Abstract
Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs), with their high power density, high efficiency, and thermal stability, are widely used nowadays. PMSM magnets are composed of rare earth elements. However, rare earth elements are subject to severe price fluctuations because of their limited availability and the monopoly of some countries. Therefore, extensive research on magnets devoid of rare earth elements has been conducted recently. Although a magnet devoid of rare earth elements has a high irreversible demagnetization rate at high temperatures owing to its low coercive force, an irreversible demagnetization improvement process is proposed in this paper to compensate for this disadvantage. This process analyzes the contribution of the magnet’s back EMF (electromotive force) using the flux linkage equation, which does not change with time. Next, the location of irreversible demagnetization is moved to a position with a low contribution to the back electromotive force. Consequently, even if irreversible demagnetization occurs at the same size, the irreversible demagnetization ratio is reduced. The proposed process can minimize irreversible demagnetization while maintaining performance.
1. Introduction
In recent years, electric vehicles have attracted considerable attention from the industrial sector owing to their advantages of cleanliness, high efficiency, and low noise [1]. In general, motors with rare-earth permanent magnets that enable compact structures and high power densities are often used in traction motors for electric vehicles. However, although permanent magnets containing rare earth elements have high efficiency, power density, and thermal stability, they are not suitable for future use owing to many disadvantages. For example, rare earth’s limited reserves and the monopoly of certain countries lead to an unstable supply of rare earth PM materials, which directly affects their cost. Therefore, many recent studies have been conducted to reduce or completely exclude rare earth elements in permanent magnets [2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. However, if the content of rare earth elements in the permanent magnet is reduced or removed, the coercive force of the permanent magnet is lowered, and the thermal properties deteriorate. Poor thermal properties make it susceptible to irreversible demagnetization. Therefore, research to inhibit irreversible demagnetization caused by a low coercive force has recently been studied [9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. For example, prior research, such as studies to minimize irreversible demagnetization by changing the rotor shape [16,17] by modifying the volume and thickness of the magnet and by adjusting the number of poles and slots, are underway. In this paper, a process for minimizing irreversible demagnetization by using permanent magnets completely devoid of rare earth, maintaining equivalent performance, and compensating for low coercive force is proposed. The design process for irreversible demagnetization minimization is illustrated in Figure 1. For the given process, several rotor parameters are changed to determine its shape initially. In other words, after determining the rotor shape (bar type, V-shaped type, or spoke type), the performance and irreversible demagnetization ratio are analyzed. If the target performance is not met or the irreversible demagnetization ratio is not reduced, the rotor shape must be redesigned. If the target performance is satisfied, the back EMF (electromotive force) contribution of the magnet is analyzed. The analysis is performed using the flux linkage equation, which does not change with time. This is because the back EMF of the magnet changes depending on the rotor position when it changes with time. After analyzing the back EMF according to the position of the magnet, a design is carried out to shift the region where irreversible demagnetization occurs. That is, the position where irreversible demagnetization occurs is shifted to the side where the back EMF contribution of the magnet is low. This is because even if irreversible demagnetization occurs in the same range, the irreversible demagnetization ratio is reduced. Next, the barriers and bridges are redesigned. If the target performance is satisfied, the process continues. However, if it is not satisfied or the irreversible demagnetization ratio is not reduced, the barrier and bridge should be redesigned. Then, an air hole is inserted into the pole piece in front of the region where irreversible demagnetization occurs. By inserting an air hole, the irreversible demagnetization area is reduced, and it is moved to a part with a low contribution to the back EMF. The following process was performed to reduce irreversible demagnetization.
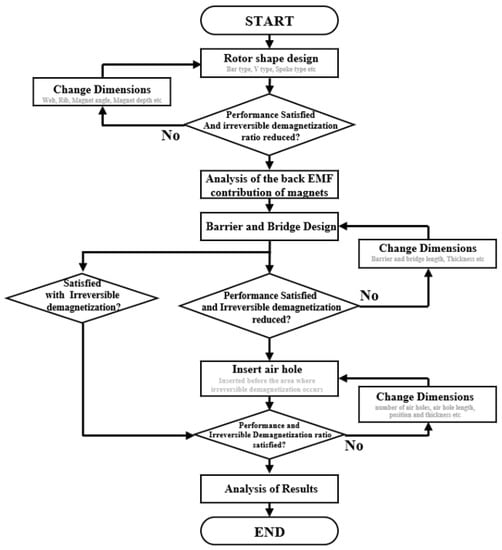
Figure 1.
Rotor design process to minimize irreversible demagnetization.
