Global Stiffness Modeling of Robot Drilling System Incorporating End-Effector and Arm Flexibility Based on Virtual Joint Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Structure of the Paper
2. The Global Stiffness Modeling of the Robot Drilling System
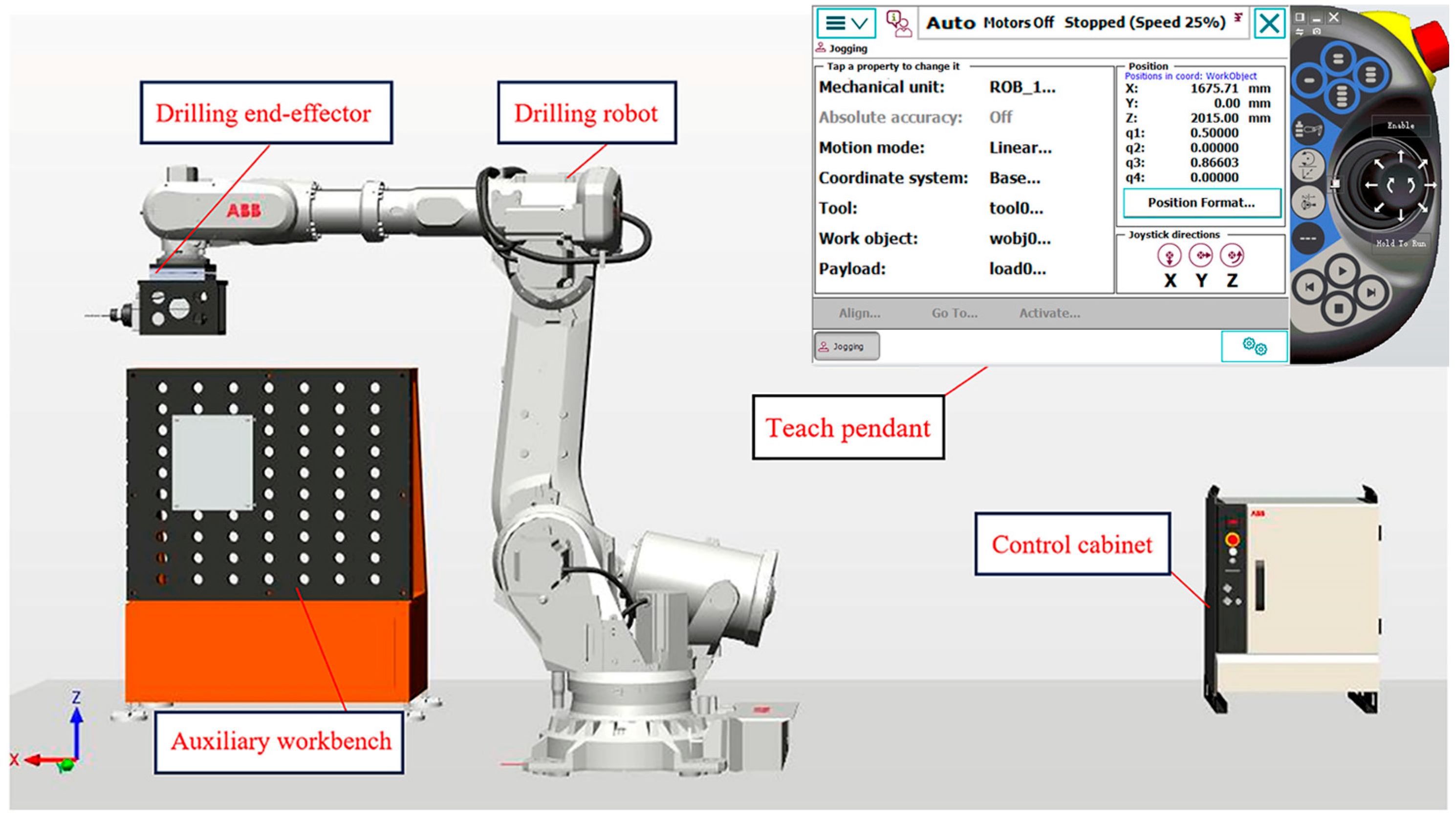
2.1. Robot Drilling Workstation
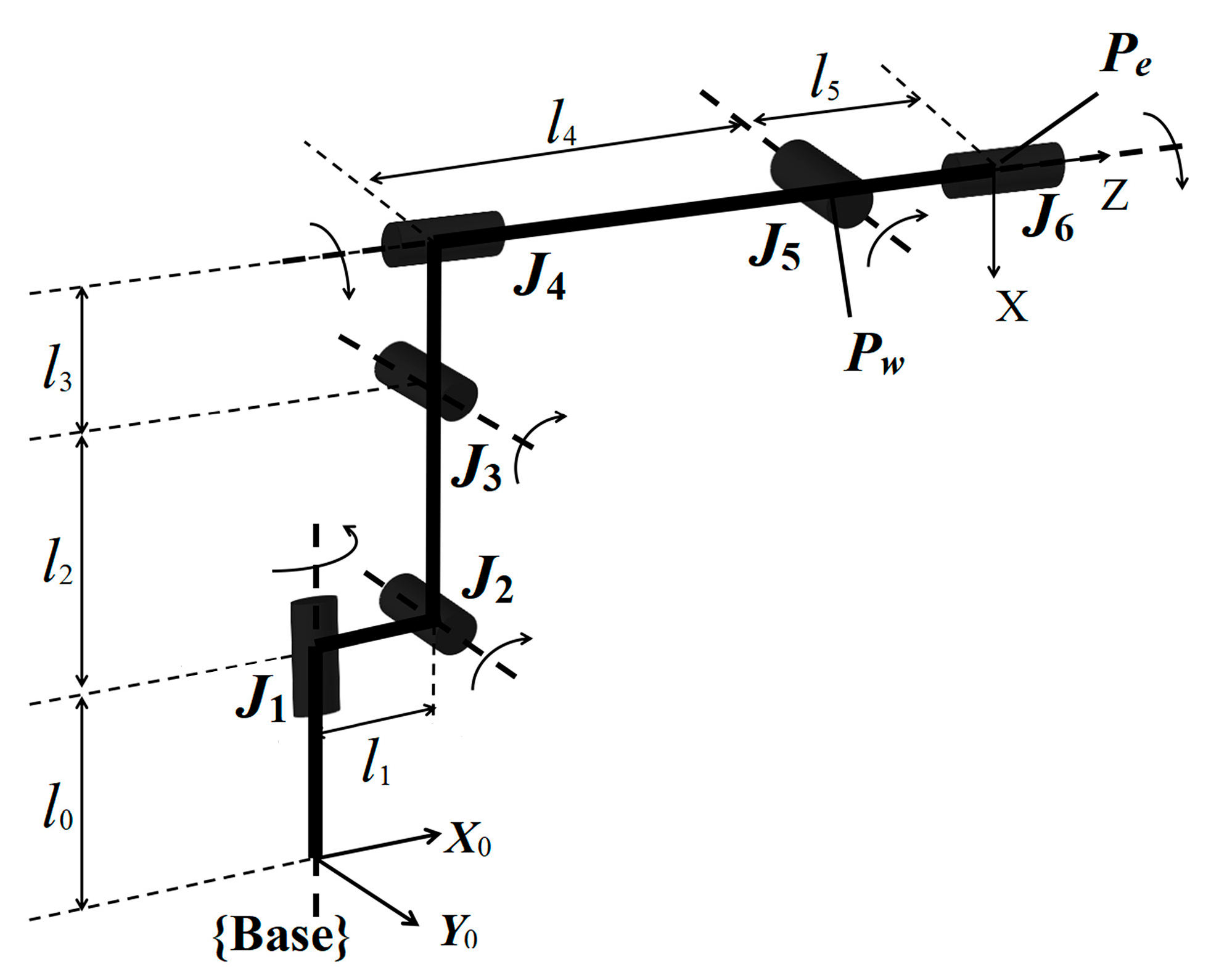
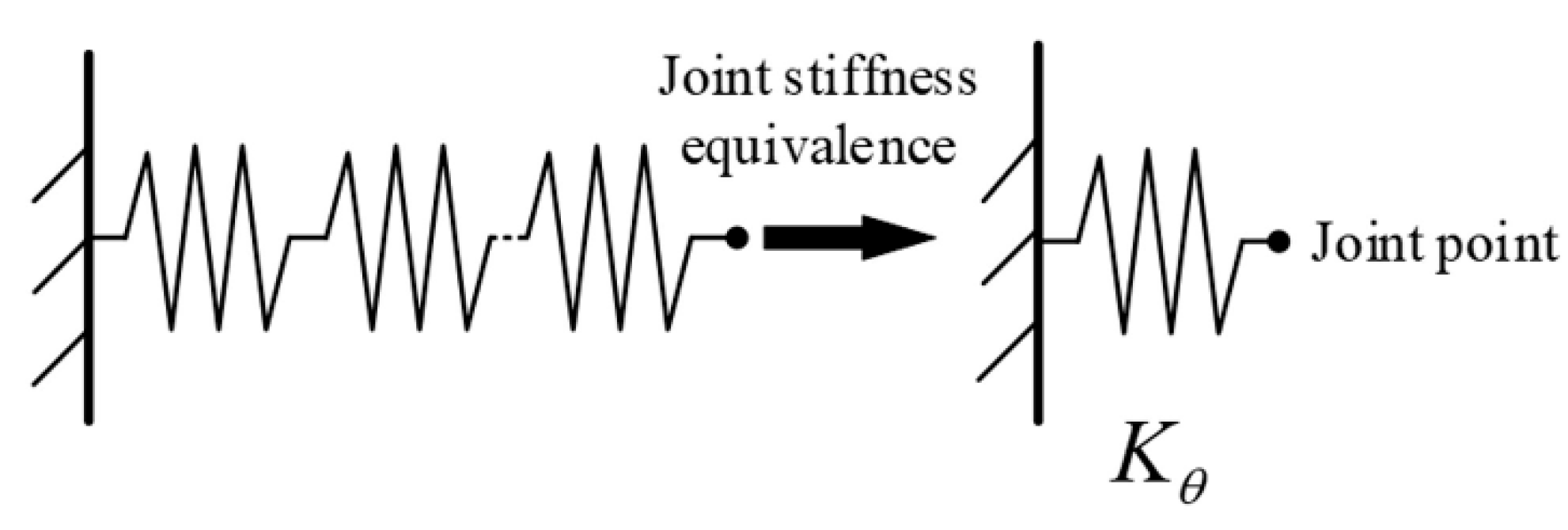
2.2. Joint Stiffness Modeling of Drilling Robot
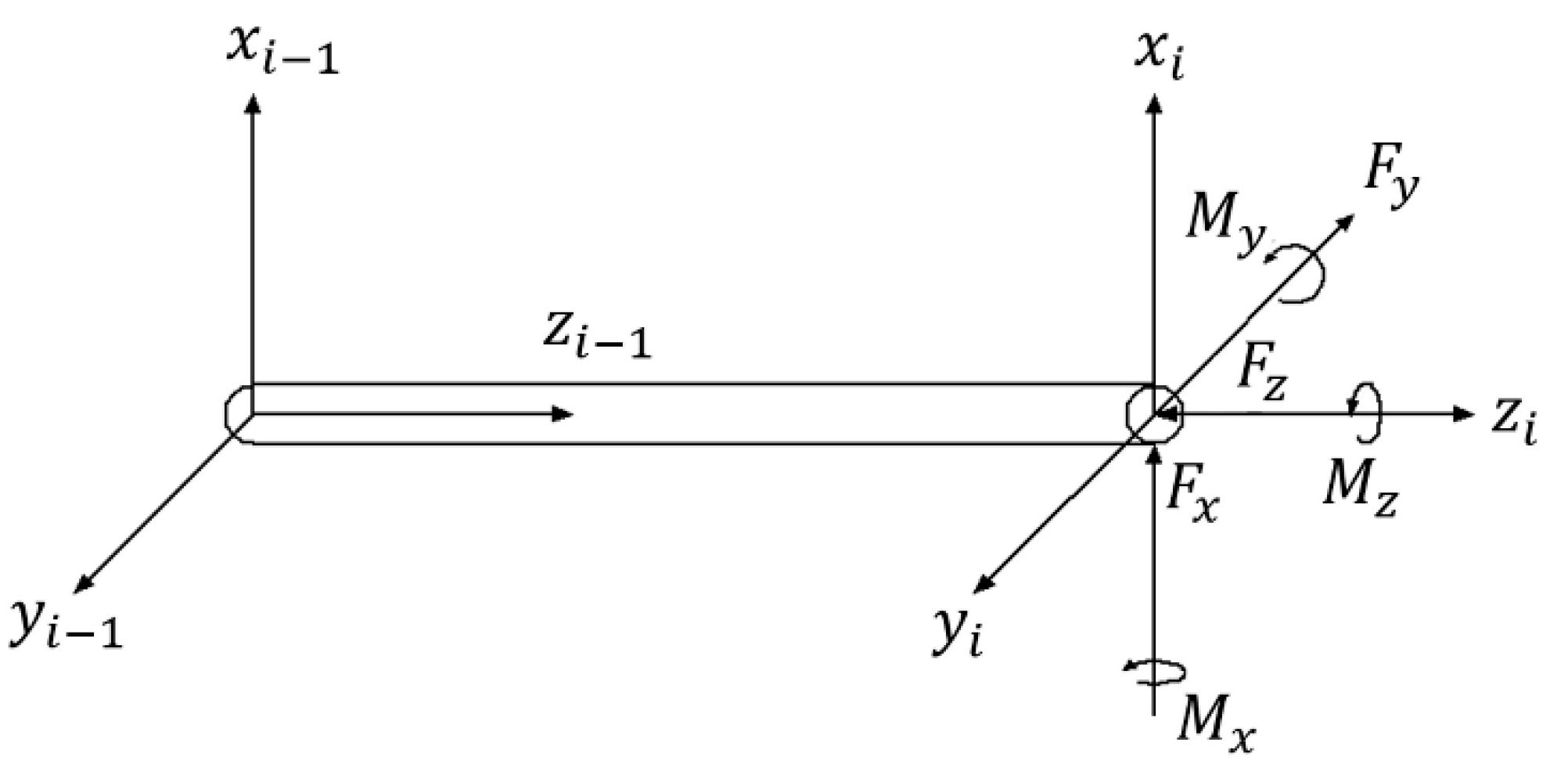
2.3. End-Effector Stiffness Modeling
2.4. The Overall Stiffness Modeling of the Robot Drilling System
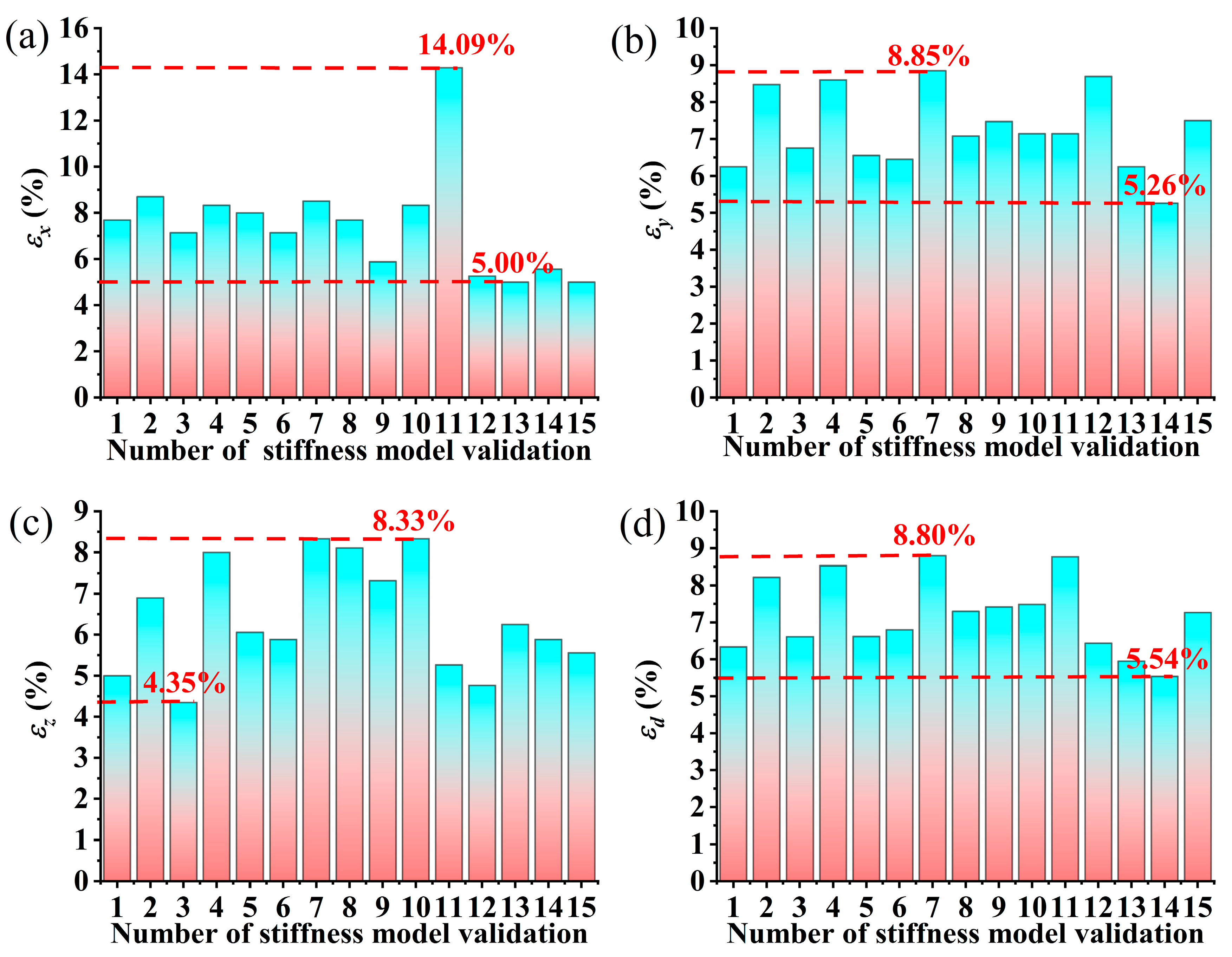
3. Experiments and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOF | Degrees-of-freedom |
| FEA | Finite element analysis |
| MSA | Matrix structure analysis |
| VJM | Virtual joint method |
| CCT | Conservative congruence transformation |
| MBS | Multi-body simulation method |
| IK | Inverse kinematic |
| KCI | Kinetostatic Conditioning Index |
| D-H | Denavit–Hartenberg |
References
- Wu, K.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhong, Y. Review of Industrial Robot Stiffness Identification and Modelling. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.; Khoshdarregi, M. Automatic Structural Identification and Vibration Suppression of Industrial Robots using a Custom Active Damper. In Proceedings of the 2022 22nd International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 27 November 2022–1 December 2022; pp. 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozakyol, H.; Karaman, C.; Bingul, Z. Advanced robotics analysis toolbox for kinematic and dynamic design and analysis of high-DOF redundant serial manipulators. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2019, 27, 1429–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Wang, L. Industrial Robotic Machining: A Review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, M.; Hintze, W.; Altintas, Y. Chatter stability in robotic milling. Robot. Comput. Int. Manuf. 