Abstract
Traditional mobile robots with fixed structures lack the ability to cope with complex terrains and tasks. Reconfigurable modular mobile robots have received considerable attention as they can automatically reassemble according to the changing environment or task. In this paper, a new self-reconfiguration wave-like crawling (SWC) robot is presented to improve the mobile robots’ locomotion capacity. First, the mechanical design of the wave-like crawling mechanism is detailed. Then, the series and parallel connections are introduced to achieve self-reconfiguration. In addition, the kinematic model of the SWC robot is established. Finally, experiments were performed to verify the robotic system with wireless data transmission.
1. Introduction
Mobile robots have been widely used in transportation, rescue, service, and security [1]. However, traditional mobile robots’ structures are fixed and unable to adapt to complicated environments, so they lack the ability to cope with complex terrains and tasks. Different from fixed structures, self-reconfiguration would improve mobile robotic systems’ efficiency and locomotion capacity, a behavior that can often be observed in social insects. For example, army ants assemble their bodies in the form of a bridge to fill holes or span gaps on the ground, which can provide a roadway for their nestmates [2]. Inspired by such organisms, reconfigurable modular mobile (RMM) robots consist of multiple mobile robot modules that can automatically reassemble according to the changing environment or task [3]. Recently, RMM robots have received considerable attention, and they can be generally divided into three categories: wheeled robots [4,5,6], tracked robots [7,8], and legged robots [9,10]. Compared with fixed-structure mobile robots, RMM robots can self-assemble to avoid obstacles that a single mobile robot cannot. In addition, RMM robots are very robust; that is, when an RMM robot module fails, it can be rapidly replaced by a redundant module, referred to as self-repair [11]. Furthermore, RMM robots have stronger reusability and can be built with various configurations to reduce the economic costs. However, the existing RMM robots encounter the following problems: (1) the obstacle-crossing ability of the wheeled or tracked robots still needs to be improved when facing complex surfaces, even with the ability to reconfigure; (2) the legged mechanism is complex and needs to be driven by multiple actuators, increasing the energy costs.
Bioinspired crawling robots have generated significant interest due to their ability to move on various surfaces and around multiple obstacles, which can be categorized into inchworm-like robots [12,13], earthworm-like robots [14,15], and snake-like robots [16,17]. Recently, a novel wave-like mechanism has been proposed, which imitates the locomotion of snakes and the flagellar swimming of microscopic organisms and can advance over anisotropic and flexible terrains with varying surface properties [18,19,20,21]. Based on this, it uses a single motor to actuate the locomotion of the entire mechanism, which meets the requirement of the high integration of RMM robots.
In this paper, a new self-reconfiguration wave-like crawling (SWC) robot is presented to fully use the advantages of being modular and crawling while avoiding the shortcomings of its separate applications. SWC robots comprise several independent modules, each with a power supply, control board, communication module, and mechanism system. Then, the wave-like crawling mechanism is used in the SWC robot to realize its locomotion. Furthermore, many connection methods of modular robots have been proposed, such as self-soldering [22] and electromagnets [23]. However, most of the existing connection methods suffer from significant energy costs. Based on this, the series and parallel connection mechanisms were designed to perform self-reconfiguration with less energy. Moreover, 3D printing was applied to manufacture the robots and shorten the manufacturing cycle.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- 1.
- The wave-like crawling mechanism was applied in the SWC robot and improved the robot’s ability to move on various surfaces and around multiple obstacles.
- 2.
- The series and parallel connections were designed to achieve self-reconfiguration so that the SWC robots can cooperate to perform complicated tasks.
- 3.
- The kinematic model of the parallel-connected SWC robot was established to provide a basis for future work.
2. Mechanical Design
Figure 1 shows the overview of the SWC robot. The wave-like crawling mechanism driven by a direct current (DC) motor is applied to perform the locomotion of the robot. In addition, the series and parallel connection mechanisms are designed to implement the self-reconfiguration. In particular, passive connectors were designed to enhance the parallel connection’s stability. The joint with two degrees of freedom (DoFs) was utilized to achieve the pitch and yaw rotations in the series connection. The wave-like crawling and connection’s mechanical design is detailed in this section.
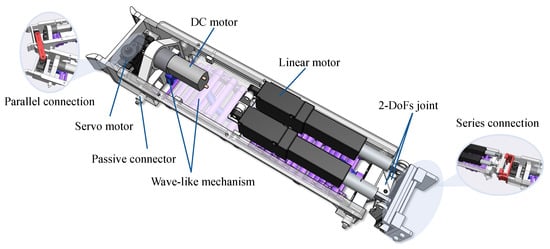
Figure 1.