2. Rotor Irreversible Demagnetization Minimizing Design
2.1. 35 kW Hybrid Traction Motor Analysis
Figure 2 depicts the conventional motor and the T–N curve. In Table 1, a 35 kW hybrid traction motor was selected as the conventional motor, with the following specifications. The conventional model used an NdFeB magnet. Figure 3 shows the B–H curves of the NdFeB magnet and the Dy-free NdFeB magnet at 150 °C. Dy-free NdFeB magnets have smaller coercive forces and smaller knee points than conventional NdFeB magnets. Therefore, the Dy-free NdFeB magnet is unfavorable for irreversible demagnetization. This is because irreversible demagnetization occurs when the motor operates below the knee point present in the B–H curve of the magnet. Therefore, this study was aimed at minimizing the irreversible demagnetization of a Dy-free NdFeB magnet. The temperature was 150 °C, and 1.2 times the maximum current was applied.
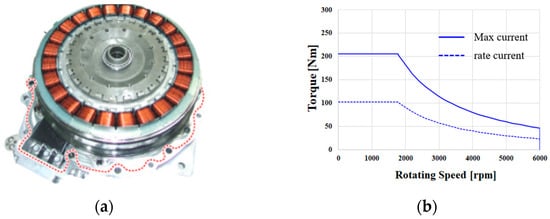
Figure 2.
Picture and T–N curve of the 35 kW conventional hybrid traction model: (a) production model, (b) T–N curve of the conventional model.

Table 1.
35 kW hybrid traction motor specifications.
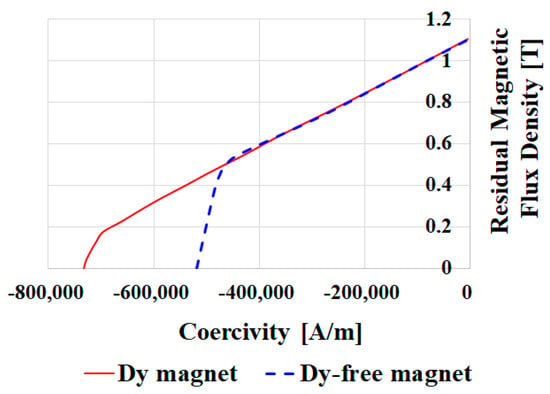
Figure 3.
B-H curve of NdFeB and Dy−free NdFeB magnet (temperature: 150 °C).
Figure 4 shows the irreversible demagnetization when the NdFeB magnet and the Dy-free NdFeB magnet are inserted into the conventional motor. In Figure 4, blue represents the irreversible demagnetization area, and red represents the remaining area. The figure indicates that the area of irreversible demagnetization of the Dy-free NdFeB magnet was large. Under the same conditions, the irreversible demagnetization ratio was less than 0.5% for NdFeB magnets and approximately 20% for Dy-free NdFeB magnets.
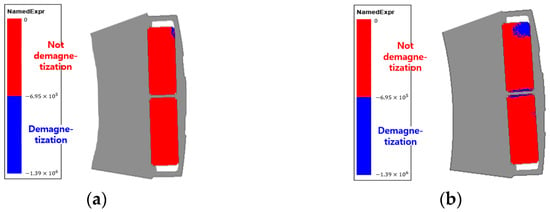
Figure 4.
Irreversible demagnetization area obtained on inserting two magnets into a conventional model: (a) NdFeB magnet inserted, (b) Dy−free NdFeB magnet inserted.
2.2. Rotor Design Resistant to Irreversible Demagnetization
The armature reaction magnetic flux generated by the stator winding acts as a reverse magnetic field in the direction opposite to the main flux from the permanent magnet. Therefore, as the reverse magnetic field generated by the armature reaction hits the magnet strongly, the magnet loses its properties. This is called irreversible demagnetization. Irreversible demagnetization can be controlled depending on the insertion type of the magnet. Figure 5 shows the magnetic flux density vector diagrams for the bar and V-shaped types.
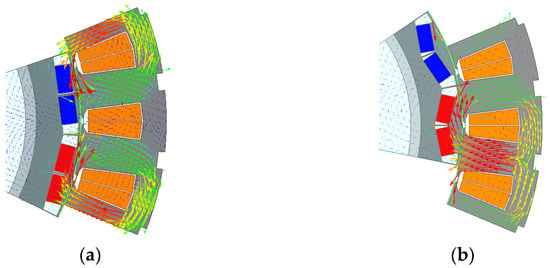
Figure 5.
Magnetic flux density plot depending on magnet type: (a) Bar type, (b) V-shaped type.
The existing bar type is vulnerable to irreversible demagnetization because the magnetic path of the demagnetization magnetic flux emitted by the stator winding is not secured and directly hits the permanent magnet. However, when the V-shaped magnet type is inserted, the magnetic path of the demagnetization magnetic flux can be sufficiently secured compared to the existing bar type; therefore, it has a more robust structure for preventing irreversible demagnetization. Therefore, in this study, a V-shaped rotor was selected, and an optimal design was carried out. Figure 6 shows the demagnetization ratio and back EMF depending on the magnet depth and angle.
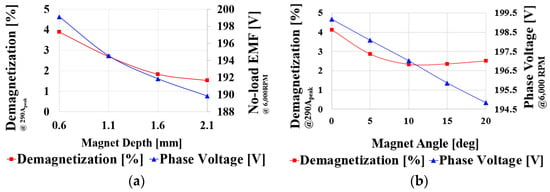
Figure 6.