2019, 55, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; Bai, K.; Li, M.; Dong, W. A Robotic Milling System Based on 3D Point Cloud. Machines 2021, 9, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souflas, T.; Gerontas, C.; Bikas, H.; Stavropoulos, P. On the Optimization of Robot Machining: A Simulation-Based Process Planning Approach. Machines 2024, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cui, G.; Tian, W.; Liao, W. Vibration suppression of an industrial robot with AGV in drilling applications by configuration optimization. Appl. Math. Model. 2022, 112, 614–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zheng, L.; Shi, M.; Zhang, Y. Controlling harmful milling vibration for robotic milling system based on the optimization of milling posture and spindle speed. Proc. IMechE. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukas, C.; Pandremenos, J.; Stavropoulos, P.; Foteinopoulos, P.; Chryssolouris, G. On an Empirical Investigation of the Structural Behavior of Robots. Procedia CIRP 2012, 3, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marie, S.; Courteille, E.; Maurine, P. Elasto-geometrical modeling and calibration of robot manipulators: Application to machining and forming applications. Mech. Mach. Theory 2013, 69, 13–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermanian, A.; Kamali, E.A.; Taghvaeipour, A. Dynamic analysis of flexible parallel robots via enhanced co-rotational and rigid finite element formulations. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 139, 144–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Song, A.; Ang, L.J. Design and Calibration of a Six-axis Force/torque Sensor with Large Measurement Range Used for the Space Manipulator. Procedia Eng. 2015, 99, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouritem, S.A.; Abouheaf, M.I.; Nahas, N.; Hassan, M. A multi-objective optimization design of industrial robot arms. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 12847–12867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoofian, A.; Taghvaeipour, A.; Kamali, E.A. On the stiffness analysis of robotic manipulators and calculation of stiffness indices. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 130, 382–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarata, A. Unified formulation for the stiffness analysis of spatial mechanisms. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 105, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xue, J.; Guo, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D. Stiffness Optimization of a Robotic Drilling System for Enhanced Accuracy in Aerospace Assembly. Actuators 2025, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, C. Stiffness mapping for parallel manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1990, 6, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimchik, A.; Pashkevich, A.; Caro, S.; Chablat, D. Stiffness Matrix of Manipulators with Passive Joints: Computational Aspects. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, C.; Caro, S.; Garnier, S.; Furet, B. Joint stiffness identification of six-revolute industrial serial robots. Robot. Comput. Int. Manuf. 2011, 27, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgulu, I.; Dede, M.; Kiper, G. Stiffness modeling of a 2-DoF over-constrained planar parallel mechanism. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 185, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Padayachee, J.; Bright, G. An experimental approach to improve the joint stiffness of industrial robots through dexterous posture identification. South Afr. J. Ind. Eng. 2021, 32, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Ding, H. A method for stiffness modeling of 3R2T overconstrained parallel robotic mechanisms based on screw theory and strain energy. Precis. Eng. 2018, 51, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, P.; Gerontas, C.; Bikas, H.; Souflas, T. Multi-Body dynamic simulation of a machining robot driven by CAM. Procedia CIRP 2022, 107, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, H.; Assadi, H.; Dambly, V.; Rivière-Lorphèvre, E.; Verlinden, O. Direct method for updating flexible multibody systems applied to a milling robot. