Abstract
Rotor bar breakage in induction motors is often detected by analysing the signatures in the stator current. However, due to the alteration of the current spectrum, traditional methods may fail when inverter-fed motors operate with closed-loop control using a cascade structure to regulate the speed. In this paper, the potential of zero-sequence voltage analysis to detect this fault is investigated, and a new index to quantify the severity of the fault based on this signal is proposed. Signals from motors operating under different control strategies and signals from motors powered from the mains are considered to verify the robustness of the proposed fault severity index. As a result, in all the analysed conditions the value of the proposed index for the healthy motor is found to be approximately 0.010, while for the faulty machine it is between 0.110 and 0.252.
1. Introduction
Induction motors (IMs) are still the most used electrical machines in the industry due to their robustness and low costs compared to other types of electrical rotating machines. Additionally, they hold significant importance in other sectors, such as transportation (automotive and railway transport) or services (air conditioning, elevators, pumping systems, or compressors). Despite their high fault-tolerance capability, failures may occur in several components of the induction motor, such as stator winding and insulation, shaft, bearing, and rotor cage.
Regarding the latter statement, based on several studies, including those found in [1,2,3], the occurrence of faults in the rotor cage in induction motors ranges from 7 to 12% of the total number of faults. The rotor circuit fault leads to a 50% increase in currents in the neighbouring bars, while the stator current changes are minimal [4]. In squirrel cage motors, faults in the rotor circuit can happen in the end ring or can be related to the breakage of a bar [5]. In both cases, an asymmetry is introduced in the rotor circuit, inducing components in the spectra of the voltage and the current of the stator winding. The position in the spectrum of these components depends solely on the mechanical frequency of the rotor, not on the element of the cage in which the failure occurs [2]. The probability of this fault is closely tied to the way the rotor is made. It frequently happens in fabricated rotors because of bar breakage close to the weld connecting the bar and end ring. Die-cast rotors, in contrast, offer increased resistance to this issue. Deep-well submersible motors are a specific case because they feature fabricated copper bars but utilise multiple copper sheets for the end ring instead of a solid piece. This type of end ring tends to wear out frequently due to internal cooling water and high-speed rotation [6]. Furthermore, deficiencies in the rotor cage can arise from manufacturing defects, such as material impurities, the presence of porosity (air bubbles), magnetic anisotropy of the laminations, or imperfections. These factors intensify during overextended operation, particularly due to magnetic stresses from forces, variable frequency content, additional harmonics (causing magnetic saturation), local magnetic field peaks at sharp edges and corners, and uneven eddy current distribution [7].
Numerous studies have been carried out to examine rotor cage faults by analysing various signals. There are studies available on the use of stray flux signature analysis (SFSA) [8,9,10,11], thermal images [12,13,14], and motor current signature analysis (MCSA) [15,16]. However, most of the cited works focus on fault analysis in stationary and non-stationary conditions [3], such as start-up transients and operation under load oscillations, particularly in motors powered by the mains or pulse width modulation (PWM) open-loop power converters. With the increasing demand for precise control in closed-loop systems, especially in manufacturing processes, the detection of broken bars in motors operating under closed-loop control presents a challenging task. This is due to the potential implementation of different control strategies and the likely variance of fault indicators from the traditional ones described in the existing literature [17,18]. Furthermore, in numerous applications where stationary conditions are not always achieved, the use of various complex techniques, such as time-frequency analysis to track the evolution of harmonics over time, may be necessary.
An example of the impact of different closed-loop controllers in the detection of the rotor cage fault is given in [19]. The authors carried out experimental tests on faulty motors driven by indirect rotor field-oriented control (IRFOC) with and without flux control loop (IRFOC-FC) and direct rotor field-oriented controllers (DRFOC), stating that the signatures given in the fault in the electromagnetic signals are strongly related to the type of controller used. The same researchers proposed, in [20], a model-based diagnostic technique, called the virtual current technique (VCT), for the diagnosis of rotor faults in DRFOC induction motor drives, which consists of the measurement of the oscillations at two times the slip frequency found in the rotor flux of the machine. By conjugating this information with parameters to produce a virtual magnetising current, the authors were able to identify the fault in the current closed-loop controller under study.
In [21], an analysis was made on a faulty induction motor controlled with a state vector control based on direct torque control (DTC). The authors suggest using FFT analysis of the current envelope, Park’s vector plot, and FFT analysis of Park’s vector modulus, concluding that Park’s vector approach is more informative as a diagnostic tool, despite the significant influence of inverter-fed harmonics on Park’s vector modulus. In a recent study [22], the authors compared the detection of the rotor cage faults between motors operating under V/f or scalar open-loop control with the case of closed-loop space vector control (SVC), introducing a new signal analysis technique named adaptive window short-time ESPRIT (AWSTE).
In a study (based on simulations and lab experiments) conducted by Bellini et al. [23], it was demonstrated that the spectrum of the magnetising current component () in a field-oriented controlled (FOC) induction motor serves as an effective diagnostic indicator for detecting broken bar-faults under speed closed-loop operation. In another interesting study, Kral et al. [24,25] proposed the Vienna monitoring method (VMM) as a model-based diagnostic technique for detecting broken rotor bars in a vector-controlled induction motor. The VMM calculates two values of the electromagnetic torque generated by the motor using a current model and a voltage model and can be implemented with or without a position or speed sensor. It is worth noting that the VMM is sensitive to several parameters, including tuning the current, flux, and the speed controllers of the drive.
In [26], the authors analysed the rotor bar breakage signatures using different electromagnetic signals, such as stator phase current and voltage applied to several control architectures: FOC, with and without speed feedback, and DTC. After the analysis, they proposed a signal-injection-based index to evaluate the severity of the fault which is not dependent on the type of control strategy. Finally, in the research published in [27], a method based on the signature analysis of the zero-sequence voltage (ZSV) to detect one broken rotor bar (BRB) in a wye-connected induction motor in both open- and speed closed-loop has been developed. After the analysis of the faulty motor under different control-loop operations, the authors stated that the applied diagnostic method is not dependent on the control scheme used by the power converter.