Demagnetization ratio and back EMF depending on the magnet depth and angle (a) magnet depth, (b) magnet angle.
As shown in Figure 6, as the magnet depth increases, the demagnetization ratio and back EMF decrease. As a result, irreversible demagnetization is improved, but the performance is degraded. When the magnet angle increased, the demagnetization ratio decreased and remained constant from a certain point; however, the back EMF continued to decrease. Considering these factors, an optimal design was achieved. Figure 7 shows the basic V-shaped type model and irreversible demagnetization, with the same performance as the conventional motor and a minimum irreversible demagnetization ratio.
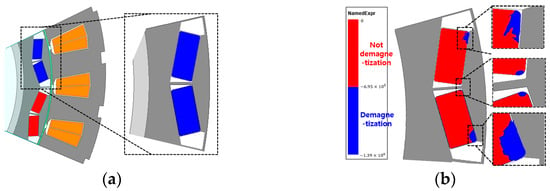
Figure 7.
Basic model and its irreversible demagnetization area: (a) Basic model, (b) Irreversible demagnetization area.
In Figure 7, the irreversible demagnetization ratio of the V-shaped type model was reduced; however, the target irreversible demagnetization ratio was not yet achieved. Therefore, the following process was carried out.
3. Analysis of the Contribution of Permanent Magnets to No-Load Back EMF Generation
Analysis of Back EMF Contribution Depending on the Magnet Part
The general linkage flux equation is shown in Equation (1).
The general linkage flux is the flux at which the magnetic flux generated in the permanent magnet is linked to the coil. It is calculated using the area where the magnetic flux is generated from the permanent magnet interlinks on the surface of the coil. However, the general flux linkage equation cannot be used to obtain the back electromotive force generated by the permanent magnet. Therefore, it must be calculated using the integral of the magnetic quantity in the shape of a permanent magnet rather than on the coil side. In doing so, the contribution of each microvolume does not depend on the time and has a constant value. The back electromotive force per permanent magnet volume, which does not change with time, can be obtained from the following equation.
Equation (2) shows the average no-load counter electromotive force calculated using an arbitrary current and the magnetic field strength at the moment . The contribution of each microvolume does not depend on the time and has a constant value. The back electromotive force per permanent magnet volume, which does not change with time, can be obtained from the following equation. If the conventional flux linkage equation is used, it has a value that varies with time; however, if Equation (2) is used, it has a constant time-independent value. Then, the contribution of the back electromotive force according to the position of the permanent magnet can be obtained. Based on the equations obtained above, the actual implementation was calculated using the finite element method. Equation (2) was used to calculate the contribution of the back electromotive force for each minute volume of the permanent magnet. The calculated results are shown in Figure 8. Figure 8 shows that the contribution of the back electromotive force of the front of the permanent magnet to its barrier side is significant. In addition, the contribution of the back electromotive force of the back end and the remaining part is low compared to that of the front. Therefore, the irreversible demagnetization ratio can be reduced by moving the irreversible demagnetization region to a part with a low contribution to the back EMF. The irreversible demagnetization was assumed to have occurred at an arbitrary position in the permanent magnet of the basic model, and the permanent magnet was divided into several parts and numbered, thereby demonstrating the calculated contribution of the permanent magnet’s back electromotive force that was calculated using the finite element method in the previous section. Figure 9 shows the assumed irreversible demagnetization region and the number of permanent magnets. In this case, the assumed irreversible demagnetization region is a square with a side length of 1.5 mm.
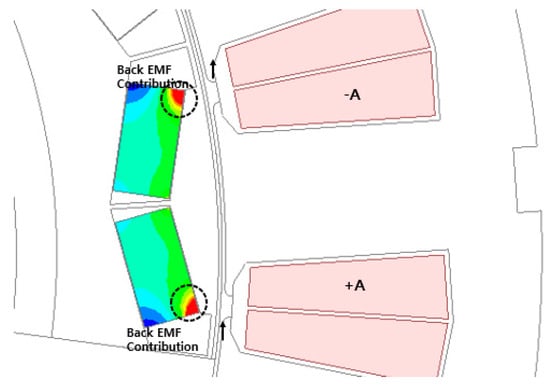
Figure 8.
Contribution of Back EMF in Permanent Magnets Calculated Using Finite Element Method.
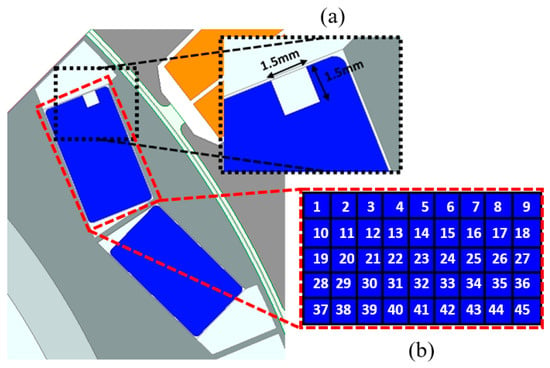
Figure 9.
