Canine Lafora Disease: An Unstable Repeat Expansion Disorder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohort
2.2. Patient Consent and Ethical Committees
2.3. DNA Testing
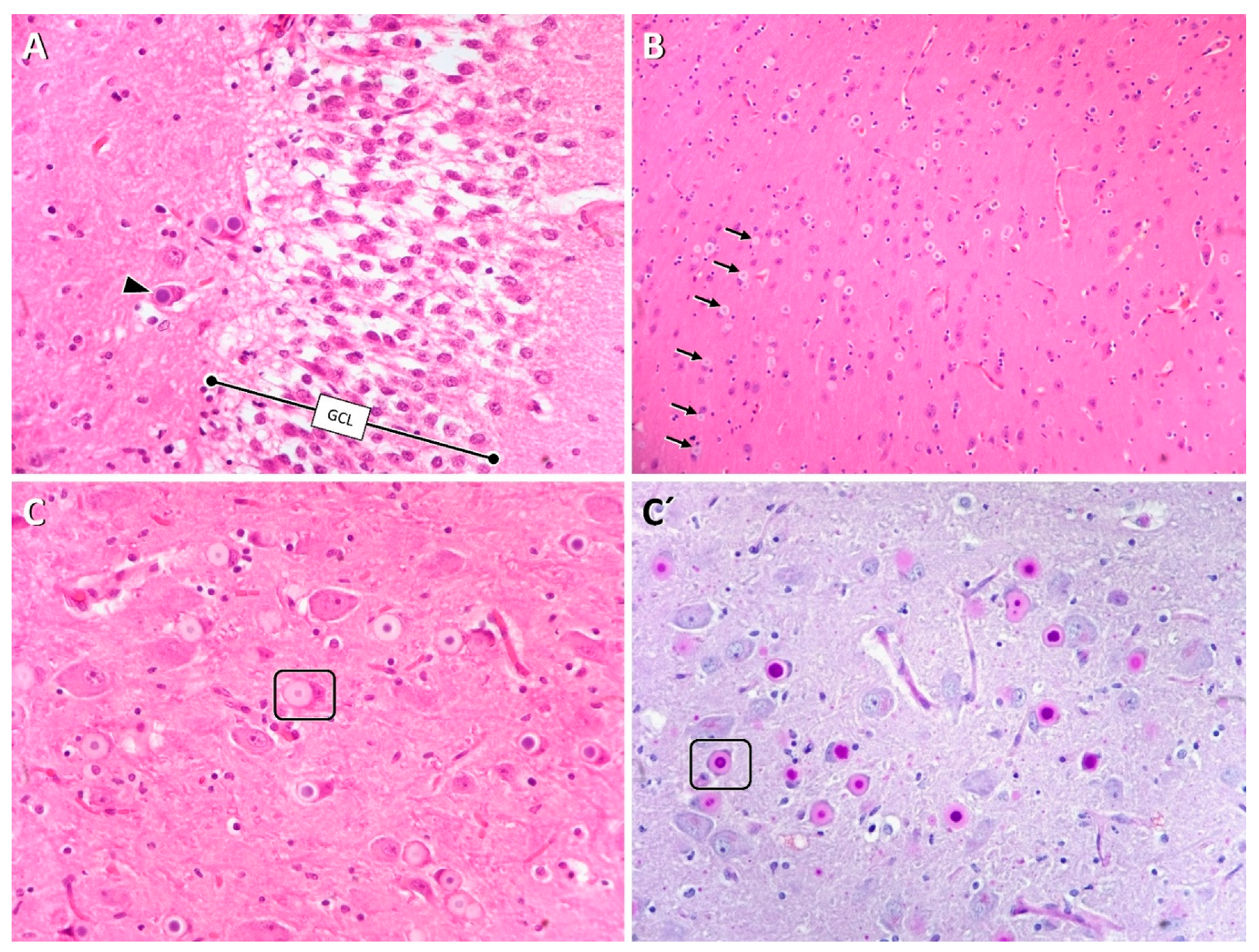
2.4. Histopathology
3. Results
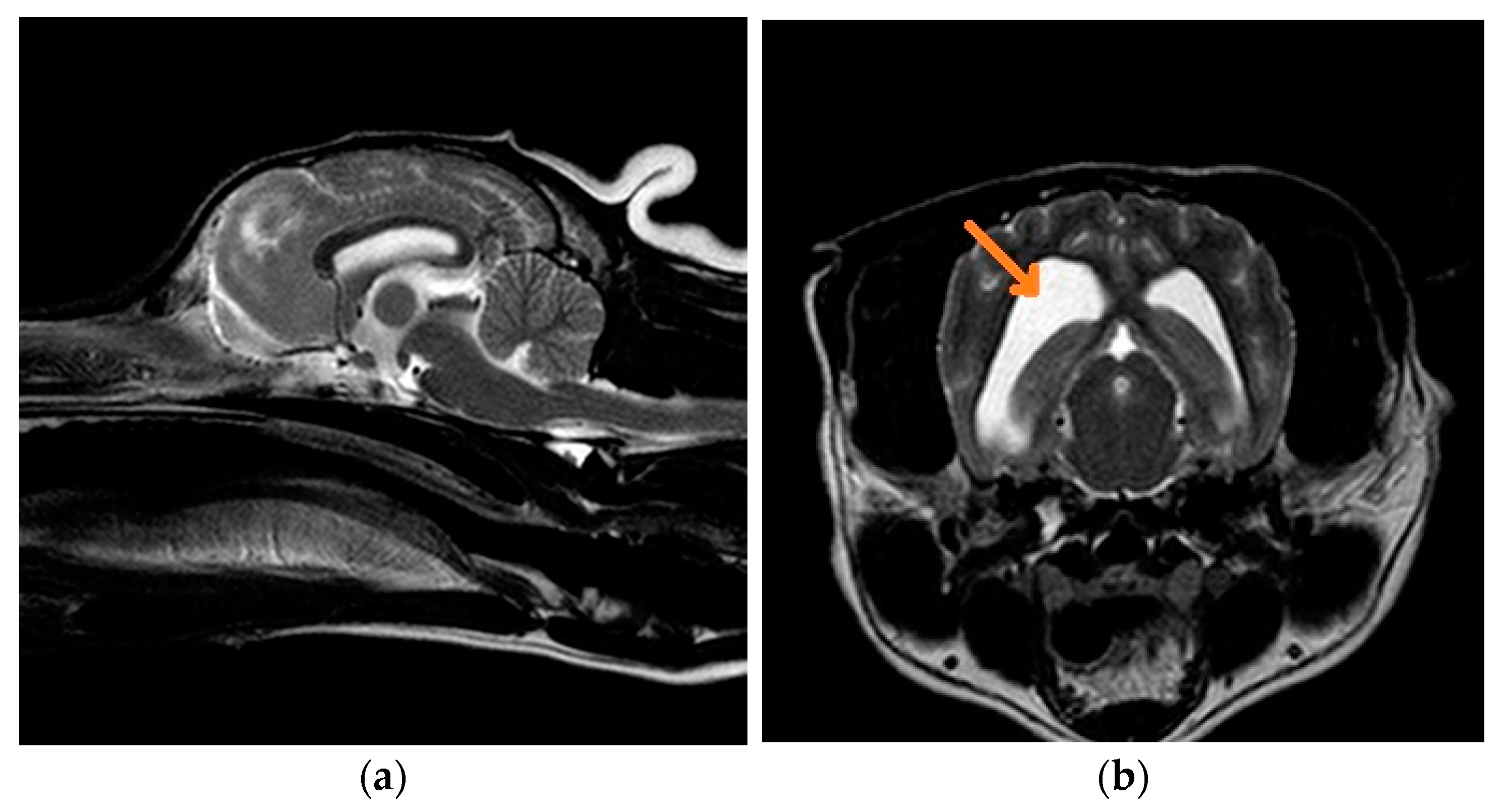
3.1. Clinical Findings
3.1.1. Case 1: Chihuahua
3.1.2. Case 2: French Bulldog
3.1.3. Case 3: French Bulldog
3.1.4. Case 4: Griffon Bruxellois
3.1.5. Case 5: Mixed-Breed Dog
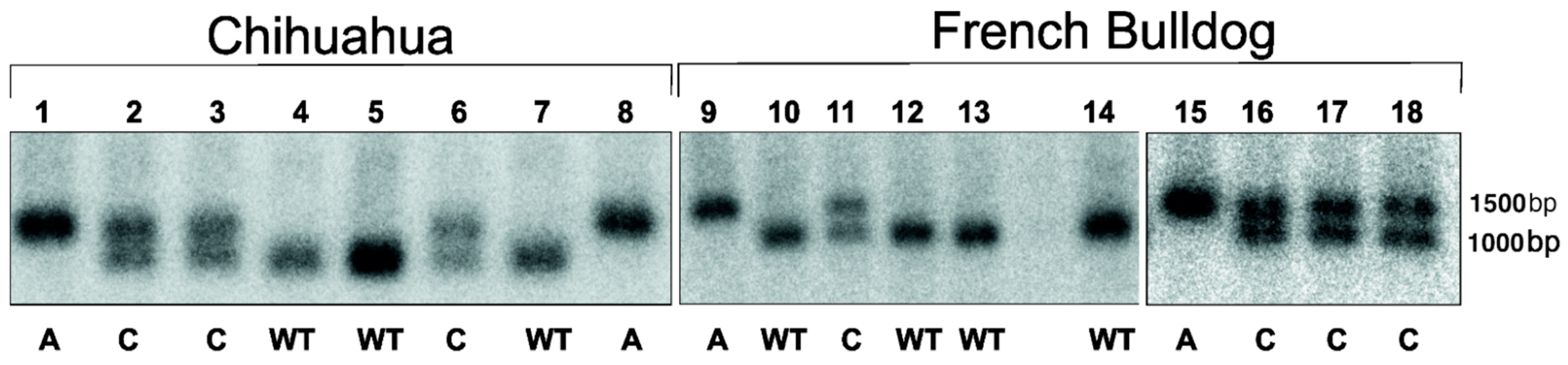
3.2. DNA Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Minassian, B.A.; Lee, J.R.; Herbrick, J.A.; Huizenga, J.; Soder, S.; Mungall, A.J.; Dunham, I.; Gardner, R.; Fong, C.Y.; Carpenter, S.; et al. Mutations in a gene encoding a novel protein tyrosine phosphatase cause progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Nat. Genet. 1998, 20, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serratosa, J.M.; Gómez-Garre, P.; Gallardo, M.E.; Anta, B.; de Bernabé, D.B.-V.; Lindhout, D.; Augustijn, P.B.; Tassinari, C.A.; Michelucci, R.; Malafosse, A.; et al. A Novel Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Gene Is Mutated in Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy of the Lafora Type (EPM2). Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.M.; Young, E.J.; Ianzano, L.; Munteanu, I.; Zhao, X.; Christopoulos, C.C.; Avanzini, G.; Elia, M.; Ackerley, C.A.; Jovic, N.J.; et al. Mutations in NHLRC1 cause progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minassian, B.A. Lafora’s disease: Towards a clinical, pathologic, and molecular synthesis. Pediatric Neurol. 2001, 25, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, L.; Key, G.; Tauro, A.; Ahonen, S.; Wang, P.; Ackerley, C.; Minassian, B.A.; Rusbridge, C. Lafora disease in miniature Wirehaired Dachshunds. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duran, J.; Tevy, M.F.; Garcia-Rocha, M.; Calbó, J.; Milán, M.; Guinovart, J.J. Deleterious effects of neuronal accumulation of glycogen in flies and mice. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, J.; Hervera, A.; Markussen, K.H.; Varea, O.; López-Soldado, I.; Sun, R.C.; Del Río, J.A.; Gentry, M.S.; Guinovart, J.J. Astrocytic glycogen accumulation drives the pathophysiology of neurodegeneration in Lafora disease. Brain A J. Neurol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahuerta, M.; Gonzalez, D.; Aguado, C.; Fathinajafabadi, A.; García-Giménez, J.L.; Moreno-Estellés, M.; Romá-Mateo, C.; Knecht, E.; Pallardó, F.V.; Sanz, P. Reactive Glia-Derived Neuroinflammation: A Novel Hallmark in Lafora Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy That Progresses with Age. