Role of PTEN, PI3K, and mTOR in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Immunohistochemistry
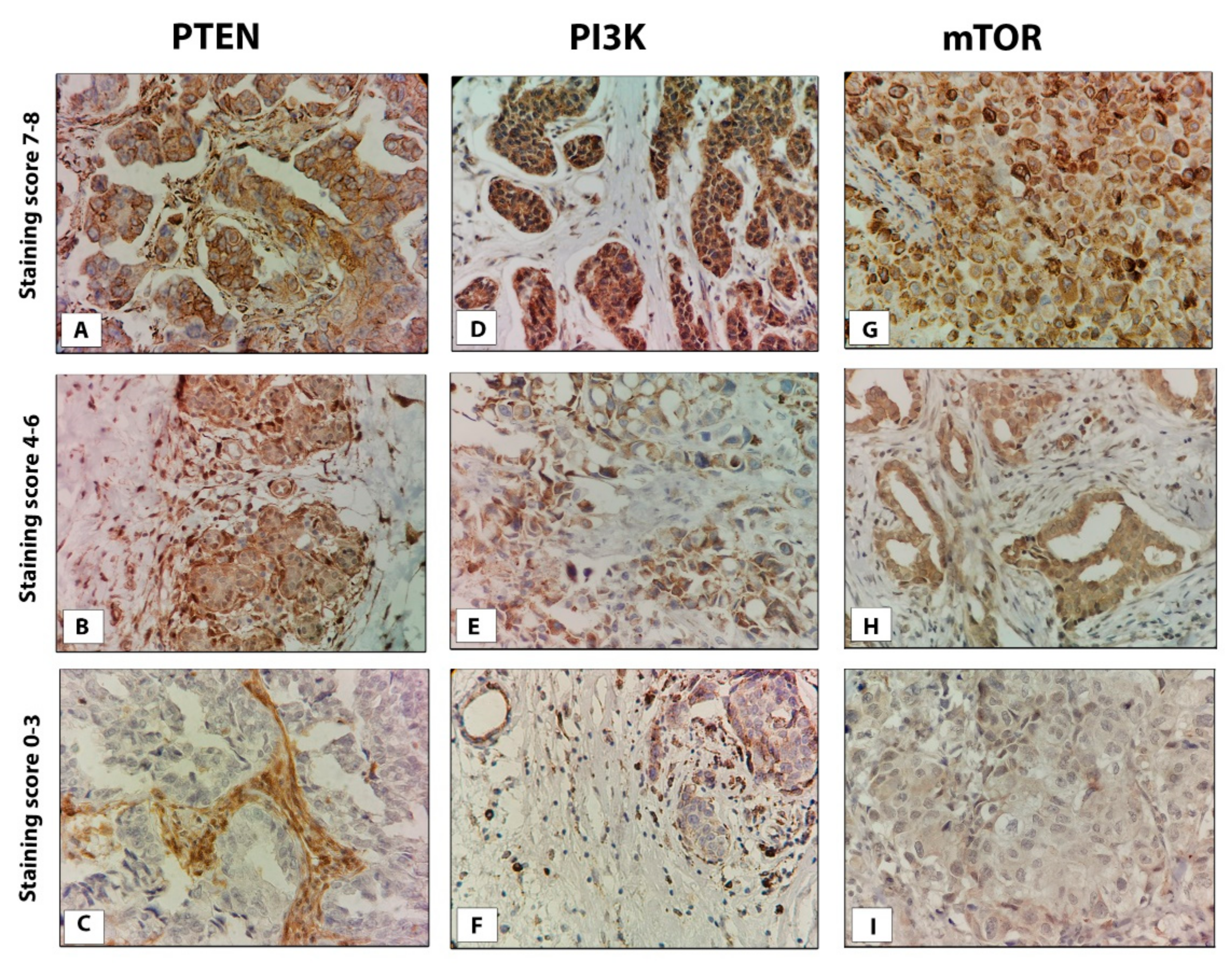
2.2. Evaluation of Staining
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. PTEN Copy Number Analysis by Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
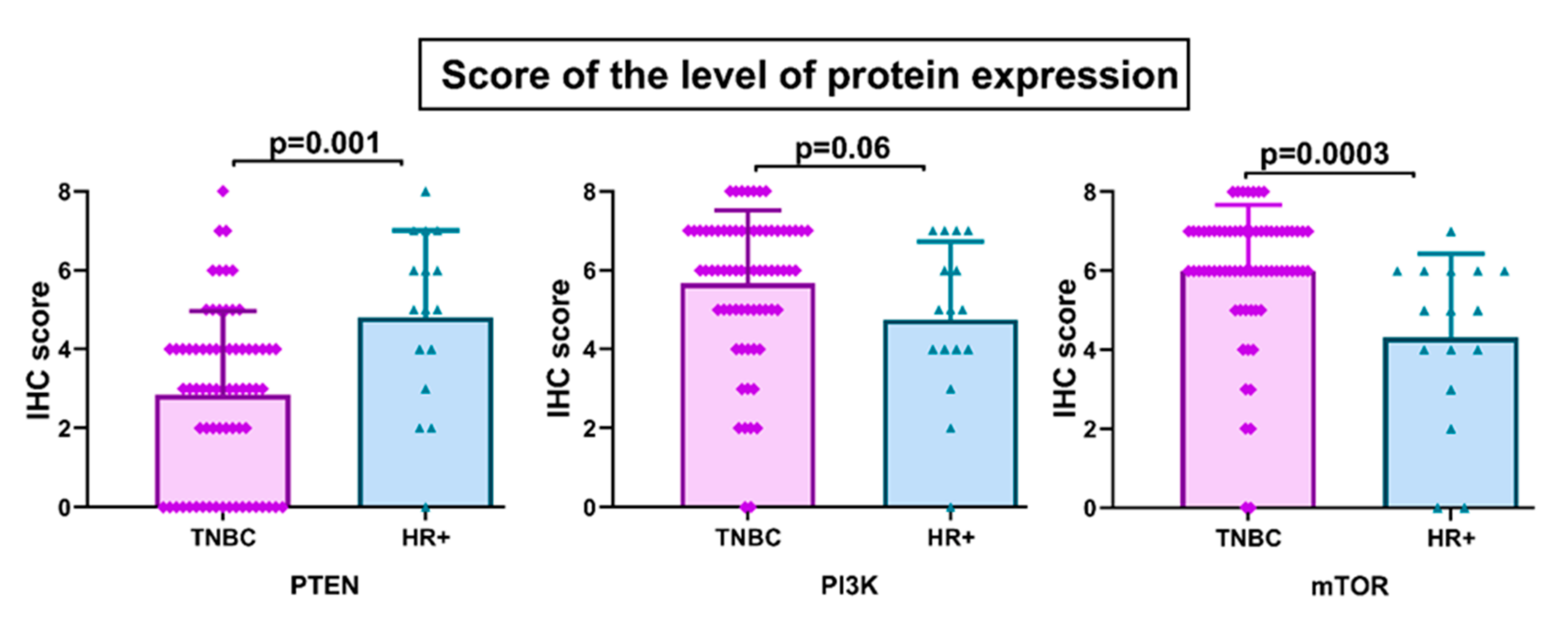
3.1. PTEN, PI3k, and mTOR Protein Expression
3.2. Copy Number Alterations of PTEN Gene
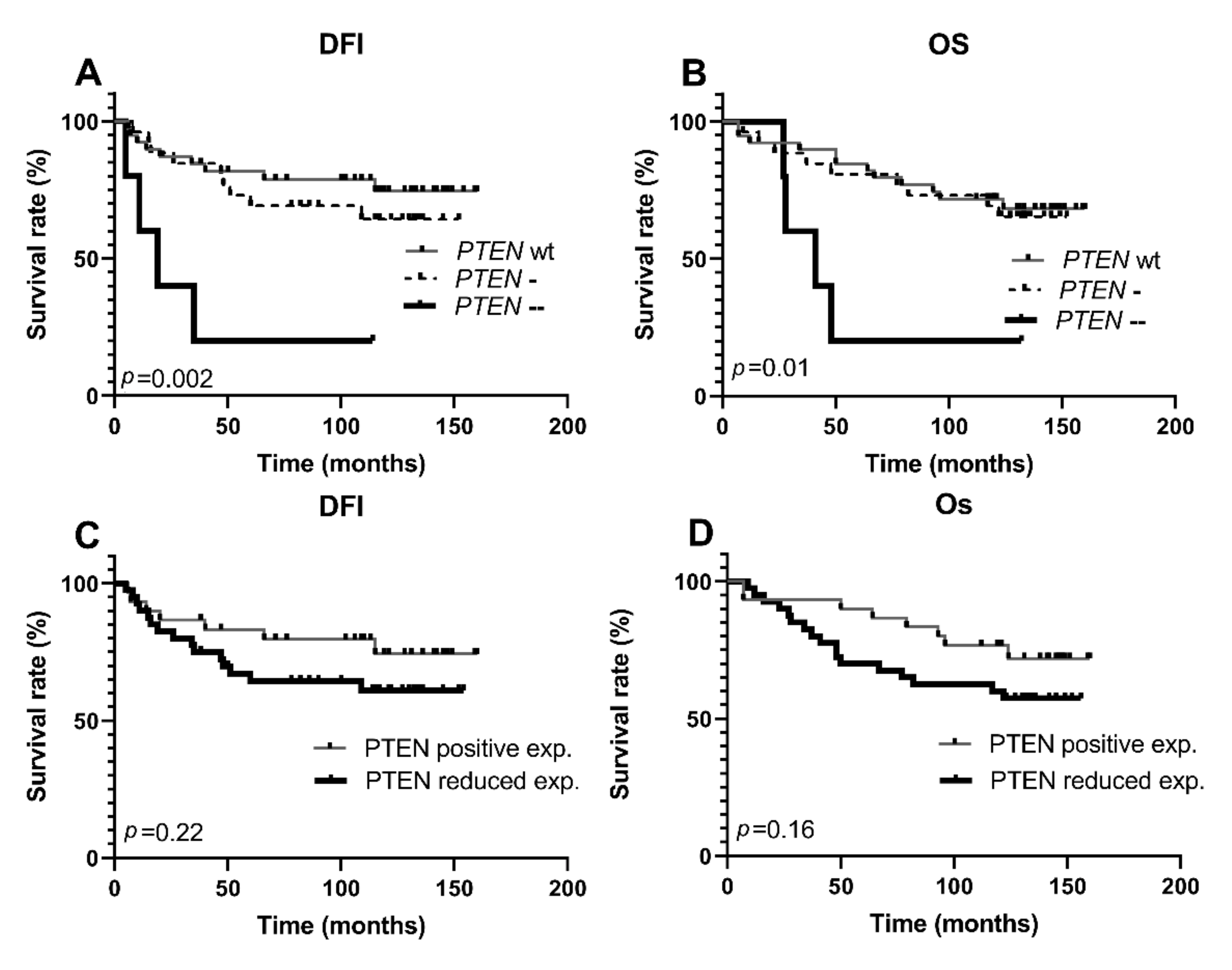
3.3. Clinicopathologic Features According to PTEN, PI3K, and mTOR Protein Expression and PTEN Gene Copy Number
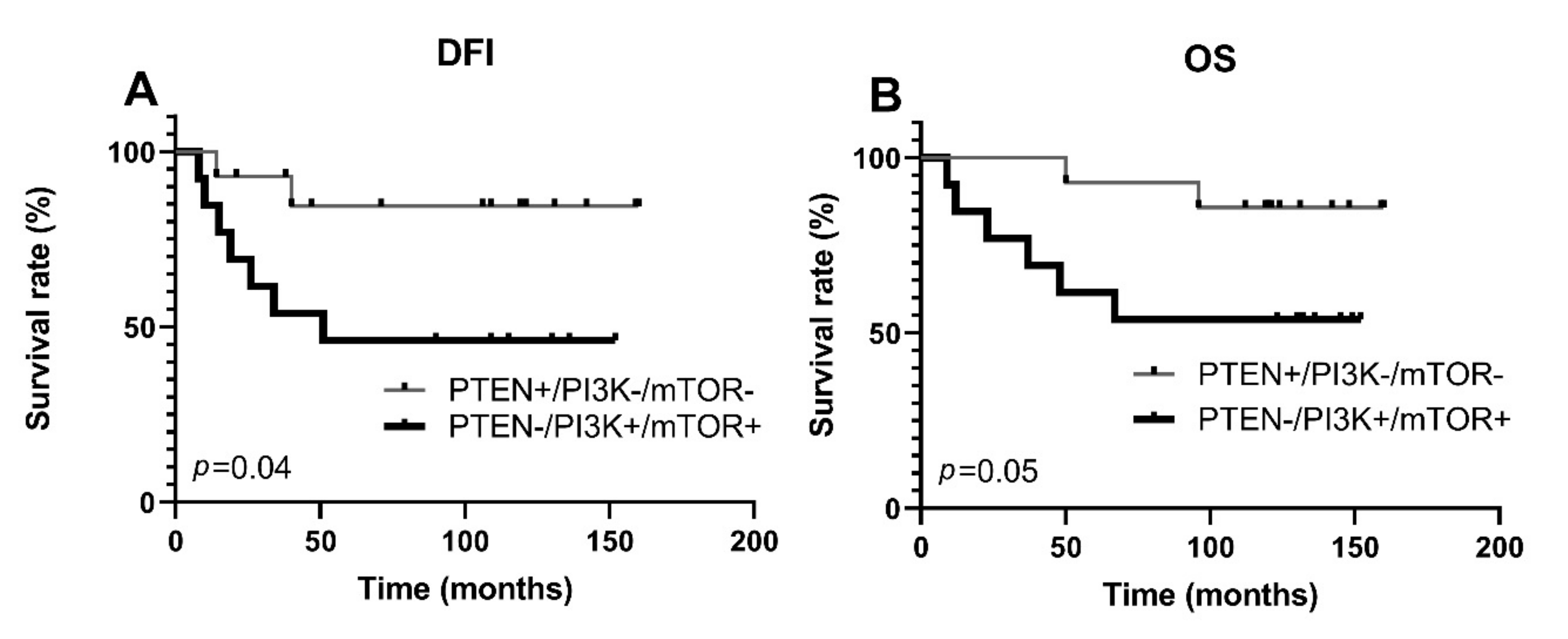
3.4. Activation of PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR Pathway and Protein Expression of ABCG2, ABCC1, and ABCB1 Transporters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dent, R.; Trudeau, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Hanna, W.M.; Kahn, H.K.; Sawka, C.A.; Lickley, L.A.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kennecke, H.; Yerushalmi, R.; Woods, R.; Cheang, M.C.U.; Voduc, D.; Speers, C.H.; Nielsen, T.O.; Gelmon, K. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitariu, A.-A.; Cîmpean, A.M.; Ribatti, D.; Raica, M. Triple negative breast cancer: The kiss of death. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46652–46662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nedeljković, M.; Damjanović, A. Mechanisms of Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—How We Can Rise to the Challenge. Cells 2019, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjbar, S.; Khonkarn, R.; Moreno, A.; Baubichon-Cortay, H.; Miri, R.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Saso, L.; Edraki, N.; Falson, P.; Firuzi, O. 5-Oxo-hexahydroquinoline derivatives as modulators of P-gp, MRP1 and BCRP transporters to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 362, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljković, M.; Tanić, N.; Prvanović, M.; Milovanović, Z.; Tanić, N. Friend or foe: ABCG2, ABCC1 and ABCB1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2021, 28, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.S. PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: At the bench and bedside. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Song, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Nie, J.; Chen, C. Activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Causes Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 628690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luongo, F.; Colonna, F.; Calapà, F.; Vitale, S.; Fiori, M.E.; De Maria, R. Pten tumor-suppressor: The dam of stemness in cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, S.; Denk, S.; Wiegering, A. Targeting protein synthesis in colorectal cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth Control and Disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAuliffe, P.F.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Mills, G.B.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. Deciphering the role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in breast cancer biology and pathogenesis. Clin. Breast Cancer 2010, 10 (Suppl. 3), S59–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinou, C.; Papadopoulos, S.; Alexopoulos, A.; Aganti, N.; Batistatou, A.; Harisis, H. Expression and Clinical Significance of Claudin-, PDL-1. In Vivo 2018, 32, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, F.; Esnakula, A.; Ricks-Santi, L.J.; Zafar, R.; Kanaan, Y.; Naab, T. Loss of PTEN in high grade advanced stage triple negative breast ductal cancers in African American women. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inanc, M.; Ozkan, M.; Karaca, H.; Berk, V.; Bozkurt, O.; Duran, A.O.; Ozaslan, E.; Akgun, H.; Tekelioglu, F.; Elmali, F. Cytokeratin 5/6, c-Met expressions, and PTEN loss prognostic indicators in triple-negative breast cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, S.; Siraj, A.K.; Prabhakaran, S.; Jehan, Z.; Ajarim, D.; Al-Dayel, F.; Tulbah, A.; Al-Kuraya, K.S. Loss