Optimization Design of Blade Profile Parameters of Low-Speed and High-Torque Turbodrill Based on GA-LSSVM-MOPSO-TOPSIS Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model Study
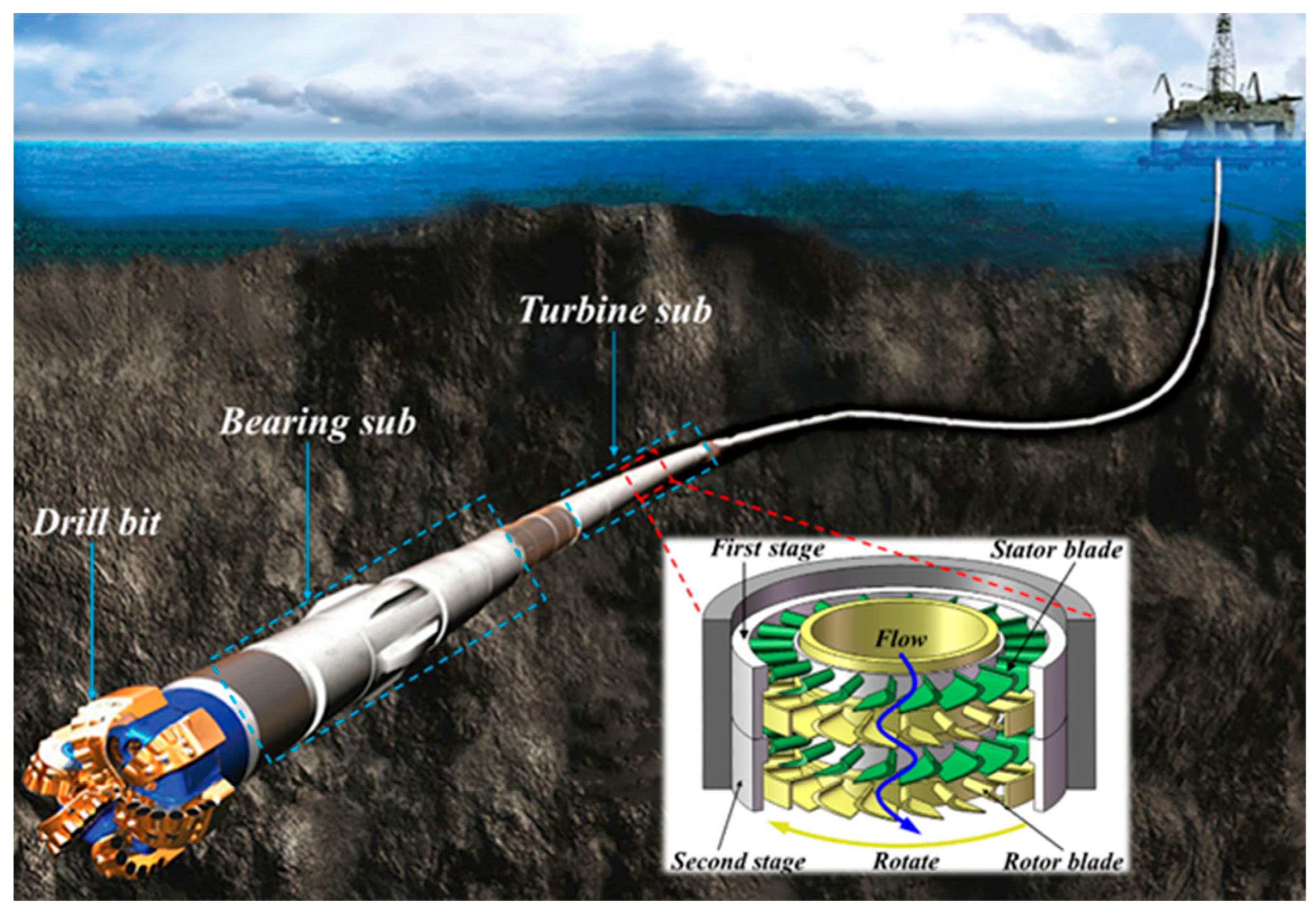
2.1. Working Principle of Turbodrill
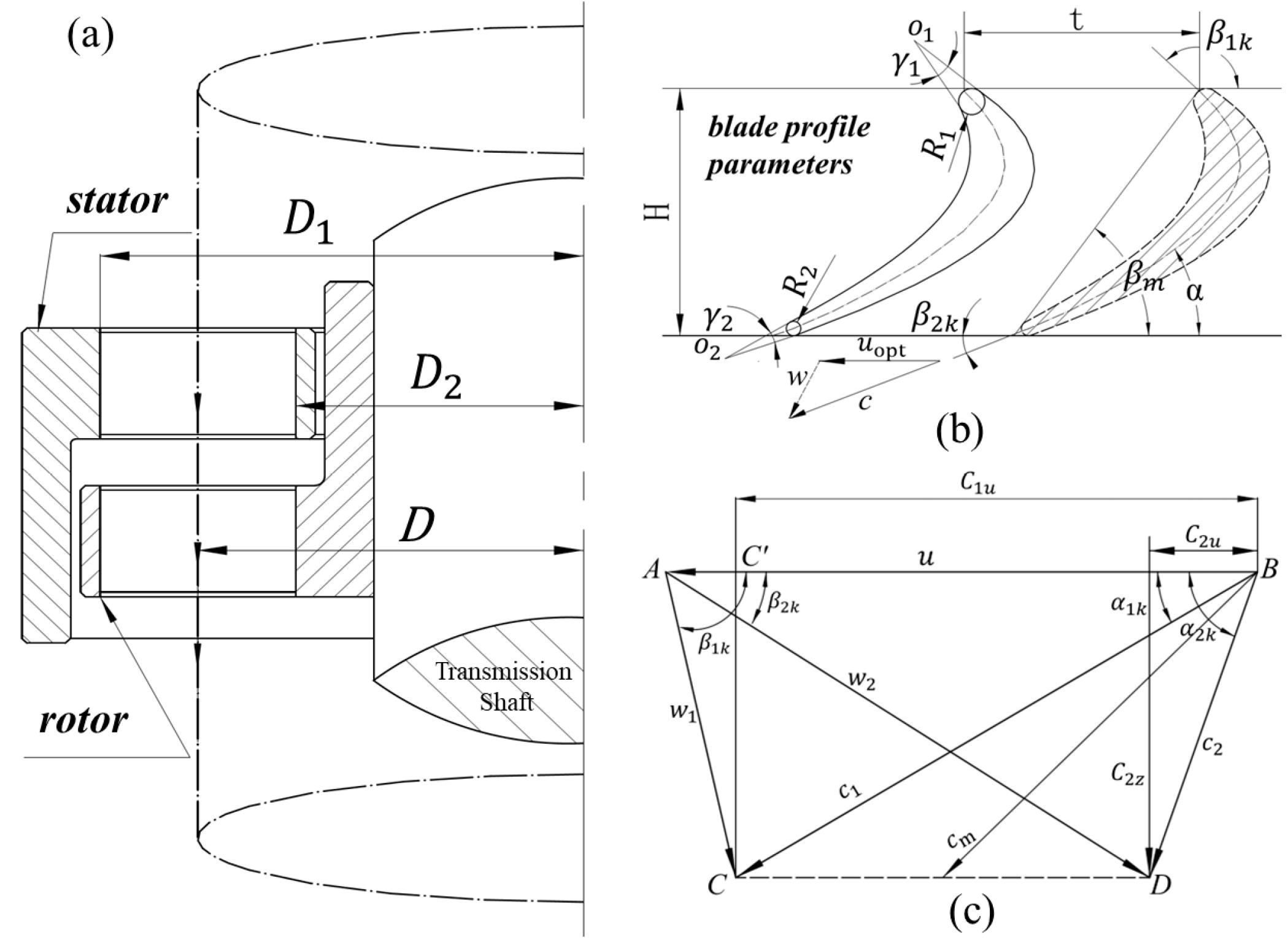
2.2. Theoretical Model of Turbodrill Output Characteristics
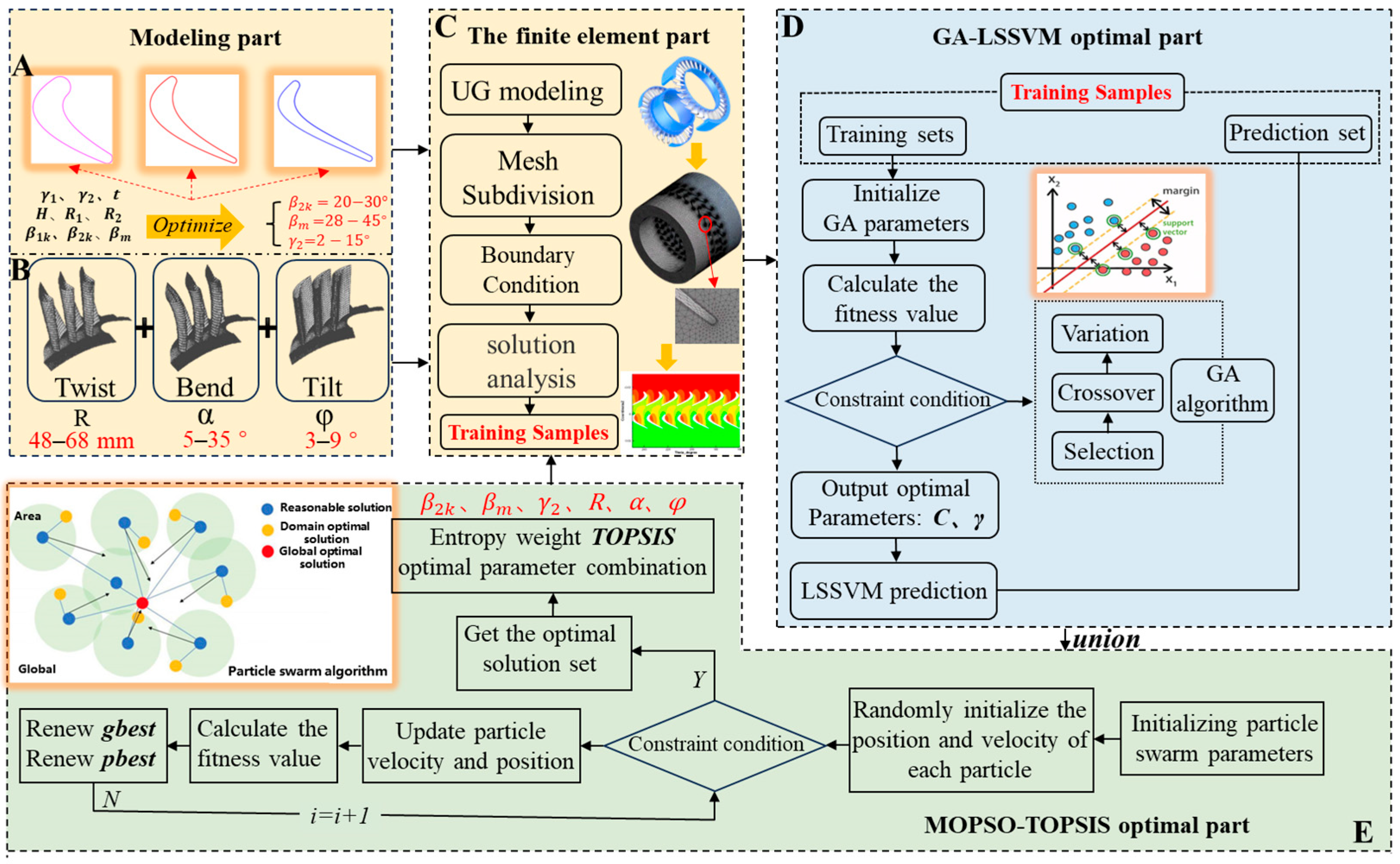
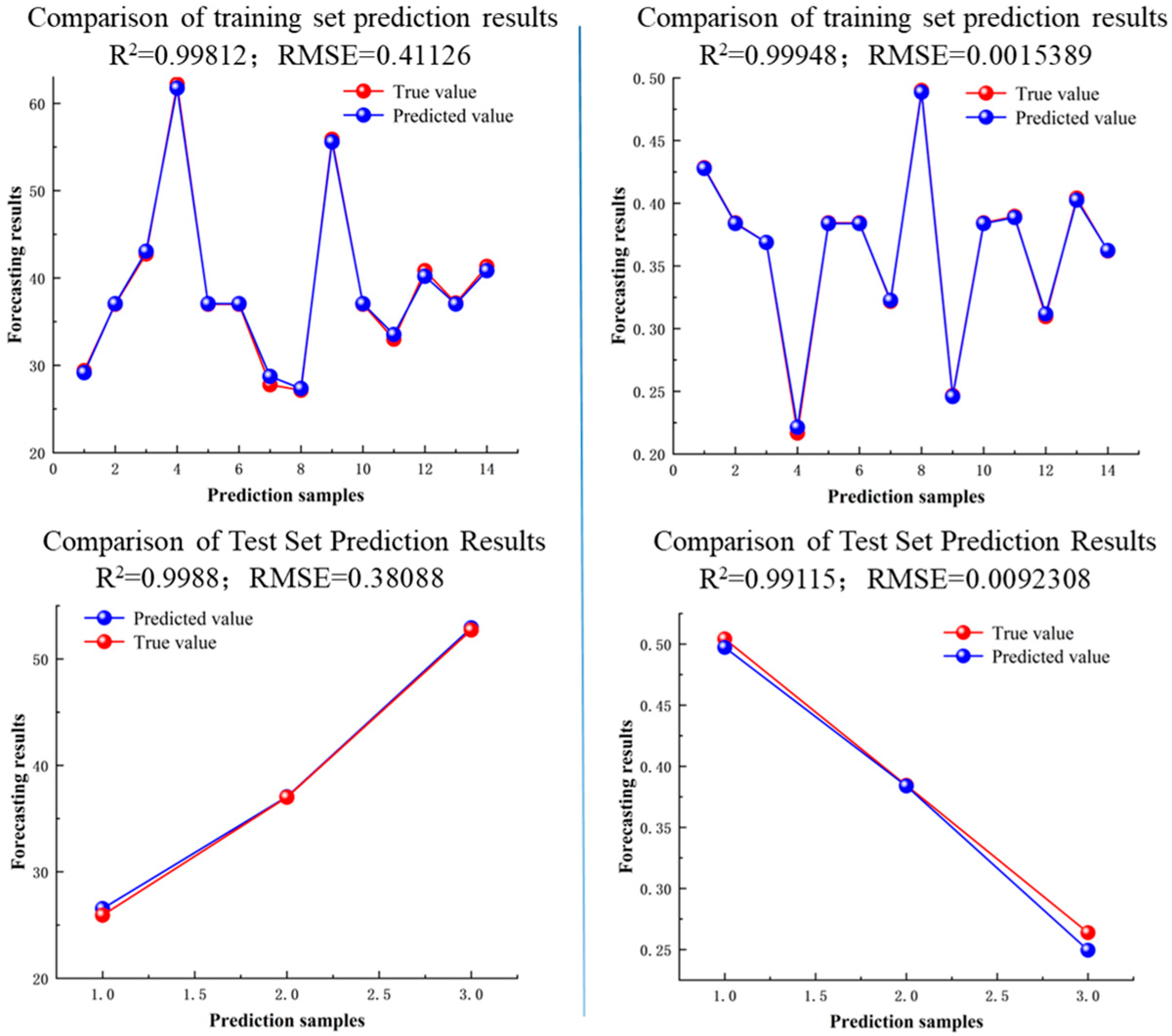
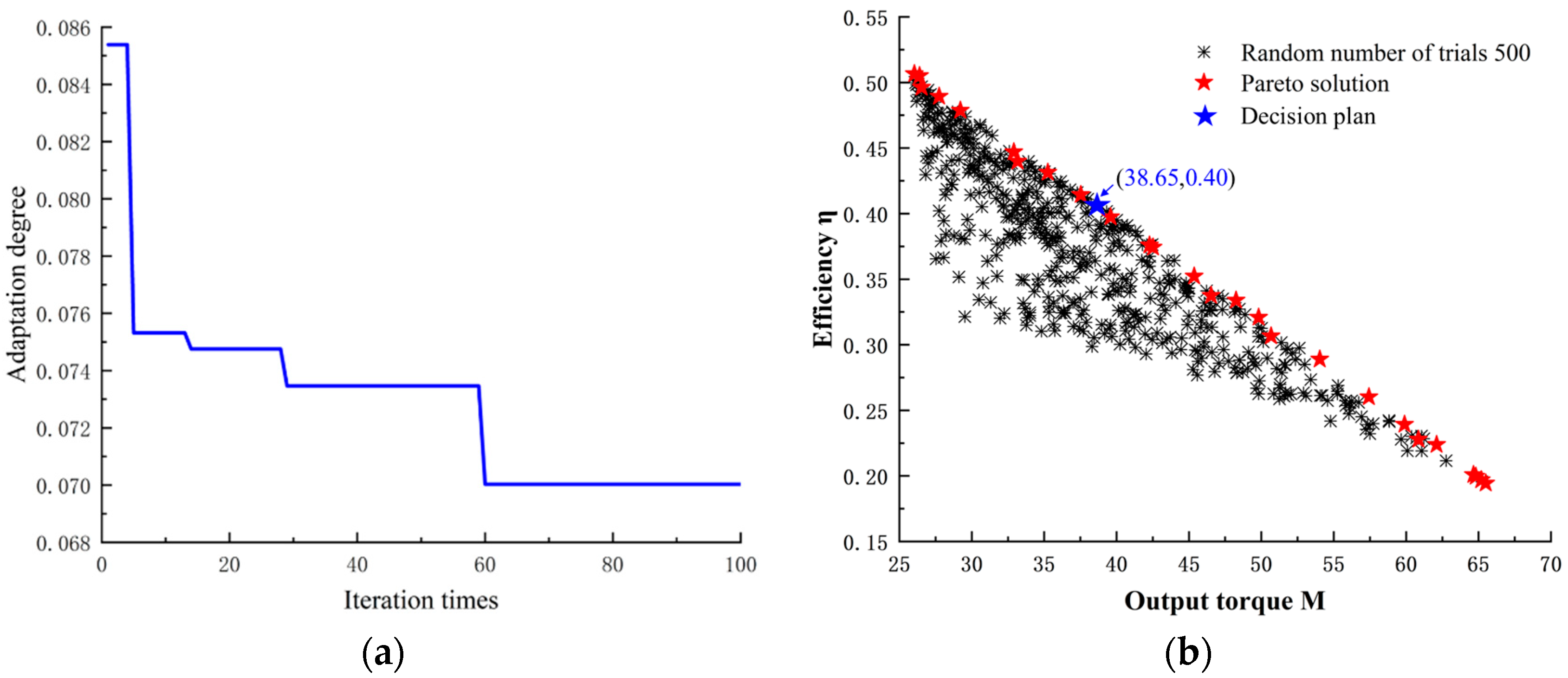
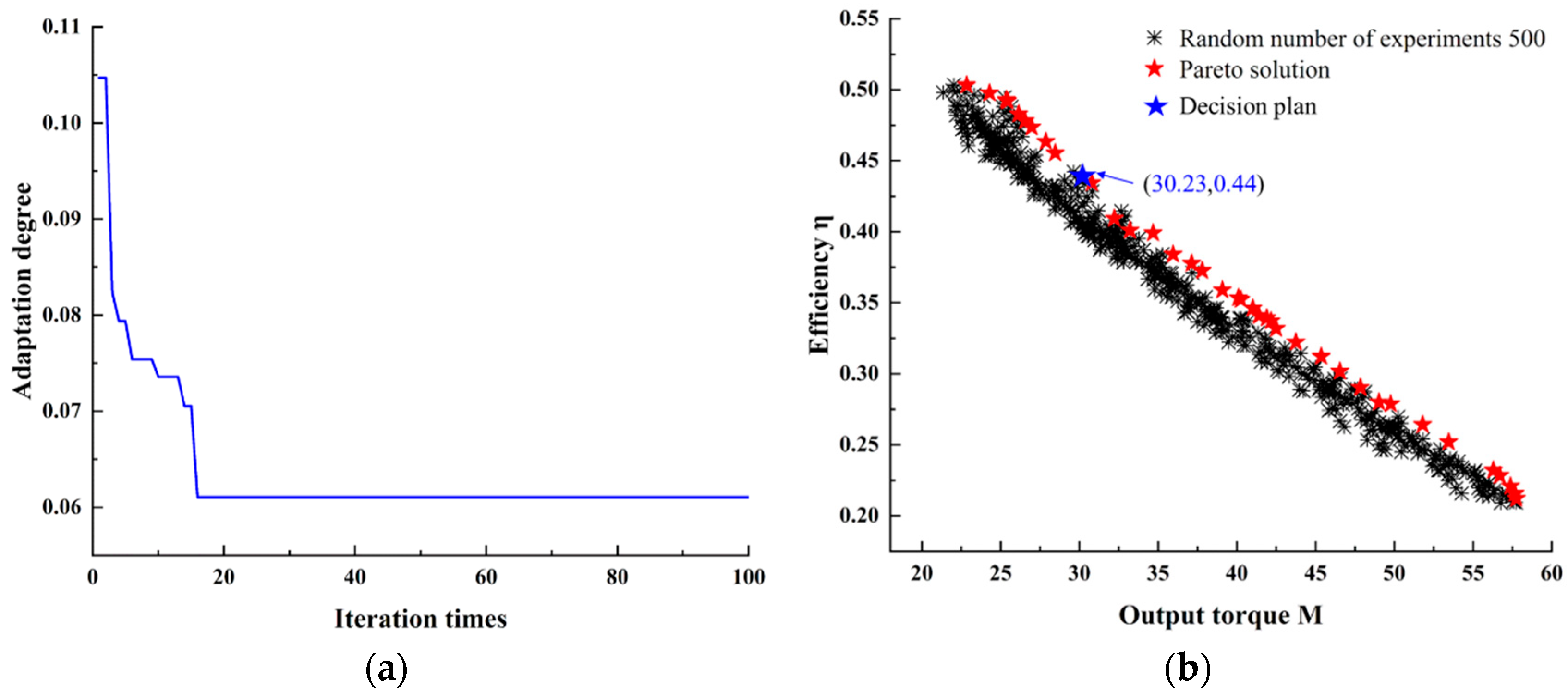
2.3. Intelligent Optimization Algorithm Model
3. Modeling Optimization and Result Analysis
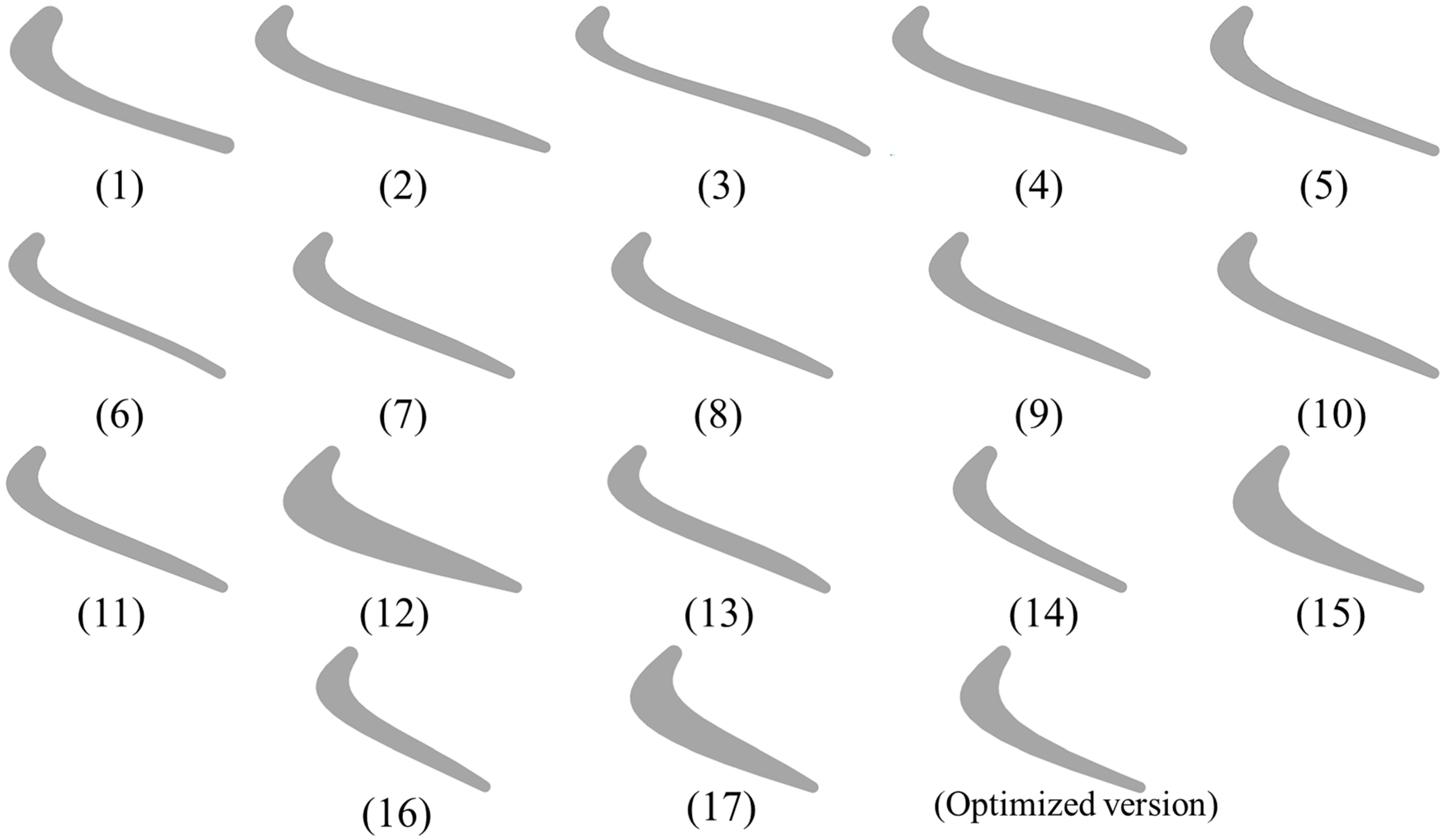
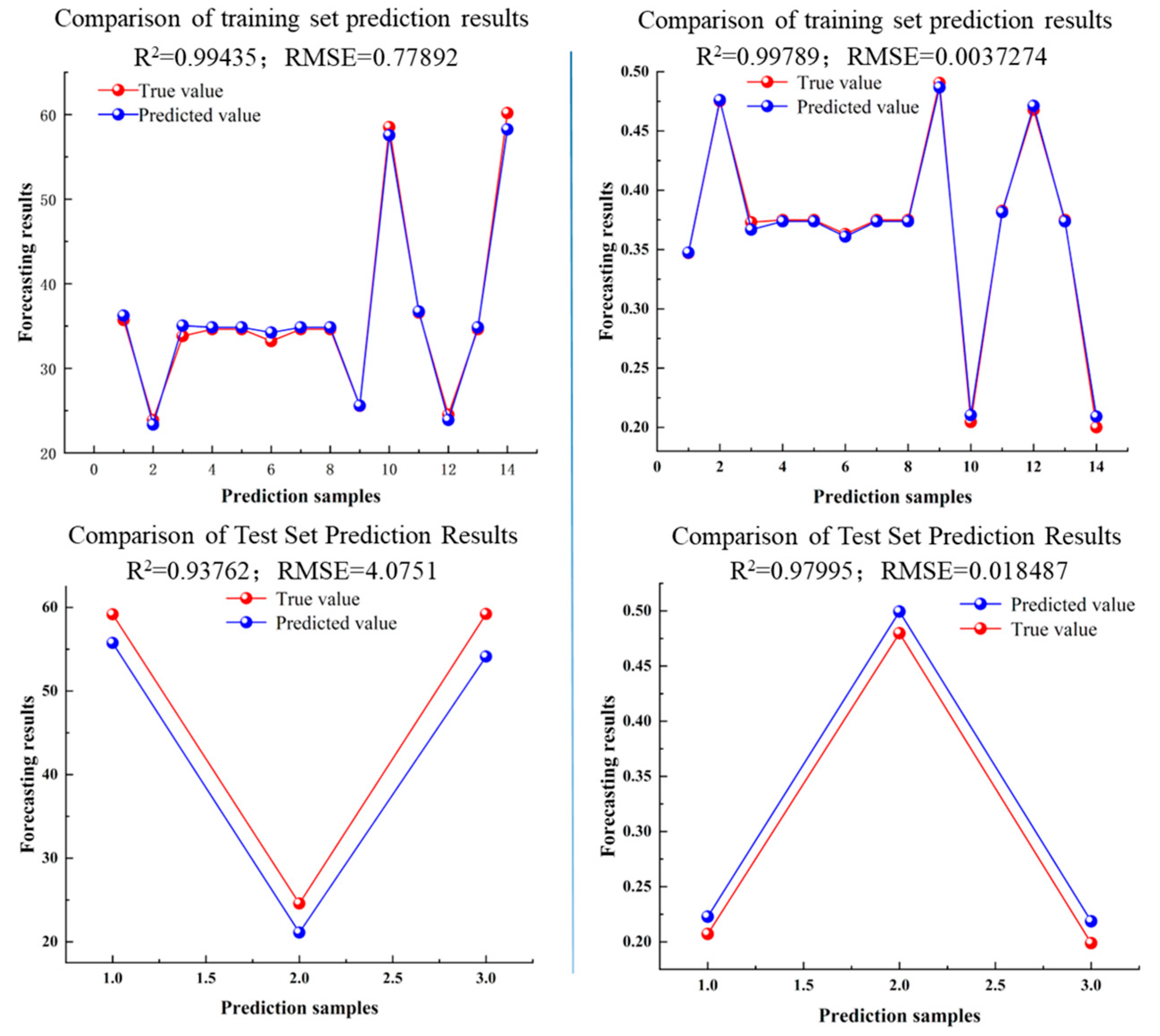
3.1. Intelligent Optimization Analysis of the Core Parameters of the Two-Dimensional Blade Profile Line
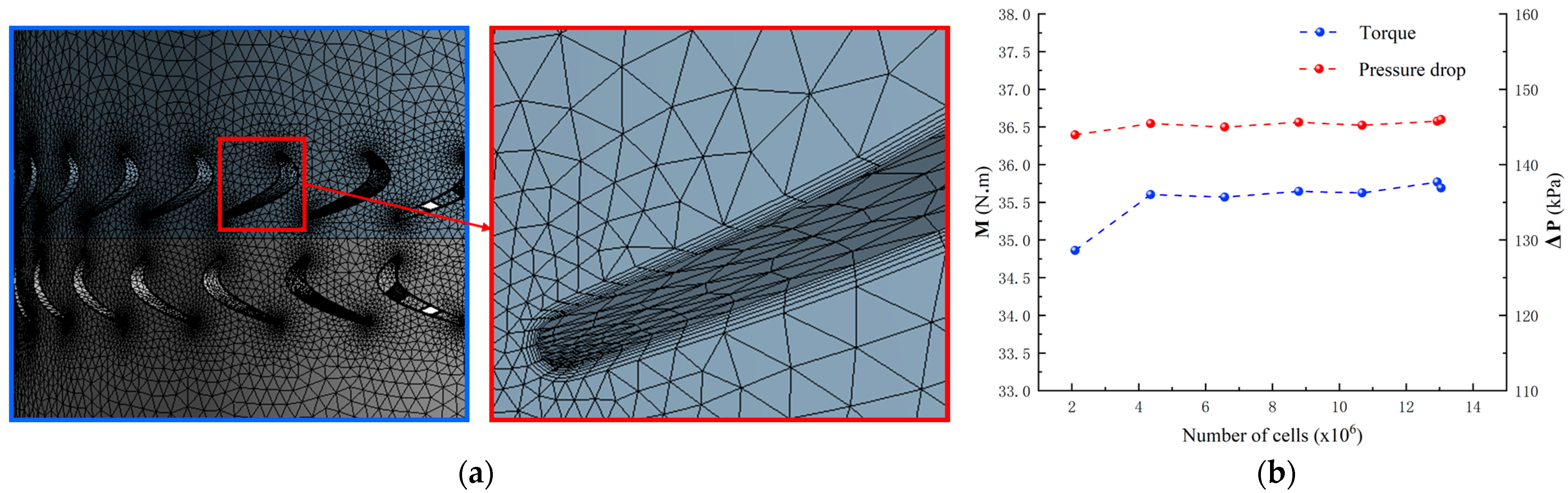
3.2. Numerical Simulation Model of Blade Motor Clearance Leakage
3.3. Blade Forming Method and Simulation Setting
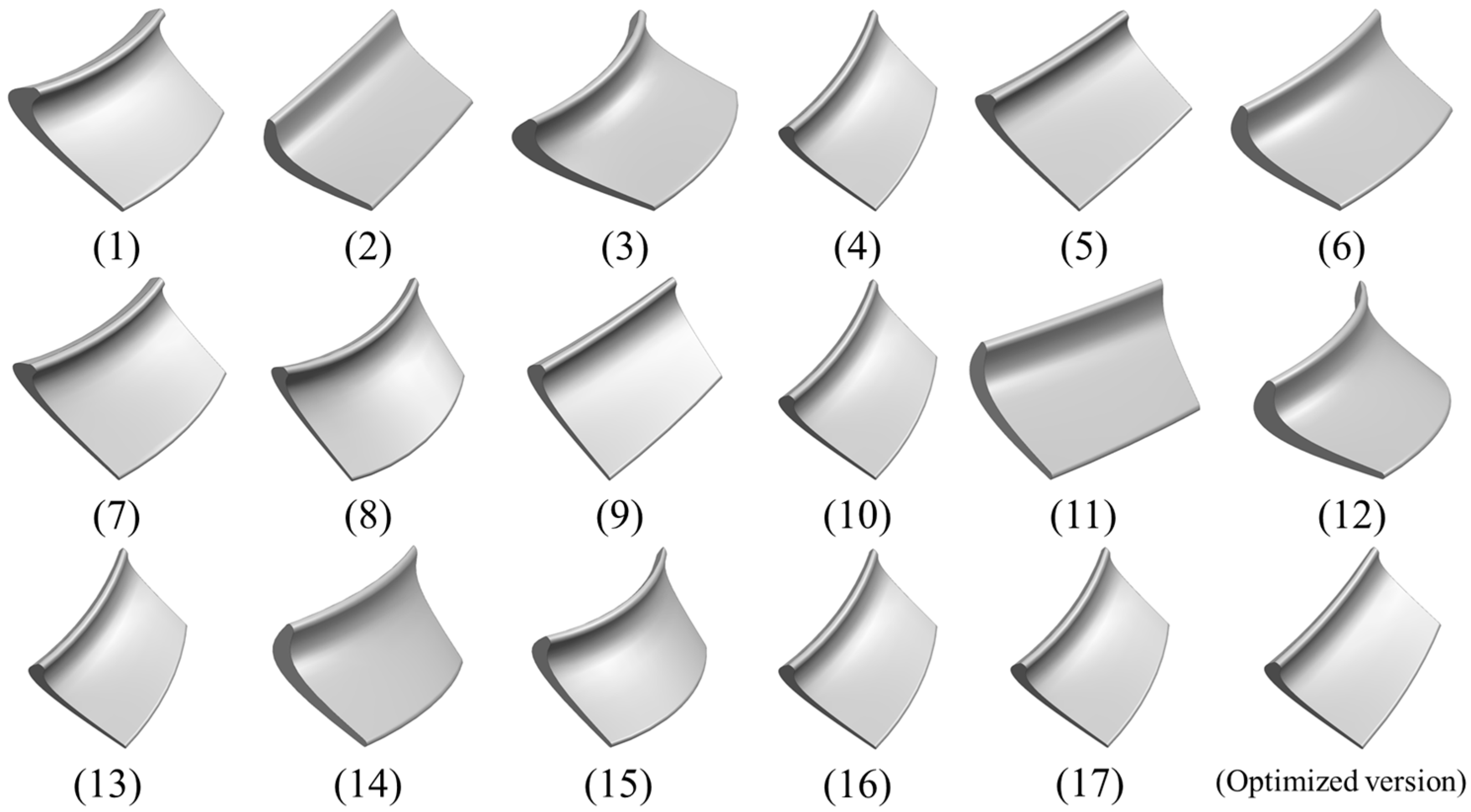
3.4. Research on Simulation Analysis of Turbine Blade
4. Conclusions
- (1)
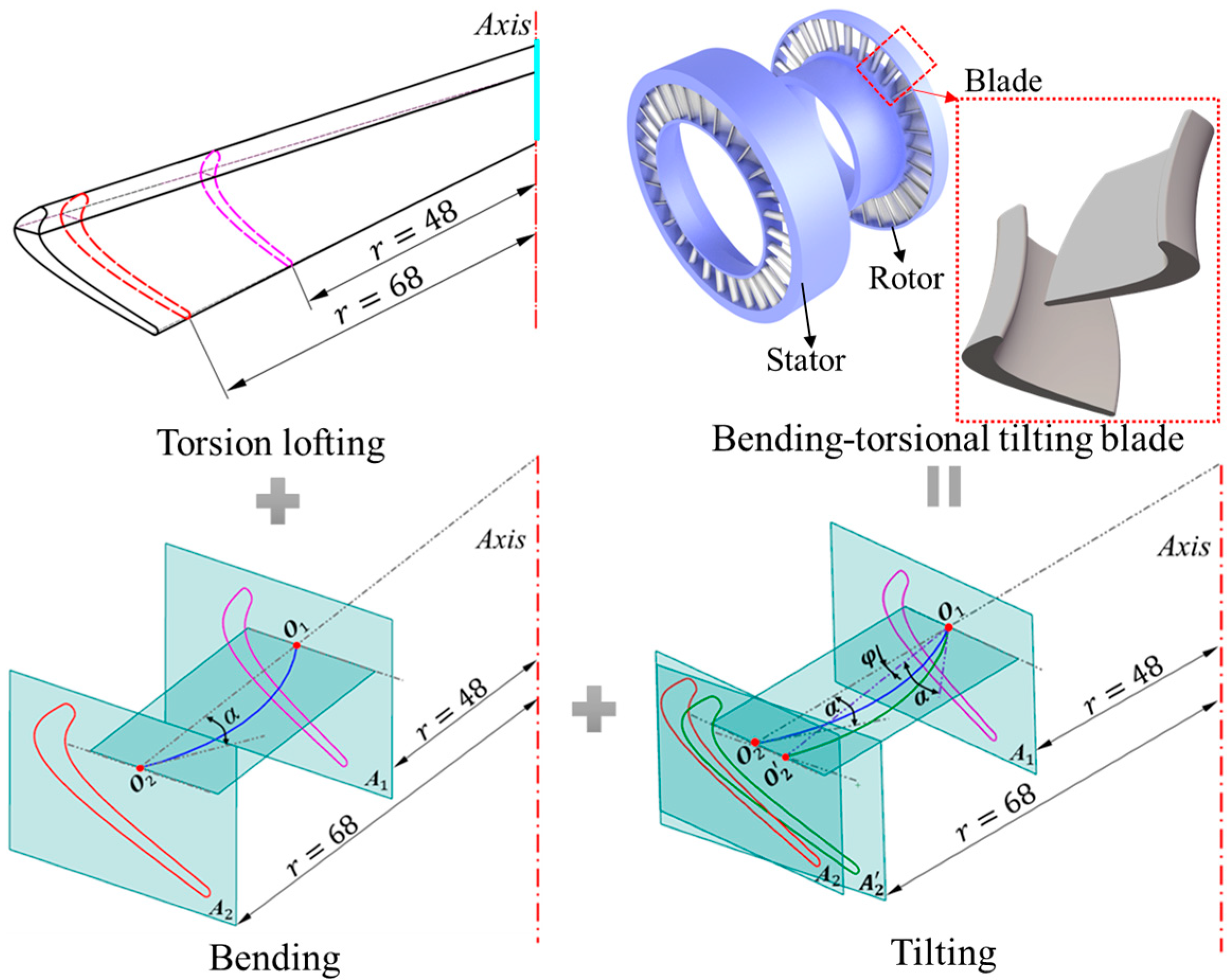
- Based on the theoretical model of the output characteristics of the turbodrill, the key blade profile parameters affecting the output performance are identified. We innovatively propose a three-dimensional modeling method for curved-twisted-tilted blades and summarize six core parameters that have a significant impact on the output characteristics:
- (2)