The reader must note that when the authors of the works cited refer to closed-loop control, they are referring to the use of the speed signal as a feedback signal in the FOC algorithm. In this study, and based on previous work [28], when closed-loop control is mentioned, it also refers to the control of motor speed as a process signal. This adds a more external control loop to those referred to above. This new structure is called cascade control, and its effect on the detectability of broken rotor bars has not been studied previously. In addition, this study also includes, for the first time, the evaluation of the impact on fault detection of the type of speed proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller used. The study will focus on the spectral analysis of the stator current signal and the zero-sequence voltage. To assess this impact on fault detectability, a comparative study will be conducted on fault detection when the motor is supplied from the mains, with scalar control in open-loop and space vector control without and with an external speed feedback (cascade closed-loop control). The fault will be quantified using the fault severity indicator proposed by Bellini et al. [4] and a new one proposed based on the spectral content of the zero-sequence voltage. The structure of the paper is as follows: After the introductory section, the second section will explain the fundamental theoretical aspects to understand this work. The third section will describe the experimental work carried out. In the fourth section, the experimental results will be presented and analysed. In the last section, these results will be discussed and conclusions will be drawn.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Closed-Loop Control of Induction Motors
The induction or asynchronous motor is widely used in many sectors, as discussed in the introduction. One reason for this is that it can be powered directly from the mains and has starting torque. The three-phase stator winding fed by a three-phase system of voltages produces a rotating magnetic field which moves at the synchronous speed given by:
This speed (in rpm) depends on the frequency of the supply voltage (, in Hz) and the number of pole pairs of the machine. Due to Faraday’s induction law, the rotor starts to rotate in the same direction as the rotating magnetic field. However, the mechanical speed (n, expressed in rpm) is lower than the synchronous speed. The higher the load torque, the more significant this difference is, quantified by the slip as follows:
Therefore, the rotational speed cannot be set exactly without a control. However, in some applications, setting this speed more precisely is necessary. In these cases, the motor is fed via a power electronic converter (PEC), which allows the motor supply voltage and its frequency to be set, ultimately determining the value of the synchronous speed. The PEC consists of a rectifier, a DC bus, and an inverter, usually built with insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs). The operation of the inverter can be regulated in different ways that will affect the dynamic response of the motor. Scalar control, or variable voltage-variable frequency control, is one of the most commonly used controls. In the induction machine, the motor torque is proportional to the magnetic flux, which, in turn, is proportional to the ratio between the supply voltage and its frequency. In this type of control, the voltage and frequency are fixed, keeping their ratio constant. This control is used where control accuracy is not essential. Conversely, when control accuracy is required, vector or field-oriented control (FOC) is used. This uses a reference system aligned with the rotating magnetic flux. In this reference system, the three-phase current system is decomposed into two components along two axes, known as d-q. One component is responsible for flux control, and the other is for torque control.
The PEC has a very fast control loop to set the motor supply current. Its total delay is estimated to be 1.5 or 2 times the sampling period [29,30]. Scalar control and vector control can improve the accuracy of the power frequency by using an encoder to learn the mechanical speed of the rotor (slip-based feedback controller). In the case of vector control, if an encoder is not available, observers can be used to estimate the speed (sensorless FOC) [31]. The use of an encoder also has its drawbacks. It can be expensive, it needs to be mechanically coupled to the rotor, and it is a source of noise in the control system [32], especially if the connection cable from the encoder to the inverter is very long [30].
In some industrial applications, the inverter allows the implementation of a second, more external control loop to regulate a process variable (pressure, flow, temperature). This process variable can also be speed, as in conveying, vehicles, elevators, or pump applications. A second outer loop, slower than the current loop controller, is added in a so-called cascade structure, as shown in Figure 1, where is the speed reference, is the rotor speed signal, is the reference current, i is the motor current, is the torque developed by the motor, is the load torque, J is the drive’s moment of inertia, and B is the damping coefficient.
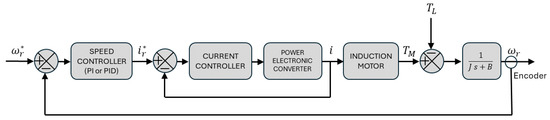
Figure 1.
Simplified block diagram of closed-loop control (cascade structure) of an inverter-fed induction motor. Where is the speed reference, is the reference current, is the actual speed reference, and i is the actual motor current.
The most commonly used controllers are PI or PID. There are many methods in the literature for tuning these controllers, but knowledge of the plant’s transfer function is required. If the transfer function is unknown, which is usually the case, experimental procedures such as the Ziegler–Nichols procedure can be used. However, this requires the plant to be brought to its stability limit. If this is not possible, as will be the case, other procedures, such as internal model control (IMC) [33], are based on subjecting the open-loop system to a step input. In the case of an electric drive, the most effective step input is a start-up. This experimental technique allows the choice of the PID controller type. It can provide an underdamped response, which is also faster, or an overdamped response, which offers a slower system response. For control purposes, the load torque is considered a disturbance.
As mentioned in the introduction, the operation of the inverter and its current controller affect fault detection in these machines. Due to its supply voltage generation strategy (usually for some variant of pulse width modulation), the inverter generates harmonics, inter-harmonics, and sub-harmonics in the stator current. In addition, it raises the signal’s noise level, making it challenging to observe fault harmonics. This has been extensively studied, as seen in the introduction. However, only a few authors have addressed the impact of the cascade control structure on fault detection using the current supply. The effect of the type of speed controller and the quality of the encoder signal on fault detection using stator current also remains to be studied.