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, J.; Gruart, A.; Garcia-Rocha, M.; Delgado-Garcia, J.M.; Guinovart, J.J. Glycogen accumulation underlies neurodegeneration and autophagy impairment in Lafora disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 3147–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turnbull, J.; DePaoli-Roach, A.A.; Zhao, X.; Cortez, M.A.; Pencea, N.; Tiberia, E.; Piliguian, M.; Roach, P.J.; Wang, P.; Ackerley, C.A.; et al. PTG depletion removes Lafora bodies and rescues the fatal epilepsy of Lafora disease. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pederson, B.A.; Turnbull, J.; Epp, J.R.; Weaver, S.A.; Zhao, X.; Pencea, N.; Roach, P.J.; Frankland, P.W.; Ackerley, C.A.; Minassian, B.A. Inhibiting glycogen synthesis prevents Lafora disease in a mouse model. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohi, H.; Young, E.J.; Fitzmaurice, S.N.; Rusbridge, C.; Chan, E.M.; Vervoort, M.; Turnbull, J.; Zhao, X.-C.; Ianzano, L.; Paterson, A.D.; et al. Expanded repeat in canine epilepsy. Science 2005, 307, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajek, I.; Kettner, F.; Simerdova, V.; Rusbridge, C.; Wang, P.; Minassian, B.A.; Palus, V. NHLRC1 repeat expansion in two beagles with Lafora disease. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 57, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostrander, E.A.; Wayne, R.K. The canine genome. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gredal, H.; Berendt, M.; Leifsson, P.S. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy in a beagle. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2003, 44, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrientos, L.; Maiolini, A.; Häni, A.; Jagannathan, V.; Leeb, T. NHLRC1 dodecamer repeat expansion demonstrated by whole genome sequencing in a Chihuahua with Lafora disease. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kehl, A.; Cizinauskas, S.; Langbein-Detsch, I.; Mueller, E. NHLRC1 dodecamer expansion in a Welsh Corgi (Pembroke) with Lafora disease. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.M.; Davis, W.C.; Prieur, D.J.; Collins, G.H. Lafora’s disease in the dog. A comparative study. Am. J. Pathol. 1970, 58, 509–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cusick, P.K.; Cameron, A.M.; Parker, A.J. Canine neuronal glycoproteinosis--Lafora’s disease in the dog [Hereditary diseases]. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1976, 12, 518–521. [Google Scholar]
