1. Introduction
With the rapid advancement of automotive technologies in electrification, intelligent control, lightweight design, and system integration, brake-by-wire technologies have garnered significant attention within the industry [
1,
2]. Among these, Electro-Mechanical Braking (EMB) systems have emerged as a promising solution due to their high control precision, fast response speed, improved linearity, and higher level of integration. EMB technology is currently undergoing rapid iterations and vehicle-level testing [
3,
4].
However, compared to conventional hydraulic calipers, EMB units are typically heavier, which increases the unsprung mass of the vehicle. In addition, most test vehicles equipped with EMB systems adopt a distributed drive architecture, commonly utilizing in-wheel or wheel-side motors integrated with gear reduction mechanisms. These motors are rigidly coupled to the wheels, eliminating the need for a traditional clutch system [
5]. As a result, the increased unsprung mass introduced by the EMB system, along with the damping characteristics of the electric motor, alters the natural frequency of the wheel-end system. Real-vehicle data acquisition has shown that wheel speed frequently exhibits abnormal oscillations with a cycle of approximately 75 to 90 ms [
6,
7]. During braking, such high-frequency wheel speed fluctuations can be easily triggered, leading to repeated torque reductions under ABS intervention. This not only degrades braking performance and extends stopping distances, but also increases the potential risk of severe traffic accidents [
8]. Therefore, the implementation of targeted control strategies to suppress high-frequency wheel speed oscillations is essential for ensuring the effective operation of ABS in distributed drive vehicle architectures.
Experimental observations indicate that vibration frequencies associated with high-frequency wheel speed oscillations typically fall within the 10–30 Hz range [
9], while disturbances induced by rough or uneven road surfaces are generally irregular and less predictable. Recent research on ABS performance under such conditions has predominantly concentrated on road surface classification and adaptive pressure modulation strategies aimed at minimizing braking force degradation. V. Ciupe et al. utilized a scaled experimental test rig to investigate the impact of uneven road surfaces on ABS braking performance. Their findings revealed that a vertical disturbance of 46 mm led to a notable reduction in braking efficiency and a corresponding increase in stopping distance [
10]. Sven Mayer et al. reported that specific uneven surfaces, such as speed bumps, reduced system interaction accuracy by up to 19%, thus impacting the driving experience [
11]. Li et al. proposed a sliding mode controller for slip ratio regulation, leveraging wheel speed characteristics under rough road conditions. Their approach effectively reduced braking distance by 4.65 m [
12]. Yu developed a hydraulic ABS test platform and implemented a wheel speed correction strategy combining high-pass filtering with a threshold-crossing count method, effectively suppressing abnormal pressure drops under rough road conditions [
13]. Nico A. evaluated ABS performance on Belgian pavé road surfaces using Bosch control algorithms and observed vibration phenomena at approximately 100 Hz in SUV tires [
14].
In addition to uneven road surfaces, electric motors themselves represent a significant source of wheel vibration in distributed drive vehicles. Zhao identified three primary approaches to mitigate vibration issues in in-wheel motor systems: structural optimization of the motor design, enhancement of control strategies, and the incorporation of supplementary suspension components [
15]. Yu Mao investigated the origins of 50–100 Hz vibrations in single-wheel systems equipped with in-wheel motors. Through detailed modeling and analysis, he attributed the vibrations to torque ripple, compounded by the bidirectional rotational dynamics between the hub and the motor, and proposed corresponding optimization strategies to mitigate these effects [
16].
The motor can mitigate partial vibration conditions, but when the tire is worn or the damping characteristics of the suspension change over a long period, the vibration will reappear [
17], especially when the motor is not involved in the working condition of the brake. Therefore, it is more appropriate to solve the problem by the brake control method. Based on the EMB architecture, this paper proposes a control strategy to identify and suppress the wheel shaking. The main innovations and contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
To investigate the origin of tire resonance in distributed drive systems, an integrated tire–motor–suspension dynamic model is established.
The vibration behavior of in-wheel motors is affected by multiple factors, including unsprung mass, suspension stiffness, tire stiffness, and motor damping. The circumferential vibration of in-wheel motors is primarily influenced by unsprung mass and motor damping.
The wheel speed oscillation characteristics are extracted, and the inherent resonance frequency of the tire is identified by using the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT). Analysis reveals that the fundamental resonance frequency of the tire lies within the range of 12.1 to 12.8 Hz.
A model-based predictive and logic threshold control (MP-LC) strategy for ABS is proposed to actively suppress wheel vibrations.
The structure of this paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 presents the single-wheel mathematical model of the distributed drive system and analyzes the underlying resonance mechanisms, highlighting the effects of unsprung mass, motor damping, and suspension stiffness as key parameters influencing the natural characteristics of the tire.
Section 3 introduces a vibration frequency identification method and a control strategy designed to suppress resonance.
Section 4 analyzes the resonance behavior, revealing that wheel speed fluctuations primarily originate from torsional vibration, with minimal correlation to vertical oscillations.
Section 5 describes low-friction ABS simulations conducted using a co-simulation platform combining CarSim and Simulink, along with real-vehicle experiments. The results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm effectively reduces wheel-end vibrations and enhances braking performance. Finally,
Section 6 provides the concluding remarks and outlines potential directions for future research.
2. Single-Wheel Model for Distributed Drive Vehicles
A single-wheel dynamic model is developed to analyze the variations in wheel rotational speed during braking, as illustrated in
Figure 1. The Basic Wheel Caliper (BWC) functions as the actuator component of the Electro-Mechanical Brake system, receiving braking commands from the Electro-Mechanical Brake Controller (EMBC) via CAN communication. During braking events, the wheel primarily experiences three forces: vertical load, braking torque transmitted through the disc, and longitudinal resistance exerted by the ground [
18].
In parallel, a tire damping characteristic model is constructed to examine the effect of vertical load on wheel speed during braking, as illustrated in
Figure 1. The vehicle is modeled as a two-mass system, partitioned into sprung and unsprung masses connected via a suspension assembly composed of springs and dampers [
19]. Furthermore, the interface between the tire and the motor is represented as an elastic coupling, capturing the compliance introduced by the motor–tire interaction.