2.2. Broken Rotor Bar Detection and Severity Quantification
As was said in the introduction, rotor faults in induction motors, specifically broken bar and cracked end-ring faults, comprise only 7 to 12% of total motor faults. While the motor operation is limited to a few seconds after a failed stator, rotor faults do not immediately restrict motor operation, although precautionary measures during maintenance are necessary [1]. A broken bar increases the adjacent bar current by up to 50%, while the stator current variation is minimal.
Motor current signature analysis (MCSA) is widely used to identify faults in broken rotor bars and end-rings. According to the theory of rotating fields, rotor asymmetries generate components at in the stator current spectrum, assuming constant speed or infinite inertia. Without these assumptions, a component at also appears. These components, also known as sideband components, are spaced around the fundamental frequency, with their distance from it increasing with load, making frequency analysis resolution easier. The general equation to determine harmonics related to broken bars faults (, expressed in Hz) is [34]:
where k assumes integer values . Usually, these sidebands are studied for [1]. The frequency component positioned at relative to the fundamental frequency is referred to as the lower sideband harmonic (LSH), whereas the harmonic at is known as the upper sideband harmonic (USH). Figure 2 illustrates the presence of frequency components related to this fault in the stator current spectrum around the first harmonic. In stator current analysis, the spectrum is typically presented on a logarithmic scale. This figure illustrates the primary harmonic at 50 Hz and the surrounding sidebands for values of k equal to 1, 2, and 3. The figure also indicates the fault-related components’ LSH and USH () positions.
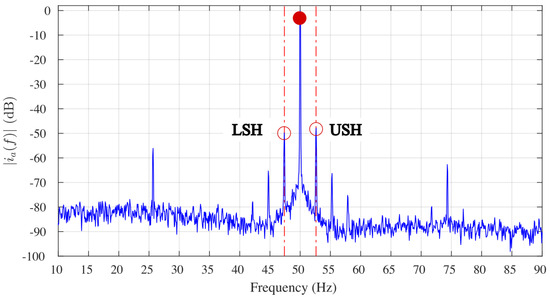
Figure 2.
Spectrum of the stator current of an inverter−fed motor with a broken rotor bar. The drive operates in an open loop with scalar control.
The amplitude of these fault-related harmonics is influenced by the number of broken adjacent rotor bars [35]. Furthermore, a threshold can be established to determine the presence of rotor faults. For example, if the amplitude of detected harmonics differs from the fundamental by at least 50 dB, the motor is considered healthy [17]. However, it is important to note that these thresholds may vary based on factors such as the number of rotor bars and the machine’s pole pairs. When multiple consecutive rotor bars are broken, there is a progressive increase in the amplitude of fault harmonics. This increase continues until the number of broken bars exceeds the ratio , where R represents the total number of rotor bars and p denotes the number of pole pairs in the motor [36].
Bellini et al. proposed a fault severity index in [4]. This index, which compares the sum of the magnitudes of the sidebands at to the magnitude of the fundamental supply current, does not require detailed motor design information. Extensive case histories and industrial applications have validated this index as a reliable fault indicator for motors fed from the line and inverters operating in open-loop. This severity index (n) is calculated as follows:
where is the sum of the amplitudes (in A) of the first sideband components (LSH and USH), is the amplitude of the fundamental frequency harmonic, and R is the number of rotor bars. All currents are expressed in ampere.
Stator current spectral analysis and severity indices, such as those proposed by Bellini et al., have consistently proven effective in identifying and quantifying rotor faults in motors powered by the grid and by inverters operating in open loop.
Not many studies have addressed this issue in speed-controlled induction motors. Some previous research has focused on inverters that use FOC with an encoder to determine speed. In this study, closed-loop speed control refers to a cascade control where the speed is the regulated process variable.
Two recent studies have partially addressed this topic [27,29]. In the study by [29], the authors propose a fault severity index involving measurements of currents, voltages, and phase angles, testing it successfully on a lab setup with a custom-made inverter implementing three FOC variants. In the second study [27], the same authors suggest analysing the zero-sequence voltage () to detect rotor faults. This can be calculated as follows:
where , , and are the phase voltages (in V). The authors demonstrate through an elegant mathematical analysis that broken rotor bars introduce the following specific frequencies in the zero-sequence voltage:
This formulation applies to star-connected motors, but the authors believe it could also be relevant to delta-connected motors. The authors conducted their study using the same test rig as in [29], focusing on the same FOC variants. However, they do not account for the second speed control loop in their study, nor do they consider the potential influence of the type of PID controller on fault detection and quantification.
3. Laboratory Setup and Speed Controller Tuning
3.1. Laboratory Assembly
The following are the components used in the laboratory setup (Figure 3) to conduct the experimental study:
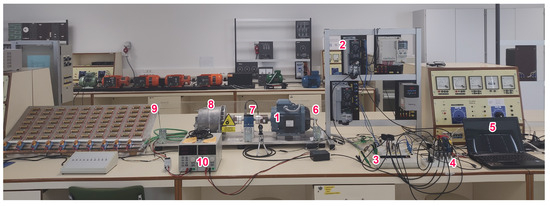
Figure 3.
The laboratory setup consists of the following components: (1) Induction motor; (2) Inverter; (3) Custom-made board with Hall effect sensors for voltage and current measurements; (4) DAQ board; (5) Laptop PC; (6) Encoder; (7) Torque transducer; (8) Truck alternator; (9) Bank of resistors; (10) DC voltage supply for truck alternator and torque transducer.
- Three-phase induction motor ABB (Västerås, Sweden), with the following specifications: Model M2AA 100 LC-4; Star connection; Rated power of 2.2 kW; Rated voltage of 400 V; Rated current 4.6 A; Rated speed 1450 rpm; Moment of inertia 0.009 kg/m2; 26 rotor bars.
- Power electronic converter from Danfoss (Nordborg, Denmark), model VTL Midi Drive FC 280 134U777.
- Custom-made board with Hall effect sensors by LEM (Meyrin, Switzerland): for voltage measurement (LEM LV25-P) and current measurement (LEM LA25-NP).