The overview of the SWC robot.
2.1. The Wave-like Crawling Mechanism’s Design
Figure 2 shows the wave-like crawling mechanism’s design and the definition of the helix’s and links’ mechanical specifications. More specifically, the wave-like crawling mechanism is composed of a helix and 17 links. Among them, the helix can be characterized by the helix pitch L (60 mm), the shaft diameter (6 mm), and the helix diameter (12 mm). Furthermore, the links have a length of 40 mm and a height of 12.5 mm. Increasing and would improve the robot’s velocity at the same motor speed; however, it may result in collisions between the links [18]. A compromise between the desired speed and collision avoidance was considered in our design.
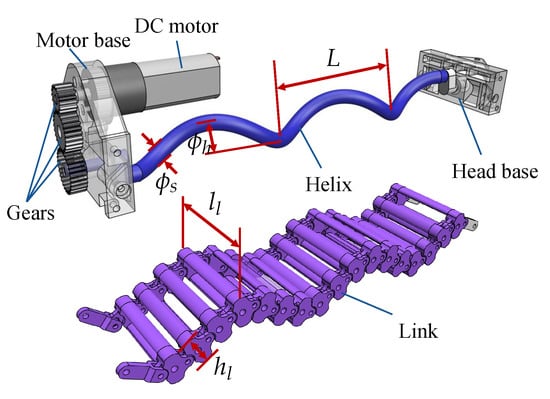
Figure 2.
The wave-like crawling mechanism.
A DC motor (rated voltage: 6 V, rated torque: 0.6 ) was installed in the motor base, and its output shaft rotates three gears with a gear ratio of 4:7. The lowest gear rotates the helix, which produces the wave-like locomotion through the links. In particular, the motor tail is connected to an encoder, which can accurately measure the motor speed.
2.2. The Connection Design
In this subsection, two connection structures of the SWC robot are introduced, including the series and parallel connections.
A. The Series Connection
Figure 3 illustrates the series connector’s mechanical structure, which was designed to enable the SWC robots to perform more complex tasks, such as crossing gaps and climbing steps. The series connector mainly consists of an active lock and an arc slider. The above-mentioned active lock comprises a sliding rail, two linear servo motors (working voltage: 5 V), and two sliding blocks. Two arc guide rails were designed at the end of the arc slider to improve the fault tolerance of the docking. The number of robot modules must be at least three to ensure the stability of the robot’s center of mass.
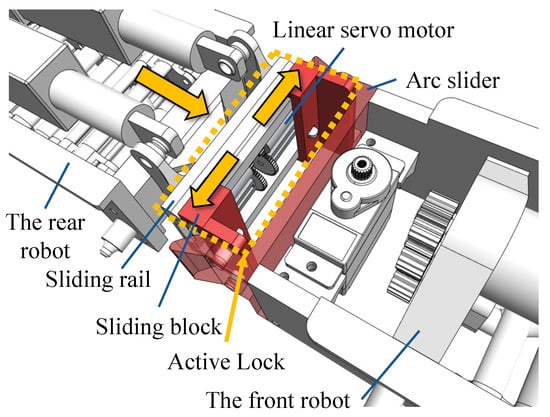
Figure 3.
The series connector of the SWC robots.
In the series connecting process, two linear servo motors drive the sliding blocks to move on the sliding rail after one robot’s active lock slides into another robot’s arc slider. Then, the pins on the sliding blocks are inserted into the holes of the arc slider, thus achieving a series connection.
Figure 4 illustrates the mechanical design of the 2-DoF joint, which is connected to the active lock to achieve a pitch rotation (−45° to 45°) and a yaw rotation (−15° to 15°). More specifically, the 2-DoF joint of the robot module is composed of two linear motors, four spherical joints, a connecting base, a yaw joint, and a pitch joint. The linear motors (rated voltage: 6 V, length: 50 mm) connect to the connecting base and active lock through the spherical universal joints. Their lengths can be determined to achieve the target pitch and yaw angles based on the kinematic inverse solution [8].