Irreversible demagnetization contribution depending on magnet position: (a) Assumed irreversible demagnetization region, (b) Magnet position.
Assuming that irreversible demagnetization occurs at one position of the magnet, the counter electromotive force can be calculated for each position of the magnet and analyzed. For example, assuming that irreversible demagnetization occurs at position 1, if the back EMF is greatly reduced, it can be said that the contribution of the permanent magnet to the back EMF at position number 1 is high. Conversely, if it is assumed that irreversible demagnetization occurs at position 37, if the reduction in back EMF is minimal, it can be said that the contribution of the permanent magnet back EMF is negligible. The back electromotive force reduction rate can be calculated using Equation (3).
where E1 and E2 are the back EMFs before and after irreversible demagnetization, respectively. Figure 10 shows the demagnetization ratio and no-load EMF when irreversible demagnetization occurs depending on the order of each magnet position.
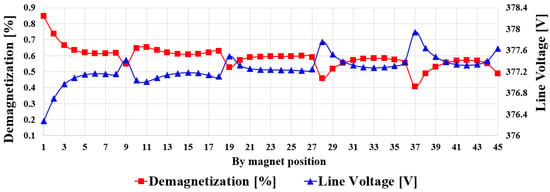
Figure 10.
Demagnetization ratio according to each part of the magnet.
In Figure 10, the back EMF of each part of the magnet is analyzed under the assumption that irreversible demagnetization occurs in each part. In this analysis, the part with a low back EMF has a high back EMF contribution. Therefore, when the part with a high back EMF contribution undergoes irreversible demagnetization, it has a high irreversible demagnetization ratio. As shown in Figure 10, the analysis results show the same pattern as the back EMF contribution calculated in the previous section. By analyzing the contribution of the back EMF depending on the position of the permanent magnet, a study was carried out to reduce the irreversible demagnetization by moving its region of occurrence to the position where the contribution of the back EMF is low. If the irreversible demagnetization is moved to a position with a low contribution to the back electromotive force, the irreversible demagnetization ratio can be reduced even if the irreversible demagnetization generating area is the same in the permanent magnet.
4. Design for Minimizing Irreversible Demagnetization by Analyzing the Back Emf Contribution
4.1. Design of the Inner Shape of Magnet for Securing Irreversible Demagnetization Magnetic Flux Passage
Irreversible demagnetization occurs when the demagnetization magnetic flux, which is generated from the winding of the stator, hits the magnet. Therefore, by creating a passage for the demagnetization magnetic flux where the flow is high, the irreversible demagnetization area can be moved to the part with a low back EMF contribution, and the irreversible demagnetization ratio can be reduced. As shown in Figure 7b, irreversible demagnetization usually occurs on the barrier and bridge sides. First, this paper proposes a method for reducing irreversible demagnetization on bridge sides. Irreversible demagnetization can be reduced or displaced by inserting a steel plate as a demagnetization magnetic flux passage near the bridge sides that acts as a support structure for the magnet. The irreversible demagnetization can thus be minimized because the magnetic flux generated from the stator winding enters the rotor and escapes through the magnetic flux passage. Figure 11 presents the irreversible demagnetization area before and after inserting the steel plate into the bridge. As shown above, irreversible demagnetization was reduced after the insertion of a steel plate in the bridge. In terms of performance, there was little change in counter-electromotive force, cogging torque, and torque ripple. In other words, demagnetization was improved by inserting a steel plate into the bridge, but there was little change in performance and the same.
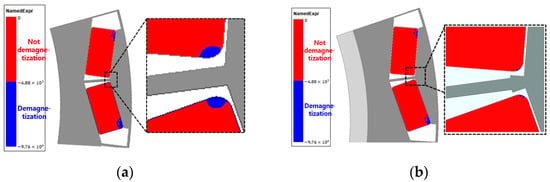
Figure 11.
Irreversible demagnetization area before and after inserting a steel plate in bridge: (a) Basic model, (b) Irreversible demagnetization area.
4.2. Design of the Outer Shape of Magnet for Securing Irreversible Demagnetization Magnetic Flux Passage
Similarly, a steel plate that acts as a magnet support structure and a magnetic flux passage is inserted into the barrier region. If the thickness of the steel plate inserted into the barrier part is too thin, its mechanical rigidity may be compromised. Therefore, a minimum plate thickness of 0.6 mm was selected, and the irreversible demagnetization area was analyzed based on the lengths of the steel plate. This is illustrated in Figure 12. As shown in Figure 12, the longer the length of the steel plate inserted into the barrier, the smaller the irreversible demagnetization region. In addition, according to the back EMF analyzed in the previous section, the irreversible demagnetization area shifts from the part where the back EMF contribution is high to the part where it is low. In other words, if the two different parts of the magnet have the same demagnetization region, the demagnetization ratio will decrease when it occurs in the part that has a low back EMF contribution. Figure 13 shows the demagnetization region of the model comprising the inserted steel plates in the barrier and bridge.
