Algorithm for Compression Design Allowable Determination of Composite Laminates with Initial Delaminations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Statistical Analysis of Delamination
2.1. Distribution Fitting of Delamination Size
2.2. Goodness-of-Fit Test
2.3. Initial Damage
3. Experimental Study
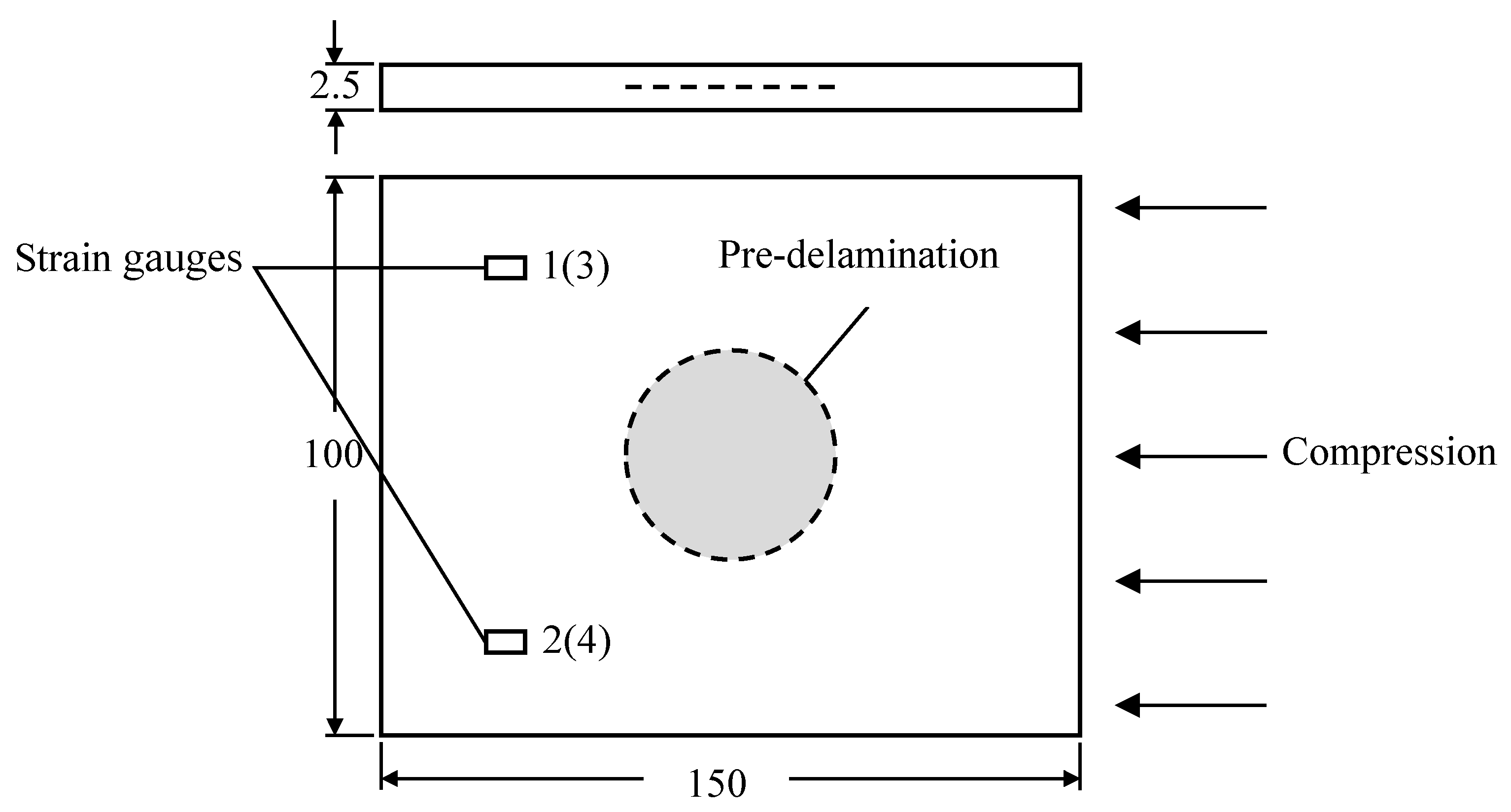
3.1. Material and Specimen
3.2. Compression Test
4. Results and Discussion
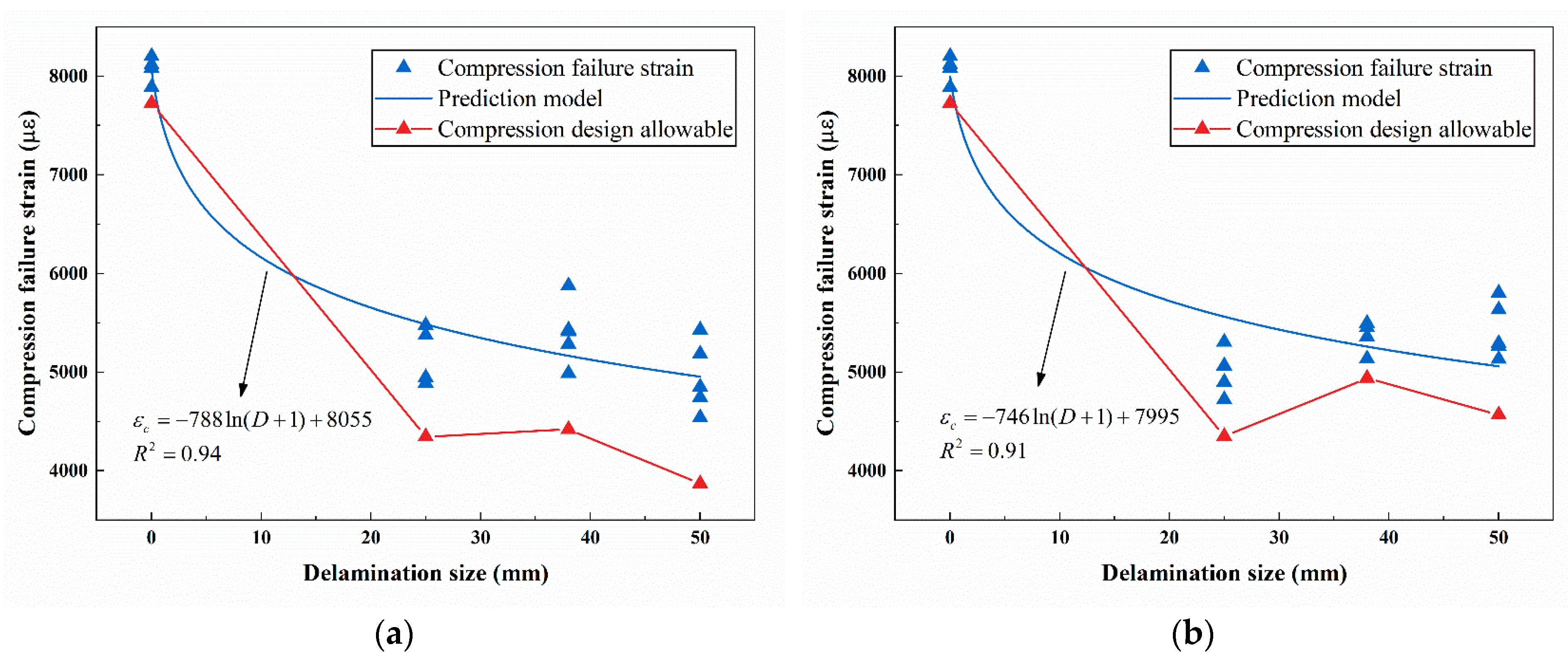
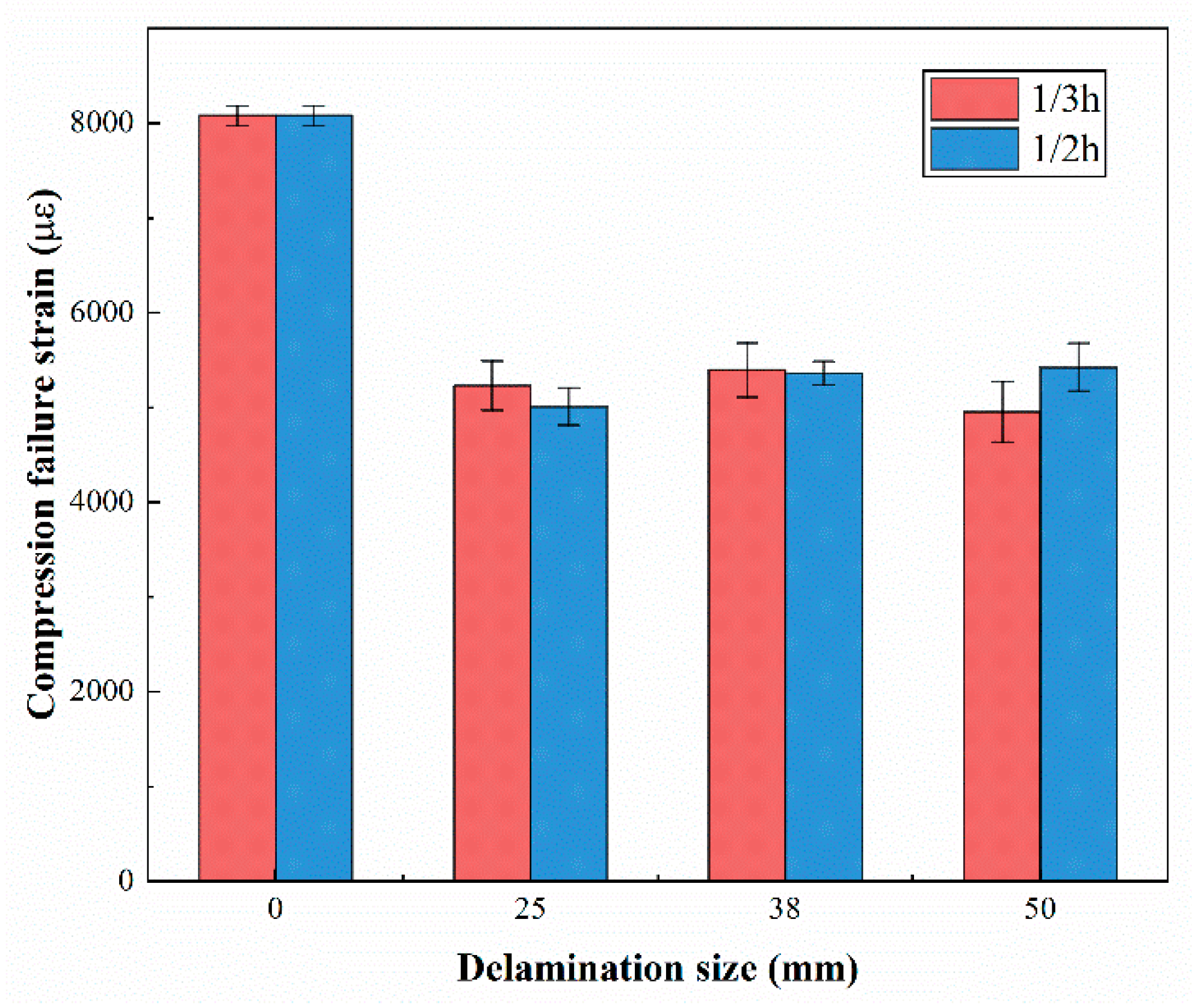
4.1. Effects of Delamination Size and Depth Position
4.2. Compression Failure Strain Estimation
| Algorithm 1. EKF for Parameter Estimation. |
| Initialize with: |
| , |
| Time update: |
| Linearization: |
| Measurement update: |
4.3. Compression Design Allowable Determination
4.4. Comparison
4.5. Implementation of the Developed Design Allowable Determination Algorithm
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Wencheng, L. Principles for determining material allowable and design allowable values of composite aircraft structures. Procedia Eng. 2011, 17, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spendley, P.R. Design Allowables for Composite Aerospace Structures; University of Surrey: Surrey, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mangalgiri, P.D. Design Allowable Considerations for use of Laminated Composites in Aircraft Structures. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2013, 93, 571–592. [Google Scholar]
- MIL-HDBK-17-1F, Composite Materials Handbook, Volume 1 Polymer Matrix Composites Guidelines for Characterisation of Structural Materials; Department of Defense: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- CHM-17, Composite Materials Handbook: Volume 1: Polymer Matrix Composites; SAE International: New York, NY, USA, 2012.
- Vallmajó, O.; Cózar, I.R.; Furtado, C.; Tavares, R.; Arteiro, A.; Turon, A.; Camanho, P.P. Virtual calculation of the B-value allowables of notched composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2019, 212, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, C.; Pereira, L.F.; Tavares, R.P.; Salgado, M.; Otero, F.; Catalanotti, G.; Arteiro, A.; Bessa, M.A.; Camanho, P.P. A methodology to generate design allowables of composite laminates using machine learning. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2021, 233, 111095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.D.; Melo, J.D.D.; Cimini, C.A.; Ridha, M. Evaluation of Notched Strength of Composite Laminates for Structural Design. J. Compos. Mater. 2010, 44, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cózar, I.R.; Turon, A.; González, E.V.; Vallmajó, O.; Sasikumar, A. A methodology to obtain material design allowables from high-fidelity compression after impact simulations on composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 139, 106069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumeri, G.; Abdi, F.; Raju, K.; Housner, J.; Bohner, R.; McCloskey, A. Cost effective computational approach for generation of polymeric composite material allowables for reduced testing. In Advances in Composite Materials—Ecodesign and Analysis; InTech Open: London, UK, 2011; pp. 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, K.; Park, K.J.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, I.-H. Estimation of Composite Laminate Design Allowables Using the Statistical Characteristics of Lamina Level Test Data. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2015, 16, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdi, F.; Clarkson, E.; Godines, C.; DorMohammadi, S. A-B Basis Allowable Test Reduction Approach and Composite Generic Basis Strength Values. In Proceedings of the 18th AIAA Non-Deterministic Approaches Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–8 