of PTEN expression is associated with aggressive behavior and poor prognosis in Middle Eastern triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 151, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, S.H.; Harvey, A.J. mTOR function and therapeutic targeting in breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 383–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leake, R. Immunohistochemical detection of steroid receptors in breast cancer: A working protocol. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 53, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Schwartz, J.N.; Hagerty, K.L.; Allred, D.C.; Cote, R.J.; Dowsett, M.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Hanna, W.M.; Langer, A.; et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 118–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Wu, K.; Ding, A.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, P. Evaluation of the prognostic stage in the 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer in locally advanced breast cancer: An analysis based on SEER 18 database. Breast 2018, 37, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ibis, K.; Ozkurt, S.; Kucucuk, S.; Yavuz, E.; Saip, P. Comparison of Pathological Prognostic Stage and Anatomic Stage Groups According to the Updated Version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Breast Cancer Staging 8th Edition. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3637–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurundkar, A.; Gao, X.; Zhang, K.; Britt, J.P.; Siegal, G.P.; Wei, S. Comparison of AJCC Anatomic and Clinical Prognostic Stage Groups in Breast Cancer: Analysis of 3322 Cases from a Single Institution. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e1347–e1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursulovic, T.; Milovanovic, Z.; Medic-Milijic, N.; Gavrilovic, D.; Plesinac-Karapandzic, V.; Susnjar, S. The influence of PTEN protein expression on disease outcome in premenopausal hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant ovarian ablation: A long-term follow-up. J. BUON 2018, 23, 902–909. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebok, P.; Kopperschmidt, V.; Kluth, M.; Hube-Magg, C.; Özden, C.; Taskin, B.; Hussein, K.; Mittenzwei, A.; Lebeau, A.; Witzel, I.; et al. Partial PTEN deletion is linked to poor prognosis in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mcfadden, B.; Heitzman-powell, L. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Wan, Y.; Yao, Y. MiRNA-21 promotes proliferation and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells through targeting PTEN. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Pai, S.K.; Hirota, S.; Hosobe, S.; Tsukada, T.; Miura, K.; Takano, Y.; Saito, K.; Commes, T.; Piquemal, D.; et al. PTEN Up-Regulates the Tumor Metastasis Suppressor Gene Drg-1 in Prostate and Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7655–7660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, N.; Bonnet, F.; Sfar, S.; Lafitte, M.; Lafon, D.; Sierankowski, G.; Brouste, V.; Banneau, G.; Tunon De Lara, C.; Debled, M.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of PTEN status in breast carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahearn, T.U.; Pettersson, A.; Ebot, E.M.; Gerke, T.; Graff, R.E.; Morais, C.L.; Hicks, J.L.; Wilson, K.M.; Rider, J.R.; Sesso, H.D.; et al. A Prospective Investigation of PTEN Loss and ERG Expression in Lethal Prostate Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djv346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stemke-Hale, K.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Lluch, A.; Neve, R.M.; Kuo, W.L.; Davies, M.; Carey, M.; Hu, Z.; Guan, Y.; Sahin, A.; et al. An integrative genomic and proteomic analysis of PIK3CA, PTEN, and AKT mutations in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6084–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sporikova, Z.; Koudelakova, V.; Trojanec, R.; Hajduch, M. Genetic