Data Acquisition and Chatter Recognition Based on Multi-Sensor Signals for Blade Whirling Milling
Abstract
1. Introduction
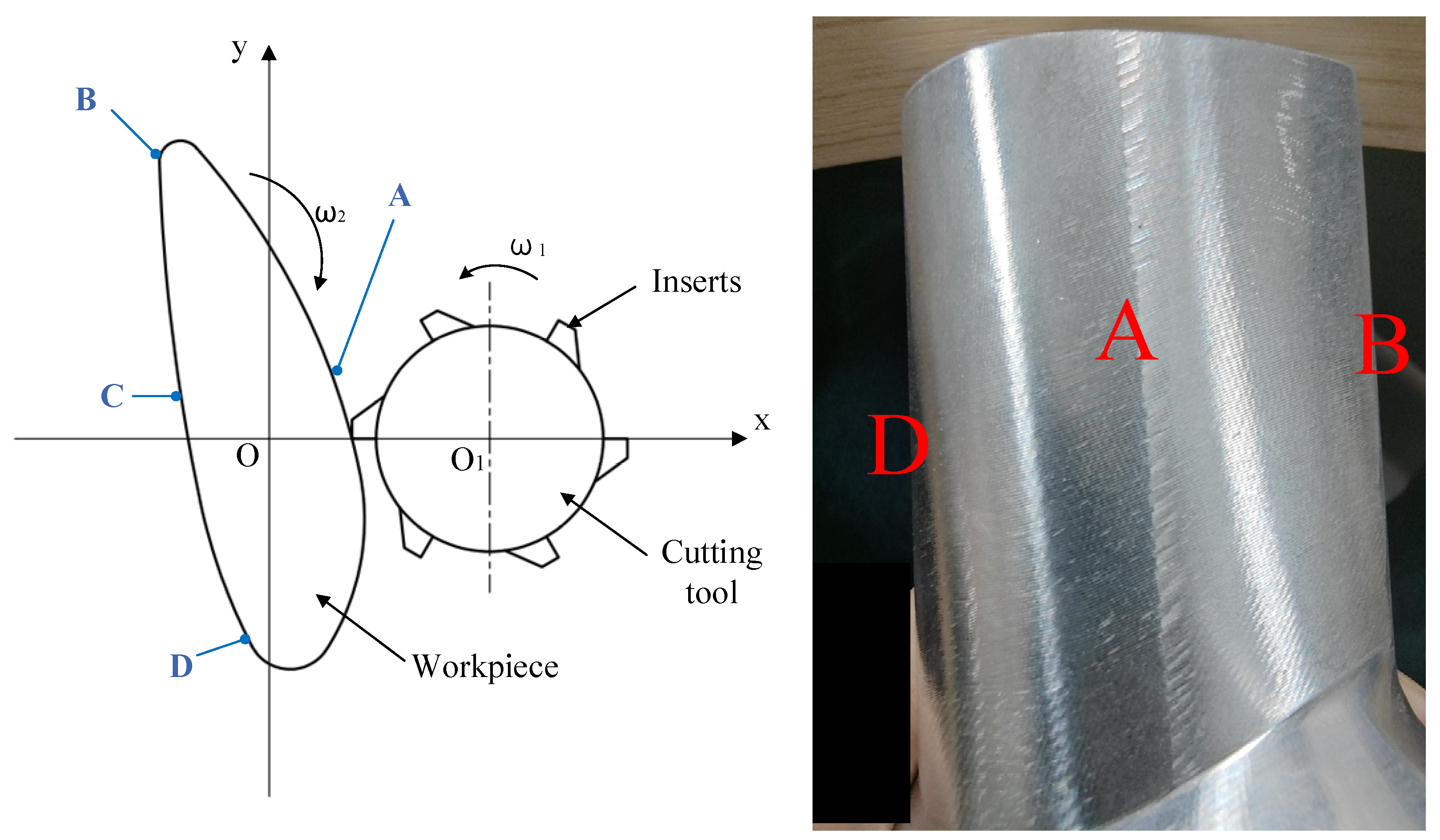
2. Overview of the Whirling Milling Process of Blades
3. Data Acquisition
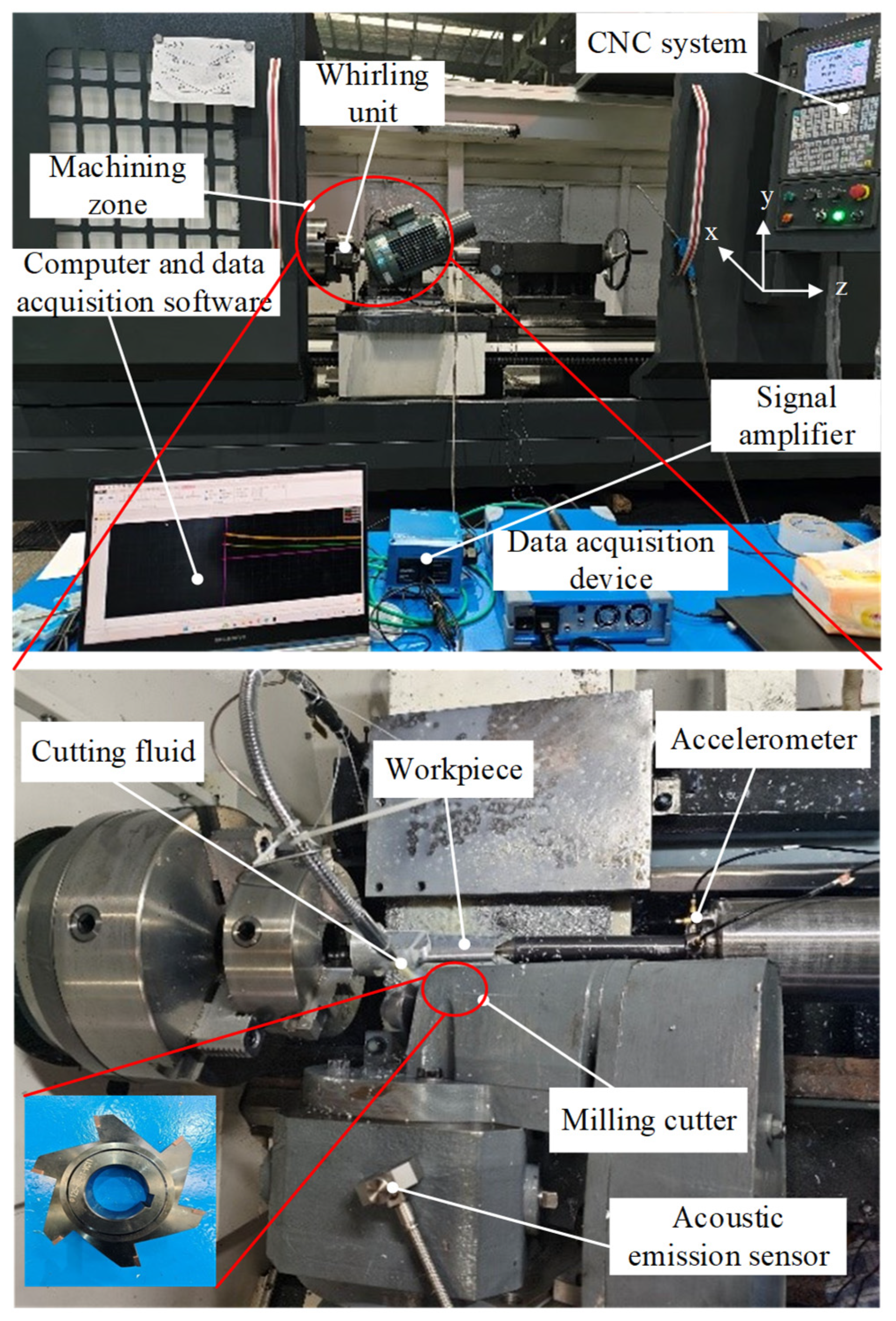
3.1. Experimental Setup
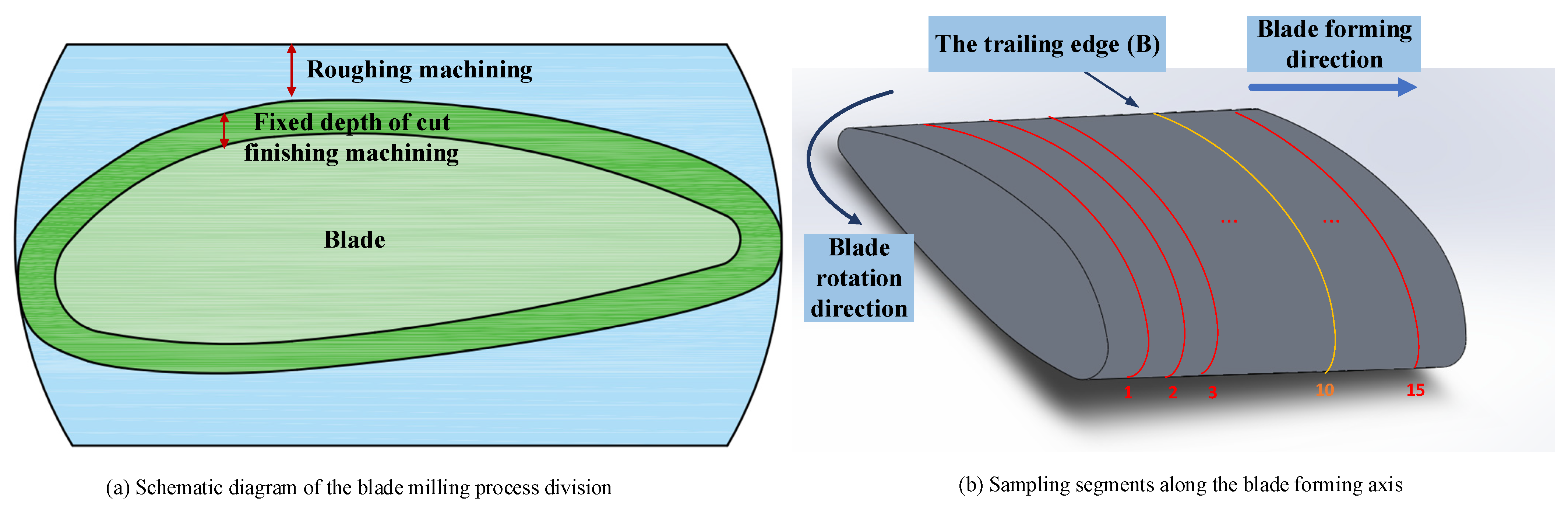
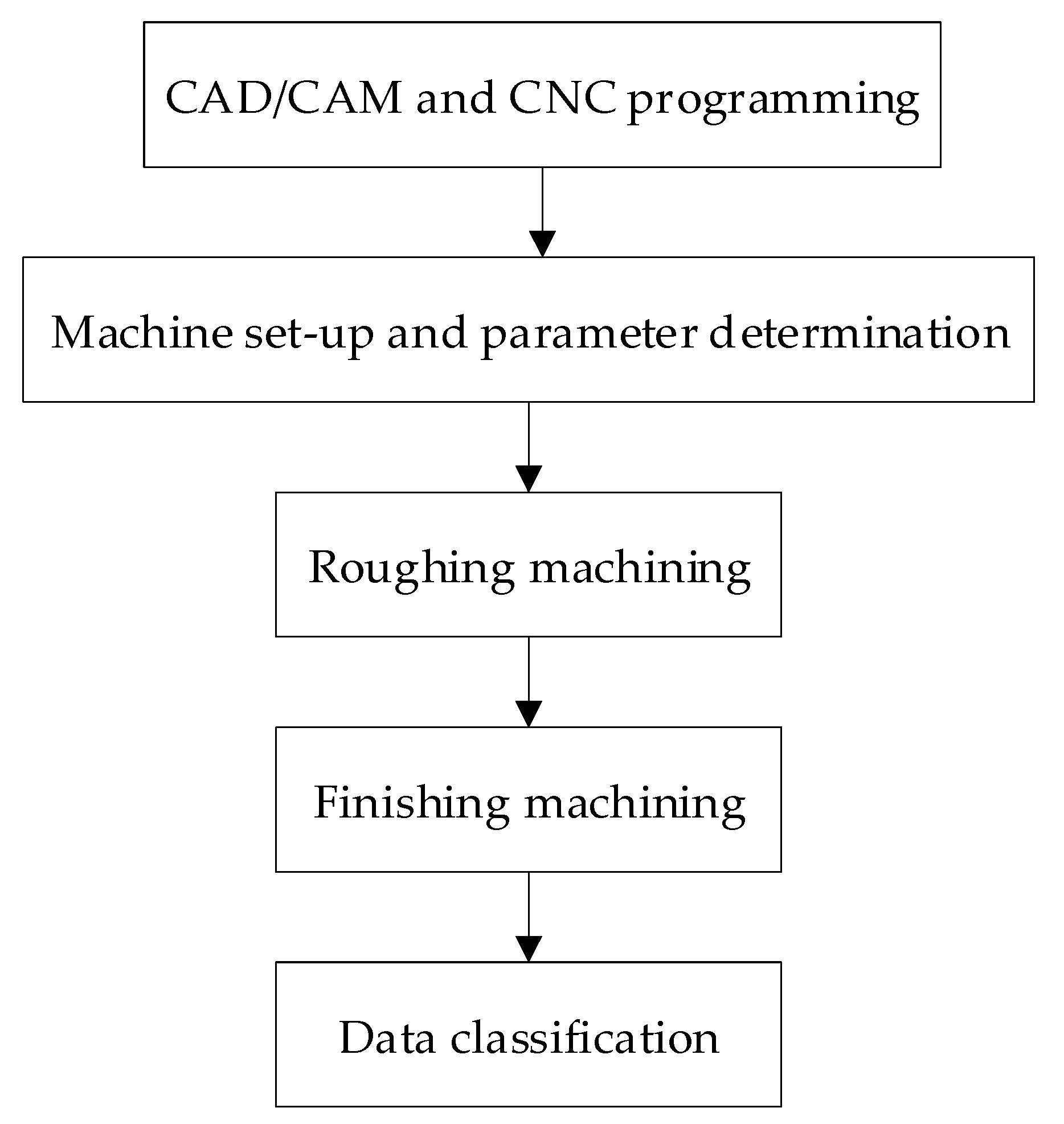
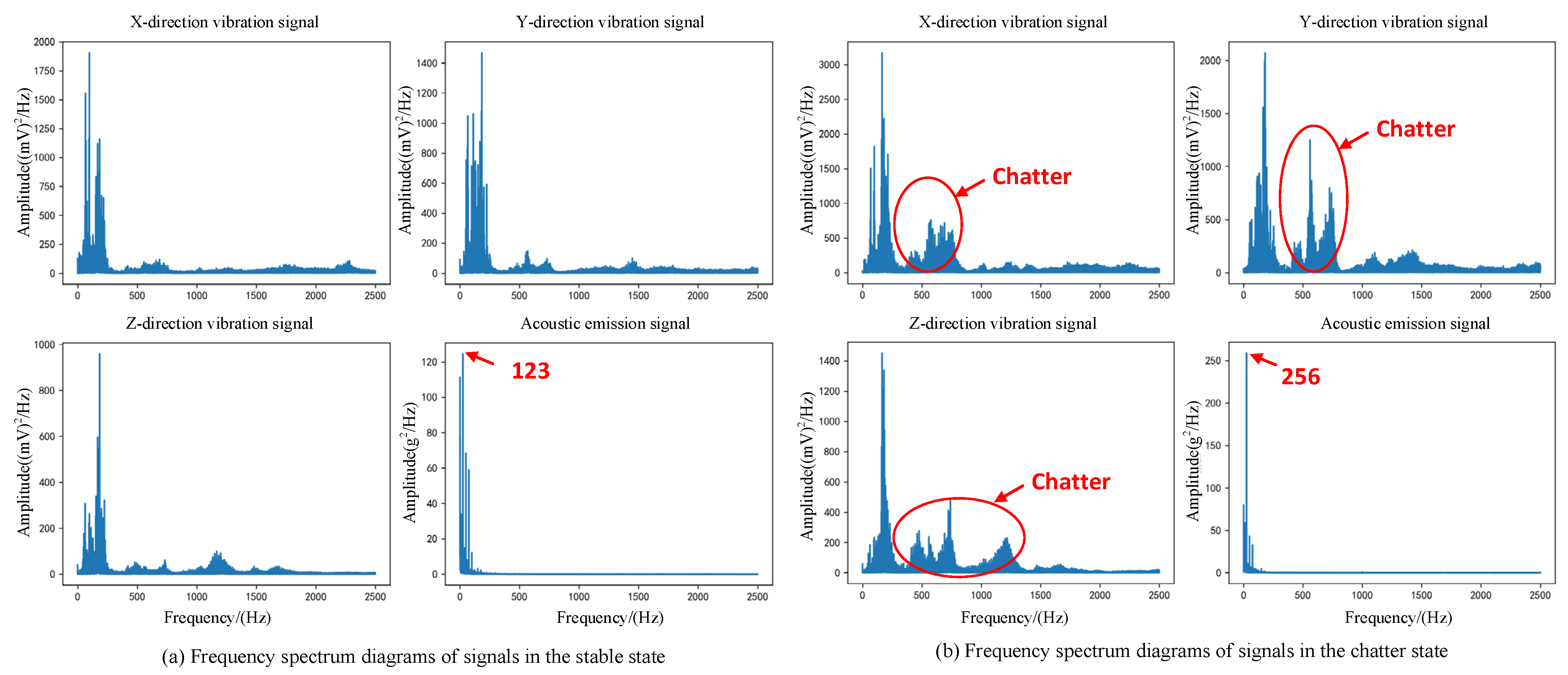
3.2. Experimental Cuts and Data Acquisition
4. Chatter Recognition Validation
4.1. Multi-Signal Feature Selection and Fusion
4.2. Chatter Recognition Model Based on PCA-MLGRU-SAM
4.3. Chatter Recognition Result Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, Z.; Ma, J.; Song, D.; Wang, F.; Liu, W. A review of contouring-error reduction method in multi-axis CNC machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2018, 125, 34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Meng, G. Chatter mitigation for the milling of thin-walled workpiece. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 138, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Liu, R.; Liu, X. Modal parameter determination and chatter prediction for blade whirling: A comparative study based on symmetric and asymmetric FRF. Adv. Manuf. 