Pose Selection Based on a Hybrid Observation Index for Robotic Accuracy Improvement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Kinematic Error Model
2.1. M-DH Kinematic Model
2.2. Pose Error Model
3. Pose Selection Based on a Hybrid Observability Index
3.1. Overview of Observability Indexes
3.2. Selecting Optimal Poses for Identification
3.3. A Novel Hybrid Observability Index
4. Parameters Identification
5. Experiment Results
5.1. Robot Calibration Experimental Platform
- (1)
- The transformation between the base coordinate frame of the Staubli TX60 robot and the measurement coordinate frame of the laser tracker Leica AT960.
- (2)
- The transformation between the frame of T-Mac tool and the tool frame of the Staubli TX60 robot.
- (3)
- The base coordinate frame of the Staubli TX60 robot was used as the reference coordinate system.
5.2. Robot Calibration Based on the Proposed Hybrid Observability Index
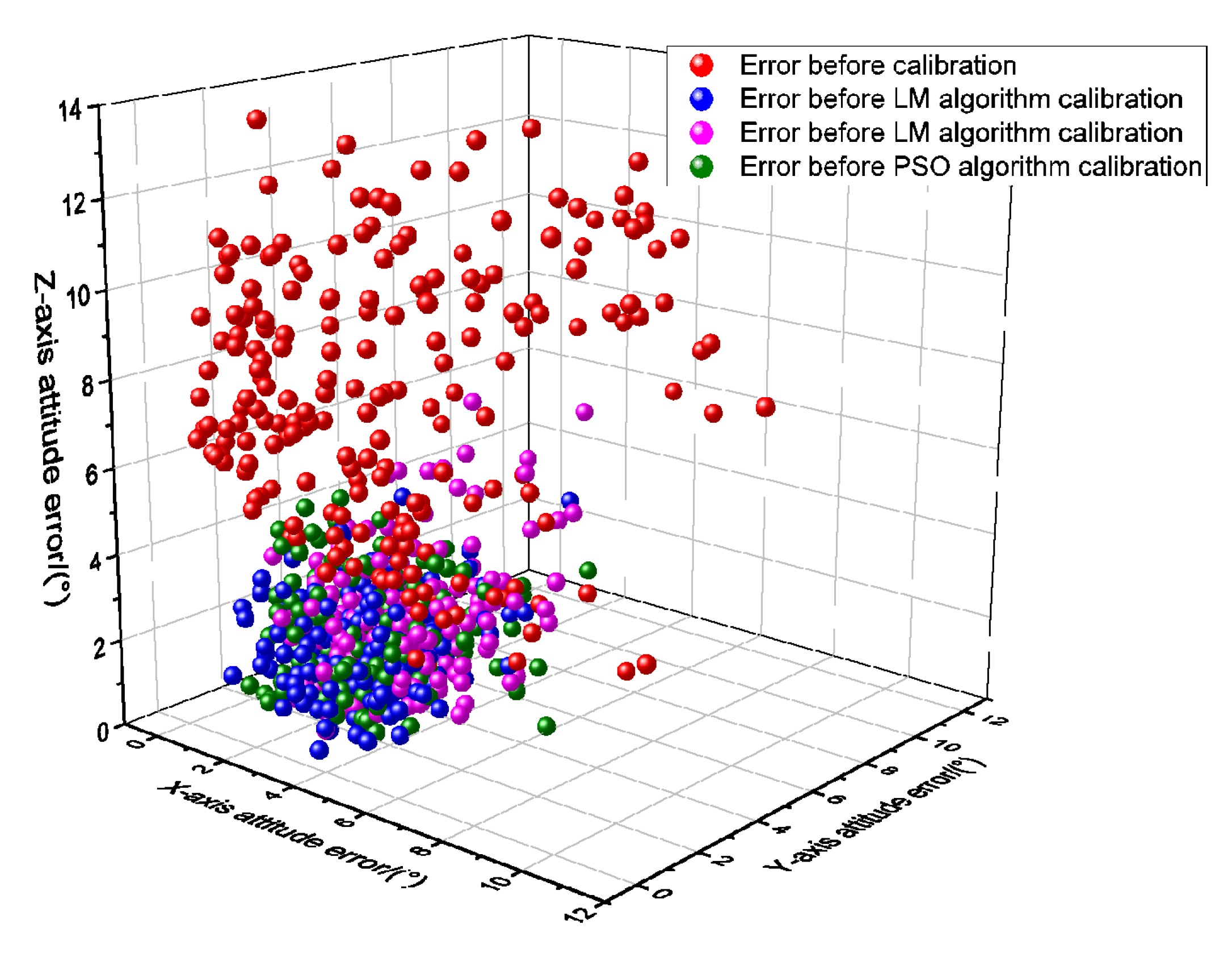
5.3. Comparison of Robot Calibration Algorithms
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Cao, B.; Xie, Z.; Ma, B.; Sun, K.; Liu, Y. Kinematic Calibration of a Space Manipulator Based on Visual Measurement System with Extended Kalman Filter. Machines 2023, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Sun, W. An integrated kinematic calibration and dynamic identification method with only static measurements for serial robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2023, 28, 2762–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borboni, A.; Pagani, R.; Sandrini, S.; Carbone, G.; Pellegrini, N. Role of reference frames for a safe human–robot interaction. Sensors 2023, 23, 