Markers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e841–e850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yu, B.; Li, D.; Ke, H.; Guo, X.; Xiao, X. PI3K expression and PIK3CA mutations are related to colorectal cancer metastases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 3745–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Luo, J.U.N.; You, J.; Liao, L.; Li, M. Clinical value of CagA, c-Met, PI3K and Beclin-1 expressed in gastric cancer and their association with prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Liu, C. The expression and clinical significance of PI3K, pAkt and VEGF in colon cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Lei, W.; Hou, X.; Li, H.; Ni, W. PUF60 accelerates the progression of breast cancer through downregulation of PTEN expression. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ueng, S.H.; Chen, S.C.; Chang, Y.S.; Hsueh, S.; Lin, Y.C.; Chien, H.P.; Lo, Y.F.; Shen, S.C.; Hsueh, C. Phosphorylated mTOR expression correlates with poor outcome in early-stage triple negative breast carcinomas. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2012, 5, 806–813. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, S.; Flanagan, L.; Quinn, C.; Evoy, D.; McDermott, E.W.; Pierce, A.; Duffy, M.J. MTOR in breast cancer: Differential expression in triple-negative and non-triple-negative tumors. Breast 2012, 21, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-B.; Dent, R.; Im, S.-A.; Espié, M.; Blau, S.; Tan, A.R.; Isakoff, S.J.; Oliveira, M.; Saura, C.; Wongchenko, M.J.; et al. Ipatasertib plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel as first-line therapy for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (LOTUS): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | np (%) |
|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis | |
| <50 | 19 (27) |
| ≥50 | 51 (73) |
| Tumor type | |
| Ductal | 41 (58) |
| Lobular | 13 (18) |
| Other * | 16 (24) |
| Lymphovascular/perineural invasion | |
| Absent | 54 (77) |
| Present | 14 (20) |
| Unknown | 2 (3) |