- Through the GA-LSSVM-MOPSO-TOPSIS intelligent optimization algorithm, we optimized these key two-dimensional and three-dimensional design parameters, and determined the core parameters of the two-dimensional blade profile with the best comprehensive hydraulic performance of the turbodrill: , , ; the optimal spatial parameter combination of bending and twisting blades is: , ,
- (3)
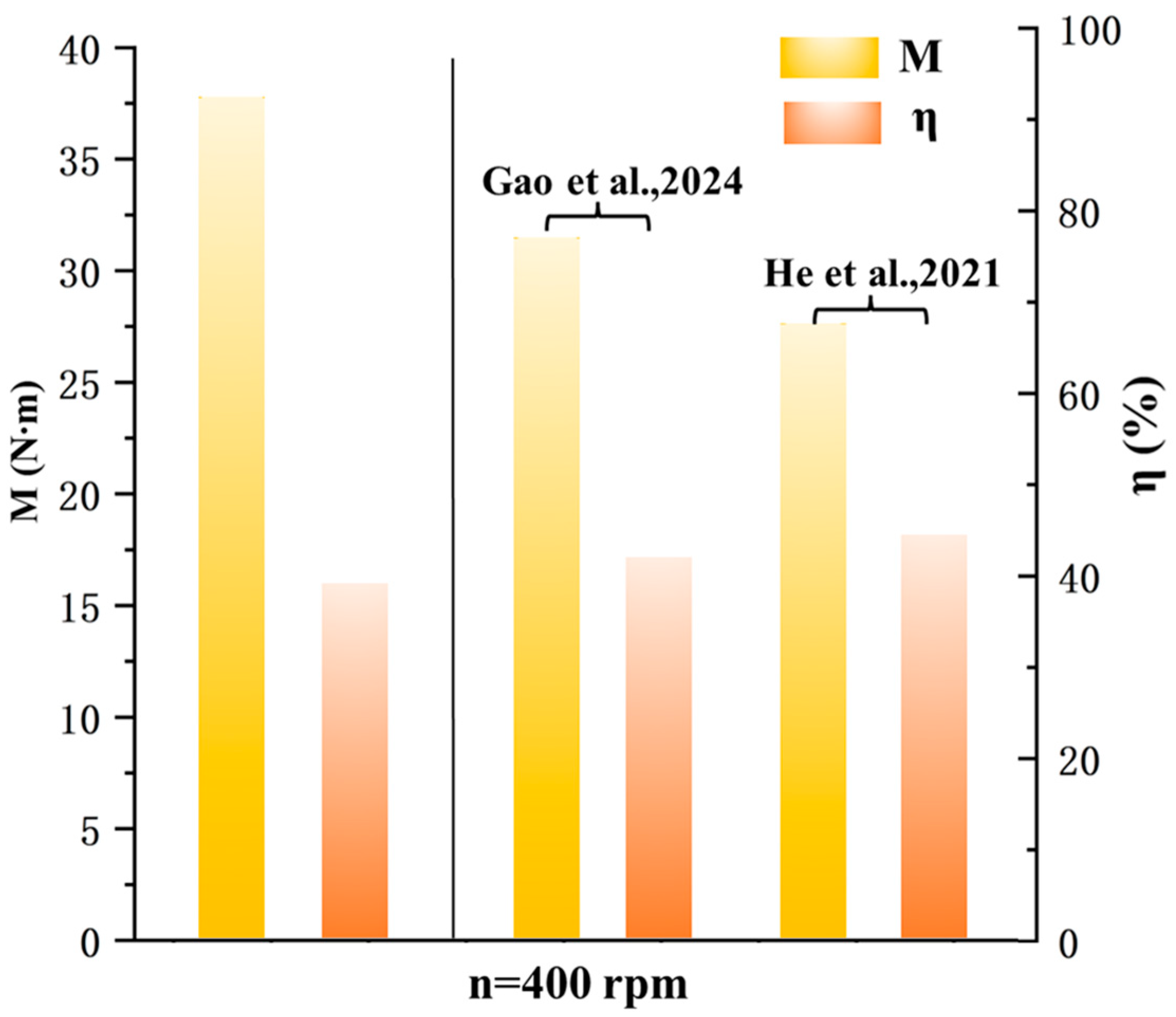
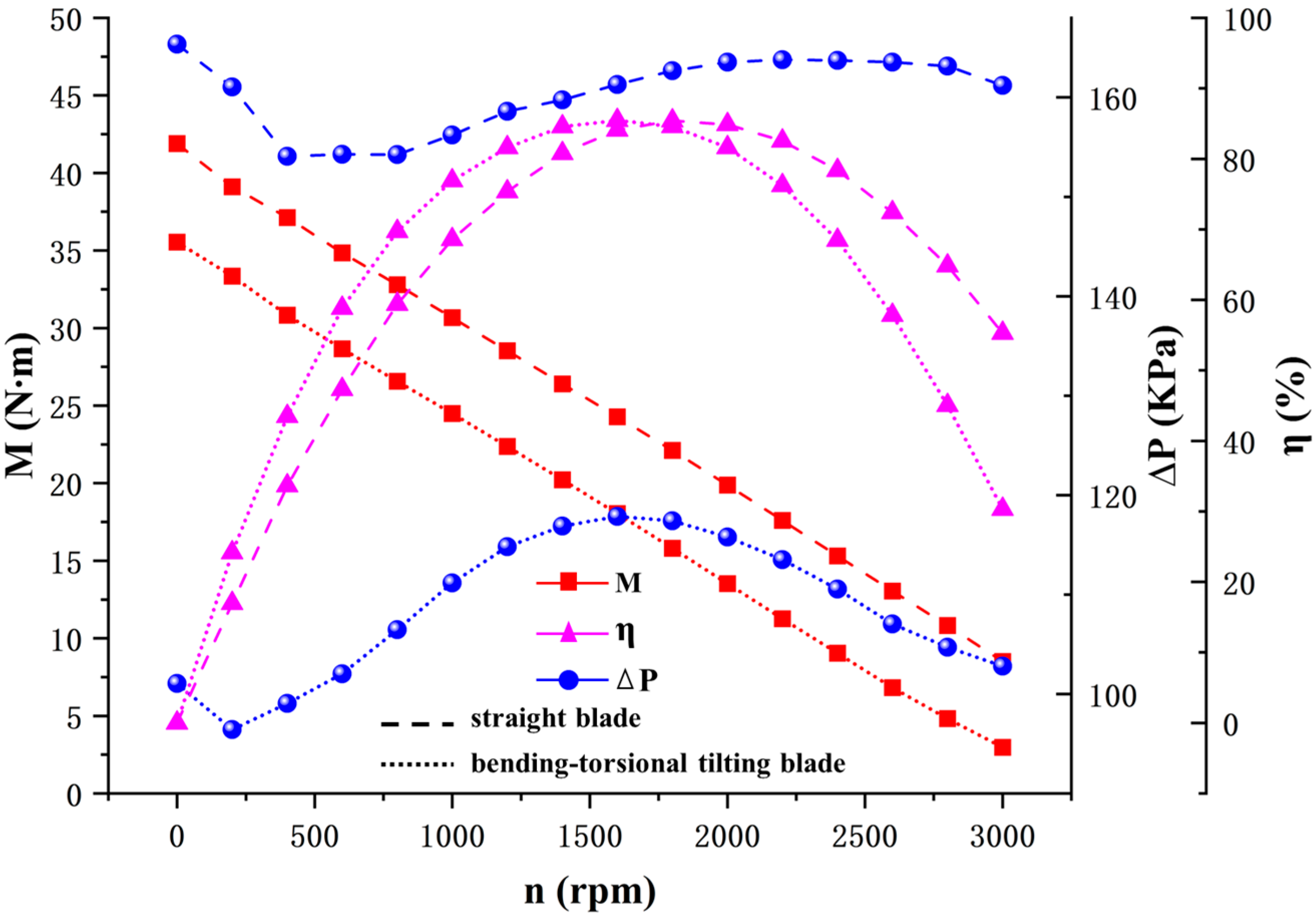
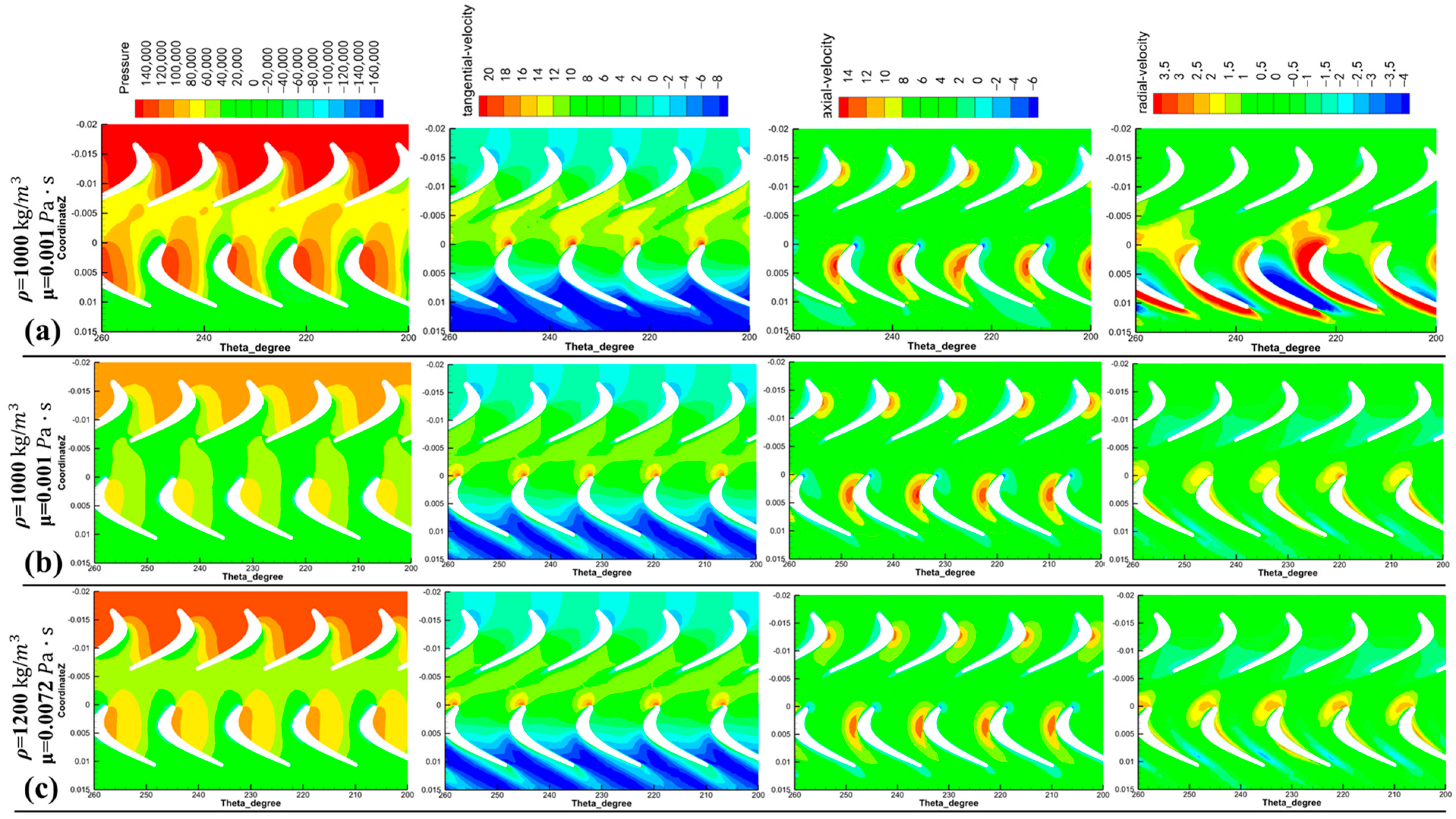
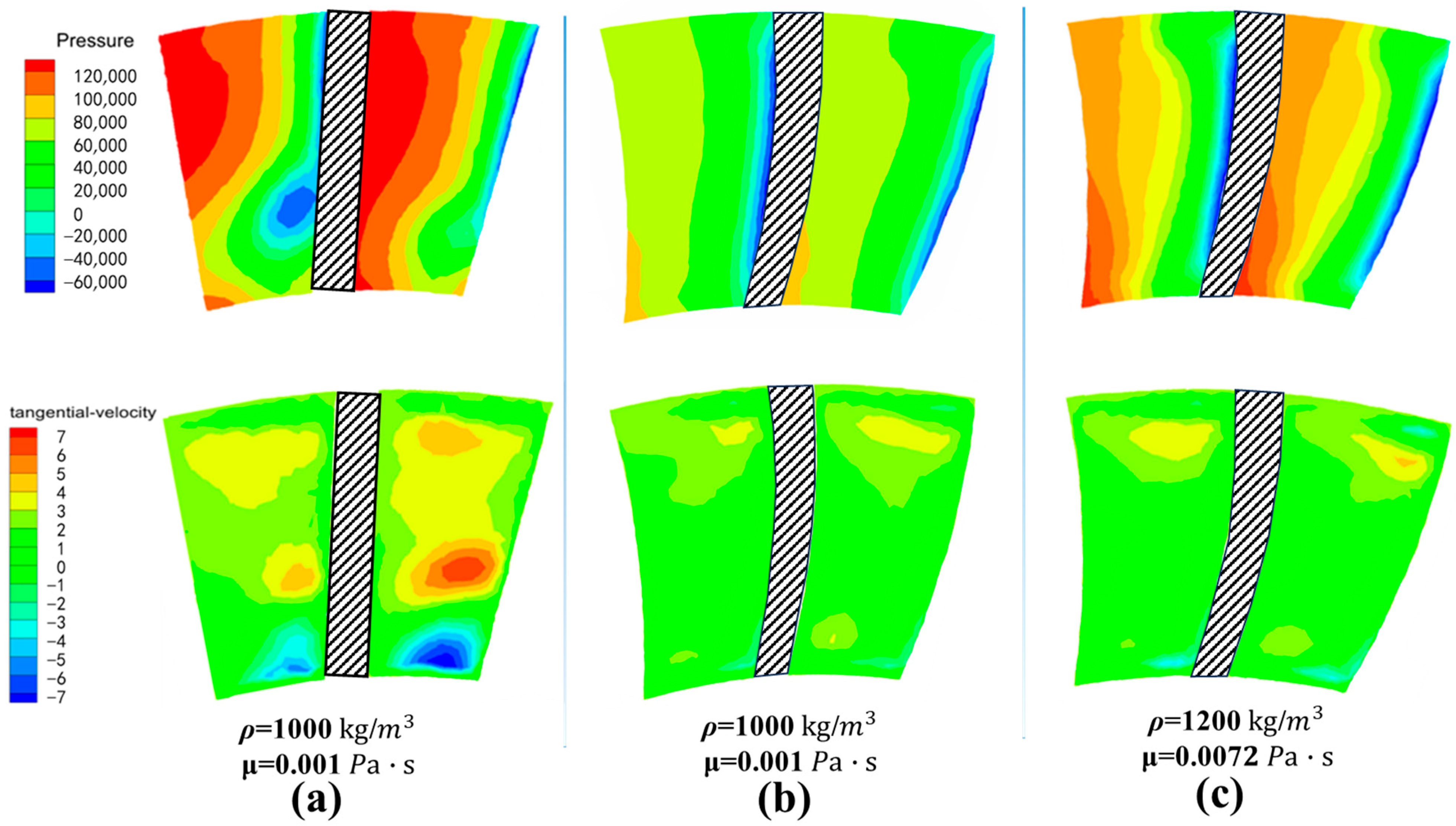
- The results of CFD simulation analysis verify the accuracy of the intelligent optimization algorithm and show that the curved-twisted-tilted blade is significantly better than the straight blade in the pressure and velocity distribution of the flow field, and the hydraulic loss is effectively reduced. At 400 rpm, the single-stage turbine output torque of the curved-twisted-tilted blade is 37.4296 N·m, which is 36.61% higher than the existing design, and only 4.9% of the hydraulic efficiency is sacrificed, which lays a certain foundation for the design of low-speed and high-torque turbodrill blades.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, C.; Wang, C.; Peng, C.; Wu, C.; Gao, Y. Development of the Chinese continental scientific deep drilling: Perspectives and suggestions. Geoscience 2023, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xue, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Jiang, H.; Wang, R. Progress and development directions of deep oil and gas exploration and development in China. China Pet. Explor. 