5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xie, L.; Jiang, M.; He, K.; Chen, Y. Kinematic calibration and feedforward control of a heavy-load manipulator using parameters optimization by an ant colony algorithm. Robotica 2024, 42, 728–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharaaty, S.; Shu, T.; Joubair, A.; Xie, W.F.; Bonev, I.A. Online pose correction of an industrial robot using an optical coordinate measure machine system. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, S.; Luo, X. A Highly-Accurate Robot Calibration Method with Line Constraint. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control, Marseille, France, 25–27 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Sun, G.; Na, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X. Structural parameter identification for 6 DOF industrial robots. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 113, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Tao, Z.; Qi, J. A whole-path posture optimization method of robotic grinding based on multi-performance evaluation indices. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2024, 89, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, G.; Ceccarelli, M. Comparison of indices for stiffness performance evaluation. Front. Mech. Eng. China 2010, 5, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, S.; Webb, P. Managing Delays for Realtime Error Correction and Compensation of an Industrial Robot in an Open Network. Machines 2023, 11, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitschegger, W.K.; Wu, C. Robot calibration and compensation. IEEE J. Robot. Autom. 1988, 4, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, Z.; Mooring, B.; Ravani, B. An overview of robot calibration. IEEE J. Robot. Autom. 1987, 3, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nubiola, A.; Bonev, I.A. Absolute robot calibration with a single telescoping ballbar. Precis. Eng. 2014, 38, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Ni, F.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Lee, C.-H. A robot positional error compensation method based on improved kriging interpolation and kronecker products. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 3884–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultman, E.; Leijon, M. Six-Degrees-of-Freedom (6-DOF) Work Object Positional Calibration Using a Robot-Held Proximity Sensor. Machines 2013, 1, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denavit, J.; Hartenberg, R.S. A kinematic notation for lower-pair mechanisms based on matrices. J. Appl. Mech. 1955, 22, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Dong, H.; Ke, Y. An improved kinematic model for serial robot calibration based on local POE formula using position measurement. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2018, 45, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.C. Solution Manual for Mechanics and Control of Robots; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hayati, S.A. Robot arm geometric link parameter estimation. In Proceedings of the 22nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, San Antonio, TX, USA, 14–16 December 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, G.; Jiang, X.; Nie, X.; Gao, C. Accuracy Improvement for Industrial Robot Based on Joint Position Sensitive Virtual Tool Transformation Fitting Method. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Robotics, Control and Automation Engineering, Suzhou, China, 3–5 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Dong, C.; Guo, H.; Tian, W. Kinematic calibration based on the multicollinearity diagnosis of a 6-DOF polishing hybrid robot using a laser tracker. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 5602397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamani, M.; Joubair, A.; Bonev, I.A. A comparative evaluation of three industrial robots using three reference measuring techniques. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2015, 42, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Qiao, Y. A novel robot kinematic calibration method based on common perpendicular line model. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2018, 45, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Zhang, P. IMU-based online kinematic calibration of robot manipulator. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 139738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ding, H. Posture optimization methodology of 6R industrial robots for machining using performance evaluation indexes. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2017, 48, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Bazzoli, P.; Sammons, P.M.; Landers, R.G.; Bristow, D.A. Modeling and calibration of high-order joint-dependent kinematic errors for industrial robots. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2018, 50, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhan, Q. The kinematic calibration of a drilling robot with optimal measurement configurations based on an improved multi-objective PSO algorithm. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2021, 22, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hollerbach, J.M. Active robot calibration algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Menq, C.-H.; Borm, J.-H.; Lai, J.Z. Identification and observability measure of a basis set of error parameters in robot calibration. J. Mech. Des. 1989, 111, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driels, M.R.; Pathre, U.S. Significance of observation strategy on the design of robot calibration experiments. J. Robot. Syst. 1990, 7, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahvi, A.; Hollerbach, J.M. The noise amplification index for optimal pose selection in robot calibration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 22–28 April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Hollerbach, J.M. Observability index selection for robot calibration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Slamani, M.; Makri, H.; Boudilmi, A.; Bonev, I.A.; Chatelain, J.-F. Calibration strategies for enhancing accuracy in serial industrial robots for orbital milling applications. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2024, 51, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huang, M.; Tang, X.; Song, B.; Guo, Y. Observability index optimization of robot calibration based on multiple identification spaces. Auton. Robot. 2020, 44, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Wang, S.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, H. A novel optimal design of measurement configurations in robot calibration. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 4689710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, F. Kinematic Calibration Method for Six-Hard point Positioning Mechanisms Using Optimal Measurement Pose. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, A.; Notash, L. Comparison of pose selection criteria for kinematic calibration through simulation. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Computational Kinematics, Duisburg, Germany, 6 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Song, H.; Yan, Z.; Sun, L.; Du, Z. A universal index and an improved PSO algorithm for optimal pose selection in kinematic calibration of a novel surgical robot. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2018, 50, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daney, D.; Papegay, Y.; Madeline, B. Choosing measurement poses for robot calibration with the local convergence method and tabu search. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2005, 24, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Sun, D.; Song, G.; Wen, X.; Wei, Z.; Song, A. A rapid coordinate transformation method for serial robot calibration system. J. Mech. Eng. 2020, 56, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9283; Manipulating Industrial Robots–Performance Criteria and Related Test Methods. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
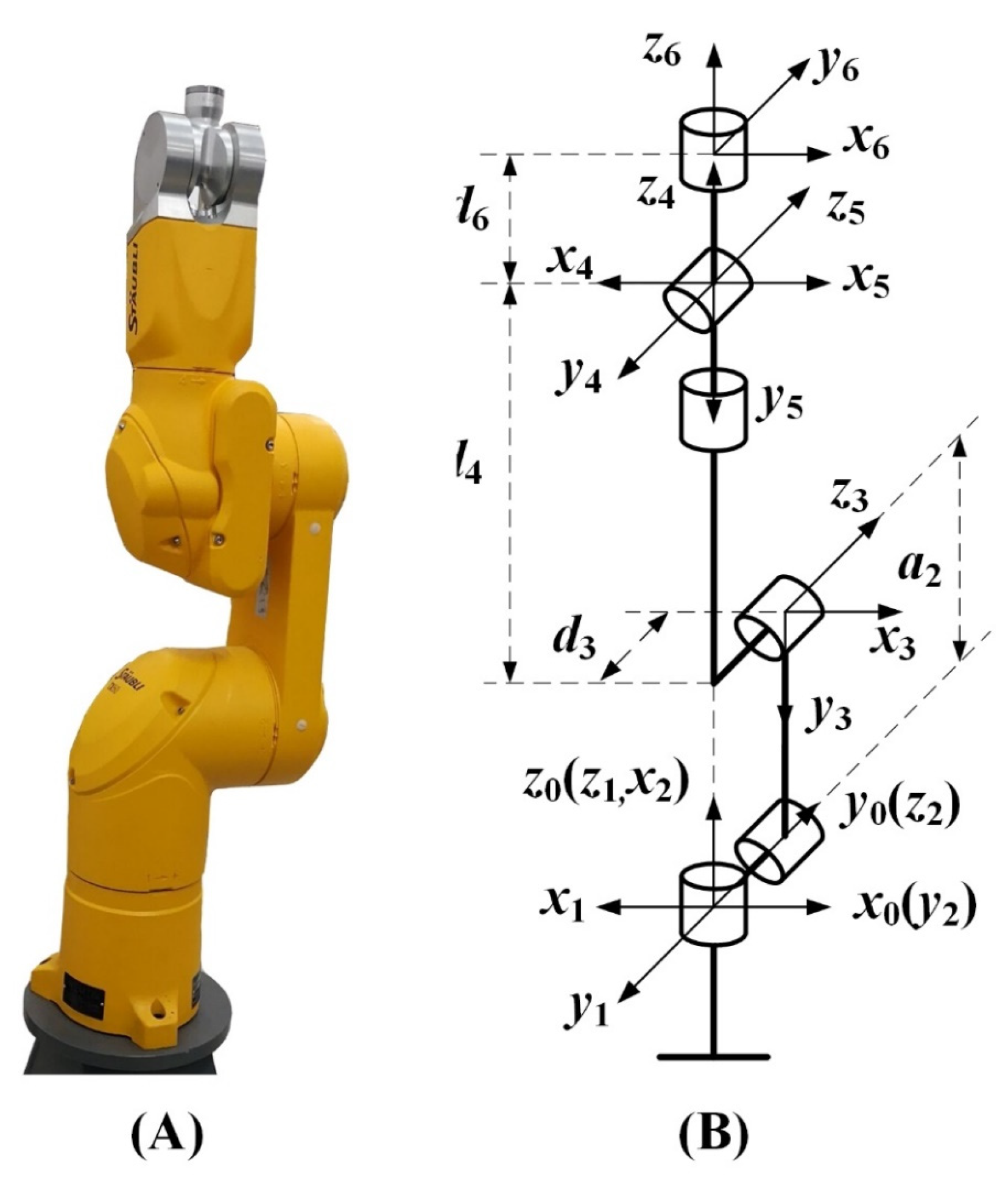
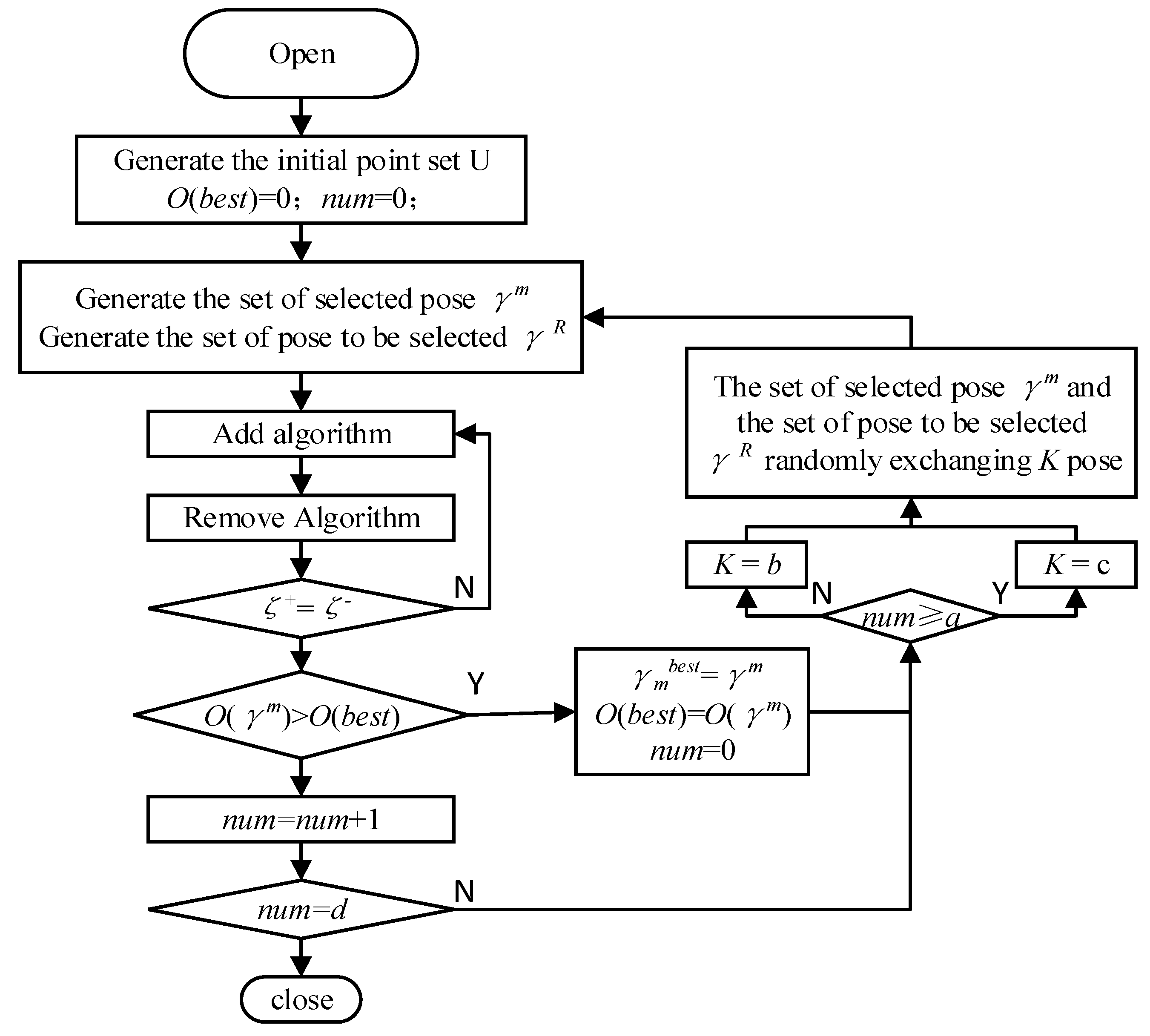

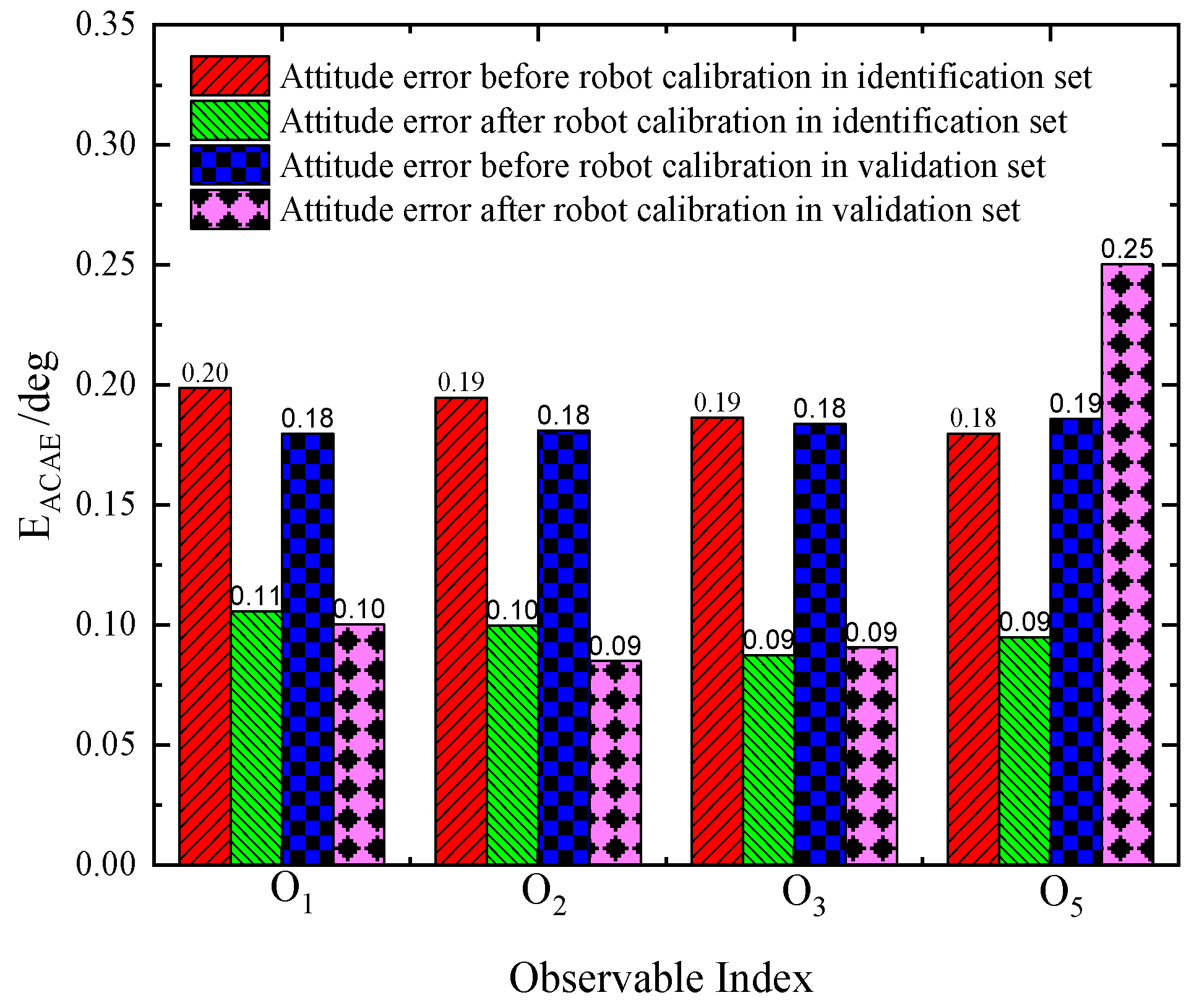
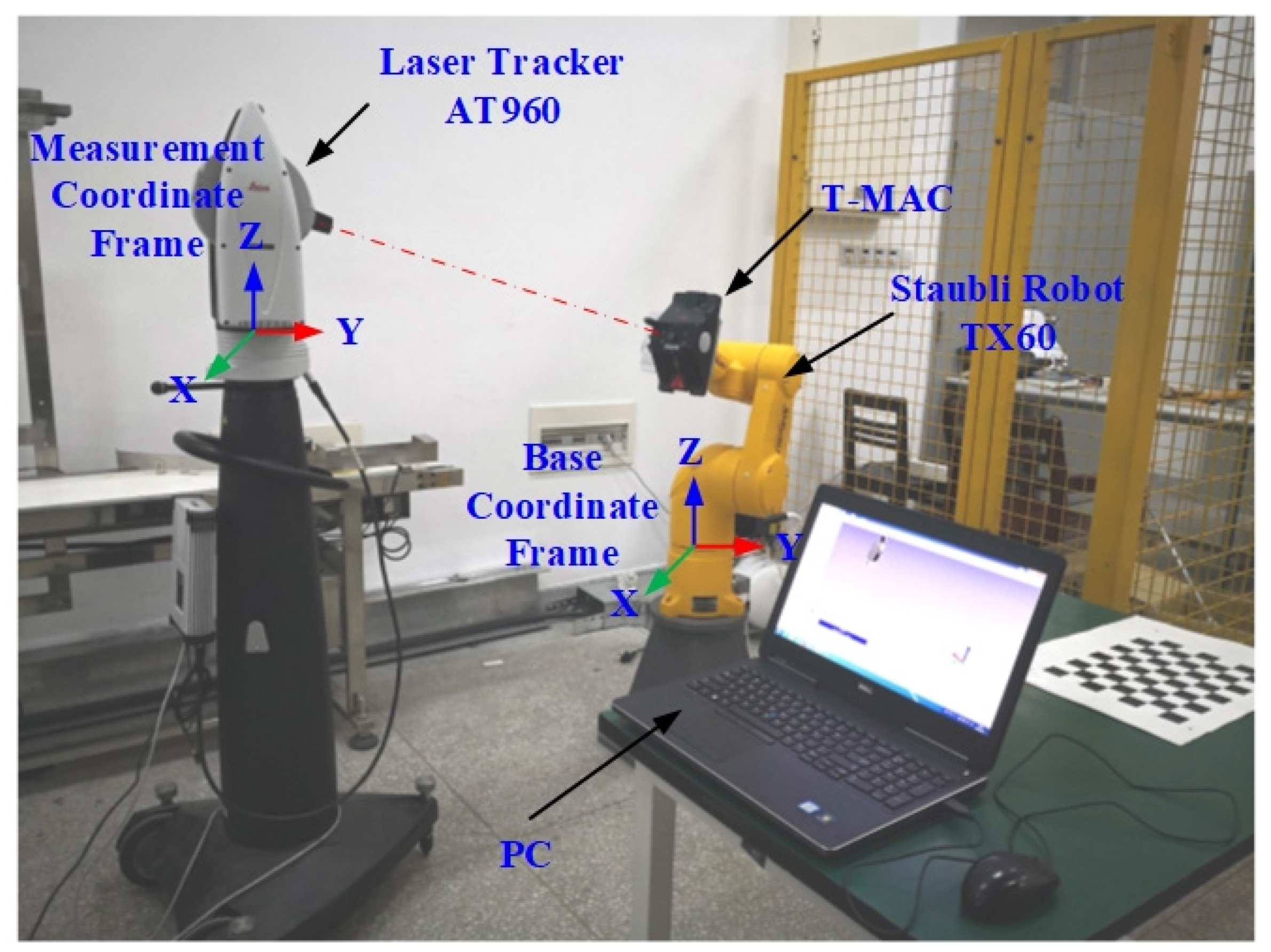
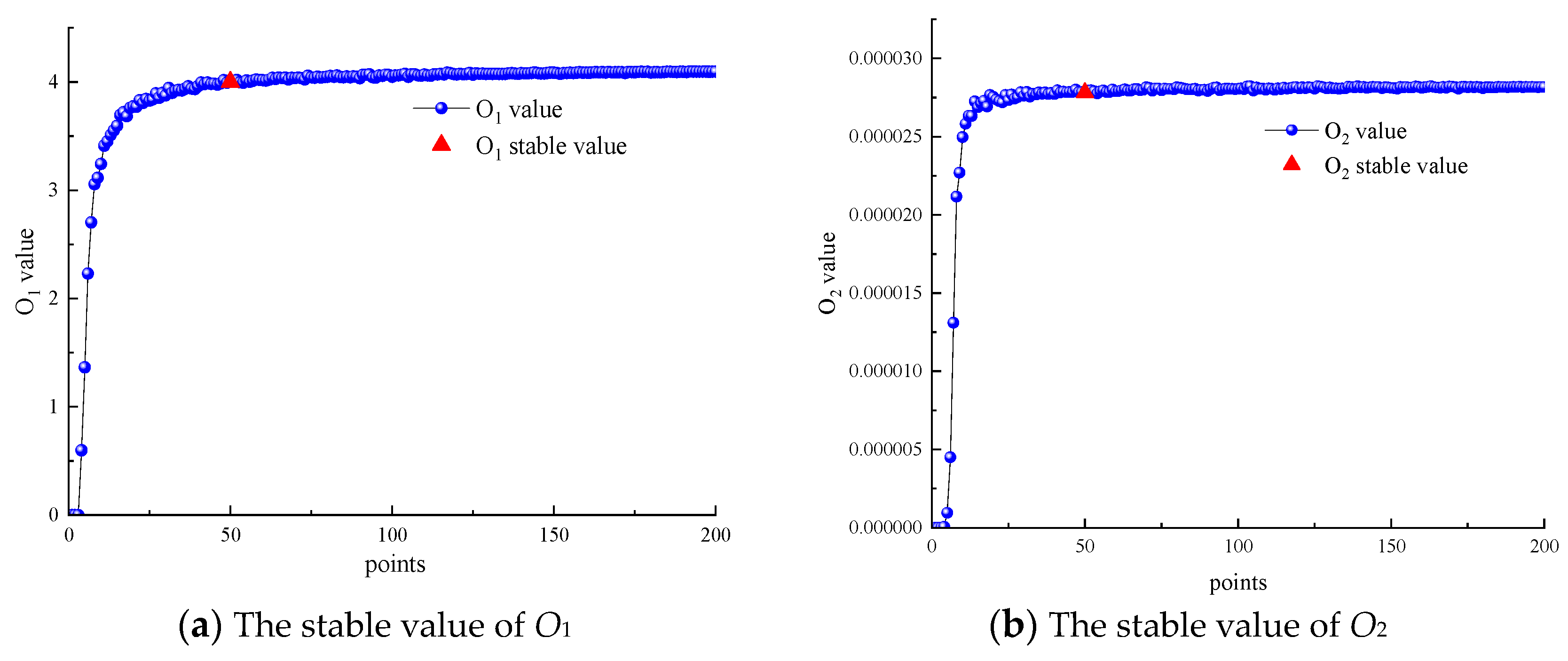

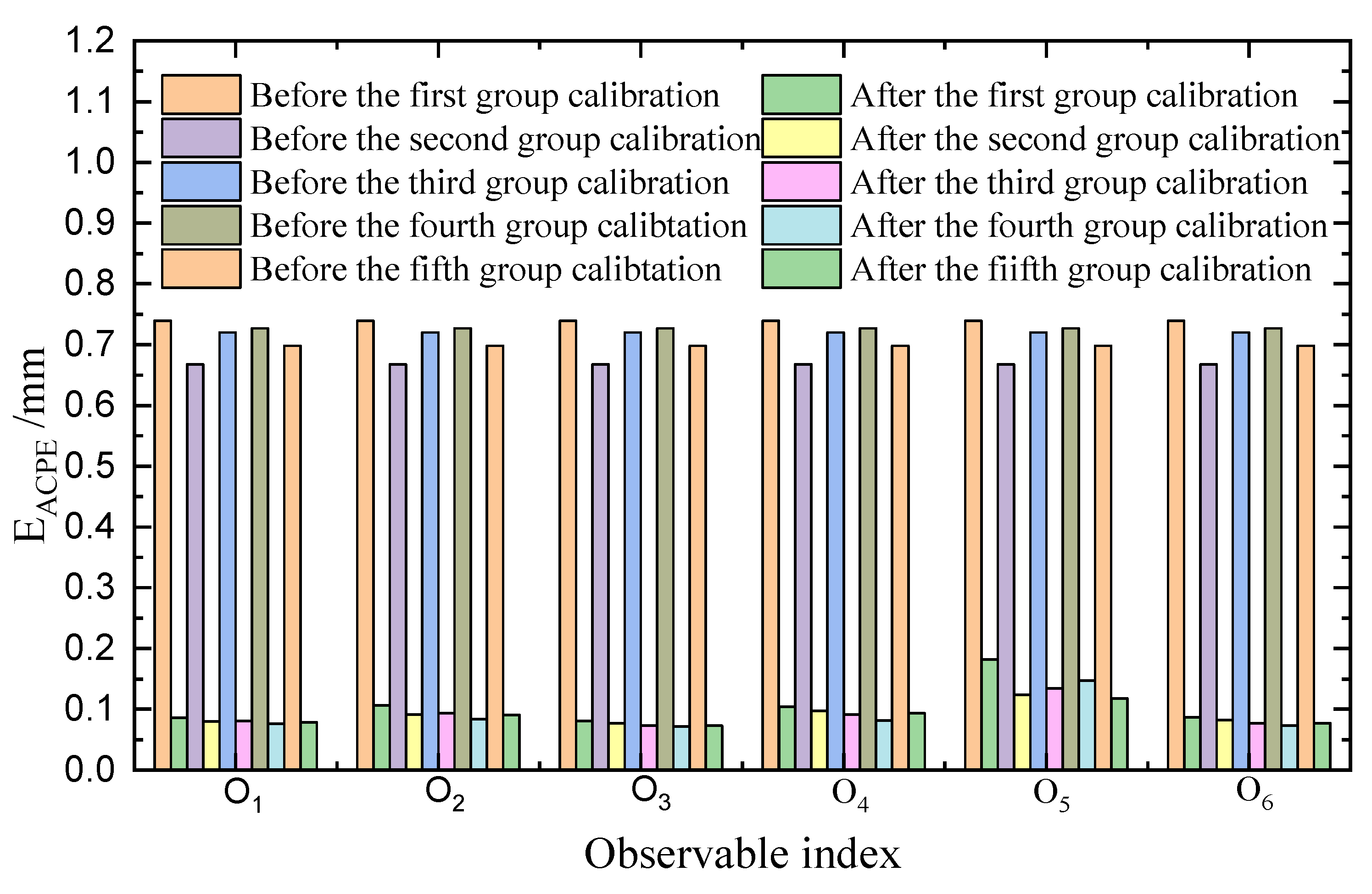
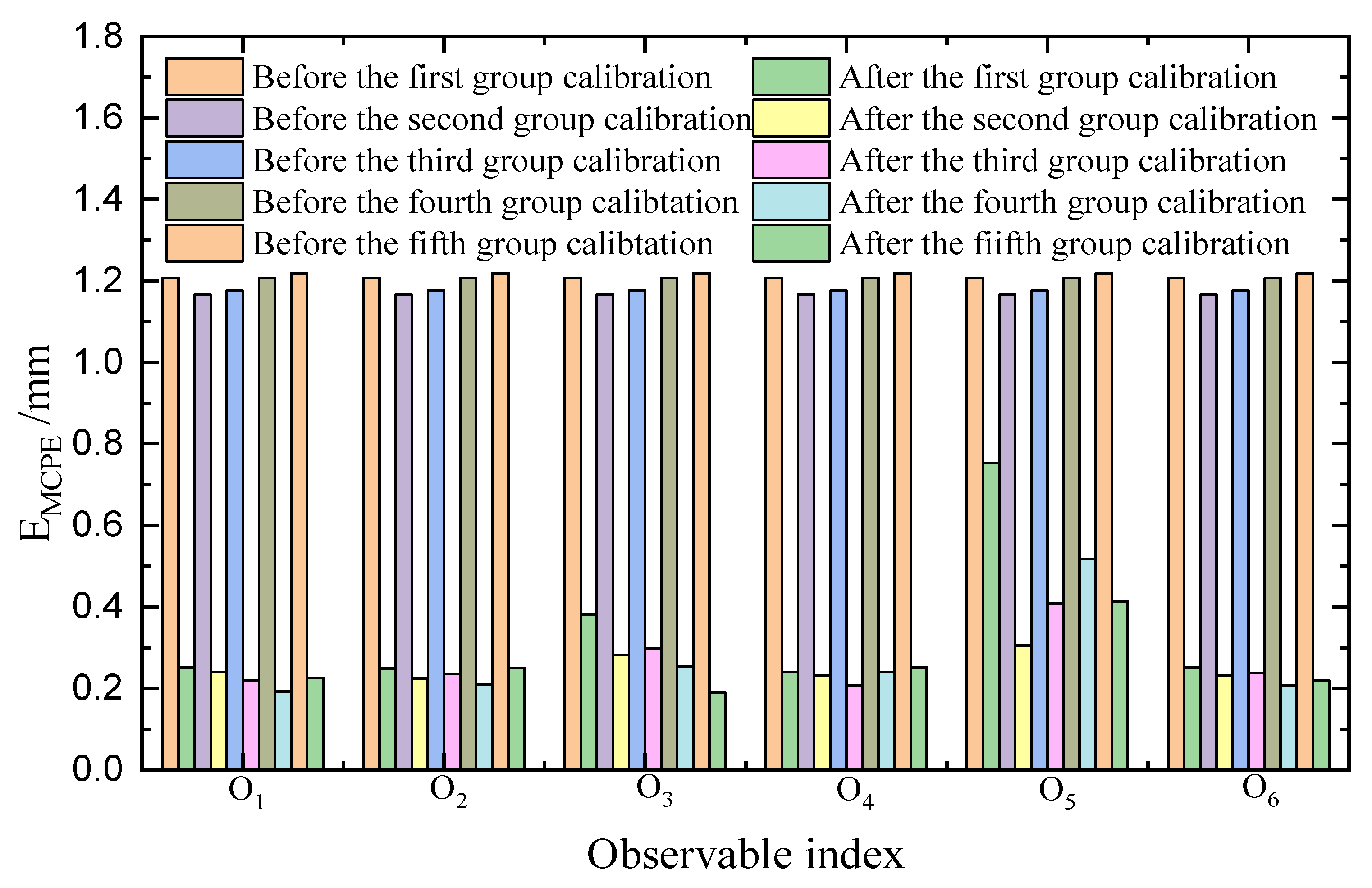
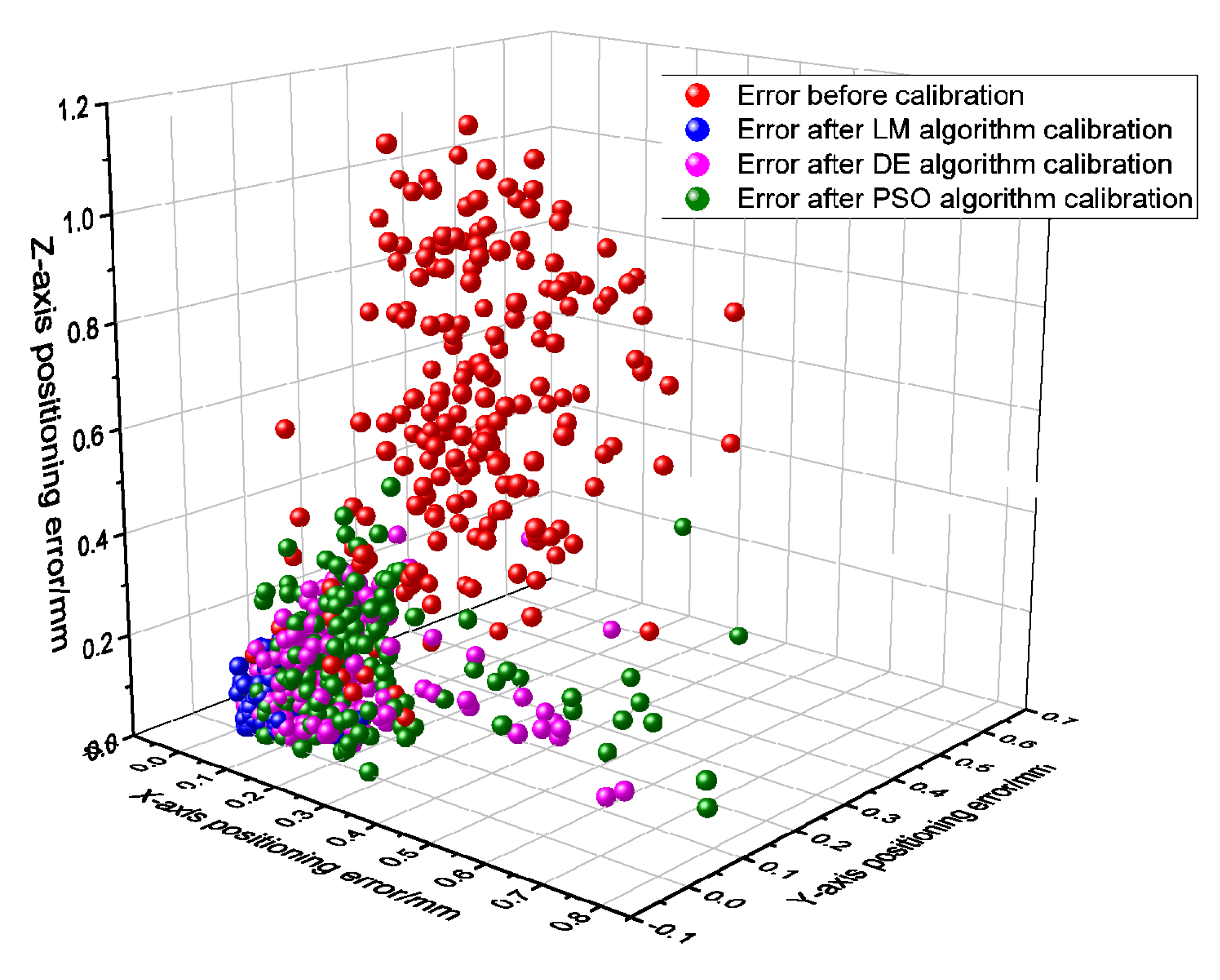