- Data acquisition board from National Instruments (Austin, TX, USA), model NI cDAQ-9174 chassis, equipped with 4 NI-9215 modules.
- Laptop PC with National Instruments libraries (NI DAQmx version 2023 Q3.1) and MATLAB software (Version R2023b).
- Incremental encoder from Kübler (Villingen-Schwenningen, Germany), model D-70054 with 1024 PPR.
- Torque transducer from Lorenz Messtechnik (Alfdorf, Germany), model DR-2112-R.
- 24 V truck alternator from Delco Remy (Piracicaba, Brazil), model 19025331.
- Bank of resistors: This consists of 70 resistors of 50 W arranged in 10 columns placed in parallel. Each column contains 7 resistors, also in parallel.
The induction motor, torque transducer, and truck alternator are connected using elastic couplings. The alternator and the bank of resistors are used as the motor load. Each column can be manually disconnected or connected to the alternator, allowing for manual regulation of the motor’s load level.
The breakage of a rotor bar is emulated by drilling a hole in the end ring of the squirrel cage, as shown in Figure 4. Damage to the rotor magnetic lamination is avoided to prevent undesirable magnetic imbalances during machine operation.
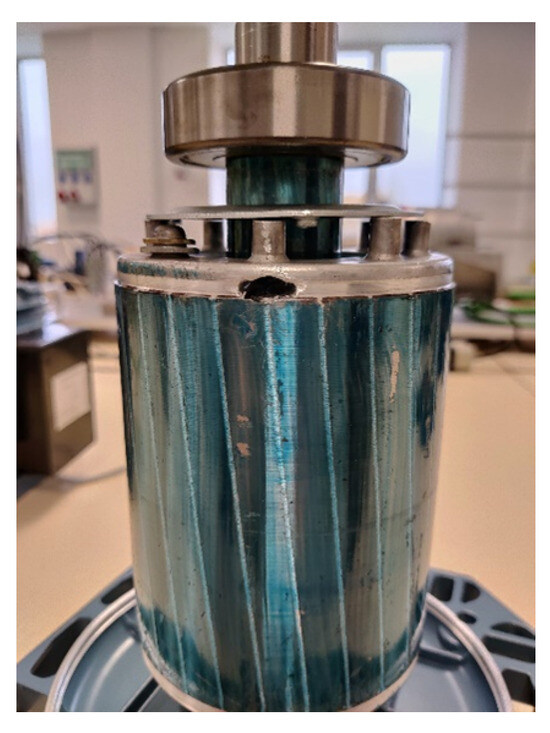

Figure 4.
Broken rotor bar emulation by drilling a hole in the rotor end-ring.
PID closed-loop speed control is enabled by using a 1024 PPR incremental encoder from Kluber. This represents a notable change from a previous laboratory setup, which utilized an Omron encoder with 500 PPR [28]. Compared to the second one, this first encoder facilitates a more stable steady-state motor operation without disturbances and with less noise. The encoder’s signal is transmitted to the Danfoss inverter for the closed-loop configuration. The sensed speed signal is affected by white noise introduced into the system through this feedback loop [32].
3.2. PID Tuning
The closed-loop speed control is implemented through a PID controller in the inverter, utilising the encoder signal for feedback. The transfer function of the PID controller is as follows:
where is the proportional gain, is the integral time (in s), and is the differentiation time (in s).
The PID parameters were syntonised using the IMC method [33]. The tuning process has already been explained and used in [28,37]. This experimental method involves subjecting the open-loop plant to a step input (direct motor start-up) and measuring its response in the time domain. The IMC method has a degree of freedom and tuning rules [33,37]. If a low value is chosen for this parameter, the resulting controller will provide a fast or underdamped response. If, on the other hand, this parameter is set to a high value, the resulting controller will provide a slow or overdamped response.
As one of the objectives of this work is to study whether or not the type of controller affects broken rotor bar fault detection, two different controllers were tuned: one with an underdamped or fast response (FR) and a second with an overdamped or slower response (SR). The configuration parameters of both controllers are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
PID tunning parameters.
Figure 5 illustrates the behaviour of the motor operating in closed-loop control with the two controllers. In this figure, the motor speed during a startup is represented. The underdamped or fast controller (in blue) shows a slight overshoot and a short oscillation before quickly reaching the steady state. The slight overshoot exhibited by the underdamped controller is tolerable in many industrial applications but not in continuous industrial process control, where an overdamped response is more suitable. The overdamped or slow controller (in red) takes longer to advance to the steady state and does not exhibit any overshoot.
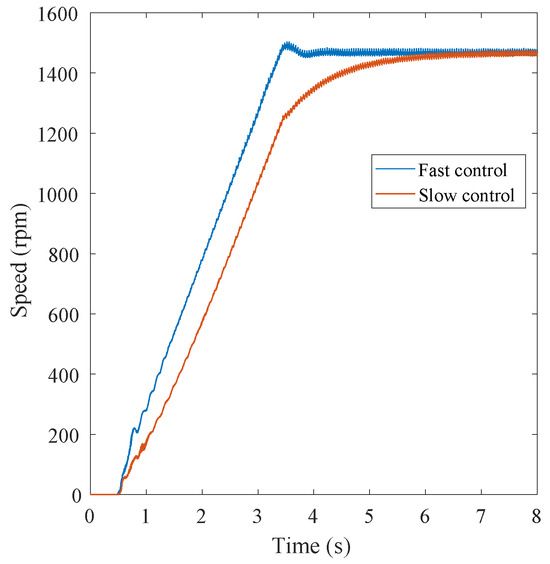
Figure 5.
Speed response of the induction motor operating in closed-loop control to a start-up transient with the two different PID controllers: Fast or underdamped controller in blue; Slow or overdamped controller in red.