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Suemasu, H. On the instability of multiple annular delaminations of axisymmetric laminates with arbitrary boundary conditions subjected to transverse load. Compos. Struct. 2020, 251, 112678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluch, A.H.; Falcó, O.; Jiménez, J.L.; Tijs, B.; Lopes, C.S. An efficient numerical approach to the prediction of laminate tolerance to Barely Visible Impact Damage. Compos. Struct. 2019, 225, 111017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köllner, A.; Nielsen, M.W.; Srisuriyachot, J.; Rhead, A.T.; Butler, R. Buckle-driven delamination models for laminate strength prediction and damage tolerant design. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 161, 107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipek, G.; Arman, Y.; Çelik, A. The effect of delamination size and location to buckling behavior of composite materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 155, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharghani, N.; Soares, C.G. Analytical and experimental study of the ultimate strength of delaminated composite laminates under compressive loading. Compos. Struct. 2019, 228, 111355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, Z.; Şahin, M. Buckling behavior and compressive failure of composite laminates containing multiple large delaminations. Compos. Struct. 2009, 89, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Xu, P.; Xia, F.; Liang, H.; Yao, S.; Xue, J. Buckling of composite laminates with multiple delaminations: Part I Theoretical and numerical analysis. Compos. Struct. 2020, 250, 112491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.-H.; Shin, H.; Nam, W.; Om, J.; Jeong, C. Approximation of modified Anderson–Darling test statistics for extreme value distributions with unknown shape parameter. J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.M. A method of two-dimensional one-sided torlerance factors. Acta Aeronaut. Et Astronaut. Sin. 1993, 14, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yao, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B. The effects of delamination deficiencies on compressive mechanical properties of reinforced composite skin structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 155, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Hong, H.; Wang, K.; Zhao, J. Compressive failure analysis for low length-width ratio composite laminates with embedded delamination. Compos. Commun. 