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 68, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Y.; Wang, S. Kinematic calibration of serial robot using dual quaternions. Ind. Robot 2019, 46, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Y.; Wang, S. Joint Stiffness Identification and Deformation Compensation of Serial Robots Based on Dual Quaternion Algebra. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souflas, T.; Papaioannou, C.; Manitaras, D.; Gerontas, C.; Stavropoulos, P. In-process Detection of Low and High Frequency Chatter in Robot Machining. Procedia CIRP 2024, 130, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Yao, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, K.; Senthil, K.; Lu, W.; Bi, G. Stiffness modeling of an industrial robot with a gravity compensator considering link weights. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 161, 104331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Kao, I. Conservative Congruence Transformation for Joint and Cartesian Stiffness Matrices of Robotic Hands and Fingers. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2000, 19, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, M.; Cecot, W. On Moore-Penrose Pseudoinverse Computation for Stiffness Matrices Resulting from Higher Order Approximation. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 5060397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, C.; Caro, S.; Chérif, M.; Garnier, S.; Furet, B. Joint stiffness identification of industrial serial robots. Robotica 2011, 30, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Zhang, D. Impact Dynamics of Multi-Link Robots with Link and Joint Flexibility. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 226–228, 685–692. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.; Hou, P.; Yang, G.; Huang, G.; Yin, F.; Shi, X. Research on the Stiffness Performance for Robot Machining Systems. Hangkong Xuebao/Acta Aeronaut. 