Helios Expression in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Correlates with Overall Survival of Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Samples
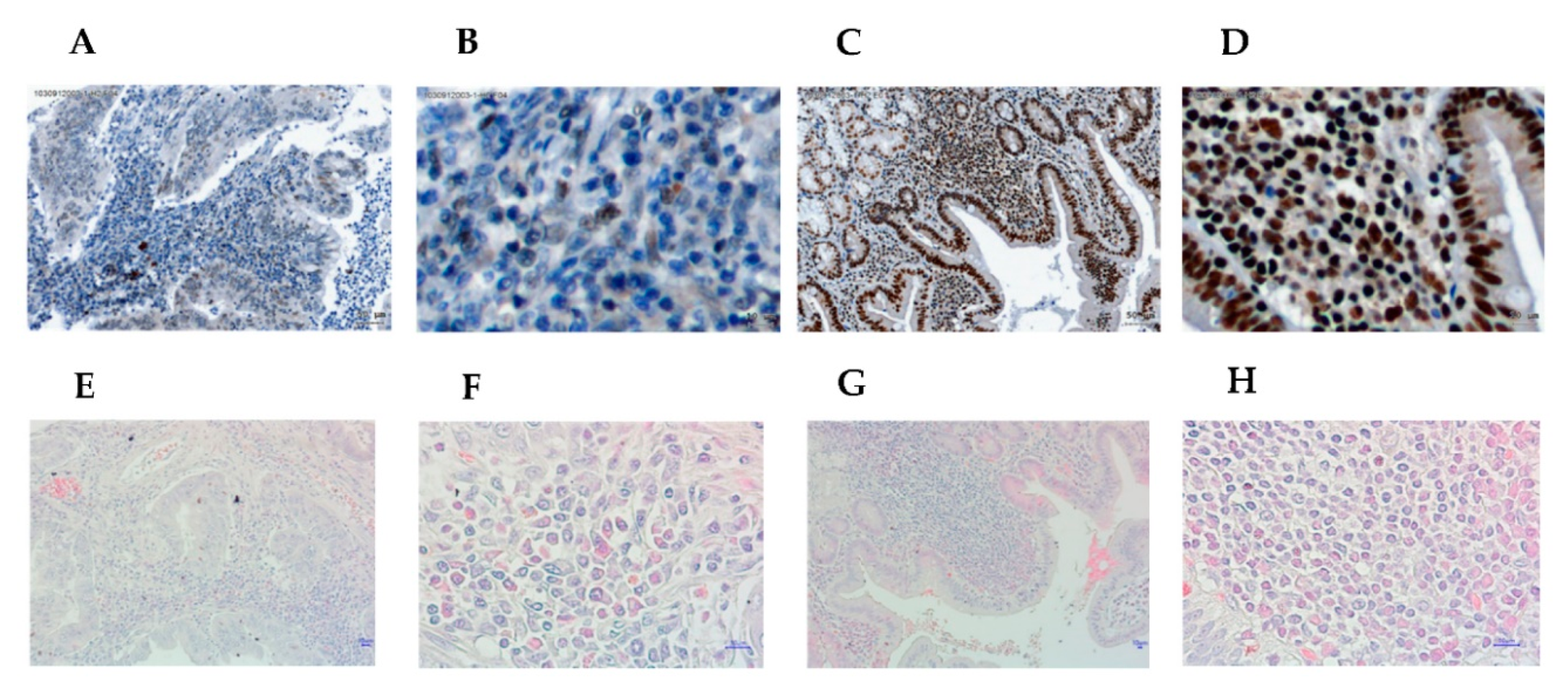
2.2. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
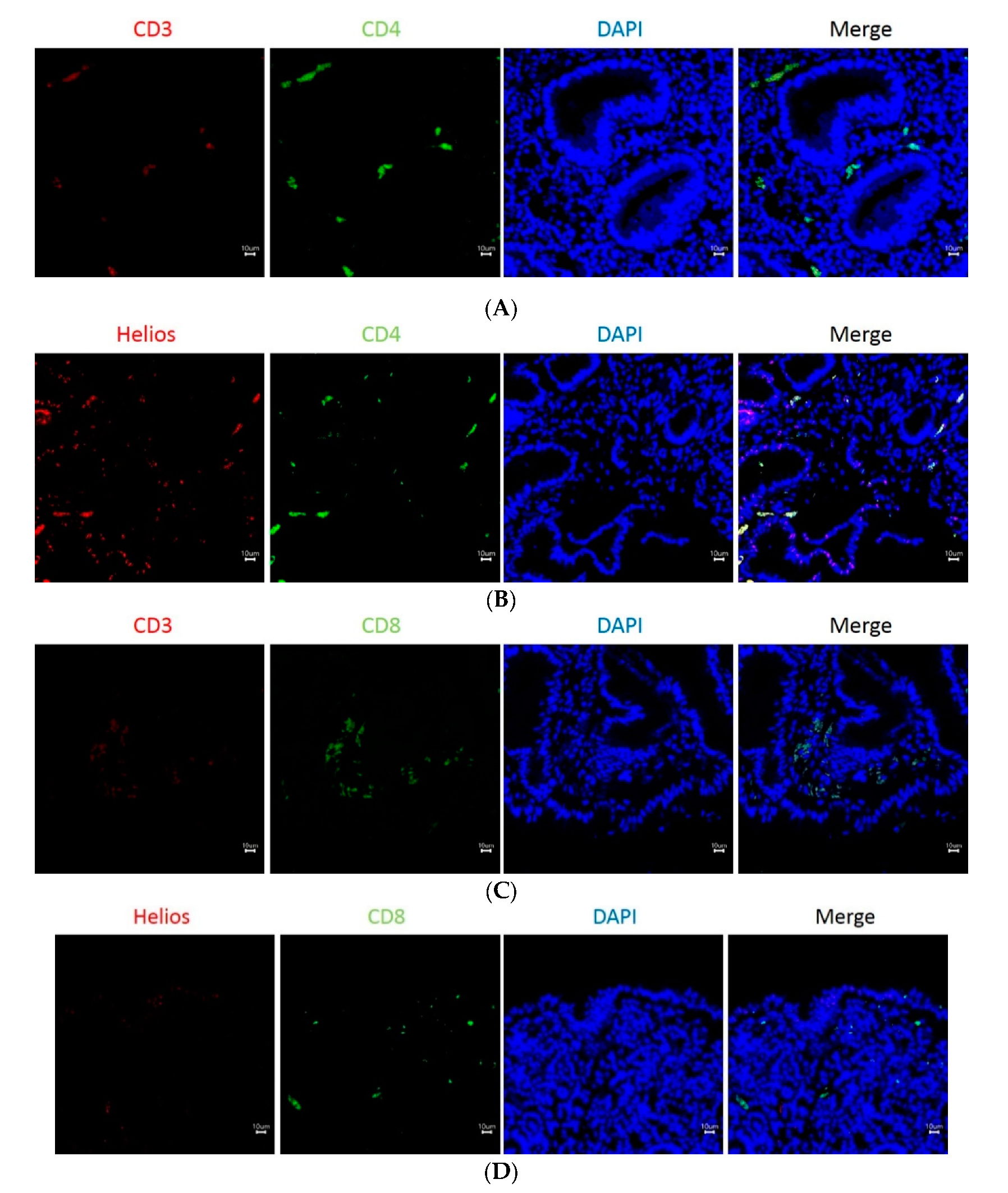
2.3. Double Staining Immunofluoresecence
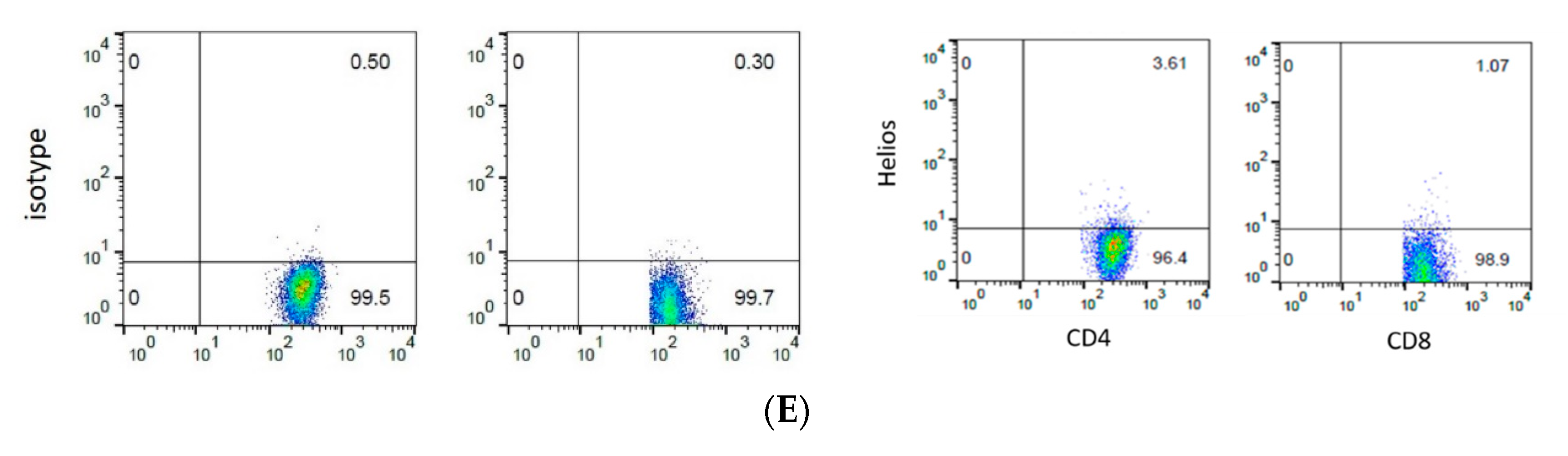
2.4. Flow Cytometry
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
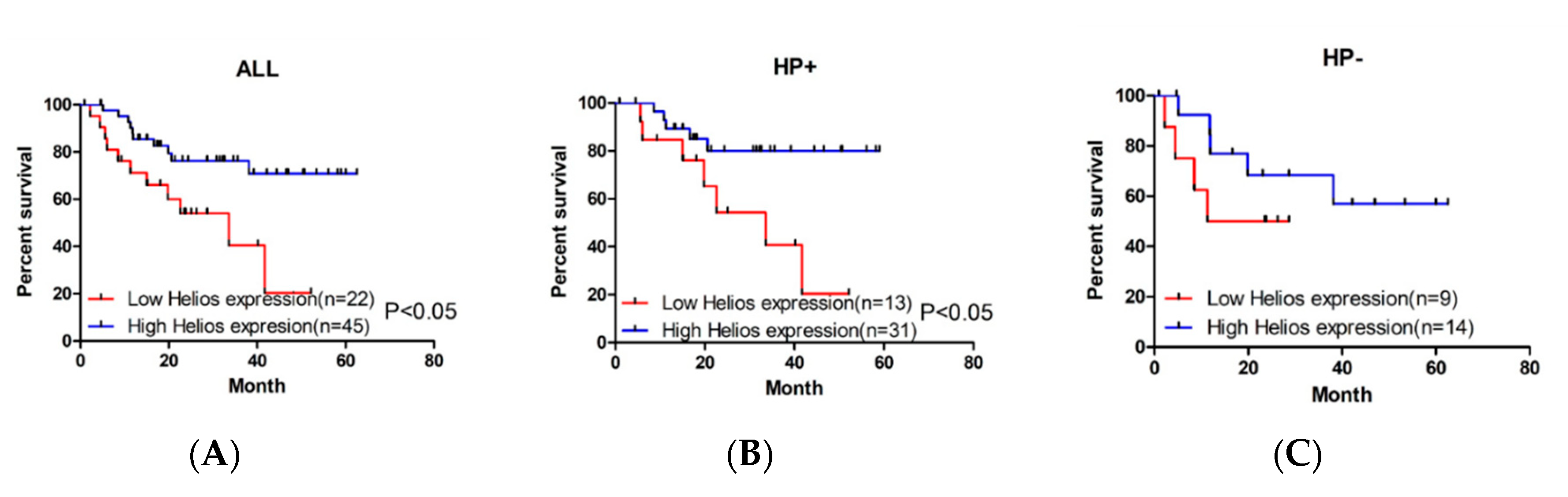
3.1. Higher Expression of Helios in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Correlates with Better Overall Survival in Gastric Cancer Patients and Helicobacter Pylori-Positive Gastric Cancer Patients
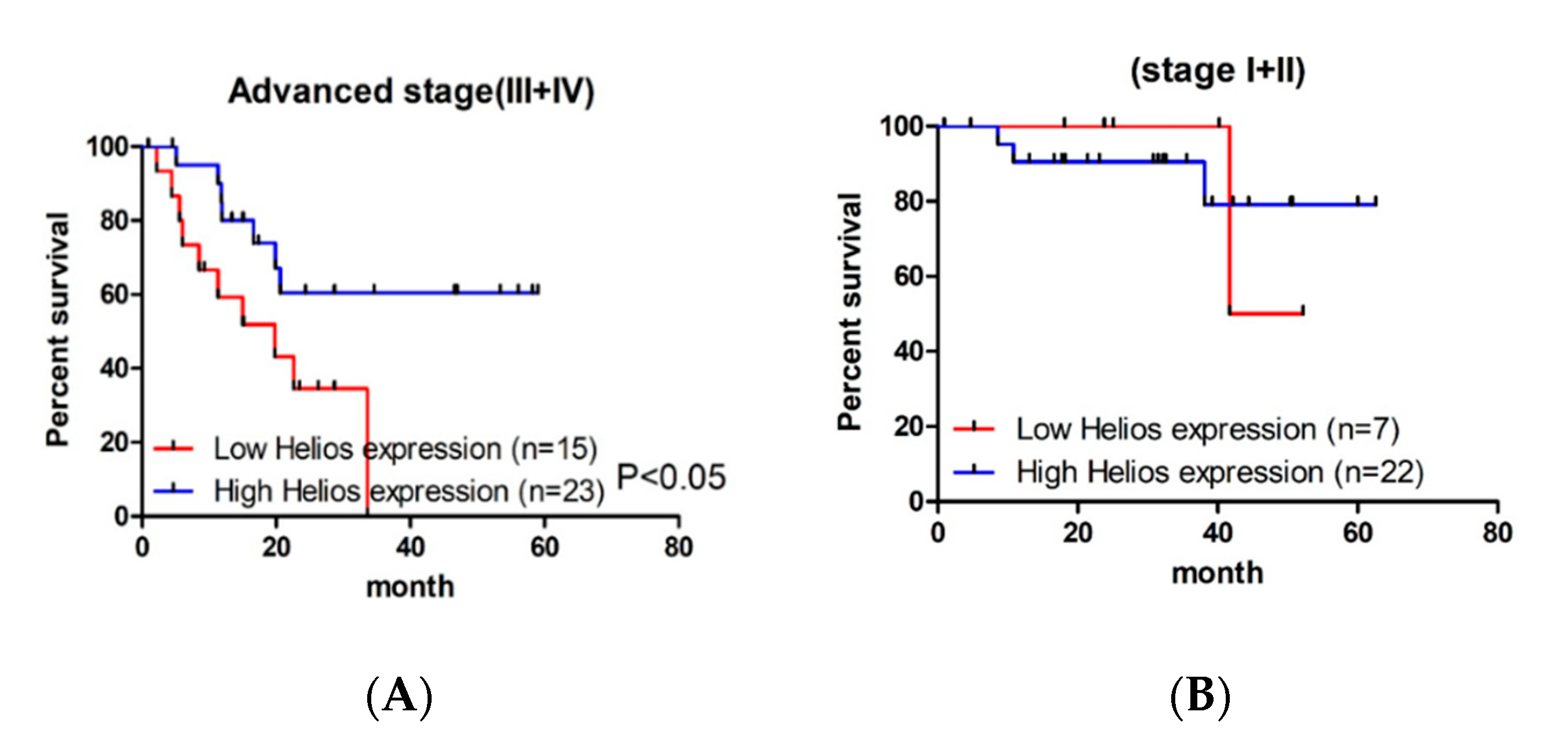
3.2. Helios Expression in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Was an Independent Factor for Survival in Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients
3.3. The Expression of Helios, CD3, CD4, and CD8 in Gastric Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GC | Gastric cancer |
| TILs | Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes |
| Treg | Regulatory T |
| HP | Helicobacter pylori |
| PBMCs | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| TNM | Tumor-node-metastasis |
| LN | Lymph node |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, J.S.; Teng, M.W.L.; Smyth, M.J. Cancer immunoediting and resistance to T cell-based immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.R.; Ho, P.C. Sculpting tumor microenvironment with immune system: From immunometabolism to immunoediting. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellman, I.; Coukos, G.; Dranoff, G. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature 2011, 480, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, W.; Wu, C.; Tan, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Jiang, J. Scoring System for Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Its Prognostic Value for Gastric Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, J.; Ahrends, T.; Babala, N.; Melief, C.J.M.; Kastenmuller, W. CD4(+) T cell help in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2018, 18, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulos, K. Haematopoietic cell-fate decisions, chromatin regulation and ikaros. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, L.B.; Ward, A.C. The Ikaros gene family: Transcriptional regulators of hematopoiesis and immunity. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Su, X.; Zhang, J.; Radtke, I.; Phillips, L.A.; Miller, C.B.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Cheng, C.; Schulman, B.A.; et al. Deletion of IKZF1 and prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baine, I.U.; Basu, S.; Ames, R.; Sellers, R.S.; Macian, F. Helios induces epigenetic silencing of IL2 gene expression in regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatori, H.; Kawashima, H.; Matsuki, A.; Meguro, K.; Tanaka, S.; Iwamoto, T.; Sanayama, Y.; Nishikawa, N.; Tamachi, T.; Ikeda, K.; et al. Helios Enhances Treg Cell Function in Cooperation with FoxP3. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, M.; Lopez-Ocasio, M.; Metidji, A.; Rieder, S.A.; Shevach, E.M.; Thornton, A.M. Helios Controls a Limited Subset of Regulatory T Cell Functions. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Cho, H.; Thornton, A.M.; Barlowe, T.S.; Chou, T.; Chhangawala, S.; Fairchild, L.; Taggart, J.; Chow, A.; Schurer, A.; et al. IKZF2 Drives Leukemia Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Inhibits Myeloid Differentiation. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, R.; Smale, S.T. Predominant interaction of both Ikaros and Helios with the NuRD complex in immature thymocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 30227–30238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimova, T.; Beier, U.H.; Wang, L.; Levine, M.H.; Hancock, W.W. Helios expression is a marker of T cell activation and proliferation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skadow, M.; Penna, V.R.; Galant-Swafford, J.; Shevach, E.M.; Thornton, A.M. Helios Deficiency Predisposes the Differentiation of CD4(+)Foxp3(−) T Cells into Peripherally Derived Regulatory T Cells. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.M.; Wu, C.S.; Liu, J.L.; Yeh, C.M.; Tseng, L.; Huang, H.C.; Chang, P.J.; Wu, S.F. Expression of Helios in gastric tumor cells predicts better survival in gastric cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Tarpin, C.; Bardou, V.J.; Bertucci, F.; Ginestier, C.; Braud, A.C.; Puig, B.; Geneix, J.; Hassoun, J.; Birnbaum, D.; et al. Immunophenotypic analysis of inflammatory breast cancers: Identification of an ‘inflammatory signature’. J. Pathol. 2004, 202, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, R.L.; Dolled-Filhart, M.; Rimm, D.L. X-tile: A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7252–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi-Kanemitsu, A.; Knight, C.T.; Hatakeyama, M. Molecular anatomy and pathogenic actions of Helicobacter pylori CagA that underpin gastric carcinogenesis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, S.; Nomura, T.; Sakaguchi, S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 2003, 299, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, C.M.; Ikeda, T.; Koipally, J.; Avitahl, N.; Wu, L.; Georgopoulos, K.; Morgan, B.A. Helios, a novel dimerization partner of Ikaros expressed in the earliest hematopoietic progenitors. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, K.; Cobb, B.S.; McCarty, A.S.; Brown, K.E.; Klug, C.A.; Lee, R.; Akashi, K.; Weissman, I.L.; Fisher, A.G.; Smale, S.T. Helios, a T cell-restricted Ikaros family member that quantitatively associates with Ikaros at centromeric heterochromatin. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, A.M.; Shevach, E.M. Helios: Still behind the clouds. Immunology 2019, 158, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, A.M.; Korty, P.E.; Tran, D.Q.; Wohlfert, E.A.; Murray, P.E.; Belkaid, Y.; Shevach, E.M. Expression of Helios, an Ikaros transcription factor family member, differentiates thymic-derived from peripherally induced Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3433–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.W.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, I.H.; Bae, H.I.; Seo, A.N. Clinical significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes for gastric cancer in the era of immunology. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2017, 9, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratti, M.; Lampis, A.; Hahne, J.C.; Passalacqua, R.; Valeri, N. Microsatellite instability in gastric cancer: Molecular bases, clinical perspectives, and new treatment approaches. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4151–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrantonio, F.; Miceli, R.; Raimondi, A.; Kim, Y.W.; Kang, W.K.; Langley, R.E.; Choi, Y.Y.; Kim, K.M.; Nankivell, M.G.; Morano, F.; et al. Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis of the Value of Microsatellite Instability As a Biomarker in Gastric Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3392–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, T.J. The number of Foxp3-positive regulatory T cells is increased in Helicobacter pylori gastritis and gastric cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2010, 206, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.W.; Seo, A.N.; Yoon, S.; Bae, H.I.; Jeon, S.W.; Kwon, O.K.; Chung, H.Y.; Yu, W.; Kang, H.; Kim, J.G. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Yoshimi, R.; Yoshii, H.; Kim, D.; Dey, A.; Xiong, H.; Munasinghe, J.; Yazawa, I.; O’Donovan, M.J.; Maximova, O.A.; et al. The transcription factor IRF8 activates integrin-mediated TGF-beta signaling and promotes neuroinflammation. Immunity 2014, 40, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santegoets, S.J.; van Ham, V.J.; Ehsan, I.; Charoentong, P.; Duurland, C.L.; van Unen, V.; Hollt, T.; van der Velden, L.A.; van Egmond, S.L.; Kortekaas, K.E.; et al. The Anatomical Location Shapes the Immune Infiltrate in Tumors of Same Etiology and Affects Survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All (n=67) | High (n = 45) | Low (n = 22) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 68.5 ± 10.0 | 69.2 ± 10.1 | 67.1 ± 10.0 | 0.413 |
| Gender | 0.415 | |||
| Male | 47 | 33 | 14 | |
| Female | 20 | 12 | 8 | |
| TNM stage | 0.185 | |||
| I + II | 29 | 22 | 7 | |
| Advanced (III + IV) | 38 | 23 | 15 | |
| LN metastasis | 0.395 | |||
| Yes | 44 | 28 | 16 | |
| No | 23 | 17 | 6 | |
| Distal metastasis | 0.047 | |||
| Yes | 10 | 4 | 6 | |
| No | 57 | 41 | 16 | |
| HP infection | 0.428 | |||
| Yes | 44 | 31 | 13 | |
| No | 23 | 14 | 9 | |
| CD4 | 0.911 | |||
| High | 25 | 17 | 8 | |
| Low | 42 | 28 | 14 | |
| Foxp3 | 0.926 | |||
| High | 31 | 21 | 10 | |
| Low | 36 | 24 | 12 |
| All (n = 38) | High (n = 23) | Low (n = 15) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 67.7 ± 11.1 | 68.7 ± 11.5 | 66.2 ± 10.8 | 0.507 |
| Gender | 0.544 | |||
| Male | 25 | 16 | 9 | |
| Female | 13 | 7 | 6 | |
| LN metastasis | 0.210 | |||
| Yes | 37 | 23 | 14 | |
| No | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Distal metastasis | 0.122 | |||
| Yes | 10 | 4 | 6 | |
| No | 28 | 19 | 9 | |
| HP infection | 0.311 | |||
| Yes | 24 | 16 | 8 | |
| No | 14 | 7 | 7 | |
| CD4 | 0.851 | |||
| High | 12 | 7 | 5 | |
| Low | 26 | 16 | 10 | |
| Foxp3 | 0.376 | |||
| High | 16 | 11 | 5 | |
| Low | 22 | 12 | 10 |