This study hypothesizes that the elastic coupling between the motor and tire is a primary factor contributing to wheel speed oscillations. All parameters utilized in the model are summarized in
Table 1.
2.1. Tire Dynamics Model
According to vehicle dynamics theory, the vehicle dynamics during braking can be expressed by the following equation:
where
denotes the longitudinal slip ratio of the wheel, and
represents the utilized adhesion coefficient, i.e., the friction coefficient between the tire and the road surface as a function of the slip ratio
[
20]. The wheel dynamics during braking can be described by the following equation:
where
is the friction coefficient between the brake pad and the disc.
is the effective braking radius of the disc.
is the normal force applied by the on the brake disc. This force is typically calculated by multiplying the braking pressure by the effective contact area. The factor of 2 accounts for the two-sided clamping force applied to both sides of the disc.
Accordingly, the vertical load can be calculated from Equation (
2) as follows:
The longitudinal slip ratio of the wheel can be defined by the following set of equations:
where
is a small regularization term introduced to prevent division by zero at low speeds. The variation in wheel load is calculated using Equation (
3) as follows:
From the perspective of full vehicle dynamics, the vertical load acting on a wheel comprises both a static component and a dynamically transferred component. The dynamic load transfer is primarily caused by the vehicle’s longitudinal acceleration during braking or traction events as follows [
21]:
where
denotes the height of the vehicle’s center of gravity from the ground,
a is the distance from the center of gravity to the front axle, and
b is the distance from the center of gravity to the rear axle.
represents the total vertical load on a single front wheel at time
t, while
represents the total vertical load on a single rear wheel at time
t.
2.2. Tire Model for Suspension Dynamics
A single-wheel suspension dynamics model, illustrated in
Figure 1b, is developed in this study. The model is based on a MacPherson independent suspension configuration and incorporates an air spring as the primary elastic element. The vibration characteristics of the wheel are analyzed in three degrees of freedom: vertical (Z-axis), longitudinal (X-axis), and rotational about the Y-axis (circumferential direction). For each degree of freedom, the respective elastic and damping properties are explicitly considered to accurately capture the dynamic behavior of the system.
Among the three directions, variations in stiffness and damping along the longitudinal axis are relatively minor and therefore exert limited influence on the overall wheel vibration behavior. Both experimental measurements and simulation results indicate that the dominant contributors to wheel vibration are the vertical and circumferential modes, with the circumferential mode having a particularly significant impact on the stability of the wheel speed signal.
Based on the above analysis, it is concluded that the jitter observed in the wheel speed signal is primarily induced by the circumferential vibration of the wheel as follows [
22,
23]:
Road tests have shown that electric vehicles (EVs) are more susceptible to wheel vibration than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles [
24]. This tendency can be attributed to two primary factors. First, the structural characteristics of electric drivetrains, where the motor inherently introduces damping-like behavior, alter the system’s dynamic response. Second, EVs often employ air springs or low-stiffness suspension systems to improve ride comfort, which increases the dynamic compliance of the suspension and consequently heightens the wheel’s sensitivity to circumferential vibrations [
25].
By analyzing the internal force distribution within the tire model and its associated dynamic differential equations, the total force acting on the wheel can be decomposed into a static load component and a dynamic load component. This relationship can be expressed as follows [
26]:
where
represents the total vertical load acting on the wheel at time
t,
denotes the static vertical load under equilibrium conditions, and
is the dynamic load variation, which arises primarily from the vehicle’s longitudinal acceleration and road surface excitation.
Accordingly, the dynamic differential equation governing the suspension system can be reformulated as follows:
where
represents the bulk elastic force, while
denotes the damping force generated by the damper, which is a function of the piston velocity in the variable damping system. Accordingly, the variation in vertical load at the wheel end can be expressed as follows:
By analyzing Equation (
11), the natural (resonant) frequency of the tire system can be derived. Based on the variation in vertical force and the corresponding motion equations, it becomes evident that the masses
(unsprung mass) and
M (sprung mass) are dynamically coupled, contributing to the system’s vibrational behavior.
If the unsprung mass is assumed to be stationary (i.e., ), the system simplifies to a single-degree-of-freedom undamped vibration model for the sprung mass. The corresponding natural circular frequency is given by the following equation:
Conversely, if the sprung mass M is considered stationary (i.e., the vehicle body does not move), and the unsprung mass is allowed to vibrate freely, the system again behaves as a single-degree-of-freedom undamped oscillator. The resulting natural circular frequency is as follows:
In the analysis of rotational (circumferential) motion, the system can be modeled such that the tire provides torsional stiffness, while the damping torque is primarily introduced by the electric motor. The motor’s damping effect is represented by a viscous damping coefficient , which defines the relationship between the damping torque and the angular velocity. When the electric motor is back-driven by the wheel during braking, the coupled rotational system—comprising the tire and motor—exhibits a characteristic natural frequency. Assuming a simplified single-degree-of-freedom torsional vibration model, this natural circular frequency can be expressed as follows:
In practical applications, the vibration frequency of the vehicle body is substantially lower than that of the wheel—typically by a factor of approximately 1/100. Moreover, to simplify the computation and satisfy the constraints of real-time execution on the embedded brake controller, the model is deliberately streamlined. Consequently, this analysis focuses exclusively on the vibration of the tire (unsprung mass), while the dynamic influence of the vehicle body (sprung mass) is neglected for simplification.
Under this assumption, the vertical dynamics of the tire can be simplified and expressed [
27] as follows in Equation (
12):
According to vehicle dynamics theory, the vertical amplitude–frequency response of the sprung mass (
) relative to the road excitation (
q) can be derived. The amplitude ratio
, as a function of excitation frequency, reveals a resonance behavior determined by the system’s stiffness and mass properties. The corresponding analytical expression is given in Equation (
13):
In this context, the term
is defined in Equation (
14), where
denotes the stiffness ratio, and
represents the mass ratio,
represents the frequency ratio.