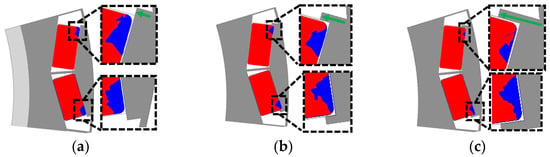
Figure 12.
Irreversible demagnetization area according to different lengths of steel plate inserted in the barrier: (a) 0 mm, (b) 0.6 mm, (c) 1.2 mm.
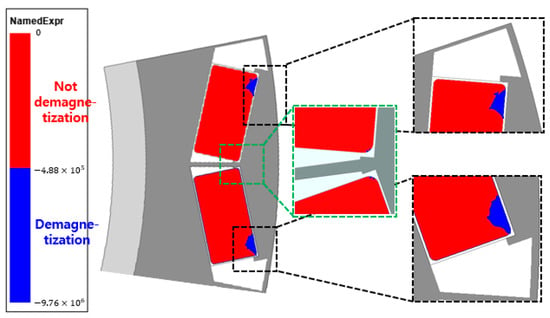
Figure 13.
Demagnetization region of the model.
The thickness of the steel plate inserted into the barrier and bridge was set at 0.6 mm. If the steel plate is thicker, the demagnetization area decreases; however, the performance decreases as well. To solve this problem, the ideal thickness for having the smallest irreversible demagnetization region was selected as 0.6 mm based on previous performance. Consequently, the irreversible demagnetization area was significantly reduced compared to that of the basic model. However, the irreversible demagnetization ratio is still higher than that of the conventional model that uses an NdFeB magnet.
4.3. Air Hole Shape Design
Irreversible demagnetization can be reduced by inserting an air hole into the pole piece on the side where most of the demagnetization magnetic flux generated by the stator winding flows into the rotor, thereby avoiding the concentration of demagnetization magnetic flux. The demagnetization magnetic flux dispersed toward both ends of an air hole flows into the steel plate in the barrier and bridge, further reducing the irreversible demagnetization area. Moreover, by inserting an air hole in front of the magnet with a high back EMF contribution, the irreversible demagnetization area can be moved to the part with a low back EMF contribution. As a result, the total demagnetization rate decreases. The thickness and length of the air hole were set as 1 mm, and the irreversible demagnetization was analyzed according to the position of the air hole as it moved toward the bridge. Figure 14 shows the irreversible demagnetization area when the air hole is gradually moved by 0.6 mm each toward the bridge.
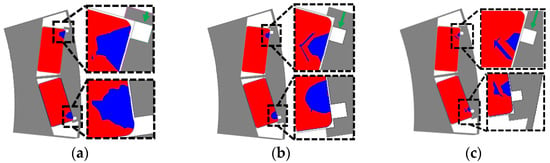
Figure 14.
Irreversible demagnetization region with different air hole positions toward the bridge: (a) 0 mm, (b) 0.6 mm, (c) 1.2 mm.
The results showed that when the air hole position was moved to the bridge, the irreversible demagnetization decreased and moved to the part with a low back EMF contribution. Figure 15 presents the irreversible demagnetization area when the air hole position is gradually moved 0.4 mm toward the air gap. The irreversible demagnetization area is not significantly reduced when the position of the air hole moves toward the air gap. However, the irreversible demagnetization region moves to the side where the back EMF contribution of the magnet is low. Accordingly, despite the same region, the demagnetization ratio decreases when the magnet moves to the side where it has a low back EMF contribution. The irreversible demagnetization region of the first air hole-inserted model is shown in Figure 16.
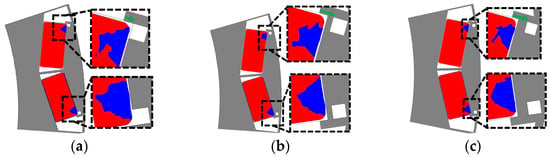
Figure 15.
Irreversible demagnetization region with different air hole positions towards an air gap: (a) 0 mm, (b) 0.4 mm, (c) 0.8 mm.
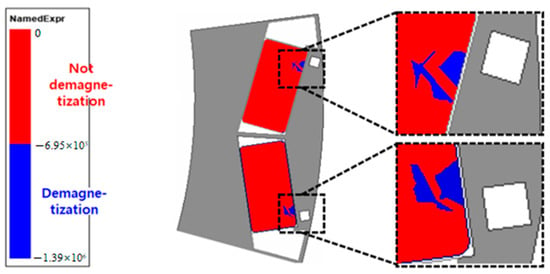
Figure 16.
Irreversible demagnetization area of the model with the first air hole inserted.