2013, 34, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, T.; Hu, T. Stiffness modeling and error compensation method of 6-DOF milling robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 29, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Posture | Joint Rotation Angle (°) | (N, N, N, N·m, N·m, N·m) | ) (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (0.69, −10.52, 46.04, −1.15, −36.12, 182.16) | (1770.25, −778.50, 1133.60, −2.99 × 105, −2.90 × 105, −7.54 × 105) | (0.33, −1.28, −1.25) |
| (1610.98, −472.72, 892.64, −3.01 × 104, 2.53 × 105, −2.43 × 105) | (−0.15, −0.51, −0.13) | ||
| (1588.61, −673.75, 706.61, −8.67 × 104, 6.11 × 105, −6.24 × 105) | (−0.41, −1.32, −0.31) | ||
| 2 | (2.48, 12.24, 20.30, 0.58, 57.02, 91.13) | (2001.42, −218.76, 1170.64, 2.63 × 104, −5.01 × 105, 3.65 × 105 | (−0.32, −0.83, −0.10) |
| (1846.22, −655.67, 792.49, −1.06 × 105, 2.96 × 105, −4.99 × 105) | (0.35, −1.31, 0.93) | ||
| (2068.95, −174.51, 915.41, 1.42 × 105, −6.68 × 104, 4.71 × 105) | (−0.37, −0.98, 0.28) | ||
| 3 | (3.58, −19.55, 47.11, 0.54, 61.99, 92.30) | (1718.11, −522.88, −48.82, −1.15 × 105, −1.02 × 105, −2.98 × 105) | (0.07, −0.56, −0.15) |
| (1673.29, −433.74, 1003.38, −4.53 × 104, 9.50 × 103, −1.49 × 105) | (0.06, −0.25, 0.11) | ||
| (1706.20, −467.53, 948.36, −4.65 × 104, 9.17 × 104, −1.99 × 105) | (0.10, −0.39, 0.26) | ||
| 4 | (0.94, −13.23, 45.53, 182.69, 32.24, 0.80) | (1708.22, −490.13, 1068.68, −1.02 × 105, −1.33 × 105, −2.41 × 105) | (0.18, −0.51, −0.60) |
| (1725.45, −565.85, 829.61, −6.44 × 104, 3.01 × 105, −3.76× 105) | (−0.34, −0.73, −0.62) | ||
| (1800.51, −657.77, 837.28, −1.23 × 105, 2.47 × 105, −5.20 × 105) | (−0.48, −0.92, −1.02) | ||
| 5 | (6.45, −5.73, 56.42, −0.01, 39.30, 6.45) | (2038.88, −177.64, 1023.05, 1.03 × 105, −2.48 × 105, 4.55 × 105) | (−1.12, −0.71, 0.58) |
| (1998.64, −160.10, 931.37, 1.46 × 105, −5.38 × 104, 4.73 × 105) | (0.63, −0.85, 0.57) | ||
| (1878.51, −56.16, 780.87, 2.61 × 105, 2.98 × 105, 6.24 × 105) | (0.29, −0.85, 0.44) | ||
| 6 | (169.13, −34.85, −168.16, −2.24, −68.34, 174.59) | (1753.28, −324.17, 1011.00, 1.84 × 104, −5.31 × 104, 8.28 × 104) | (0.44, −0.14, 0.32) |
| (1684.76, −321.17, 985.54, 2.91 × 104, 3.57 × 104, 6.44 × 104) | (−0.15, −0.05, 0.21) | ||