The natural frequency of the simplified vertical vibration system is given by the following equation: , and the corresponding damping ratio is expressed as follows: .
In the circumferential (rotational) direction, the natural frequency and damping ratio are respectively defined as follows: and .
The damping coefficient of the motor primarily arises from the back electromotive force (EMF) generated during rotation. This electromagnetic damping effect can be approximated by the following expression: , where is the motor back EMF constant, and is the armature resistance.
To facilitate analysis of the system’s frequency response characteristics, the circumferential dynamic equation (Equation (
8)) is transformed into the frequency domain using the Fourier Transform.
The variable
can be interpreted as the ratio of vehicle speed to wheel radius. This formulation is primarily introduced to highlight the influence of the slip ratio on tire dynamics. When the slip ratio remains within a relatively small range, the longitudinal force generated at the tire–road interface can be reasonably approximated as being linearly proportional to the slip ratio. Accordingly, the slip ratio serves as a key parameter characterizing the longitudinal force transmission between the tire and the road surface [
28]. Based on this, the frequency-domain transfer function of the system can be expressed as Equation (
16).
By introducing the frequency ratio
and the damping ratio
, the frequency-domain transfer function can be reformulated in a normalized form, as shown in Equation (
17).
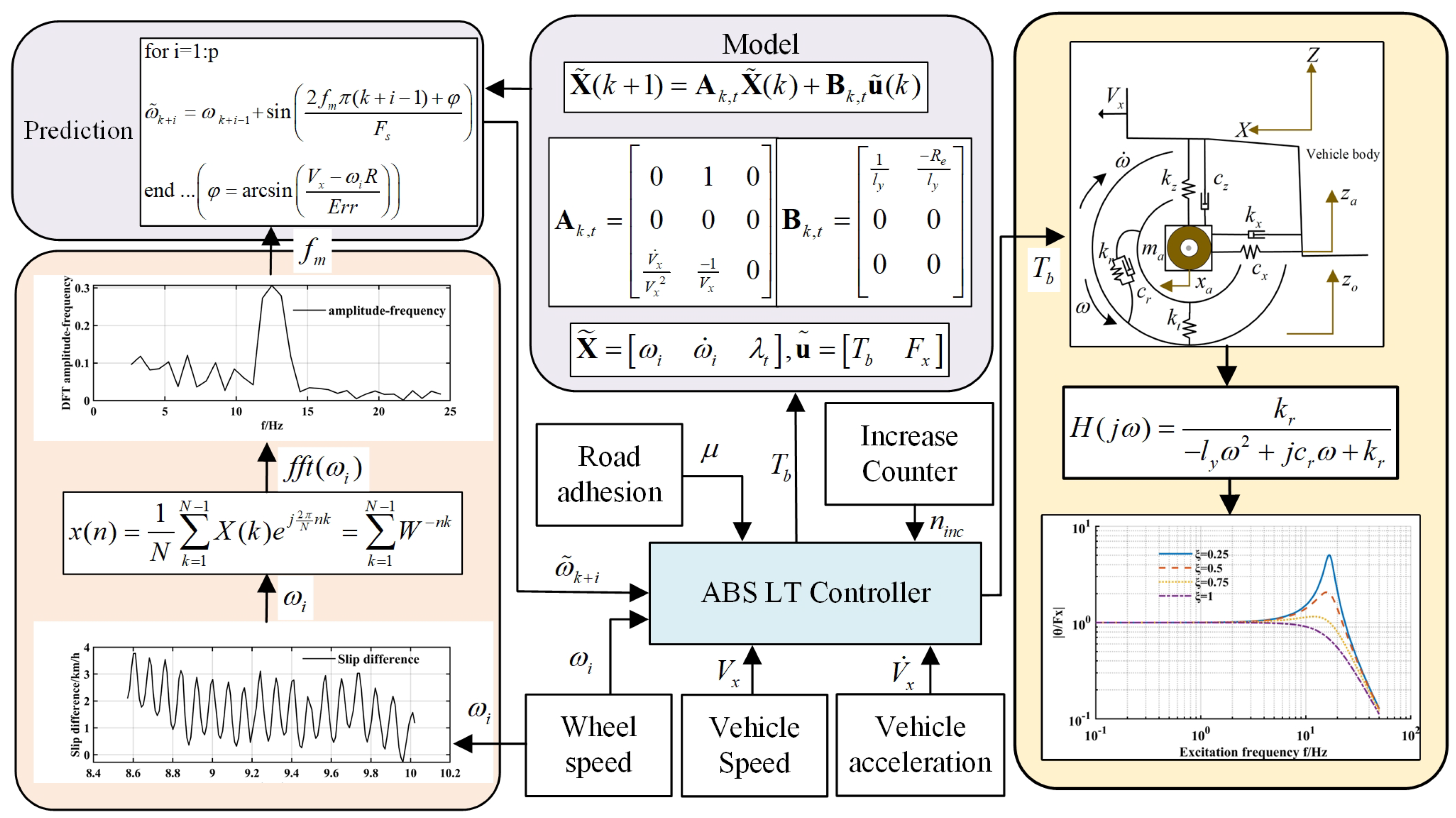
3. Model Prediction Logic Threshold Control (MP-LC) and Adaptive Braking Intensity Field Regulation
(ABIFR)
The overall control logic is illustrated in
Figure 2. Based on a single-wheel dynamic model, the inherent characteristics of the tire are analyzed, and the actual resonance frequency is identified using empirical data. A model-based prediction of wheel speed variation is then performed, and an adaptive torque reduction strategy is integrated to regulate the final braking force.
3.1. Model Prediction
This study proposes a hybrid control strategy that integrates logical threshold-based decision-making with a model-based predictive framework to detect and forecast wheel vibration phenomena. Specifically, when an abnormal slip ratio is identified—such as a condition where the braking force is relatively low while the slip ratio remains unexpectedly high, often indicative of self-excited wheel oscillations—the controller suppresses the conventional torque reduction response. Instead, it sustains or incrementally increases the braking force to maintain braking effectiveness and ensure system stability.
