RISE-Based Composite Adaptive Control of Electro-Hydrostatic Actuator with Asymptotic Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dynamics Modeling
3. RISE-Based Composite Adaptive Controller Design
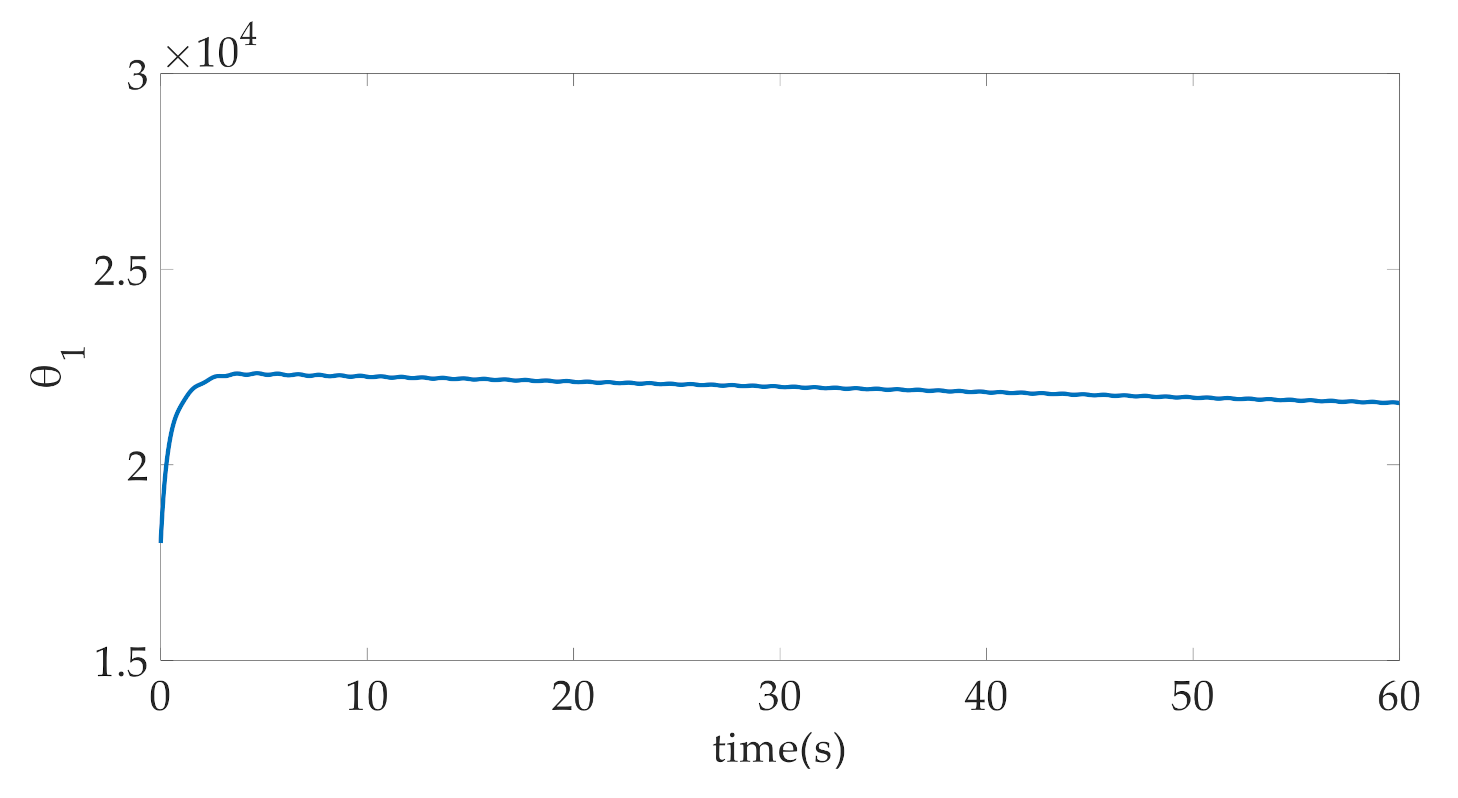
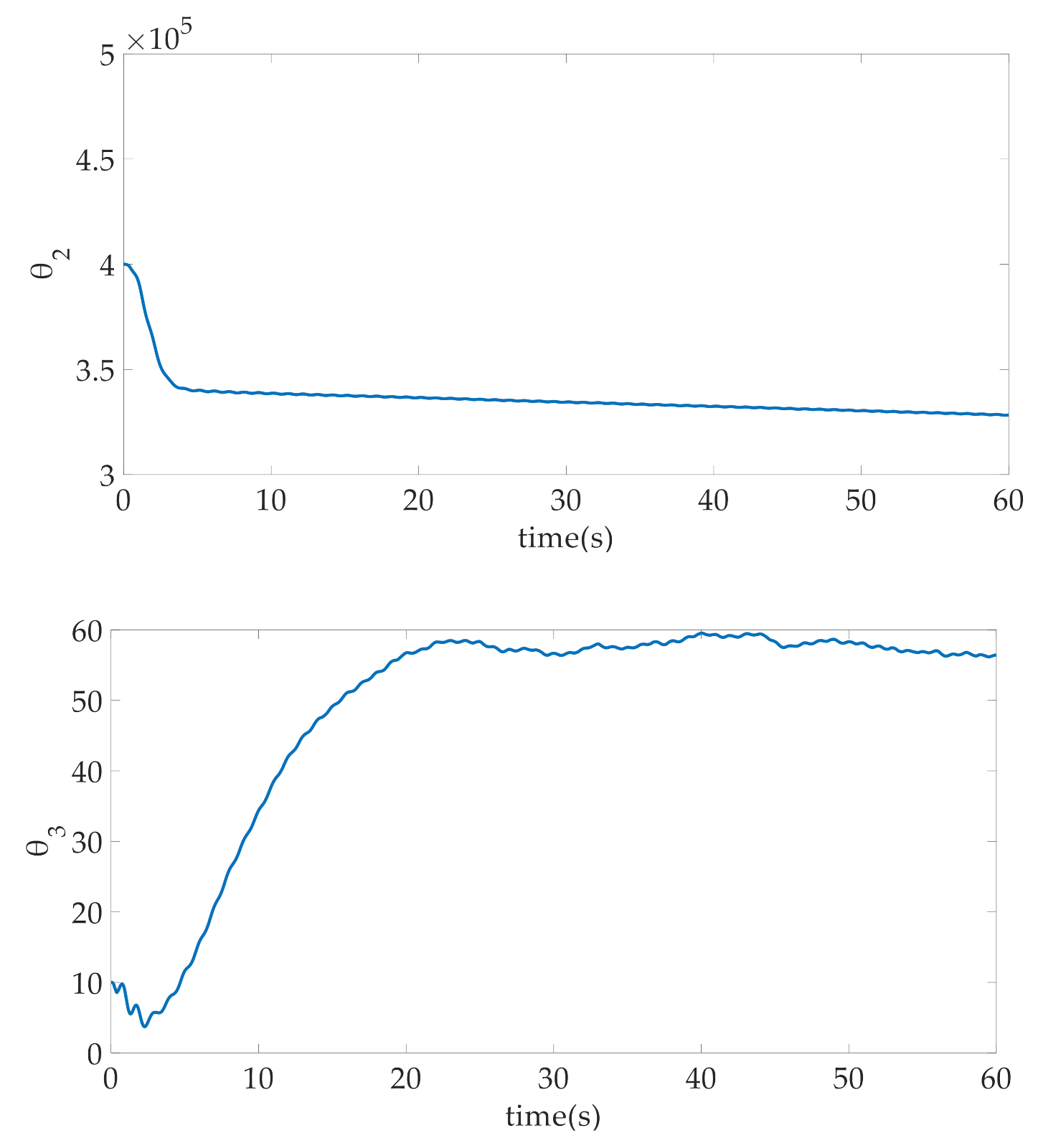
3.1. Composite Parameter Adaptation
3.2. Controller Design
3.3. Closed-Loop Stability Analysis