- Whitenack, D.L. Neuronal glycoproteinosis (Lafora’s disease) in the dog. In Proceedings of the American Association of Veterinary Laboratory Diagnosticians, Madison, WI, USA, 22–26 October 1978; pp. 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Rusbridge, C.; Long, S.; Jovanovik, J.; Milne, M.; Berendt, M.; Bhatti, S.F.; De Risio, L.; Farqhuar, R.G.; Fischer, A.; Matiasek, K. International Veterinary Epilepsy Task Force recommendations for a veterinary epilepsy-specific MRI protocol. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matiasek, K.; Pumarola i Batlle, M.; Rosati, M.; Fernández-Flores, F.; Fischer, A.; Wagner, E.; Berendt, M.; Bhatti, S.F.M.; De Risio, L.; Farquhar, R.G.; et al. International veterinary epilepsy task force recommendations for systematic sampling and processing of brains from epileptic dogs and cats. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nitschke, F.; Wang, P.; Schmieder, P.; Girard, J.M.; Awrey, D.E.; Wang, T.; Israelian, J.; Zhao, X.; Turnbull, J.; Heydenreich, M.; et al. Hyperphosphorylation of glucosyl C6 carbons and altered structure of glycogen in the neurodegenerative epilepsy Lafora disease. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tagliabracci, V.S.; Heiss, C.; Karthik, C.; Contreras, C.J.; Glushka, J.; Ishihara, M.; Azadi, P.; Hurley, T.D.; De Paoli-Roach, A.A.; Roach, P.J. Phosphate incorporation during glycogen synthesis and Lafora disease. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Paoli-Roach, A.A.; Contreras, C.J.; Segvich, D.M.; Heiss, C.; Ishihara, M.; Azadi, P.; Roach, P.J. Glycogen phosphomonoester distribution in mouse models of the progressive myoclonic epilepsy, Lafora disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nitschke, F.; Sullivan, M.A.; Wang, P.; Zhao, X.; Chown, E.E.; Perri, A.M.; Israelian, L.; Juana-López, L.; Bovolenta, P.; Rodríguez de Córdoba, S.; et al. Abnormal glycogen chain length pattern, not hyperphosphorylation, is critical in Lafora disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzmaurice, S.N.; Rusbridge, C.; Shelton, G.D.; Minassian, B.A.; Scherer, S.W. Familial myoclonic epilepsy