Chemical-Mediated Targeted Protein Degradation in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Protein Aggregates and Neurodegenerative Diseases
2.1. Tau
2.2. α-Synuclein
2.3. Huntingtin
2.4. β-Amyloid
3. Protein Degradation Machinery in Cells
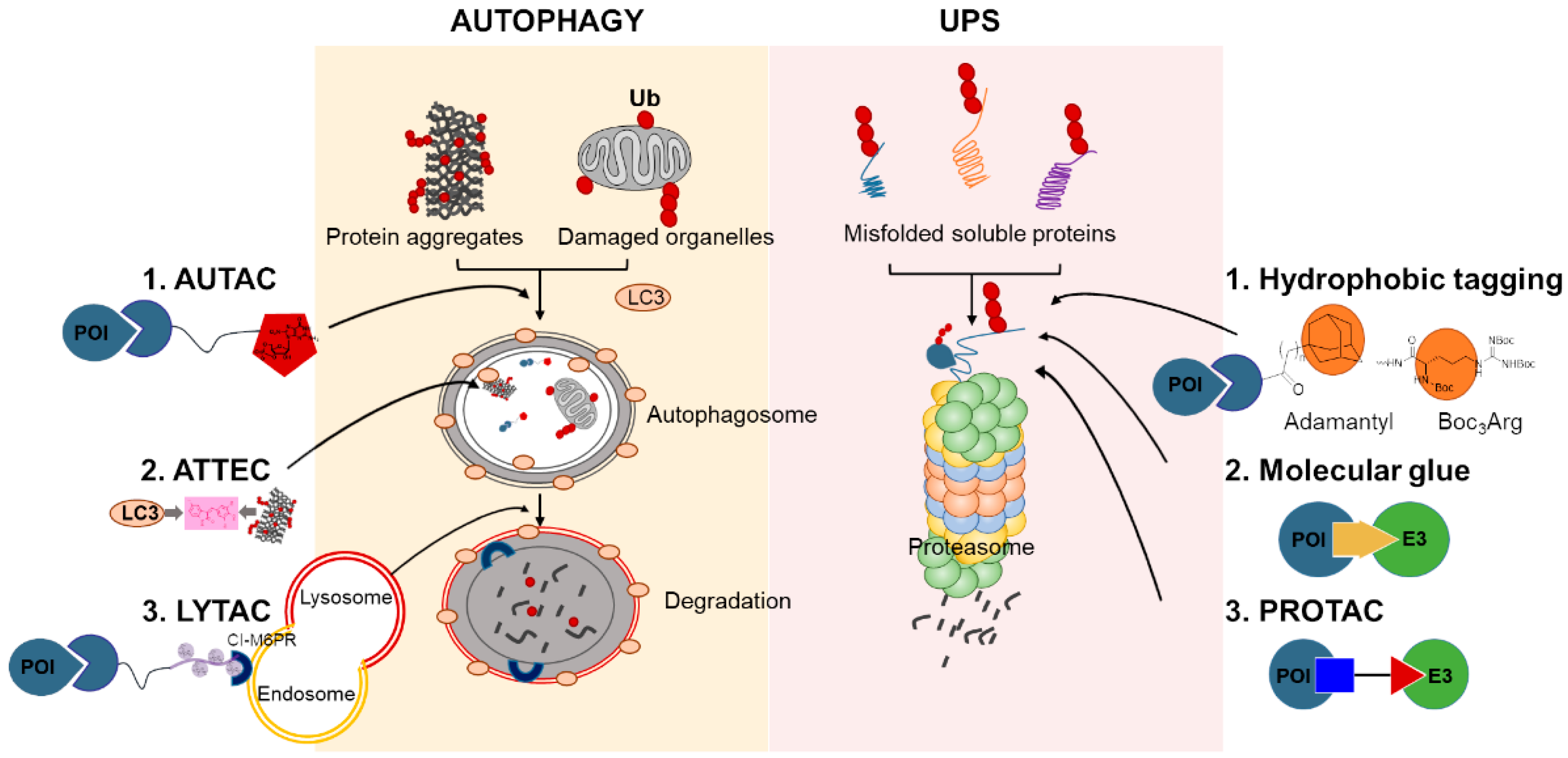
4. Chemical-Mediated Targeted Protein Degradation Methods
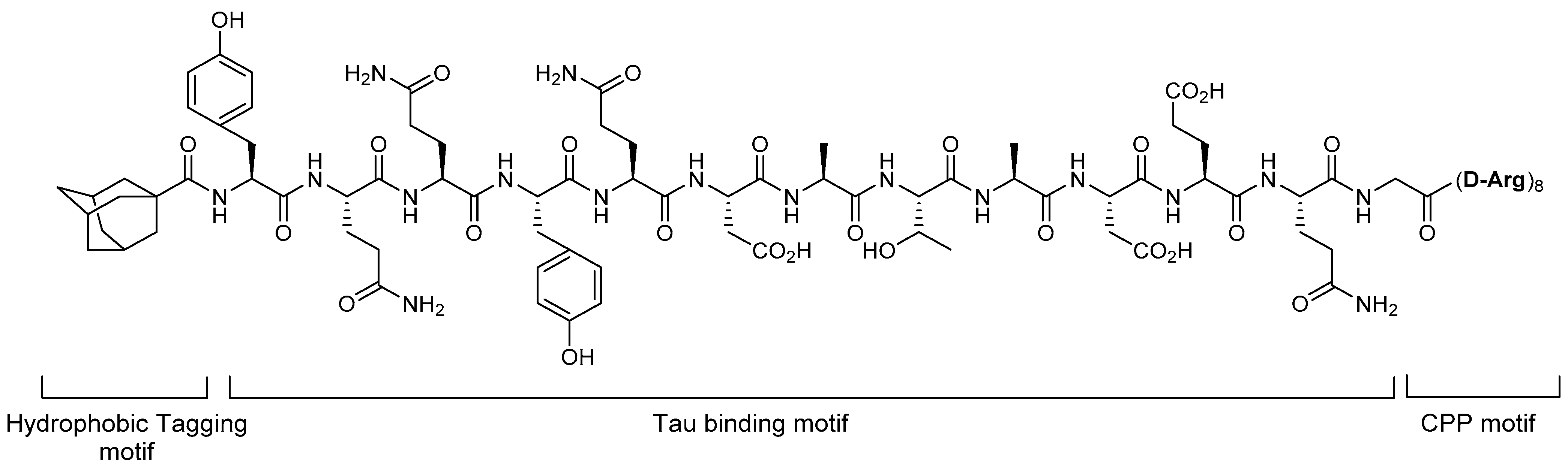
4.1. Hydrophobic Tagging
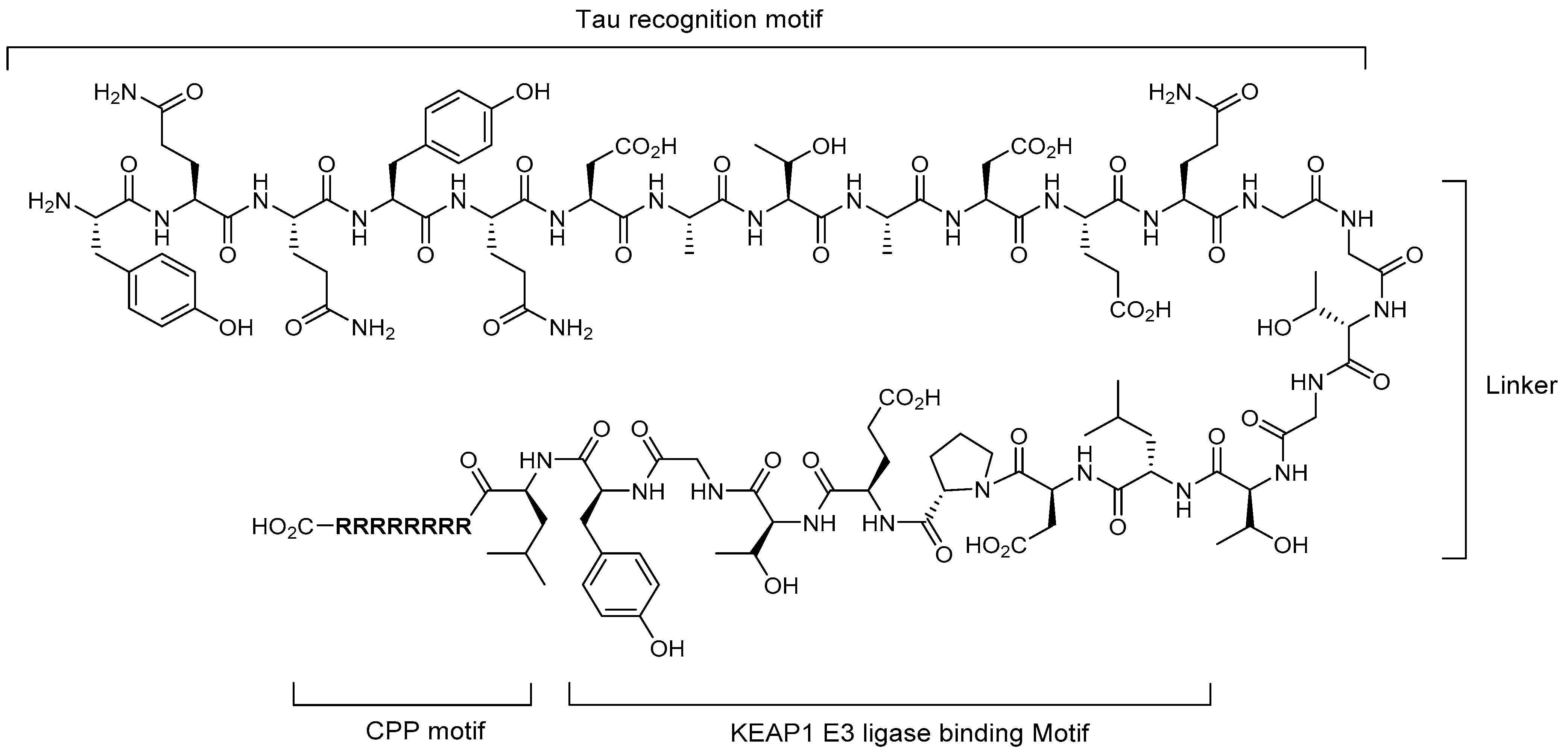
4.2. Molecular Glues
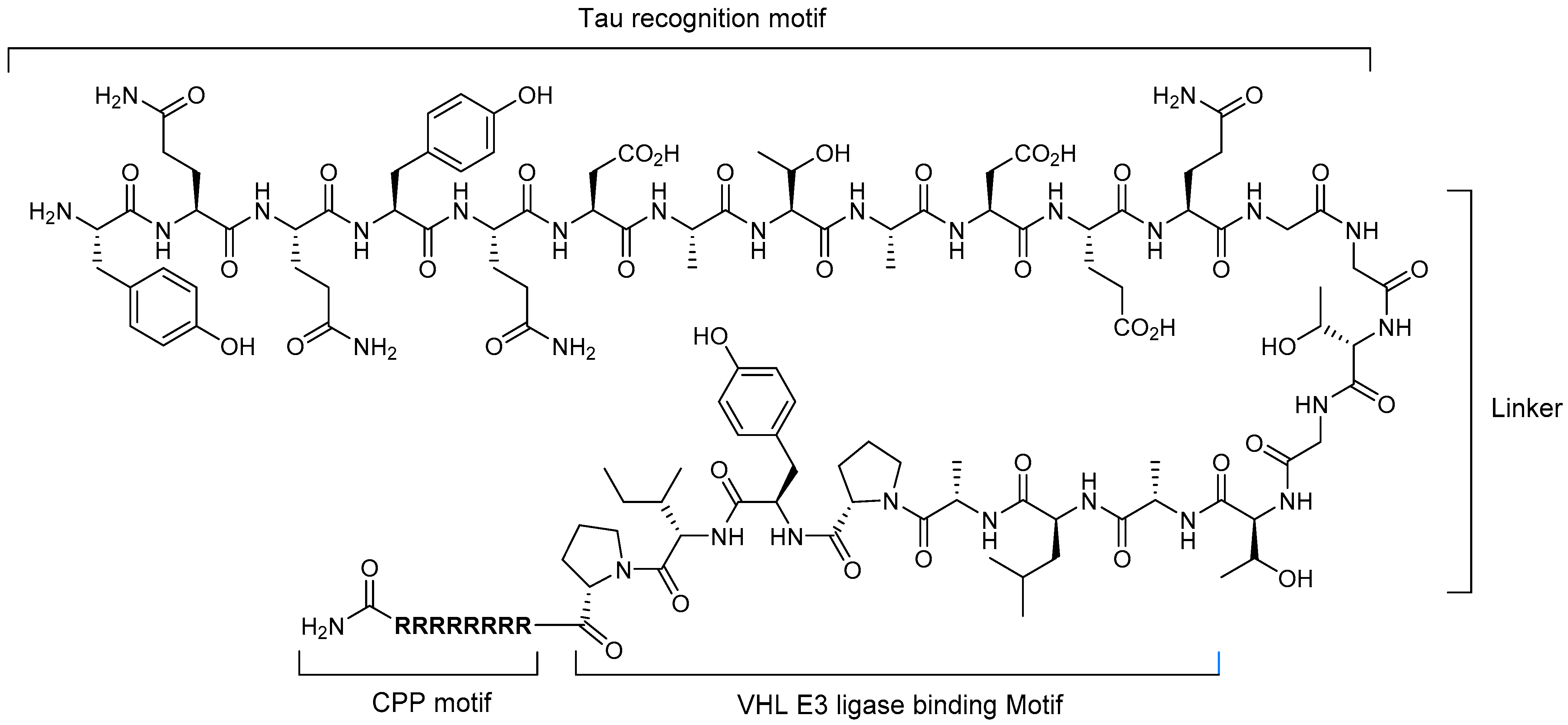
4.3. PROTACs
4.4. Autophagy-Targeting Chimeras, Autophagosome-Tethering Compound, and Lysosome-Targeting Chimeras
5. Targeted Protein Degradation for Neurodegenerative Diseases
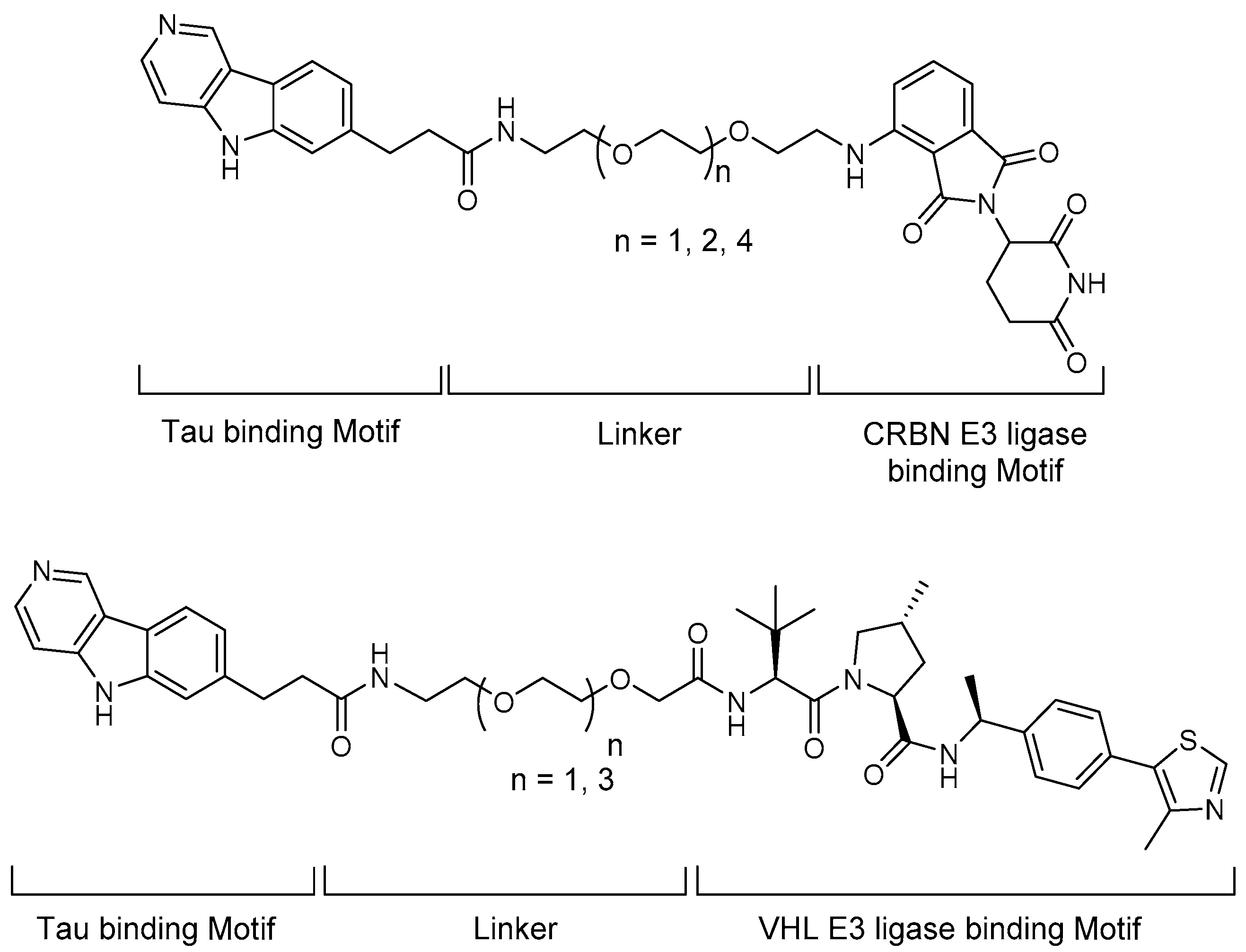
5.1. Tau
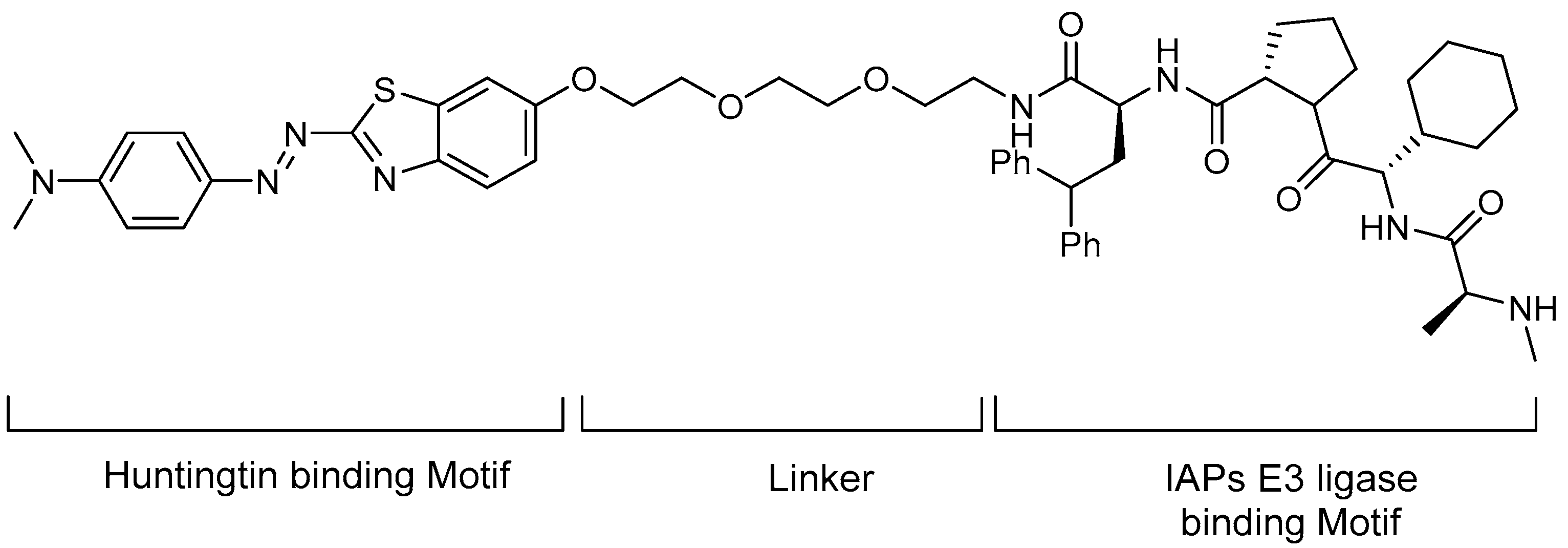
5.2. Huntingtin
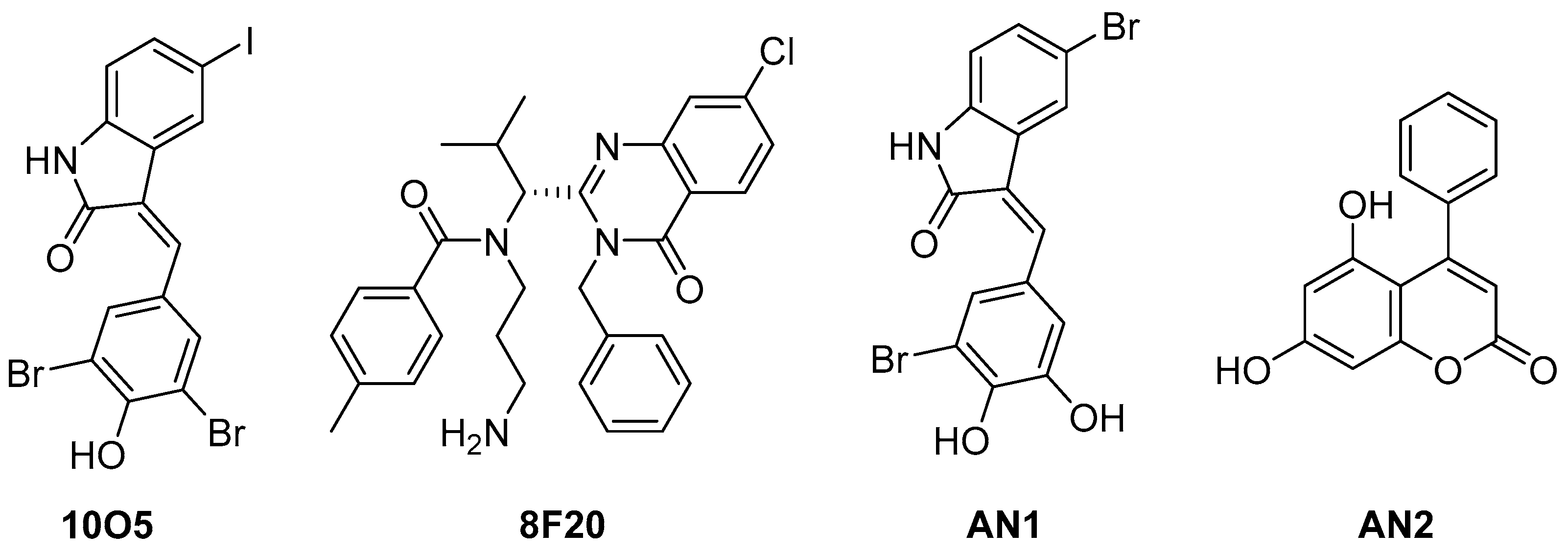
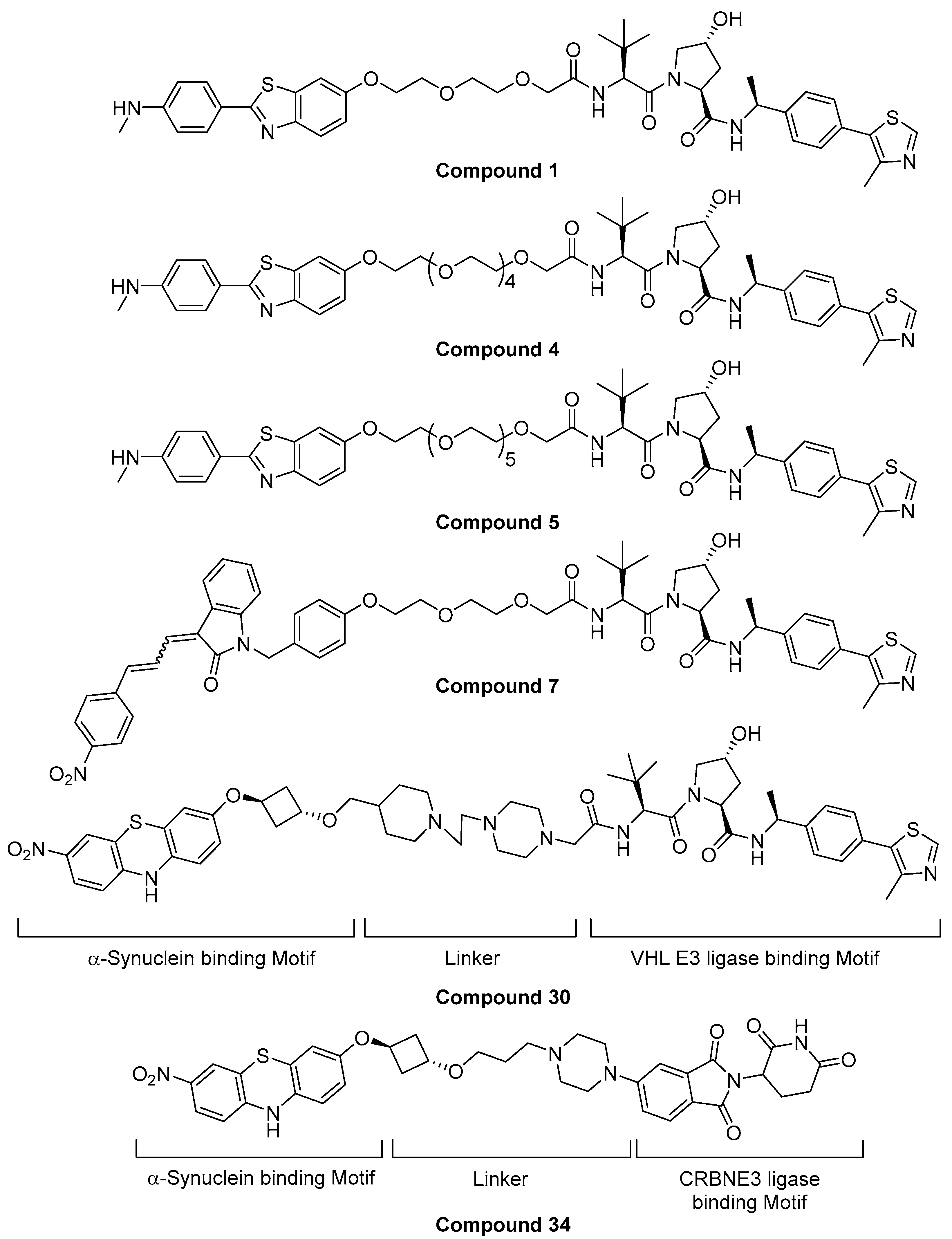
5.3. Alpha-Synuclein
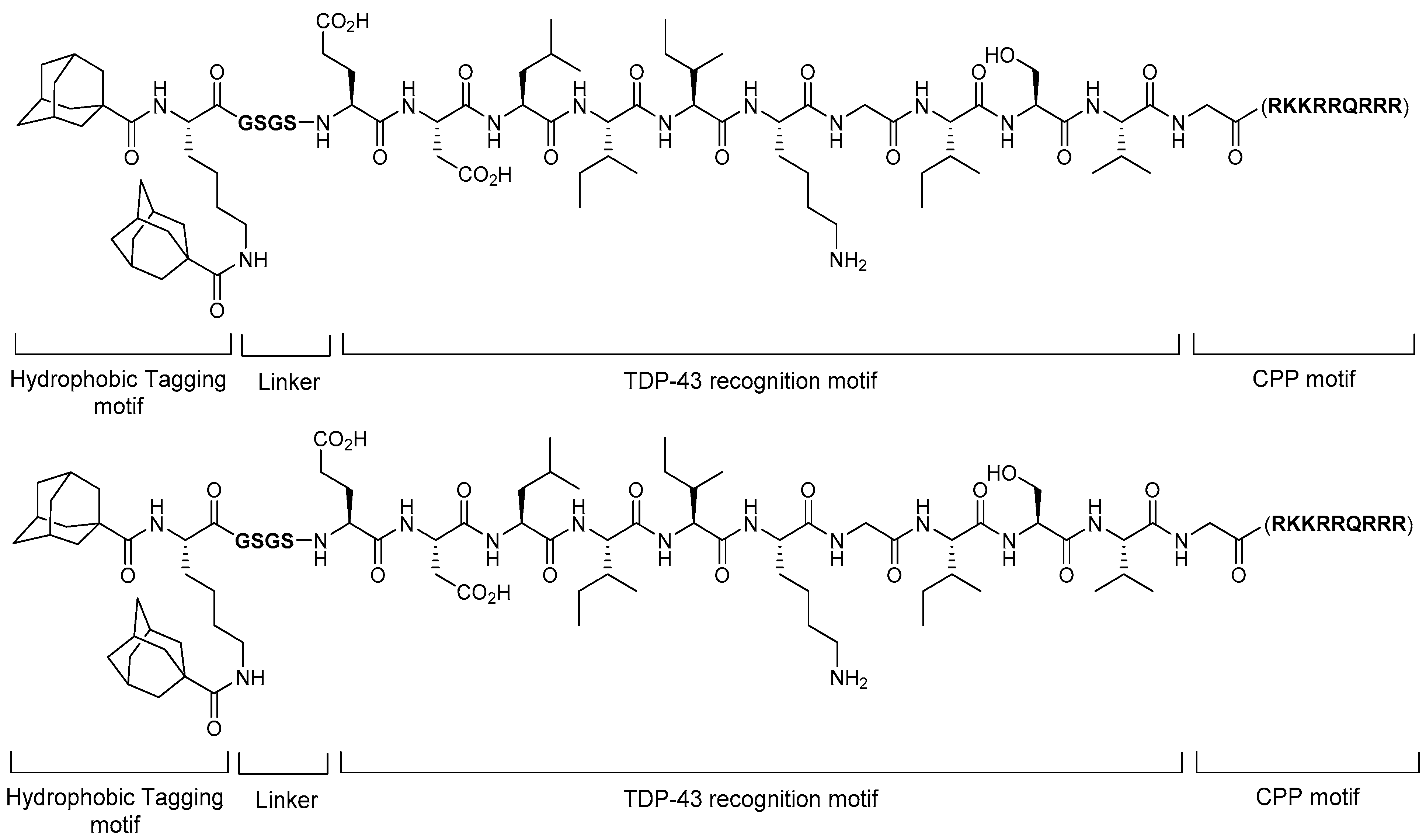
5.4. TDP-43-Targeting Degrader
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartl, F.U. Protein Misfolding Diseases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tracy, T.E.; Gan, L. Tau-mediated synaptic and neuronal dysfunction in neurodegenerative disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 51, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, K.; Liu, F.; Gong, C.X.; Grundke-Iqbal, I. Tau in Alzheimer Disease and Related Tauopathies. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2010, 7, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, F.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Fu, Y.; He, W.; Zhang, J. Tau Pathology in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexander, G.E. Biology of Parkinson’s disease: Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of a multisystem neurodegenerative disorder. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2004, 6, 259–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Benito, M.; Granado, N.; García-Sanz, P.; Michel, A.; Dumoulin, M.; Moratalla, R. Modeling Parkinson’s Disease With the Alpha-Synuclein Protein. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayalu, P.; Albin, R.L. Huntington disease: Pathogenesis and treatment. Neurol. Clin. 2015, 33, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daldin, M.; Fodale, V.; Cariulo, C.; Azzollini, L.; Verani, M.; Martufi, P.; Spiezia, M.C.; Deguire, S.M.; Cherubini, M.; Macdonald, D.; et al. Polyglutamine expansion affects huntingtin conformation in multiple Huntington’s disease models. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jimenez-Sanchez, M.; Licitra, F.; Underwood, B.R.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Huntington’s Disease: Mechanisms of Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a024240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arrasate, M.; Finkbeiner, S. Protein aggregates in Huntington’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 238, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, M.P.; LeVine, H., III. Alzheimer’s Disease and the Amyloid-β Peptide. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 19, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, R.J.; Wong, P.C. Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pohl, C.; Dikic, I. Cellular quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy. Science 2019, 366, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deol, K.K.; Lorenz, S.; Strieter, E.R. Enzymatic Logic of Ubiquitin Chain Assembly. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heride, C.; Urbé, S.; Clague, M.J. Ubiquitin code assembly and disassembly. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R215–R220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; He, D.; Yao, Z.; Klionsky, D.J. The machinery of macroautophagy. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tai, H.-C.; Schuman, E.M. Ubiquitin, the proteasome and protein degradation in neuronal function and dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Cecarini, V.; Keller, J.N. Interplay between protein synthesis and degradation in the CNS: Physiological and pathological implications. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, M. An Overview on the Clinical Development of Tau-Based Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cromm, P.M.; Crews, C.M. Targeted Protein Degradation: From Chemical Biology to Drug Discovery. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schreiber, S.L. The Rise of Molecular Glues. Cell 2021, 184, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.-M.; Dong, J.; Xu, Z.-Y.; Cheng, X.-D.; Zhang, W.-D.; Qin, J.-J. PROTAC: An Effective Targeted Protein Degradation Strategy for Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, D.; Moriyama, J.; Nakamura, T.; Miki, E.; Takahashi, E.; Sato, A.; Akaike, T.; Itto-Nakama, K.; Arimoto, H. AUTACs: Cargo-Specific Degraders Using Selective Autophagy. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, S.M.; Pedram, K.; Wisnovsky, S.; Ahn, G.; Riley, N.M.; Bertozzi, C.R. Lysosome-targeting chimaeras for degradation of extracellular proteins. Nature 2020, 584, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.-T.; Gao, N.; Li, Q.-Q.; Chen, P.-G.; Yang, X.-F.; Chen, Y.-X.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-M. Specific Knockdown of Endogenous Tau Protein by Peptide-Directed Ubiquitin-Proteasome Degradation. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, N.; Chu, T.-T.; Li, Q.-Q.; Lim, Y.-J.; Qiu, T.; Ma, M.-R.; Hu, Z.-W.; Yang, X.-F.; Chen, Y.-X.; Zhao, Y.-F.; et al. Hydrophobic tagging-mediated degradation of Alzheimer’s disease related Tau. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 40362–40366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, N.; Chen, Y.-X.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-M. Chemical Methods to Knock Down the Amyloid Proteins. Molecules 2017, 22, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.; Liu, T.; Jiao, Q.; Ji, J.; Tao, M.; Liu, Y.; You, Q.; Jiang, Z. Discovery of a Keap1-dependent peptide PROTAC to knockdown Tau by ubiquitination-proteasome degradation pathway. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 146, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copple, I.M.; Goldring, C.E.; Kitteringham, N.R.; Park, B.K. The Nrf2–Keap1 defence pathway: Role in protection against drug-induced toxicity. Toxicology 2008, 246, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargbo, R.B. Treatment of Alzheimer’s by PROTAC-Tau Protein Degradation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gray, N.S.; Haggarty, S.J.; Cai, Q.; Telo Baptista Lima Da Silva, M.C.; Zhang, T.; Ferguson, F.M. Compounds for Tau Protein Degradation. U.S. Patent WO2019014429, 17 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.C.; Ferguson, F.M.; Cai, Q.; Donovan, K.A.; Nandi, G.; Patnaik, D.; Zhang, T.; Huang, H.-T.; Lucente, D.E.; Dickerson, B.C.; et al. Targeted degradation of aberrant tau in frontotemporal dementia patient-derived neuronal cell models. eLife 2019, 8, e45457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoshige, S.; Nomura, S.; Ohgane, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Discovery of Small Molecules that Induce the Degradation of Huntingtin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11530–11533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Tomoshige, S.; Nomura, S.; Ohgane, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Application of protein knockdown strategy targeting β-sheet structure to multiple disease-associated polyglutamine proteins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoshige, S.; Nomura, S.; Ohgane, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Degradation of huntingtin mediated by a hybrid molecule composed of IAP antagonist linked to phenyldiazenyl benzothiazole derivative. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, C.; Ding, Y.; Fei, Y.; Lu, B. ATTEC: A potential new approach to target proteinopathies. Autophagy 2020, 16, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Sha, T.; Ma, L.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Allele-selective lowering of mutant HTT protein by HTT–LC3 linker compounds. Nature 2019, 575, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Jin, W.Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.T. Rapid and reversible knockdown of endogenous proteins by peptide-directed lysosomal degradation. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kargbo, R.B. PROTAC Compounds Targeting α-Synuclein Protein for Treating Neurogenerative Disorders: Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1086–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Huang, Y.-P.; Chu, T.-T.; Li, Q.-Q.; Zhou, B.; Chen, Y.-X.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-M. TDP-43 specific reduction induced by Di-hydrophobic tags conjugated peptides. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salami, J.; Crews, C.M. Waste disposal—An attractive strategy for cancer therapy. Science 2017, 355, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longhena, F.; Spano, P.; Bellucci, A. Targeting of Disordered Proteins by Small Molecules in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2018, 245, 85–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hyun, S.; Shin, D. Chemical-Mediated Targeted Protein Degradation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Life 2021, 11, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11070607
Hyun S, Shin D. Chemical-Mediated Targeted Protein Degradation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Life. 2021; 11(7):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11070607
Chicago/Turabian StyleHyun, Soonsil, and Dongyun Shin. 2021. "Chemical-Mediated Targeted Protein Degradation in Neurodegenerative Diseases" Life 11, no. 7: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11070607
APA StyleHyun, S., & Shin, D. (2021). Chemical-Mediated Targeted Protein Degradation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Life, 11(7), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11070607