2020, 25, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Dengfa, H.; Chengzao, J.; Wenzhi, Z.; Fengyin, X.; Xiaorong, L.; Wenhui, L.; Yong, T.; Shanlin, G.; Xiujuan, Z.; Di, L.; et al. Research progress and key issues of ultra-deep oil and gas exploration in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakari, A.; Musibau, H. Sustainable economic development in OECD countries: Does energy security matter? Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 1337–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Huang, W. Research and development suggestions on theory and techniques in ultra-deep well engineering. Pet. Drill. Tech. 2024, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mokaramian, A.; Rasouli, V.; Cavanough, G. Numerical simulations of small turbodrill performance. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Turbomachinery: Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics, Lappeenranta, Finland, 15–19 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, W.; Weng, W.; Duan, L. A study of the application of turbine coring drilling technology to hot dry rock drilling. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2021, 48, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Zeng, D.; Li, R.; Huang, W.; Shi, T. On the new blade shape of the turodrill and its CAD. J. Chongqing Univ. 2004, 27, 24–27, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, S.; Gong, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhou, Q. Modeling and optimization for turbine blades based on bezier curve. J. Mech. Strength 2015, 37, 266–271. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Ma, C.; Chen, M.; Feng, J.; Zhou, S.; Zeng, Y. Influence of radial thickness distribution of turbodrill blades on their performance. China Pet. Mach. 2025, 53, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, S.; Gong, Y.; Li, Y. Optimization design for turbodrill blades based on response surface method. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1687814015624833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Three-Dimensional Cascade Design and Simulation of Small Size Turbodrill. Doctoral Dissertation, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H. Optimization Study of Output Performance of Small-size Turbodrills. Doctoral Dissertation, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoynikov, M.V.; Sidorkin, D.I.; Kunshin, A.A.; Kovalev, D.A. Development of hydraulic turbodrills for deep well drilling. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, M.; Gong, Y.; Hao, R.; Yang, L. Design and performance analysis of turbodrill blade based on joukowski transformation. China Mech. Eng. 2020, 31, 968–974. [Google Scholar]