in the Miniature Wirehaired Dachshund. In Proceedings of the European Society of Veterinary Neurology 14th Annual Symposium, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 21–23 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nitschke, F.; Ahonen, S.J.; Nitschke, S.; Mitra, S.; Minassian, B.A. Lafora disease-from pathogenesis to treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striano, P.; Manganelli, F.; Boccella, P.; Perretti, A.; Striano, S. Levetiracetam in patients with cortical myoclonus: A clinical and electrophysiological study. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2005, 20, 1610–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, A.; Chen, R. Myoclonus: Pathophysiology and Treatment Options. Curr. Treat. Opt. Neurol. 2016, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Villena, C.; Viana, R.; Bonet, J.; Garcia-Gimeno, M.A.; Casado, M.; Heredia, M.; Sanz, P. Astrocytes: New players in progressive myoclonus epilepsy of Lafora type. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romá-Mateo, C.; Aguado, C.; García-Giménez, J.L.; Knecht, E.; Sanz, P.; Pallardó, F.V. Oxidative stress, a new hallmark in the pathophysiology of Lafora progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanz, P.; Serratosa, J.M. Neuroinflammation and progressive myoclonus epilepsies: From basic science to therapeutic opportunities. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2020, 22, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.J.; vonHoldt, B.; Horvath, S.; Pellegrini, M. An epigenetic aging clock for dogs and wolves. Aging 2017, 9, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusbridge, C.; Fitzmaurice, S.N.; Lohi, H.; Young, E.J.; Minassian, B.A. Treatment of Lafora disease (inherited myoclonic epilepsy) in dogs. In Proceedings of the European Society of Veterinary Neurology 18th Annual Symposium, Glasgow, UK, 24–25 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinali, S.; Canafoglia, L.; Bertoli, S.; Franceschetti, S.; Lanzi, G.; Tagliabue, A.; Veggiotti, P. A pilot study of a ketogenic diet in patients with Lafora body disease. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 69, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelian, L.; Wang, P.; Gabrielian, S.; Zhao, X.; Minassian, B.A. Ketogenic diet reduces Lafora bodies in murine Lafora disease. Neurol. Genet. 