Physicochemical Parameters Limiting Growth of Debaryomyces hansenii in Solutions of Hygroscopic Compounds and Their Effects on the Habitability of Martian Brines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Organisms and Culture Conditions
2.2. Determination of Solute Tolerances
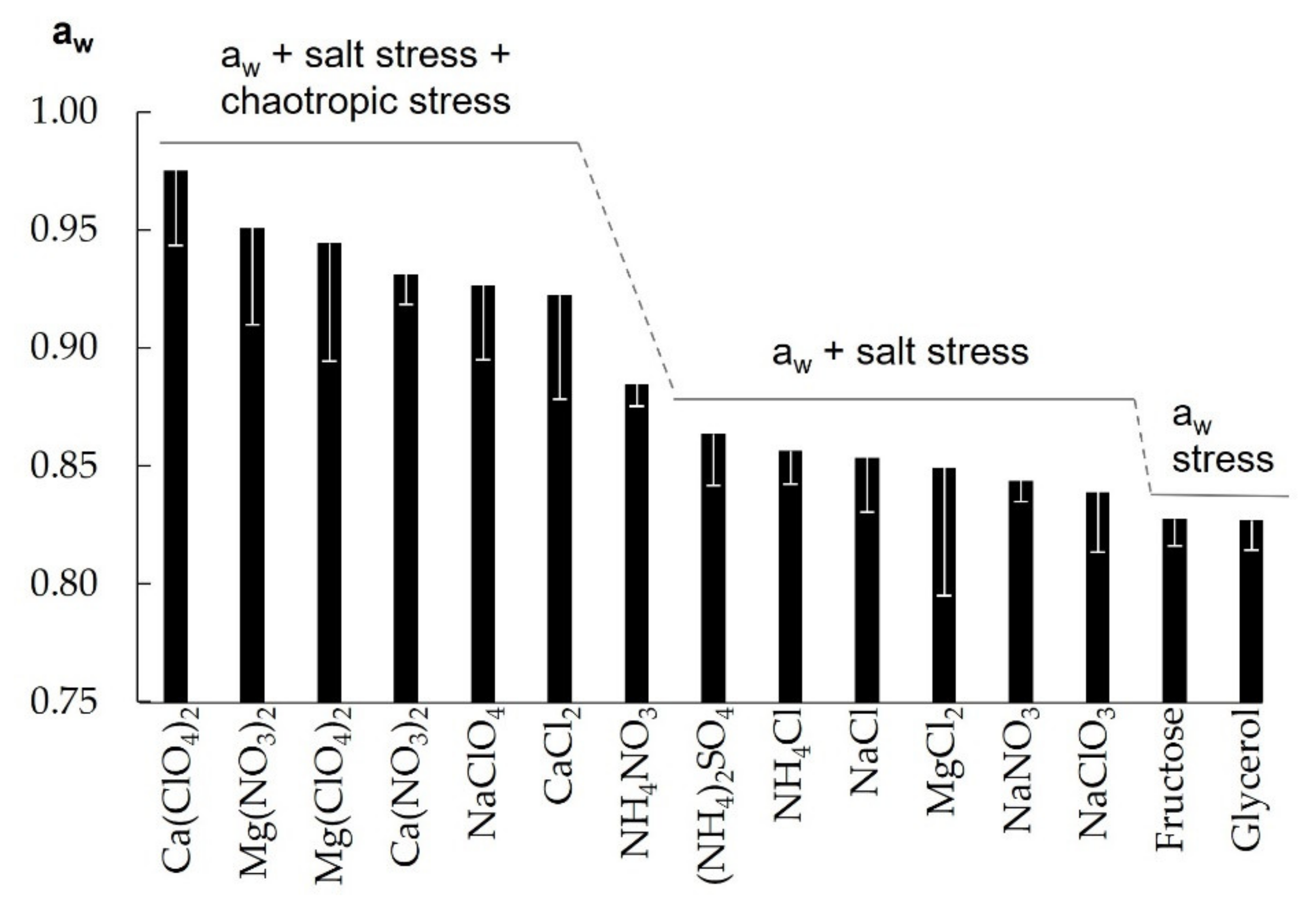
2.3. Water Activity Measurements
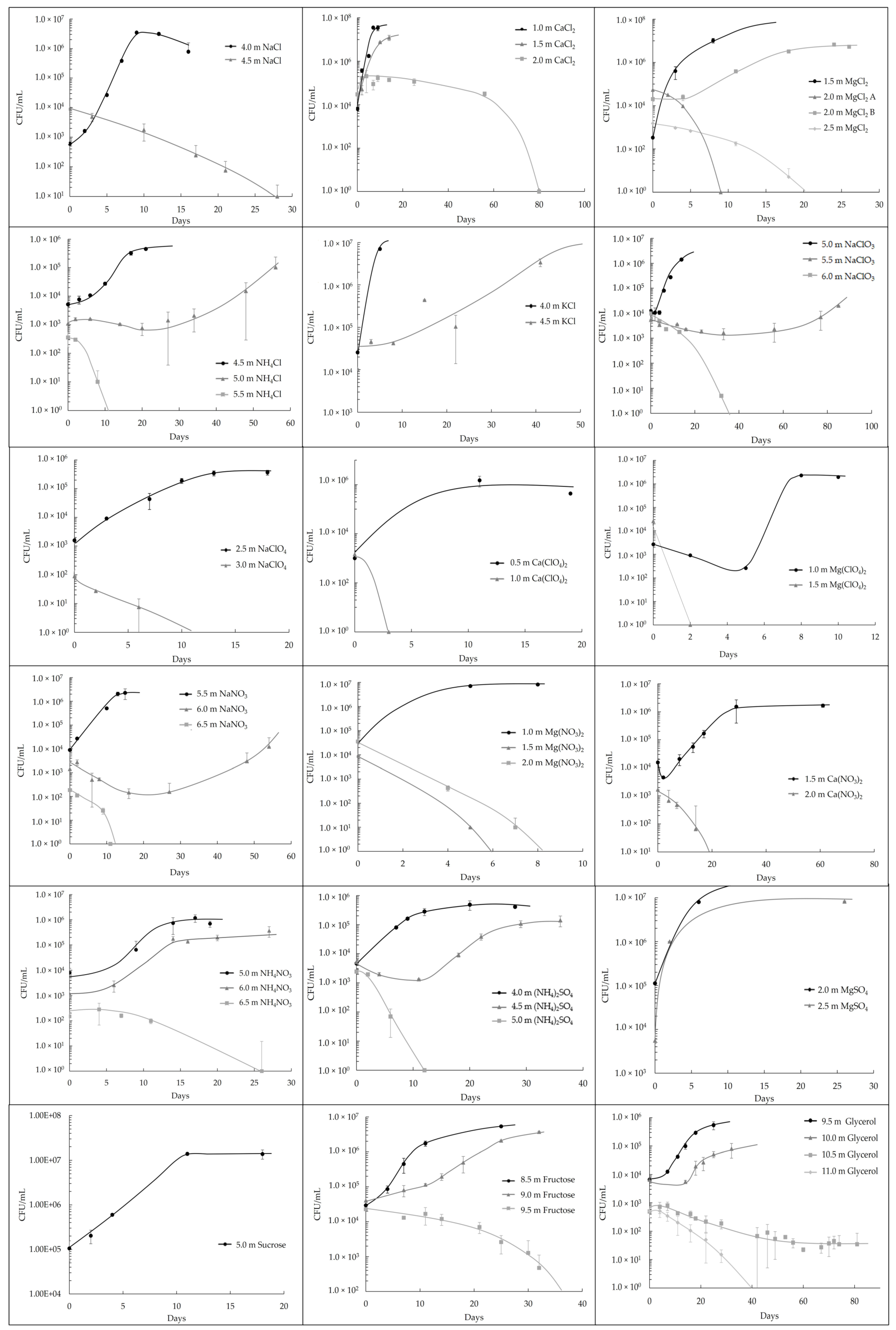
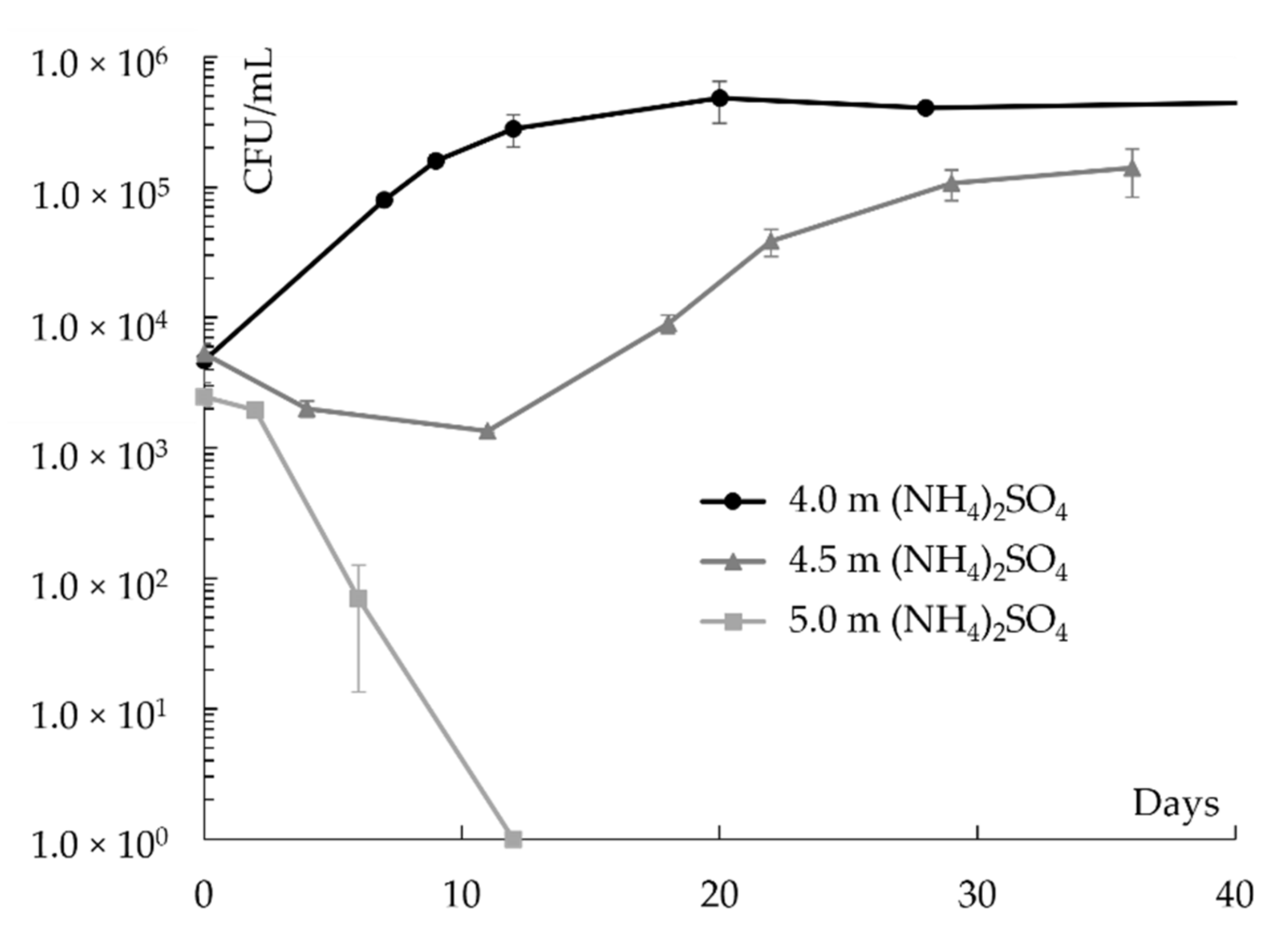
3. Results
4. Discussion
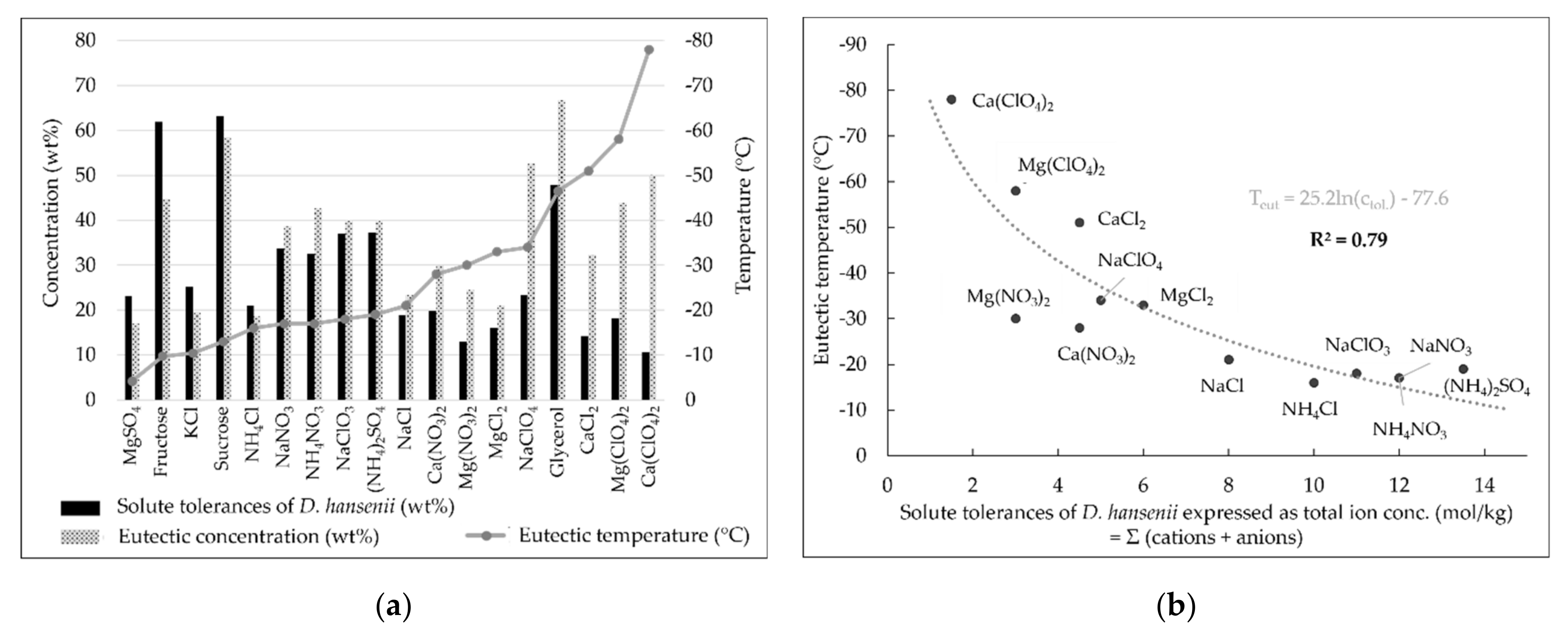
4.1. Growth-Limiting Parameters
4.2. Implications for the Habitability of Martian Brines
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Solute | Ctol | Density at Ctol | MIC | aw at MIC | Eutectic Point [5,55,56,57,58,59] | DRH [9,60,61,62,63,64] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [mol/kg] | [g/mL] | [mol/kg] | Conc. [wt%] | Temp. [°C] | [%] | ||
| Salts | |||||||
| NaCl | 4.0 | 1.12 | 4.5 | 0.830 | 23.3 | −21 | 75 |
| NH4Cl | 5.0 | 1.05 | 5.5 | 0.842 | 18.7 | −16 | 77 |
| CaCl2 | 1.5 | 1.08 | 2.0 | 0.878 | 32.3 | −51 | 30 |
| MgCl2 | 2.0 | 1.12 | 2.5 | 0.795 | 21.0 | −33 | 33 |
| KCl | (4.5) | 1.15 | – | – | 19.7 | −10 | 84 |
| NaClO3 | 5.5 | 1.29 | 6.0 | 0.813 | 39.8 | −18 | 68 |
| NaClO4 | 2.5 | 1.14 | 3.0 | 0.895 | 52.7 | −34 | 51 |
| Ca(ClO4)2 | 0.5 | 1.05 | 1.0 | 0.943 | 50.1 | −78 | 13 |
| Mg(ClO4)2 | 1.0 | 1.10 | 1.5 | 0.894 | 43.9 | −58 | 42 |
| NaNO3 | 6.0 | 1.22 | 6.5 | 0.835 | 38.6 | −17 | 72 |
| NH4NO3 | 6.0 | 1.13 | 6.5 | 0.875 | 42.7 | −17 | 59 |
| Ca(NO3)2 | 1.5 | 1.15 | 2.0 | 0.919 | 29.9 | −28 | 47 |
| Mg(NO3)2 | 1.0 | 1.10 | 1.5 | 0.910 | 24.6 | −30 | 53 |
| (NH4)2SO4 | 4.5 | 1.20 | 5.0 | 0.842 | 39.8 | −19 | 79 |
| MgSO4 | (2.5) | 1.25 | – | – | 17.0 | −4 | 91 |
| Organic solutes | |||||||
| Sucrose | (5) | 1.28 | – | – | 58.5 | −13 | 85 |
| Fructose | 9.0 | 1.28 | 9.5 | 0.816 | 44.7 | −10 | 62 |
| Glycerol | 10.0 | 1.12 | 11.0 a | 0.814 | 66.7 | −47 | – |
References
- Bastida, F.; Eldridge, D.J.; García, C.; Kenny Png, G.; Bardgett, R.D.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Soil microbial diversity–biomass relationships are driven by soil carbon content across global biomes. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pointing, S.B.; Chan, Y.; Lacap, D.C.; Lau, M.C.Y.; Jurgens, J.A.; Farrell, R.L. Highly specialized microbial diversity in hyper-arid polar desert. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19964–19969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maus, D.; Heinz, J.; Schirmack, J.; Airo, A.; Kounaves, S.P.; Wagner, D.; Schulze-Makuch, D. Methanogenic Archaea Can Produce Methane in Deliquescence-Driven Mars Analog Environments. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davila, A.F.; Hawes, I.; Ascaso, C.; Wierzchos, J. Salt deliquescence drives photosynthesis in the hyperarid Atacama Desert. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhlmann, D.; Thomsen, K. Properties of cryobrines on Mars. Icarus 2011, 212, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, M.H.; Kounaves, S.P.; Quinn, R.C.; West, S.J.; Young, S.M.M.; Ming, D.W.; Catling, D.C.; Clark, B.C.; Boynton, W.V.; Hoffman, J.; et al. Detection of perchlorate and the soluble chemistry of martian soil at the Phoenix lander site. Science 2009, 325, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biver, N.; Bockelée-Morvan, D.; Moreno, R.; Crovisier, J.; Colom, P.; Lis, D.C.; Sandqvist, A.; Boissier, J.; Despois, D.; Milam, S.N. Ethyl alcohol and sugar in comet C/2014 Q2 (Lovejoy). Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohl, F. Revealing Titan’s Interior. Science 2010, 327, 1338–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winston, P.W.; Bates, D.H. Saturated Solutions For the Control of Humidity in Biological Research. Ecology 1960, 41, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, A.; Cray, J.A.; Williams, J.P.; Santos, R.; Sahay, R.; Neuenkirchen, N.; McClure, C.D.; Grant, I.R.; Houghton, J.; Quinn, J.P.; et al. Is there a common water-activity limit for the three domains of life? ISME J. 2015, 9, 1333–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, A.; Hamill, P.G.; Medina, Á.; Kminek, G.; Rummel, J.D.; Dijksterhuis, J.; Timson, D.J.; Magan, N.; Leong, S.-L.L.; Hallsworth, J.E. Glycerol enhances fungal germination at the water-activity limit for life. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 947–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Powell, M.G.; Hallsworth, J.E.; Cousins, C.R.; Cockell, C.S. Ionic Strength Is a Barrier to the Habitability of Mars. Astrobiology 2016, 16, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallsworth, J.E.; Heim, S.; Timmis, K.N. Chaotropic solutes cause water stress in Pseudomonas putida. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallsworth, J.E.; Yakimov, M.M.; Golyshin, P.N.; Gillion, J.L.M.; D’Auria, G.; de Lima Alves, F.; La Cono, V.; Genovese, M.; McKew, B.A.; Hayes, S.L.; et al. Limits of life in MgCl2-containing environments: Chaotropicity defines the window. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima Alves, F.; Stevenson, A.; Baxter, E.; Gillion, J.L.M.; Hejazi, F.; Hayes, S.; Morrison, I.E.G.; Prior, B.A.; McGenity, T.J.; Rangel, D.E.N.; et al. Concomitant osmotic and chaotropicity-induced stresses in Aspergillus wentii: Compatible solutes determine the biotic window. Curr. Genet. 2015, 61, 457–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, J.; Schirmack, J.; Airo, A.; Kounaves, S.P.; Schulze-Makuch, D. Enhanced Microbial Survivability in Subzero Brines. Astrobiology 2018, 18, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waajen, A.C.; Heinz, J.; Airo, A.; Schulze-Makuch, D. Physicochemical Salt Solution Parameters Limit the Survival of Planococcus halocryophilus in Martian Cryobrines. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prista, C.; Michán, C.; Miranda, I.M.; Ramos, J. The halotolerant Debaryomyces hansenii, the Cinderella of non-conventional yeasts. Yeast 2016, 33, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, J.; Krahn, T.; Schulze-Makuch, D. A New Record for Microbial Perchlorate Tolerance: Fungal Growth in NaClO4 Brines and its Implications for Putative Life on Mars. Life 2020, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, J.; Waajen, A.C.; Airo, A.; Alibrandi, A.; Schirmack, J.; Schulze-Makuch, D. Bacterial Growth in Chloride and Perchlorate Brines: Halotolerances and Salt Stress Responses of Planococcus halocryophilus. Astrobiology 2019, 19, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.L.; Oliveira, R.P.; Lucas, C.M. Metabolic flux response to salt-induced stress in the halotolerant yeast Debaryomyces hansenii. Microbiology 1997, 143, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oren, A. Microbial life at high salt concentrations: Phylogenetic and metabolic diversity. Saline Syst. 2008, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baere, L.A.; Devocht, M.; van Assche, P.; Verstraete, W. Influence of high NaCl and NH4Cl salt levels on methanogenic associations. Water Res. 1984, 18, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajc, J.; Džeroski, S.; Kocev, D.; Oren, A.; Sonjak, S.; Tkavc, R.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Chaophilic or chaotolerant fungi: A new category of extremophiles? Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Soudi, A.F.; Farhat, O.; Chen, F.; Clark, B.C.; Schneegurt, M.A. Bacterial growth tolerance to concentrations of chlorate and perchlorate salts relevant to Mars. Int.J. Astrobiol. 