Quantifying the Performance of Micro-Compartmentalized Directed Evolution Protocols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling High-Throughput Directed Evolution Protocols
2.1. Two Categories of Experimental Parameters
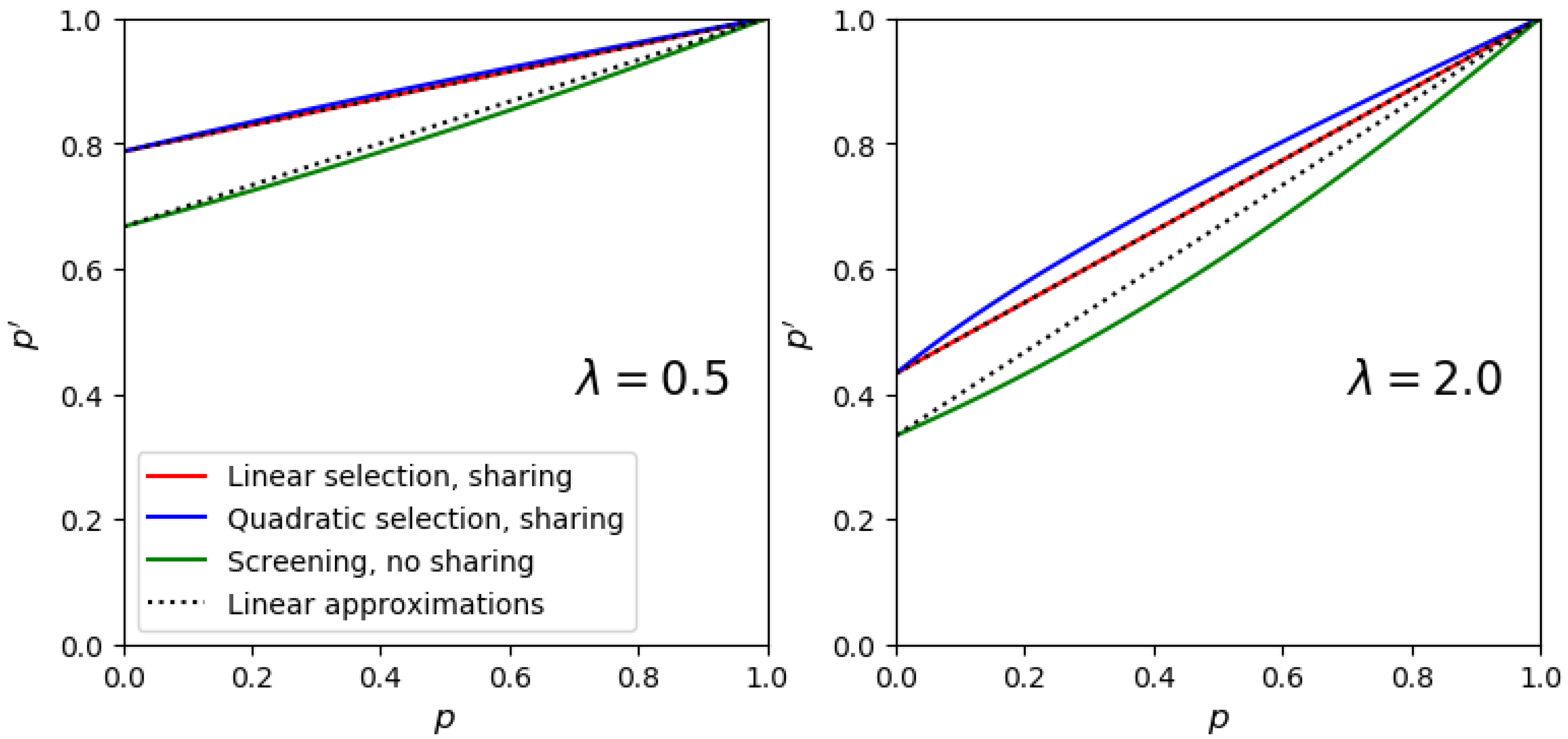
2.2. The Mathematical Model
2.3. Computing the Frequency Jump in Mock Libraries
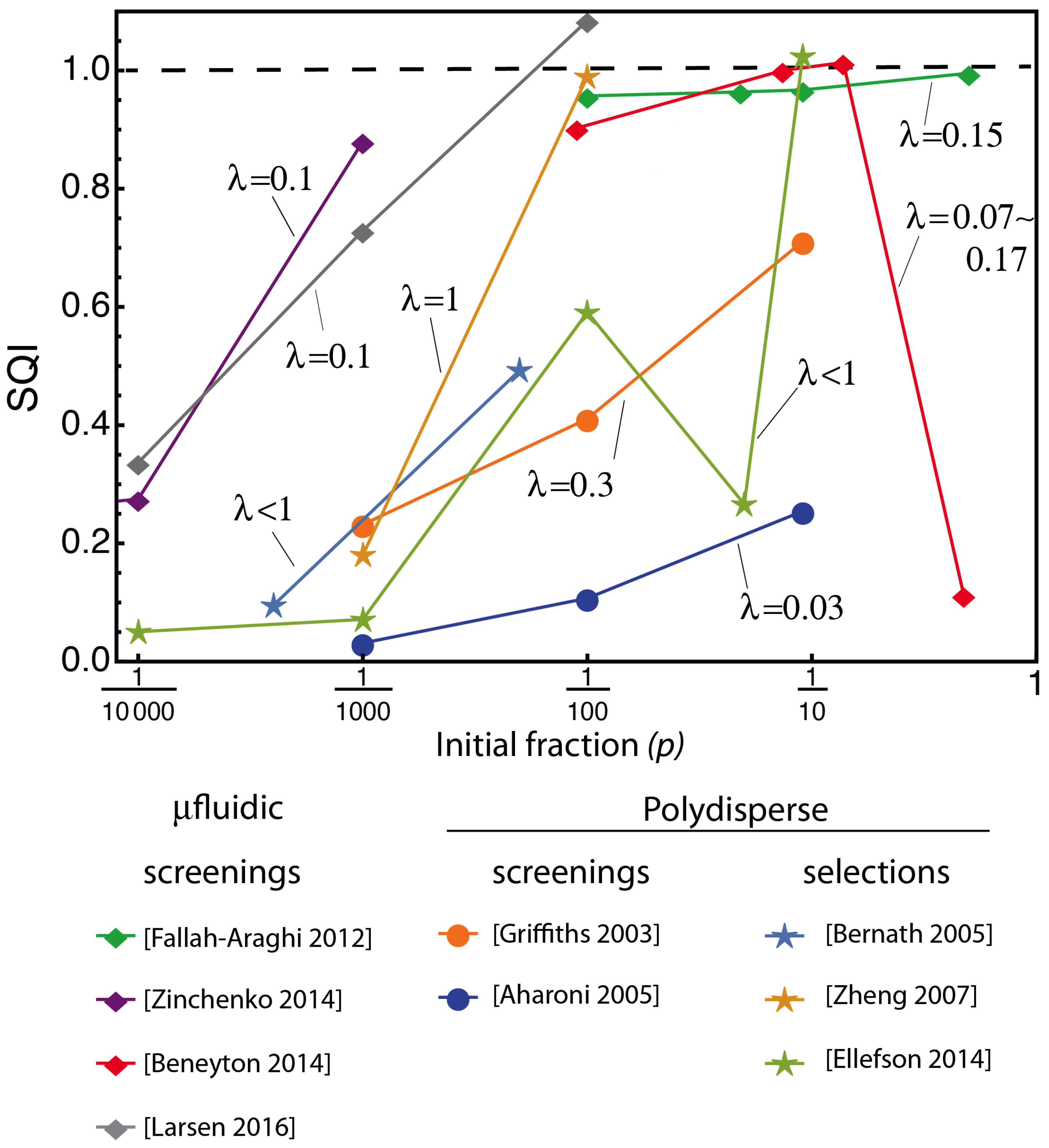
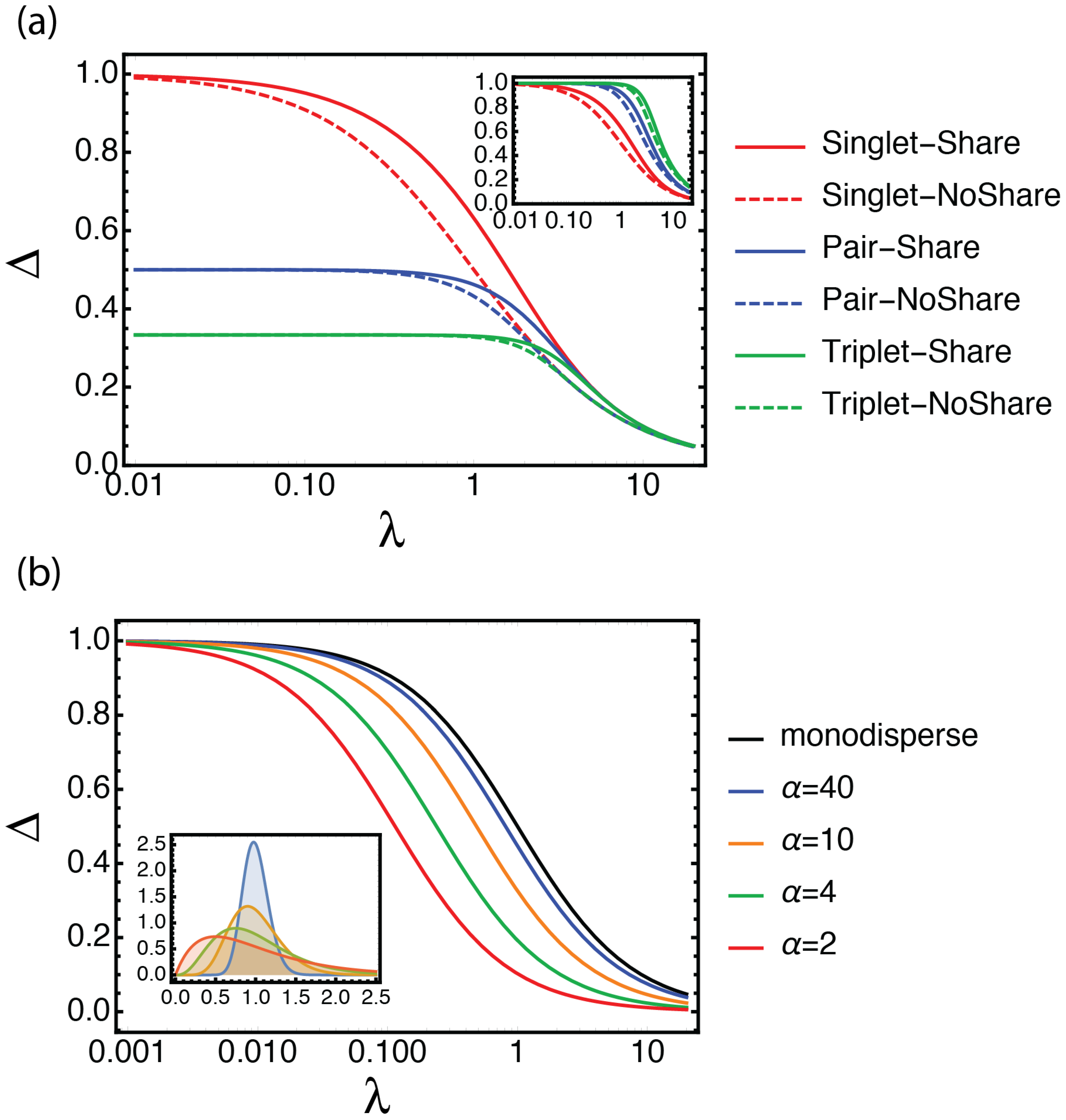
2.4. Definition of the Selection Quality Index (SQI)
3. Results and Discussion
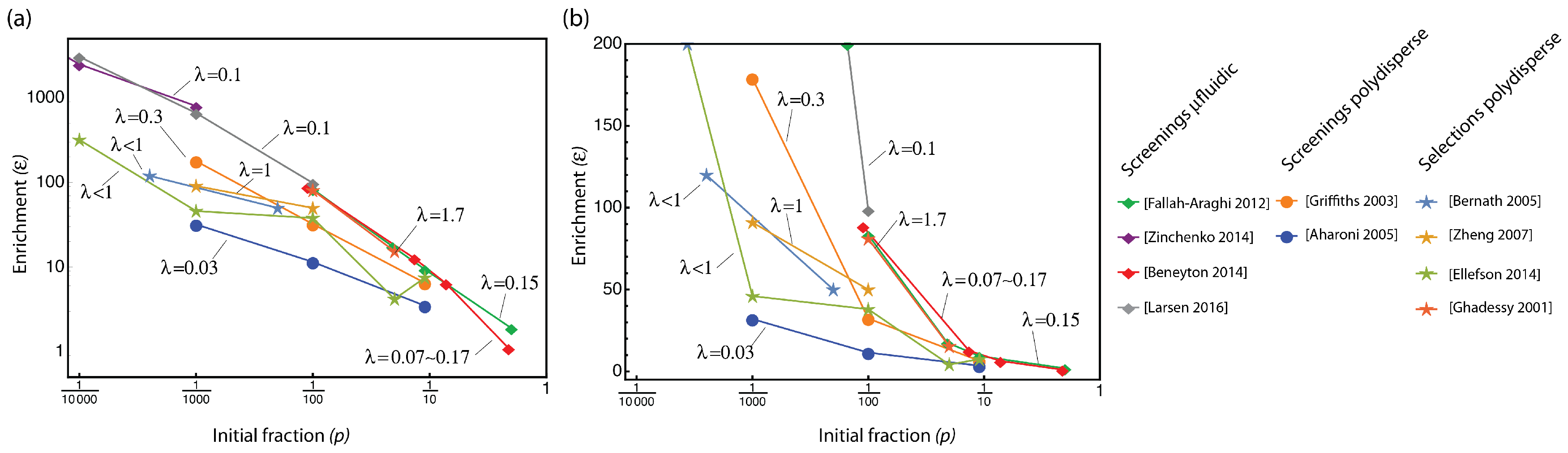
3.1. Looking at Experiments through SQI and Enrichment Factor
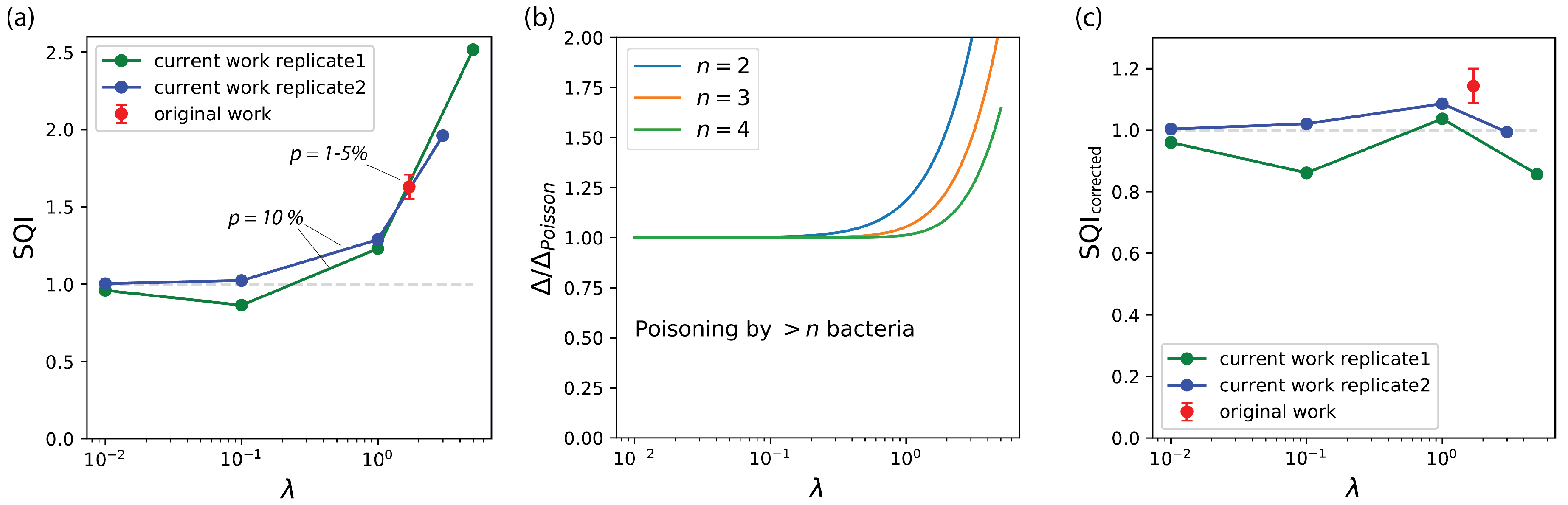
3.2. The Compartmentalized Self-Replication (CSR) Protocol Has an Abnormal SQI
3.3. The Abnormal SQI of CSR Reveals a Hidden Beneficial Mechanism
3.4. The Case of Non-Random Compartmentalization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, D.E.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Arnold, F.H. Tuning the activity of an enzyme for unusual environments: Sequential random mutagenesis of subtilisin E for catalysis in dimethylformamide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5618–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, F.H. Directed Evolution: Bringing New Chemistry to Life. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4143–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frances, H.A.; George Georgiou, G. Directed Enzyme Evolution: Screening and Selection Methods, 2003rd ed.; Totowa, N.J., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zeymer, C.; Hilvert, D. Directed Evolution of Protein Catalysts. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 131–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, D.S.; Griffiths, A.D. Man-made cell-like compartments for molecular evolution. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadessy, F.J.; Ong, J.L.; Holliger, P. Directed evolution of polymerase function by compartmentalized self-replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4552–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellefson, J.W.; Meyer, A.J.; Hughes, R.A.; Cannon, J.R.; Brodbelt, J.S.; Ellington, A.D. Directed evolution of genetic parts and circuits by compartmentalized partnered replication. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, A.D.; Tawfik, D.S. Directed evolution of an extremely fast phosphotriesterase by in vitro compartmentalization. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, J.C.; Miller, O.L.; Taly, V.; Ryckelynck, M.; El-Harrak, A.; Frenz, L.; Rick, C.; Samuels, M.L.; Hutchison, J.B.; Agresti, J.J.; et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting (FADS): Efficient microfluidic cell sorting based on enzymatic activity. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintses, B.; Hein, C.; Mohamed, M.F.; Fischlechner, M.; Courtois, F.; Leine, C.; Hollfelder, F. Picoliter Cell Lysate Assays in Microfluidic Droplet Compartments for Directed Enzyme Evolution. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, P.-Y.; Zinchenko, A.; Hollfelder, F. Enzyme engineering in biomimetic compartments. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 33, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povilaitis, T.; Alzbutas, G.; Sukackaite, R.; Siurkus, J.; Skirgaila, R. In vitro evolution of phi29 DNA polymerase using isothermal compartmentalized self replication technique. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2016, 29, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agresti, J.J.; Antipov, E.; Abate, A.R.; Ahn, K.; Rowat, A.C.; Baret, J.C.; Marquez, M.; Klibanov, A.M.; Griffiths, A.D.; Weitz, D.A. Ultrahigh-throughput screening in drop-based microfluidics for directed evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4004–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneyton, T.; Coldren, F.; Baret, J.-C.; Griffiths, A.D.; Taly, V. CotA laccase: High-throughput manipulation and analysis of recombinant enzyme libraries expressed in E. coli using droplet-based microfluidics. Analyst 2014, 139, 3314–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah-Araghi, A.; Baret, J.