| (1696.50, −300.85, 953.10, 5.28 × 104, 8.88 × 104, 1.06 × 105) | (0.20, −0.17, 0.29) | ||
| 7 | (168.12, −29.40, −176.2 6, −1.38, −67.99, 78.67) | (1636.90, −267.16, 960.01, 7.07 × 104, 1.12 × 105, 1.48 × 105) | (0.25, −0.11, 0.18) |
| (1675.84, −221.22, 980.08, 9.15 × 104, 5.13 × 104, 2.47 × 105) | (0.21, −0.04, 0.36) | ||
| (1631.69, −181.80, 860.59, 1.57 × 105, 3.00 × 105, 3.04 × 105) | (0.50, −0.37, 0.43) | ||
| 8 | (169.53, −37.18, −164.63, −1.26, −67.15, 257.83) | (1796.83, −251.28, 901.44, 1.01 × 105, 1.24 × 105, 2.33 × 105) | (−0.21, −0.43, 0.35) |
| (1639.75, −369.52, 943.39, 1.46 × 104, 1.41 × 105, −4.11 × 104) | (0.15, −0.28, 0.26) | ||
| (1639.30, −485.30, 908.94, −4.34 × 104, 2.05 × 105, −2.56 × 105) | (0.94, −0.73, 0.56) | ||
| 9 | (168.07, −34.74, −177.73, −1.45, −61.99, 168.82) | (1888.07, −199.11, 839.03, 1.54 × 105, 1.85 × 105, 3.62 × 105) | (0.87, −0.29, 0.36) |
| (1753.77, −238.39, 872.75, 1.19 × 105, 2.03 × 105, 2.42 × 105) | (0.20, −0.21, 0.53) | ||
| (1850.06, −299.35, 981.58, 4.37 × 104, −5.71 × 104, 1.63 × 105) | (0.27, −0.06, 0.40) | ||
| 10 | (168.52, −39.09, −161.67, −1.30, −71.95, −11.03) | (1347.98, −374.87, 925.40, 1.76 × 104, 3.51 × 105, −1.53 × 105) | (0.69, −0.51, 0.44) |
| (1384.50, −360.66, 909.98, 3.16 × 104, 3.58 × 105, −1.14 × 105) | (0.62, −0.42, 0.47) | ||
| (1489.67, −329.45, 892.74, 5.66 × 104, 3.26 × 105, −1.93 × 104) | (0.44, −0.32, 0.52) |
| Posture | (N, N, N, N·m, N·m, N·m) | Actual End Deformation Value ) (mm) | Theoretical End Deformation Value () (mm) | Relative End Deformation Error ( ) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (1530.16, −454.39, 1090.01, −8.82 × 104, −6.46 × 104, −2.37 × 105) (1414.39, −511.27, 1096.12, −1.25 × 105, −5.88 × 103, −3.83 × 105) (1669.30, −364.78, 1122.40, −4.52 × 104, −2.09 × 105, −2.20 × 104) | (−0.26, −0.64, −0.20) (−0.23, −0.59, −0.29) (−0.28, −0.74, −0.23) | (−0.24, −0.60, −0.19) (−0.21, −0.54, −0.27) (−0.26, −0.69, −0.22) | (7.69, 6.25, 5.00) (8.70, 8.47, 6.90) (7.14, 6.76, 4.35) |