2017, 16, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laye, V.J.; DasSarma, S. An Antarctic Extreme Halophile and Its Polyextremophilic Enzyme: Effects of Perchlorate Salts. Astrobiology 2018, 18, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamekura, M.; Onishi, H. Cell-associated cations of the moderate halophile Micrococcus varians ssp. halophilus grown in media of high concentrations of LiCl, NaCl, KCl, RbCl, or CsCl. Can. J. Microbiol. 1982, 28, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.P.; Hallsworth, J.E. Limits of life in hostile environments: No barriers to biosphere function? Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 3292–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.; Walter, B.; Wirtz, A.; Burkovski, A. Ammonium toxicity in bacteria. Curr. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, J.M.; Chen, F.; Clark, B.C.; Schneegurt, M.A. Bacterial growth in saturated and eutectic solutions of magnesium sulphate and potassium chlorate with relevance to Mars and the ocean worlds. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2019, 18, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praphailong, W.; Fleet, G.H. Debaryomyces. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 515–520. ISBN 9780122270703. [Google Scholar]
- Butinar, L.; Santos, S.; Spencer-Martins, I.; Oren, A.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Yeast diversity in hypersaline habitats. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 244, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cray, J.A.; Russell, J.T.; Timson, D.J.; Singhal, R.S.; Hallsworth, J.E. A universal measure of chaotropicity and kosmotropicity. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeister, F. Zur Lehre von der Wirkung der Salze. Arch. Experiment. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1888, 24, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Life in Magnesium- and Calcium-Rich Hypersaline Environments: Salt Stress by Chaotropic Ions. In Polyextremophiles: Life Under Multiple Forms of Stress; Seckbach, J., Oren, A., Stan-Lotter, H., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 215–232. ISBN 978-94-007-6487-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, A.M.; Zultanski, S.L.; Waldman, J.H.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Shevlin, M.; Peng, F. General Principles and Strategies for Salting-Out Informed by the Hofmeister Series. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 93rd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781439880494. [Google Scholar]