| i | θi/rad | di/mm | ai/mm | αi/rad | βi/rad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | π | 0 | 0 | π/2 | 0 |
| 2 | π/2 | 0 | 290 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | π/2 | 20 | 0 | π/2 | 0 |
| 4 | π | 310 | 0 | π/2 | 0 |
| 5 | π | 0 | 0 | π/2 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 70 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Parameters | Clarification |
|---|---|
| U | Initial pose set, a randomly generated pose set in the measured poses |
| γm | The selected pose set |
| γm+1 | The pose set γm is added by 1, and the set of selected pose set is γm+1 |
| γR | The alternative pose set, γR = U − γm |
| O(γm) | Observability index of the selected pose set |
| γmbest | Current best pose set |
| ζi | Pose (i = 1, 2, …, n) |
| ζ+ | The pose satisfying the condition max {O6(γm + ζi)} |
| ζ− | The pose satisfying the condition max {O6(γm+1 − ζi)} |
| O(best) | Observability index of the current best pose set |
| num | O(best) Number of times constant or approximate |
| K | Randomly exchanged the number of poses between γm and γR |
| a | The growth threshold of num |
| b | When num does not reach a, K = b |
| c | When num reaches a, K = c |
| d | The growth threshold 2 of num, algorithm terminates when num reaches d |
| Improvement Ratio | Different Set | Observability Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | O2 | O3 | O5 | ||
| Attitude accuracy | Identification set | 45.0% | 47.4% | 52.6% | 50.0% |
| Validation set | 44.4% | 50.0% | 50.0% | −31.6% | |
| Positioning accuracy | Identification set | 88.2% | 85.9% | 88.1% | 79.1% |
| Validation set | 87.3% | 86.8% | 89.6% | 89.2% | |
