Optimal Placement of Sensors Based on Data Fusion for Condition Monitoring of Pulley Group under Speed Variation Condition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background of Theory
2.1. Refining Signal by Kalman Filter
2.2. Variable Periodicity Strength Calculation
2.3. Maximum Likelihood Estimation
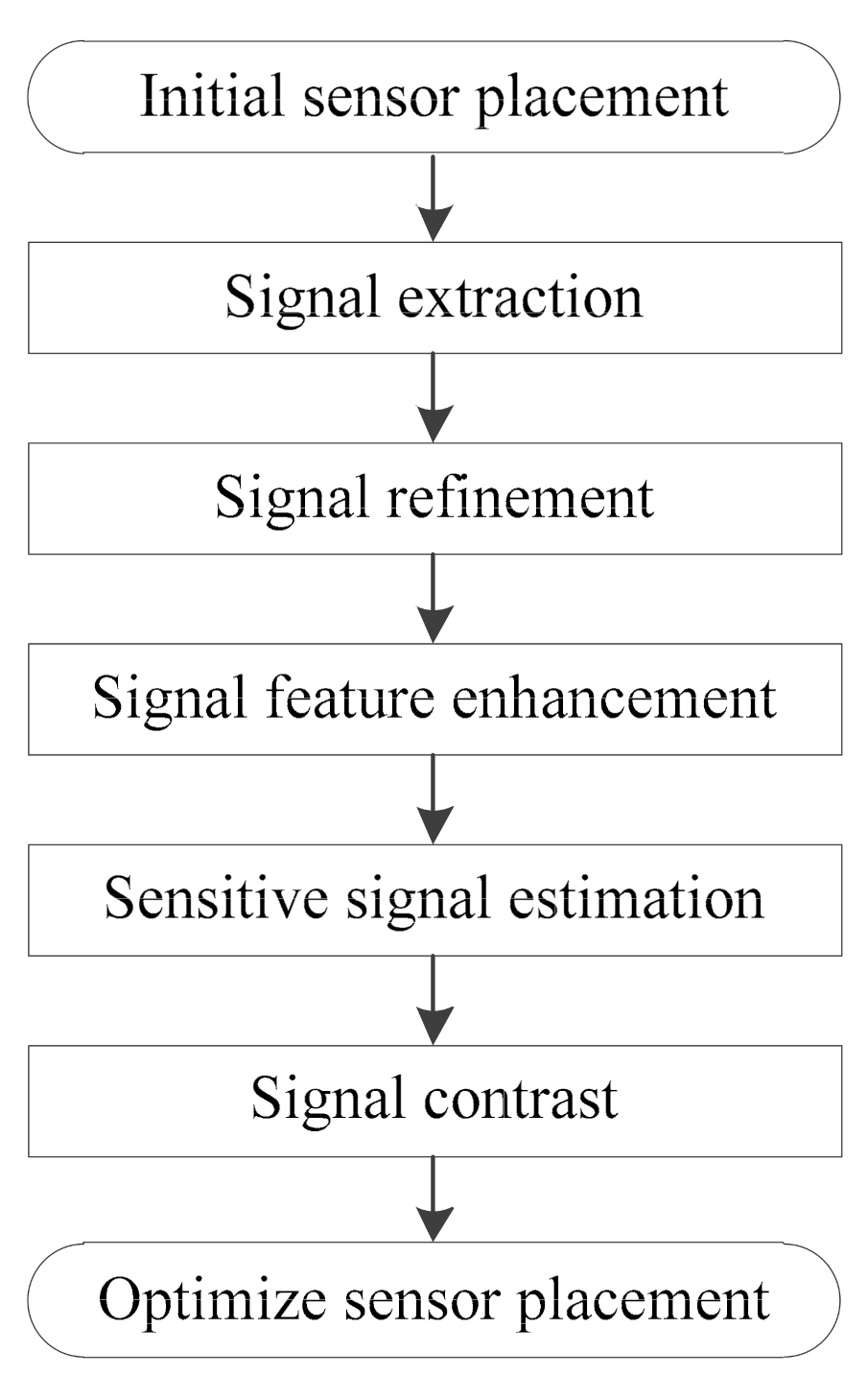
3. Procedure of the Proposed Optimal Sensor Placement Technique
3.1. Initial Sensor Placement
3.2. Signal Extraction
3.3. Signal Refinement
3.4. Signal Feature Enhancement
3.5. Sensitive Signal Estimation
3.6. Signal Contrast
3.7. Sensors Placement Evaluation
4. Experimental Validations on Transient Conditions
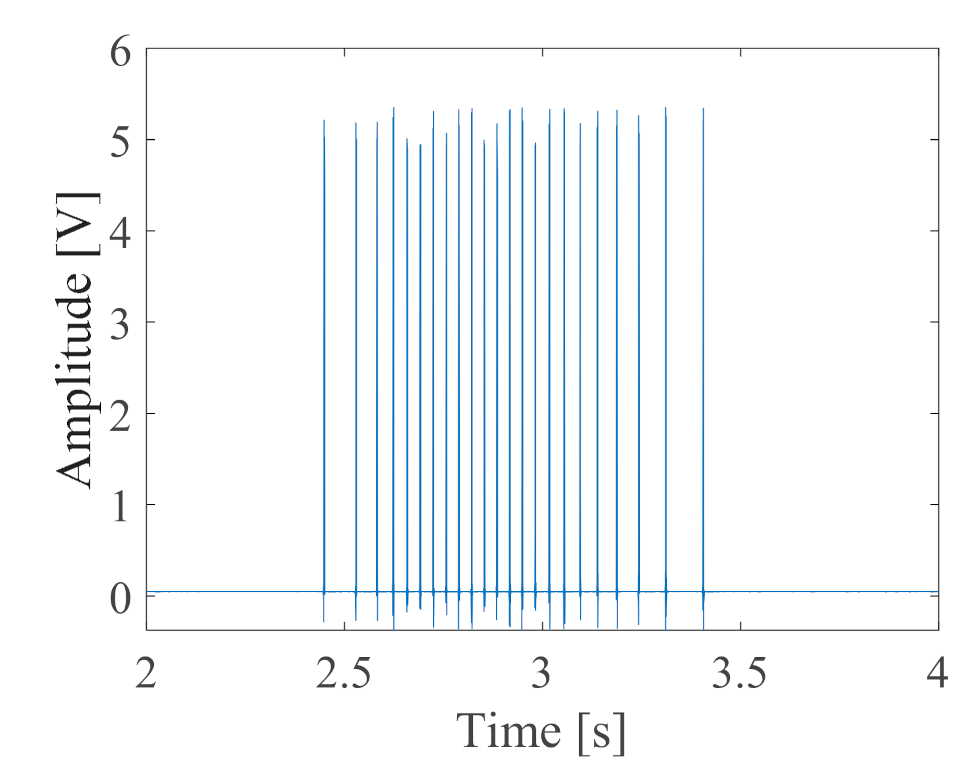
4.1. Experiment Setup
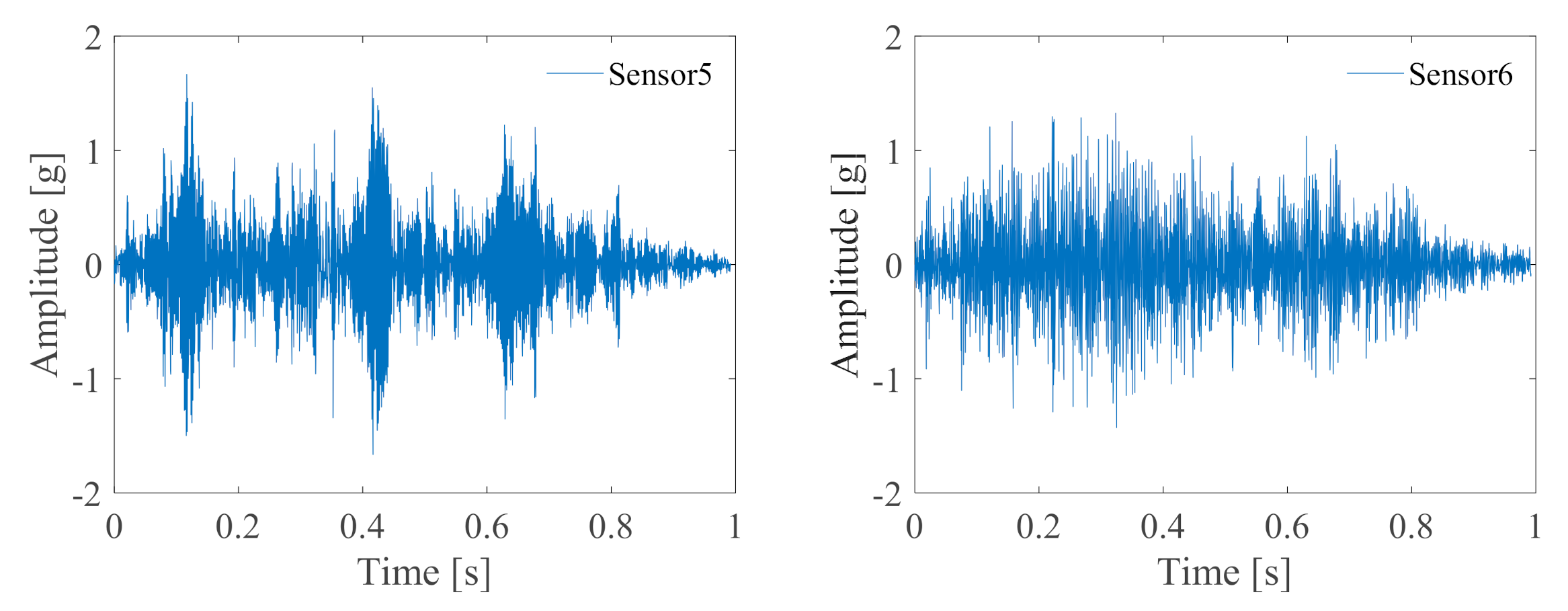
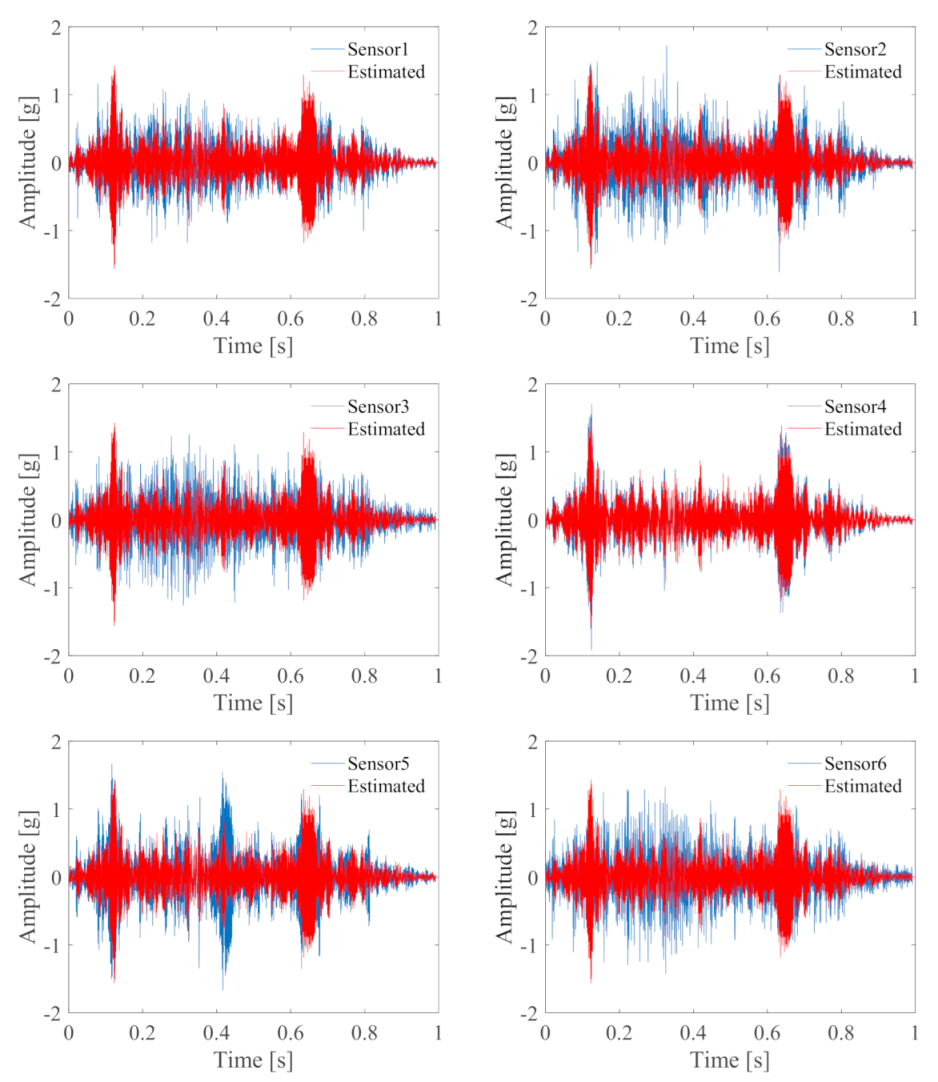
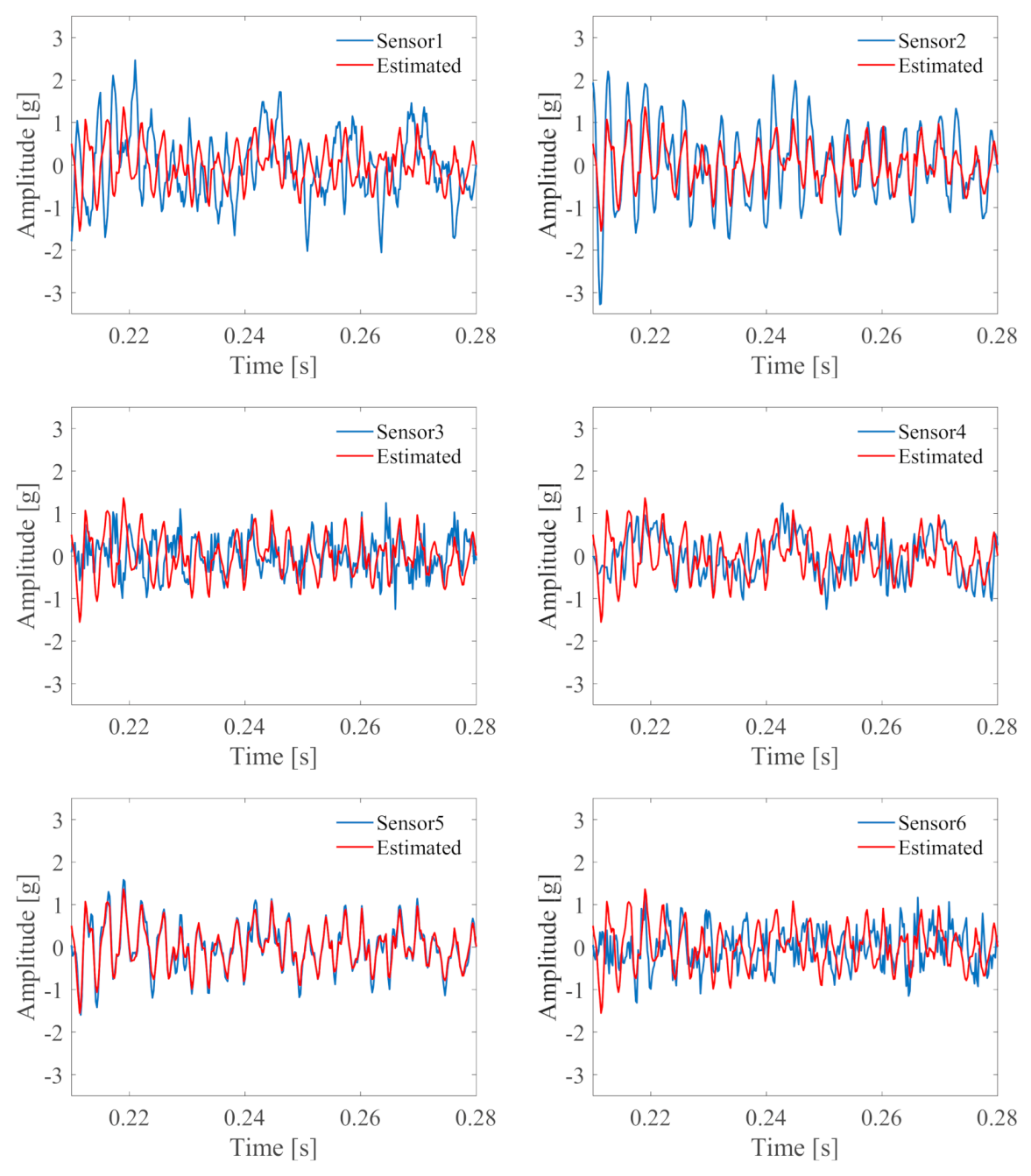
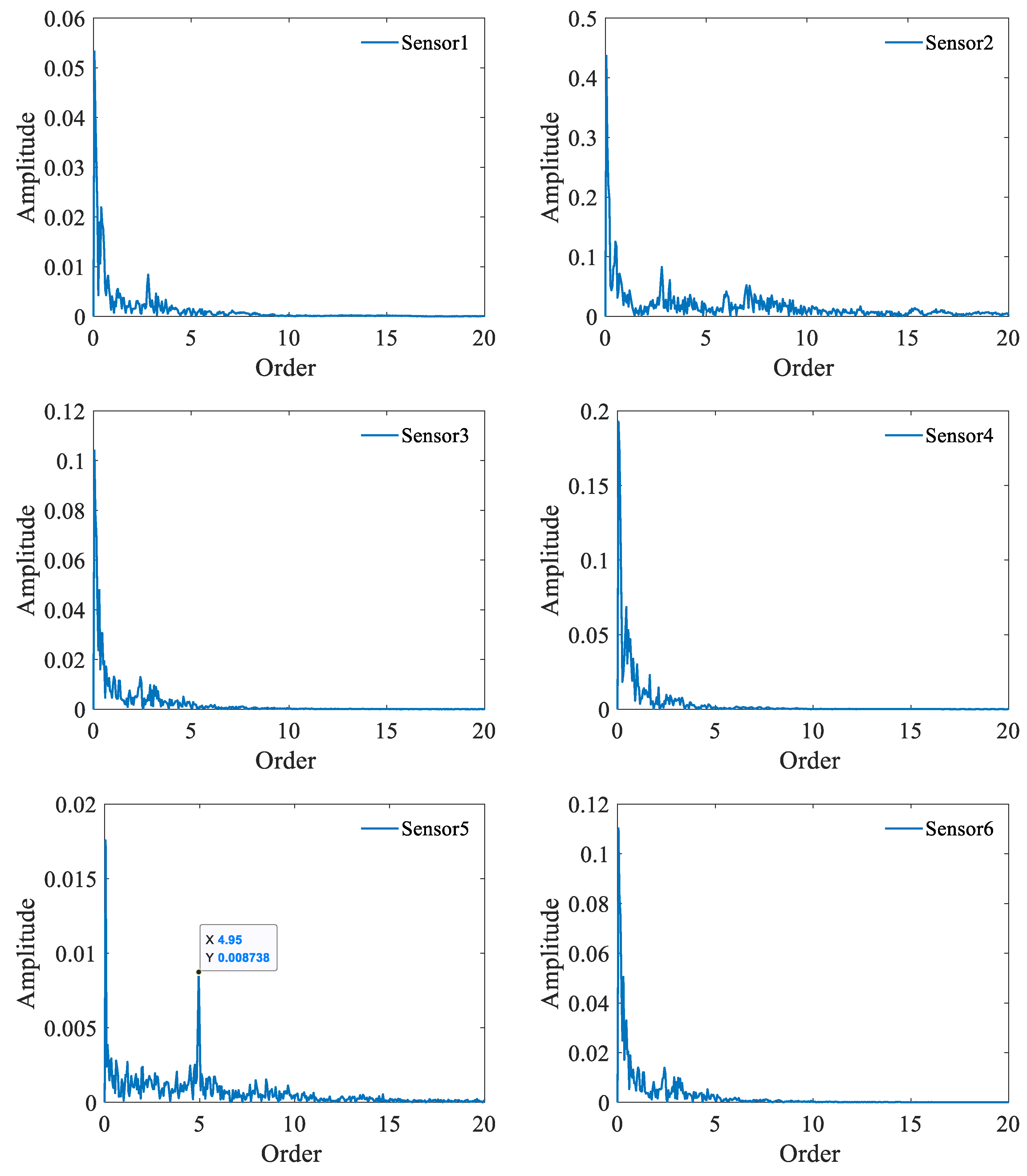
4.2. Data Processing and Verification
5. Conclusions
6. Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Han, L.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S. Design of a high-resolution instantaneous torque sensor based on the double-eccentric modulation principle. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 6595–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urda, P.; Aceituno, J.F.; Muñoz, S.; Escalona, J.L. Artificial neural networks applied to the measurement of lateral wheel-rail contact force: A comparison with a harmonic cancellation method. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 153, 103968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; Tang, Q.; Chen, Z. Modeling and nonlinear dynamics analysis of a rotating beam with dry friction support boundary conditions. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 498, 115978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayem, F.; Rivet, B.; Farias, R.C.; Jutten, C. Robust Sensor Placement for Signal Extraction. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 4513–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R. Noise power spectral density estimation based on optimal smoothing and minimum statistics. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio. Process. 2001, 9, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.; Guo, L.; Gao, H.; Zhang, L. Deep Coupled Joint Distribution Adaptation Network: A Method for Intelligent Fault Diagnosis Between Artificial and Real Damages. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.; Singh, A.; Guestrin, C. Near-optimal sensor placements in Gaussian processes: Theory, efficient algorithms and empirical studies. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 235–248. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ayoub, R.; Sundaram, S. Sensor selection for Kalman filtering of linear dynamical systems: Complexity, limitations and greedy algorithms. Automatica 2017, 78, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duro, J.A.; Padget, J.A.; Bowen, C.R.; Kim, H.A.; Nassehi, A. Multi-sensor data fusion framework for CNC machining monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Processing 2016, 66, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fortino, G.; Galzarano, S.; Gravina, R.; Li, W. A framework for collaborative computing and multi-sensor data fusion in body sensor networks. Inf. Fusion 2015, 22, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, A.; Hu, C.; Laflamme, S. Optimal sensor placement within a hybrid dense sensor network using an adaptive genetic algorithm with learning gene pool. Struct. Heal. Monit. 2018, 17, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayat, A.; Shaaban, H.; Giakas, G.; Lees, V.C. The pulley system of the thumb: Anatomic and biomechanical study. J. Hand Surg. 2002, 27, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; El Naggar, M.H.; Wang, K.; Wu, J. Three-dimensional axisymmetric analysis of pile vertical vibration. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 494, 115881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, J.T.; Klein, D.J.; Hespanha, J.P. Optimal sensor placement for time difference of arrival localization. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 48h IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) Held Jointly with 2009 28th Chinese Control Conference, Shanghai, China, 15–18 December 2019; pp. 7878–7884. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.Q.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y. Optimal coordinate sensor placements for estimating mean and variance components of variation sources. IIE Trans. 2005, 37, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.-H.; Li, H.-N.; Gu, M. A new method for optimal selection of sensor location on a high-rise building using simplified finite element model. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2011, 37, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyris, C.; Papadimitriou, C.; Panetsos, P. Bayesian Optimal Sensor Placement for Modal Identification of Civil Infrastructures. J. Smart Cities 2017, 2, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Lei, Y.; Cao, J. A tacho-less order tracking technique for large speed variations. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 40, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Q.; Han, L. In Processing Fault Detection of Machinery Based on Instantaneous Phase Signal. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 123535–123543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lei, Y.; Li, N.; Yan, T.; Li, N. Machinery health indicator construction based on convolutional neural networks considering trend burr. Neurocomputing 2018, 292, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piat, E.; Abadie, J.; Oster, S. Nanoforce estimation based on Kalman filtering and applied to a force sensor using diamagnetic levitation. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2012, 179, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L. Unbiased-estimation-based and computation-efficient adaptive MPC for four-wheel-independently-actuated electric vehicles. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 154, 104100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, T.R.; Wolf, W.R.; Moffitt, N.J.; Kreitzman, J.R.; Bent, P. Numerical noise prediction and source identification of a realistic landing gear. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 496, 115933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zi, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Z. A modified tacho-less order tracking method for the surveillance and diagnosis of machine under sharp speed variation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 128, 508–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Heyns, P.; De Villiers, J. A tacholess order tracking methodology based on a probabilistic approach to incorporate angular acceleration information into the maxima tracking process. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 100, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, L.; Zhao, M.; Li, P.; Xu, X. A convolutional neural network based feature learning and fault diagnosis method for the condition monitoring of gearbox. Measurement 2017, 111, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, I.J. Tutorial on maximum likelihood estimation. J. Math. Psychol. 