Heterocyst Development and Diazotrophic Growth of Anabaena variabilis under Different Nitrogen Availability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Stock Culture
2.2. Preparation of Culture Medium
2.3. Experimental Preparation
2.4. Microscopic Count of Vegetative Cells and Heterocysts
2.5. Chlorophyll-a Analysis
- v = volume of 90% acetone used (mL); V = volume of sample filtered (mL);
- Y = 11.64 X1 − 2.16 X2 + 0.10 X3;
- X1 = A(663 nm) − A(750 nm); X2 = A(645 nm) − A(750 nm); X3 = A(630 nm) − A(750 nm).
2.6. Growth Rate Analysis
- N0: Cell density (cells mL−1) at the beginning of the sampling interval, t0;
- N1: Cell density (cells mL−1) at the end of the sampling interval, t1;
- : time interval of sampling (d).
2.7. Cellular Nitrogen Measurement
2.8. Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen Measurement
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Changes in A. variabilis under Nitrate Treatment
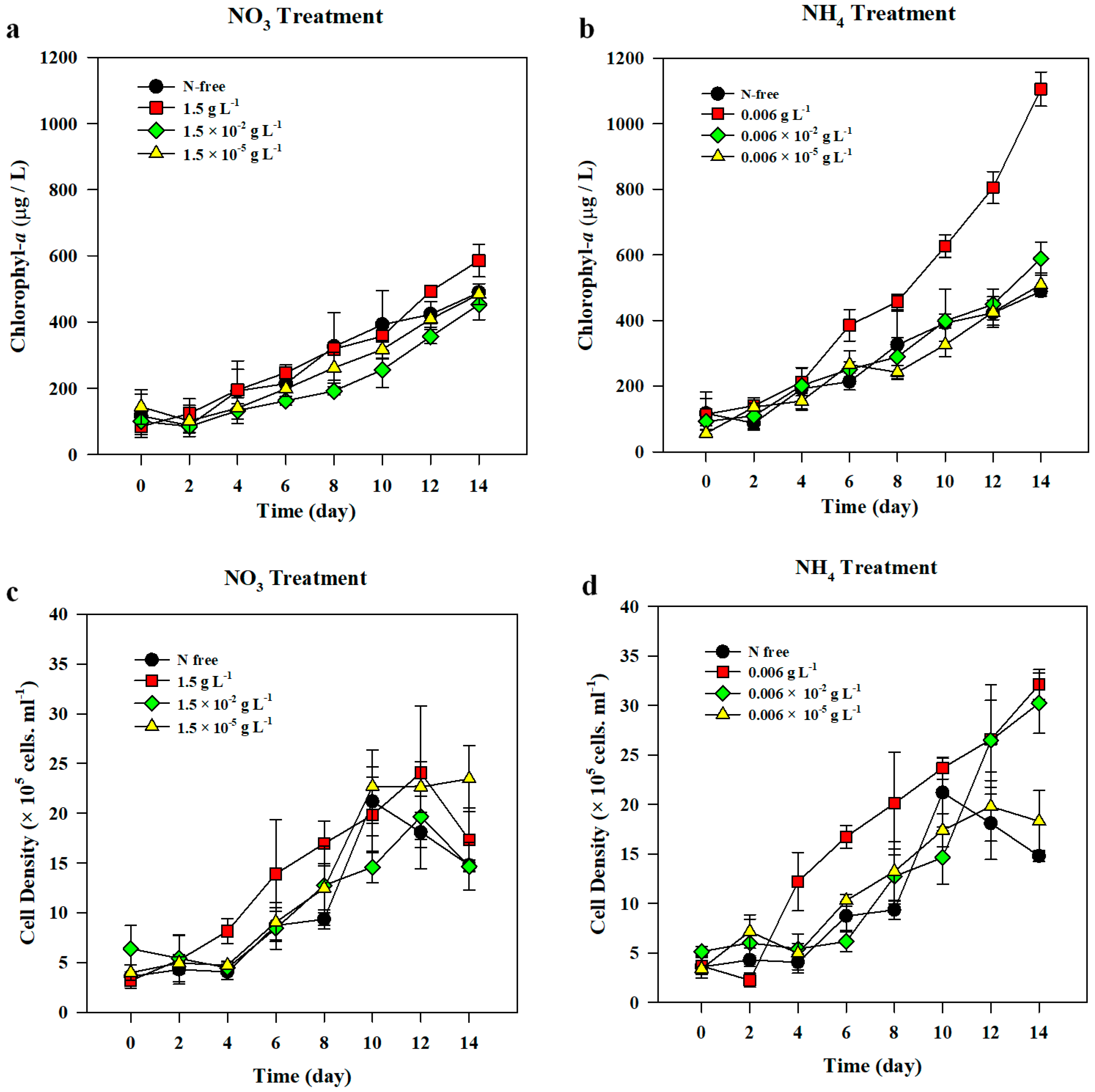
3.1.1. Chl-a, Cell Density, and Growth Rate
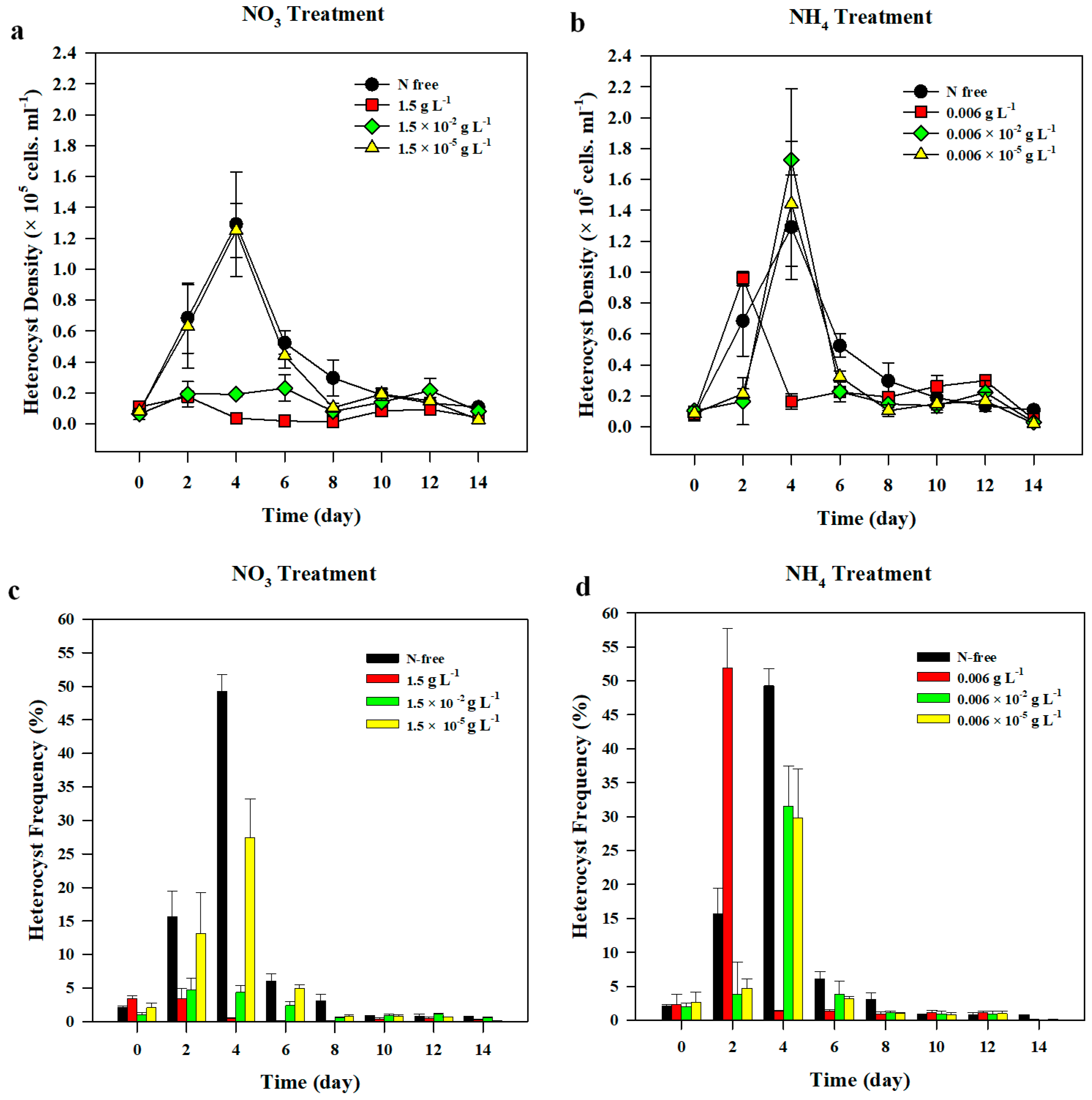
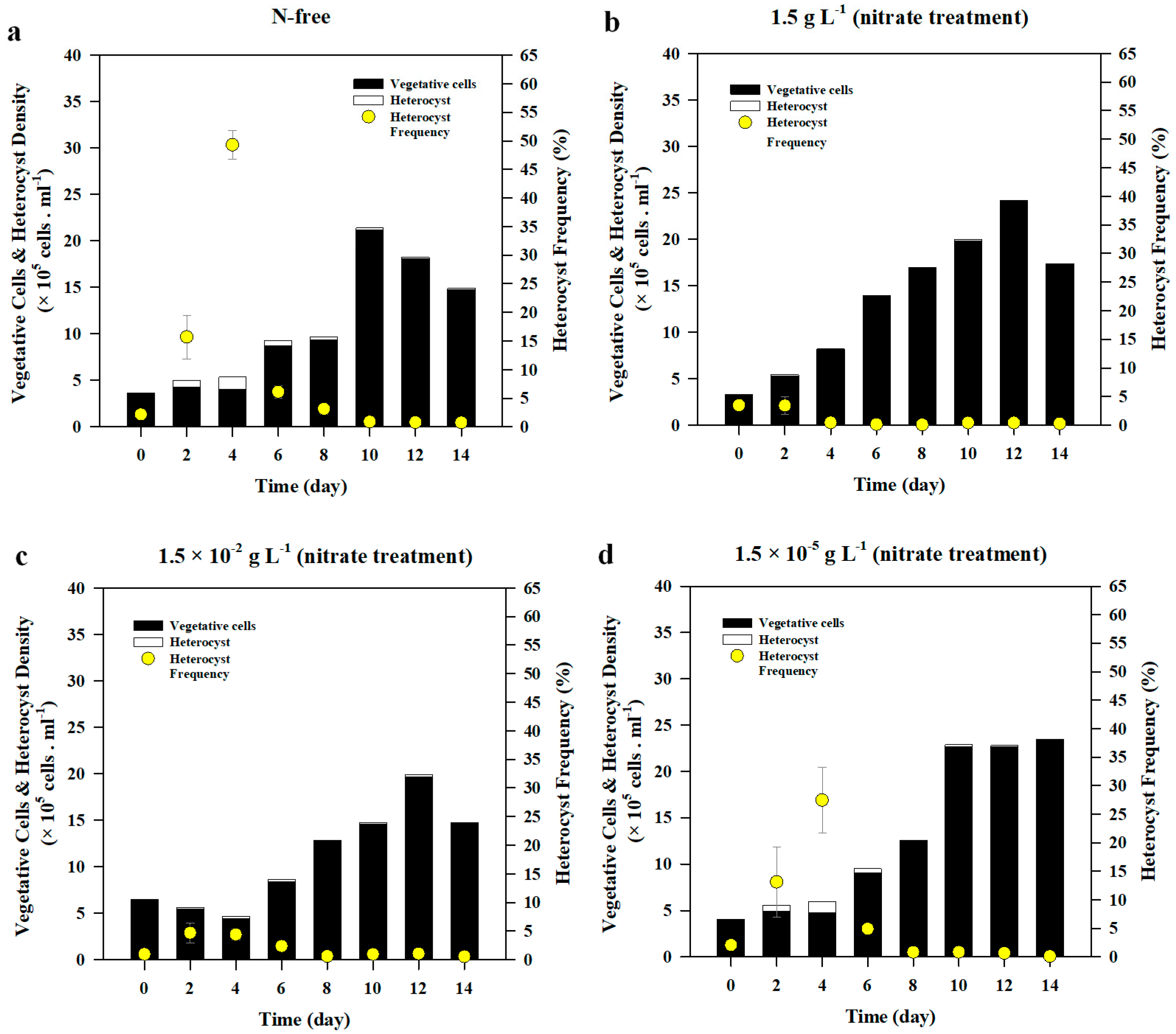
3.1.2. Heterocyst Development
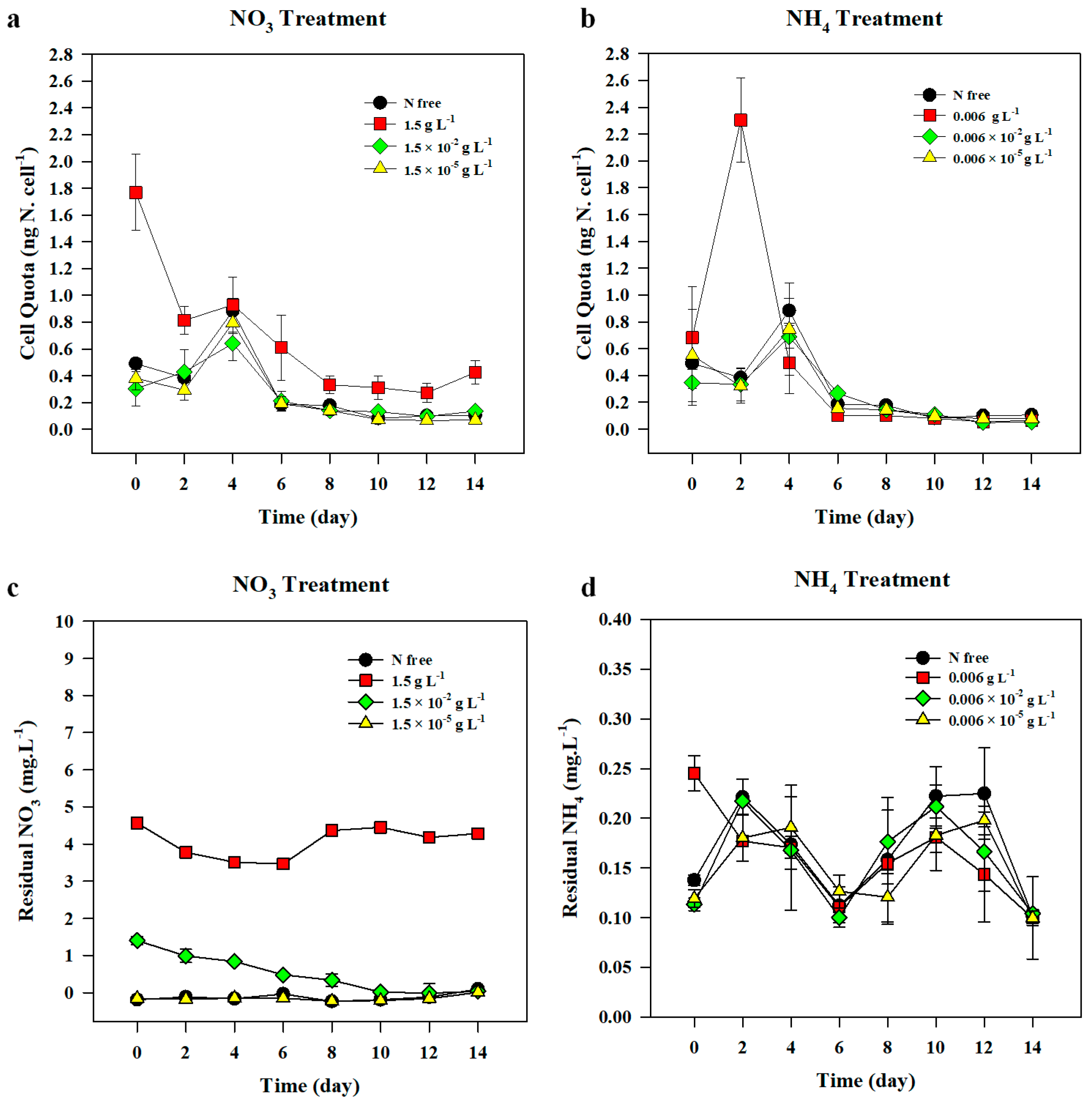
3.1.3. Nitrogen Cell Quota
3.1.4. Residual Nitrate in the Medium
3.2. Changes in A. variabilis under Ammonium Treatment
3.2.1. Chl-a, Cell Density, and Growth Rate
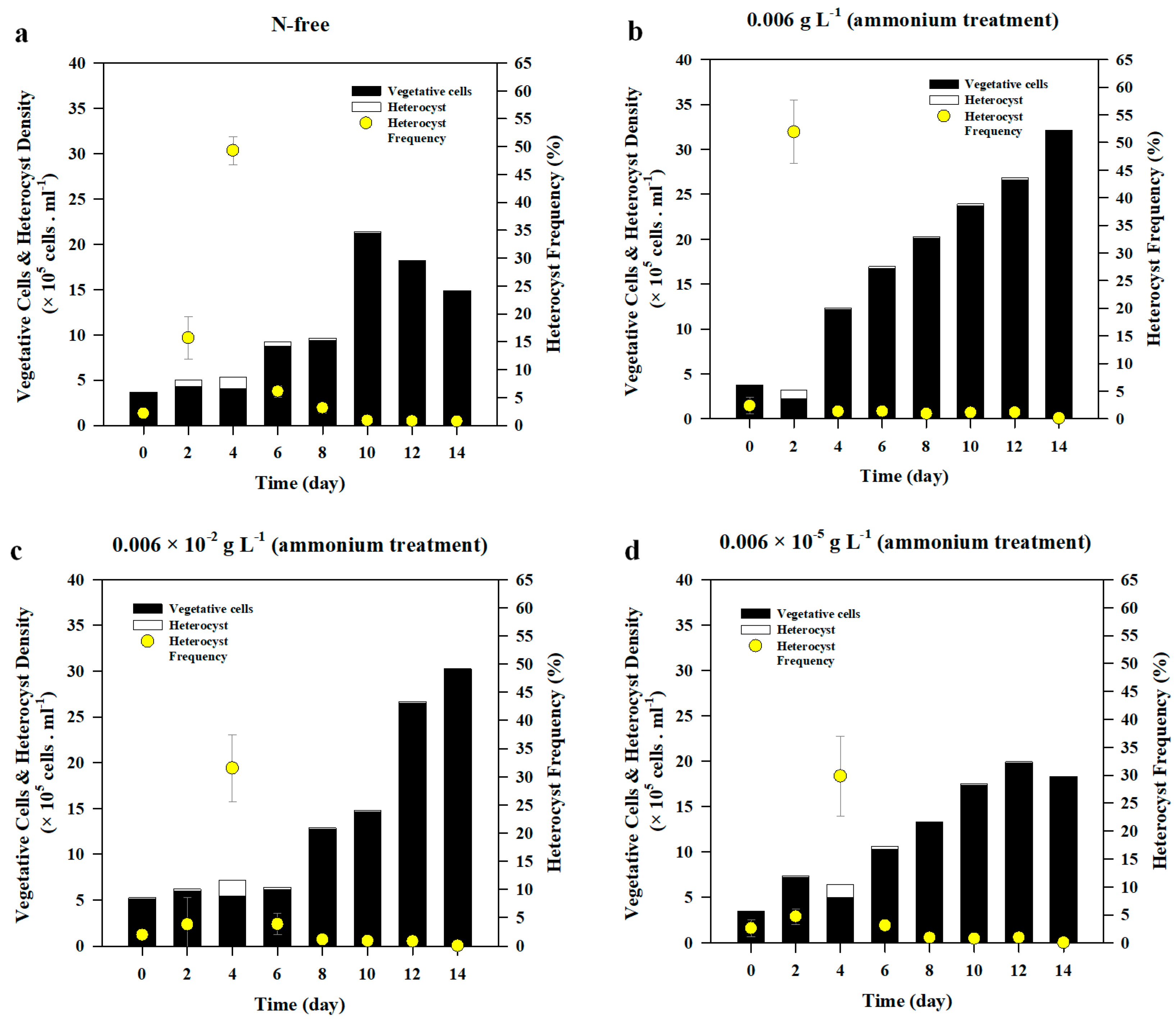
3.2.2. Heterocyst Development
3.2.3. Nitrogen Cell Quota
3.2.4. Residual Ammonium in the Medium
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlichting, J.; Harold, E. Survival of some fresh-water algae under extreme environmental conditions. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1974, 93, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, C.C.; Ibelings, B.W.; Hoffmann, E.P.; Hamilton, D.P.; Brookes, J.D. Eco-physiological adaptations that favour freshwater cyanobacteria in a changing climate. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsberg, J.H. The effects of harmful algal blooms on aquatic organisms. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2002, 10, 113–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Havens, K.E. Cyanobacterial toxins: A qualitative meta–analysis of concentrations, dosage and effects in freshwater, estuarine and marine biota. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 675–732. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, D.P.; Wood, S.A.; Dietrich, D.R.; Puddick, J. Costs of harmful blooms of freshwater cyanobacteria. In Cyanobacteria: An Economic Perspective; John Wiley Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Hall, N.; Wu, Y. Determining critical nutrient thresholds needed to control harmful cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Controlling cyanobacterial harmful blooms in freshwater ecosystems. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolzau, S.; Dolman, A.M.; Voss, M.; Wiedner, C. The response of nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria to a reduction in nitrogen loading. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2018, 103, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dortch, Q. The interaction between ammonium and nitrate uptake in phytoplankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Series Oldend. 1990, 61, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprőber, P.; Shafik, H.M.; Présing, M.; Kovács, A.W.; Herodek, S. Nitrogen uptake and fixation in the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii under different nitrogen conditions. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, R.W.; Marino, R.; Cole, J.J. Nitrogen fixation in freshwater, estuarine, and marine ecosystems. 2. Biogeochemical controls1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, B.; Klawonn, I.; Svedén, J.B.; Bergkvist, J.; Nahar, N.; Walve, J.; Littmann, S.; Whitehouse, M.J.; Lavik, G.; Kuypers, M.M. N 2-fixation, ammonium release and N-transfer to the microbial and classical food web within a plankton community. ISME J. 2016, 10, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Porath, J.; Zehr, J. Detection and characterization of cyanobacterial nifH genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fay, P. Oxygen relations of nitrogen fixation in cyanobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1992, 56, 340–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H. The cyanobacterial nitrogen fixation paradox in natural waters. F1000Research 2017, 6, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stal, L.J. The effect of oxygen concentration and temperature on nitrogenase activity in the heterocystous cyanobacterium Fischerella sp. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Mella-Herrera, R.A.; Golden, J.W. Cyanobacterial heterocysts. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, C.P. Movement of carbon from vegetative cells to heterocysts in Anabaena cylindrica. J. Bacteriol. 