| 2 | (1622.84, 549.23, 812.21, 2.88 × 105, 3.95 × 105, 6.49 × 105) (1811.02, −158.42, 864.27, 1.70 × 105, 1.84 × 105, 4.11 × 105) (1788.64, −266.74, 988.35, 6.11 × 104, −3.24 × 104, 2.02 × 105) | (−0.36, −0.93, −0.25) (−0.25, −0.61, 0.33) (0.42, −0.31, 0.17) | (−0.33, −0.85, −0.23) (−0.23, −0.57, 0.31) (0.39, −0.29, 0.16) | (8.33, 8.60, 8.00) (8.00, 6.56, 6.06) (7.14, 6.45, 5.88) |
| 3 | (1508.01, −79.93, 965.83, 1.82 × 105, 1.79 × 105, 4.50 × 105) (1457.17, −20.77, 1067.37, 1.82 × 105, 2.16 × 104, 5.42 × 105) (1607.32, −120.16, 892.32, 1.83 × 105, 2.56 × 105, 4.10 × 105) | (−0.47, −1.13, 0.12) (−0.65, −1.13, −0.37) (−0.17, −1.07, −0.41) | (−0.43, −1.03, 0.11) (−0.60, −1.05, −0.34) (−0.16, −0.99, −0.38) | (8.51, 8.85, 8.33) (7.69, 7.08, 8.11) (5.88, 7.48, 7.32) |
| 4 | (1527.92, −415.79, 927.15, −7.74× 103, 2.39 × 105, −1.66 × 105) (1603.52, −306.89, 916.25, 6.20 × 104, 2.13 × 105, 6.24 × 104) (1625.42, −371.78, 981.66, 1.63 × 103, −3.72 × 102, 9.82 × 102) | (−0.24, −0.42, 0.12) (0.28, −0.42, −0.19) (0.19, −0.23, −0.21) | (−0.22, −0.39, 0.11) (0.24, −0.39, −0.18) (0.18, −0.21, −0.20) | (8.33, 7.14, 8.33) (14.29, 7.14, 5.26) (5.26, 8.70, 4.76) |
| 5 | (1607.13, −454.34, 943.38, −3.68 × 104, 1.61 × 105, −2.10 × 105) (1623.55, −669.43, 925.26, −1.61 × 105, 1.85 × 105, −6.03 × 105) (1641.85, −611.41, 848.49, −9.86 × 104, 3.16 × 105, −4.89 × 105) | (0.20, −0.32, −0.16) (−0.18, −0.19, −0.17) (−0.20, −0.80, −0.18) | (0.19, −0.30, −0.15) (−0.17, −0.18, −0.16) (−0.19, −0.74, −0.17) | (5.00, 6.25, 6.25) (5.56, 5.26, 5.88) (5.00, 7.50, 5.56) |
| Posture | Standard Uncertainty of Type A for Load in (x,y,z) of Base (N, N, N) | Estimated Uncertainty of Type B for Load in (x,y,z) of Base (N, N, N) | Standard Uncertainty of Type A for End Deformation in (x,y,z) (mm) | Estimated Uncertainty of Type B for End Deformation in (x,y,z) (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (0.282, 0.153, 0.282) (0.532, 0.217, 0.333) (0.379, 0.355, 0.571) | (0.883, 0.262, 0.629) (0.817, 0.295, 0.633) (0.964, 0.211, 0.648) | (0.0054, 0.0073, 0.0018) (0.0036, 0.0075, 0.0052) (0.0057, 0.0082, 0.0022) | 0.0069 |