-C.; Ryckelynck, M.; Griffiths, A.D. A completely in vitro ultrahigh-throughput droplet-based microfluidic screening system for protein engineering and directed evolution. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, V.B.; Taylor, A.I.; Cozens, C.; Abramov, M.; Renders, M.; Zhang, S.; Chaput, J.C.; Wengel, J.; Peak-Chew, J.C.; McLaughlin, S.H.; et al. Synthetic Genetic Polymers Capable of Heredity and Evolution. Science 2012, 336, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, A.; Nakashima, T.; Tokuriki, N.; Hosokawa, M.; Nogami, H.; Arioka, S.; Urabe, I.; Yomo, T. Evolvability of random polypeptides through functional selection within a small library. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2002, 15, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondelez, Y.; Tresset, G.; Tabata, K.V.; Arata, H.; Fujita, H.; Takeuchi, S.; Noji, H. Microfabricated arrays of femtoliter chambers allow single molecule enzymology. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorin, A.S.; Rondelez, Y. Natural selection in compartmentalized environment with reshuffling. J. Math. Biol. 2019, 79, 1401–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorin, A.S.; Rondelez, Y. Selection strategies for randomly partitioned genetic replicators. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 062416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klenow, H.; Henningsen, I. Selective Elimination of the Exonuclease Activity of the Deoxyribonucleic Acid Polymerase from Escherichia coli B by Limited Proteolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 65, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermekchiev, M.B.; Kirilova, L.I.; Vail, E.E.; Barnes, W.M. Mutants of Taq DNA polymerase resistant to PCR inhibitors allow DNA amplification from whole blood and crude soil samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemna, E.W.M.; Schoeman, R.M.; Wolbers, F.; Vermes, I.; Weitz, D.A.; van den Berg, A. High-yield cell ordering and deterministic cell-in-droplet encapsulation using Dean flow in a curved microchannel. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2881–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, D.J.; Neild, A.; deMello, A.; Liu, A.-Q.; Ai, Y. The Poisson distribution and beyond: Methods for microfluidic droplet production and single cell encapsulation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3439–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Carlo, D.; Irimia, D.; Tompkins, R.G.; Toner, M. Continuous inertial focusing, ordering, and separation of particles in microchannels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18892–18897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edd, J.F.; Di Carlo, D.; Humphry, K.J.; Köster, S.; Irimia, D.; Weitz, D.A.; Toner, M. Controlled encapsulation of single-cells into monodisperse picolitre drops. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1262–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prileszky, T.A.; Ogunnaike, B.A.; Furst, E.M. Statistics of droplet sizes generated by a microfluidic device. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 2923–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dramé-Maigné, A.; Zadorin, A.S.; Golovkova, I.; Rondelez, Y. Quantifying the Performance of Micro-Compartmentalized Directed Evolution Protocols. Life 2020, 10, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10020017
Dramé-Maigné A, Zadorin AS, Golovkova I, Rondelez Y. Quantifying the Performance of Micro-Compartmentalized Directed Evolution Protocols. Life. 2020; 10(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleDramé-Maigné, Adèle, Anton S. Zadorin, Iaroslava Golovkova, and Yannick Rondelez. 2020. "Quantifying the Performance of Micro-Compartmentalized Directed Evolution Protocols" Life 10, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10020017
APA StyleDramé-Maigné, A., Zadorin, A. S., Golovkova, I., & Rondelez, Y. (2020). Quantifying the Performance of Micro-Compartmentalized Directed Evolution Protocols. Life, 10(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10020017