1968, 96, 2138–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J. Absence of the Pigments of Photosystem II of Photosynthesis in Heterocysts of a Blue–Green Alga. Nature 1970, 228, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.; Stavans, J.; Flores, E. The multicellular nature of filamentous heterocyst-forming cyanobacteria. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 831–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laamanen, M.; Kuosa, H. Annual variability of biomass and heterocysts of the N. Boreal Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- González-Madina, L.; Pacheco, J.P.; Yema, L.; de Tezanos, P.; Levrini, P.; Clemente, J.; Crisci, C.; Lagomarsino, J.J.; Méndez, G.; Fosalba, C. Drivers of cyanobacteria dominance, composition and nitrogen fixing behavior in a shallow lake with alternative regimes in time and space, Laguna del Sauce (Maldonado, Uruguay). Hydrobiologia 2019, 829, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J, K. Cyanoprokaryota 3. Teil/3rd Part: Heterocytous genera. In Süswasserflora von Mitteleuropa–Freshwater Flora of Central Europe; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kangatharalingam, N.; Priscu, J.C.; Paerl, H.W. Heterocyst envelope thickness, heterocyst frequency and nitrogenase activity in Anabaena flos-aquae: Influence of exogenous oxygen tension. Microbiology 1992, 138, 2673–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Kováčik, L.U. Trichome structure of fourAphanizomenon taxa (Cyanophyceae) from Czechoslovakia, with notes on the taxonomy and delimitation of the genus. Plant Syst. Evol. 1989, 164, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.-S.; Golden, J.W. Heterocyst pattern formation controlled by a diffusible peptide. Science 1998, 282, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, R.E.; Carr, J.F. The Influence of Nitrogen on Heterocyst Production in Blue-Green Algae 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1969, 14, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, A.; Chuang, A.W.; Burford, M.A. Nitrogen fixation by the diazotroph Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanophyceae). J. Phycol. 2016, 52, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xiao, J.; Wan, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Song, C.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, X. Mutual dependence of nitrogen and phosphorus as key nutrient elements: One facilitates Dolichospermum flos-aquae to overcome the limitations of the other. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5653–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, A.; Adams, M.P.; Chuang, A.W.; Orr, P.T.; O’Brien, K.R.; Burford, M.A. Constitutive toxin production under various nitrogen and phosphorus regimes of three ecotypes of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii ((Wołoszyńska) Seenayya et Subba Raju). Harmful Algae 2015, 47, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, W.; Andrews, S. Iron regulation of growth and heterocyst formation in the nitrogen fixing cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. PCC 7120. J. Ecol. Health Environ. 2016, 4, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffin, J.D.; Bridgeman, T.B. Organic and inorganic nitrogen utilization by nitrogen-stressed cyanobacteria during bloom conditions. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Furuya, K.; Kodama, T.; Takeda, S.; Harrison, P.J. Ammonium uptake and dinitrogen fixation by the unicellular nanocyanobacterium Crocosphaera watsonii in nitrogen-limited continuous cultures. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickelson, J.C.; Davis, E.B.; Tischer, R. The effect of various nitrogen sources upon heterocyst formation in Anabaena flos-aquae A–37. J. Exp. Bot. 1967, 18, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, T.; Pratte, B. Effect on Heterocyst Differentiation of Nitrogen Fixation in Vegetative Cells of the Cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis ATCC 29413. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilen, Y.; Elena, L.; Paula, d.T.P. The role of heterocytes in the physiology and ecology of bloom-forming harmful cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 2016, 60, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videau, P.; Cozy, L.M. Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120: Laboratory Maintenance, Cultivation, and Heterocyst Induction. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2019, 52, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolk, C.P. Heterocyst formation in Anabaena. In Prokaryotic Development; American Society of Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 83–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, S.; Carr, N. Heterocyst and nitrogenase development in Anabaena cylindrica. Microbiology 1976, 96, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, J.W.; Yoon, H.-S. Heterocyst development in Anabaena. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, M.; Mitchison, G.; Smith, R. Pattern formation in the blue-green alga, Anabaena: I. Basic mechanisms. J. Cell Sci. 1973, 12, 707–723. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J. The kinetics of nutrient utilization. Can. Bull. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1981, 210, 211–233. [Google Scholar]