2003, 47, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.R.A. On the mathematical foundations of theoretical statistics. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1922, 222, 309–368. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.-X.; Fang, K.-T. Maximum Likelihood Estimation, Growth Curve Models and Statistical Diagnostics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 77–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ghayem, F.; Rivet, B.; Jutten, C.; Farias, R.C. Gradient-based algorithm with spatial regularization for optimal sensor placement. In Proceeding of the ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 5655–5659. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Byun, N.; Shin, D.H. A Damage Localization Approach for Rahmen Bridge Based on Convolutional Neural Network. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Vasudevan, V.; Ramanathan, C.; Jia, P. Non-Local Mean Filtering for Electrophysiological Signals. U.S. Patent No. 9,974,458, 22 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, P.F.; Davi, G.S.; Friday, R.J. Location of Wireless Nodes Using Signal Strength Weighting Metric. U.S. Patent No. 7,116,988, 3 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mabkhot, M.M.; Darmoul, S.; Al-Samhan, A.M.; Badwelan, A. A Multi-Criteria Decision Framework Considering Different Levels of Decision-Maker Involvement to Reconfigure Manufacturing Systems. Machines 2020, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, P.; West, S.G.; Aiken, L.S. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi. Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Lin, J.; Xu, X.; Lei, Y. Tacholess Envelope Order Analysis and Its Application to Fault Detection of Rolling Element Bearings with Varying Speeds. Sensors 2013, 13, 10856–10875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Han, L.; Zhou, Y. Quantitative evaluation of the impurity content of grease for low-speed heavy-duty bearing using an acoustic emission technique. Meas. Control 2019, 52, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
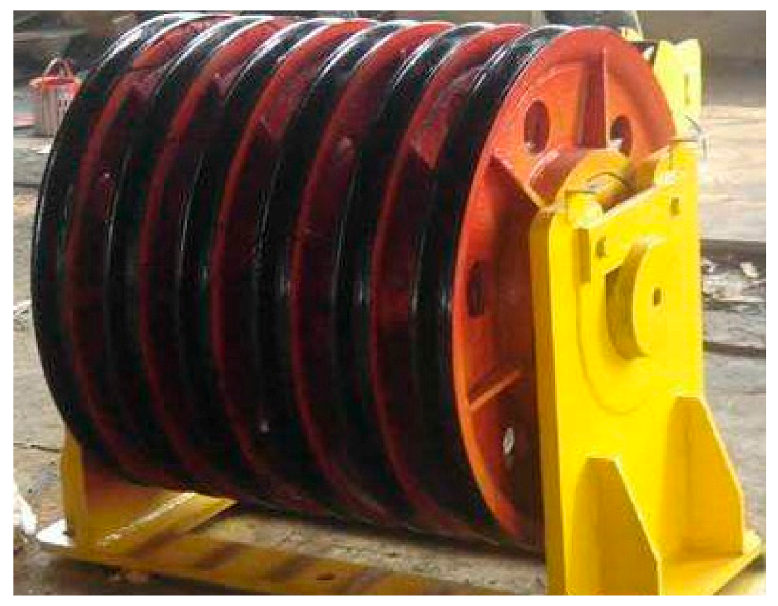
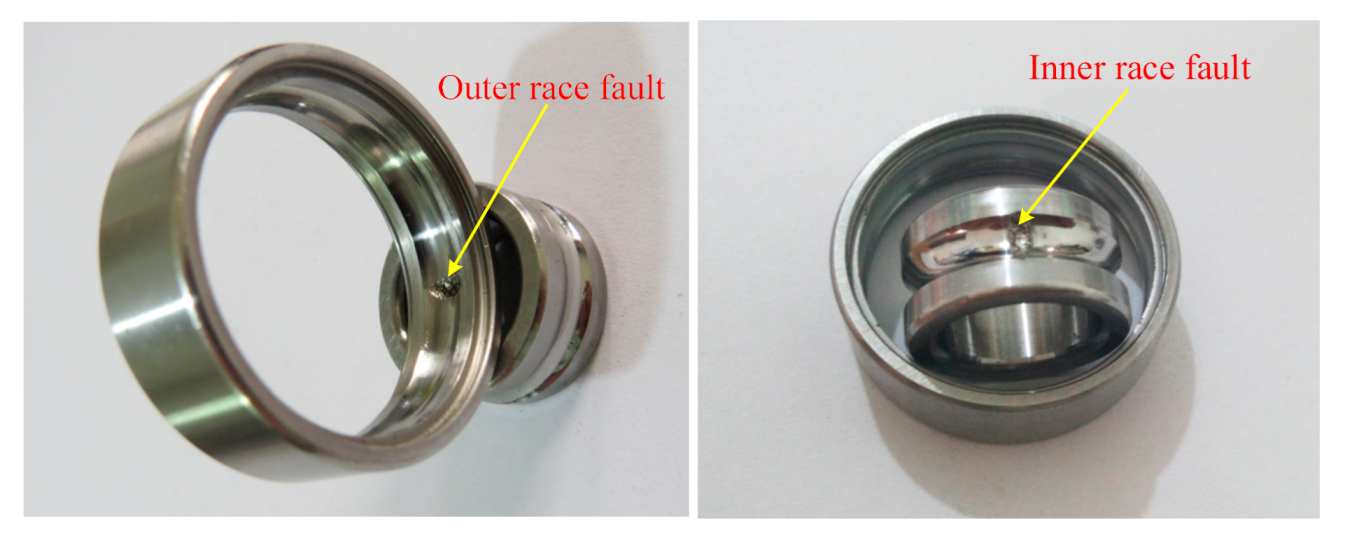








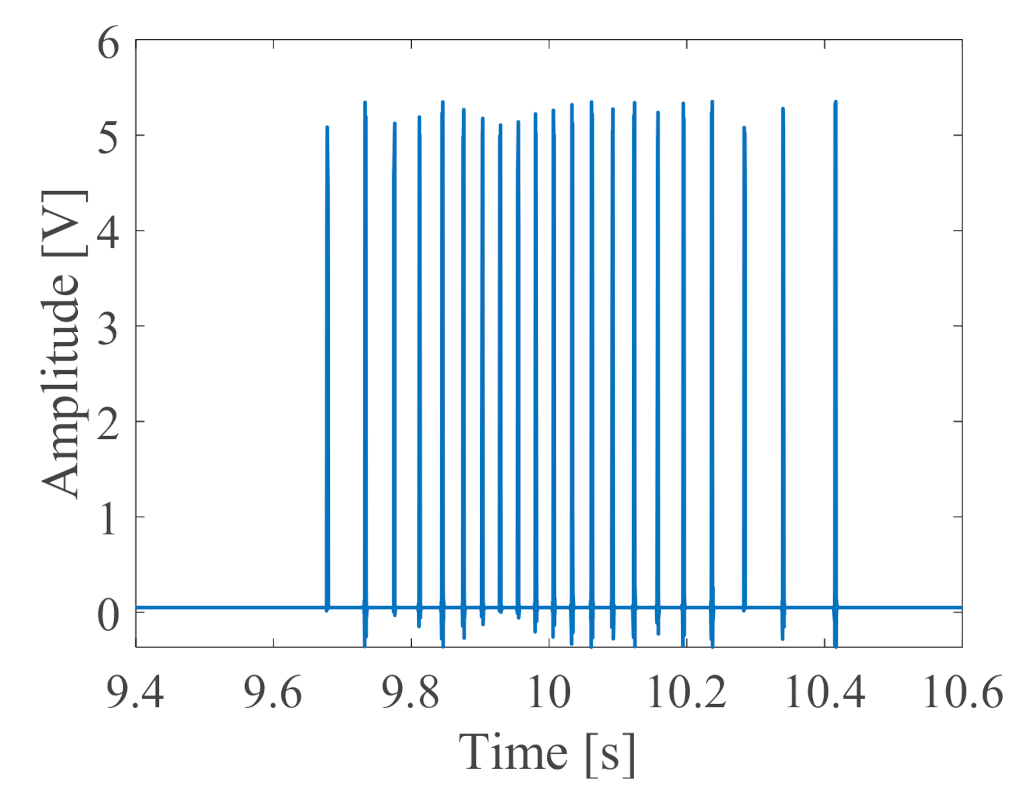
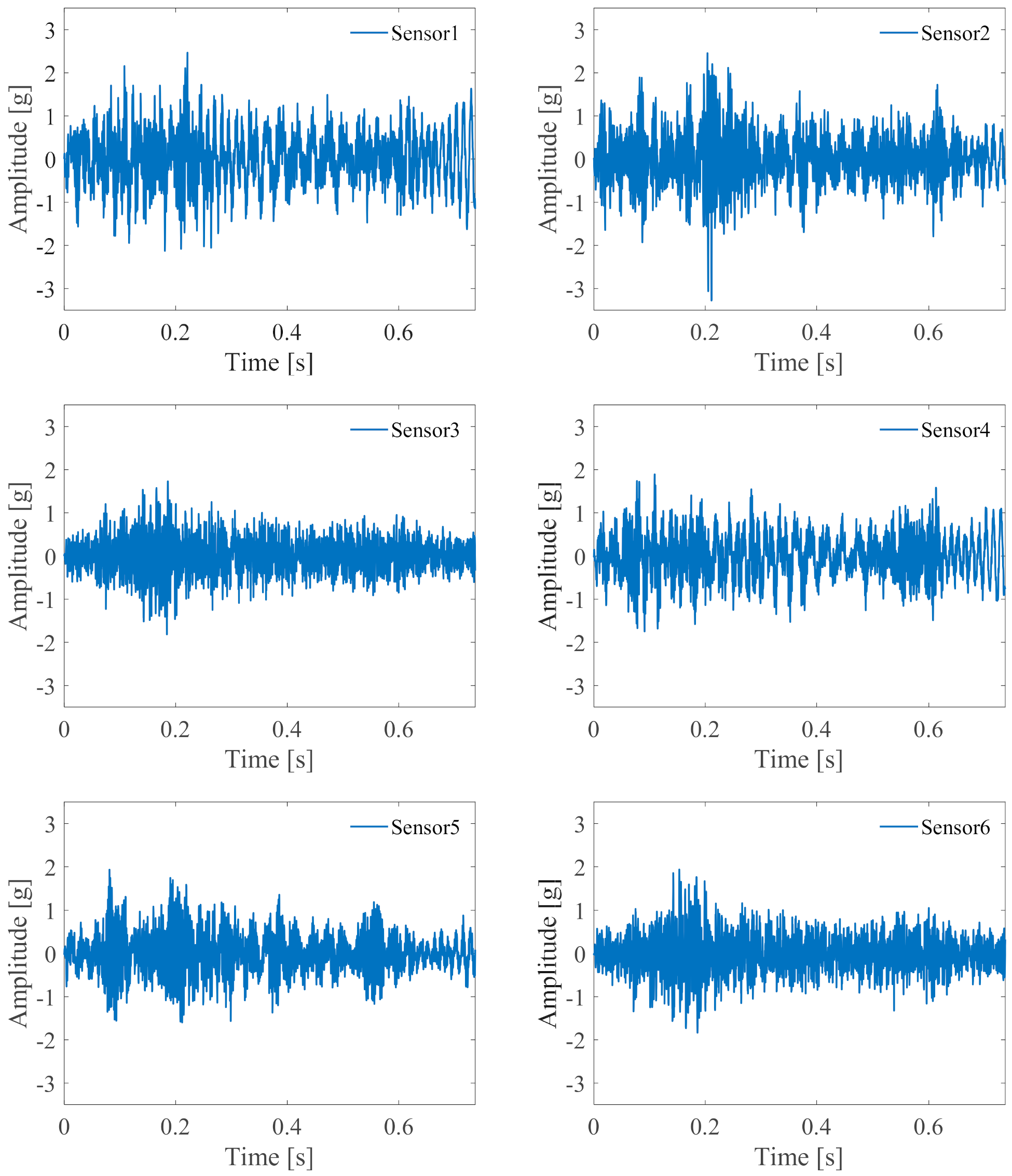
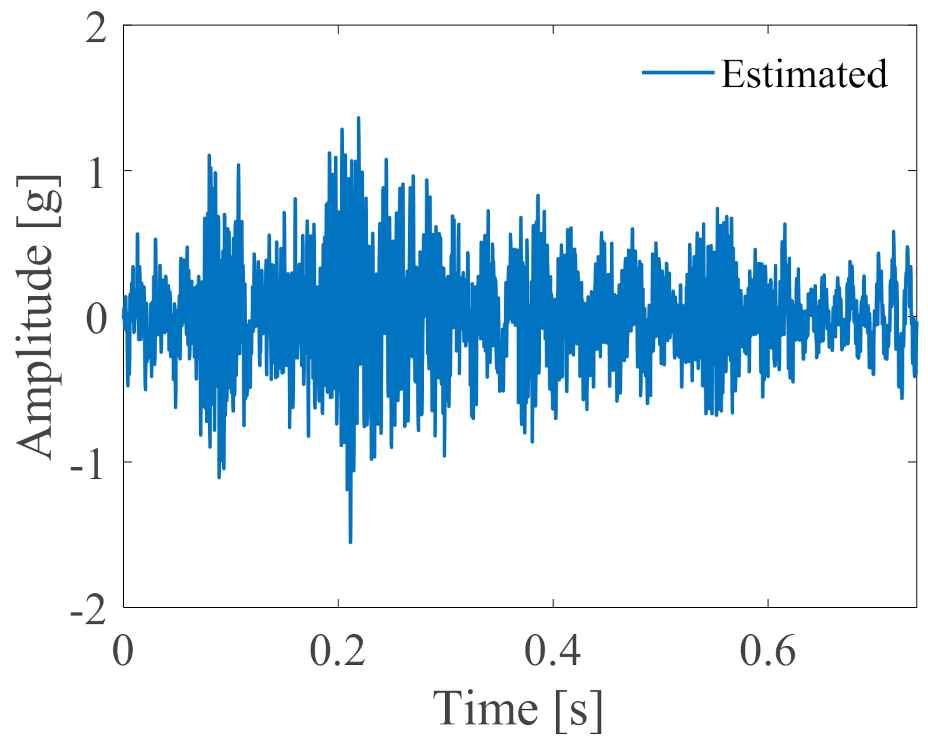

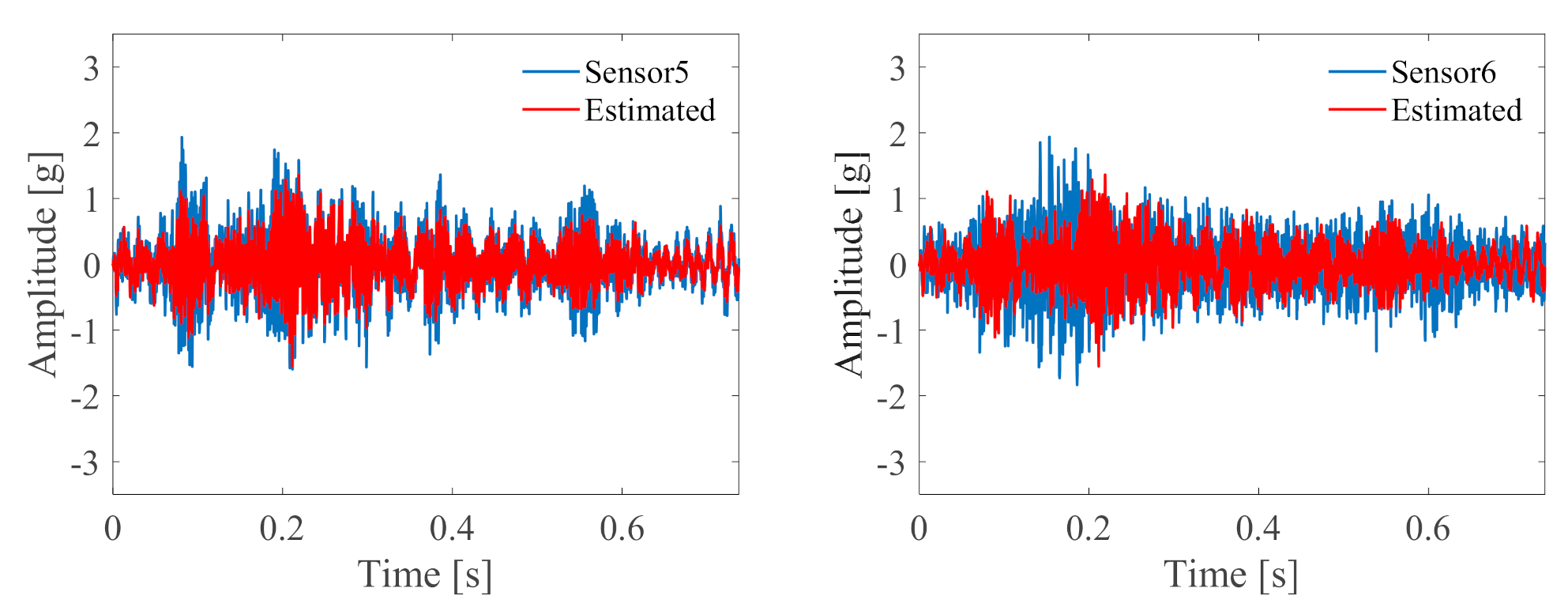