| 2 | (0.788, 0.283, 0.433) (0.527, 0.065, 0.279) (0.338, 0.095, 0.398) | (0.937, 0.317, 0.469) (1.046, 0.091, 0.499) (1.033, 0.154, 0.571) | (0.0049, 0.0083, 0.0044) (0.0028, 0.0066, 0.0063) (0.0067, 0.0054, 0.0040) | 0.0069 |
| 3 | (0.564, 0.033, 0.328) (0.368, 0.012, 0.287) (0.257, 0.055, 0.230) | (0.871, 0.046, 0.558) (0.841, 0.012, 0.616) (0.928, 0.069, 0.515) | (0.0059, 0.0100, 0.0018) (0.0080, 0.0108, 0.0046) (0.0022, 0.0091, 0.0073) | 0.0069 |
| 4 | (0.413, 0.102, 0.377) (0.442, 0.166, 0.349) (0.430, 0.184, 0.411) | (0.882, 0.240, 0.535) (0.926, 0.177, 0.529) (0.938, 0.215, 0.567) | (0.0036, 0.0061, 0.0022) (0.0066, 0.0052, 0.0033) (0.0044, 0.0018, 0.0059) | 0.0069 |
| 5 | (0.464, 0.221, 0.272) (0.410, 0.343, 0.336) (0.382, 0.183, 0.221) | (0.928, 0.262, 0.545) (0.937, 0.386, 0.534) (0.948, 0.353, 0.490) | (0.0052, 0.0061, 0.0046) (0.0028, 0.0018, 0.0036) (0.0033, 0.0098, 0.0057) | 0.0069 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.-F.; Yao, B.-G.; Zhang, F.; Liang, X.-F.; Tao, G.; Ge, Y.-X.; Niu, T.-F. Global Stiffness Modeling of Robot Drilling System Incorporating End-Effector and Arm Flexibility Based on Virtual Joint Method. Machines 2025, 13, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090837
Zhang Y-F, Yao B-G, Zhang F, Liang X-F, Tao G, Ge Y-X, Niu T-F. Global Stiffness Modeling of Robot Drilling System Incorporating End-Effector and Arm Flexibility Based on Virtual Joint Method. Machines. 2025; 13(9):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090837
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yao-Feng, Bao-Guo Yao, Fei Zhang, Xi-Feng Liang, Geng Tao, Yu-Xun Ge, and Teng-Fei Niu. 2025. "Global Stiffness Modeling of Robot Drilling System Incorporating End-Effector and Arm Flexibility Based on Virtual Joint Method" Machines 13, no. 9: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090837
APA StyleZhang, Y.-F., Yao, B.-G., Zhang, F., Liang, X.-F., Tao, G., Ge, Y.-X., & Niu, T.-F. (2025). Global Stiffness Modeling of Robot Drilling System Incorporating End-Effector and Arm Flexibility Based on Virtual Joint Method. Machines, 13(9), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13090837








