A Novel Principal Component Analysis-Informer Model for Fault Prediction of Nuclear Valves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theories and Methods
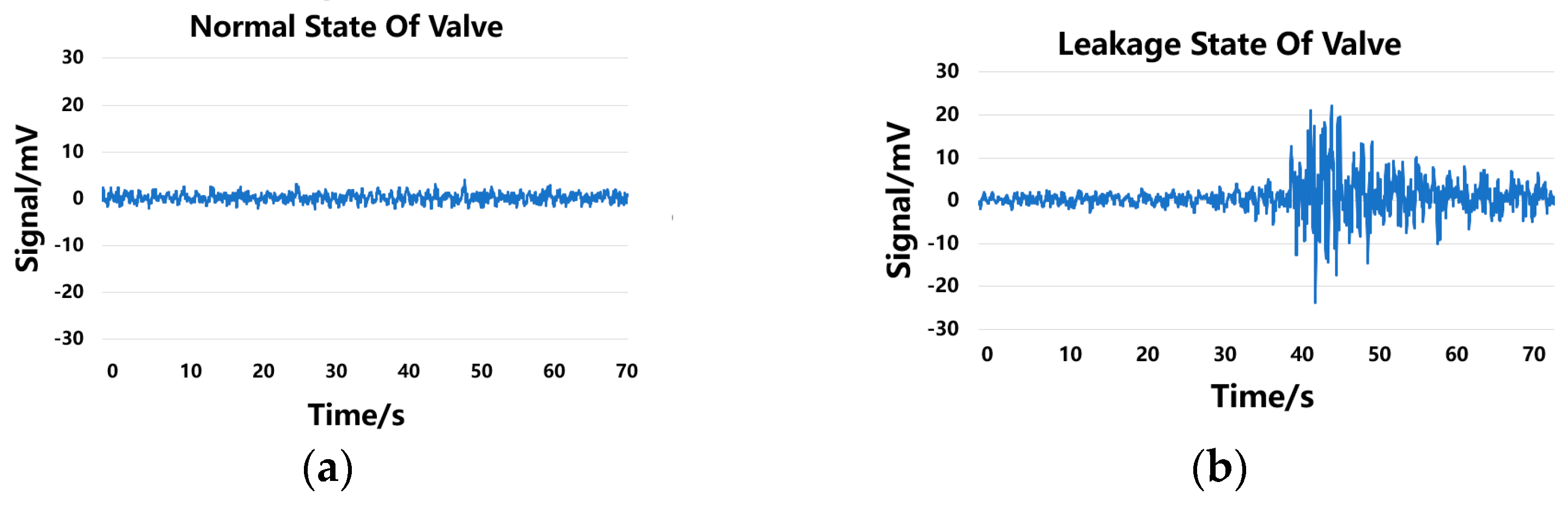
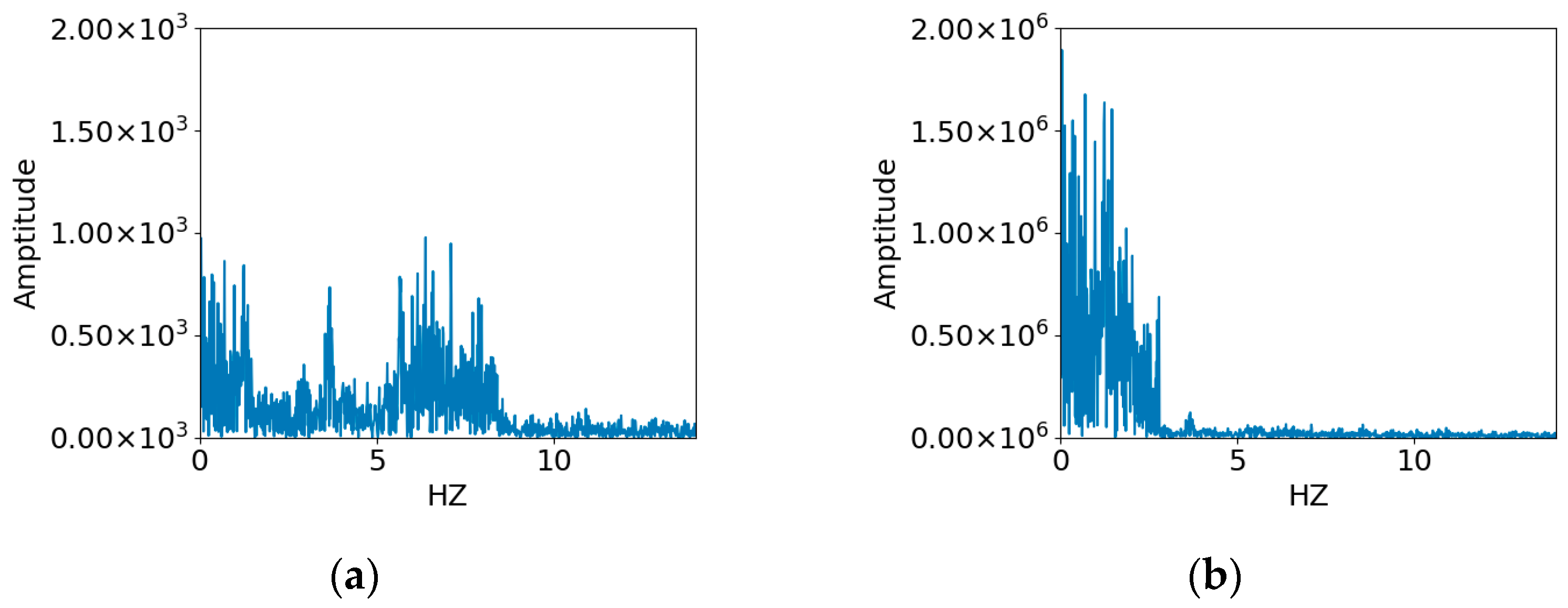
2.1. Valve Leakage Acoustic Signals
2.2. Valve Leakage Represented by AE Signals
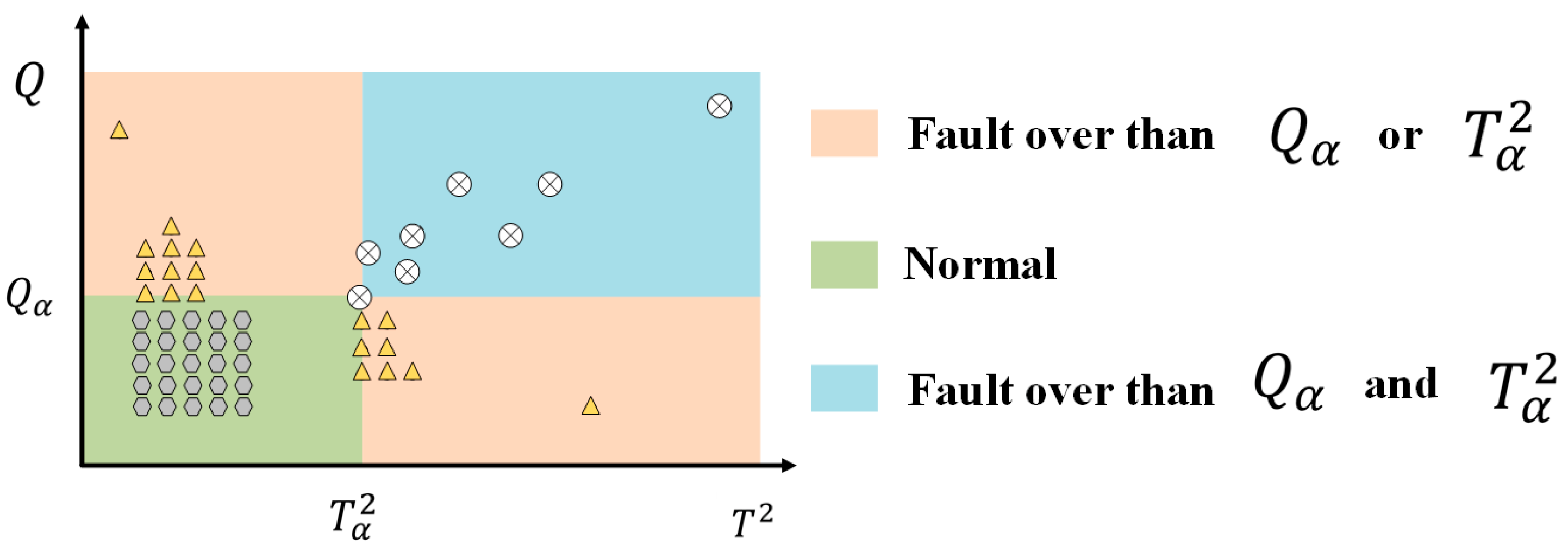
2.3. Fault Diagnosis Method
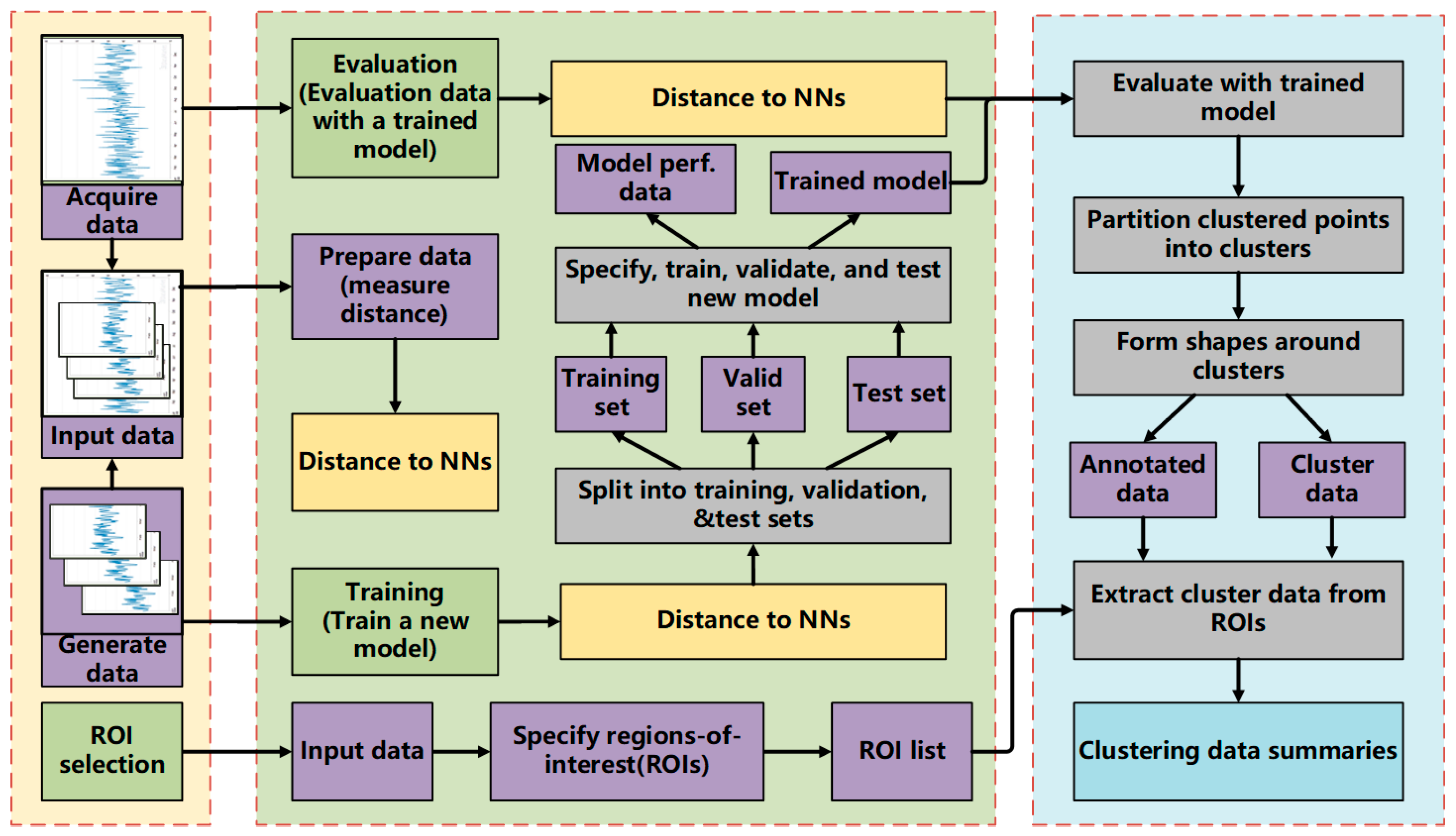
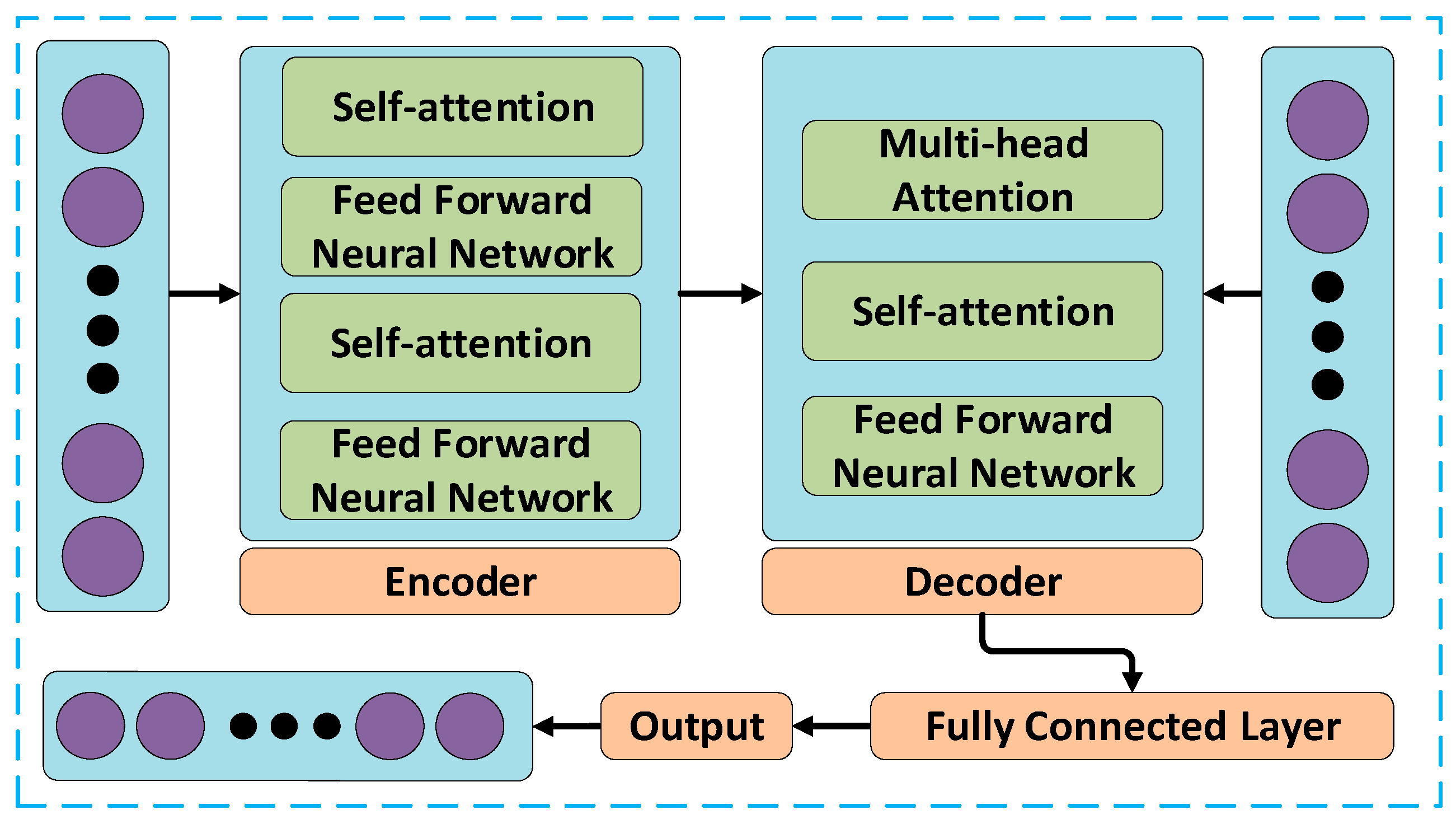
2.4. Fault Prediction Models Using Deep Learning Method
2.4.1. Efficient Self-Attention Mechanism
2.4.2. Decoder with Temporal Attention
3. Experiments
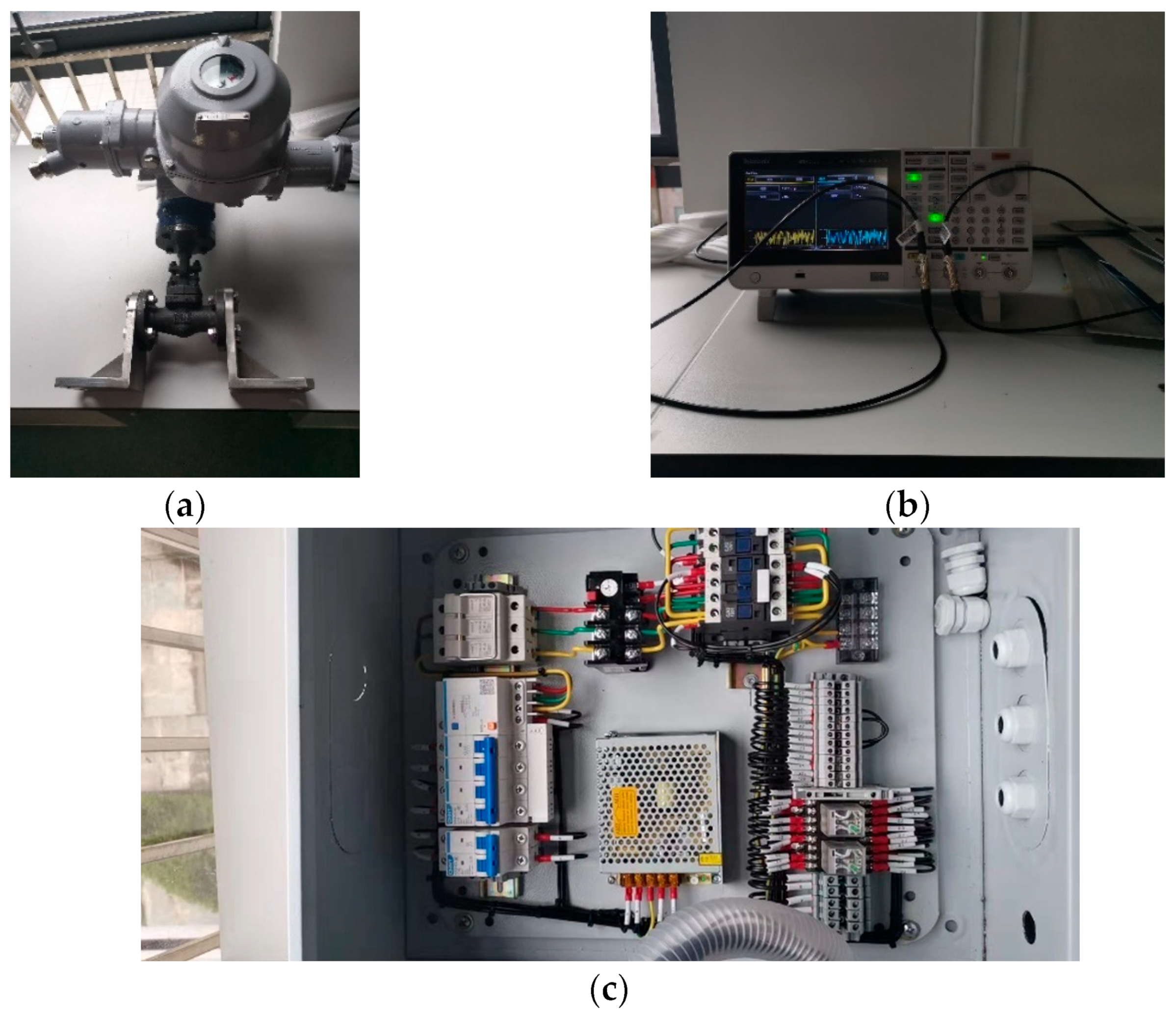
3.1. Experiment Setup
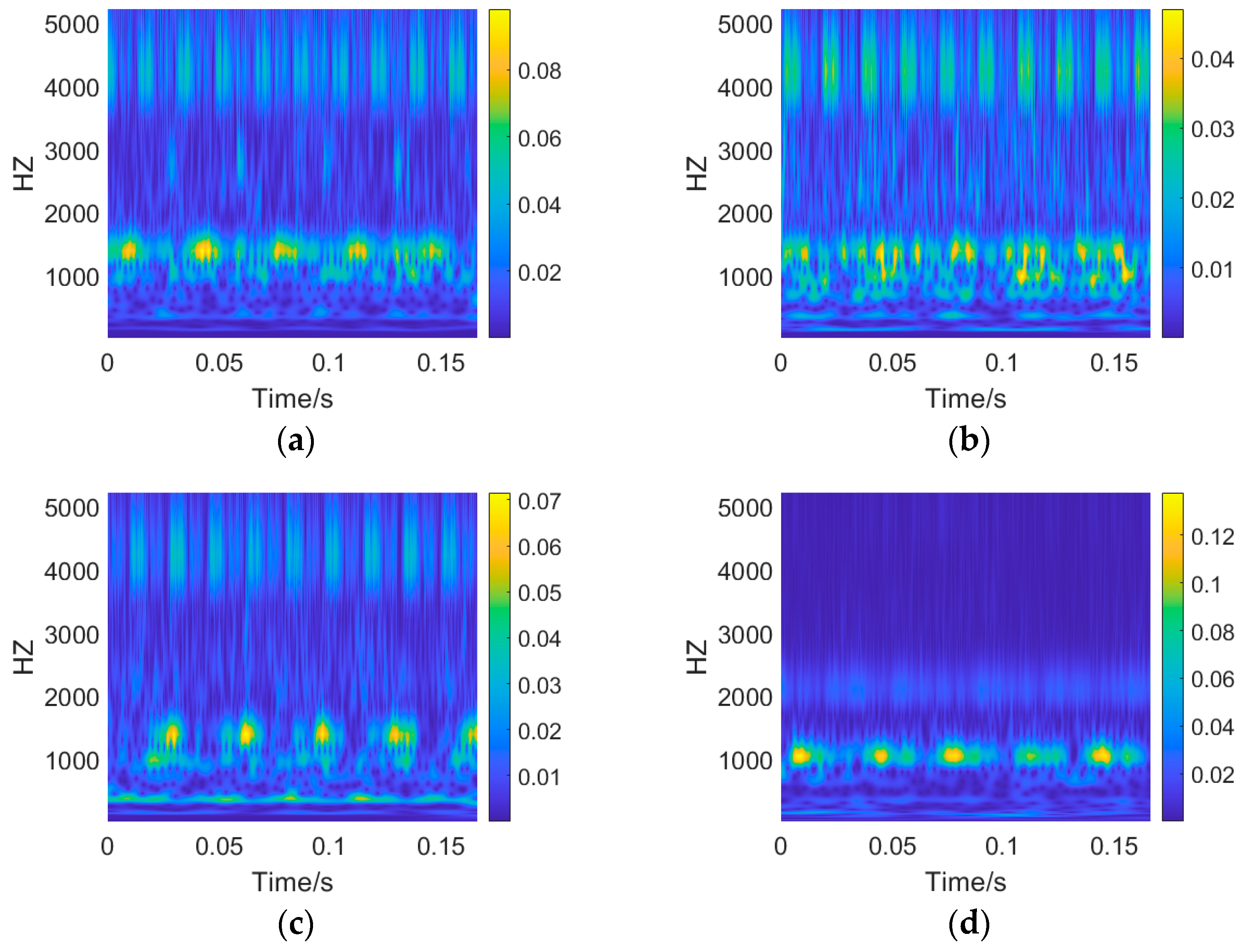
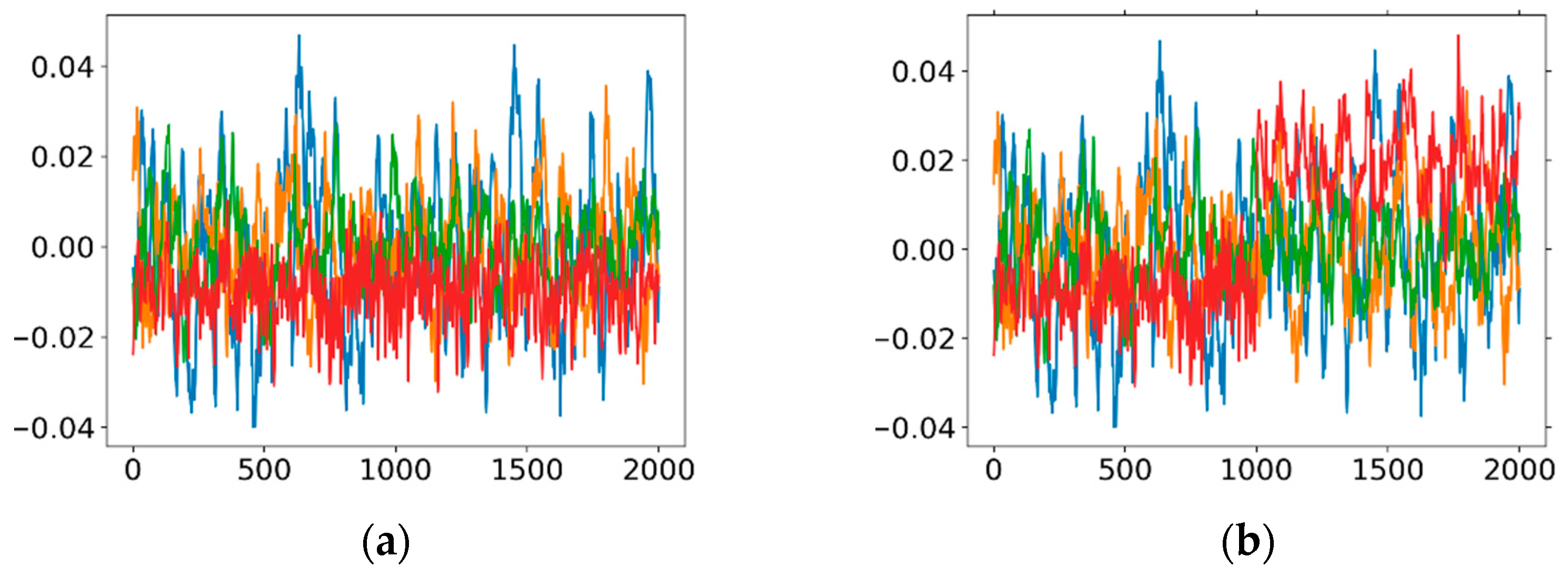
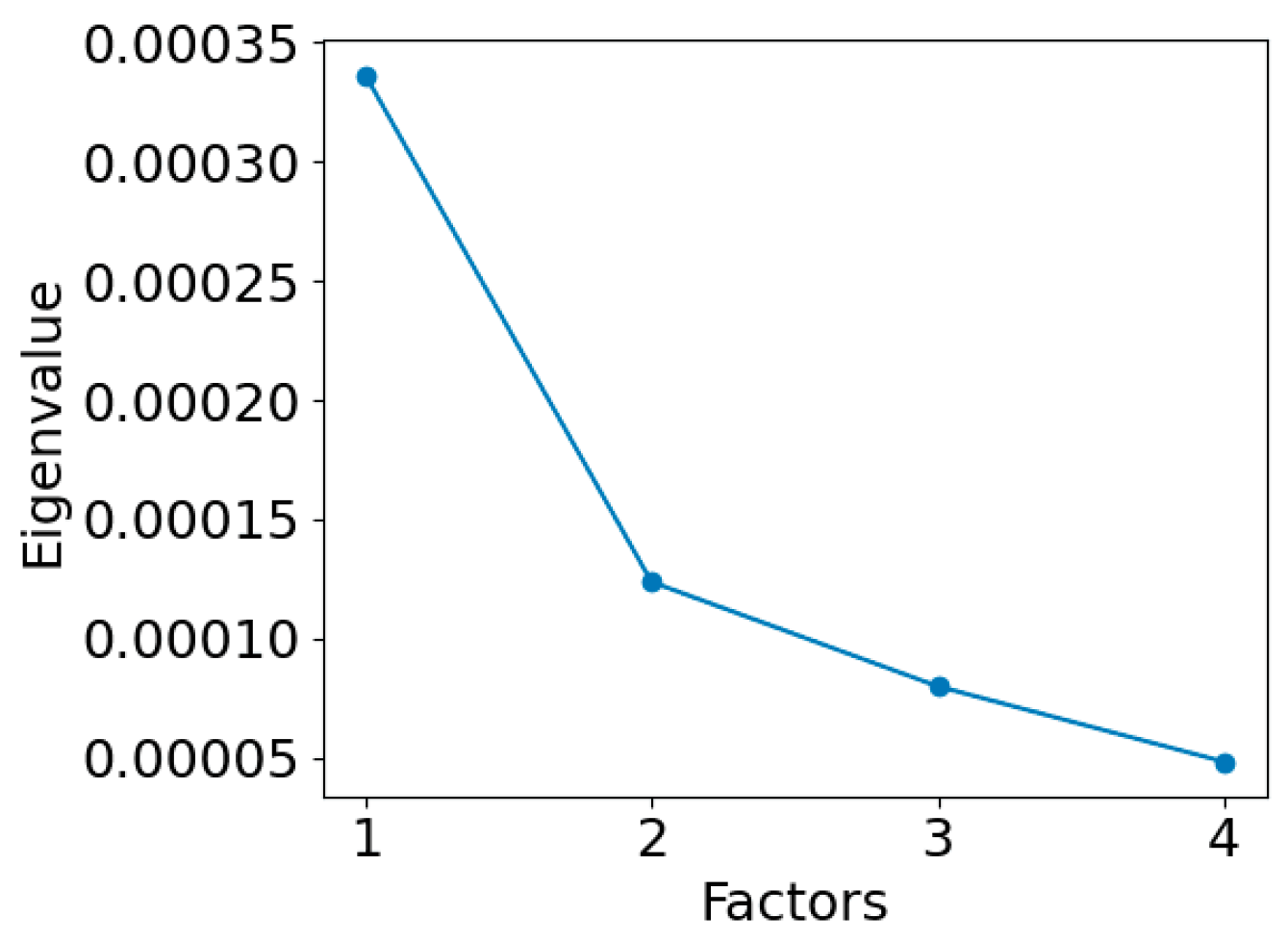
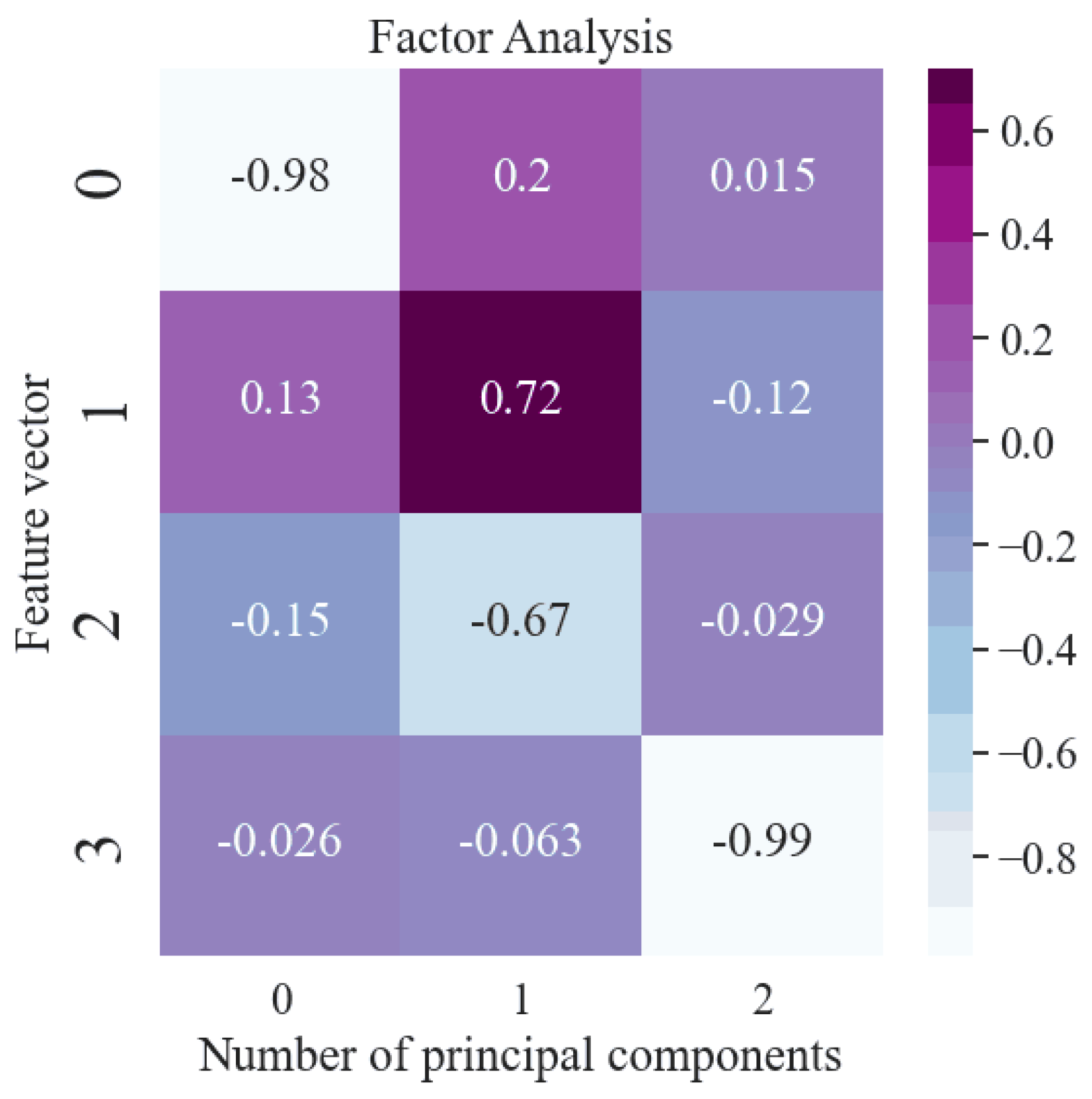
3.2. Data Preprocessing
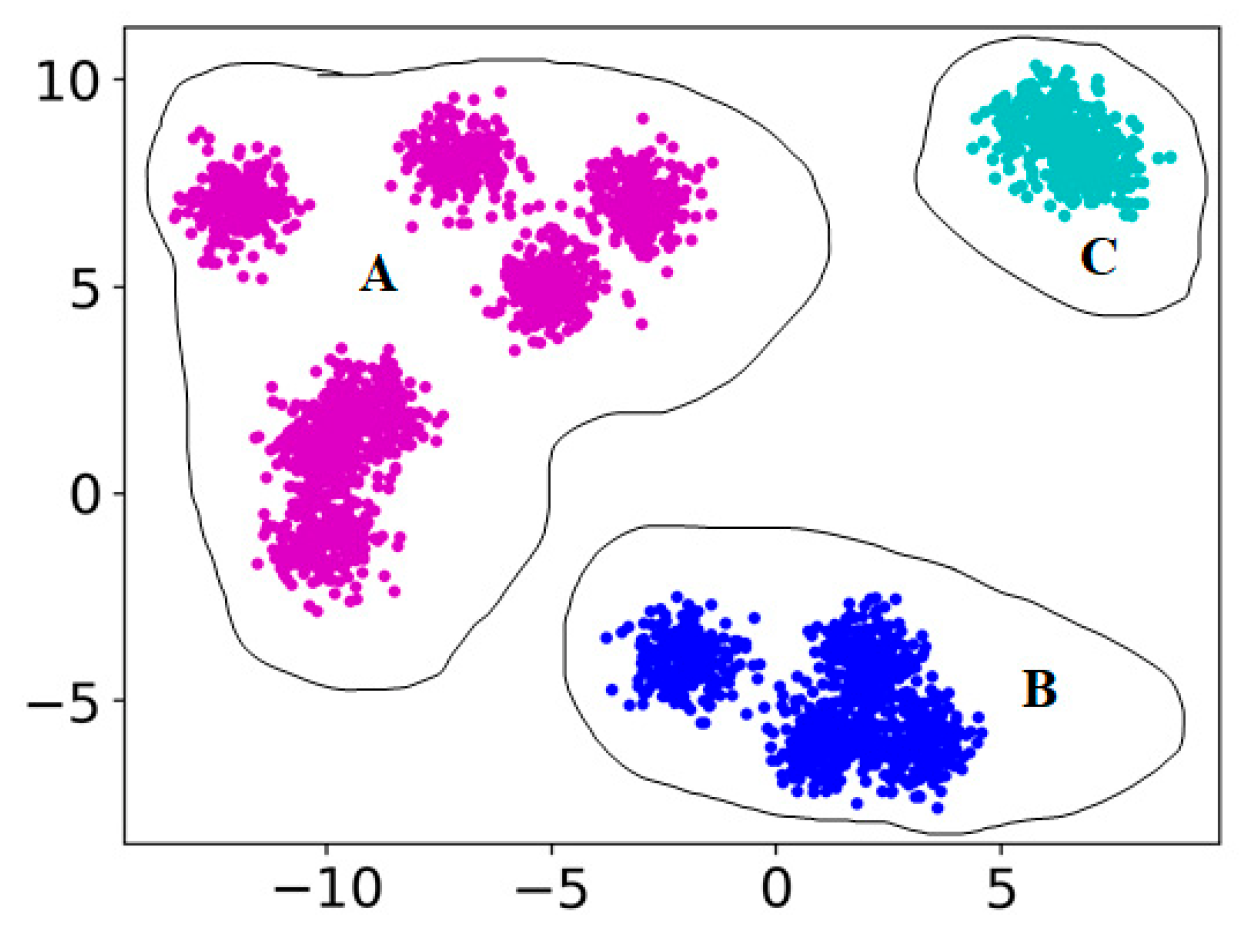
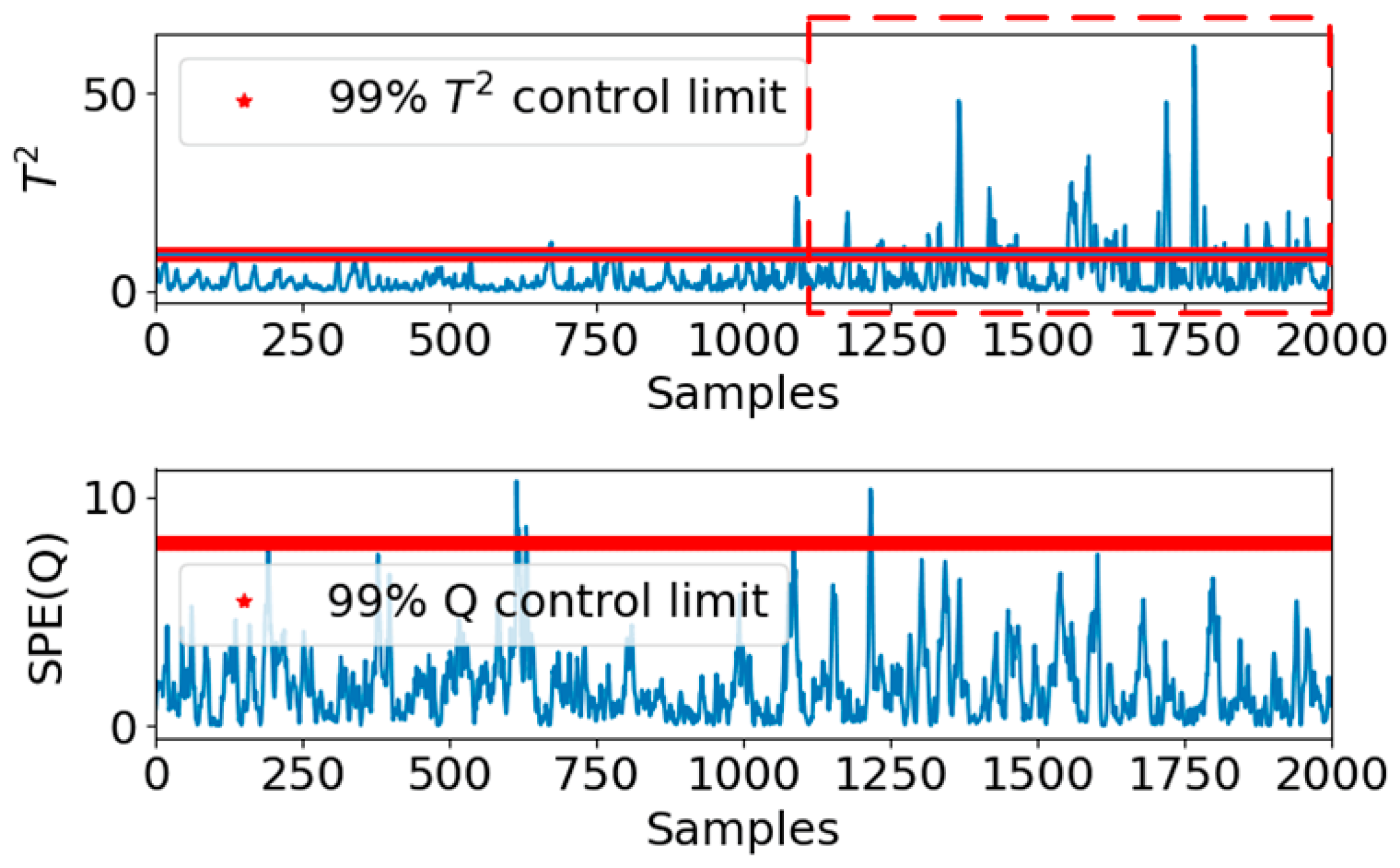
3.3. Fault Detection Results for Electric Valves
3.4. Fault Prediction Results for Electric Valves
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Z.; Cecati, C.; Ding, S.X. A Survey of Fault Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Techniques—Part I: Fault Diagnosis with Model-Based and Signal-Based Approaches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3757–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, B.; Jiang, X.; Jia, F.; Li, N.; Nandi, A.K. Applications of machine learning to machine fault diagnosis: A review and roadmap. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 138, 106587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, B.; Zio, E.; Chen, X. Artificial intelligence for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery: A review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 108, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhao, M.; Lin, J.; Liang, K. A comprehensive review on convolutional neural network in machine fault diagnosis. Neurocomputing 2020, 417, 36–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordestani, M.; Zanj, A.; Orchard, M.E.; Saif, M. A modular fault diagnosis and prognosis method for hydro-control valve system based on redundancy in multi-sensor data information. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2018, 68, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Pan, T.; Zheng, G. Fault diagnosis of electro-hydraulic servo valve using extreme learning machine. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, e12419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucesan, Y.A.; Dourado, A.; Viana, F. A survey of modeling for prognosis and health management of industrial equipment. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 101404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Shen, J.; Liu, S.; Su, Q.; Zhang, J. Research and Development of Electro-hydraulic Control Valves Oriented to Industry 4.0: A Review. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2020, 33, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djeziri, M.; Djedidi, O.; Benmoussa, S.; Bendahan, M.; Seguin, J.L. Failure Prognosis Based on Relevant Measurements Identification and Data-Driven Trend-Modeling: Application to a Fuel Cell System. Processes 2021, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, P.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, X.; Peng, X. A p−V Diagram Based Fault Identification for Compressor Valve by Means of Linear Discrimination Analysis. Machines 2022, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, S.; Song, Z.; Hu, Z.; Liu, F. Multi-Sensor Data Driven with PARAFAC-IPSO-PNN for Identification of Mechanical Nonstationary Multi-Fault Mode. Machines 2022, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Li, G.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Sun, S. An efficient VRF system fault diagnosis strategy for refrigerant charge amount based on PCA and dual neural network model. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 129, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Nie, C.; Xia, Y.; Zhan, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, L. Fault Critical Point Prediction Method of Nuclear Gate Valve with Small Samples Based on Characteristic Analysis