- Vessaz, C.; Tournier, C.; Münch, C.; Avellan, F. Design optimization of a 2D blade by means of milling tool path. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2013, 6, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, C. Hydraulic loss analysis of turbodrill blade cascades based on entropy production theory. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 241, 213093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, F.; Cao, M.; Ma, T.; Ning, W.; Zhang, M.; He, T.; Wang, X. Comprehensive analysis of the output characteristics of flow field in turbodrill motor. Machines 2025, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Y. Optimization design for turbodrill blades based on a twisting method. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y. Key drilling technologies for increasing ROP in ultra-deep well yuanshen 1. Pet. Drill. Tech. 2024, 52, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan, R.M.; Liang, Z.; Heddam, S.; Zounemat-Kermani, M.; Kisi, O.; Li, B. Least square support vector machine and multivariate adaptive regression splines for streamflow prediction in mountainous basin using hydro-meteorological data as inputs. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z. Survey of multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithms and their applications. J. Zhejiang Univ. Eng. Sci. 2024, 58, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, T.; Ma, W.; Nie, L. Research on performance optimization of small-sized turbine drilling tools based on machine learning. Mach. Tool Hydraul. 2024, 52, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Fierro, M.; Atencio, N.; Solano, R.; Varela, R.; Iturrizaga, F.; Toribio, L.; Tufano, A.; Guzman, F. Finding the breakeven point of diamond impregnated bit wear in turbodrill applications. In Proceedings of the OTC Brasil, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 27–29 October 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyants, S.L. Turbodrill and screw motor: Development dialectics. In Proceedings of the SPE Russian Petroleum Technology Conference and Exhibition, Moscow, Russia, 24–26 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z. Principle and Application of Low Speed High Torque Turbodrill. Oil Field Equip. 1976, 5, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, Z. Development of turbine section of 3fwz-195 turbodrill with floating stator. Oil Field Equip. 1990, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R.; Xu, J.; Lin, B. ROI-based study on impact factors of distributed PV projects by LSSVM-PSO. Energy 2017, 124, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Dong, X.H.; Zhang, F.; Luo, K.J. Coiled tubing small turbo drill cascade design optimization and numerical simulation of the flow field. In Advances in Engineering Materials and Applied Mechanics; Zhang, G., Gao, Q., Xu, Q., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 475–479. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Kong, L.