According to the prediction model, by differentiating Equation (
4), the value of
can be obtained. The relationship between the slip ratio at the current time step and that at the subsequent time step is expressed by Equation (
18) [
29].
Accordingly, the control-oriented state-space equations can be formulated as shown in Equation (
21).
where
,
,
,
.
The slip ratio
is obtained from Equation (
4), which can be calculated directly from the vehicle speed and wheel speed. Based on the current state of the vehicle, the predictive model estimates the evolution of the slip ratio over the next
sampling intervals. To regulate the wheel slip ratio
towards its optimal value—thereby maximizing road adhesion and braking efficiency—the desired braking torque is determined in accordance with the road–tire friction characteristics.
Using Equation (
21), future values of wheel speed and vehicle speed over a prediction horizon of
steps can be forecast based on historical wheel speed data, current road adhesion conditions, and the actual braking force. By employing the EMB caliper, the clamping force can be measured with high accuracy, enabling precise calculation of the braking torque
. In this study,
is considered as the longitudinal resistance, which primarily consists of aerodynamic drag and rolling resistance.
In addition, the vehicle’s resonance characteristics should be taken into account. A Fourier Transform is performed on the wheel speed data over a past time window of at least 80–90 ms to extract the wheel’s inherent rotational characteristics. By identifying the spectral peak, the resonance frequency can be determined [
30].
where
represents the DFT transformed data,
is the sampled analog signal, and
N is the total number of sampling points. For the signal with a period of 80 ms, the sampling frequency is 5 ms once, there are 16 data points in total, and at least 8 points are enough to ensure the accuracy [
31]. In this paper,
N = 150 is selected.
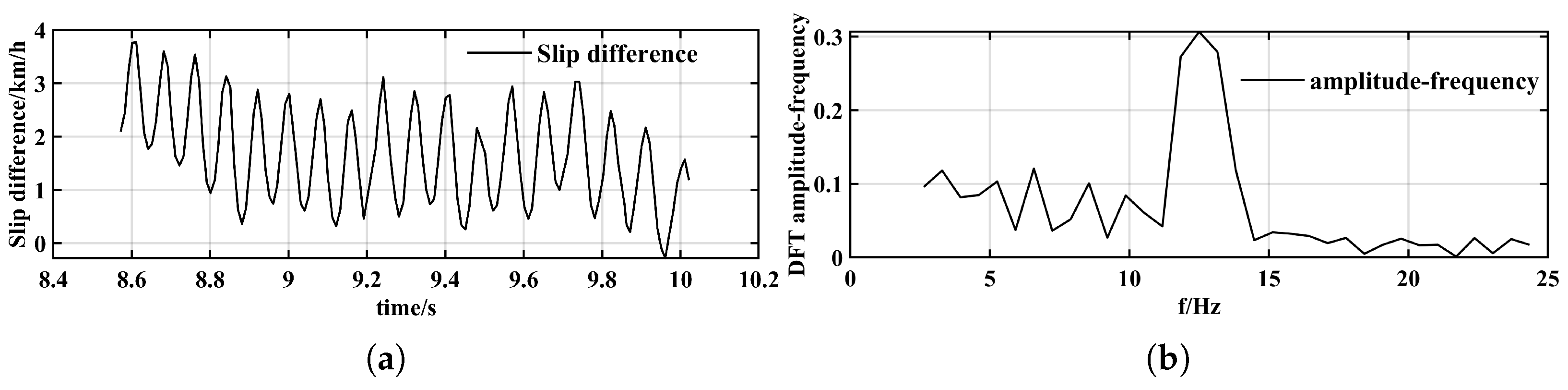
The results of the Fourier Transform are shown in
Figure 3. A segment of the wheel speed and vehicle speed deviation is extracted and analyzed using a DFT, revealing a consistent frequency component
in the range of 12–13 Hz. Extensive testing on the M917 vehicle—over 100 datasets—confirmed this observation, with no significant oscillations detected at other frequencies. Therefore, the peak resonance frequency can be identified either online in real time or offline and calibrated into the control algorithm for a specific vehicle. Furthermore, by applying the inverse Fourier Transform, the original time-domain signal can be reconstructed based on the identified natural frequency.
Therefore, the predicted oscillatory wheel speed over the future time horizon from step
k to
is given by the following equation:
where
denotes the phase angle, which can be calculated as follows:
. During each torque reduction event, the phase is corrected and set to
.
is the amplitude. Even for special road surfaces such as cobblestone, the same phase reset strategy during each torque reduction is necessary to prevent multiple unnecessary interventions. During ABS braking, the wheel-speed oscillation can be approximated by a sinusoid. Each time the wheel speed reaches its minimum, the ABS reduces torque; in a sinusoidal representation, this event corresponds to a phase of
. To counteract this, the wheel-speed compensation term is designed to be quadrature to the oscillation—i.e., with a phase of
—so that the two signals complement each other and attenuate the oscillatory component.
In cases of sudden road surface transitions—e.g., from asphalt to ice—the detection cycle is typically around 100 ms, and the processing cycle is approximately 300 ms. This corresponds to a control algorithm operating at a different frequency band.
3.2. Adaptive Braking Intensity Field Regulation
To mitigate excessive torque reduction during braking, an Average Braking Intensity Field strategy is proposed. The vehicle’s average deceleration during braking reflects the spatiotemporal evolution of braking intensity under current road adhesion conditions. Based on this intensity field, a reasonable lower bound for torque reduction is established to prevent over-intervention, thereby enhancing both braking stability and efficiency [
32].
The braking strength
is given by the ratio of the braking force
of the vehicle to the vertical load
:
. The average braking strength
represents the braking state in the past period (window width T):
Based on the current braking intensity, the upper and lower bounds of the allowable braking force can be estimated. Torque reduction is permitted only when the torque increase over a past time window is significant, the current wheel deceleration lies within the stable range, and the actual braking force approaches its estimated upper bound. Otherwise, the reduction in torque is suppressed proportionally to the difference between the actual braking force and its lower bound, in order to prevent excessive braking force attenuation.