2018, 9, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASTM D7137/D7137M-17. Standard Test Method for Compressive Residual Strength Properties of Damaged Polymer Matrix Composite Plates; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D6641/D6641M-16. Standard Test Method for Compressive Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials Using a Combined Loading Compression (CLC) Test Fixture; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhe, L.A.; Pl, B.; Ns, C. Effect of delamination on the flexural response of [+45/45/0]2s carbon fibre reinforced polymer laminates. Compos. Struct. 2019, 209, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, G.W.; Hu, B.; Butler, R.; Almond, D.P.; Wright, J.E. Nonlinear Modeling of Delaminated Struts. AIAA J. 2004, 42, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H∞, and Nonlinear Approaches; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 298–305. [Google Scholar]

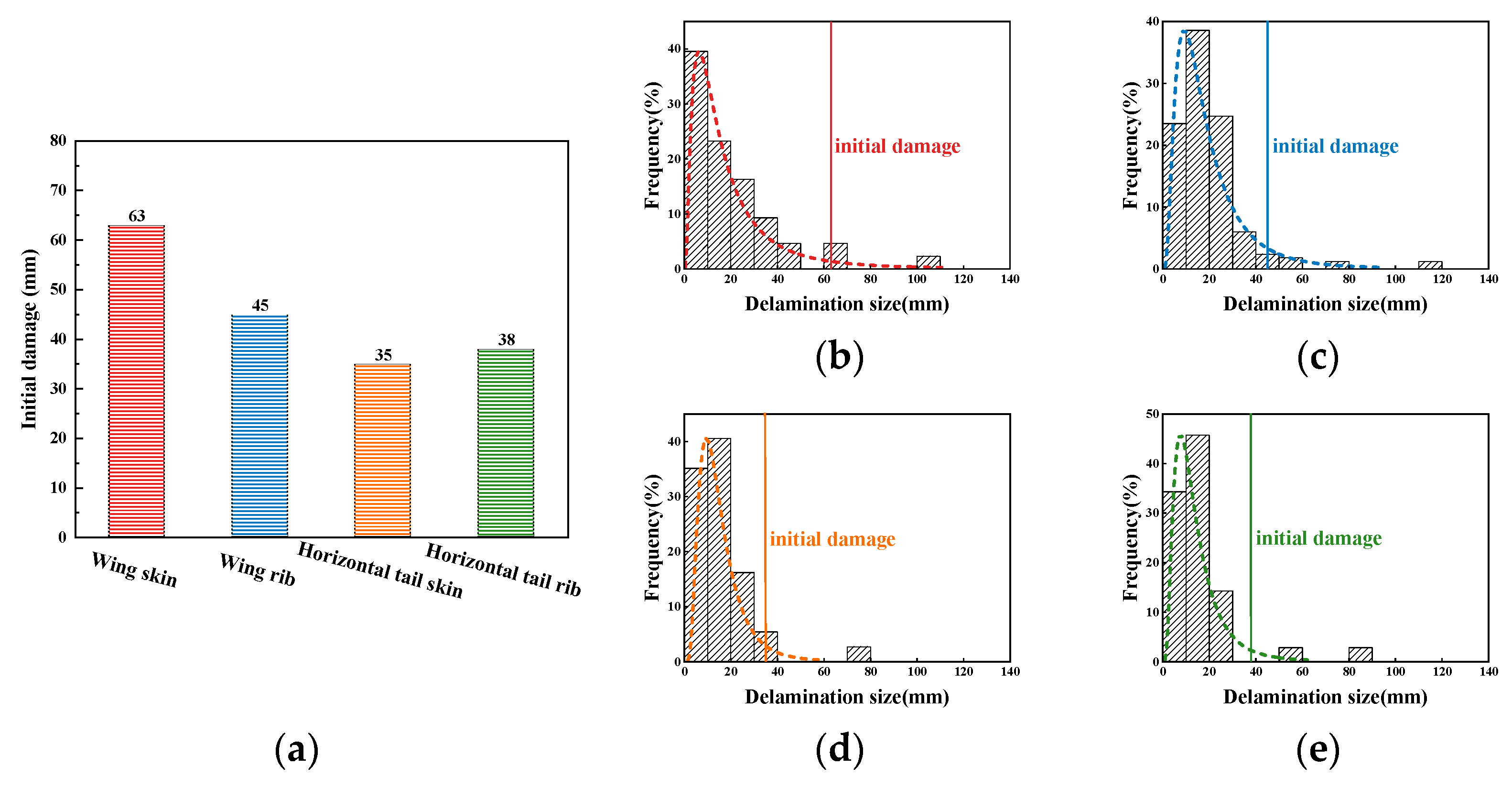
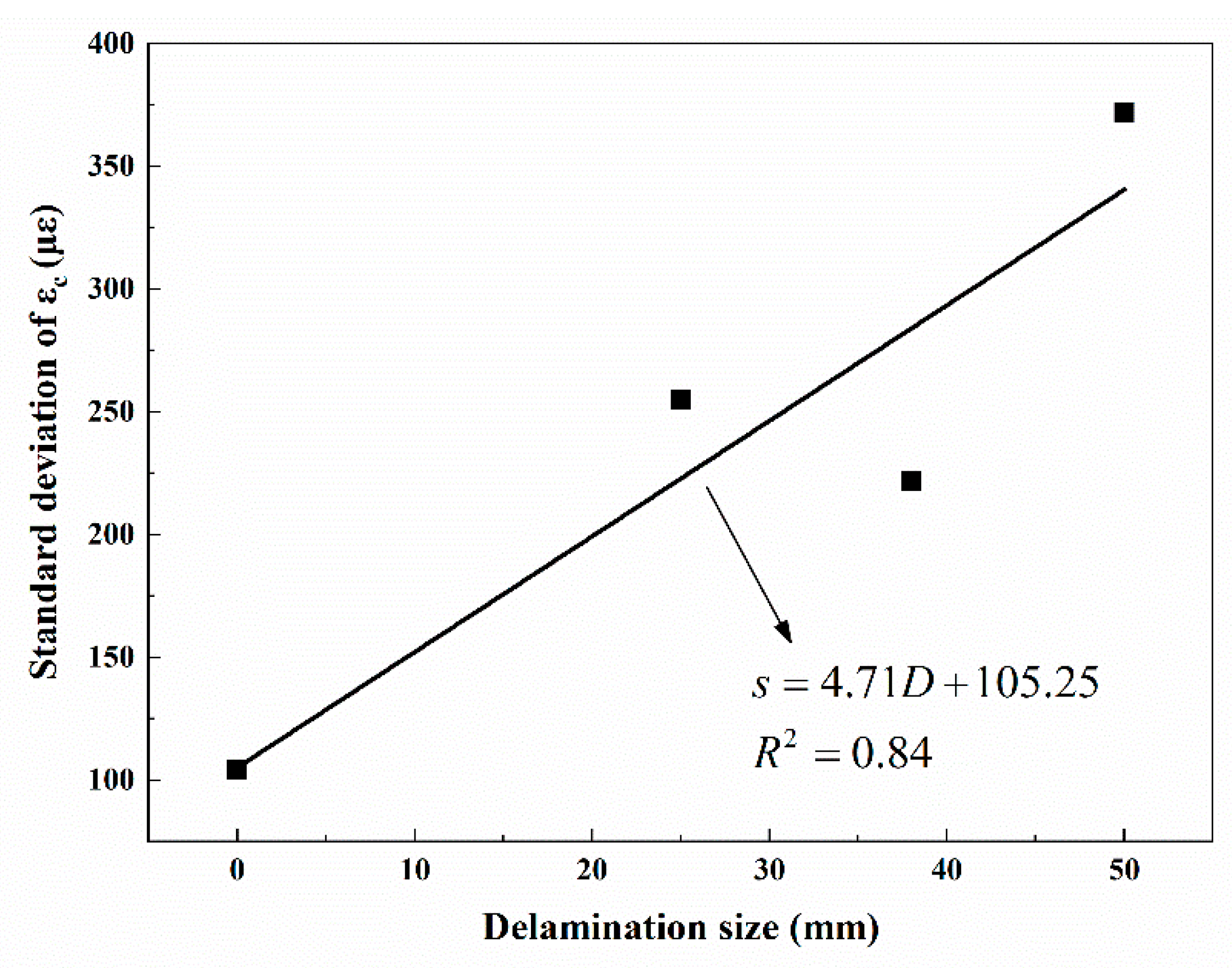
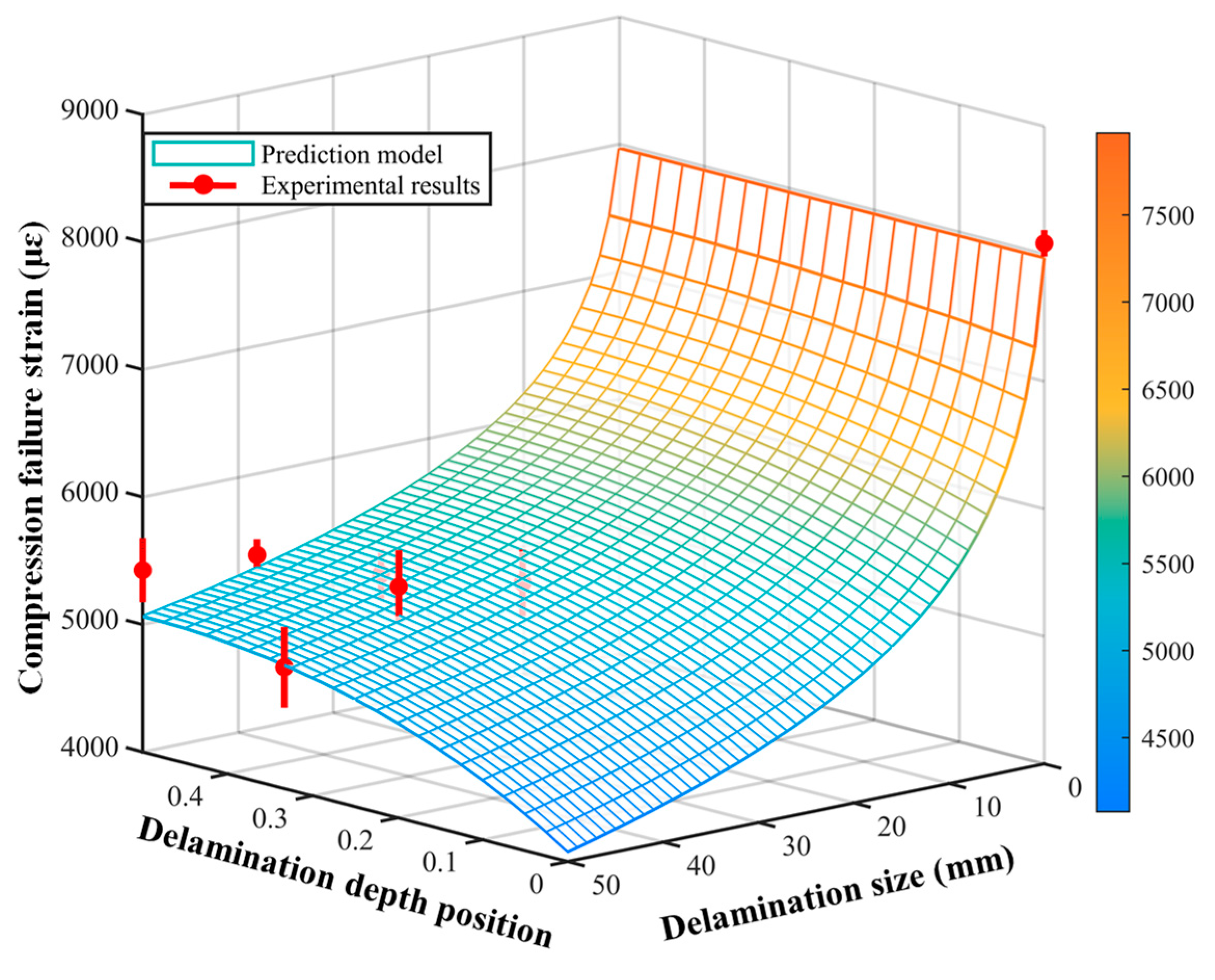
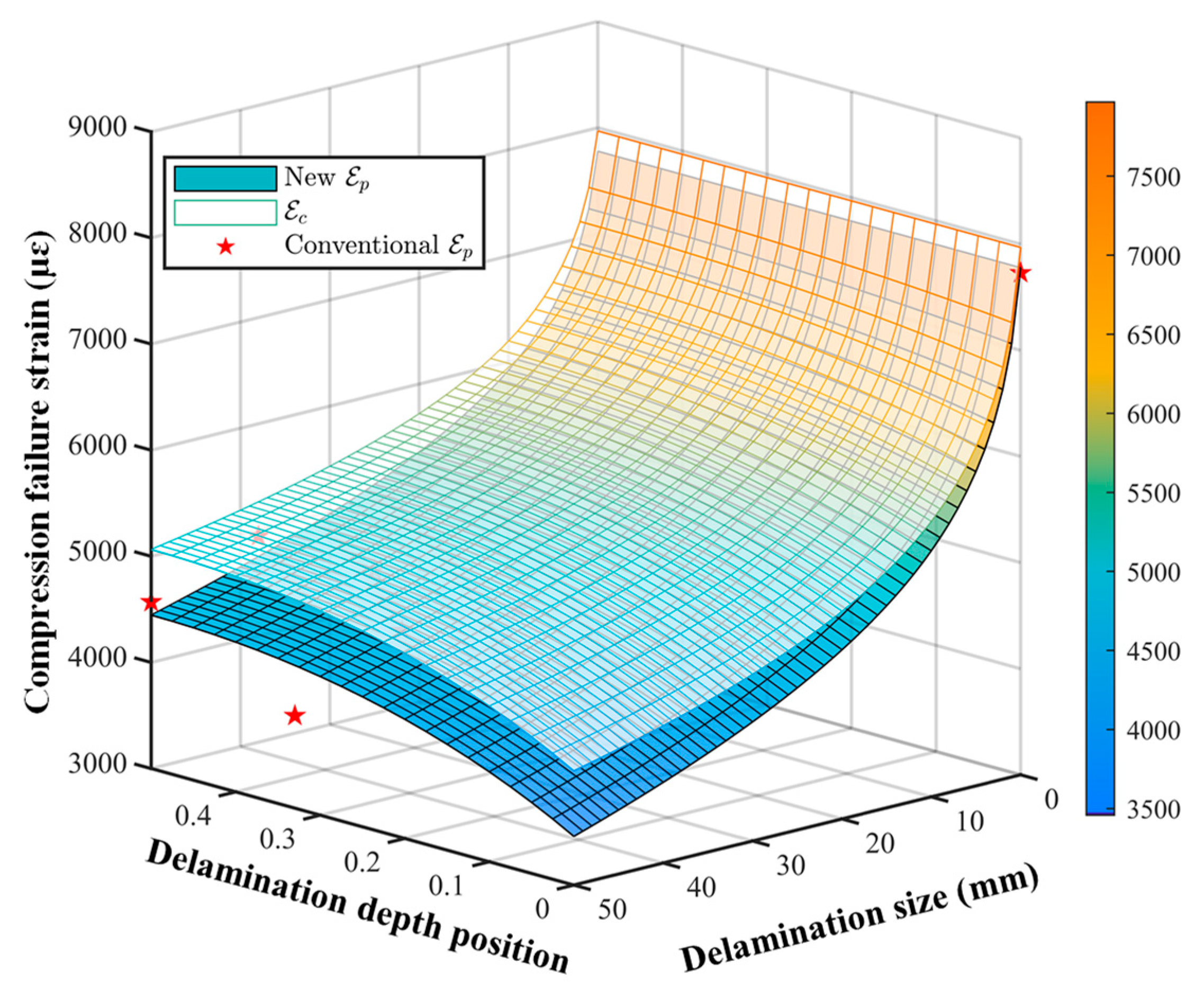
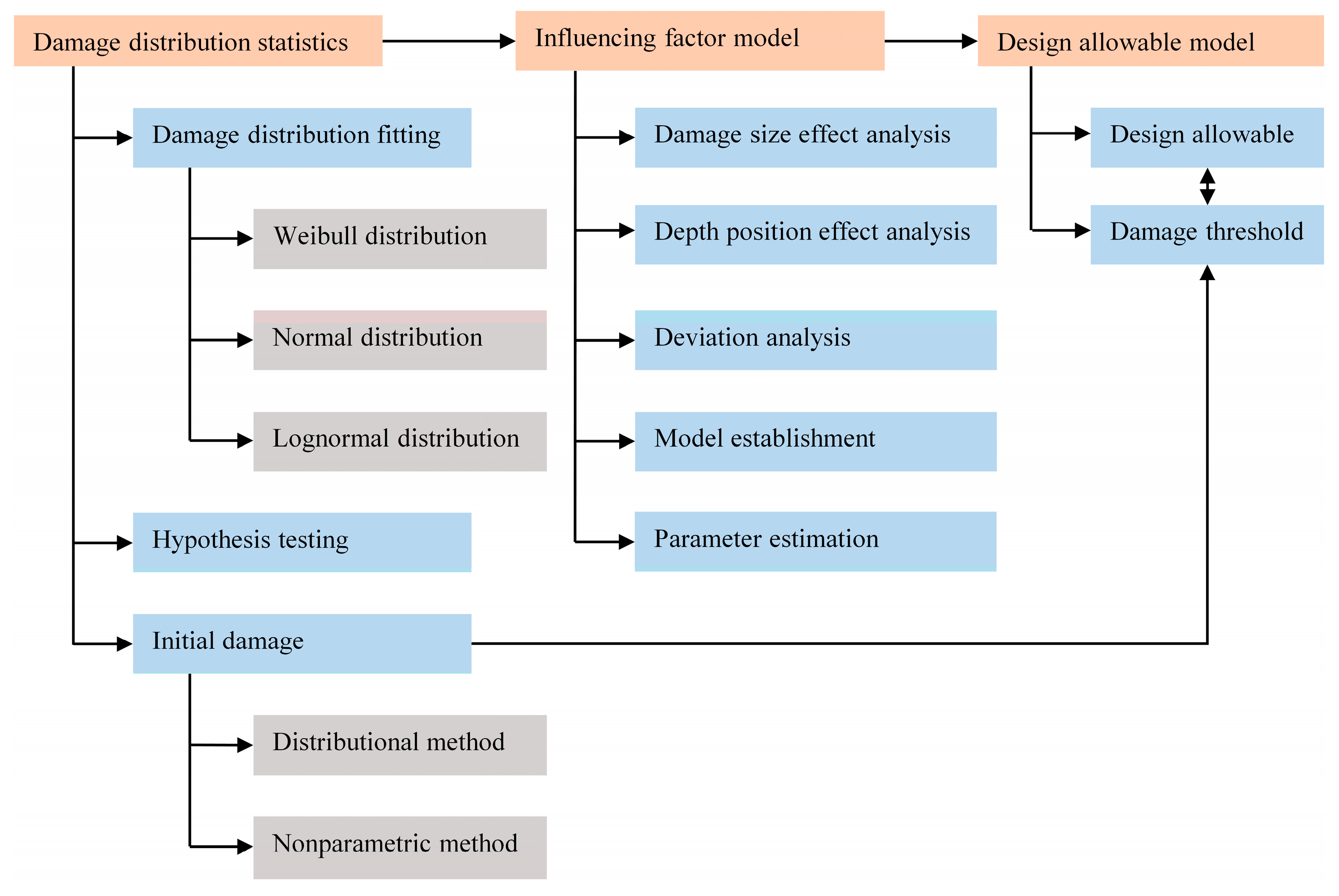
| Distribution | Wing Skin | Wing Rib | Horizontal Tail Skin | Horizontal Tail Rib | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weibull | 21.34 | 22.13 | 17.54 | 16.52 | |