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, L. Optimised design of downhole turbodrills with bending-torsional tilting blade. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 234, 212661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Serial | /° | /° | /° | Torque/N·m | Efficiency/% | Serial | /° | /° | /° | Torque/N·m | Efficiency/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 2 | 28 | 27.77 | 32.17 | 10 | 25 | 8.5 | 36.5 | 37.00 | 38.44 |
| 2 | 20 | 8.5 | 28 | 55.88 | 24.66 | 11 | 25 | 8.5 | 36.5 | 37.00 | 38.44 |
| 3 | 30 | 8.5 | 28 | 40.85 | 30.96 | 12 | 20 | 15 | 36.5 | 62.20 | 21.68 |
| 4 | 25 | 15 | 28 | 52.71 | 26.38 | 13 | 30 | 15 | 36.5 | 32.99 | 38.96 |
| 5 | 20 | 2 | 36.5 | 41.33 | 36.20 | 14 | 25 | 2 | 45 | 27.16 | 49.00 |
| 6 | 30 | 2 | 36.5 | 29.39 | 42.84 | 15 | 20 | 8.5 | 45 | 42.76 | 36.88 |
| 7 | 25 | 8.5 | 36.5 | 37.00 | 38.44 | 16 | 30 | 8.5 | 45 | 25.92 | 50.42 |
| 8 | 25 | 8.5 | 36.5 | 37.00 | 38.44 | 17 | 25 | 15 | 45 | 37.14 | 40.41 |
| 9 | 25 | 8.5 | 36.5 | 37.00 | 38.44 |
| Serial | /mm | /° | /° | Torque/N·m | Efficiency/% | Serial | /mm | /° | /° | Torque/N·m | Efficiency/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48 | 20 | 3 | 58.52 | 20.46 | 10 | 58 | 20 | 6 | 34.63 | 37.50 |
| 2 | 68 | 5 | 6 | 24.58 | 47.98 | 11 | 58 | 5 | 9 | 33.21 | 36.31 |
| 3 | 48 | 35 | 6 | 59.21 | 19.87 | 12 | 58 | 35 | 9 | 33.81 | 37.31 |
| 4 | 58 | 20 | 6 | 34.63 | 37.50 | 13 | 58 | 20 | 6 | 34.63 | 37.50 |