of Operation. Materials 2022, 15, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Peng, M.; Wang, H. Study on the Condition Monitoring Technology of Electric Valve Based on Principal Component Analysis. In Proceedings of the International Congress and Workshop on Industrial AI 2021, Luleå, Sweden, 5–7 October 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Jiang, J.; Xu, A.; Huang, X.; Pei, C.; Sun, Y. Fault Detection of Pneumatic Control Valves Based on Canonical Variate Analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 13603–13615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Yu, X.; Ma, H.; Ye, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, X. Applications of Machine Learning to Reciprocating Compressor Fault Diagnosis: A Review. Processes 2021, 9, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Lu, R.; Wada, S.; Zhang, Y. Real-time penetration state monitoring using convolutional neural network for laser welding of tailor rolled blanks. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 54, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Hati, A.S. Review on machine learning algorithm based fault detection in induction motors. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, S.U.; Lee, Y.D.; Koo, I.S. A distributed sensor-fault detection and diagnosis framework using machine learning. Inf. Sci. 2021, 547, 777–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, G.; Thul, S.; Baranski, M.; Müller, D. Real-world application of machine-learning-based fault detection trained with experimental data. Energy 2020, 198, 117323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wu, N.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearing Based on Shift Invariant Sparse Feature and Optimized Support Vector Machine. Machines 2021, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Y.H. Artificial intelligence application in machine condition monitoring and fault diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Emerg. Trends Appl. 2018, 275, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.G.; Udmale, S.S.; Singh, S.K. Role of artificial intelligence in rotor fault diagnosis: A comprehensive review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 2609–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sony, S.; LaVenture, S.; Sadhu, A. A literature review of next-generation smart sensing technology in structural health monitoring. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.W.; Jin, T.; Yun, C.B. A review on deep learning-based structural health monitoring of civil infrastructures. Smart Struct. Syst. 2019, 24, 567–585. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Xiao, A.; Wu, E.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y. Transformer in transformer. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.; Green, B.; Ben, X.; O’Banion, S. Deep transformer models for time series forecasting: The influenza prevalence case. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.08317. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, W. Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting. In Proceedings of the AAAI virtually, New York, NY, USA, 2–9 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kitaev, N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Levskaya, A. Reformer: The efficient transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.04451. [Google Scholar]
- Correia, G.M.; Niculae, V.; Martins, A.F. Adaptively sparse transformers. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.00015. [Google Scholar]
- Beltagy, I.; Peters, M.E.; Cohan, A. Longformer: The long-document transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05150. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, U.K.; Pal, S. Data Mining: A prediction of performer or underperformer using classification. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1104.4163. [Google Scholar]
- Child, R.; Gray, S.; Radford, A.; Sutskever, I. Generating long sequences with sparse transformers. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.10509. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.; Le, Q.; Salakhutdinov, R. Transformer-xl: Attentive language models beyond a fixed-length context. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.02860. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.R.; Cho, J.; Yu, K. A systematic review on model selection in high-dimensional regression. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 2018, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, K.; Laverty, D.; Xue, Y. Synchrophasor-Based Islanding Detection for Distributed Generation Systems Using Systematic Principal Component Analysis Approaches. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2015, 30, 2544–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, Z.; Mourshed, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Feng, S. Electric Vehicle Charging Load Forecasting: A Comparative Study of Deep Learning Approaches. Energies 2019, 12, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, H.; Sun, B.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ling, J.; Feng, W. A parallel deep learning algorithm with applications in process monitoring and fault prediction. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 99, 107724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
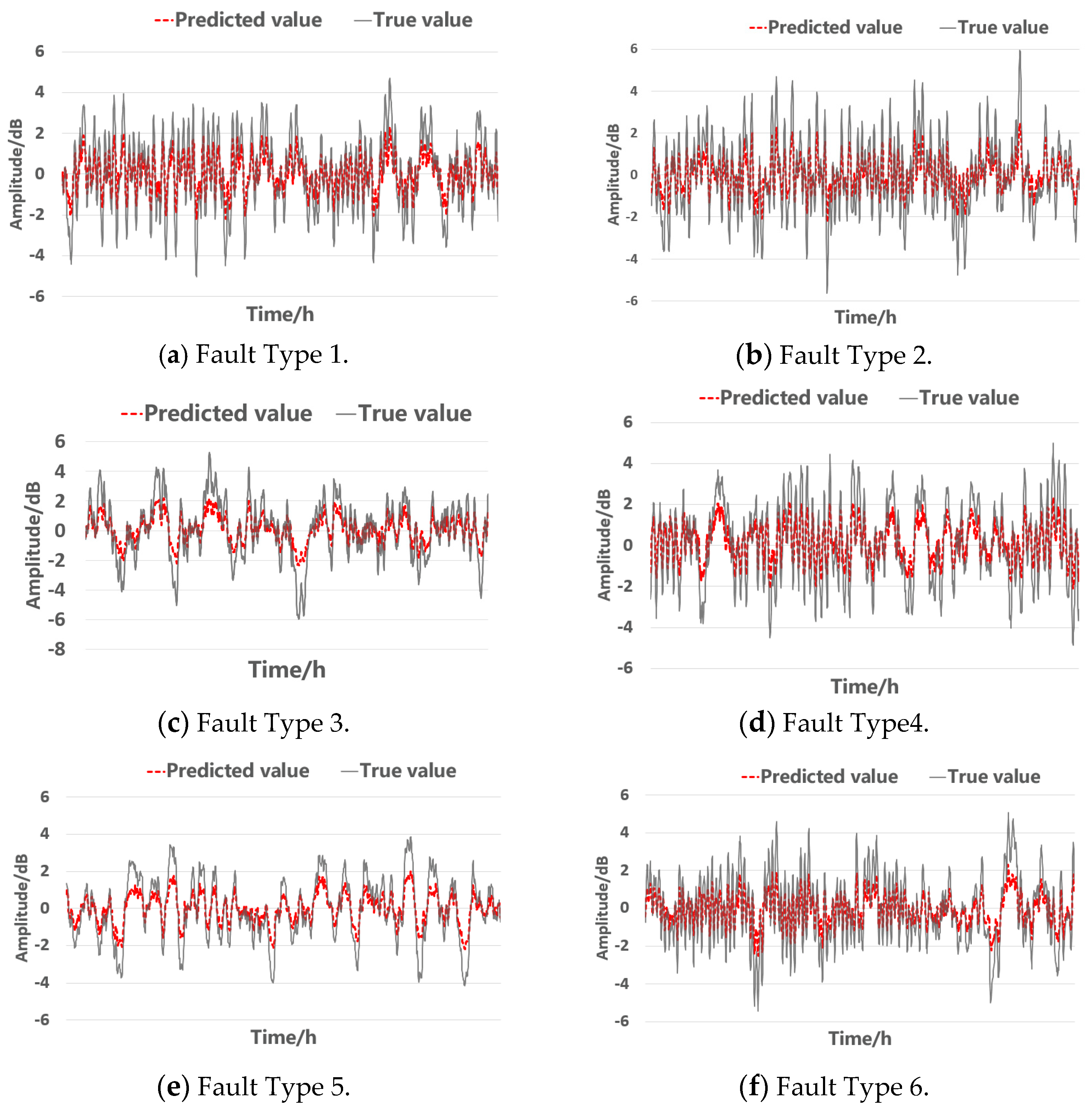
| True & Pred | MAE | MSE | RMSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0.5464955 | 0.49104416 | 0.7007454 | 2.1672266 |
| b | 0.5304586 | 0.45938802 | 0.6777817 | 2.4918344 |
| c | 0.6368491 | 0.70024675 | 0.83680749 | 5.0315237 |