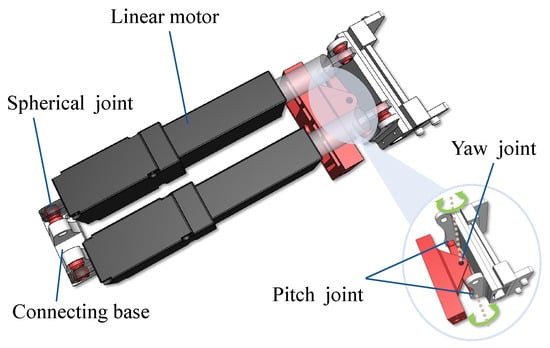
Figure 4.
The joint with two DoFs.
B. The Parallel Connection
Figure 5 details the parallel connection’s mechanical structure, which enables the robot to realize steering through the differential speeds of the robots. To be more specific, a servo motor (rated voltage: 6 V) is installed at the rear of the SWC robot as a parallel connector. Based on this, two robots with the mirror-symmetrically installed servo motors can be connected in parallel through a servo arm. The angle between two servo motors’ horizontal central axes is defined as with a range from 0° to 30°. Furthermore, the number of SWC robots in the parallel connection is limited to 2.
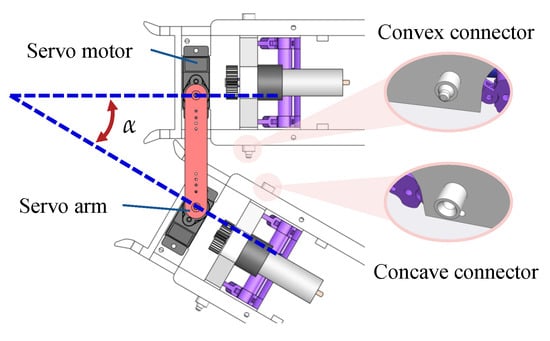
Figure 5.
The parallel connection of the SWC robots.
As shown in the right of Figure 5, the convex and concave connectors were designed to be distributed on the left and right sides of the SWC robot, respectively. As equals zero, the convex connectors are inserted into the concave connectors to enhance the parallel connection’s stability.
3. Kinematic Modeling
In this section, the kinematic model of the parallel-connected SWC robots is established as a basic locomotion mode. A single SWC robot can only move forward or backward in a straight line, so its linear velocity can be used to describe the locomotion. The linear velocity of a single SWC robot is equal to the motion velocity of the links contacting the ground and is approximately proportional to the rotation frequency f of the helix. The relationship between and f is [18]
where is the helix diameter, is the link height, and L is the helix pitch.
Based on this, Figure 6 shows the rotation motion of the parallel-connected SWC robot. The states of the parallel-connected SWC robot are defined as , referring to the system’s position and orientation in the world frame. In addition, the system’s linear velocity is defined as and the angular velocity is defined as .
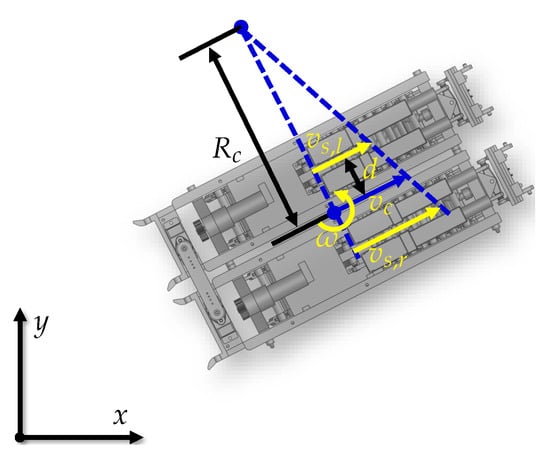
Figure 6.
The rotation motion of the parallel-connected SWC robot.
Considering that the system moves in a circle [24], the rotation equation of the system can be obtained as
where and are the linear velocities of the left and right SWC robots, respectively, is the rotation radius, and d is the distance between the central axis of one SWC robot and the central axis of the system. From (2), the rotation radius can be calculated as
Then, the system’s linear velocity can be expressed as
Finally, the kinematic model of the parallel-connected SWC robot can be established as
where and can be approximately estimated by (1).