| 1.16 | 1.25 | 1.51 | 1.30 | ||
| 0.97 (accept) | 0.95 (reject) | 0.90 (reject) | 0.89 (reject) | ||
| Normal | 20.14 | 20.35 | 15.62 | 15.03 | |
| 20.15 | 21.37 | 12.33 | 14.85 | ||
| 0.83 (reject) | 0.79 (reject) | 0.79 (reject) | 0.70 (reject) | ||
| Lognormal | 2.62 | 2.73 | 2.57 | 2.46 | |
| 0.88 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 0.65 | ||
| 0.99 (accept) | 0.99 (accept) | 0.94 (accept) | 0.96 (accept) | ||
| Composite materials | ZT7H/5429 | ||||
| Stacking sequence | [-45/0/45/90/0/0/-45/90/45/0]S | ||||
| Dimensions (mm3) | 150 × 100 × 2.5 | ||||
| Delamination size (mm) | 0 | Φ25 | Φ38 | Φ50 | |
| Delamination depth position | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | |||
| Number of specimen | 5 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| Parameters | Estimation | Error |
|---|---|---|
| −739 | 3.11 | |
| 1.17 | 0.67 | |
| 7969 | 9.65 |
| Composite Structure | Initial Damage | Compression Design Allowable (με) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size (mm) | Depth Position | ||
| Wing skin | Φ63 | 3934 | |
| Wing rib | Φ45 | 4350 | |
| Horizontal tail skin | Φ35 | 4630 | |
| Horizontal tail rib | Φ38 | 4541 | |
| Delamination | Compression Design Allowable (με) | % Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Point Method | Novel Method | ||
| No delamination | 7729 | 7787 | 0.76 |
| 4347 | 5095 | 17.21 | |
| 4351 | 5175 | 18.95 | |
| 4423 | 4679 | 5.81 | |
| 4940 | 4770 | −3.46 | |
| 3871 | 4377 | 13.07 | |
| 4570 | 4474 | −2.11 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K. Algorithm for Compression Design Allowable Determination of Composite Laminates with Initial Delaminations. Machines 2021, 9, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120307
Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen K. Algorithm for Compression Design Allowable Determination of Composite Laminates with Initial Delaminations. Machines. 2021; 9(12):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120307
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jianchao, Yongbo Zhang, and Ke Chen. 2021. "Algorithm for Compression Design Allowable Determination of Composite Laminates with Initial Delaminations" Machines 9, no. 12: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120307
APA StyleGuo, J., Zhang, Y., & Chen, K. (2021). Algorithm for Compression Design Allowable Determination of Composite Laminates with Initial Delaminations. Machines, 9(12), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120307