The position of the first air hole was set at 0.8 mm toward the bridge side and 0.6 mm toward the air gap. When inserting an air hole, it is not only necessary to consider performance and demagnetization ratio but also mechanical rigidity. If the air hole is too close to the magnet pocket or an air gap, the mechanical rigidity may be compromised, resulting in failure. Therefore, the position of the first air hole was set as mentioned, considering rigidity. The irreversible demagnetization can be further improved by inserting a second air hole. Figure 17 presents the irreversible demagnetization area when the second air hole is moved toward the bridge by 0.6 mm. The position of the second air hole was set to 1 mm from the bridge. In the final model, the fillet was given to the air hole while considering the productivity. The irreversible demagnetization region of the final model and final full model is shown in Figure 18. The demagnetization region in the final model comprising Dy-free magnets decreased and moved to the part where the demagnetization contribution was low. As a result, the final demagnetization ratio decreased significantly. The demagnetization ratio of the final model was 0.55%, which is the same as that of the conventional model in which an NdFeB magnet was used.
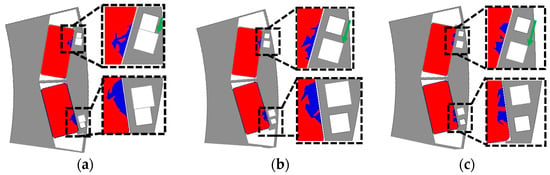
Figure 17.
Irreversible demagnetization region by the second air hole position: (a) 0 mm, (b) 0.6 mm, (c) 1.2 mm.
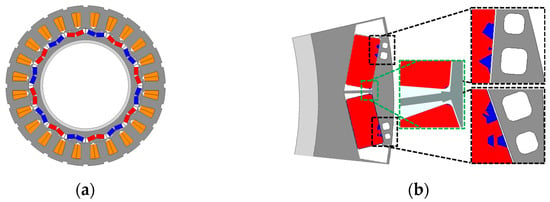
Figure 18.
Irreversible demagnetization area of final model: (a) Final full model, (b) Irreversible demagnetization region in final model.
5. Characteristic Comparison through Simulation
5.1. Electromagnetic Performance Analysis
A comparative analysis of the electromagnetic performance between the conventional and final models was conducted. Figure 19 shows the cogging torque and no-load back EMF at the rated speed of the conventional model and the final model. As shown in the cogging torque waveform in Figure 19, the cogging torques of the conventional and final models are 3.7 N∙m and 2.8 N∙m, respectively, confirming that the cogging torque of the conventional model is low. Moreover, the no-load back EMF of the conventional model and the final model is similar. For traction motors, the cogging torque, torque ripple, and performance are important factors. Figure 20 shows the maximum and rated torques at the maximum and rated speeds.
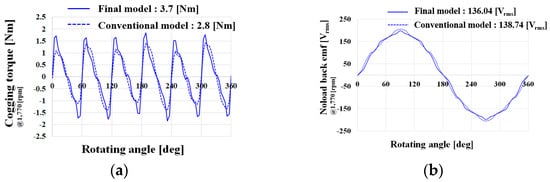
Figure 19.
Cogging torque waveforms and no-load back EMF at rated speed of conventional model and final model: (a) Cogging torque, (b) Noload back EMF.
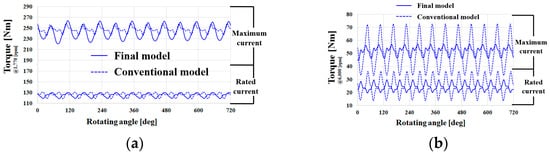
Figure 20.
Comparison of rated and maximum torque waveforms at rated and maximum speed of the conventional model and final proposed model: (a) Torque at rated speed, (b) Torque at maximum speed.
As shown in Figure 20, if the torque ripple result is checked when the rated current is applied at the rated speed, a similar waveform appears, and when the maximum current is applied, the torque ripple of the final model is slightly larger. However, the final model has a small torque ripple when rated, and the maximum current is applied at maximum speed. Table 2 shows the electromagnetic performances of the conventional and final models. As shown in Table 2, the conventional model is advantageous in terms of cogging torque. However, in terms of torque ripple, it can be seen that the final model has an overall advantage. In addition, in terms of torque, the existing and final models are similar. In other words, the final model that used the Dy-free NdFeB magnet designed through the process is similar in performance to the conventional model that used the NdFeB magnet. Subsequently, an irreversible demagnetization analysis was performed. Table 3 compares the results of the FEM analysis of the back electromotive force and irreversible demagnetization ratio before and after demagnetization of the conventional and final models.

Table 2.
Comparative analysis of the electromagnetic performance of the conventional model that used the NDFEB magnet and the final model that used the Dy-free NDFEB magnet.

Table 3.
Comparison of the back electromotive force and demagnetization ratio and FEM results of the conventional model that used a magnet containing Dy and the final proposed model that USED a Dy-free magnet.
The irreversible demagnetization ratios of the conventional and final models were 0.37% and 0.55%, respectively. In addition, the final model satisfied the target irreversible demagnetization ratio of less than 1%. The operating points and B–H curves, which determine the extent of irreversible demagnetization, were analyzed for both models. This is because irreversible demagnetization occurs when the operating point of the motor lies in the region below the knee point in the B–H curve of the magnet. Here, the operating point is the point at which the permeance line and B–H curve of the magnet meet. The formula to determine the permeance line is given by Equation (4).