4. Experiments
Figure 7 shows the diagram of the SWC robotic system with wireless data transmission, where two SWC robots are connected in parallel. Each robot weighs 0.487 kg, with a length of 25.88 cm, a width of 6.44 cm, and a height of 12.45 cm. Furthermore, an Arduino UNO microcontroller is used as the control module. In addition, a lithium polymer battery (voltage: 7.4 V, capacity: 1000 mAh) is used as a power supply, and the tb6612FNG chips are used to drive the main DC motor and linear motors. Moreover, a wireless serial port module (working frequency: 410 to 441 MHz) is applied to realize the wireless communication between the robot and the upper computer system. In particular, three reflective markers are pasted on the top of the robots to record the motion trajectory using a motion capture system. Based on this, the upper computer receives the robots’ motion data from the motion capture system (Qualisys A12). It is also linked to a wireless transmitter consisting of a wireless serial port module and a USB-TTL module. Thus, the upper computer runs the ROS nodes and transmits the control commands (based on the JSON format) of the moving direction, active lock, and 2-DoF joint through the wireless transmitter in broadcast mode.
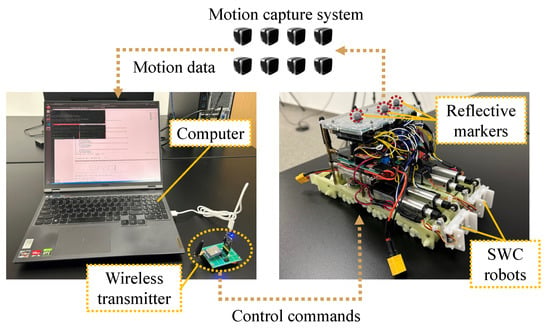
Figure 7.
The SWC robotic system with wireless data transmission.
Four advancing and circular trajectory motion experiments were performed to test the SWC robotic system. In the experiments, the control commands of the motors’ speeds were sent to the robot by the upper computer. First, the upper computer sends a forward command to the parallel-connected SWC robot, and the robot moves in a straight line after receiving the command. Then, 30 s later, the system sends the robot a left turn command, while the left and right modules’ speeds are different, and the robot performs a circle trajectory. After another 120 s, the system sends the robot a stop command.
Figure 8 shows the screenshots of the experimental results, and Figure 9 shows four trajectories of the parallel-connected SWC robot recorded by the motion capture system. According to the experimental results, the parallel-connected SWC robot can efficiently perform linear motion and differential steering, and the wireless control system and circular motion hypothesis was effectively verified. However, the trajectories of the four experiments were not repeated due to the lack of closed-loop control and the influence of disturbances, such as slight differences in initial states and ground friction anisotropy.
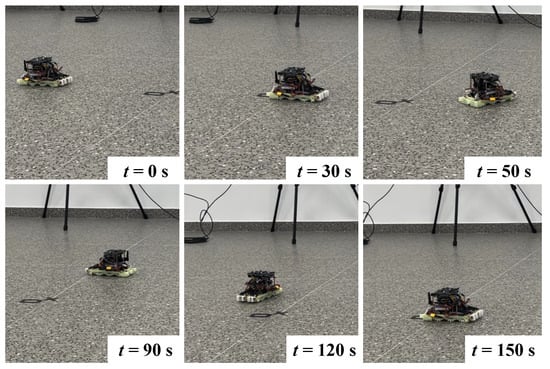
Figure 8.
The screenshots of the experimental results.
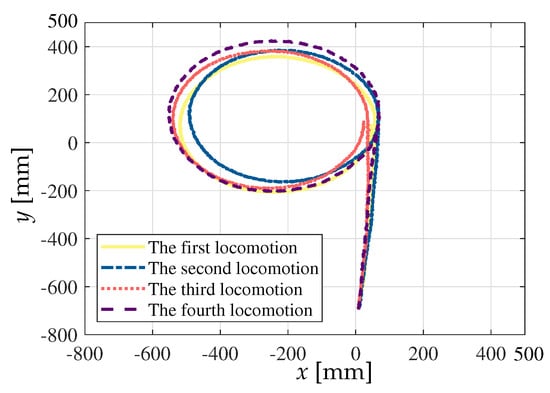
Figure 9.
Four trajectories of the parallel-connected SWC robots in the experiments.