| Roller Diameter (mm) | Pitch Diameter (mm) | Contact Angle (Degree) | Number of Rollers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 25 | 15 | 8 |
| Items | NBCFs in Order |
|---|---|
| BPFO | 3.0727 |
| BPFI | 4.9272 |
| BSF | 1.9714 |
| Sensor | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Fault deep 0.15 mm | ||||||
| Rotation speed: 1200 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.8378 | 0.65118 | 0.11872 | 0.79489 | 0.43821 | −0.092311 |
| 2 | −0.043148 | −0.21816 | 0.083649 | 0.68746 | 0.26696 | −0.064068 |
| 3 | 0.81171 | 0.63377 | 0.11713 | 0.75772 | 0.39468 | −0.0821 |
| 4 | 0.88134 | 0.77305 | 0.10273 | 0.86465 | 0.65758 | −0.065752 |
| Rotation speed: 1500 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | −0.13319 | 0.18459 | 0.2272 | −0.14122 | 0.80972 | 0.17178 |
| 2 | 0.38469 | 0.86491 | −0.14787 | −0.021357 | 0.014771 | 0.24464 |
| 3 | −0.0042855 | −0.19781 | 0.2531 | 0.89836 | −0.21098 | −0.1662 |
| 4 | −0.11907 | −0.21735 | 0.27394 | 0.14633 | 0.83721 | 0.049634 |
| Rotation speed: 1800 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.014726 | 0.54459 | −0.17195 | 0.076277 | 0.77362 | 0.33751 |
| 2 | 0.35303 | 0.44771 | −0.096397 | 0.29201 | 0.82486 | 0.25566 |
| 3 | 0.19818 | 0.48196 | −0.21451 | 0.1379 | 0.8096 | 0.33548 |
| 4 | −0.12076 | 0.66541 | −0.23356 | −0.16056 | 0.60031 | 0.45627 |
| Rotation speed: 2000 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.052065 | 0.7064 | −0.048851 | −0.49595 | 0.57692 | 0.28651 |
| 2 | −0.5829 | −0.02877 | 0.14892 | 0.92297 | −0.16231 | 0.034755 |
| 3 | 0.48612 | 0.36457 | 0.050586 | 0.53298 | 0.85274 | 0.15909 |
| 4 | 0.26348 | 0.53061 | −0.26052 | 0.28457 | 0.80696 | 0.30294 |
| Rotation speed: 2200 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.33239 | 0.14154 | 0.06525 | 0.54739 | 0.8587 | 0.19482 |
| 2 | 0.70272 | 0.59215 | 0.14437 | 0.53196 | −0.22917 | −0.14489 |
| 3 | 0.33919 | 0.27357 | −0.03602 | 0.47337 | 0.9445 | 0.12273 |
| 4 | 0.467 | 0.24703 | 0.036992 | 0.64429 | 0.8477 | 0.16971 |
| Rotation speed: 2500 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.85301 | 0.66882 | 0.17658 | 0.82162 | 0.28622 | −0.18471 |
| 2 | 0.85088 | 0.69699 | 0.1864 | 0.83002 | 0.44305 | −0.14017 |
| 3 | 0.8317 | 0.6277 | 0.087378 | 0.77267 | 0.11598 | −0.10468 |
| 4 | 0.48575 | −0.035884 | 0.21363 | 0.78474 | 0.22605 | 0.065409 |
| Fault deep 0.05 mm | ||||||
| Rotation speed: 1200 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | −0.56671 | −0.19487 | −0.024053 | −0.054572 | 0.62178 | 0.38272 |