- Urbansky, E.T. Perchlorate Chemistry: Implications for Analysis and Remediation. Bioremediation J. 1998, 2, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busti, S.; Mapelli, V.; Tripodi, F.; Sanvito, R.; Magni, F.; Coccetti, P.; Rocchetti, M.; Nielsen, J.; Alberghina, L.; Vanoni, M. Respiratory metabolism and calorie restriction relieve persistent endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by calcium shortage in yeast. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounaves, S.P.; Hecht, M.H.; Kapit, J.; Quinn, R.C.; Catling, D.C.; Clark, B.C.; Ming, D.W.; Gospodinova, K.; Hredzak, P.; McElhoney, K.; et al. Soluble sulfate in the martian soil at the Phoenix landing site. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L09201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, J.C.; Sutter, B.; Freissinet, C.; Navarro-González, R.; McKay, C.P.; Archer, P.D.; Buch, A.; Brunner, A.E.; Coll, P.; Eigenbrode, J.L.; et al. Evidence for indigenous nitrogen in sedimentary and aeolian deposits from the Curiosity rover investigations at Gale crater, Mars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4245–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounaves, S.P.; Carrier, B.L.; O’Neil, G.D.; Stroble, S.T.; Claire, M.W. Evidence of martian perchlorate, chlorate, and nitrate in Mars meteorite EETA79001: Implications for oxidants and organics. Icarus 2014, 229, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.C.; Morris, R.V.; McLennan, S.M.; Gellert, R.; Jolliff, B.; Knoll, A.H.; Squyres, S.W.; Lowenstein, T.K.; Ming, D.W.; Tosca, N.J.; et al. Chemistry and mineralogy of outcrops at Meridiani Planum. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 240, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Makuch, D.; Wagner, D.; Kounaves, S.P.; Mangelsdorf, K.; Devine, K.G.; de Vera, J.-P.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Grossart, H.-P.; Parro, V.; Kaupenjohann, M.; et al. Transitory microbial habitat in the hyperarid Atacama Desert. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2670–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounaves, S.P.; Stroble, S.T.; Anderson, R.M.; Moore, Q.; Catling, D.C.; Douglas, S.; McKay, C.P.; Ming, D.W.; Smith, P.H.; Tamppari, L.K.; et al. Discovery of natural perchlorate in the Antarctic Dry Valleys and its global implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2360–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.C.; Kounaves, S.P. Evidence for the distribution of perchlorates on Mars. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2016, 15, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.; Chevrier, V.F.; Berget, D.J.; Adams, R.D. Chlorate salts and solutions on Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toner, J.D.; Catling, D.C. Chlorate brines on Mars: Implications for the occurrence of liquid water and deliquescence. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 497, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, P.B.; Sowers, T. Temperature dependence of metabolic rates for microbial growth, maintenance, and survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4631–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.D.; Washabaugh, M.W. The Hofmeister effect and the behaviour of water at interfaces. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1985, 18, 323–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansure, J.J.C.; Panek, A.D.; Crowe, L.M.; Crowe, J.H. Trehalose inhibits ethanol effects on intact yeast cells and liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 1994, 1191, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.S.; York, P.; Williams, A.C.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Mehta, V.; Jackson, G.S.; Badcoe, I.G.; Clarke, A.R. Sucrose reduces the efficiency of protein denaturation by a chaotropic agent. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1995, 1253, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, D.; Wagner, D. Stress response of methanogenic archaea from Siberian permafrost compared with methanogens from nonpermafrost habitats. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 61, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, J.P.; Megaw, J.; Magill, C.L.; Nowotarski, K.; Williams, J.P.; Bhaganna, P.; Linton, M.; Patterson, M.F.; Underwood, G.J.C.; Mswaka, A.Y.; et al. Solutes determine the temperature windows for microbial survival and growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7835–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennings, E. Cryo Brines: Phasengleichgewichte von Salz-Wasser-Systemen Bei Tiefen Temperaturen. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Zeng, D.; Yin, X.; Han, H.; Guo, L.; Yao, Y. Phase diagrams and thermochemical modeling of salt lake brine systems. II. NaCl+H2O, KCl+H2O, MgCl2+H2O and CaCl2+H2O systems. Calphad 2016, 53, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudotvortsev, I.G.; Yatsenko, O.B. Concentration and temperature of eutectic points in glucose-water and saccharose-water systems, determined by the method of fractional melting of ice. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2007, 80, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, F.E.; Jones, F.T.; Lewis, H.J. D-Fructose–Water Phase Diagram. J. Phys. Chem. 1952, 56, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, L.B. Freezing Points of Glycerol and Its Aqueous Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1925, 17, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, L. Humidity fixed points of binary saturated aqueous solutions. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stan. Sect. A 1977, 81A, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.D.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Studies of concentrated electrolyte solutions using the electrodynamic balance. 1. Water activities for single-electrolyte solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 4563–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuding, D.L.; Rivera-Valentin, E.G.; Davis, R.D.; Gough, R.V.; Chevrier, V.F.; Tolbert, M.A. Deliquescence and efflorescence of calcium perchlorate: An investigation of stable aqueous solutions relevant to Mars. Icarus 2014, 243, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, R.V.; Chevrier, V.F.; Tolbert, M.A. Formation of liquid water at low temperatures via the deliquescence of calcium chloride: Implications for Antarctica and Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 2016, 131, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernanders, M.S.; Gough, R.V.; Chevrier, V.F.; Schiffman, Z.R.; Ushijima, S.B.; Martinez, G.M.; Rivera-Valentín, E.G.; Archer, P.D.; Clark, J.V.; Sutter, B.; et al. Water uptake by chlorate salts under Mars-relevant conditions. Icarus 2021, 371, 114715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Solute | Solute Tolerance | I | aw | Literature Solute Tolerances [mol/L] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [mol/kg] | [mol/L] | [wt%] | [mol/kg] | D. hansenii | Other Organisms a | ||
| Salts | |||||||
| NaCl | 4.0 | 3.6 | 18.9 | 4 | 0.854 | 4.0 [21] | 6.1 c Hs [22] |
| NH4Cl | 5.0 | 4.1 | 21.1 | 5 | 0.856 | – | 1.5 M [23] |
| CaCl2 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 14.3 | 4.5 | 0.922 | – | 2.1 Ec [24] |