Accordingly, the lower bound of the braking intensity is defined as , where reflects a safety margin. The current braking force is denoted by , and the minimum allowable braking force under torque reduction is given by . The cumulative torque increase over a specified past time interval and is calculated as follows:
The final target torque reduction can be written as follows:
The final target torque reduction can be written as follows:
3.3. Increase/Decrease in Overall Brake Force of ABS
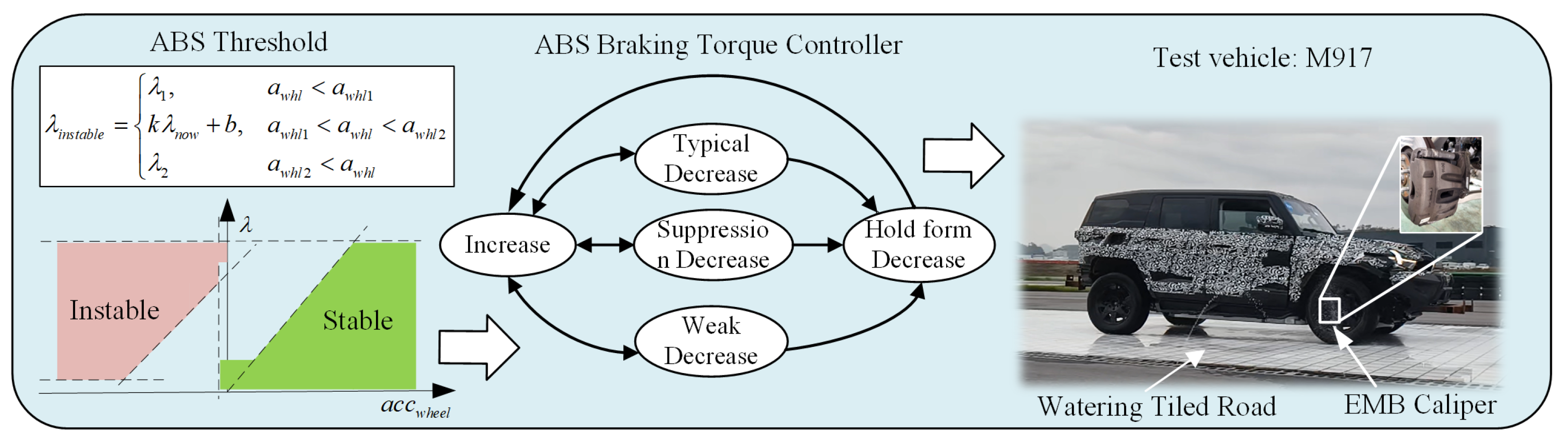
The ABS control algorithm based on estimated braking force is illustrated in
Figure 4. This algorithm evaluates the wheel’s operating condition—whether it lies within the stable or unstable region—by analyzing the slip ratio and wheel deceleration. The boundary conditions defining the unstable region are shown in the figure, where the horizontal axis represents wheel acceleration, and the vertical axis represents the slip ratio.The test vehicle used in this study was the Mengshi 917, manufactured by Dongfeng Motor Corporation, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. The vehicle was equipped with electro-mechanical brake (EMB) calipers supplied by Jonyi Automotive Co., Ltd., Suzhou, Jiangsu Province, China. The experimental tests were conducted on wetted tile surfaces and asphalt pavement. When the slip ratio–wheel deceleration point lies above the unstable boundary, the wheel is considered to be in an unstable state. Conversely, when the point is below the stable boundary, the wheel is regarded as being in the stable region. During ABS operation, when the wheel enters the stable region, the braking force is increased; conversely, when the wheel enters the unstable region, the braking force is reduced.
where
represent two slip rate threshold values, and
represents wheel acceleration.
Normal torque reduction is permitted only when the vehicle’s previously averaged braking potential energy is sufficient, the cumulative increase in braking torque is adequate, and the MP-LC prediction confirms that the current decrease in wheel speed is due to normal deceleration rather than resonance-induced oscillations. If the torque increase is insufficient, the system applies a moderated torque reduction—referred to as a weak decrease—based on the ABIFR. During torque reduction, the MP-LC method resets the phase component of the oscillatory wheel speed to zero and monitors the actual wheel speed oscillation over the subsequent 80 ms. If abnormal oscillations are detected, further torque reduction is suppressed.
By integrating a logic-threshold-based control approach, the slip ratio of the tire is maintained within an optimal range of approximately 5% to 15%. This range is known to correspond to the maximum achievable longitudinal tire force. This strategy ensures the effective utilization of tire–road friction, thereby improving overall braking performance under varying operating conditions.
4. Wheel Vibration Characterization and Frequency Spectrum Analysis
To validate the proposed theory, all algorithms were verified through full-scale vehicle tests using M917, with a total mass of 3.8 t. The vehicle was equipped with EMB calipers on all four wheels, with the front calipers providing a braking force range of 0–65 kN and the rear calipers 0–45 kN. The algorithms were deployed on the S32K344 microcontroller, featuring a 300 MHz processing capability, manufactured by NXP Semiconductors, Eindhoven, the Netherlands, and data acquisition was performed using a ZLG-CANFD device, manufactured by Guangzhou Zhoulizgong Electronics Co., Ltd., Guangdong, China. All tests were conducted in spring at the Huanggang Proving Ground in Hubei. The high-adhesion surface consisted of dry asphalt with an adhesion coefficient of approximately 1.0, while the low-adhesion surface was a water-sprayed tile road with an adhesion coefficient of 0.1–0.2.
In the single-wheel system model, the vehicle body mass is set to 1000 kg, the wheel mass to 100 kg, the suspension stiffness to
, and the tire stiffness to
. The damping coefficient
C varies within the range of 5000 to 20,000 N·s/m. Four damping ratios are analyzed: 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1.0. The resulting vertical vibration frequency response of the tire is illustrated in
Figure 5a, where the transfer function from ground excitation
to tire vertical displacement
is evaluated.