| 2 | −0.36415 | −0.27012 | −0.0083773 | 0.36407 | 0.66405 | 0.34641 |
| 3 | 0.752 | 0.63308 | 0.065164 | 0.45277 | −0.052138 | −0.23672 |
| 4 | 0.8217 | 0.65458 | 0.031942 | 0.72359 | 0.28336 | −0.13674 |
| Rotation speed: 1500 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | −0.15253 | 0.33123 | 0.25596 | 0.26764 | 0.83146 | −0.020051 |
| 2 | −0.17953 | 0.16843 | 0.20128 | 0.62737 | 0.66717 | 0.07225 |
| 3 | 0.084364 | 0.046028 | 0.21814 | 0.76107 | −0.16335 | 0.10599 |
| 4 | −0.17227 | 0.44514 | 0.17006 | 0.74056 | 0.16786 | 0.0033331 |
| Rotation speed: 1800 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.93467 | 0.43286 | −0.041334 | 0.77831 | 0.24774 | −0.10228 |
| 2 | 0.89796 | 0.6179 | 0.011283 | 0.84089 | 0.64185 | −0.054629 |
| 3 | 0.92433 | 0.68623 | −0.047705 | 0.90295 | 0.55805 | −0.097335 |
| 4 | 0.90296 | 0.65449 | 0.073867 | 0.86005 | 0.60988 | −0.076486 |
| Rotation speed: 2000 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.90758 | 0.64251 | 0.00088641 | 0.85778 | 0.65353 | −0.12146 |
| 2 | 0.68443 | 0.63261 | 0.15101 | 0.33907 | −0.29137 | −0.16928 |
| 3 | 0.85686 | 0.63724 | −0.010471 | 0.70741 | 0.3065 | −0.090043 |
| 4 | −0.52338 | 0.042015 | 0.12485 | 0.92774 | −0.081668 | 0.036343 |
| Rotation speed: 2200 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.86625 | 0.68243 | 0.061761 | 0.76309 | 0.28737 | −0.11667 |
| 2 | 0.86654 | 0.64276 | −0.10236 | 0.79173 | 0.1828 | −0.067055 |
| 3 | 0.83913 | 0.72018 | 0.050905 | 0.72879 | 0.40057 | −0.086646 |
| 4 | −0.27576 | 0.31614 | 0.15722 | 0.80876 | 0.25902 | 0.027931 |
| Rotation speed: 2500 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.91112 | 0.70128 | 0.0010863 | 0.88614 | 0.47057 | −0.11252 |
| 2 | 0.92646 | −0.089778 | 0.078002 | −0.36902 | −0.044464 | 0.036145 |
| 3 | 0.92546 | 0.61891 | −0.056825 | 0.85057 | 0.39395 | −0.017999 |
| 4 | 0.89949 | 0.67274 | −0.031394 | 0.85101 | 0.32548 | −0.026165 |
| Sensor | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Fault deep 0.15 mm | ||||||
| Rotation speed: 1200 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.85222 | 0.80894 | 0.14656 | 0.8317 | 0.7761 | −0.12351 |
| 2 | 0.635 | 0.75966 | 0.021778 | 0.15385 | −0.23207 | −0.15742 |
| 3 | 0.84931 | 0.80969 | 0.097673 | 0.83221 | 0.7561 | −0.094068 |
| 4 | 0.57979 | 0.80772 | 0.39349 | 0.24828 | 0.30959 | −0.32808 |