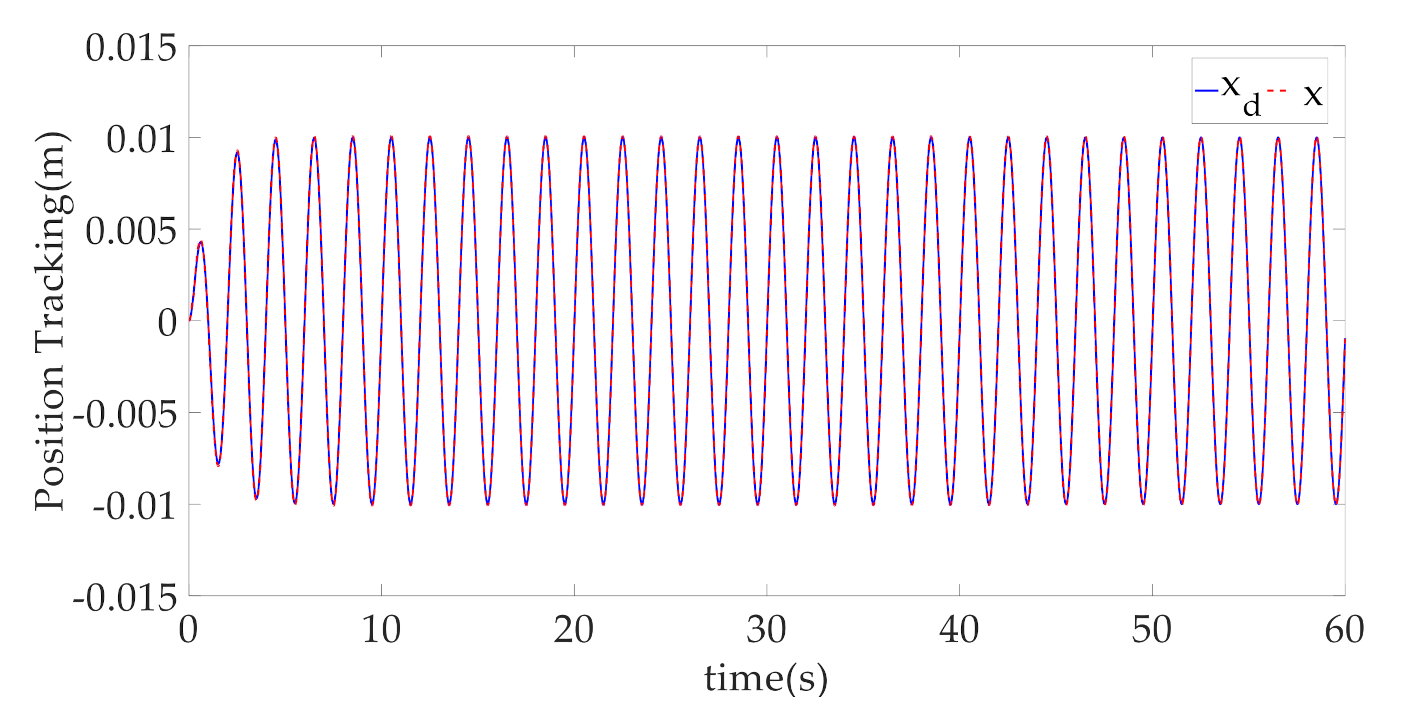
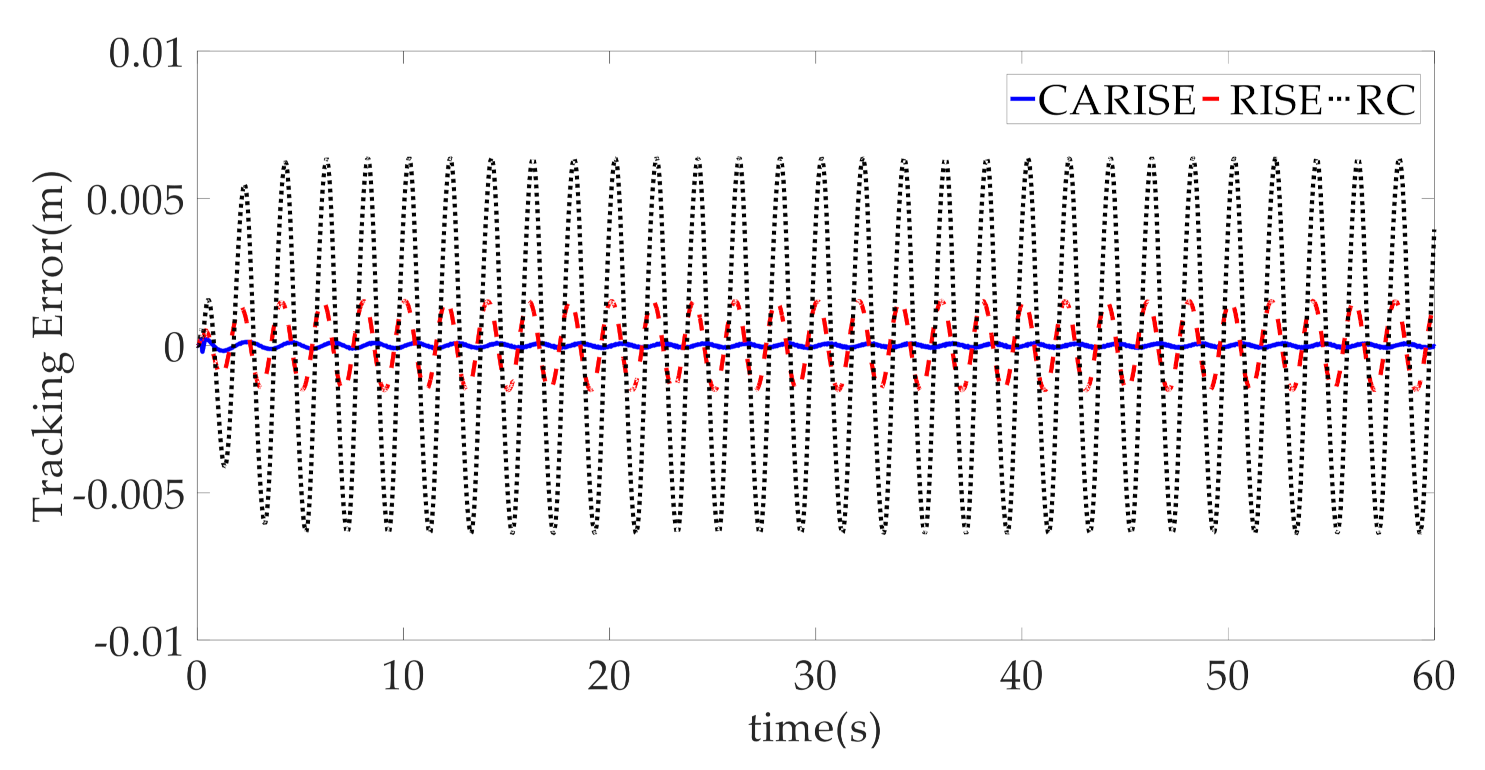
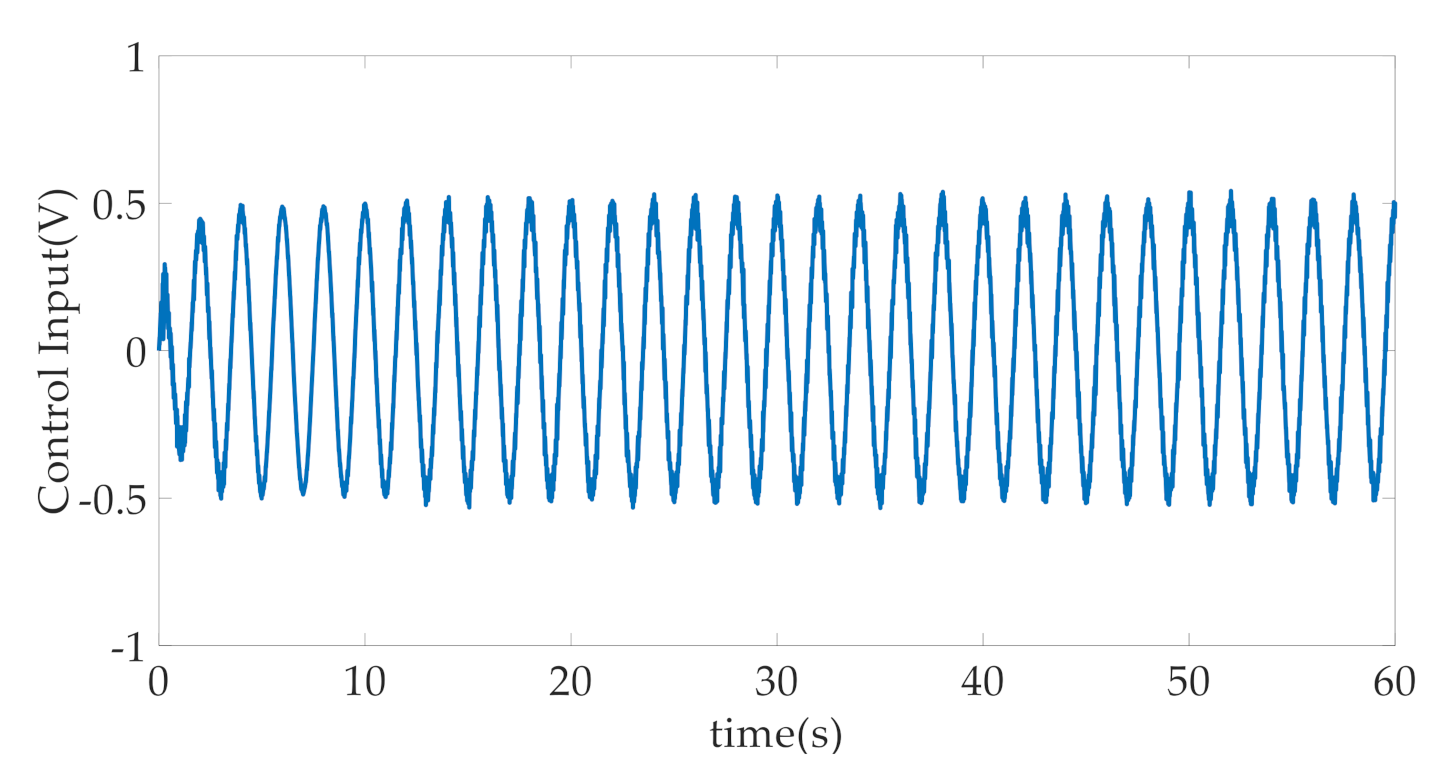
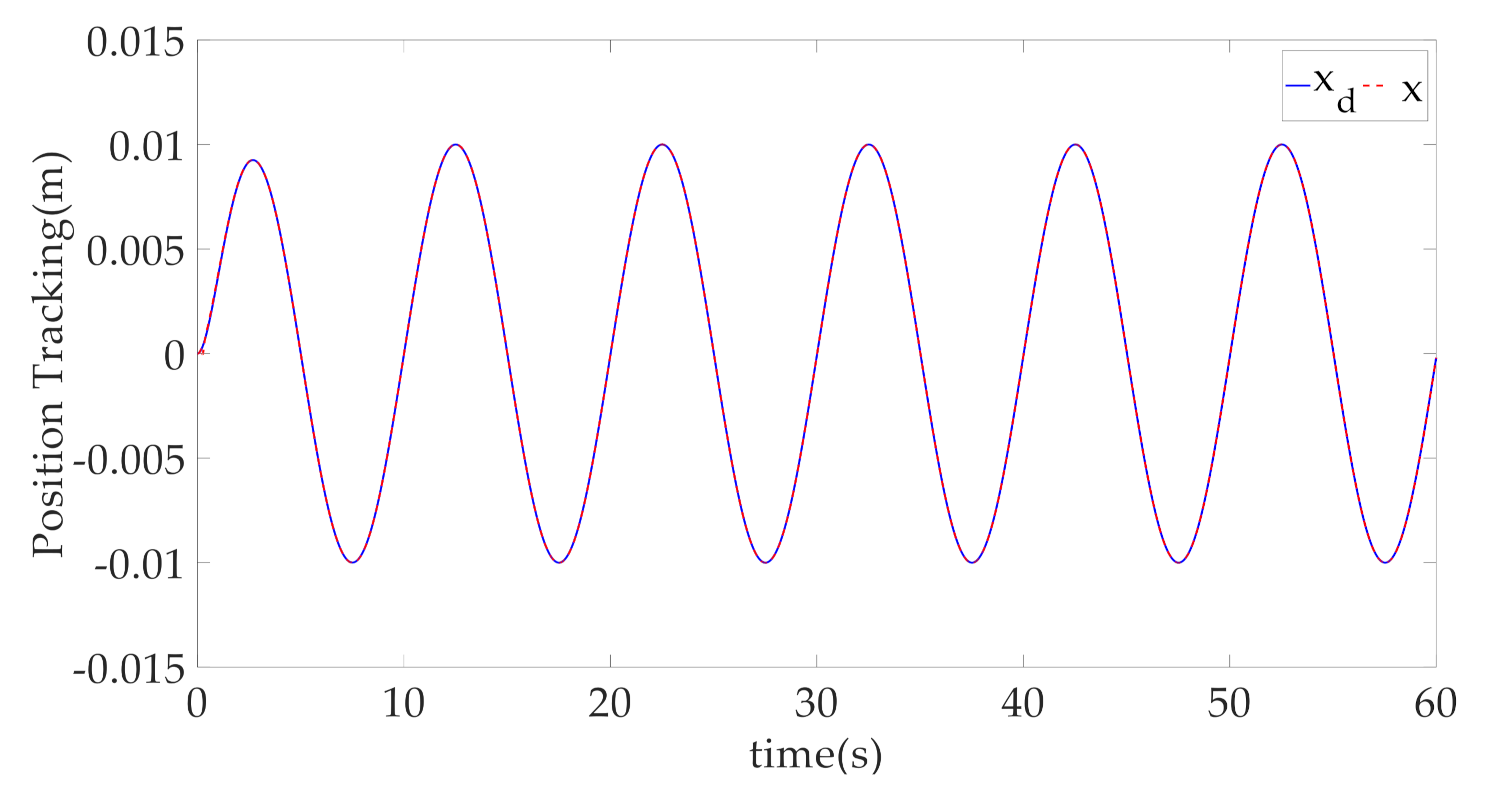