5. Conclusions
This paper presented a new self-reconfiguration wave-like crawling robot. The wave-like crawling mechanism was applied to the SWC robot to move on different terrains. Then, the series and parallel connection mechanisms were designed to realize the self-reconfiguration of the SWC robots. Furthermore, the kinematic model of the SWC robots was established. In addition, the experiments were performed to verify the robotic system. In the future, further experiments of the series-connected SWC robot will be performed, and the kinematic model of the parallel-connected SWC robot will be improved.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.S., N.S., Q.W. and X.W.; methodology, H.S.; software, H.S.; validation, H.S.; formal analysis, H.S.; investigation, H.S.; resources, N.S. and X.W.; data curation, H.S.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S.; writing—review and editing, Q.W., X.W., T.Y. and N.S.; visualization, H.S.; supervision, Q.W. and N.S.; project administration, N.S.; funding acquisition, N.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Tianjin Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars under Grant 22JCJQJC00140, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant U20A20198 and Grant 52205019, the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation under Grant 2023A1515012669, and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2021M701779.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fragapane, G.; De Koster, R.; Sgarbossa, F.; Strandhagen, J.O. Planning and control of autonomous mobile robots for intralogistics: Literature review and research agenda. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 294, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.R.; Lutz, M.J.; Powell, S.; Kao, A.B.; Couzin, I.D.; Garnier, S. Army ants dynamically adjust living bridges in response to a cost–benefit trade-off. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15113–15118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moubarak, P.; Ben-Tzvi, P. Modular and reconfigurable mobile robotics. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2012, 60, 1648–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, R.; Bonani, M.; Mondada, F.; Dorigo, M. Autonomous self-assembly in swarm-bots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2006, 22, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Guo, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, X. A path-integral-based reinforcement learning algorithm for path following of an autoassembly mobile robot. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 4487–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Lam, T.L. SnailBot: A continuously dockable modular self-reconfigurable robot using rocker-bogie suspension. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 4261–4267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Salvietti, G.; Wang, W.; Li, G.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J. Efficient kinematic solution to a multi-robot with serial and parallel mechanisms. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 6101–6106. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, H.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; Wei, Q.; Xia, J. Design and experiments of a compact self-assembling mobile modular robot with joint actuation and onboard visual-based perception. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahkam, N.; Bakir, A.; Özcan, O. Miniature modular legged robot with compliant backbones. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3923–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan-Aydin, Y.; Goldman, D.I. Self-reconfigurable multilegged robot swarms collectively accomplish challenging terradynamic tasks. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Ye, Z.; Wang, C. Path planning for self-reconfigurable modular robots: A survey. Sci. Sin. Inform. 2018, 48, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, G.; Yin, J. Switchable adhesion actuator for amphibious climbing soft robot. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Ji, Q.; Huang, M.; Chang, L.; Zhang, C.; Wu, G.; Zi, B.; Bao, N.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y. Light-driven self-oscillating actuators with phototactic locomotion based on black phosphorus heterostructure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20511–20517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Yamauchi, Y.; Araoka, F.; Kim, Y.S.; Bergueiro, J.; Ishida, Y.; Ebina, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Hikima, T.; Aida, T. An anisotropic hydrogel actuator enabling earthworm-like directed peristaltic crawling. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 15998–16002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothemund, P.; Ainla, A.; Belding, L.; Preston, D.J.; Kurihara, S.; Suo, Z.; Whitesides, G.M. A soft, bistable valve for autonomous control of soft actuators. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, 7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Yang, G.Z. Design and fabrication of a 3-D printed metallic flexible joint for snake-like surgical robot. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yuan, H.; Cao, Z. Environmental adaptive control of a snake-like robot with variable stiffness actuators. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrouk, D.; Mann, M.; Degani, N.; Yehuda, T.; Jarbi, N.; Hess, A. Single actuator wave-like robot (SAW): Design, modeling, and experiments. Bioinspir. Biomimetics 2016, 11, 046004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drory, L.H.; Zarrouk, D. Locomotion dynamics of a miniature wave-like robot, modeling and experiments. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 8422–8428. [Google Scholar]
- Shachaf, D.; Inbar, O.; Zarrouk, D. RSAW, a highly reconfigurable wave robot: Analysis, design, and experiments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 4475–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, R.; Shachaf, D.; Zarrouk, D. Energy-based design optimization of a miniature wave-like robot inside curved compliant tubes. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 12427–12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, J.; Lipson, H. Soldercubes: A self-soldering self-reconfiguring modular robot system. Auton. Robot. 2016, 40, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisser, M.; Cheng, L.; Makaram, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Mueller, S. ElectroVoxel: Electromagnetically actuated pivoting for scalable modular self-reconfigurable robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 4254–4260. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaouadi, R.; Hatab, A.A. Dynamic modelling of differential-drive mobile robots using lagrange and newton-euler methodologies: A unified framework. Adv. Robot. Autom. 2013, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).