| Pathological prognostic stage | |
| I | 10 (14) |
| II | 37 (53) |
| III and IV | 23 (33) |
| pT stage | |
| T1 | 18 (26) |
| T2 | 43 (61) |
| T3 and T4 | 9 (13) |
| pN stage | |
| N0 | 36 (52) |
| N1 | 17 (24) |
| N2 and N3 | 17 (24) |
| Histologic grade | |
| I and II | 45 (64) |
| III | 25 (36) |
| Metastases | |
| M0 | 55 (79) |
| M1 | 15 (21) |
| PTEN Reduced Expression | PTEN Gene Deletions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | p Value | Kappa Value | |
| Yes | 31 | 9 | <0.0001 | 0.75 |
| No | 0 | 30 | ||
| Parameters | PTEN Copy Number Status | PTEN Expression | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| np (%) | np (%) | ||||||
| Wt | Hemi | Homo | p Value | Positive | Reduced | p Value | |
| Patients | 39 (56) | 26 (37) | 5 (7) | 30 (43) | 40 (57) | ||
| Age at diagnosis | |||||||
| <50 | 11 (28) | 5 (19) | 3 (60) | pA 0.99 | 7 (23) | 12 (30) | 0.59 |
| ≥50 | 28 (72) | 21 (81) | 2 (40) | pB 0.31 | 23 (77) | 28 (70) | |
| pC 0.4 | |||||||
| Tumor type | |||||||
| Ductal | 23 (59) | 15 (58) | 3 (60) | pA 0.06 | 19 (63) | 22 (55) | 0.07 |
| Lobular | 4 (10) | 7 (27) | 2 (40) | pB 0.11 | 2 (7) | 11 (27) | |
| Other * | 12 (31) | 4 (15) | 0 (0) | pC 0.13 | 9 (30) | 7 (18) | |
| Invasion # | |||||||
| Absent | 30 (81) | 22 (85) | 2 (40) | pA 0.77 | 25 (86) | 29 (74) | 0.36 |
| Present | 7 (19) | 4 (15) | 3 (60) | pB 0.08 | 4 (14) | 10 (26) | |
| pC > 0.99 | |||||||
| pp stage | |||||||
| I | 8 (21) | 2 (8) | 0 (0) | pA 0.24 | 6 (20) | 4 (10) | 0.49 |
| II | 18 (46) | 16 (61) | 2 (40) | pB 0.38 | 15 (50) | 22 (55) | |
| III and IV | 13 (33) | 8 (31) | 3 (60) | pC 0.31 | 9 (30) | 14 (35) | |
| pT stage | |||||||
| T1 | 11 (28) | 7 (27) | 0 (0) | pA 0.98 | 9 (30) | 9 (23) | 0.69 |
| T2 | 23 (59) | 16 (61) | 4 (80) | pB 0.39 | 18 (57) | 25 (62) | |
| T3 and T4 | 5 (13) | 3 (12) | 1 (20) | pC 0.97 | 3 (13) | 6 (15) | |
| pN stage | |||||||
| N0 | 24 (62) | 11 (42) | 1 (20) | pA 0.14 | 19 (63) | 17 (42) | 0.21 |
| N1 | 6 (15) | 9 (35) | 2 (40) | pB 0.19 | 5 (17) | 12 (30) | |