3.3. Laboratory Tests
The induction motor was tested in two conditions: healthy and with a broken rotor bar (Figure 4). In each laboratory test, several signals were captured: currents, voltages, torque, and speed. The capture parameters were as follows:
- Sampling time: 15.5 s.
- Sampling frequency: 100 kS/s or kHz.
Tests were conducted with the motor operating at different loads, represented by the number of resistor columns connected to the truck alternator (from 0 columns, or no load, to five columns, almost full load).
The motor was also tested using the following power supply options:
- Mains power supply.
- Inverter power supply (Danfoss inverter):
- -
- With open-loop control:
- *
- Scalar control.
- -
- With closed-loop control:
- *
- Sensorless space vector control or voltage vector control (according to the inverter manufacturer’s designation).
- *
- Voltage vector control with the two differently tuned PID controllers.
It is important to underline that the closed-loop voltage vector control, called VVC+ by the inverter manufacturer, has been used in this research in three modes. The first mode, which was renamed “sensorless VVC”, does not include a sensor to measure the speed but only a compensation loop of the amplitude and angle of the voltage vector based on a model of the motor; therefore, in this case, there is only a closed-loop, which does not intervene directly on the speed. On the contrary, the second and the third modes include an additional compensation loop based on the measurement of the actual speed using an encoder, in which the PID controller is tuned in two different ways: with slow response (SR) and with fast response (FR). Using all these power sources will allow us to determine how the closed-loop speed control and the type of PID controller used can impact the detection of broken rotor bars. The tests with the inverter were carried out at various set frequencies, but this paper will only present the results for the 50 Hz frequency.
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Current Signature Analysis of Motors Powered by Different Voltage Sources
This section presents the classical motor current signature analysis, or MCSA. This analysis focuses on a low-frequency region (from 34 to 66 Hz), which is where the nominal frequency and the fault-related harmonics are commonly located in the current spectrum (remember Equation (3)). The first results of this analysis are shown in Figure 6, where the stator current spectrum for motors operating in open loop at 85% of rated load torque is presented. Figure 6a displays the spectra of motors fed by line voltage, whereas Figure 6b shows the inverter-fed case operating with a scalar control. The spectra corresponding to the healthy case (motor without broken rotor bar) are shown in blue. On the other hand, the spectra corresponding to the case of the motor with a broken rotor bar (BRB) are shown in red.
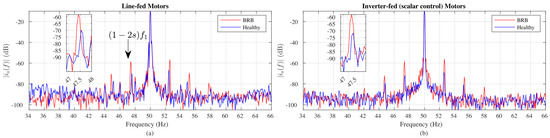
Figure 6.
Motor current signature analysis of induction motors in open loop: (a) Line-fed, (b) Inverter-fed with scalar control.
In the former case, the main frequency component is located at 50 Hz. The amplitude of the current spectral density is dB in both cases (healthy and BRB condition). The spectrum of the healthy motor (solid blue line) presents a magnitude difference of 62 dB between the main component at 50 Hz and the lower side harmonic or LSH at 47.6 Hz. On the other hand, the motor with rotor failure (solid red line) presents a difference lower than 50 dB. These measurements allow correct fault detection using the severity indexes proposed by Bellini et al. [4].
Similarly, the rotor fault in the inverter-fed motors (scalar control) can be correctly diagnosed with the traditional severity factors. In this case, see Figure 6b, the healthy motor presents a difference in dB greater than 63. In contrast, for the damaged rotor, it is lower than 50, which is expected because of the crack in the rotor bar. These results show an example of the MCSA and its effectiveness for BRB detection in open-loop controlled motors.
Figure 7 presents three case studies on the application of MCSA to detect broken bars in motors controlled by different speed closed-loop control strategies.The motor load level is the same as the results displayed in Figure 6. These three cases are the following: sensorless VVC, VVC with a PID controller with slow response, and VVC with a PID controller with fast response. These analyses are presented in Figure 7a, Figure 7b, and Figure 7c, respectively.
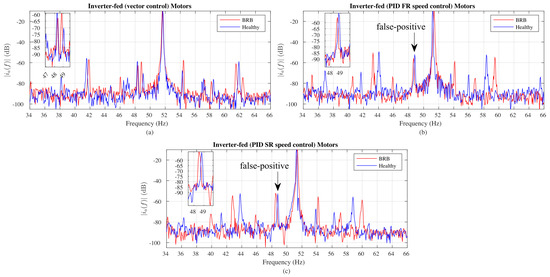
Figure 7.
Motor current signature analysis of induction motors operating in closed-loop speed control: (a) sensorless voltage vector control (VVC), (b) VVC with a fast−response (FR) or overdamped PID speed controller, (c) VVC with a slow−response (SR) or underdamped PID speed controller.
The analysis of these spectra is interesting. The first point to note is that the first harmonic is no longer at 50 Hz. The VVC increases this frequency to compensate for the slip caused by the motor load. The resulting spectra of the three case studies show side bands around the first component coincident with (LSH and USH), but also with ). This last frequency component can be considered as the third band () in Equation (3).
In Figure 7a, it is important to note that two bands ( and ) appear to the left of the main harmonic. These bands show the same amplitude, regardless of the rotor condition, which makes fault detection difficult in vector-controlled motors and invalidates the use of Equation (3). Similar outcomes can be observed in the other two figures (Figure 7b,c), in which the motor operates in a closed loop and a PID controller regulates its speed. These sidebands at and are observable in all these figures, with a difference of magnitudes with the fundamental component around −50 dB. Therefore, the vector control strategy (both with and without using speed as a feedback signal) negatively affects the detection of this type of fault.
The previously mentioned frequency components found in the stator current spectra can wrongly indicate rotor faults in both motors, regardless of the actual rotor condition. The nearly identical spectra show that the feedback control introduces additional harmonics in the current, leading to incorrect fault detection. In other words, it can produce false positives. Therefore, the results shown in Figure 7 demonstrate that the classical current analysis (MCSA) is unsuccessful due to the influence of the closed-loop controllers, resulting in inaccurate diagnoses.