| EMCPE after Calibration in Five Groups | O1 | O2 | O3 | O4 | O5 | O6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum value | 0.2504 | 0.2502 | 0.3817 | 0.2510 | 0.7526 | 0.2509 |
| Minimum value | 0.1923 | 0.2077 | 0.1894 | 0.2096 | 0.3047 | 0.2201 |
| Absolute deviation | 0.0581 | 0.0425 | 0.1923 | 0.0414 | 0.4479 | 0.0308 |
| i | θi/rad | di/mm | ai/mm | αi/rad | βi/rad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −3.2792 × 10−4 | −0.2226 | −0.2389 | 5.3341 × 10−5 | - |
| 2 | 7.8894 × 10−4 | - | 0.3223 | −5.4318 × 10−5 | 3.8910 × 10−5 |
| 3 | 2.3603 × 10−4 | 0.0826 | 0.0484 | 3.7122 × 10−4 | - |
| 4 | 0.0014 | 0.2044 | −0.0812 | 1.1155 × 10−4 | - |
| 5 | 5.1444 × 10−4 | 7.4762 × 10−5 | 0.0205 | 3.9926 × 10−5 | - |
| 6 | 4.0758 × 10−4 | −0.0624 | −0.1351 | 0.0033 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, T.; Gao, C.; Du, B.; Qiao, G.; Zuo, H. Pose Selection Based on a Hybrid Observation Index for Robotic Accuracy Improvement. Machines 2024, 12, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080501
Xiang T, Gao C, Du B, Qiao G, Zuo H. Pose Selection Based on a Hybrid Observation Index for Robotic Accuracy Improvement. Machines. 2024; 12(8):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080501
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Tiewu, Chunhui Gao, Baoan Du, Guifang Qiao, and Hongfu Zuo. 2024. "Pose Selection Based on a Hybrid Observation Index for Robotic Accuracy Improvement" Machines 12, no. 8: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080501
APA StyleXiang, T., Gao, C., Du, B., Qiao, G., & Zuo, H. (2024). Pose Selection Based on a Hybrid Observation Index for Robotic Accuracy Improvement. Machines, 12(8), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080501







