Optimization Design of Cogging Torque for Electric Power Steering Motors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analysis of the Mechanism of Cogging Torque
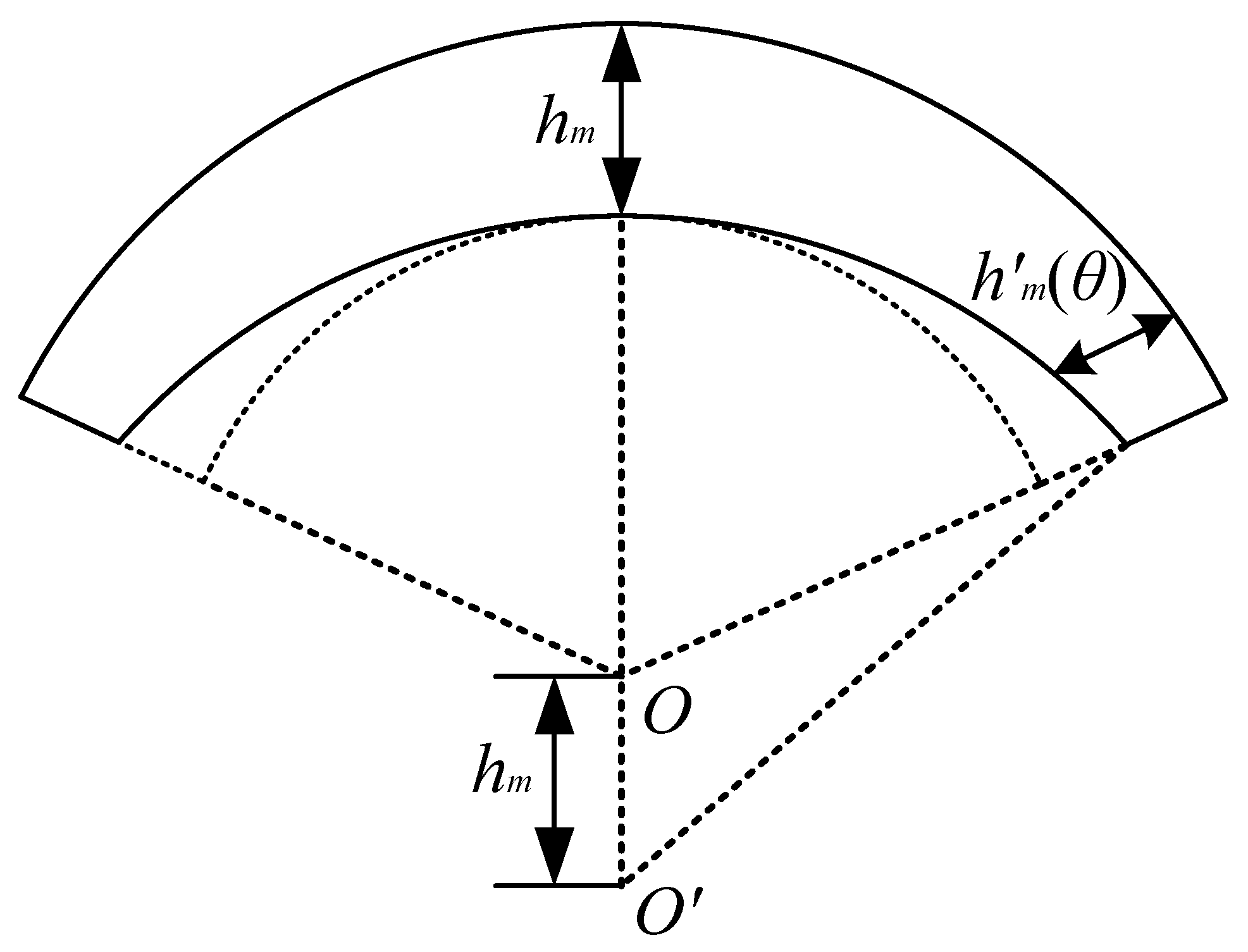
2.1. Deduction of a Mathematical Model for Cogging Torque
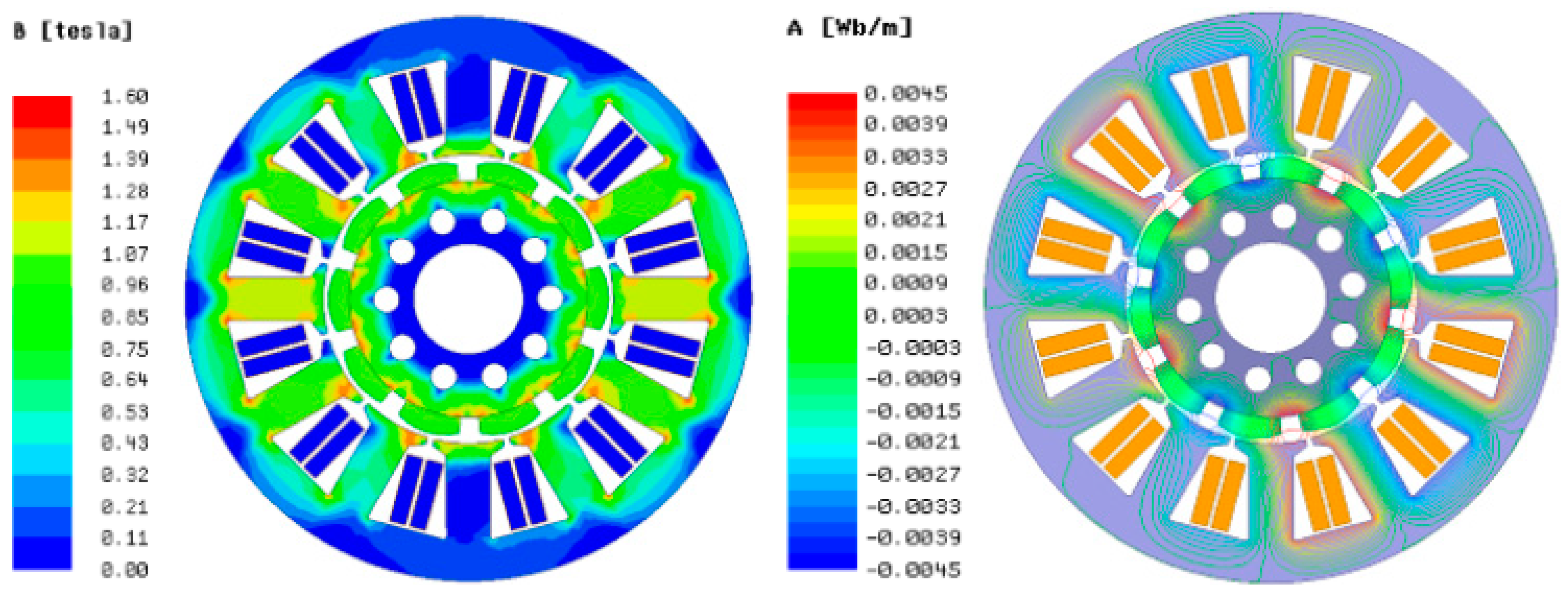
2.2. Structural Parameters of the EPS
3. Parameter Analysis and Optimization
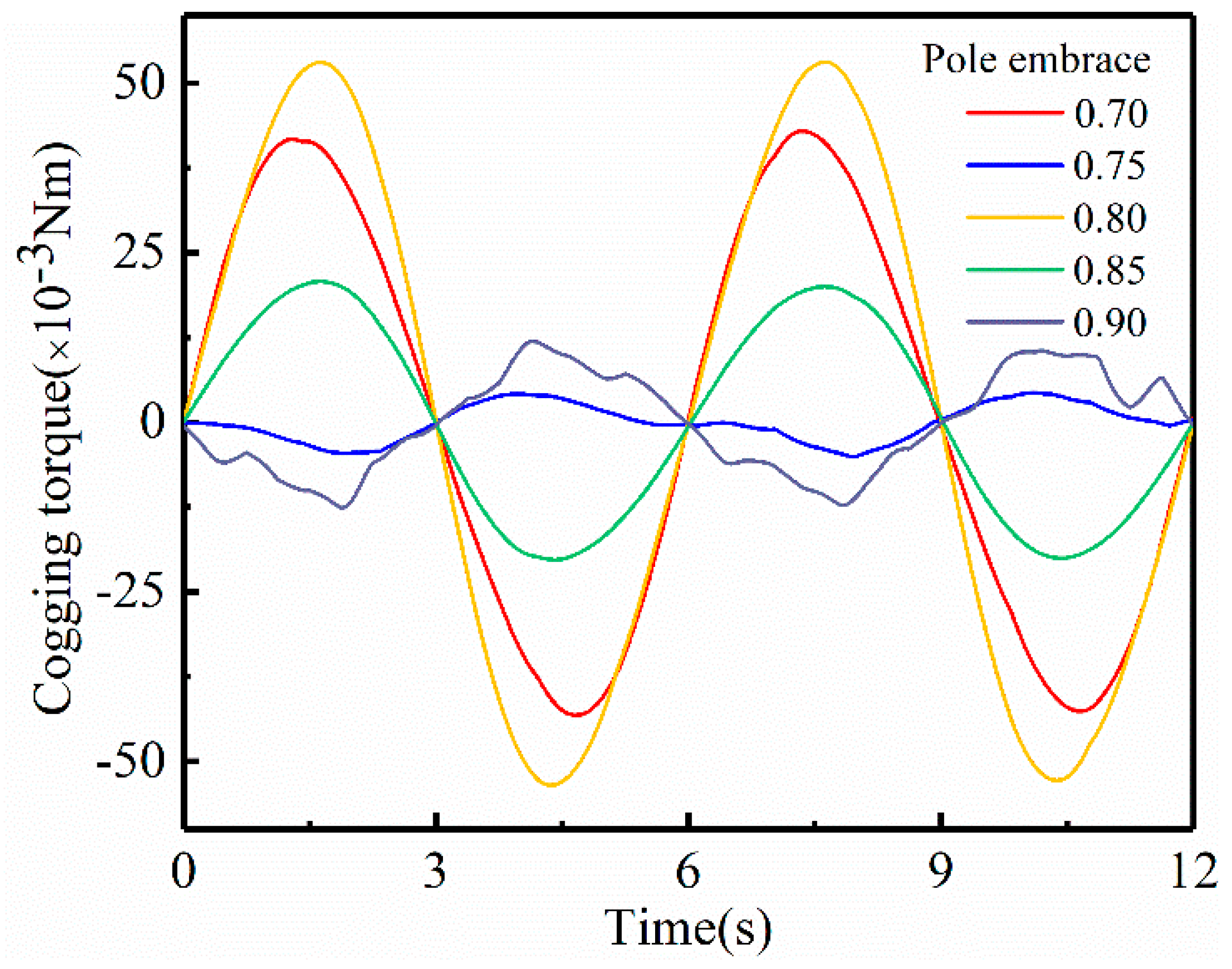
3.1. Analysis and Optimization of the Polar Arc Coefficient
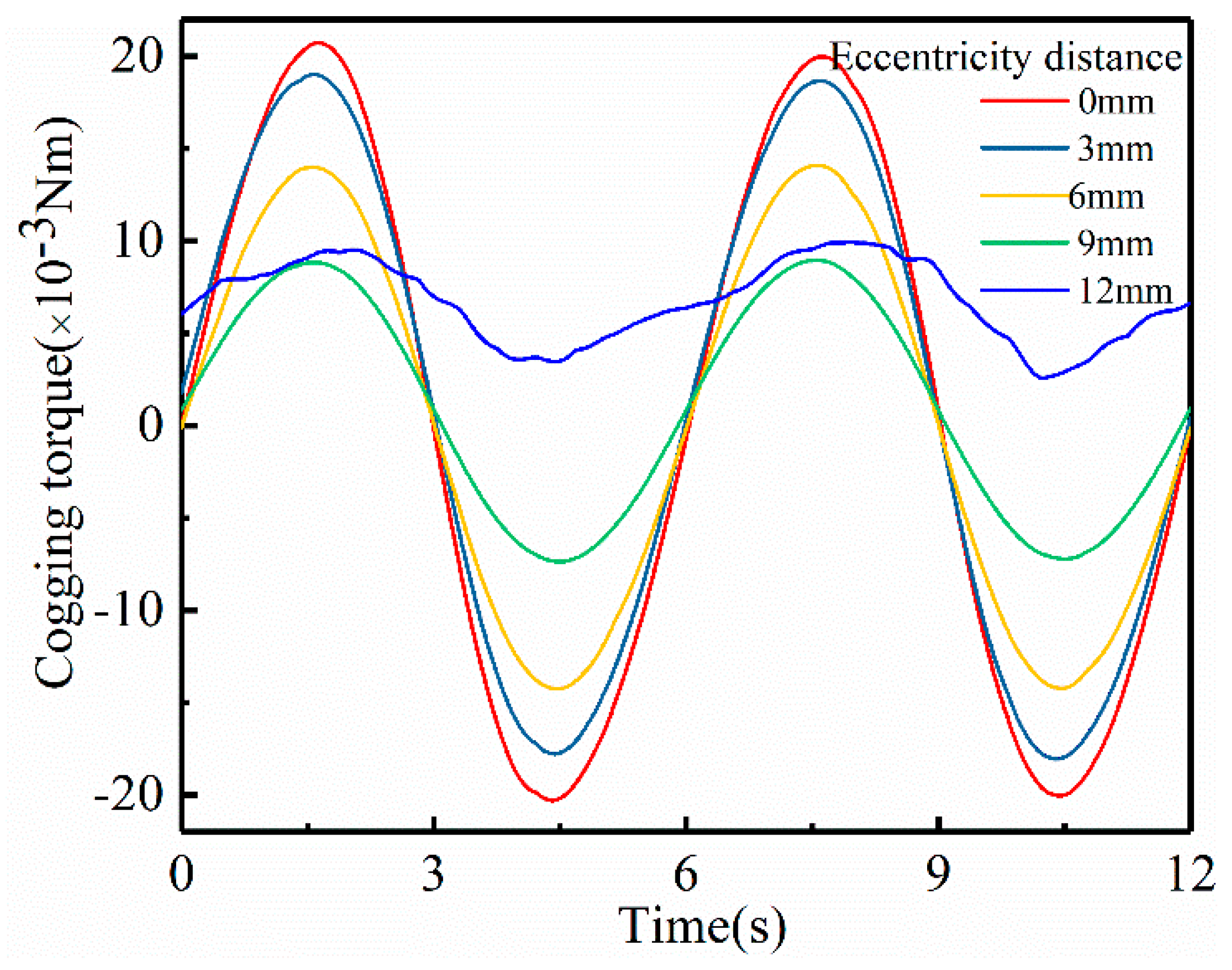
3.2. Analysis and Optimization of Eccentricity
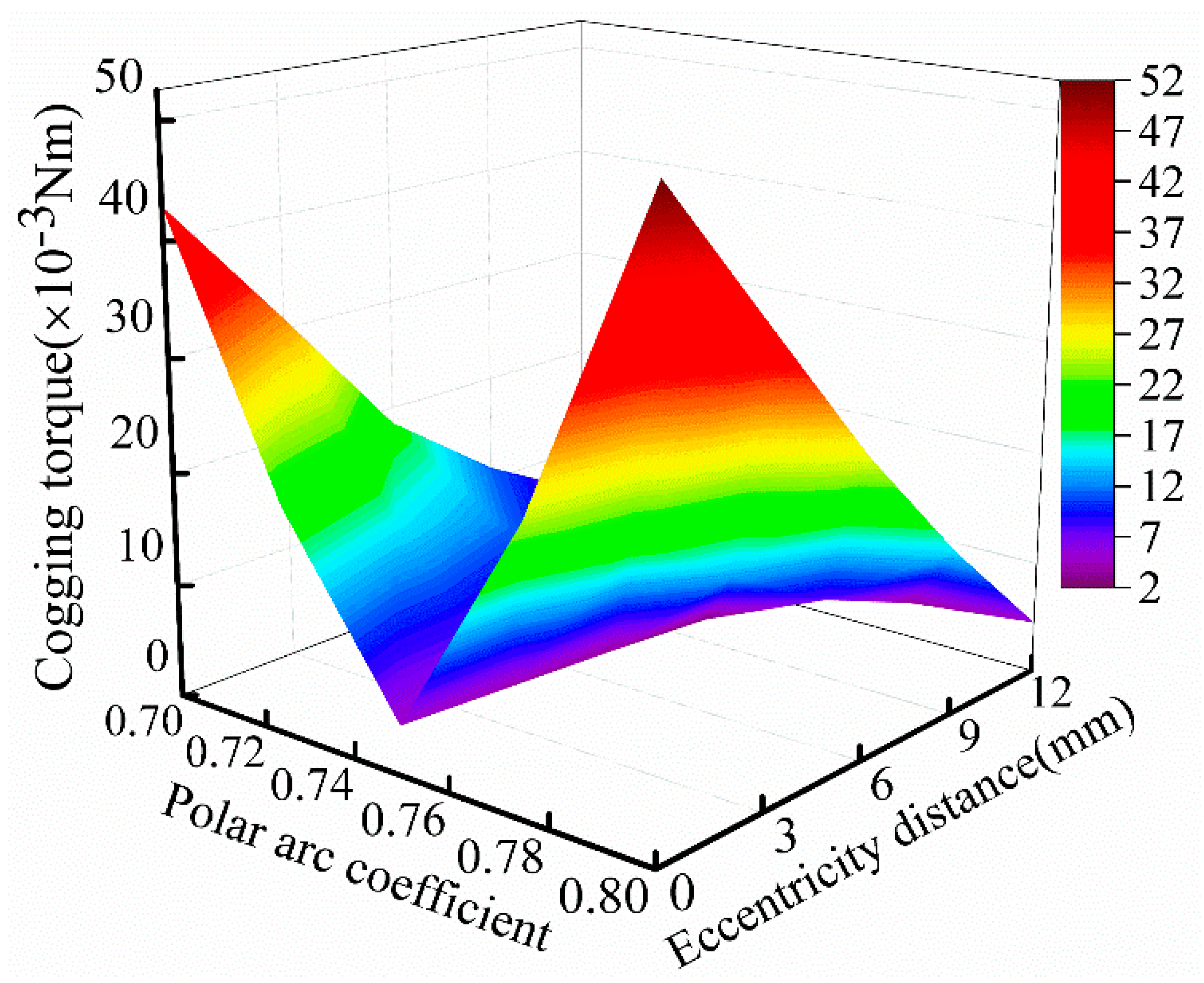
3.3. Double Parameter Optimization of the Polar Arc Coefficient and Eccentricity
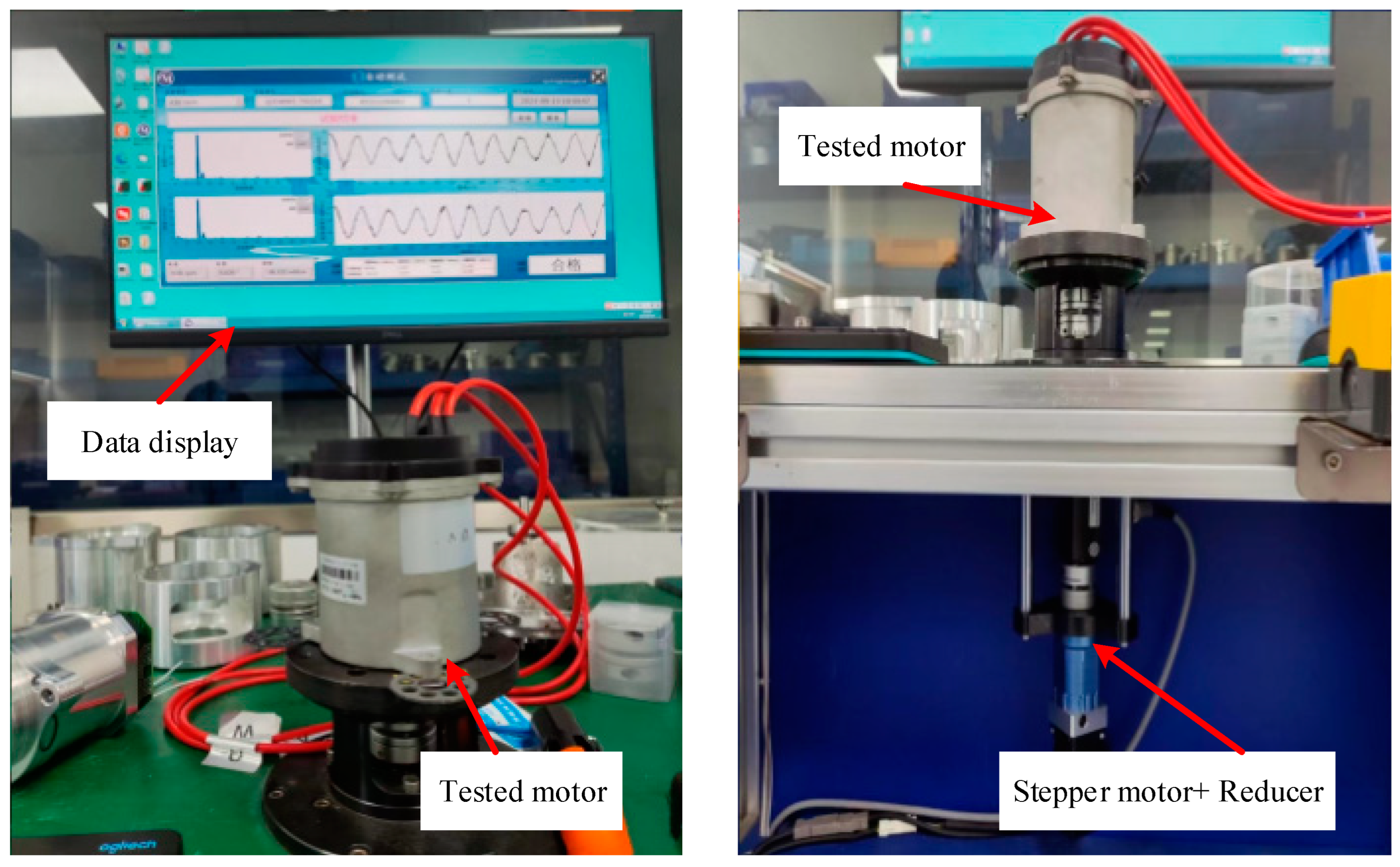
4. EPS Motor Experimental Testing
4.1. Comparison of EPS Motor Performance before and after Optimization
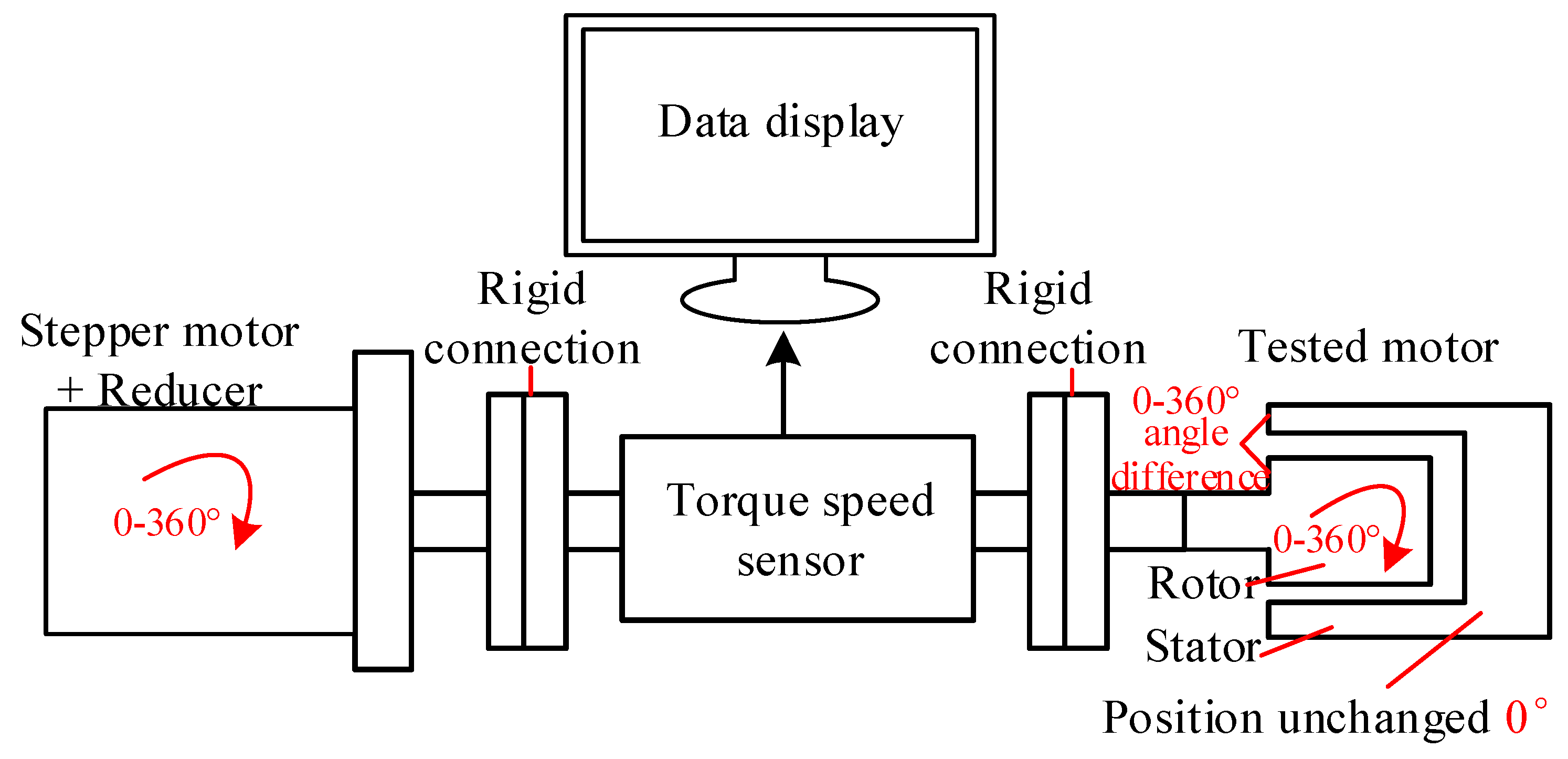
4.2. Experimental Testing of EPS Motor Cogging Torque