- Lindell, D.; Post, A.F. Ecological Aspects of ntcA Gene Expression and Its Use as an Indicator of the Nitrogen Status of Marine Synechococcus spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3340–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanier, R.; Kunisawa, R.; Mandel, M.; Cohen-Bazire, G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol. Rev. 1971, 35, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabour, B.; Sbiyyaa, B.; Loudiki, M.; Oudra, B.; Belkoura, M.; Vasconcelos, V. Effect of light and temperature on the population dynamics of two toxic bloom forming Cyanobacteria–Microcystis ichthyoblabe and Anabaena aphanizomenoides. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 25, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Beardall, J. Growth and photosynthetic characteristics of toxic and non-toxic strains of the cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and Anabaena circinalis in relation to light. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, P.; Yunes, J.S.; Cretoiu, M.S.; Stal, L.J. Growth Characteristics of an Estuarine Heterocystous Cyanobacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogg, G. Growth and Heterocyst Production in Anabaena cylindrica Lemm. New Phytol. 1944, 43, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Muro-Pastor, M.I.; Reyes, J.C.; Florencio, F.J. Cyanobacteria perceive nitrogen status by sensing intracellular 2-oxoglutarate levels. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38320–38328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herrero, A.; Muro-Pastor, A.M.; Flores, E. Nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Alférez, S.; del Campo, F.F. Relationship between nitrogen fixation and nitrate metabolism in the Nodularia strains M1 and M2. Planta 1994, 194, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, M.; Egardt, J.; Singh, A.; Ploug, H. Inorganic phosphorus enrichments in Baltic Sea water have large effects on growth, carbon fixation, and N2 fixation by Nodularia spumigena. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 77, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, A.; Mohlin, M.; Sundbäck, K. Intraspecific variation in the response of the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena to moderate UV-B radiation. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogg, G. Growth and heterocyst production in Anabaena cylindrica lemm.: II. in relation to carbon and nitrogen metabolism. Ann. Bot. 1949, 13, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tezanos Pinto, P.; Litchman, E. Interactive effects of N: P ratios and light on nitrogen-fixer abundance. Oikos 2010, 119, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Wilkerson, F.P.; Dugdale, R.C.; Raven, J.A.; Dupont, C.L.; Leavitt, P.R.; Parker, A.E.; Burkholder, J.M.; Kana, T.M. Pluses and minuses of ammonium and nitrate uptake and assimilation by phytoplankton and implications for productivity and community composition, with emphasis on nitrogen-enriched conditions. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 165–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, D.B.; Bogard, M.J.; Finlay, K.; Leavitt, P.R. Comparative effects of urea, ammonium, and nitrate on phytoplankton abundance, community composition, and toxicity in hypereutrophic freshwaters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Berg, G.M. Nitrogen form, fate and phytoplankton composition. In Experimental Ecosystems and Scale: Tools for Understanding and Managing Coastal Ecosystems; Kennedy, V.S., Kemp, W.M., Peterson, J.E., Dennison, W.C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Wolk, C.P.; Ernst, A.; Elhai, J. Heterocyst metabolism and development. In The Molecular Biology of Cyanobacteria; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 769–823. [Google Scholar]
- Walve, J.; Larsson, U. Blooms of Baltic Sea Aphanizomenon sp. (Cyanobacteria) collapse after internal phosphorus depletion. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 49, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gaoa, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-X.; Jiang, Y.-L.; Zhao, M.-X.; Cai, K.; Liu, S.; Wen, B.; Lv, P.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhong, H. Structural insights into HetR− PatS interaction involved in cyanobacterial pattern formation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plominsky, Á.M.; Delherbe, N.; Mandakovic, D.; Riquelme, B.; González, K.; Bergman, B.; Mariscal, V.; Vásquez, M. Intercellular transfer along the trichomes of the invasive terminal heterocyst forming cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii CS-505. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnu009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, A.J.; Goldman, C.R. Nitrogen fixation in Clear Lake, California. I. Seasonal variation and the role of heterocysts 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1972, 17, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beversdorf, L.J.; Miller, T.R.; McMahon, K.D. The role of nitrogen fixation in cyanobacterial bloom toxicity in a temperate, eutrophic lake. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisander, P.H.; Cheshire, L.A.; Braddy, J.; Calandrino, E.S.; Hoffman, M.; Piehler, M.F.; Paerl, H.W. Facultative diazotrophy increases Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii competitiveness under fluctuating nitrogen availability. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, N.J.; von Schaewen, A. The oxidative pentose phosphate pathway: Structure and organisation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, P.D.; Schulz-Vogt, H.N.; Vogts, A.; Nausch, M. Differences in the accumulation of phosphorus between vegetative cells and heterocysts in the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenesi, G.; Shafik, H.M.; Kovács, A.W.; Herodek, S.; Présing, M. Effect of nitrogen forms on growth, cell composition and N 2 fixation of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in phosphorus-limited chemostat cultures. Hydrobiologia 2009, 623, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, W.; Alexander, G. Phosphorus availability and nitrogenase activity in aquatic blue-green algae. Freshw. Biol. 1971, 1, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohlin, M.; Wulff, A. Interaction effects of ambient UV radiation and nutrient limitation on the toxic cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vintila, S.; El-Shehawy, R. Ammonium ions inhibit nitrogen fixation but do not affect heterocyst frequency in the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena strain AV1. Microbiology 2007, 153, 3704–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klawonn, I.; Nahar, N.; Walve, J.; Andersson, B.; Olofsson, M.; Svedén, J.; Littmann, S.; Whitehouse, M.J.; Kuypers, M.; Ploug, H. Cell-specific nitrogen-and carbon-fixation of cyanobacteria in a temperate marine system (Baltic Sea). Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4596–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, W.J.; Kulasooriya, S. The relation of acetylene reduction to heterocyst frequency in blue-green algae. J. Exp. Bot. 1970, 21, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.; Pace, M.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Marino, R.M. Bloom formation in heterocystic nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria: The dependence on colony size and zooplankton grazing. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, X.; Yan, L.; Wang, J.; Kang, X.; Cui, L. Cyanobacterial nitrogen fixation influences the nitrogen removal efficiency in a constructed wetland. Water 2017, 9, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, A.M.; Duberg, J.; Motwani, N.H.; Hogfors, H.; Klawonn, I.; Ploug, H.; Svedén, J.B.; Garbaras, A.; Sundelin, B.; Hajdu, S. Nitrogen fixation by cyanobacteria stimulates production in Baltic food webs. Ambio 2015, 44, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Component | Concentration (g L−1. dH2O) |
|---|---|
| NaNO3 | 1.5 |
| K2HPO4 | 0.04 |
| MgSO4.7H2O | 0.075 |
| CaCl2.2H2O | 0.036 |
| Citric acid | 0.006 |
| Ferric ammonium citrate (Fe-NH4-citrate) | 0.006 |
| EDTA Na2 | 0.001 |
| Na2CO3 | 0.02 |
| H3BO3 | 2.86 |
| MnCl2.4H2O | 1.81 |
| ZnSO4.7H20 | 0.22 |
| CuSO4.5H2O | 0.08 |
| Na2MoO4.2H2O | 0.39 |
| Co(NO3)2.6H2O | 0.05 |
| Treatment | N Source | Concentration (g L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| A | Absent | - |
| B | NaNO3 (nitrate) | 1.5 |
| C | 1.5 × 10−2 | |
| D | 1.5 × 10−5 | |
| E | Fe-NH4-citrate (ammonium) | 0.006 |
| F | 0.006 × 10−2 | |
| G | 0.006 × 10−5 |
| Treatment | N Source | Concentration (g L−1) | Growth Rate (μ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-free | Absent | 0 | 0.103 ± 0.024 |
| Nitrate | NaNO3 | 1.5 | 0.121 ± 0.023 |
| 1.5 × 10−2 | 0.063 ± 0.023 | ||
| 1.5 × 10−5 | 0.127 ± 0.006 | ||
| Ammonium | Fe-NH4-citrate | 0.006 | 0.156 ± 0.013 |
| 0.006 ×10−2 | 0.126 ± 0.001 | ||
| 0.006 ×10−5 | 0.125 ± 0.012 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zulkefli, N.S.; Hwang, S.-J. Heterocyst Development and Diazotrophic Growth of Anabaena variabilis under Different Nitrogen Availability. Life 2020, 10, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10110279
Zulkefli NS, Hwang S-J. Heterocyst Development and Diazotrophic Growth of Anabaena variabilis under Different Nitrogen Availability. Life. 2020; 10(11):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10110279
Chicago/Turabian StyleZulkefli, Nur Syahidah, and Soon-Jin Hwang. 2020. "Heterocyst Development and Diazotrophic Growth of Anabaena variabilis under Different Nitrogen Availability" Life 10, no. 11: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10110279
APA StyleZulkefli, N. S., & Hwang, S.-J. (2020). Heterocyst Development and Diazotrophic Growth of Anabaena variabilis under Different Nitrogen Availability. Life, 10(11), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10110279