| Risk Factors | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Helios | 0.046 | |
| High | 1 | |
| Low | 2.90 (1.02–8.20) | |
| Gender | 0.063 | |
| Male | 1 | |
| Female | 3.50 (0.94–12.99) | |
| Distal metastasis | 0.091 | |
| Yes | 1 | |
| No | 3.72 (0.81–16.95) | |
| HP infection | 0.239 | |
| Yes | 1 | |
| No | 1.92 (0.65–5.68) | |
| CD4 | 0.495 | |
| High | 1 | |
| Low | 0.63 (0.16–2.39) | |
| Foxp3 | 0.901 | |
| High | 1 | |
| Low | 0.93 (0.30–2.87) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.-M.; Liu, J.-L.; Chuang, H.-C.; Chang, Y.-L.; Yeh, C.-M.; Wu, C.-S.; Wu, S.-F. Helios Expression in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Correlates with Overall Survival of Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients. Life 2020, 10, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10090189
Chen W-M, Liu J-L, Chuang H-C, Chang Y-L, Yeh C-M, Wu C-S, Wu S-F. Helios Expression in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Correlates with Overall Survival of Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients. Life. 2020; 10(9):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10090189
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wei-Ming, Jing-Lan Liu, Huei-Chieh Chuang, Yong-Lin Chang, Chia-Ming Yeh, Cheng-Shyong Wu, and Shu-Fen Wu. 2020. "Helios Expression in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Correlates with Overall Survival of Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients" Life 10, no. 9: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10090189
APA StyleChen, W.-M., Liu, J.-L., Chuang, H.-C., Chang, Y.-L., Yeh, C.-M., Wu, C.-S., & Wu, S.-F. (2020). Helios Expression in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Correlates with Overall Survival of Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients. Life, 10(9), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10090189