Bellini et al. [4] proposed an index (Equation (4)) to evaluate the fault severity. This index was applied to the five case studies analysed, and the results are shown in Table 2. This index correctly quantifies the failure for the mains and inverter case with scalar control, even for lower load levels than those used in Figure 6 and Figure 7. When the failure occurs, the index increases compared to the healthy motor case. In addition, the higher the motor load level, the higher the severity index. For example, in the case of the mains-powered motor at 85% load, the index increases from 0.054 for the healthy motor to 0.193 for the motor with a broken bar. The index has been multiplied by 3.6. A similar index behaviour is not observed for the closed-loop cases. In the case of sensorless VVC, the index increases when the motor condition changes from healthy to faulty, but the index has no relation to the motor load level. In the cases of PID speed control, the index takes similar values for the two motor conditions, although some differences are observed between the two PID controllers. This severity index is useless in the case of the fast-response PID controller, where it even decreases when the motor operates at full load. The index appears to be performing well in the slow-response PID controller. When the motor condition changes to faulty, the index increases. However, the problem is that the index values for the healthy motor are similar to the values it takes for the faulty and mains-powered motor. Therefore, stator current analysis and fault quantification using this severity index are not useful for detecting BRB in motors operating with closed-loop speed control. Interestingly, there are differences in fault severity quantification among the three closed-loop control cases. The type of PID also has a different impact on fault quantification.

Table 2.
Fault severity quantification using the index (Equation (4)) proposed by Bellini et al. in [4].
4.2. Zero-Sequence Voltage Analysis of Induction Motors Powered by Different Voltage Sources
One of the signals proposed in [27] for fault detection in inverter-fed induction motors is the zero-sequence voltage. Next, Figure 8 and Figure 9 present the study of this signal for the different motor supplies considered in this study (mains and inverter with open and closed-loop control). As discussed in Section 2, the fault-related spectral activity appears to the left of the third harmonic in the ZSV signal. Figure 8 and Figure 9 show that this occurs with all the power supply and control variants studied in this work.
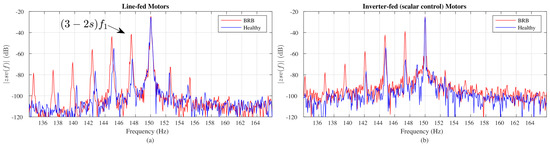
Figure 8.
Zero sequence voltage analysis of induction motors in open-loop operation: (a) Line−fed, (b) Inverter−fed with scalar control.
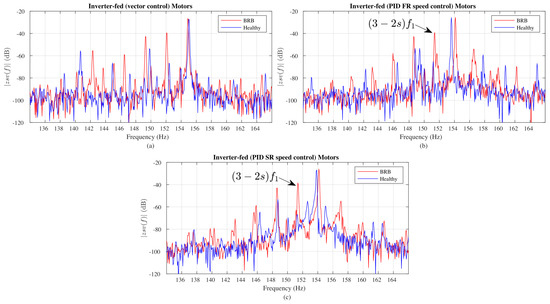
Figure 9.
Zero sequence voltage analysis of induction motors in closed-loop operation: (a) Sensorless VVC, (b) VVC with the fast−response (FR) or underdamped PID controller, (c) VVC with the slow−response (SR) or overdamped PID controller.
Figure 8 shows the spectral analysis of the ZSV signal for the two cases without closed-loop control operating at a frequency of 50 Hz: line-fed motor and inverter-fed motor with scalar control. As expected, the third harmonic at 150 Hz appears in all figures. In both types of power supply, the amplitude of the frequency component related to the bar fault increases by more than 20 dB compared with the healthy case. Therefore, the BRB fault is detected effectively using the ZSV signal. The voltage harmonics for the scalar control case, Figure 8b, present less spectral spillover due to the action of the PWM, which sets the operating frequency statically.
Figure 9 shows the ZSV spectral analysis for the closed-loop controlled cases. Figure 7 shows that, in these cases, the frequency of the first component of the voltage supply is above 50 Hz to compensate for the speed decrease produced by the motor load. The control detects this speed reduction and increases the main harmonic until the speed reaches the established setpoint. This means the third harmonic voltage is above 150 Hz. Hence, all motors operate at a frequency superior to 50 Hz. Figure 9a shows the spectra for the motor operating in sensorless VVC. The third harmonics for the healthy and faulty cases are around 155.04 Hz, which means an operating frequency close to 51.68 Hz. For this control strategy, the first fault harmonic presents an increment of more than 30 dB when the rotor is damaged. It is important to note that a BRB failure impacts on the speed and efficiency of induction motors. When a broken bar failure occurs, the motor presents a reduction and a ripple effect on the rotational speed [15,38]. This speed change is barely noticeable in the low-frequency fault components of the MCSA, i.e., the LSH and RSH, whereas it is more noticeable in the ZSV spectra at the side components or the third harmonic. Figure 9b,c show the ZSV voltage spectra for motors with speed regulated by PID controllers. Both controller configurations exhibit a frequency difference in the third harmonic between the healthy and the damaged motor; this effect reveals the corrective action of the PID controller, i.e., the lower the rotational speed, the higher the power frequency to compensate for the speed error. Figure 9b indicates a −65 dB magnitude component when the motor is healthy. When the test is repeated for the damaged motor, the harmonic increases by more than 25 dB. This value undoubtedly indicates an induced voltage due to the asymmetry in the rotor when the speed is regulated by the fast-response (FR) or underdamped PID controller.
In contrast, Figure 9c illustrates the outcomes of the ZSV analysis when the speed is commanded by the slow-response (SR) or overdamped PID controller. These results were obtained under the same test conditions as those depicted in Figure 7c. The spectra exhibited an amplitude discrepancy, with the fault harmonic demonstrating a deviation of over 25 dB compared to the healthy state. These empirical findings unequivocally establish that the detection of a broken bar is feasible, regardless of the control strategy employed, through the analysis of the ZSV signal, while the MCSA method is prone to yielding false positives.