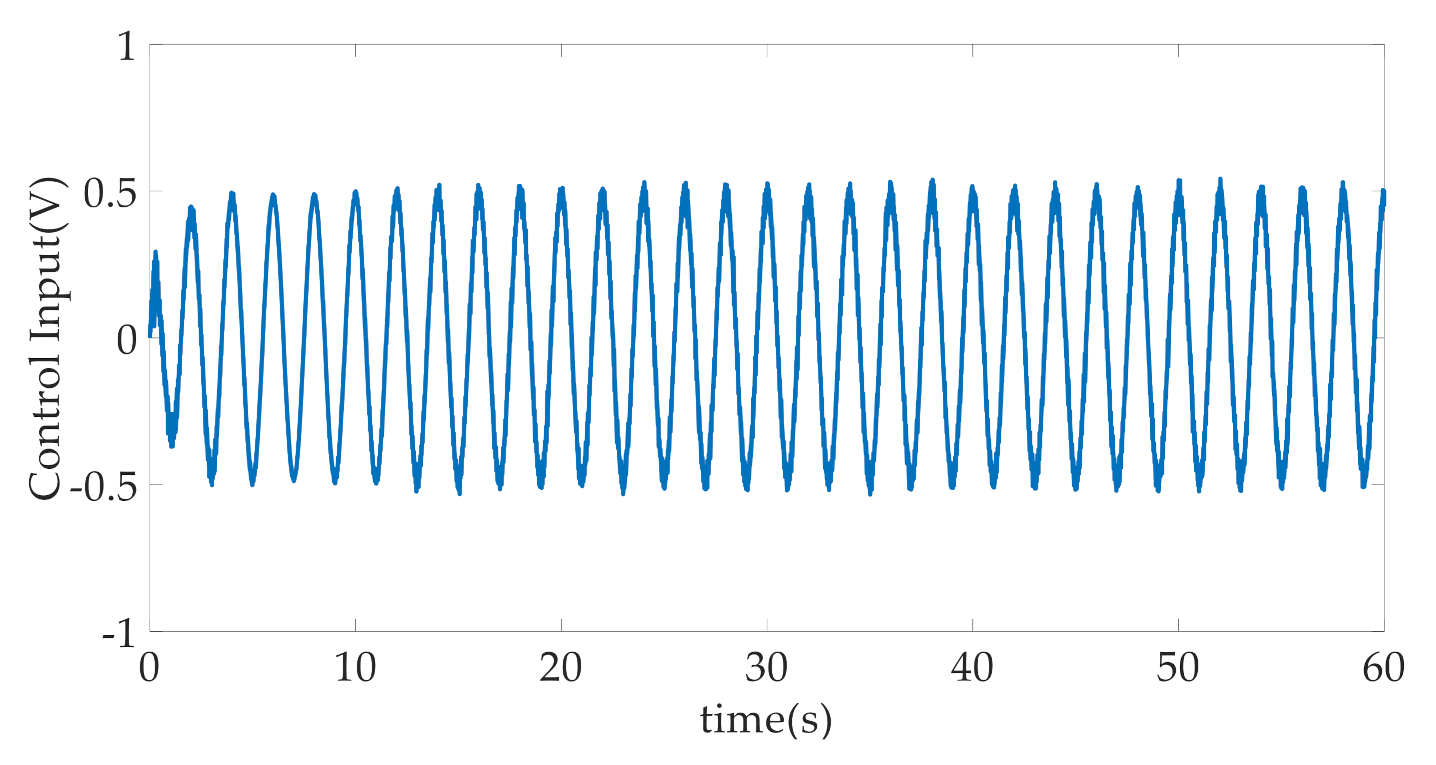
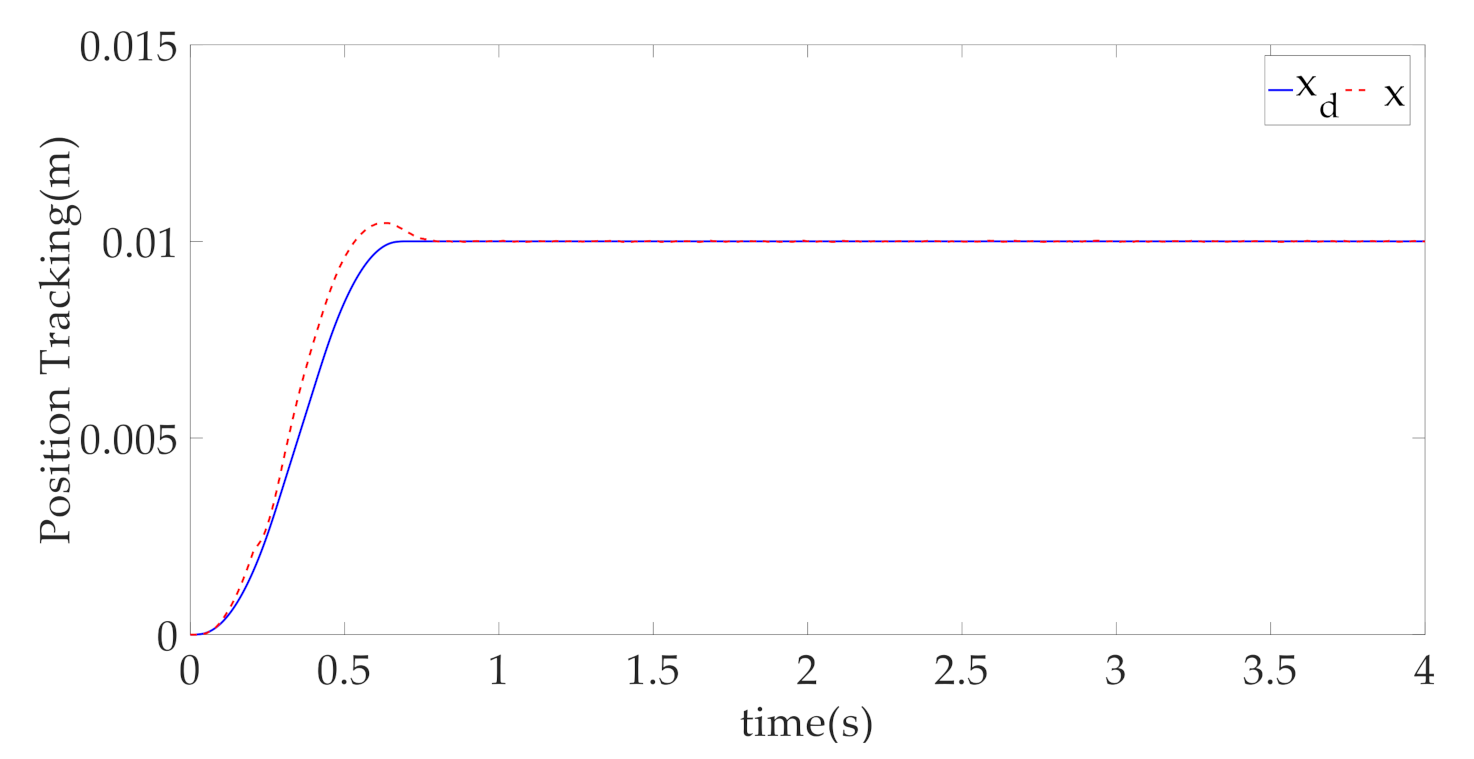
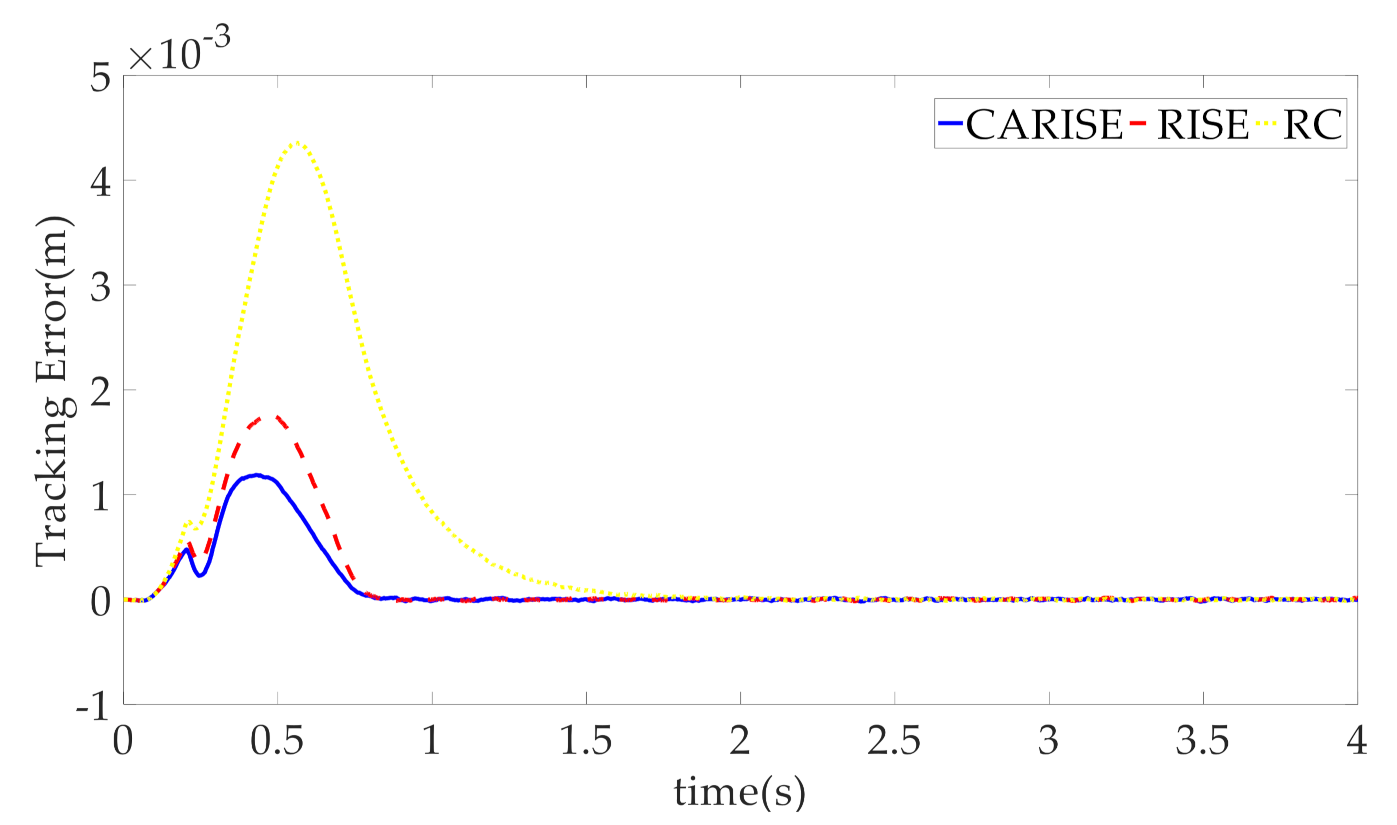
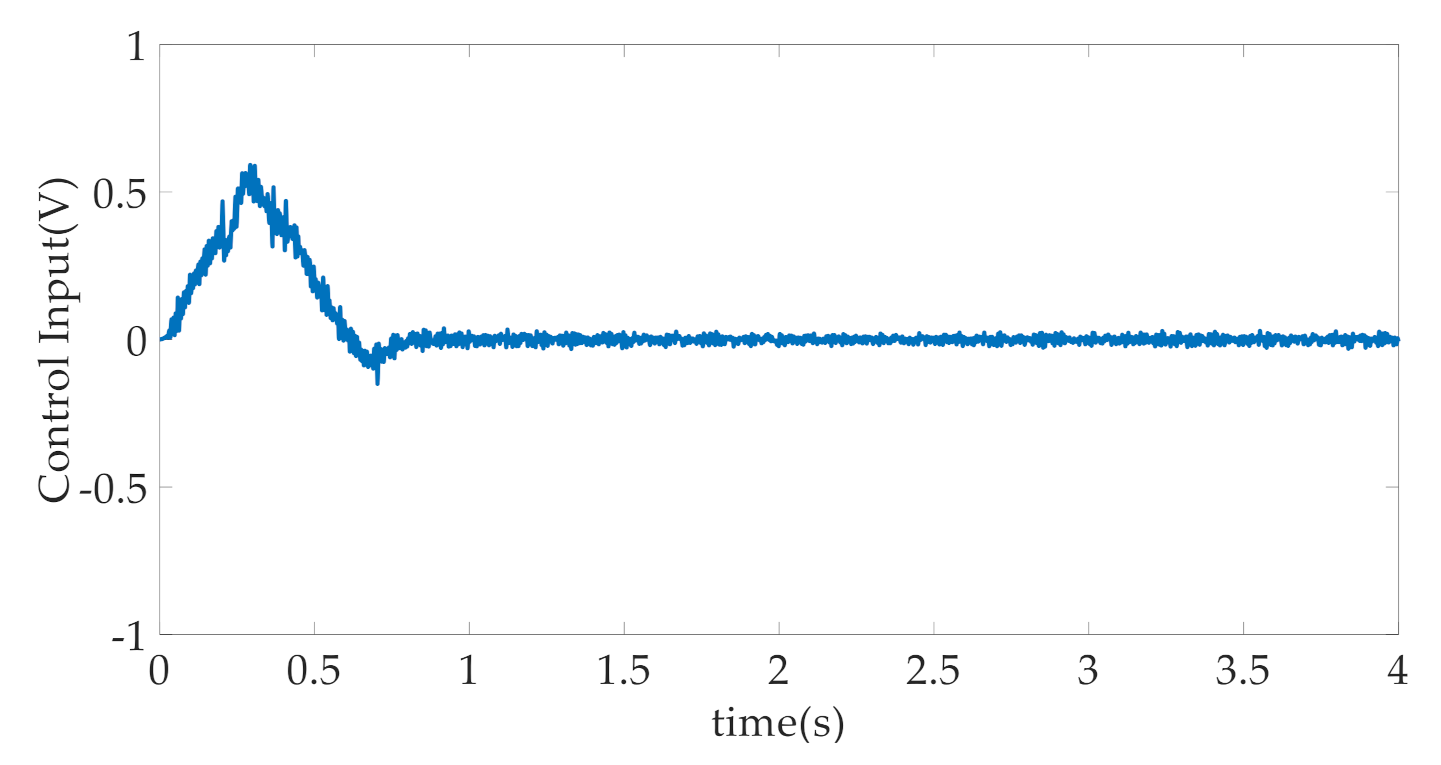
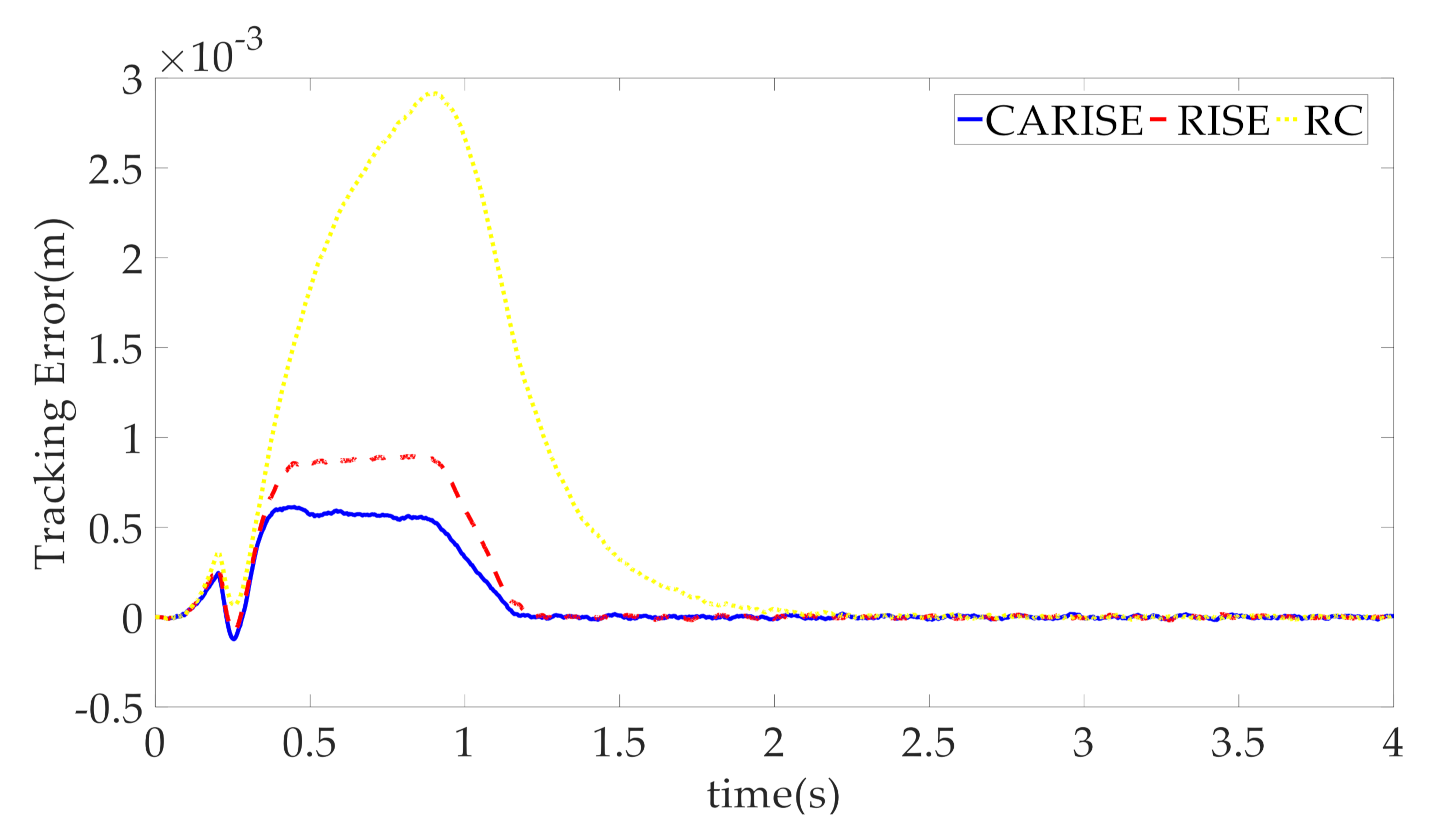
