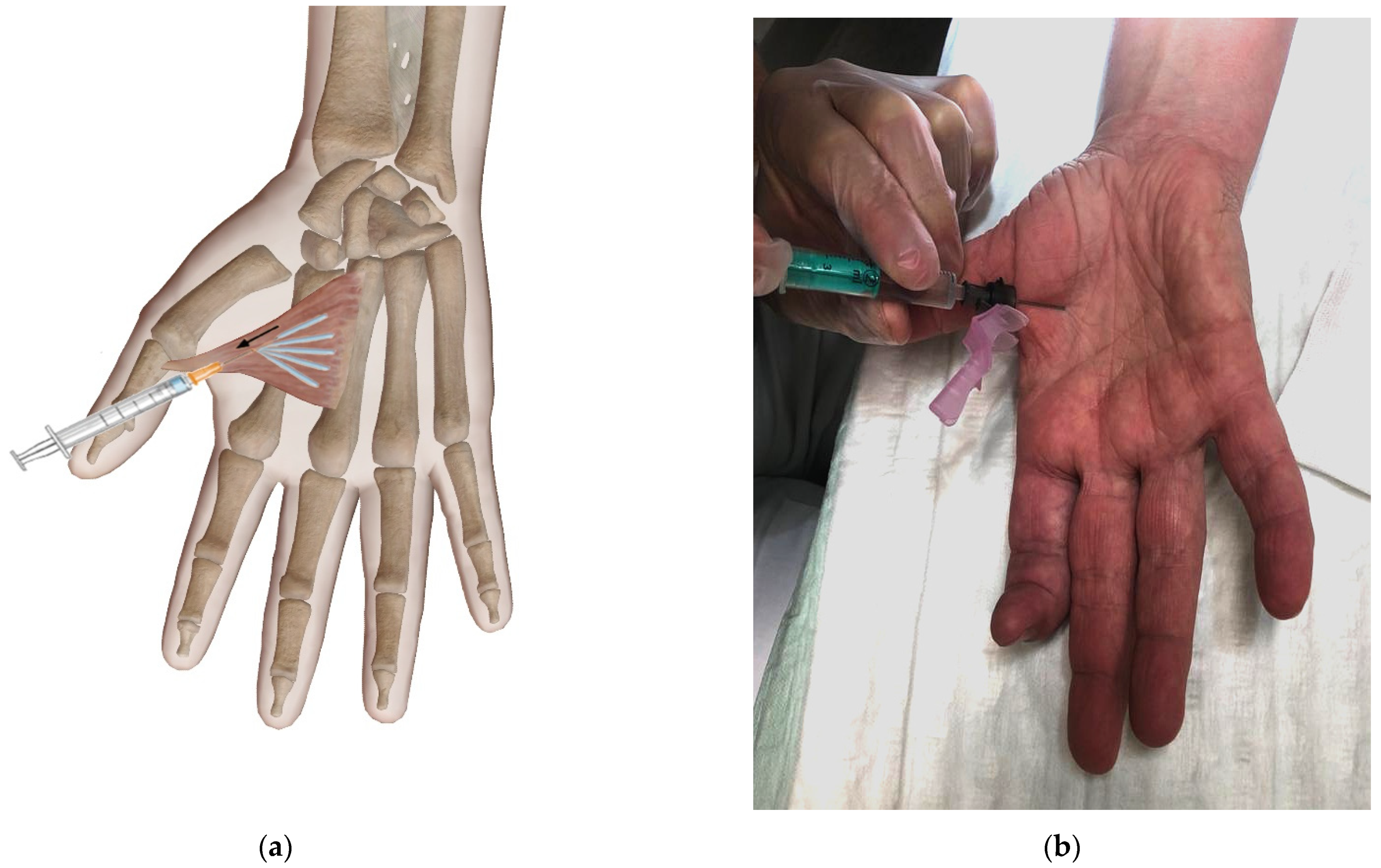
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merle, M.; Lim, A.Y.T. Elective Hand Surgery: Rheumatological and Degenerative Conditions, Nerve Compression Syndromes, English ed.; World Scientific Pub: Singapore; Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 9814277878. [Google Scholar]
- Wouters, R.M.; Tsehaie, J.; Slijper, H.P.; Hovius, S.E.R.; Feitz, R.; Selles, R.W. Exercise Therapy in Addition to an Orthosis Reduces Pain More Than an Orthosis Alone in Patients with Thumb Base Osteoarthritis: A Propensity Score Matching Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, R.; Chandrasenan, J.; Rajaratnam, V.; Burke, F.D. Basal thumb arthritis. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, R.G.; Glickel, S.Z. Trapeziometacarpal osteoarthritis. Staging as a rationale for treatment. Hand Clin. 1987, 3, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, M.M.; Roddey, T.S.; Costello, C.; Olson, S. Diagnostic value of clinical grind test for carpometacarpal osteoarthritis of the thumb. J. Hand Ther. 2010, 23, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froschauer, S.M.; Holzbauer, M.; Hager, D.; Schnelzer, R.; Kwasny, O.; Duscher, D. Elektra prosthesis versus resection-suspension arthroplasty for thumb carpometacarpal osteoarthritis: A long-term cohort study. J. Hand Surg. (Eur. Vol.) 2020, 45, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzbauer, M.; Hopfner, M.; Haslhofer, D.; Kwasny, O.; Duscher, D.; Froschauer, S.M. Radial and palmar active range of motion measurement: Reliability of six methods in healthy adults. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2021, 55, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J. Botulinum toxin in clinical practice. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonfria, E.; Maignel, J.; Lezmi, S.; Martin, V.; Splevins, A.; Shubber, S.; Kalinichev, M.; Foster, K.; Picaut, P.; Krupp, J. The Expanding Therapeutic Utility of Botulinum Neurotoxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freund, B.; Schwartz, M. Temporal relationship of muscle weakness and pain reduction in subjects treated with botulinum toxin A. J. Pain 2003, 4, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caleo, M.; Restani, L. Direct central nervous system effects of botulinum neurotoxin. Toxicon 2018, 147, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.; Hulsopple, C.; Boyce, B. Utilization of Botulinum Toxin for Musculoskeletal Disorders. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2020, 19, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, C.; Abdoul, H.; Campagna, R.; Guerini, H.; Ieong, E.; Chagny, F.; Bedin, C.; Roren, A.; Lefèvre-Colau, M.-M.; Poiraudeau, S.; et al. Intra-articular botulinum toxin A for base-of-thumb osteoarthritis: Protocol for a randomised trial (RHIBOT). BMJ Open 2018, 8, e022337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Yang, Y.C.; Özçakar, L. Ultrasound imaging and guided hydro-dissection for injury of the recurrent motor branch of the median nerve. Med. Ultrason. 2021, 23, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.; Kaymak, B.; Ulaşli, A.M.; Tok, F.; Öztürk, G.T.; Chang, K.-V.; Hsiao, M.-Y.; Hung, C.-Y.; On, A.Y.; Özçakar, L. Sonographic guide for botulinum toxin injections of the upper limb: EUROMUSCULUS/USPRM spasticity approach. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 54, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Preint. | 2 W | 3 M | 6 M |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DASH | 56 | 34 | 39 | 59 |
| MHQ | 40 | 74 | 63 | 33 |
| PRWE | 67 | 29 | 39 | 57 |
| Pain at rest | 8 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| Pain at activity | 8 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Radial Abduction | 30° | 35° | 35° | 30° |
| Palmar Abduction | 40° | 45° | 45° | 40° |
| Opposition | 0 cm | 0 cm | 0 cm | 0 cm |
| Hand grip | 15 kg | 19 kg | 21 kg | 14 kg |
| Pinch grip | 3.5 kg | 4 kg | 3.5 kg | 3 kg |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holzbauer, M.; Großbötzl, G.; Froschauer, S.M. Botulinum Toxin Injection for Painful Adductor Pollicis Contracture after Thumb Carpometacarpal Resection Arthroplasty. Life 2022, 12, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010110
Holzbauer M, Großbötzl G, Froschauer SM. Botulinum Toxin Injection for Painful Adductor Pollicis Contracture after Thumb Carpometacarpal Resection Arthroplasty. Life. 2022; 12(1):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010110
Chicago/Turabian StyleHolzbauer, Matthias, Gerhard Großbötzl, and Stefan Mathias Froschauer. 2022. "Botulinum Toxin Injection for Painful Adductor Pollicis Contracture after Thumb Carpometacarpal Resection Arthroplasty" Life 12, no. 1: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010110
APA StyleHolzbauer, M., Großbötzl, G., & Froschauer, S. M. (2022). Botulinum Toxin Injection for Painful Adductor Pollicis Contracture after Thumb Carpometacarpal Resection Arthroplasty. Life, 12(1), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010110