The results indicate that when the damping ratio is below 0.5, two distinct resonance peaks emerge. The low-frequency resonance near 1–2 Hz has minimal impact on tire dynamics, whereas the resonance observed in the 10–20 Hz range significantly influences the tire’s response. Suspension height sensor data indicate vertical vibrations occur below 2 Hz, ruling out vertical dynamics as the source of high-frequency tire oscillations.
The 1–2 Hz low-frequency components, however, align well with the measured suspension height variations, supporting this interpretation.
Figure 5b illustrates the frequency response characteristics of the wheel’s rotational motion with respect to circumferential force. When the damping is low, a resonance peak tends to appear around 10–11 Hz, which aligns well with the resonance frequency observed in the experimental data in
Figure 3.
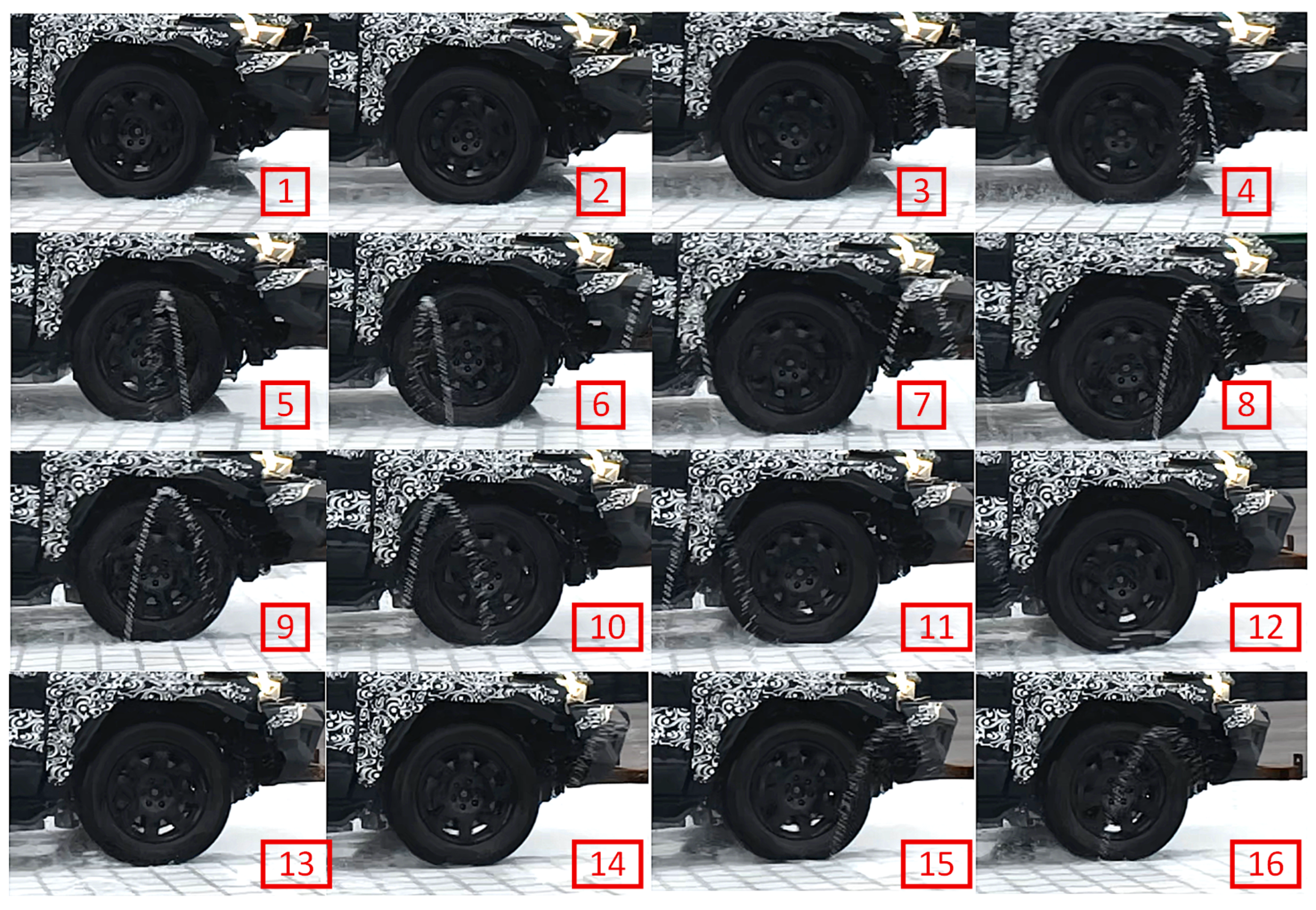
A high-speed camera was employed to focus on the wheel during braking in order to investigate its oscillation characteristics. The objective was to determine whether the source of the vibration originated from vertical, lateral, or circumferential motion. Given that the observed wheel speed oscillation period is approximately 80 ms, the Nyquist sampling theorem requires a sampling interval shorter than half the period—at least 25 Hz (i.e., one sample every 40 ms). The video was recorded in 4× slow motion, and 8 frames were extracted per second, resulting in an effective sampling frequency of 32 Hz, which satisfies the Nyquist criterion.
As shown in
Figure 6, The numbers 1–16 indicate the chronological order of captured frames. The consecutive frames recorded during braking reveal no observable vertical displacement of the tire relative to the vehicle body, suggesting that vertical oscillation is unlikely to be the primary cause.