The fault severity quantification results, based on the index proposed in [4] and calculated using information from the stator current spectrum, indicate that this index is ineffective in all three scenarios of closed-loop motor control. To address this issue, a new fault severity index () is proposed that utilizes information from the ZSV spectrum:
where is the amplitude in volts of the ZSV frequency component at and is the amplitude in volts of the third harmonic of the ZSV signal computed using Equation (5). The quantification results using this new index are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Fault severity quantification using the new fault severity index defined in (8).
The results from Table 3 yield some interesting findings. To begin with, the zero-sequence voltage consistently identifies faults in all five cases examined. Whenever the motor transitions from a healthy to a faulty state, there is always a rise in the fault severity index (Equation (8)). Notably, the fault severity index exhibits similar values for the healthy motor across the five power supply and control types assessed. In all instances involving a faulty motor, the index value increases with the motor load level. There are no significant discrepancies between the three cases of closed-loop control. A higher index value is only evident for the highest load level in the case of closed-loop speed control. Hence, in comparison to stator current analysis, the ZSV analysis proves to be more effective in detecting broken rotor bars in closed-loop speed control with PID controllers.
5. Conclusions
In this study, it has been shown that the detection of broken-bar failure in inverter-fed, closed-loop speed-controlled induction motors is a challenge. Classical analysis of the stator current spectrum is not an option, as the control action alters the spectral content of the stator current. This results in erroneous fault quantification using indexes, such as the one proposed in [4], and can lead to false positive detection. However, the analysis of the zero-sequence voltage and the newly proposed fault severity index provides positive fault detection, as this signal is very sensitive around the third harmonic to the occurrence of the fault. The new severity index produces very different values for the two evaluated rotor states and all the feedings and control variants considered in this study. Furthermore, no significant differences exist between the two types of PID controllers considered, as was the case with the current stator analysis.
There are still open issues that will be addressed in future works, such as expanding the study to include drives from other manufacturers, extending the study to different main frequencies other than 50 Hz, studying the impact of encoder quality on fault detectability, investigating fault detectability during transients such as start-up, load torque disturbances, or load torque oscillations, examining the detectability of other types of faults (short circuits, bearings, and eccentricity), and analysing what happens with other motor signals, such as stray flux or vibrations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M.-S. and L.F.; methodology, T.G.-C. and D.M.-S.; software, T.G.-C., L.M. and F.M.; validation, D.M.-S., T.G.-C. and F.M.; formal analysis, D.M.-S., T.G.-C. and F.M.; investigation, F.M., T.G.-C., L.M. and D.M.-S.; resources, D.M.-S.; data curation, F.M., T.G.-C. and L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, T.G.-C., L.M. and D.M.-S.; writing—review and editing, D.M.-S. and L.F.; visualization, F.M., T.G.-C. and D.M.-S.; supervision, L.F., D.M.-S. and T.G.-C.; project administration, D.M.-S.; funding acquisition, D.M.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Department of Electrical Engineering, the Research Group ADIRE, the ITAP Institute, and the University of Valladolid have partially funded this work. The authors Francesca Muzio and Lorenzo Mantione benefited from an Erasmus+Traineeship grant that allowed them to enjoy a research stay at the University of Valladolid.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not aplicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors of this work would like to thank Danfoss for donating the inverters used in this work. They also thank MathWorks Inc. for the encoder signal capture scripts.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MCSA | Motor Current Signature Analysis |
| BRB | Broken Rotor Bar |
| ZSV | Zero-Sequence Voltage |
| IM | Induction Motor |
| SFSA | Stray Flux Signature Analysis |
| PWM | Pulse Width Modulation |
| VVC | Vector Voltage Control |
| FOC | Field-Oriented Control |
| IRFOC | Indirect Rotor Field-Oriented Control |
| DRFOC | Direct Rotor Field-Oriented Control |
| DTC | Direct Torque Control |
| VCT | Virtual Current Technique |
| VMM | Vienna Monitoring Methdod |
| PEC | Power Electronic Converter |
| PID | Proportional integral derivative |
| IMC | Internal Model Control |
| LSH | Lower Sideband Harmonic |
| USH | Upper Sideband Harmonic |
| FR | Fast-Response or underdamped PID controller |
| SR | Slow-Response or overdamped PID controller |
| PPR | Pulse per revolution |
| IGBT | Insulated-Gate-Bipolar-Transistor |
References
- Toliyat, H.A.; Nandi, S.; Choi, S.; Meshgin-Kelk, H. Electric Machines: Modeling, Condition Monitoring, and Fault Diagnosis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbanian, V.; Joksimović, G.; Faiz, J. Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motors; Institution of Engineering & Technology: Lucknow, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Rivera-Guillen, J.R.; De Santiago-Perez, J.J.; Perez-Soto, G.I.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P. Expert System Based on Autoencoders for Detection of Broken Rotor Bars in Induction Motors Employing Start-Up and Steady-State Regimes. Machines 2023, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, A.; Filippetti, F.; Tassoni, C.; Capolino, G.A. Advances in Diagnostic Techniques for Induction Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 2008, 55, 4109–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, W.T.; Culbert, I. Current Signature Analysis for Condition Monitoring of Cage Induction Motors: Industrial Application and Case Histories; IEEE Press—Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet-Jara, J.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Duque-Perez, O.; Serrano-Iribarnegaray, L.; Pons-Llinares, J. End-Ring Wear in Deep-Well Submersible Motor Pumps. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 4522–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Hyun, D.; Kang, T.j.; Yang, C.; Shin, S.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Kong, T.S.; Kim, H.D. Identification of False Rotor Fault Indications Produced by Online MCSA for Medium-Voltage Induction Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotou, P.A.; Arvanitakis, I.; Lophitis, N.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Gyftakis, K.N. A New Approach for Broken Rotor Bar Detection in Induction Motors Using Frequency Extraction in Stray Flux Signals. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 3501–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Choi, H.; Lee, S.B.; Gyftakis, K.N. Search Coil-Based Detection of Nonadjacent Rotor Bar Damage in Squirrel Cage Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 4748–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceban, A.; Pusca, R.; Romary, R. Study of Rotor Faults in Induction Motors Using External Magnetic Field Analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 2082–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio-Ramirez, I.; Mendoza-Ortiz, J.M.; Osomio-Ríos, R.A.