Experimental Analysis of a Coaxial Magnetic Gear Prototype
Abstract
1. Introduction
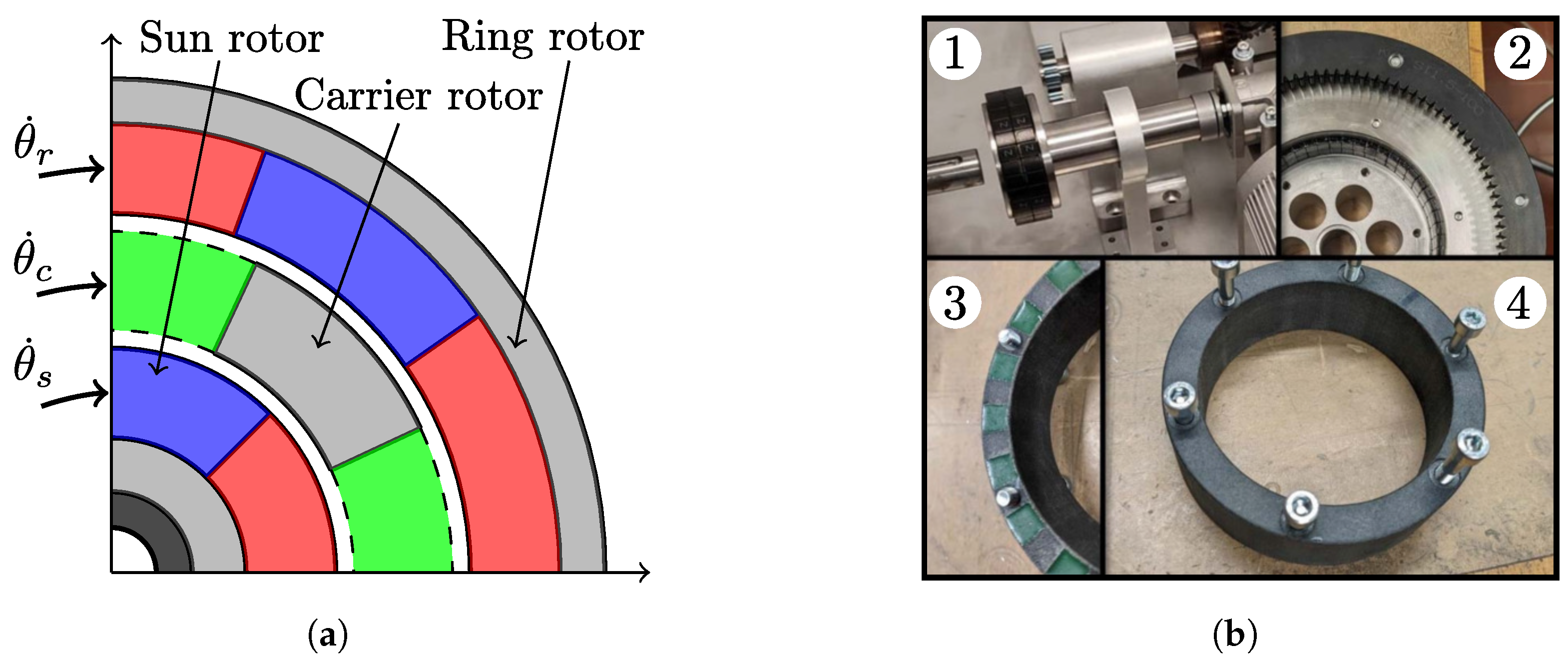
2. Fundamentals
2.1. Stationary Conditions
2.2. Dynamic Model
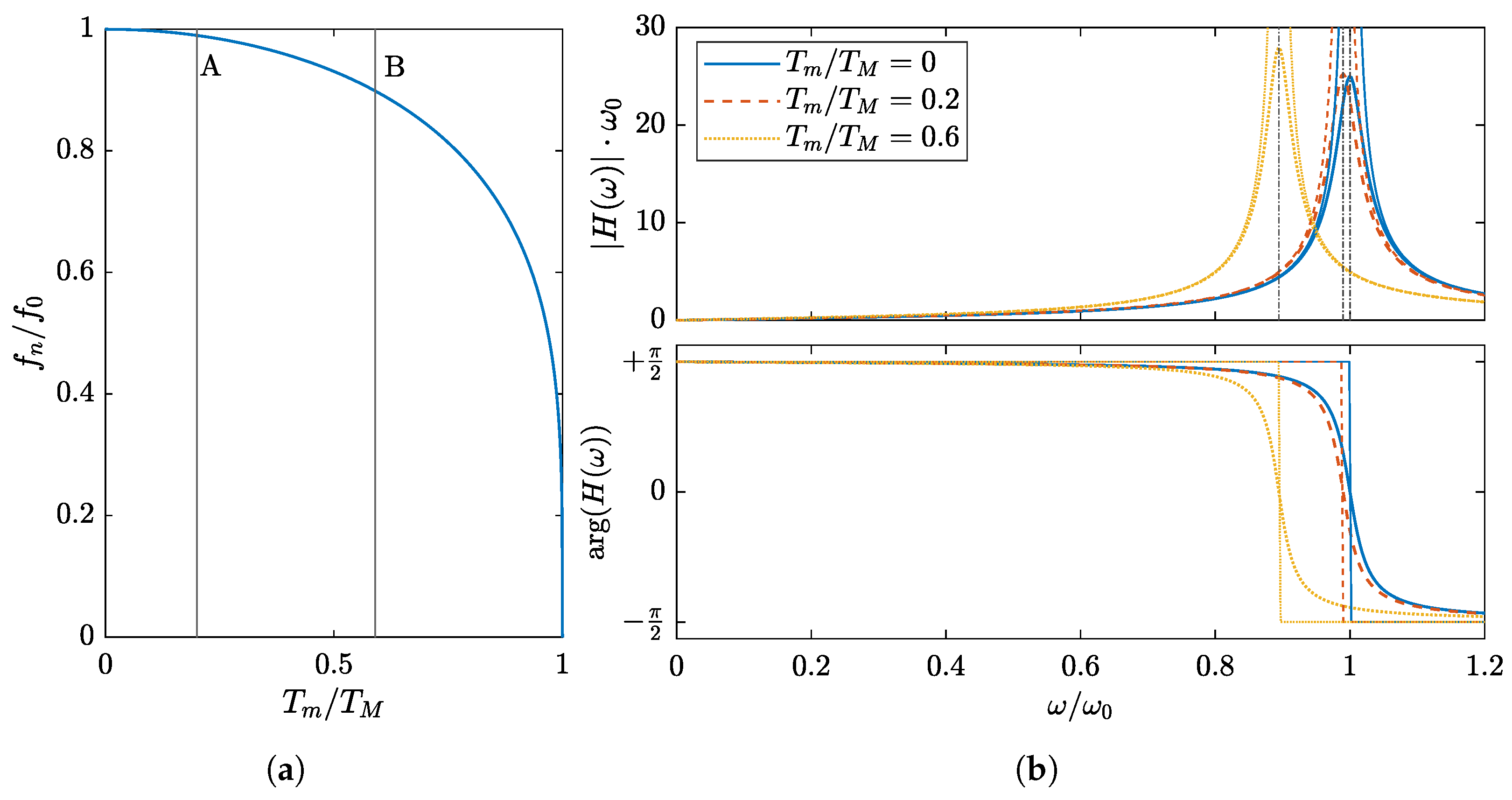
2.3. Frequency Response Function
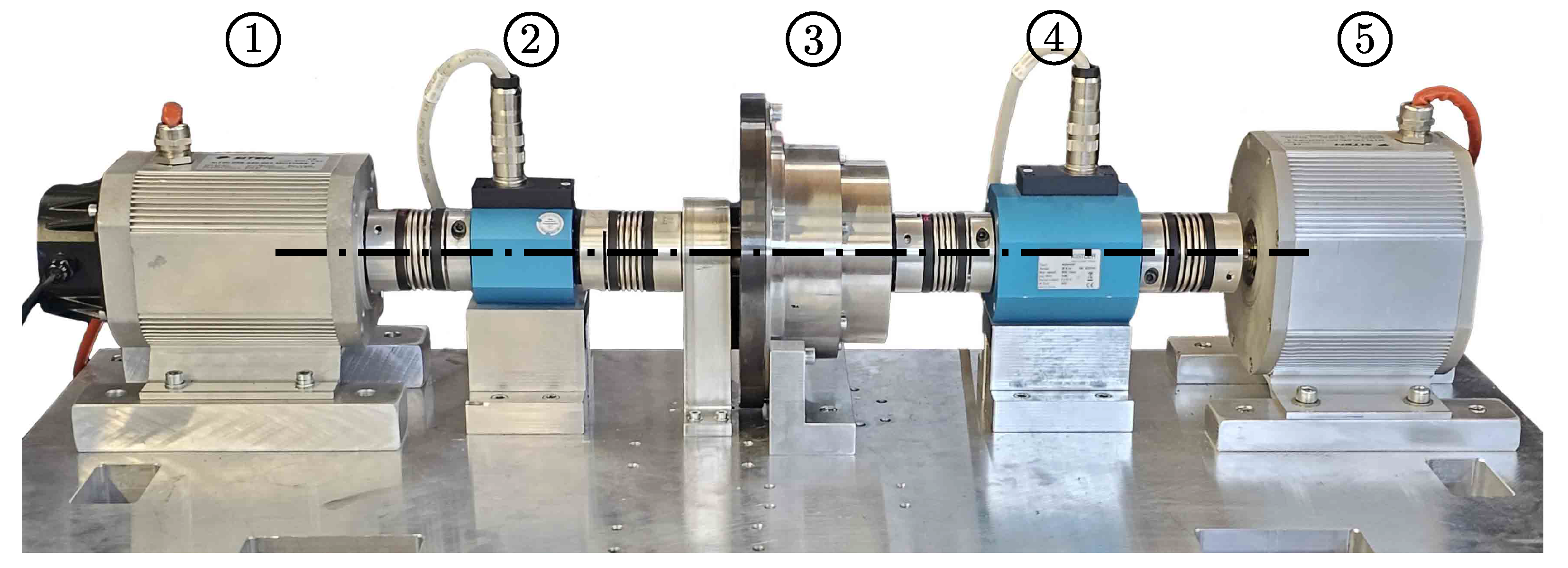
3. Experimental Set-Up
4. Experimental Test and Discussion
4.1. Velocity Ratio
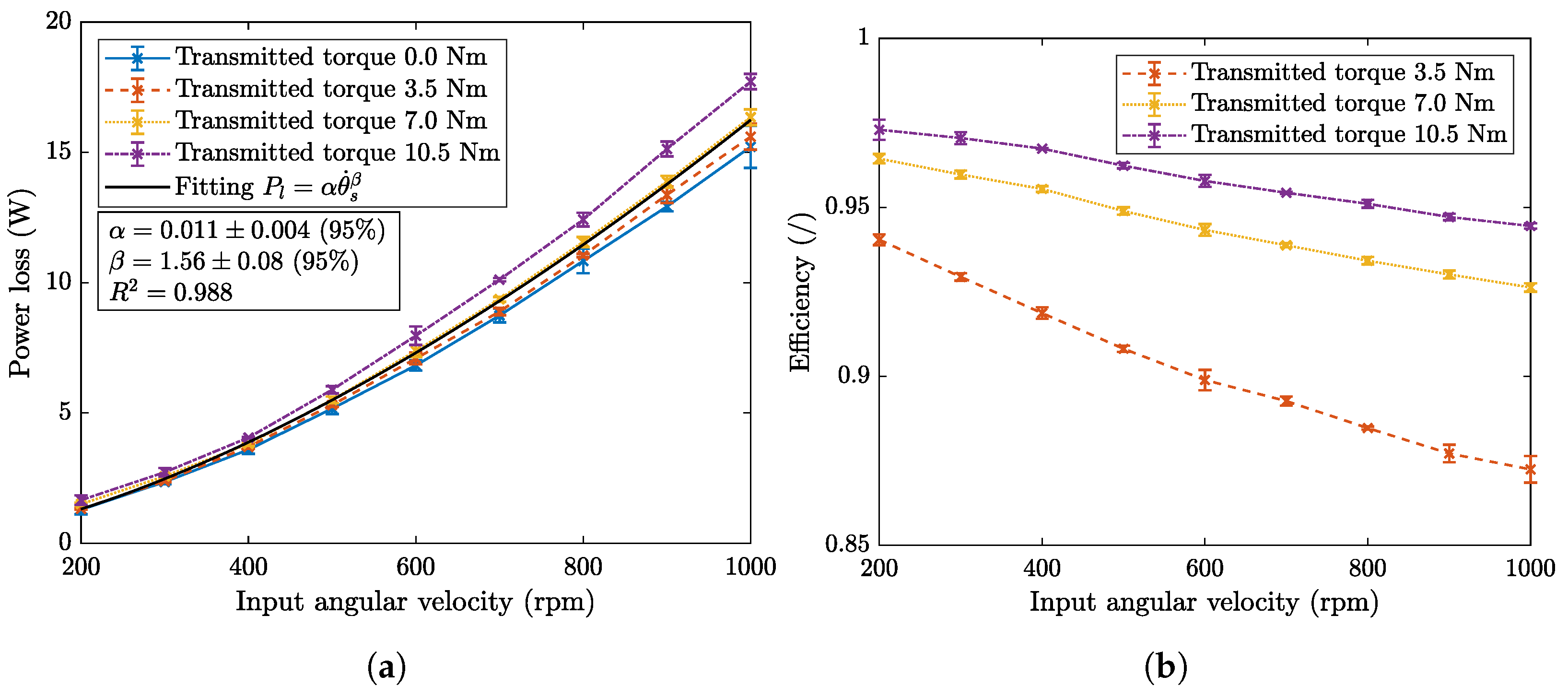
4.2. Power Losses
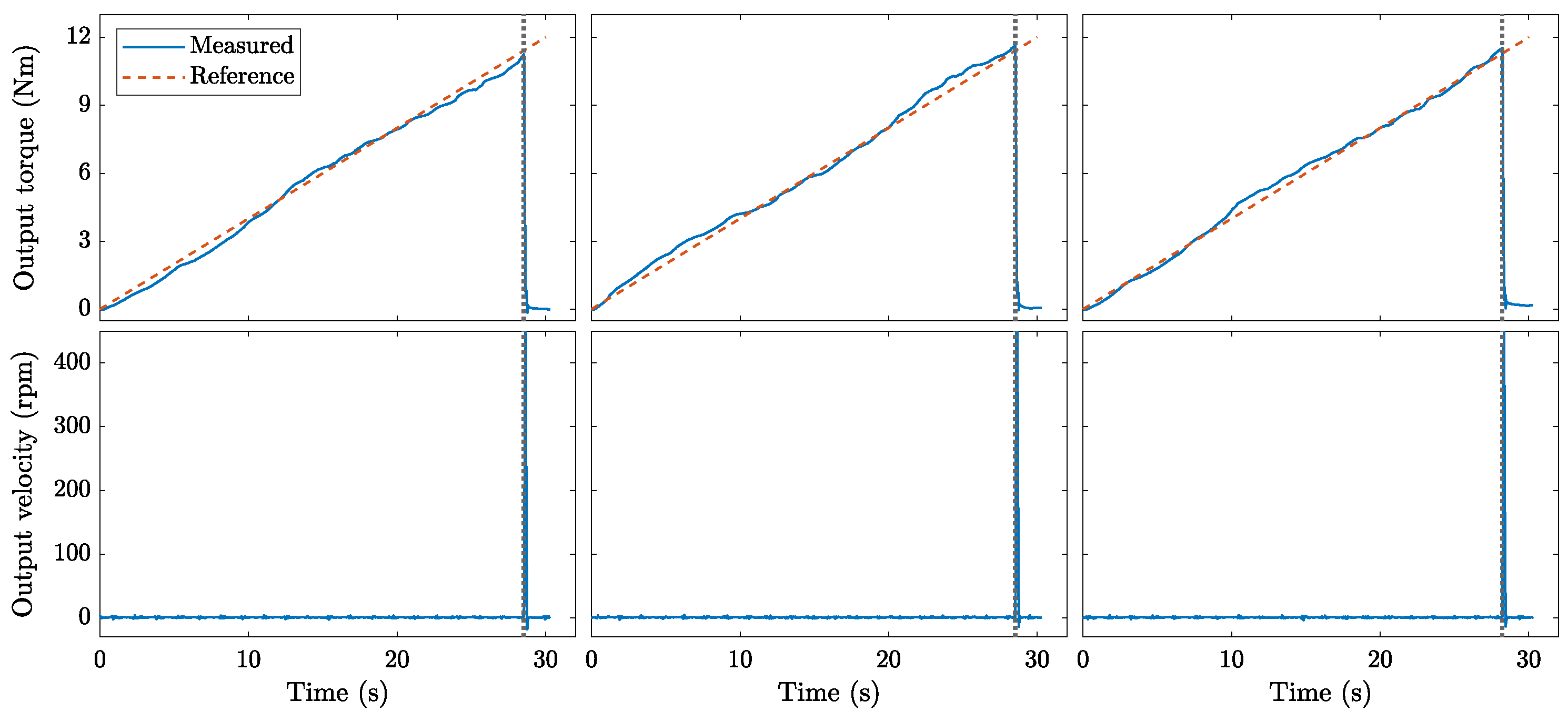
4.3. Overload Protection
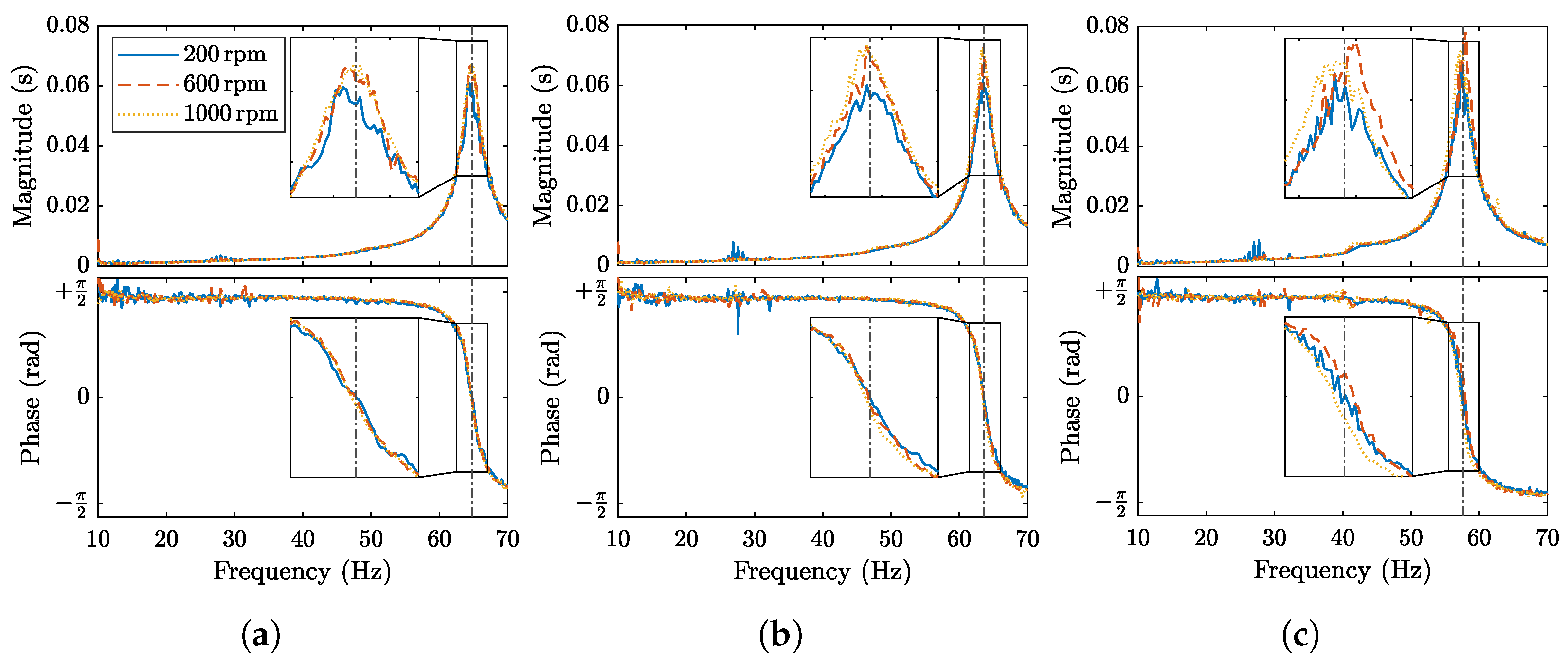
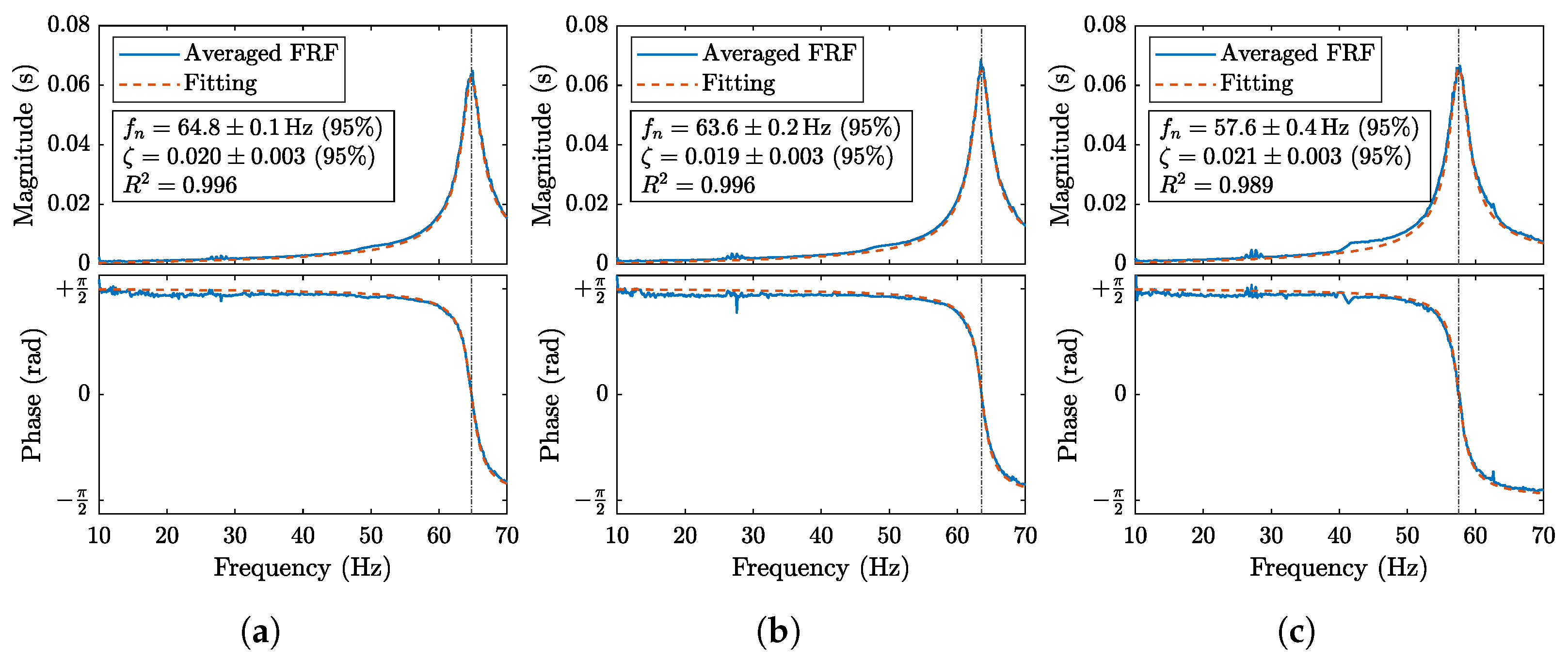
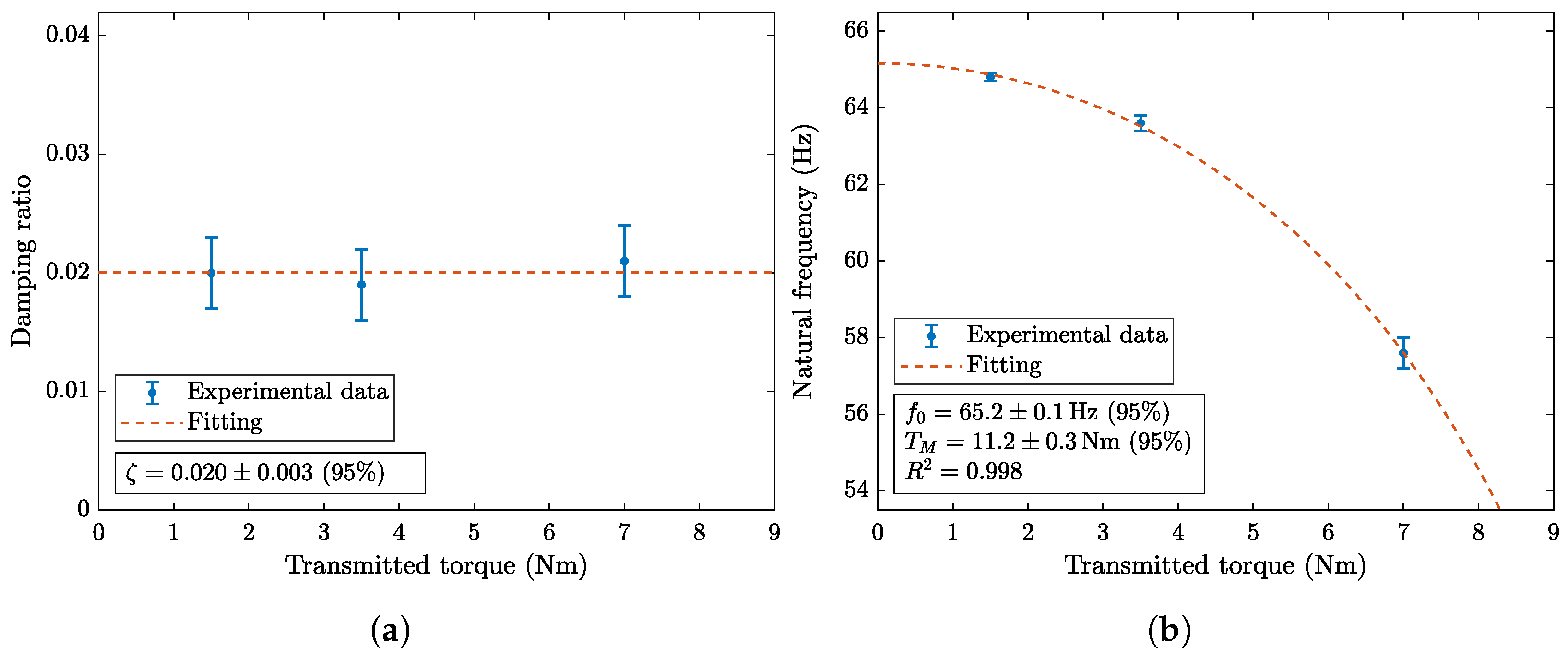
4.4. Frequency Response
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Faus, H. Magnetic Gearing. U.S. Patent 2243555A, 27 May 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J. Magnetic Transmission. U.S. Patent 3378710A, 16 April 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Atallah, K.; Howe, D. A novel high-performance magnetic gear. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 2844–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, K.; Wang, J.; Howe, D. A high-performance linear magnetic gear. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 10N516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Filippini, M.; Bianchi, N.; Alotto, P. A Review on Magnetic Gears: Topologies, Computational Models, and Design Aspects. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.; Makita, S.; Arimoto, S. Non-contact magnetic gear for micro transmission mechanism. In Proceedings of the [1991] Proceedings. IEEE Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Nara, Japan, 30 January–2 February 1991; pp. 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezani, S.; Atallah, K.; Howe, D. A high-performance axial-field magnetic gear. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08R303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rens, J.; Atallah, K.; Calverley, S.D.; Howe, D. A novel magnetic harmonic gear. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference, Antalya, Turkey, 3–5 May 2007; Volume 1, pp. 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, N.W.; Toliyat, H.A. Gearing ratios of a magnetic gear for wind turbines. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 May 2009; pp. 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.J.; Gerber, S. Magnetically geared wind generator technologies: Opportunities and challenges. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGilton, B.; Crozier, R.; McDonald, A.; Mueller, M. Review of magnetic gear technologies and their applications in marine energy. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2018, 12, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidler, J.J. NASA’s Magnetic Gearing Research for Electrified Aircraft Propulsion. In Proceedings of the 2018 AIAA/IEEE Electric Aircraft Technologies Symposium, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 9–11 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, M.; Torchio, R.; Alotto, P.; Bonisoli, E.; Dimauro, L.; Repetto, M. A New Class of Devices: Magnetic Gear Differentials for Vehicle Drivetrains. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 2382–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimauro, L.; Bonisoli, E.; Velardocchia, M.; Repetto, M.; Alotto, P.; Filippini, M.; Torchio, R. Magnetic gearbox for automotive power transmissions: An innovative industrial technology. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2023, 46, 101497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, K.; Calverley, S.D.; Howe, D. Design, Analysis and Realisation of a High-Performance Magnetic Gear. IEE Proc.-Electr. Power Appl. 2004, 151, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Tsai, M.C.; Dorrell, D.G.; Lin, B.J. Development of a Magnetic Planetary Gearbox. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, S.; Wang, R.J. Evaluation of a prototype magnetic gear. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Cape Town, South Africa, 25–28 February 2013; pp. 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ponce, G.; Arjona, M.A.; Hernandez, C.; Escarela-Perez, R. A Review of Magnetic Gear Technologies Used in Mechanical Power Transmission. Energies 2023, 16, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaei, A.; Wang, Q. A Comprehensive Review of Concentric Magnetic Gears. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 5581–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montague, R.G.; Bingham, C.M.; Atallah, K. Magnetic gear overload detection and remedial strategies for servo-drive systems. In Proceedings of the SPEEDAM 2010, Pisa, Italy, 14–16 June 2010; pp. 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, M.; Alotto, P. Coaxial Magnetic Gear Design and Optimization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 9934–9942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, K.; Wang, J.; Calverley, S.D.; Duggan, S. Design and operation of a magnetic Continuously Variable Transmission. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 15–18 May 2011; pp. 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzevich, S.P. Dudley’s Handbook of Practical Gear Design and Manufacture, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaudov, K.; Karaivanov, D.P. Planetary Gear Trains, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, P. The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: A method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 1967, 15, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, T.M.; Parker, R.G. Experimental measurement of the effects of torque on the dynamic behavior and system parameters of planetary gears. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 74, 370–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Description | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Traction motor | Load motor | |
| Maximum speed | 3000 rpm | 1500 rpm |
| Nominal torque | 5.2 Nm | 9.2 Nm |
| Nominal voltage | 400 V | 400 V |
| Torque constant | 1.5 Nm/A | 3.3 Nm/A |
| Inertia | 2.88 kg cm2 | 4.2 kg cm2 |
| Input torque sensor | Output torque sensor | |
| Maximum torque | 10 Nm | 20 Nm |
| Analog signal range | V | V |
| Sensitivity | 0.9996 Nm/V | 1.999 Nm/V |
| Torsional stiffness | 855 Nm/rad | 8690 Nm/rad |
| Inertia | 0.03 kg cm2 | 0.9 kg cm2 |
| Input elastic joint | Output elastic joint | |
| Torsional stiffness | 20,000 Nm/rad | 20,000 Nm/rad |
| Inertia | 0.6 kg cm2 | 0.6 kg cm2 |
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of sun pole pairs | 5 |
| Number of ring pole pairs | 13 |
| Number of carrier iron poles Q | 18 |
| Nominal limit torque at the carrier (from 3D FEM) | 13.1 Nm |
| Nominal velocity ratio (output/input) | 0.278 |
| Moment of inertia of the sun | 11.3 kg cm2 |
| Moment of inertia of the carrier | 12.5 kg cm2 |
| Moment of inertia of the ring | 313.3 kg cm2 |
| Maximum meshing stiffness at the carrier | 236 Nm/rad |
| Maximum meshing stiffness at the sun | 18.2 Nm/rad |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lovato, S.; Barosco, G.; Ortombina, L.; Torchio, R.; Alotto, P.; Repetto, M.; Massaro, M. Experimental Analysis of a Coaxial Magnetic Gear Prototype. Machines 2025, 13, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080716
Lovato S, Barosco G, Ortombina L, Torchio R, Alotto P, Repetto M, Massaro M. Experimental Analysis of a Coaxial Magnetic Gear Prototype. Machines. 2025; 13(8):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080716
Chicago/Turabian StyleLovato, Stefano, Giovanni Barosco, Ludovico Ortombina, Riccardo Torchio, Piergiorgio Alotto, Maurizio Repetto, and Matteo Massaro. 2025. "Experimental Analysis of a Coaxial Magnetic Gear Prototype" Machines 13, no. 8: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080716
APA StyleLovato, S., Barosco, G., Ortombina, L., Torchio, R., Alotto, P., Repetto, M., & Massaro, M. (2025). Experimental Analysis of a Coaxial Magnetic Gear Prototype. Machines, 13(8), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080716










