Topology-Aware Efficient Path Planning in Dynamic Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
- When a path is invalidated, we have a set of precomputed homology paths based on the Homology Class Planner as an alternative.
- Our path is a global optimal path rather than a local optimal path by homology class path generation and VSRRT*-based path optimization.
- A probabilistic sampling method based on the GMM can save much computational time and memory usage.
2. Related Work
3. Preliminaries
3.1. Importance Sampling
3.2. Estimation of Rare-Event Probabilities
4. Methodology
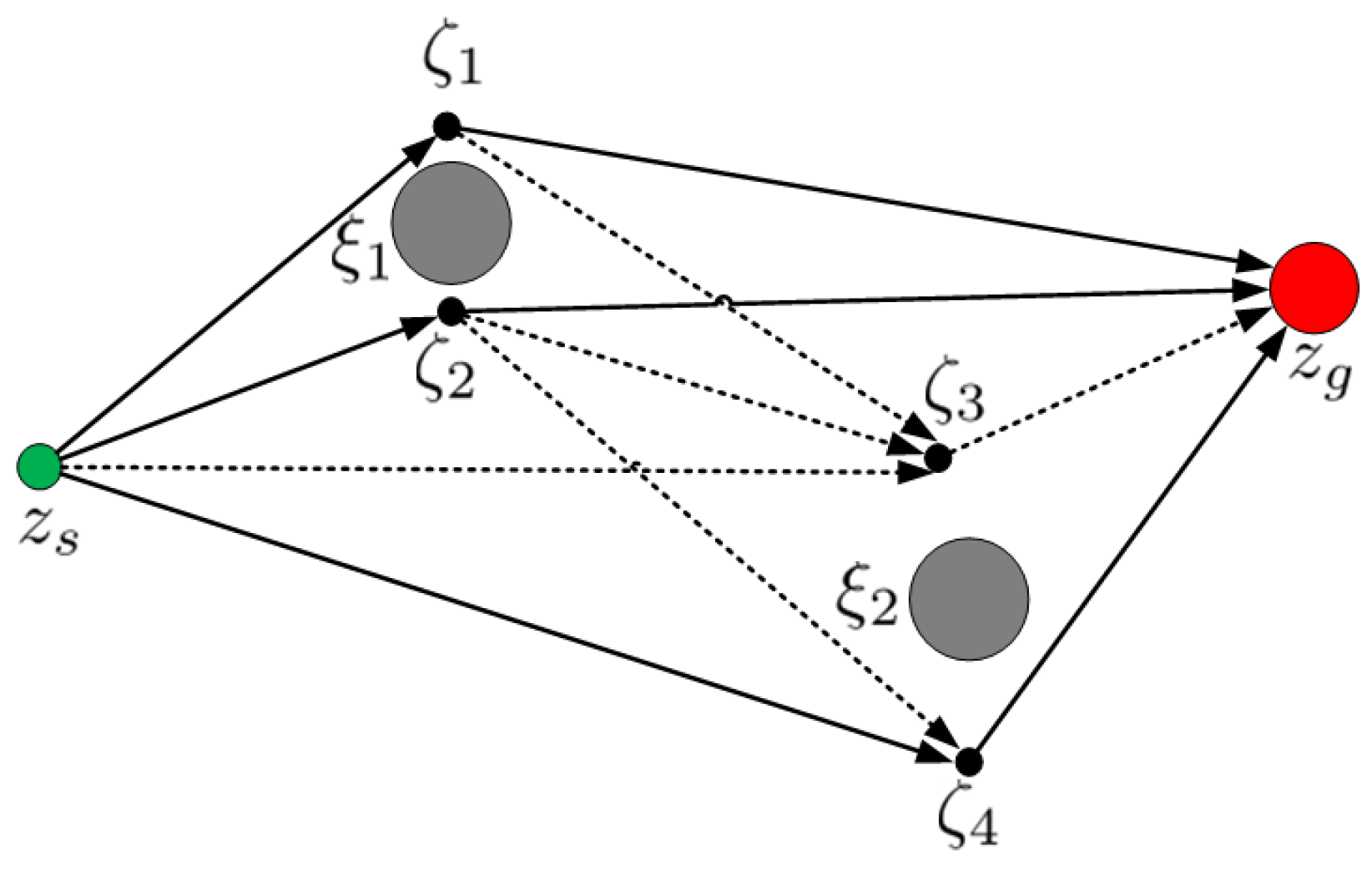
4.1. Homology Classes
4.2. Homology Class Path Generation
| Algorithm 1: Homology class path generation. |
Input: , B, ; T; H Output: Updated set of trajectories and H-signatures  |
4.3. CE Trajectory Optimization
| Algorithm 2: CE trajectory optimization. |
Input: Output: 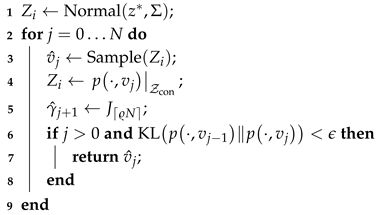 |
4.4. VSRRT* Path Optimization
| Algorithm 3: VSRRT* Planner. |
Input: , , T Output:  |
4.5. GMM Sampling Optimization
| Algorithm 4: . |
|
Input: Output: 1 ; 2 ; 3 ; 4 ; 5 return ; |
4.6. TACE-Based Path-Planning Algorithm
| Algorithm 5: TACE-based path-planning algorithm. |
Input: Output: X  |
5. Experiments
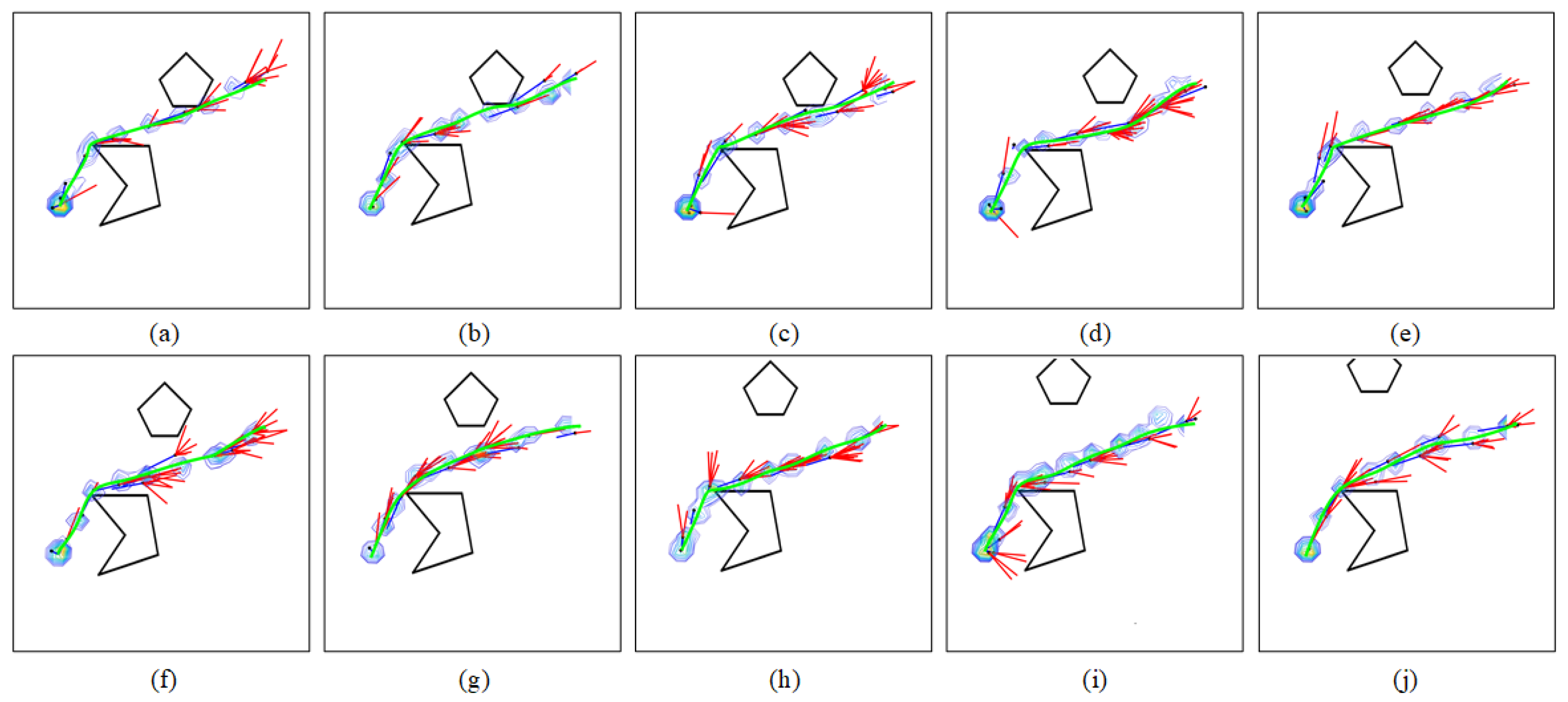
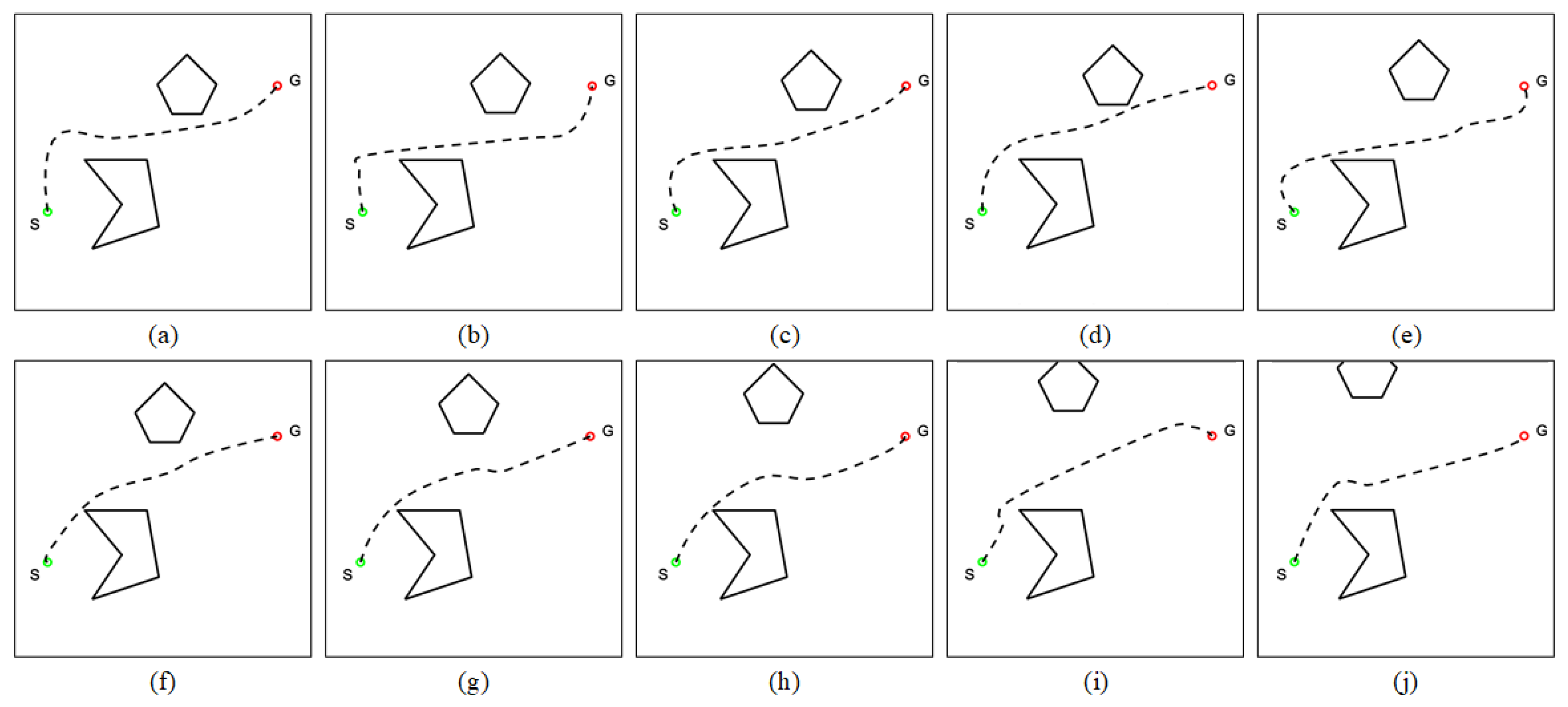
5.1. Comparison Experiment of Path-Planning Algorithms
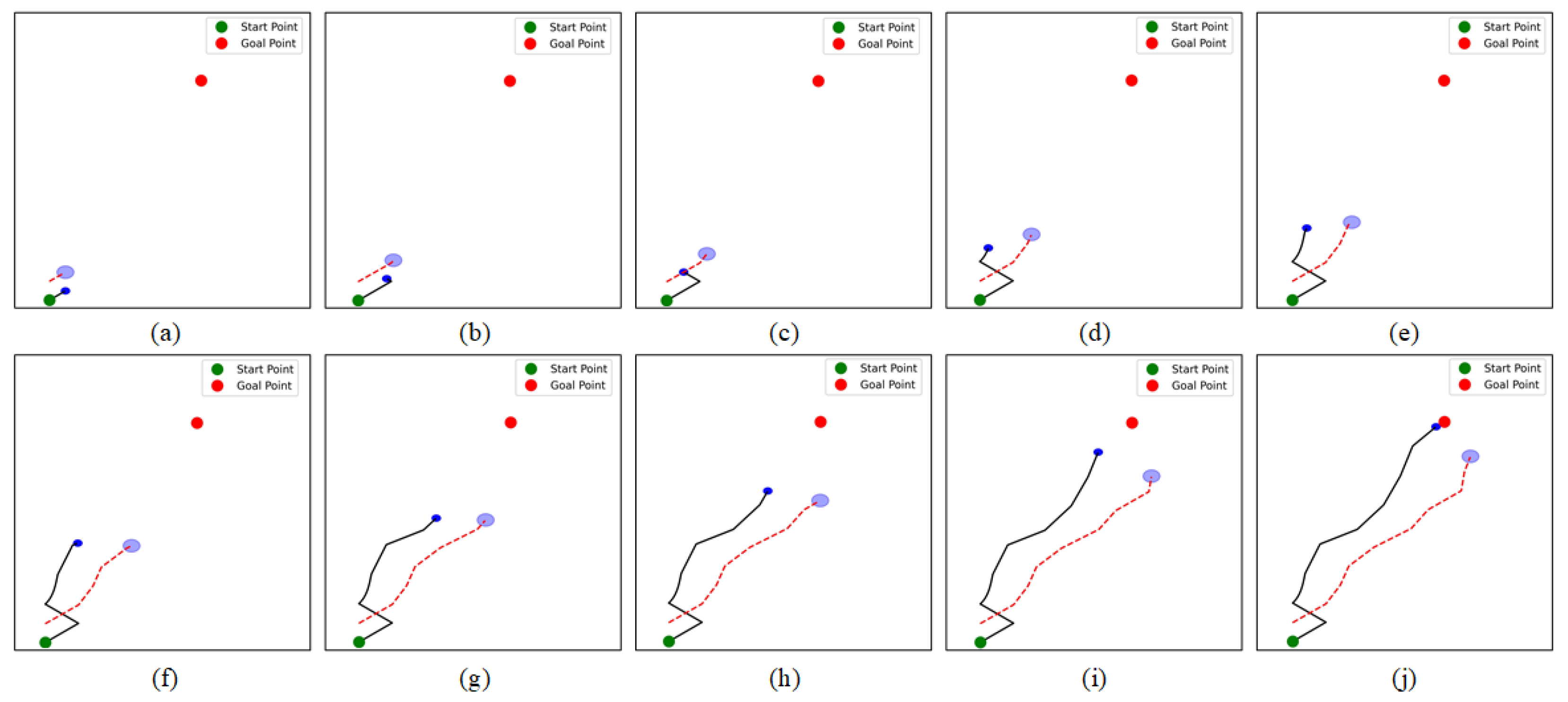
5.2. Experiment with Irregularly Moving Obstacle
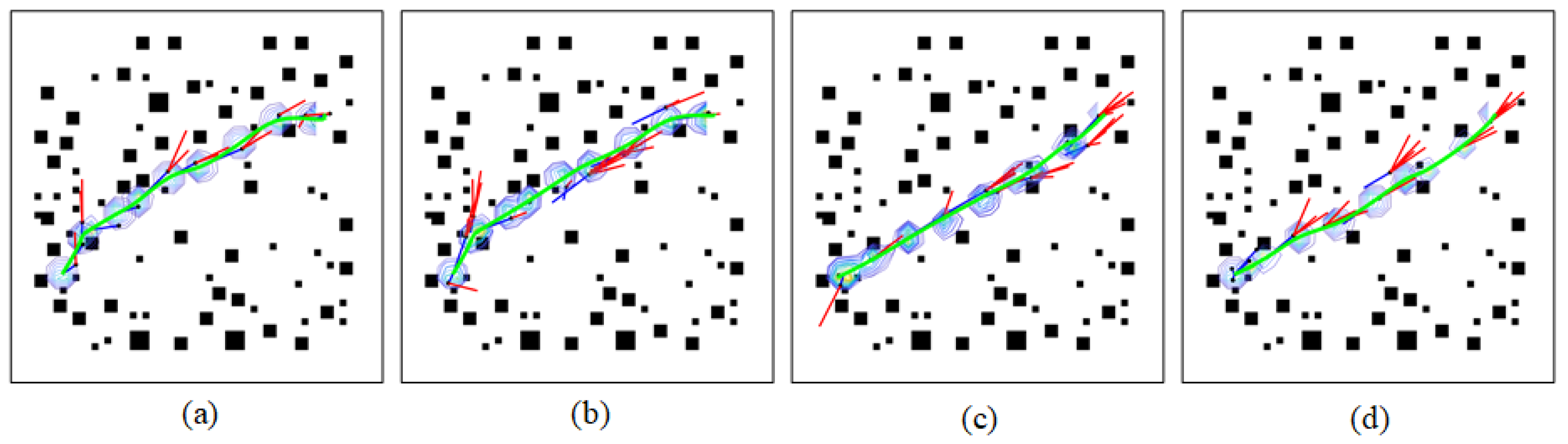
5.3. Experiment with Complex Environments
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Li, P.; Qian, S.; Quan, H.; Miao, J.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.; Memetimin, E. Path Planning Technique for Mobile Robots: A Review. Machines 2023, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Meng, L.; She, S.; Mitchell, I.M.; Li, T.; Tung, F.; Wan, W.; Meng, M.Q.H.; de Silva, C.W. Autonomous Mobile Robot Navigation in Uneven and Unstructured Indoor Environments. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ma, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Meng, M.Q.H. Efficient Autonomous Exploration with Incrementally Built Topological Map in 3-D Environments. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 9853–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, O. Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1986, 5, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Z. A Novel Planning and Tracking Approach for Mobile Robotic Arm in Obstacle Environment. Machines 2024, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, J.; Petrič, T.; Klančar, G. Potential Field Control of a Redundant Nonholonomic Mobile Manipulator with Corridor-Constrained Base Motion. Machines 2023, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhai, X.; Xu, J.; Li, C. Target Search Algorithm for AUV Based on Real-Time Perception Maps in Unknown Environment. Machines 2021, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.E.; Nilsson, N.J.; Raphael, B. A formal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum cost paths. IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. Cybern. 1968, 4, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, E.W. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numer. Math. 1959, 1, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, T.; Meng, M.Q.H.; De Silva, C. Efficient Mobile Robot Exploration with Gaussian Markov Random Fields in 3D Environments. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 5015–5021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, D.; Li, T.; Meng, M.Q.H.; De Silva, C.W. Efficient Autonomous Robotic Exploration with Semantic Road Map in Indoor Environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2989–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chi, W.; Sun, Y.; Meng, M.Q.H. Autonomous Robotic Exploration by Incremental Road Map Construction. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Meng, M.Q.H. Risk-DTRRT-Based Optimal Motion Planning Algorithm for Mobile Robots. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 1271–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhong, B.; He, J.; Gao, Z. Dual-Arm Obstacle Avoidance Motion Planning Based on Improved RRT Algorithm. Machines 2024, 12, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, Z.; Wei, Z.; Shi, C.; Yang, H. Topology-aware resilient routing protocol for FANETs: An adaptive Q-learning approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 18632–18649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englot, B.; Hover, F.S. Three-dimensional coverage planning for an underwater inspection robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 1048–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, L.; Schmerling, E.; Clark, A.; Pavone, M. Fast marching tree: A fast marching sampling-based method for optimal motion planning in many dimensions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 883–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, O.; Halperin, D. Asymptotically near-optimal RRT for fast, high-quality motion planning. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shan, Y.; Tian, W.; Li, B.; Cao, D. A Fast and Efficient Double-Tree RRT*-like Sampling-Based Planner Applying on Mobile Robotic Systems. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 2568–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanhawi, M.; Simic, M.; Jazar, R. Randomized Bidirectional B-Spline Parameterization Motion Planning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Gong, J.; Oh, S. Fast Sampling-Based Cost-Aware Path Planning with Nonmyopic Extensions Using Cross Entropy. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, R.; Rong, X.; Guo, J.; Yang, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y. Autonomous live working robot navigation with real-time detection and motion planning system on distribution line. High Volt. 2022, 7, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chi, W.; Shao, M.; Meng, M.Q.H. Finding a High-Quality Initial Solution for the RRTs Algorithms in 2D Environments. Robotica 2019, 37, 1677–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Guo, W. Robot motion planning method based on incremental high-dimensional mixture probabilistic model. Complexity 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J. Learning Probabilistic Generative Models for Fast Sampling-Based Planning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, H.; Wan, S.; Ding, H. A Gaussian Mixture Models based Multi-RRTs method for high-dimensional path planning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–15 December 2018; pp. 1659–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Chen, Y. Cyl-IRRT*: Homotopy optimal 3D path planning for AUVs by biasing the sampling into a cylindrical informed subset. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 3985–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Lang, N.; Li, H.; Xu, D. Path planning in uncertain environment with moving obstacles using warm start cross entropy. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 27, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Belta, C.; Tron, R. Adaptive sampling-based motion planning with control barrier functions. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Cancun, Mexico, 6–9 December 2022; pp. 4513–4518. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Cai, M.; Ahmad, A.; Prorok, A.; Tron, R.; Belta, C. LQR-CBF-RRT*: Safe and optimal motion planning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.00790. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, W.; Ding, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Sun, L. A generalized Voronoi diagram-based efficient heuristic path planning method for RRTs in mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 4926–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Meng, M.Q.H. Optimal path planning using generalized voronoi graph and multiple potential functions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 10621–10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Chi, W.; Chen, G.; Sun, L. A Gaussian mixture model based fast motion planning method through online environmental feature learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 3955–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fu, M.; Liu, A.; Zhang, W.; Chen, B. A Homotopy Invariant Based on Convex Dissection Topology and a Distance Optimal Path Planning Algorithm. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 7695–7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Kumar, V.; Likhachev, M. Search-Based Path Planning with Homotopy Class Constraints. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Atlanta, GA, USA, 11–15 July 2010; AAAI Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 1230–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S. Topological and Geometric Techniques in Graph Search-Based Robot Planning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rösmann, C.; Hoffmann, F.; Bertram, T. Planning of multiple robot trajectories in distinctive topologies. In Proceedings of the 2015 European Conference on Mobile Robots (ECMR), Lincoln, UK, 2–4 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rösmann, C.; Hoffmann, F.; Bertram, T. Integrated online trajectory planning and optimization in distinctive topologies. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 88, 142–153. [Google Scholar]
- Sarah, K.; Gerard, C.; Michael, C. Task-Aware Waypoint Sampling for Planning Robots. In Proceedings of the International Conferenceon Automated Planning and Scheduling (ICAPS), Guangzhou, China, 7–12 June 2021; pp. 643–651. [Google Scholar]
- Kavraki, L.E.; Svestka, P.; Latombe, J.C.; Overmars, M.H. Probabilistic roadmaps for path planning in high-dimensional configuration spaces. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1996, 12, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösmann, C.; Hoffmann, F.; Bertram, T. Kinodynamic trajectory optimization and control for car-like robots. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5681–5686. [Google Scholar]
- Kobilarov, M. Cross-entropy motion planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2012, 31, 855–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaValle, S.M.; Kuffner, J.J., Jr. Randomized Kinodynamic Planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2001, 20, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, S.; Frazzoli, E. Sampling-Based Algorithms for Optimal Motion Planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2011, 30, 846–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Rong, X.; Li, Y. Topology-Aware Efficient Path Planning in Dynamic Environments. Machines 2025, 13, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13010014
Zhao H, Guo J, Wang C, Rong X, Li Y. Topology-Aware Efficient Path Planning in Dynamic Environments. Machines. 2025; 13(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Haoning, Jiamin Guo, Chaoqun Wang, Xuewen Rong, and Yibin Li. 2025. "Topology-Aware Efficient Path Planning in Dynamic Environments" Machines 13, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13010014
APA StyleZhao, H., Guo, J., Wang, C., Rong, X., & Li, Y. (2025). Topology-Aware Efficient Path Planning in Dynamic Environments. Machines, 13(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13010014