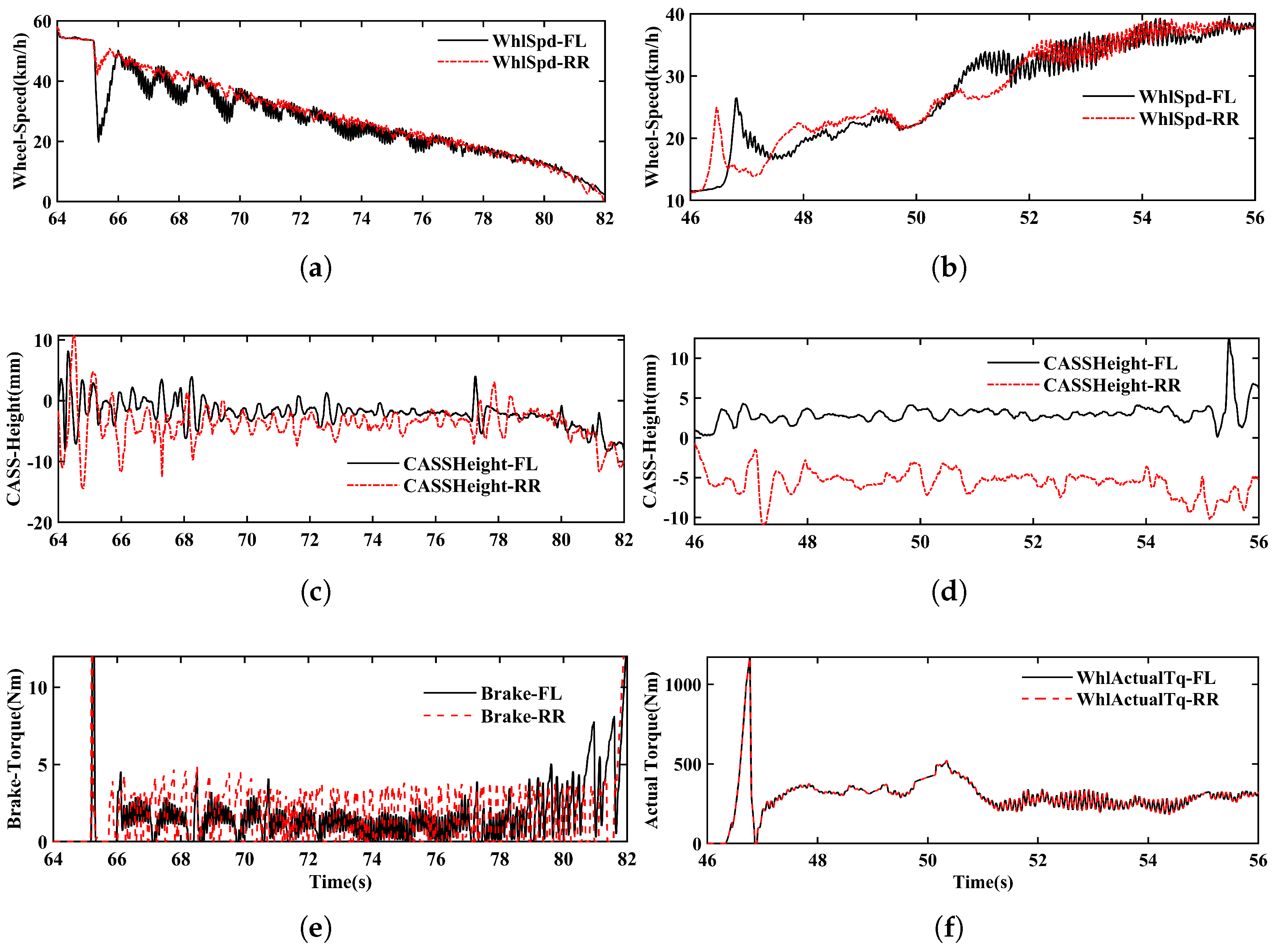
ABS and TCS tests were conducted using the M917 vehicle on a simulated low-adhesion surface (water-sprayed ceramic tiles). As shown in
Figure 7a,c,e, in the braking scenario, braking was initiated at 65 s. The wheel speeds rapidly decreased, triggering ABS intervention to maintain the wheel slip ratio within 5–15%. A high-frequency oscillation was observed in the left front wheel, with a period of approximately 80 ms. Since no suppression control was applied, the braking torque also exhibited a passive torque reduction at the same frequency (80 ms), fluctuating between 1000 and 3000 N. In contrast, the right rear wheel exhibited a normal ABS cycle of around 300 ms, with braking torque ranging between 0 and 4000 N. Analysis of the suspension height data from CASS (Controller of Air Suspension System) for both the left front and right rear wheels revealed no oscillation at 80 ms intervals; instead, the suspension vibrations occurred at much lower frequencies (300–500 ms). This indicates that there is no direct correlation between suspension vertical displacement and high-frequency wheel speed oscillation.
In the traction scenario as shown in
Figure 7b,d,f, throttle input was applied at 46.3 s, triggering immediate TCS intervention. The driving torque fluctuated between 300 and 400 Nm. From 51 to 56 s, large slip ratios and oscillations were observed, with frequencies around 12 Hz. The driving torque, influenced by the wheel speed signals, also exhibited an 80 ms oscillation pattern. Both driven wheels displayed high-frequency vibrations, which were clearly perceptible to the occupants as strong chassis vibrations, leading to a noticeable degradation in ride comfort. However, suspension height data revealed no high-frequency oscillation, only normal low-frequency movement.
In summary, based on both suspension height measurements and high-speed video observations, it is concluded that the observed chassis vibrations are not caused by vertical motion of the wheels but are primarily attributed to circumferential (rotational) oscillations of the wheels.
5. Experiments and Discussions
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, both the ABIFR and MP-LC algorithm were deployed on the main controller. Experiments were conducted using the M917 test vehicle under both simulated low-adhesion conditions (with a friction coefficient of approximately = 0.1) and high-adhesion conditions (dry asphalt with a friction coefficient of = 0.9). The acceleration measurement accuracy is 0.01 m/s2, the wheel speed accuracy is 0.0025 m/s, and the brake force output accuracy is 1 N, with a sampling period of 5 ms. Three sets of comparative tests were performed: Group 1 employed a conventional ABS strategy; Group 2 integrated the ABIFR method; Group 3 combined both the ABIFR and MP-LC control strategies.
As shown in
Figure 8, the test results under low-adhesion braking conditions for the conventional ABS strategy are illustrated in
Figure 8a,d,g, representing wheel speed, braking force, and longitudinal deceleration, respectively. Braking is initiated at 37.5 s, triggering the ABS system. Under such conditions, each torque reduction cycle in conventional ABS reduces the braking torque to nearly zero, resulting in slightly lower braking force—approximately in the range of 0–5000 N, but with no apparent high-frequency oscillation.