| Rotation speed: 1500 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | −0.089883 | 0.75002 | 0.090207 | 0.52179 | −0.028005 | −0.012712 |
| 2 | −0.047119 | 0.87901 | 0.1042 | 0.45217 | 0.20205 | −0.084225 |
| 3 | 0.5434 | 0.89041 | −0.0013436 | 0.32829 | 0.20908 | 0.00045367 |
| 4 | 0.61124 | 0.8546 | −0.10885 | 0.3909 | 0.1033 | 0.031138 |
| Rotation speed: 1800 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.7229 | 0.7608 | 0.012759 | 0.56229 | 0.40134 | −0.040798 |
| 2 | 0.69986 | 0.80329 | −0.073716 | 0.44789 | 0.22955 | −0.056911 |
| 3 | −0.073006 | 0.89297 | −0.081045 | −0.044191 | −0.21683 | 0.27441 |
| 4 | 0.62677 | 0.80844 | 0.038352 | 0.2657 | 0.31363 | −0.059033 |
| Rotation speed: 2000 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.28086 | 0.78433 | −0.065503 | 0.56802 | 0.44363 | 0.13578 |
| 2 | −0.38273 | −0.031148 | 0.06302 | 0.56622 | 0.27928 | 0.33542 |
| 3 | −0.14853 | 0.37444 | −0.033463 | 0.65276 | 0.43524 | 0.28784 |
| 4 | 0.77726 | 0.79265 | −0.010774 | 0.65349 | 0.36161 | −0.06578 |
| Rotation speed: 2200 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.16433 | −0.40993 | 0.21264 | 0.50507 | 0.1662 | 0.23851 |
| 2 | 0.73282 | 0.79497 | 0.028773 | 0.55605 | 0.25377 | −0.043044 |
| 3 | 0.6554 | 0.80358 | 0.076363 | 0.39302 | 0.22082 | −0.098408 |
| 4 | −0.33601 | −0.23633 | −0.073196 | 0.47326 | 0.5384 | 0.3367 |
| Rotation speed: 2500 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.82171 | 0.79182 | 0.025922 | 0.76555 | 0.4813 | −0.03199 |
| 2 | 0.78961 | 0.77521 | 0.027878 | 0.71427 | 0.40341 | −0.066361 |
| 3 | 0.49003 | 0.14903 | 0.28202 | 0.54463 | 0.53912 | 0.19294 |
| 4 | 0.45572 | 0.15463 | 0.27297 | 0.51557 | 0.53071 | 0.22422 |
| Fault deep 0.05 mm | ||||||
| Rotation speed: 1200 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.47224 | 0.39688 | 0.0031098 | −0.36572 | 0.70526 | −0.10261 |
| 2 | 0.73195 | 0.39799 | 0.056075 | −0.19251 | 0.33247 | −0.11556 |
| 3 | 0.85011 | 0.7358 | −0.24076 | 0.88144 | 0.85558 | 0.017053 |
| 4 | 0.64949 | 0.2298 | 0.1132 | 0.73672 | 0.49208 | −0.14148 |
| Rotation speed: 1500 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | −0.2455 | −0.13281 | 0.064996 | 0.88644 | −0.011725 | 0.079 |
| 2 | −0.24229 | 0.081754 | 0.045735 | 0.88946 | 0.041405 | 0.12309 |
| 3 | −0.30565 | −0.029588 | 0.031872 | 0.88732 | −0.02027 | 0.14228 |
| 4 | −0.29568 | −0.14833 | 0.022611 | 0.91927 | −0.114 | 0.12348 |