| N2 and N3 | 9 (23) | 6 (23) | 2 (40) | pC 0.17 | 6 (20) | 11 (28) | |
| Histologic grade | |||||||
| I and II | 21 (54) | 20 (77) | 4 (80) | pA 0.05 | 16 (53) | 29 (72) | 0.13 |
| III | 18 (46) | 6 (23) | 1 (20) | pB 0.37 | 14 (47) | 11 (28) | |
| pC 0.07 | |||||||
| Metastases | |||||||
| M0 | 35 (85) | 21 (81) | 1 (20) | pA 0.24 | 26 (87) | 29 (72) | 0.24 |
| M1 | 6 (15) | 5 (19) | 4 (80) | pB 0.007 | 4 (13) | 11 (28) | |
| pC 0.74 | |||||||
| Parameters | PI3K Expression | mTOR Expression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| np (%) | np (%) | |||||
| Low | High | p Value | Low | High | p Value | |
| Patients | 42 (60) | 28 (40) | 39 (56) | 31 (44) | ||
| Age at diagnosis | ||||||
| <50 | 12 (29) | 7 (25) | 0.79 | 10 (26) | 9 (29) | 0.79 |
| ≥50 | 30 (71) | 21 (75) | 29 (74) | 22 (71) | ||
| Tumor type | ||||||
| Ductal | 27 (64) | 14 (50) | 0.48 | 24 (62) | 17 (55) | 0.54 |
| Lobular | 7 (17) | 6 (21) | 8 (20) | 5 (16) | ||
| Other * | 8 (19) | 8 (29) | 7 (18) | 9 (29) | ||
| Invasion # | ||||||
| Absent | 33 (80) | 21 (78) | >0.99 | 31 (82) | 23 (77) | 0.76 |
| Present | 8 (20) | 6 (22) | 7 (18) | 7 (23) | ||
| pp stage | ||||||
| I | 10 (24) | 0 (0) | 0.02 | 9 (23) | 1 (3) | 0.02 |
| II | 20 (48) | 17 (61) | 21 (54) | 16 (52) | ||
| III and IV | 12 (28) | 11 (39) | 9 (23) | 14 (45) | ||
| pT stage | ||||||
| T1 | 14 (33) | 4 (14) | 0.05 | 13 (33) | 5 (16) | 0.14 |
| T2 | 21 (50) | 22 (79) | 23 (59) | 20 (65) | ||
| T3 and T4 | 7 (17) | 2 (7) | 3 (8) | 6 (19) | ||
| pN stage | ||||||
| N0 | 26 (62) | 10 (36) | 0.04 | 24 (62) | 12 (39) | 0.15 |
| N1 | 6 (14) | 11 (39) | 7 (18) | 10 (32) | ||
| N2 and N3 | 10 (24) | 7 (25) | 8 (20) | 9 (29) | ||
| Histologic grade | ||||||
| I and II | 30 (71) | 15 (54) | 0.14 | 27 (69) | 18 (58) | 0.45 |
| III | 12 (29) | 13 (46) | 12 (31) | 13 (42) | ||
| Metastases | ||||||
| M0 | 36 (86) | 19 (68) | 0.13 | 33 (85) | 22 (71) | 0.24 |
| M1 | 6 (14) | 9 (32) | 6 (15) | 9 (29) | ||
| Parameters | PTEN -/PI3K+/mTOR+ | PTEN +/PI3K-/mTOR- | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| np (%) | np (%) | ||