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A. Stray Flux Signal Analysis for Faults Detection in Induction Motors During Startup Transient By Means Of Statistical Indicators. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), Chania, Greece, 28–31 August 2023; pp. 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Mian, T.; Fatima, S. Convolutional neural network based bearing fault diagnosis of rotating machine using thermal images. Measurement 2021, 176, 109196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon-Uribe, U.; Lizarraga-Morales, R.A.; Guryev, I.V. Fault Diagnosis in Induction Motors through Infrared Thermal Images Using Convolutional Neural Network Feature Extraction. Machines 2024, 12, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Hernandez, A.I.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Zamudio-Ramirez, I.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A. Hardware Accelerated Thermal Image Processing for the Detection of Induction Motor Faults Based on Statistical Features. In Proceedings of the IECON 2023—49th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Singapore, 16–19 October 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Calva, T.A.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Fernandez-Cavero, V.; Garcia-Perez, A.; Romero-Troncoso, R.d.J. Early Detection of Broken Rotor Bars in Inverter-Fed Induction Motors Using Speed Analysis of Startup Transients. Energies 2021, 14, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Pons-Llinares, J.; Lee, S.B. Advanced Rotor Fault Diagnosis for Medium-Voltage Induction Motors via Continuous Transforms. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 4503–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippetti, F.; Bellini, A.; Capolino, G.A. Condition monitoring and diagnosis of rotor faults in induction machines: State of art and future perspectives. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Electrical Machines Design, Control and Diagnosis (WEMDCD), Torino, Italy, 26–27 March 2013; pp. 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins Cunha, C.C.; Cardoso Filho, B.J. Detection of Rotor Faults in Squirrel-Cage Induction Motors using Adjustable Speed Drives. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2006 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Forty-First IAS Annual Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 October 2006; Volume 5, pp. 2354–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, S.M.A.; Cardoso, A.J.M. Diagnosis of rotor faults in direct and indirect FOC induction motor drives. In Proceedings of the 2007 European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Aalborg, Denmark, 2–5 September 2007; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, S.M.A.; Stefani, A.; Filippetti, F.; Cardoso, A.J.M. A New Model-Based Technique for the Diagnosis of Rotor Faults in RFOC Induction Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 4218–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, B.; Vaimann, T.; Belahcen, A.; Kallaste, A. Broken Rotor Bar Fault Diagnostic of Inverter Fed Induction Motor Using FFT, Hilbert and Park’s Vector Approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 2352–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, K.; Chen, L. Broken Rotor Bars Detection in Inverter-Fed Induction Motors Under Continuous Switching of Different Speed Modes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, A.; Filippetti, F.; Franceschini, G.; Tassoni, C. Closed-loop control impact on the diagnosis of induction motors faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, C.; Wieser, R.; Pirker, F.; Schagginger, M. Sequences of field-oriented control for the detection of faulty rotor bars in induction machines-the Vienna Monitoring Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2000, 47, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, C.; Pirker, F.; Pascoli, G. Model-based detection of rotor faults without rotor position sensor-the sensorless Vienna monitoring method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concari, C.; Franceschini, G.; Tassoni, C. Rotor fault detection in closed-loop induction motors drives by electric signal analysis. In Proceedings of the 2008 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines, Vilamoura, Portugal, 6–9 September 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, H.; Ye, M.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J. Diagnosis of broken rotor bar fault in open- and closed-loop controlled wye-connected induction motors using zero-sequence voltage. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantione, L.; Fernandez-Cavero, V.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Frosini, L. A Time-Frequency Analysis for Broken Rotor Bar Detection in Closed Loop Inverter Fed Induction Motor at Imposed Speed. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), Chania, Greece, 28–31 August 2023; pp. 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, T.; Zhao, L. Quantitative broken rotor bar fault detection for closed-loop controlled induction motors. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H. AC Motor Control and Electrical Vehicle Applications, 2nd ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Antony, N.J.; Mishra, D.; Parveen, S. Sensorless Field Oriented Control of AC Induction Motor Using PI, PD & PID Controllers. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE North Karnataka Subsection Flagship International Conference (NKCon), Vijayapura, India, 20–21 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sul, S.K. Control of Electric Machine Drive Systems; IEEE Press Series on Power Engineering; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, D.E.; Morari, M.; Skogestad, S. Internal model control: PID controller design. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1986, 25, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleroi, W. Der Stabbruch im Käfiǵläufer eines Asynchronmotors. Arch. Elektr. 1984, 67, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet-Jara, J.; Quijano-Lopez, A.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Pons-Llinares, J. Sensorless Speed Estimation for the Diagnosis of Induction Motors via MCSA. Review and Commercial Devices Analysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons-Llinares, J.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Riera-Guasp, M.; Bin Lee, S.; Kang, T.j.; Yang, C. Advanced Induction Motor Rotor Fault Diagnosis Via Continuous and Discrete Time—Frequency Tools. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boni, G.; Fernandez-Cavero, V.; Frosini, L.; Duque-Perez, O.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D. Fault Harmonics Current Detection in Closed-loop Controlled Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), Chania, Greece, 28–31 August 2023; pp. 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Panagiotou, P.A.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Gyftakis, K.N. Efficiency Assessment of Induction Motors Operating Under Different Faulty Conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8072–8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).