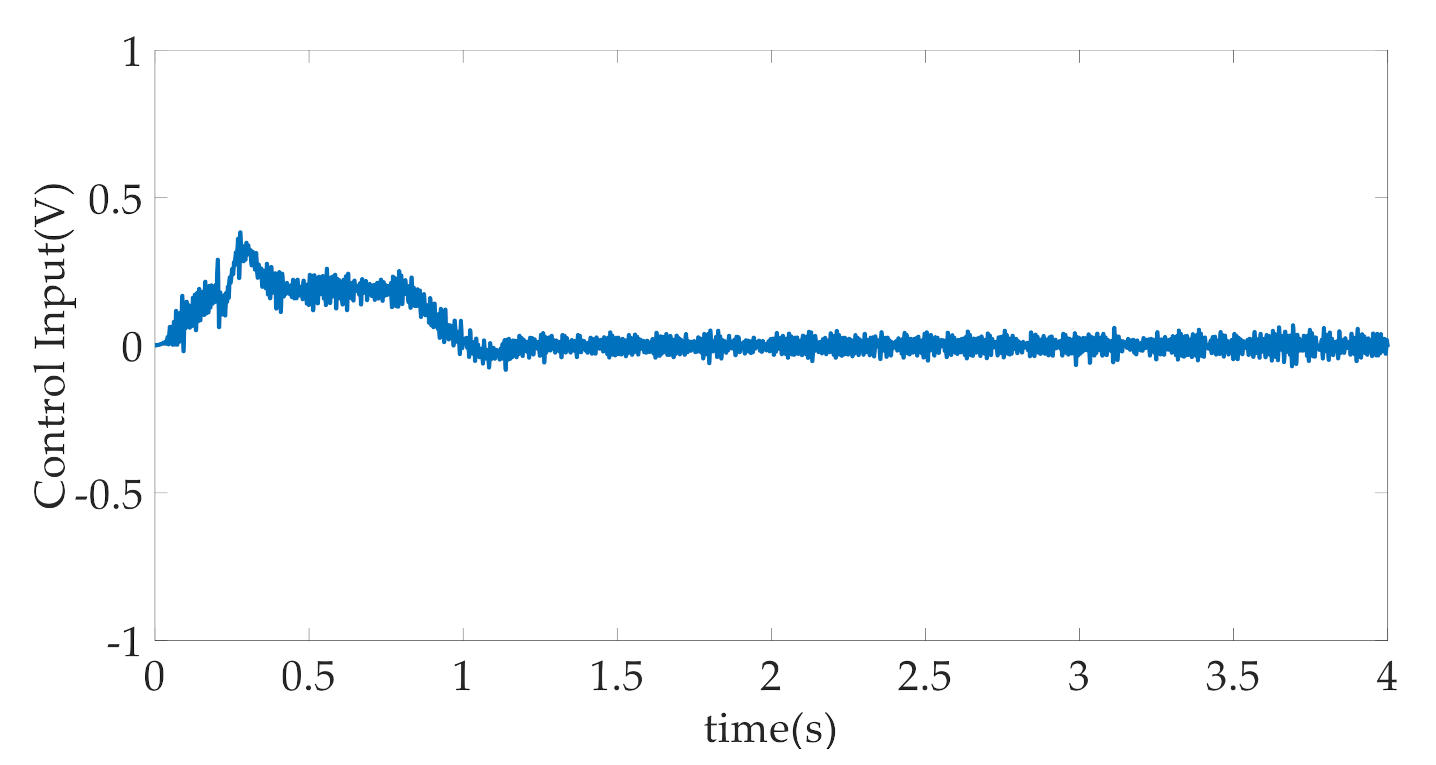
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
- (1)
- CARISE: The RISE-based composite adaptive controller is proposed in this paper and described in Section 3, whose control parameters are given by , , , , , , , and .
- (2)
- RISE: This is the RISE-based controller without the composite adaptive law. In order to ensure the fairness of the comparison, the controller parameters , , , , and are the same as CARISE, and adaptive gain matrix and other relevant parameters are given by , , .