| MgCl2 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 16.0 | 6 | 0.849 | – | 2.0 Af [24] |
| KCl | (4.5) | (3.9) | (25.1) | (4.5) | (0.852) | 4.0 [21] | 4.0 c Aw [15] |
| NaClO3 | 5.5 | 4.5 | 36.9 | 5.5 | 0.839 | – | 2.8 Hv [25] |
| NaClO4 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 23.4 | 2.5 | 0.926 | 2.1 [19] b | 1.1 Ph [20] |
| Ca(ClO4)2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 10.7 | 1.5 | 0.975 | – | 0.1 Ph [20] |
| Mg(ClO4)2 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 18.2 | 3 | 0.944 | – | 0.3 Hl [26] |
| NaNO3 | 6.0 | 4.9 | 33.8 | 6 | 0.844 | – | 3.5 Mv [27] |
| NH4NO3 | 6.0 | 4.6 | 32.4 | 6 | 0.880 | – | 5.2 JH [28] |
| Ca(NO3)2 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 19.8 | 4.5 | 0.931 | – | – |
| Mg(NO3)2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 12.9 | 3 | 0.944 | – | – |
| (NH4)2SO4 | 4.5 | 3.4 | 37.3 | 13.5 | 0.864 | – | 1.0 Cg [29] |
| MgSO4 | (2.5) | (2.4) | (23.1) | (10) | (0.946) | – | 2.7 c H [30] |
| Organic solutes | |||||||
| Sucrose | (5) | (2.4) | (63.1) | – | (0.872) | ~1.3 [31] | 2.3 Ea [28] |
| Fructose | 9.0 | 4.4 | 61.9 | – | 0.828 | – | 4.4 Ea [28] |
| Glycerol | 10.0 | 5.4 | 47.9 | – | 0.827 | ≥2.5 [32] | 7.6 Xb [28] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heinz, J.; Rambags, V.; Schulze-Makuch, D. Physicochemical Parameters Limiting Growth of Debaryomyces hansenii in Solutions of Hygroscopic Compounds and Their Effects on the Habitability of Martian Brines. Life 2021, 11, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111194
Heinz J, Rambags V, Schulze-Makuch D. Physicochemical Parameters Limiting Growth of Debaryomyces hansenii in Solutions of Hygroscopic Compounds and Their Effects on the Habitability of Martian Brines. Life. 2021; 11(11):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111194
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeinz, Jacob, Vita Rambags, and Dirk Schulze-Makuch. 2021. "Physicochemical Parameters Limiting Growth of Debaryomyces hansenii in Solutions of Hygroscopic Compounds and Their Effects on the Habitability of Martian Brines" Life 11, no. 11: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111194
APA StyleHeinz, J., Rambags, V., & Schulze-Makuch, D. (2021). Physicochemical Parameters Limiting Growth of Debaryomyces hansenii in Solutions of Hygroscopic Compounds and Their Effects on the Habitability of Martian Brines. Life, 11(11), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11111194