After integrating the ABIFR strategy, the torque reduction is no longer to zero but is moderately attenuated, as shown in
Figure 8e. However, this introduces high-frequency oscillations in the wheel speed, as evident in
Figure 8b where the right rear wheel exhibits periodic fluctuations at around 80 ms intervals. This leads to noticeable discomfort for the driver. The corresponding deceleration, shown in
Figure 8h, also demonstrates increased oscillatory behavior. When the MP-LC method is additionally incorporated, the high-frequency oscillation is effectively suppressed. As shown in
Figure 8c, the wheel speed becomes smoother, the braking force increases to approximately 0–9000 N, and the longitudinal deceleration is improved, indicating better braking performance and ride comfort.
Under fixed vehicle configuration conditions, the wheel-end oscillation frequency remains approximately 80 ms across various road surfaces, including high-adhesion asphalt, snow, and ice. This consistency allows for the inherent frequency to be pre-calibrated in advance. Although this phenomenon may not be clearly visible in
Figure 8a, extensive experimental data collected in this study confirm its inevitability. For instance, in
Figure 9a,d, at 29.7 s and 31.5 s, wheel speed oscillations are observed, accompanied by rapid reductions in braking force occurring three to four times at intervals of approximately 80–85 ms. After applying the proposed optimization method, such frequent braking force reductions are no longer present, and braking force loss is avoided. This clearly indicates that stability is not achieved through passive tire recovery but rather through our active intervention strategy.
The test results are evaluated using the Mean Fully Developed Deceleration (MFDD) metric, which serves as a key indicator of braking performance. MFDD represents the average deceleration achieved during the fully developed braking phase and can be expressed as follows:
In this formula
—the initial braking velocity of the test vehicle (km/h);
—the vehicle speed at 80% of the initial speed, i.e., (km/h);
—the vehicle speed at 10% of the initial speed, i.e., (km/h);
—the distance traveled by the vehicle while decelerating from to (m);
—the distance traveled by the vehicle while decelerating from to (m).
Additionally, the longitudinal acceleration measured by the IMU over a period of time was used as a reference. However, this signal exhibited significant fluctuations and was affected by the vehicle’s pitch angle, thus serving only as a supplementary indicator. As shown in
Table 2 under standard ABS conditions, the MFDD was measured at
. After introducing the ABIFR strategy, the MFDD decreased to
, representing an 11.8% reduction. With the implementation of the MP-LC strategy, the MFDD increased to −1.45
, representing a 14.2% improvement compared to the baseline ABS condition. The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of the longitudinal acceleration, which reflects the fluctuation level of deceleration, increased to 0.72 under ABIFR due to high-frequency oscillations. After implementing the MP-LC strategy, the RMSE value was reduced to 0.52, indicating that the proposed method not only improved the average deceleration level but also significantly suppressed the deceleration fluctuations.
Similar issues can also occur under high-adhesion conditions when the driver performs rapid acceleration or emergency braking maneuvers, such as during ABS operations. Subjectively, drivers often perceive intense vibrations at the wheels, while objective measurements reveal periodic oscillations at specific frequencies in the wheel speed signals, indicating the presence of inherent resonant modes within the system.
The corresponding test results are summarized in
Table 2.
In
Figure 9b,e, the rear wheels of the vehicle exhibit fixed-frequency oscillations during high-adhesion braking, with both wheel speed and braking force showing periodic fluctuations with a cycle of 80 ms, corresponding to a frequency of 12.5 Hz.
This type of oscillation is not prominent under conventional ABS control but can lead to more severe consequences. The frequent wheel speed fluctuations cause the ABS to misinterpret wheel recovery followed by re-locking, thereby triggering repeated torque reductions. These frequent reductions in braking force significantly degrade braking performance. As shown in
Figure 9a,d, after the front wheel speed drops at 29.5 s, it briefly rises and then drops again, resulting in abnormal fluctuations. This triggers three consecutive ABS torque reductions, decreasing the braking force to approximately 4 kN. A similar scenario occurs at 31.6 s, with the braking force dropping to around 2 kN, leading to a substantial loss in braking effectiveness. After integrating the ABIFR and MP-LC strategies, as illustrated in
Figure 9c,f, the wheel speed and braking force exhibit more stable and regular patterns. Moreover, the longitudinal deceleration shown in
Figure 9i becomes smoother and significantly higher.
A comparison of the three methods, as presented in
Table 2, shows that under conventional ABS control, the MFDD is limited to −7.46
due to frequent braking force loss. After introducing the ABIFR strategy, MFDD improves to −8.38
. With the additional integration of the MP-LC method, MFDD further increases to −8.61
, representing a 15.4% improvement over standard ABS. Moreover, the RMSE is reduced, indicating diminished fluctuation in deceleration and enhanced braking stability. In practical applications, the control performance and braking distance can be further improved through calibration procedures and the application of correction coefficients.
6. Conclusions
This study investigates the high-frequency wheel vibration phenomenon observed in DDEV, particularly under ABS operation on low-adhesion surfaces. A single-wheel dynamic model incorporating vehicle body mass, wheel mass, suspension, tire stiffness, and damping is established. Modal and frequency domain analyses reveal that the root cause of wheel speed oscillation is circumferential resonance induced by the elastic coupling between the motor and tire, rather than vertical vibrations. Simulation results indicate that tire resonance typically occurs in the 12–13 Hz range, which aligns well with experimental observations. To address this issue, an ABIFR strategy and an MP-LC scheme are proposed. These methods aim to maintain optimal slip ratios and suppress unnecessary torque reductions, thereby enhancing braking smoothness and overall performance. Experimental validation demonstrates that the proposed methods improve the MFDD by 14.8% and 15.2% under low- and high-adhesion conditions, respectively, while effectively eliminating the 12–13 Hz high-frequency oscillations. Moreover, the ABS control period is restored to a normal 300 ms, improving overall driving comfort.
Future work will focus on integrating real-time sensor data with model-based predictive control, adapting the approach to different tire and motor configurations, and conducting extensive testing across diverse road and environmental conditions to enhance robustness.