2021, 9, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanger, F.; Sellmeier, V.; Klose, J.; Bartkowiak, M.; Schulze, V. Comparison of modeling methods to determine cutting tool profile for conventional and synchronized whirling. Procedia Cirp. 2017, 58, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omirou, S.; Charalambides, M.; Chasos, C. Advanced CNC thread milling: A comprehensive canned cycle for efficient cutting of threads with fixed or variable pitch and radius. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 133, 2219–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Predicting residual properties of ball screw raceway in whirling milling based on machine learning. Measurement 2021, 173, 108605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botak, Z.; Pisačić, K.; Horvat, M.; Tomić, T. Determination of Optimal Machining Parameters Based on Roughness and Vibration Measurements of Pieces Produced by Whirling on a Lathe Machine. Machines 2024, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merticaru, V.; Nagîț, G.; Dodun, O.; Merticaru, E.; Rîpanu, M.I.; Mihalache, A.M.; Slătineanu, L. Influence of Machining Conditions on Micro-Geometric Accuracy Elements of Complex Helical Surfaces Generated by Thread Whirling. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Cao, H.; Tao, G.; Yi, H.; Chen, Z. Recent Progress of Chatter Detection and Tool Wear Online Monitoring in Machining Process: A Review and Future Prospects. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2024, 143, 106840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Li, X.; Yin, Y.; Hong, J. Milling chatter detection by multi-feature fusion and Adaboost-SVM. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 156, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, D.; Hong, D.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zan, S.; Liao, Z. Improving generalisation and accuracy of on-line milling chatter detection via a novel hybrid deep convolutional neural network. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 193, 110241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, Z. Online chatter suppression in turning by adaptive amplitude modulation of spindle speed variation. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2018, 140, 121003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y.; Song, Q.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, Z. An interpretable anti-noise convolutional neural network for online chatter detection in thin-walled parts milling. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 206, 110885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, L.; Ni, C. Chatter detection in milling process based on VMD and energy entropy. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 105, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Huang, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, M. An intelligent chatter detection method for high-speed milling under variable tool-workpiece systems and cutting parameters. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 224, 111960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumusanu, G.R.; Constantin, I.C.; Marinescu, V.; Epureanu, A. Development of a stability intelligent control system for turning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 64, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoa, J.; Beudaert, X.; Dombovari, Z.; Altintas, Y.; Budak, E.; Brecher, C.; Stepan, G. Chatter suppression techniques in metal cutting. CIRP Ann. 2016, 65, 785–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, Q.; Jin, P.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Ma, H. Chatter suppression techniques in milling processes: A state of the art review. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrelli, M.; Cosco, F.; Gagliardi, F.; Mundo, D. In-process chatter detection using signal analysis in frequency and time-frequency domain. Machines 2021, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajnik, P.; Kopač, J. Modern machining of die and mold tools. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 157, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavruska, P.; Pesice, M.; Zeman, P.; Kozlok, T. Automated feed rate optimization with consideration of angular velocity according to workpiece shape. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.K.; Wan, M.; Zhang, W.H.; Yang, Y. Chatter detection methods in the machining processes: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 77, 240–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Devia, J.H.; Chen, Y.; Dao, D.V.; Li, H. Chatter detection in milling processes—A review on signal processing and condition classification. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 3943–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Liu, R.; Liu, X.; Feng, J. Theoretical modeling and chatter prediction for the whirling process of airfoil blades with consideration of asymmetric FRF and material removal. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 2613–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, R.; Li, Y. Adapting whirling process for CNC manufacture of bespoke screws with variable pitch and diameters. Int. J. Manuf. Res. 2020, 15, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, R. An MLGRU and SAM-based Approach to Milling Chatter Detection using Multi-sensor Data. Eng. Res. Express, 2024; accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, A.; El-Henawy, I.; Salah, A.; Li, K. Optimizing deep neural networks hyperparameter positions and values. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 37, 6665–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Spindle Speed (rpm) | Cutting Depth (mm) | Feed Rate (mm/min) | Lubrication Method | Cutting Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roughing Machining | 1000 | 0.3–0.9 | 10, 20, 30, …, 150 | Cutting Fluid | Whirling Milling |
| Finishing Machining | 1000 | 0.3 | 10, 20, 30, …, 150 | Cutting Fluid | Whirling Milling |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Liu, R.; Zhu, Z. Data Acquisition and Chatter Recognition Based on Multi-Sensor Signals for Blade Whirling Milling. Machines 2025, 13, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13030206
Li X, Liu R, Zhu Z. Data Acquisition and Chatter Recognition Based on Multi-Sensor Signals for Blade Whirling Milling. Machines. 2025; 13(3):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13030206
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinyu, Riliang Liu, and Zhiying Zhu. 2025. "Data Acquisition and Chatter Recognition Based on Multi-Sensor Signals for Blade Whirling Milling" Machines 13, no. 3: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13030206
APA StyleLi, X., Liu, R., & Zhu, Z. (2025). Data Acquisition and Chatter Recognition Based on Multi-Sensor Signals for Blade Whirling Milling. Machines, 13(3), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13030206