In this equation, and are the magnetic flux density and magnetic field strength of the magnet, respectively, is the length of the magnet, is the air gap length, and is the magnetic flux concentration coefficient. The magnetic flux concentration coefficient is expressed as . Using Equation (3), the permeance line can be identified, and the operating point can be determined. The permeance line of the proposed model is higher than that of the conventional model. Figure 21 shows the operating points of the conventional and final models. Through the design of the rotor, the driving point at which the motor operates is raised upward, enabling it to operate above the coercive force of the Dy-free magnet. Therefore, irreversible demagnetization may not occur. Here, the red line is the B-H curve of the magnet and the blue dot means the operating point.
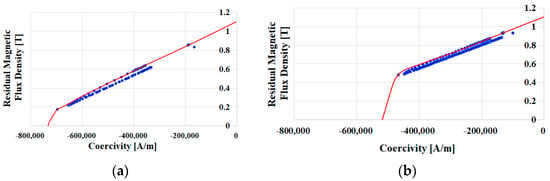
Figure 21.
Operating points of the existing and proposed models: (a) NdFeB magnet B−H curve and operating point, (b) Dy−free magnet B-H curve and operating point.
5.2. Comparison of the Mechanical Rigidity
Figure 22 presents a comparison of the rigidity of the conventional and final models. In addition, when performing the stiffness analysis, the speed was analyzed at the maximum speed standard of 6000 rpm. The equivalent stress of the conventional model and proposed models is 113.87 MPa and 148.34 MPa, respectively. Therefore, the final model is disadvantageous in terms of mechanical rigidity. However, the safety factor is similar (8 for the existing model and 7 for the final model). As the safety factor of the final model is similar to that of the existing mass-produced model, the rigidity of the final model was inferred to be adequate, and it was confirmed that there was no abnormality in the production result.
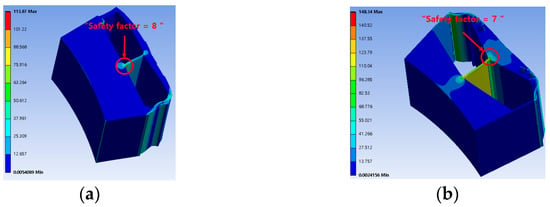
Figure 22.
Rigidity comparison between the conventional model and final model: (a) Conventional model, (b) Final model.
6. Experiments and Results
Figure 23a,b present the rotor and stator production photographs, respectively. Figure 24 presents the experimental environment and the equipment used. Figure 25 presents photographs of the experiment on applying a diamagnetic field current to both models. Figure 26 presents the line back-EMF measurement results and the diamagnetic field current waveform before and after the diamagnetic field is applied to the conventional and proposed models. The diamagnetic field currents of the conventional and proposed models were 314 Apeak and 331 Apeak, respectively. The experiments of the two models were performed at the same temperature. The input voltage of the diamagnetic current-application device was set to the same level, and the respective diamagnetic currents were then applied, resulting in an external diamagnetic field. Although there are differences in the magnitude of the demagnetizing field current owing to the difference in the parameters of the motors, a diamagnetic field current that exceeds the ratings was applied to both motors. Table 4 compares the experimental results of the back EMF and demagnetization ratio of both models. The experimental results of the conventional and proposed models, which used the NdFeB and Dy-free NdFeB magnets, respectively, were similar. Consequently, the experiments proved that irreversible demagnetization rarely occurred in both models.

Figure 23.
Final model production photograph: (a) Rotor production model, (b) Stator production model.
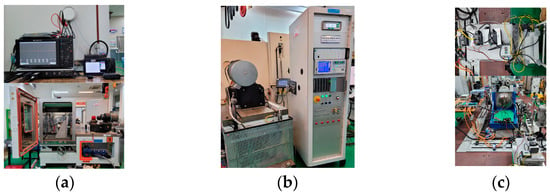
Figure 24.
(a) Oscilloscope, temperature data logger, and temperature/humidity chamber coupled dynamo test bench, (b) Power analyzer for counter EMF measurement, (c) Semi-EMF demagnetization-ratio experimental environment and diamagnetic current-application device.
Figure 25.
Photographs of the experiment on applying a diamagnetic field current to both models: (a) NdFeB magnet Apply conventional model, (b) Dy-free NdFeB magnet Apply final model.
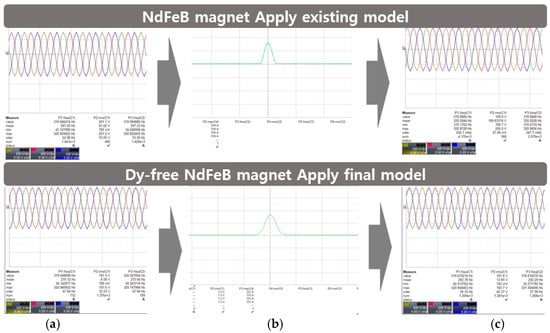
Figure 26.