| Age at diagnosis | |||
| <50 | 4 (31) | 4 (28) | 0.99 |
| ≥50 | 9 (69) | 10 (72) | |
| Tumor type | |||
| Ductal | 5 (38) | 8 (56) | 0.28 |
| Lobular | 4 (31) | 1 (8) | |
| Other * | 4 (31) | 5 (36) | |
| Invasion | |||
| Absent | 9 (69) | 12 (84) | 0.38 |
| Present | 4 (31) | 2 (16) | |
| pp stage | |||
| I | 0 (0) | 5 (36) | 0.01 |
| II | 7 (54) | 8 (57) | |
| III and IV | 6 (46) | 1 (7) | |
| pT stage | |||
| T1 | 2 (15) | 5 (36) | 0.19 |
| T2 | 9 (70) | 9 (64) | |
| T3 and T4 | 2 (15) | 0 (0) | |
| pN stage | |||
| N0 | 4 (31) | 12 (84) | 0.01 |
| N1 | 5 (38) | 1 (8) | |
| N2 and N3 | 4 (31) | 1 (8) | |
| Histologic grade | |||
| I and II | 7 (54) | 10 (72) | 0.44 |
| III | 6 (46) | 4 (28) | |
| Metastases | |||
| M0 | 7 (54) | 13 (93) | 0.03 |
| M1 | 6 (46) | 1 (7) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prvanović, M.; Nedeljković, M.; Tanić, N.; Tomić, T.; Terzić, T.; Milovanović, Z.; Maksimović, Z.; Tanić, N. Role of PTEN, PI3K, and mTOR in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Life 2021, 11, 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111247
Prvanović M, Nedeljković M, Tanić N, Tomić T, Terzić T, Milovanović Z, Maksimović Z, Tanić N. Role of PTEN, PI3K, and mTOR in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Life. 2021; 11(11):1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111247
Chicago/Turabian StylePrvanović, Mirjana, Milica Nedeljković, Nasta Tanić, Tijana Tomić, Tanja Terzić, Zorka Milovanović, Zlatko Maksimović, and Nikola Tanić. 2021. "Role of PTEN, PI3K, and mTOR in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" Life 11, no. 11: 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111247
APA StylePrvanović, M., Nedeljković, M., Tanić, N., Tomić, T., Terzić, T., Milovanović, Z., Maksimović, Z., & Tanić, N. (2021). Role of PTEN, PI3K, and mTOR in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Life, 11(11), 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111247