| d | 0.5420266 | 0.46397582 | 0.6811577 | 8.153066 |
| e | 0.53628075 | 0.47729263 | 0.69086367 | 3.9367547 |
| f | 0.56860536 | 0.5392031 | 0.7343045 | 5.1112056 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, Z.; Cheng, L.; Guo, Y.; Ren, M.; Feng, W.; Sun, B.; Ling, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.; Luo, Y.; et al. A Novel Principal Component Analysis-Informer Model for Fault Prediction of Nuclear Valves. Machines 2022, 10, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10040240
An Z, Cheng L, Guo Y, Ren M, Feng W, Sun B, Ling J, Chen H, Chen W, Luo Y, et al. A Novel Principal Component Analysis-Informer Model for Fault Prediction of Nuclear Valves. Machines. 2022; 10(4):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10040240
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Zhao, Lan Cheng, Yuanjun Guo, Mifeng Ren, Wei Feng, Bo Sun, Jun Ling, Huanlin Chen, Weihua Chen, Yalin Luo, and et al. 2022. "A Novel Principal Component Analysis-Informer Model for Fault Prediction of Nuclear Valves" Machines 10, no. 4: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10040240
APA StyleAn, Z., Cheng, L., Guo, Y., Ren, M., Feng, W., Sun, B., Ling, J., Chen, H., Chen, W., Luo, Y., & Yang, Z. (2022). A Novel Principal Component Analysis-Informer Model for Fault Prediction of Nuclear Valves. Machines, 10(4), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10040240