Waveform for conventional and proposed models: (a) Back-EMF waveform before applying the diamagnetic current, (b) Diamagnetic current waveform, (c) Back EMF waveform after applying the diamagnetic current.

Table 4.
Comparison of FEM simulation results and manufacturing experiment results.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, an irreversible demagnetization improvement process is proposed through a rotor improvement design utilizing a Dy-free NdFeB magnet. The most important aspect of the process is to analyze the back EMF contribution of the magnet using a flux linkage formula that does not change with time. After accurately analyzing the back EMF contribution of the magnet, a design is implemented that shifts the region where irreversible demagnetization occurs to a part with a low back EMF contribution. Therefore, regardless of whether the same degree of irreversible demagnetization occurs, the irreversible demagnetization ratio can be reduced if it occurs where the contribution of the magnet’s back electromotive force is low. The proposed method enables the reduction of the irreversible demagnetization ratio while maintaining the same performance. Finally, FEM simulation and experimental investigation proved that the final model, which used the Dy-free NdFeB magnet, achieved the required performance and irreversible demagnetization ratio.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-W.S.; Methodology, S.-W.S.; Validation, H.-J.P., D.-W.N. and J.L.; Formal analysis, S.-W.S.; Investigation, S.-W.S., H.-J.P. and D.-W.N.; Data curation, S.-W.S.; Writing—original draft, S.-W.S.; Writing—review & editing, S.-W.S.; Visualization, W.-H.K.; Supervision, J.L. and W.-H.K.; Project administration, S.-W.S. and W.-H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant of the Basic Research Program funded by the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (grant number: NK236J).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kim, T.; Lee, H.-W.; Kwak, S. The Internal Fault Analysis of Brushless DC Motors Based on the Winding Function Theory. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2090–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.Y.; Liu, Z.W.; Zheng, Z.G.; Zhong, X.C.; Zhang, G.Q. Hard Magnetic Properties and Thermal Stability for TbCu7-Type SmCo6.4Si0.3Zr0.3 Alloys with Sm Substituted by Various Rare-Earth Elements. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 2100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskaev, S.V.; Skokov, K.P.; Khovaylo, V.V.; Gorshenkov, M.V.; Vasiliev, A.N.; Volkova, O.S.; Bataev, D.S.; Pellenen, A.P.; Gutfleisch, O. Magnetic Properties of Nd and Sm Rare-Earth Metals After Severe Plastic Deformation. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2016, 7, 5203104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, F.; Miura, D.; Sakuma, A. Theoretical Study of Gilbert Damping in Rare-Earth Permanent Magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 2101604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.; Amiri, E.; Rastgoufard, P.; Mirafzal, B. Toward Less Rare-Earth Permanent Magnet in Electric Machines: A Review. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 900119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, X.; Guo, S.; Di, J.; Ding, G.; Yan, C.; Chen, R.; Yan, A. Coercivity Enhancement of Dy-Free Sintered Nd–Fe–B Magnets by Grain Refinement and Induction Heat Treatment. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komlev, A.S.; Gimaev, R.R.; Davydov, A.S.; Zverev, V.I. The influence of chemical impurities on the properties of heavy rare-earth metals (Tb, Dy, Ho): Experimental and theoretical approaches. Materialia 2021, 18, 101166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimaev, R.R.; Komlev, A.S.; Davydov, A.S.; Kovalev, B.B.; Zverev, V.I. Magnetic and Electronic Properties of Heavy Lanthanides (Gd, Tb, Dy, Er, Ho, Tm). Crystals 2021, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-C.; Lee, J.-H.; Kang, D.-W. A Study on the Effect of Eddy Current Loss and Demagnetization Characteristics of Magnet Division. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2020, 30, 600805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zhou, P.; Bracken, E. Generalized Algorithm to Deal with Temperature-Dependent Demagnetization Curves of Permanent Magnets for FEA. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 7402706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. A Study on the Design of IPMSM for Reliability of Demagnetization Characteristics-Based Rotor. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2020, 30, 5204805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.-Y.; Hwang, K.-Y. Optimal Design of Spoke-Type IPM Motor Allowing Irreversible Demagnetization to Minimize PM Weight. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 65721–65729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, P.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Sui, Y. Demagnetization and Permanent-Magnet Minimization Analyses of Less-Rare-Earth Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines Used for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 8109505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, W.; Jin, C.; Lee, J. Local demagnetisation analysis of a permanent magnet motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2015, 9, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Ye, M.; Yang, J. No-load losses based method to detect demagnetisation fault in permanent magnet synchronous motors with parallel branches. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Uemura, H.; Honda, Y. Highly Demagnetization Performance IPMSM Under Hot Environ-ments. Ieee Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.L.; Hur, J. Optimization Design of PMSM With Hybrid-Type Permanent Magnet Considering Irreversible Demagnetization. Ieee Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 8110904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).