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, G. Investigation of Cogging Torque in Permanent Magnet Homopolar Inductor Machines Based on Air-Gap Field Modulation Principle. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2023, 19, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Duan, S.; Yang, C. A method of reducing the cogging torque in a flux–torque regulation hybrid excitation machine with axial–radial magnetic circuit. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 2973–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Lv, B.; Li, L. Multi-Objective Optimization and Analysis of Asymmetric Hybrid-Magnet Offset Motor for Electric Vehicles. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2023, 19, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Lee, J.; Ham, S.; Chun, Y.; Kim, H. A Study on New Straight Shape Design to Reduce Cogging Torque of Small Wind Power Generator. Machines 2024, 12, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.H.; Jung, J.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, B.H.; Hong, J.P. Optimum design of SPMSM with concentrated windings and unequal tooth widths for EPS. In Proceedings of the IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 9–12 October 2012; Volume 8, pp. 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Kim, M.-K.; Jung, S.-Y. Integrated optimization of two design techniques for cogging torque reduction combined with analytical method by a simple gradient descent method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2265–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulec, M.; Aydin, M. Magnet asymmetry in reduction of cogging torque for integer slot axial flux permanent magnet motors. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2014, 8, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.X.; Luk, P.C.K.; Fei, W.Z.; Wang, C.F. Cogging torque suppression in a permanent-magnet flux-switching integrated-starter-generator. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2010, 4, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosiek, L.; Pillay, P. Cogging Torque Reduction in Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 43, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doss, M.; Christy, A.A.; Jha, A.M.; Iyer, A.; Varun, R. Cogging Torque Reduction in Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor by using Various Design Modification Techniques. Int. J. Veh. Struct. Syst. 2020, 12, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gašparin, L.; Černigoj, A.; Fišer, R. Phenomena of additional cogging torque components influenced by stator lamination stacking methods in PM motors. Compel Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 28, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harisudha, K.; Afrose, S.S.; Suresh, K. Different pole arc and different magnet combination to reduce the cogging torque in PMDC motors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Power, Control, Signals and Instrumentation Engineering, Chennai, India, 21–22 September 2017; pp. 2765–2767. [Google Scholar]
- Siregar, M.; Joe, L.E.; Nur, T. Study the Effect of Combination of Shoe Height and Slot Opening width to Reduce Cogging Torque in Permanent Magnet Generator. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 807, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.M.; Seo, H.J.; Park, Y.S.; Park, H.I.; Choi, J.Y. Design and Electromagnetic Field Characteristic Analysis of 1.5 kW Small Scale Wind Power Generator for Substitution of Nd-Fe-B to Ferrite Permanent Magnet. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2933–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brescia, E.; Costantino, D.; Massenio, P.R.; Monopoli, V.G.; Cupertino, F.; Cascella, G.L. A Design Method for the Cogging Torque Minimization of Permanent Magnet Machines with a Segmented Stator Core Based on ANN Surrogate Models. Energies 2021, 14, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuja, T.A.; Doss, M.A.N. Asymmetrical Magnets in Rotor Structure of a Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor for Cogging Torque Minimization. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2022, 17, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, M.G.; Silva, F.F.D.; Xiao, M.A. Operational Analysis of an Axial and Solid Double-Pole Configuration in a Permanent Magnet Flux-Switching Generator. Energies 2024, 17, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Niu, S. Design and Optimization of a Novel Slot-PM-Assisted Variable Flux Reluctance Generator for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 2102–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Huang, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Z. Cogging Torque Reduction by Stepped Slot-Opening Shift for Interior Permanent Magnet Motors. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 1–14 August 2019; pp. 892–894. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.K.; Jung, D.H.; Lee, K.D.; Jin, W.; Lee, G.; Lee, J.; Oh, Y.J. A Study on Analysis of Synchronous Reluctance Motor Considering Axial Flux Leakage Through End Plate. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
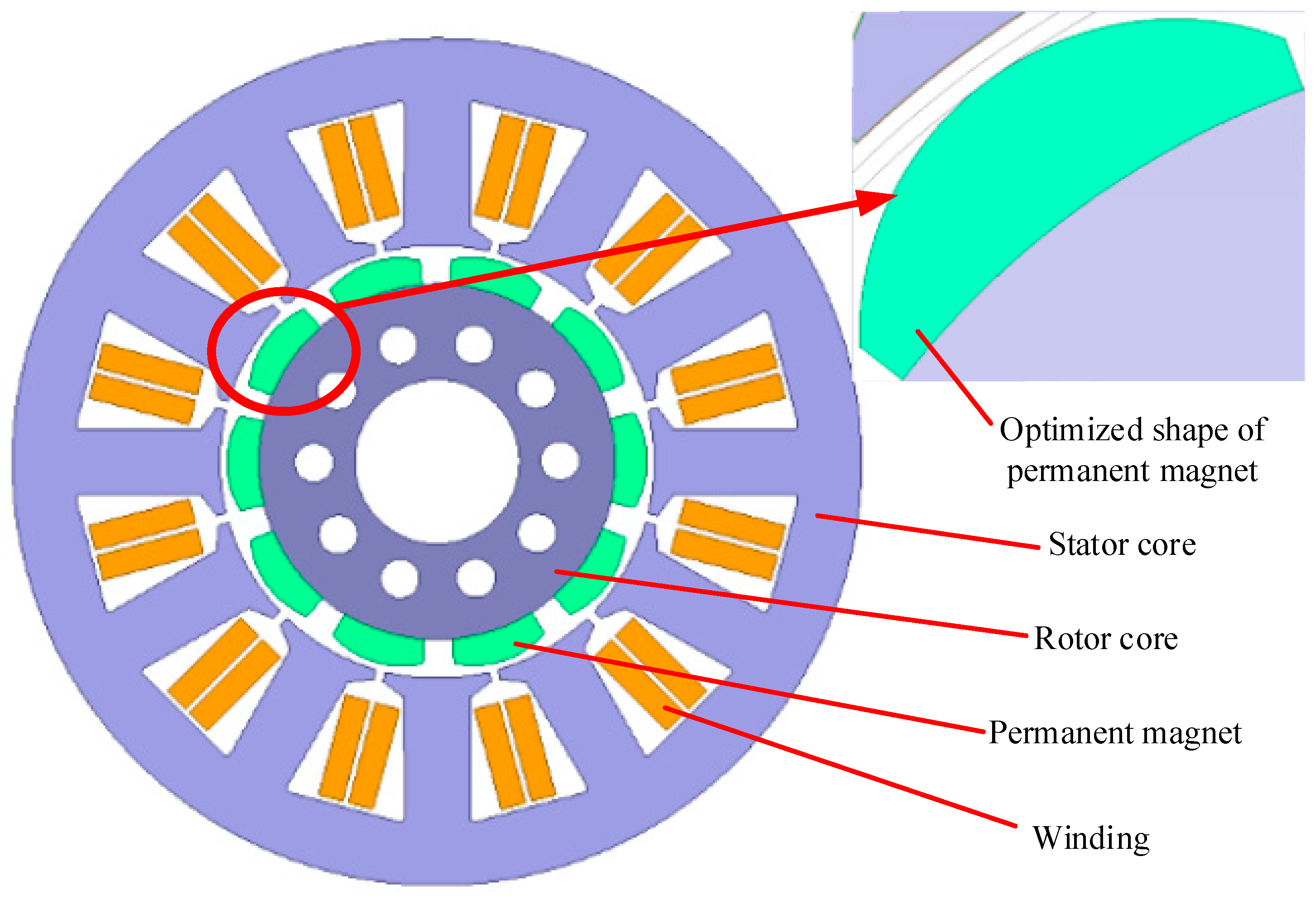


| Structural Parameter | Value | Structural Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator out diameter/mm | 85 | Axial length/mm | 77 |
| Stator in diameter/mm | 44.5 | Permanent magnet thickness/mm | 3.23 |
| Rotor out diameter/mm | 43 | Permanent magnet | NdFeB |
| Rotor in diameter/mm | 16.9 | Polar arc coefficient | 0.75 |
| Simulation Data before Optimization | Actual Measurement Data before Optimization | Optimized Simulation Data | Optimized Measured Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-load speed/(r/min) | 2082.58 | 1967.41 | 2237.19 | 2103.06 |
| Locked rotor current/A | 204.93 | 200.38 | 205.97 | 203.29 |
| Locked rotor torque/Nm | 44.17 | 42.62 | 41.85 | 40.82 |
| Motor efficiency/% | 78.95 | 77.67 | 81.63 | 80.74 |
| Before Optimization | After Optimization | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation Data | Actual Measurement Data | Simulation Data | Actual Measurement Data | |
| Cogging torque/(mNm) | 42.93 | 50.74 | 1.68 | 6.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Hou, P. Optimization Design of Cogging Torque for Electric Power Steering Motors. Machines 2024, 12, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080517
Zhang G, Hou P. Optimization Design of Cogging Torque for Electric Power Steering Motors. Machines. 2024; 12(8):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080517
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guoguang, and Peng Hou. 2024. "Optimization Design of Cogging Torque for Electric Power Steering Motors" Machines 12, no. 8: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080517
APA StyleZhang, G., & Hou, P. (2024). Optimization Design of Cogging Torque for Electric Power Steering Motors. Machines, 12(8), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080517