| 5 | 48 | 5 | 6 | 59.18 | 20.71 | 14 | 68 | 20 | 9 | 23.88 | 47.53 |
| 6 | 68 | 20 | 3 | 25.56 | 49.06 | 15 | 68 | 35 | 6 | 24.52 | 46.78 |
| 7 | 48 | 20 | 9 | 60.19 | 20.01 | 16 | 58 | 20 | 6 | 34.63 | 37.50 |
| 8 | 58 | 35 | 3 | 35.71 | 34.71 | 17 | 58 | 20 | 6 | 34.63 | 37.50 |
| 9 | 58 | 5 | 3 | 36.59 | 38.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Yan, J.; Kong, L.; Lu, Y. Optimization Design of Blade Profile Parameters of Low-Speed and High-Torque Turbodrill Based on GA-LSSVM-MOPSO-TOPSIS Method. Machines 2025, 13, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13111034
Gao Y, Wang Y, Chen G, Yan J, Kong L, Lu Y. Optimization Design of Blade Profile Parameters of Low-Speed and High-Torque Turbodrill Based on GA-LSSVM-MOPSO-TOPSIS Method. Machines. 2025; 13(11):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13111034
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yulin, Yu Wang, Guosong Chen, Jia Yan, Lingrong Kong, and Yuzuo Lu. 2025. "Optimization Design of Blade Profile Parameters of Low-Speed and High-Torque Turbodrill Based on GA-LSSVM-MOPSO-TOPSIS Method" Machines 13, no. 11: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13111034
APA StyleGao, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, G., Yan, J., Kong, L., & Lu, Y. (2025). Optimization Design of Blade Profile Parameters of Low-Speed and High-Torque Turbodrill Based on GA-LSSVM-MOPSO-TOPSIS Method. Machines, 13(11), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13111034