| Rotation speed: 1800 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | −51856 | 0.12851 | 0.031689 | 0.80088 | 0.23675 | 0.14782 |
| 2 | −0.54423 | 0.035093 | 0.012266 | 0.71599 | 0.22533 | 0.15864 |
| 3 | 0.7953 | −0.051934 | 0.0010735 | 0.43961 | 0.26138 | 0.21675 |
| 4 | 0.74131 | −0.12023 | 0.030104 | 0.67233 | −0.085943 | 0.15108 |
| Rotation speed: 2000 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | −0.41393 | 0.43174 | −0.081223 | 0.16217 | 0.72819 | 0.2286 |
| 2 | −0.46523 | 0.29217 | 0.15186 | 0.80546 | −0.02025 | 0.2303 |
| 3 | 0.68807 | 0.005264 | 0.033171 | 0.42976 | 0.29325 | 0.29485 |
| 4 | −0.67026 | −0.10662 | 0.060586 | 0.77671 | −0.11205 | 0.21197 |
| Rotation speed: 2200 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | −0.49894 | −0.01889 | 0.026208 | 0.91044 | −0.065445 | 0.11508 |
| 2 | 0.59437 | 0.65167 | 0.028777 | 0.46976 | 0.70036 | −0.13214 |
| 3 | −0.51633 | 0.031794 | −0.001065 | 0.92324 | −0.12045 | 0.14602 |
| 4 | −0.45987 | 0.38318 | −0.15735 | 0.18096 | 0.78355 | 0.21148 |
| Rotation speed: 2500 rpm | ||||||
| 1 | 0.83551 | 0.62807 | 0.15112 | 0.60059 | 0.42709 | −0.1545 |
| 2 | 0.030564 | 0.57096 | 0.023839 | 0.36198 | 0.92309 | 0.036917 |
| 3 | 0.66233 | 0.62634 | −0.047639 | 0.60311 | 0.7225 | −0.07839 |
| 4 | −0.15939 | 0.23821 | −0.1485 | 0.28316 | 0.91078 | 0.22182 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Zi, Y.; Ma, H.; Wu, Y.; Xue, X. Optimal Placement of Sensors Based on Data Fusion for Condition Monitoring of Pulley Group under Speed Variation Condition. Machines 2022, 10, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10020148
Wu J, Zi Y, Ma H, Wu Y, Xue X. Optimal Placement of Sensors Based on Data Fusion for Condition Monitoring of Pulley Group under Speed Variation Condition. Machines. 2022; 10(2):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10020148
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jie, Yanyang Zi, Hongru Ma, Yaochun Wu, and Xiaofeng Xue. 2022. "Optimal Placement of Sensors Based on Data Fusion for Condition Monitoring of Pulley Group under Speed Variation Condition" Machines 10, no. 2: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10020148
APA StyleWu, J., Zi, Y., Ma, H., Wu, Y., & Xue, X. (2022). Optimal Placement of Sensors Based on Data Fusion for Condition Monitoring of Pulley Group under Speed Variation Condition. Machines, 10(2), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10020148