2020, 6, e533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Larson, B.; Araujo, J.A.; Lau, W.; de Rivera, C.; Santana, R.; Gore, A.; Milgram, N.W. Dietary supplementation with medium-chain TAG has long-lasting cognition-enhancing effects in aged dogs. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Packer, R.M.; Law, T.H.; Davies, E.; Zanghi, B.; Pan, Y.; Volk, H.A. Effects of a ketogenic diet on ADHD-like behavior in dogs with idiopathic epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 55, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Landsberg, G.; Mougeot, I.; Kelly, S.; Xu, H.; Bhatnagar, S.; Gardner, C.L.; Milgram, N.W. Efficacy of a Therapeutic Diet on Dogs With Signs of Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome (CDS): A Prospective Double Blinded Placebo Controlled Clinical Study. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aso, E.; Andrés-Benito, P.; Grau-Escolano, J.; Caltana, L.; Brusco, A.; Sanz, P.; Ferrer, I. Cannabidiol-Enriched Extract Reduced the Cognitive Impairment but Not the Epileptic Seizures in a Lafora Disease Animal Model. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2020, 5, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
von Klopmann, T.; Ahonen, S.; Espadas-Santiuste, I.; Matiasek, K.; Sanchez-Masian, D.; Rupp, S.; Vandenberghe, H.; Rose, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; et al. Canine Lafora Disease: An Unstable Repeat Expansion Disorder. Life 2021, 11, 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11070689
von Klopmann T, Ahonen S, Espadas-Santiuste I, Matiasek K, Sanchez-Masian D, Rupp S, Vandenberghe H, Rose J, Wang T, Wang P, et al. Canine Lafora Disease: An Unstable Repeat Expansion Disorder. Life. 2021; 11(7):689. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11070689
Chicago/Turabian Stylevon Klopmann, Thilo, Saija Ahonen, Irene Espadas-Santiuste, Kaspar Matiasek, Daniel Sanchez-Masian, Stefan Rupp, Helene Vandenberghe, Jeremy Rose, Travis Wang, Peixiang Wang, and et al. 2021. "Canine Lafora Disease: An Unstable Repeat Expansion Disorder" Life 11, no. 7: 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11070689
APA Stylevon Klopmann, T., Ahonen, S., Espadas-Santiuste, I., Matiasek, K., Sanchez-Masian, D., Rupp, S., Vandenberghe, H., Rose, J., Wang, T., Wang, P., Minassian, B. A., & Rusbridge, C. (2021). Canine Lafora Disease: An Unstable Repeat Expansion Disorder. Life, 11(7), 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11070689