- (3)
- RC: This is the linear robust controller introduced in [32]. Additionally, for the convenience of comparing the controller performance, the parameters are the same as CARISE. Therefore, the controller parameters , , and are the same as CARISE, and RISE gain coefficients and adaptive gain coefficients are given by , , , , .
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, J.; Jiao, Z.; Yao, B.; Shang, Y.; Dong, W. Nonlinear adaptive robust force control of hydraulic load simulator. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2012, 25, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yuan, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, W. Application of multi-objective controller to optimal tuning of PID gains for a hydraulic turbine regulating system using adaptive grid particle swam optimization. ISA Trans. 2015, 56, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merritt, H. Hydraulic Control Systems; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, C.; Yao, J. Valve deadzone/backlash compensation for lifting motion control of hydraulic manipulators. Machines 2021, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formato, G.; Romano, R.; Formato, A.; Sorvari, J.; Koiranen, T.; Pellegrino, A.; Villecco, F. Fluid-structure interaction modeling applied to peristaltic pump flow simulations. Machines 2019, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gusustavo, C.; Nariman, S. Hydrostatic Transmissions and Actuators; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Joel, R.S. The F-18 Systems Research Aircraft Facility; NASA Technical Memorandum; NASA: Hampton, VA, USA, 1992.
- Robert, N. Performance of an Electro-Hydrostatic Actuator on the F-18 Systems Research Aircraft; NASATM-97-206224; NASA: Hampton, VA, USA, 1997.
- Stephen, C.J. Flight Test Experience with an Electromechanical Actuator on the F-18 Systems Research Aircraft; NASA: Hampton, VA, USA, 1998.
- Tessari, F.; Galluzzi, R.; Tonoli, A.; Amati, N.; Milandri, G.; Laffranchi, M.; De Michieli, L. An integrated, back-drivable electro-hydrostatic actuator for a knee prosthesis. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference for Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, New York, NY, USA, 29 November–1 December 2020; pp. 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyon, S.H.; Tanimoto, S.; Asao, S. Toward compliant, fast, high-precision, and low-cost manipulator with hydraulic hybrid servo booster. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Yu, T.; Jiao, Z.; Li, Y. Active load-sensitive electro-hydrostatic actuator for more electric aircraft. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, S.; Goldenberg, A. Design of a new high performance electrohydraulic actuator. In IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics; AIM: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, Z. Design, analysis, and verification of an electro-hydrostatic actuator for distributed actuation system. Sensors 2020, 20, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helian, B.; Chen, Z.; Yao, B. Precision motion control of a servomotor-pump direct-drive electrohydraulic system with a nonlinear pump flow mapping. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 8638–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.M.; Zhao, S.D.; Wei, S.G. Application of self-tuning fuzzy PID controller for a SRM direct drive volume control hydraulic press. Control Eng. Pract. 2009, 17, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.G.; Wang, J.; Wei, W. Model predictive control of servo motor driven constant pump hydraulic system in injection molding process based on neurodynamic optimization. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. C 2014, 15, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Zhang, J.; Xu, B.; Cheng, M.; Pan, M. Energy efficiency improvement of heavy-load mobile hydraulic manipulator with electronically tunable operating modes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 188, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Shi, Y.; Burton, R. Modeling and robust discrete-time sliding-mode control design for a fluid power electrohydraulic actuator (EHA) system. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyon, S.H.; Taniai, Y.; Hiranuma, K.; Yasunaga, K.; Mizui, H. Overpressure Compensation for Hydraulic Hybrid Servo Booster Applied to Hydraulic Manipulator. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.K.; Nam, D.N.C.; Jin, M. Adaptive backstepping control of an electrohydraulic actuator. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippalgaonkar, R.; Ivantysynova, M. Optimal power management of hydraulic hybrid mobile machines-Part I: Theoretical studies, modeling and simulation. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control Trans. ASME 2016, 138, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, B.; Dawson, D.M.; de Queiroz, M.S.; Chen, J. A continuous asymptotic tracking control strategy for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 2004, 49, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Jiao, Z.; Ma, D.; Yan, L. High-accuracy tracking control of hydraulic rotary actuators with modeling uncertainties. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Deng, W.; Jiao, Z. RISE-Based Adaptive Control of Hydraulic Systems with Asymptotic Tracking. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2017, 14, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Yao, J. Adaptive integral robust control and application to electromechanical servo systems. ISA Trans. 2017, 67, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatlicioglu, E. Adaptive control of non-linear teleoperation systems in the presence of additive input and output disturbances. Int. J. Robot. Autom. 2010, 25, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.C.; Chen, C.L. Dynamic controller design for a class of nonlinear uncertain systems subjected to time-varying disturbance. Nonlinear Dyn. 2009, 57, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Mohseni, K. Bioinspired hydrodynamic force feedforward for autonomous underwater vehicle control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, H.; Bing, C.; Zhang, Q. Asymptotic tracking control scheme for mechanical systems with external disturbances and friction. Neurocomputing 2010, 73, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Jiang, Y.; He, W.; Na, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, B. Adaptive parameter estimation and control design for robot manipulators with finite-time convergence. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 8112–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yao, J.; Deng, W. Output feedback adaptive super-twisting sliding mode control of hydraulic systems with disturbance compensation. ISA Trans. 2021, 109, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| m (kg) | 30 | V01 (m3) | 3.981 × 10−5 |
| B () | 400 | D (cc/rev) | 18 |
| A (m2) | 9.0478 × 10−4 | km (rpm/V) | 200 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, Y.; Yang, X.; Deng, W.; Yao, J. RISE-Based Composite Adaptive Control of Electro-Hydrostatic Actuator with Asymptotic Stability. Machines 2021, 9, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9090181
Ge Y, Yang X, Deng W, Yao J. RISE-Based Composite Adaptive Control of Electro-Hydrostatic Actuator with Asymptotic Stability. Machines. 2021; 9(9):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9090181
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Yaowen, Xiaowei Yang, Wenxiang Deng, and Jianyong Yao. 2021. "RISE-Based Composite Adaptive Control of Electro-Hydrostatic Actuator with Asymptotic Stability" Machines 9, no. 9: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9090181
APA StyleGe, Y., Yang, X., Deng, W., & Yao, J. (2021). RISE-Based Composite Adaptive Control of Electro-Hydrostatic Actuator with Asymptotic Stability. Machines, 9(9), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9090181







