Coupling Interface Load Identification of Sliding Bearing in Wind Turbine Gearbox Based on Polynomial Structure Selection Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Coupling Interface Load Identification Theory
2.1. POD Decoupling the Coupling Interface Load
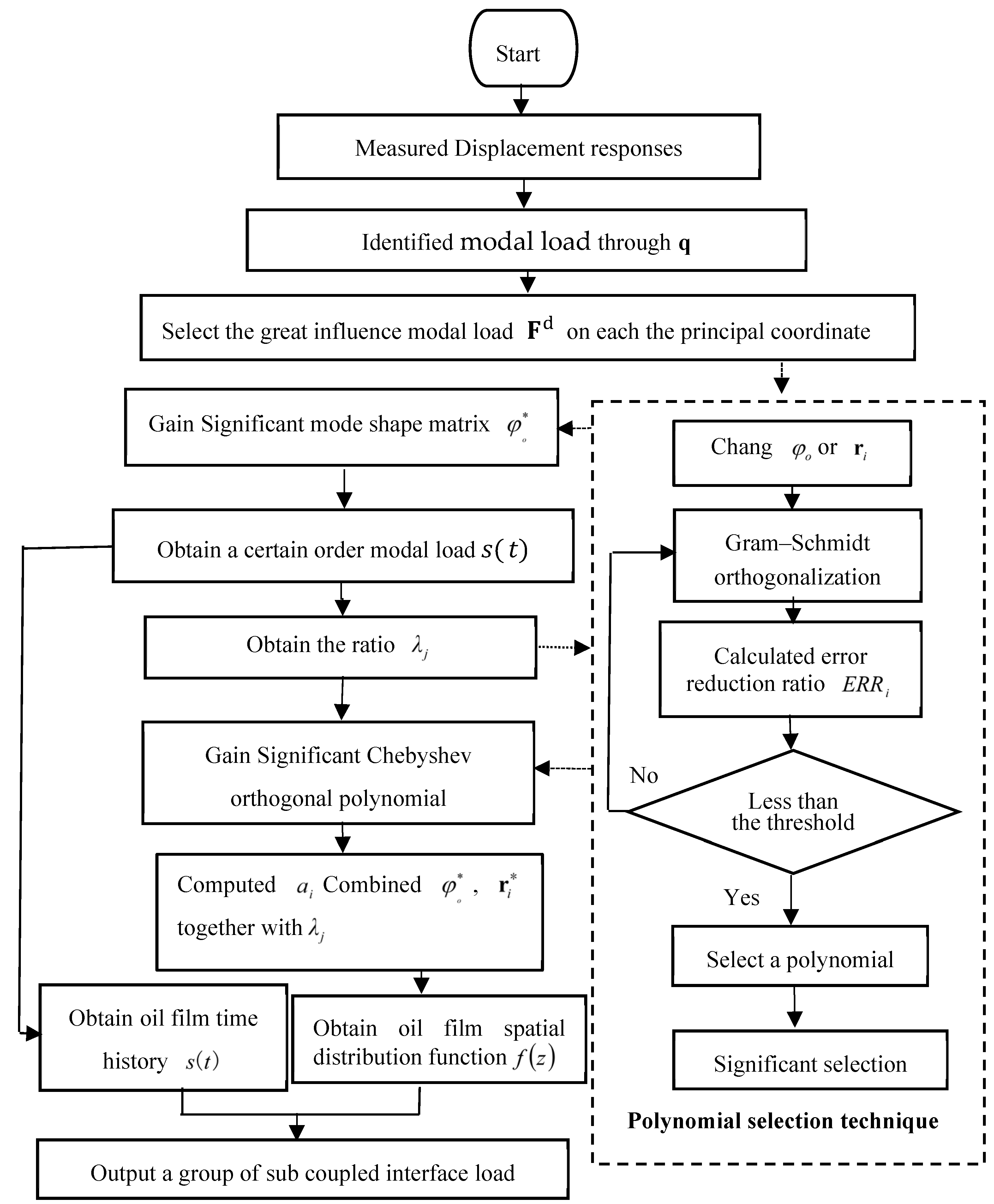
2.2. Sub-Coupled Interface Loadidentification Method Based on Polynomial Structure Selection Technique
3. The Identification Processes of Sliding Bearing Coupling Interface Load
4. Numerical Example
4.1. The Sliding Bearing Coupling Interface Load Decomposed
4.2. Obtain Displacement Response
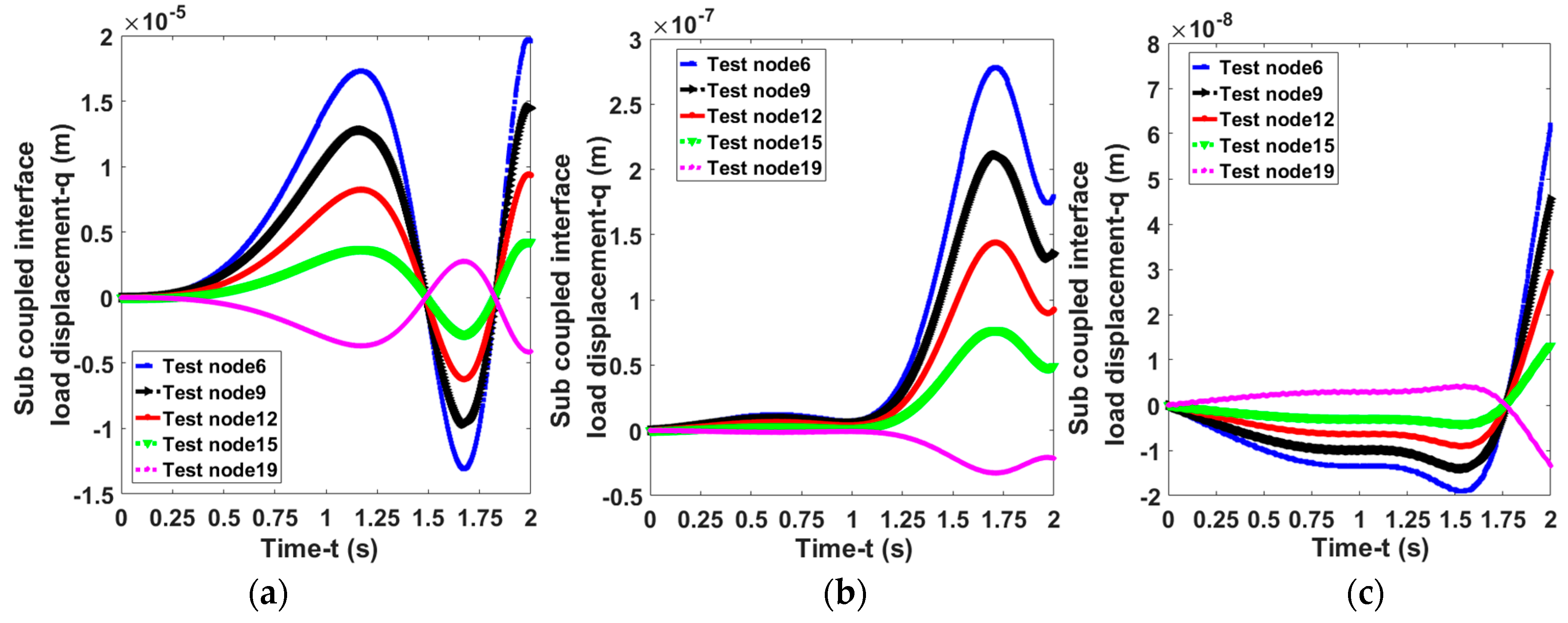
4.3. Result Discussion of Identify Sub-Coupled Interface Load
4.4. Identification of Sliding Bearing Coupling Interface Load
4.5. The Influence of Polynomial Selection Technique on Recognition Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fei, W.J.; Tan, J.J.; Li, H.; Zhu, C.C.; Sun, Z.D.; Wang, H.X. Influences of planet gear journal bearing on dynamic characteristics of megawatt-scale wind turbine drivetrains: Simulations and experiments. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 221, 111747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Georg, J.; Carsten, G.; Julian, R.; Mattheüs, L.; Benjamin, L. Multiscale-simulation method for the wear behaviour of planetary journal bearings in wind turbine gearboxes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2767, 052012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M.X.; Feng, K. Numerical and experimental investigations on thermoelastic hydrodynamic performance of planetary gear sliding bearings in wind turbine gearboxes. Tribol. Int. 2024, 191, 109081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Mermertas, Ü.; Hagemann, T.; Schwarze, H. Calculation and Validation of Planet Gear Sliding Bearings for a Three-Stage Wind Turbine Gearbox. Lubricants 2024, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Wu, Z.M. A distributed dynamic load identification method based on the hierarchical-clustering-oriented radial basis function framework using acceleration signals under convex-fuzzy hybrid uncertainties Mechanical Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 172, 108935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, K. Sparse identification of time-space coupled distributed dynamic load. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 148, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.L.; Xiao, L.F.; Liu, M.Y.; Kou, Y.F. A distributed dynamic load identification approach for thin plates based on inverse Finite Element Method and radial basis function fitting via strain response. Eng. Struct. 2025, 322, 119072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, W.P.; Zhao, Y.M.; Shen, C. Fast and efficient finite difference/finite element method for the two-dimensional multi-term time-space fractional Bloch-Torrey equation. Appl. Comput. Math. 2021, 398, 125985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, F.; Qiao, L.; Yang, X. T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding echo state network with state matrix dimensionality reduction for time series prediction. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yan, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Su, H. Blade Failure Fault Reproduction Based on High Low Cycle Composite Fatigue Test Technology. Propuls. Technol. 2020, 41, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.Y.; Xiao, Q.; Sun, S.G. Method for identifying dynamic loads on strongly coupled structures. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 57, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Ren, Z.S.; Wu, Y.M.; Wang, Y.W. Method and experimental verification of load decoupling and dimensionality reduction calibration for high-speed train frames. J. Cent. South Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 53, 1730–1739. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.G.; Guo, Y.C.; Nie, X.H. Research on Decoupling Method for Complex Load on Airframe Wall Panels. Eng. Test. 2023, 63, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.K.; Sun, C.B.; Cui, M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, K. A fast methodology for identifying thermal parameters based on improved POD and particle swarm optimization and its applications. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2024, 169, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Lwasaki, M.; Nakayama, R.; Yamamoto, R.; Nakashima, A.; Ogato, Y. Mode analysis for multiple parameter conditions of nozzle internal unsteady flow using Parametric Global Proper Orthogonal Decomposition. Fluid Dyn. Res. 2024, 56, 055501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Min, G.Y.; Hu, M.M.; Yang, S.G.; Cai, M.Q. Proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) dimensionality reduction combined with machine learning to predict the vibration characteristics of stay cables at different lengths. Measurement 2025, 242, 115827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, X. PIV Measurement and Proper Orthogonal Decomposition Analysis of Annular Gap Flow of a Hydraulic Machine. Machines 2022, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Niu, Y.P. Application of Orthogonal Polynomial Fitting Method to Extract Gravity Wave Signals from AIRS Data Related to Typhoon Deep Convection. Earth Space Sci. 2022, 9, e2022EA002408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Davey, P.G.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Lin, M.; Zheng, X.; Bao, F.; Elsheikh, A. Accuracy and reliability of orthogonal polynomials in representing corneal topography. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2022, 15, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, J.; Han, X.; Sun, X.; Jiang, C. A novel approach for distributed dynamic load reconstruction by space-time domain decoupling. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 348, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, J.; Han, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, D. Distributed dynamic load identification based on shape function method and polynomial selection technique. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2016, 25, 1323–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, F.; Mohamed, M.S. Distributed Dynamic Load Identification of Beam Structures Using a Bayesian Method. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, X.S.; Han, X.; Jiang, C.; Yu, D.J. Dynamic load identification for stochastic structures based on Gegenbauer polynomial approximation and regularization method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2014, 56–57, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.; Benaroya, H. Review of force reconstruction techniques. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 2999–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Jiang, C. Research on nonlinear model identification of the hydragas suspension based on structure-selection techniques. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerosp. Eng. 2014, 33, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Jing, J. Modified oil film force model for investigating motion characteristics of rotor-bearing system. J. Vib. Control. 2016, 22, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhu, K.D.; Qi, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Yu, R.F.; Chen, W.; Liu, H. A deterministic mixed lubrication model for parallel rough surfaces considering wear evolution. Tribol. Int. 2024, 194, 109443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.C.; Marti-Puig, P.; Caiafa, C.F.; Serra-Serra, M.; Cusidó, J.; Solé-Casals, J. Exploratory Analysis of SCADA Data from Wind Turbines Using the K-Means Clustering Algorithm for Predictive Maintenance Purposes. Machines 2023, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Pei, S.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Wang, B. An Electromagnetic Load Identification Method Based on the Polynomial Structure Selection Technique. Shock. Vib. 2024, 2024, 1842508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Han, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, J. Bearing dynamic parameters identification of a flexible rotor-bearing system based on transfer matrix method. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2015, 24, 372–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Mao, W.G.; Feng, D. Lubrication characteristic surrogate model construction of wind power sliding bearing based on Polynomial structure selection technology. Lubr. Eng. 2023, 48, 173–181. [Google Scholar]









| Load | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The first group | 0.9995 | 1 | 0.9995 | 2.83% | 0.62% | 2.99% |
| The second group | 0.9998 | 1 | 0.9999 | 1.68% | 0.61% | 1.81% |
| The third group | 0.9995 | 0.9951 | 0.9945 | 1.85% | 10.92% | 11.08% |
| Coupling interface load | — | — | 0.9995 | — | — | 3.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, W.; Wang, J.; Pei, S. Coupling Interface Load Identification of Sliding Bearing in Wind Turbine Gearbox Based on Polynomial Structure Selection Technique. Machines 2024, 12, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120848
Mao W, Wang J, Pei S. Coupling Interface Load Identification of Sliding Bearing in Wind Turbine Gearbox Based on Polynomial Structure Selection Technique. Machines. 2024; 12(12):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120848
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Wengui, Jie Wang, and Shixiong Pei. 2024. "Coupling Interface Load Identification of Sliding Bearing in Wind Turbine Gearbox Based on Polynomial Structure Selection Technique" Machines 12, no. 12: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120848
APA StyleMao, W., Wang, J., & Pei, S. (2024). Coupling Interface Load Identification of Sliding Bearing in Wind Turbine Gearbox Based on Polynomial Structure Selection Technique. Machines, 12(12), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12120848







