An Elaborate Dynamic Model of the Dual-Motor Precision Transmission Mechanism for Performance Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Component Modeling
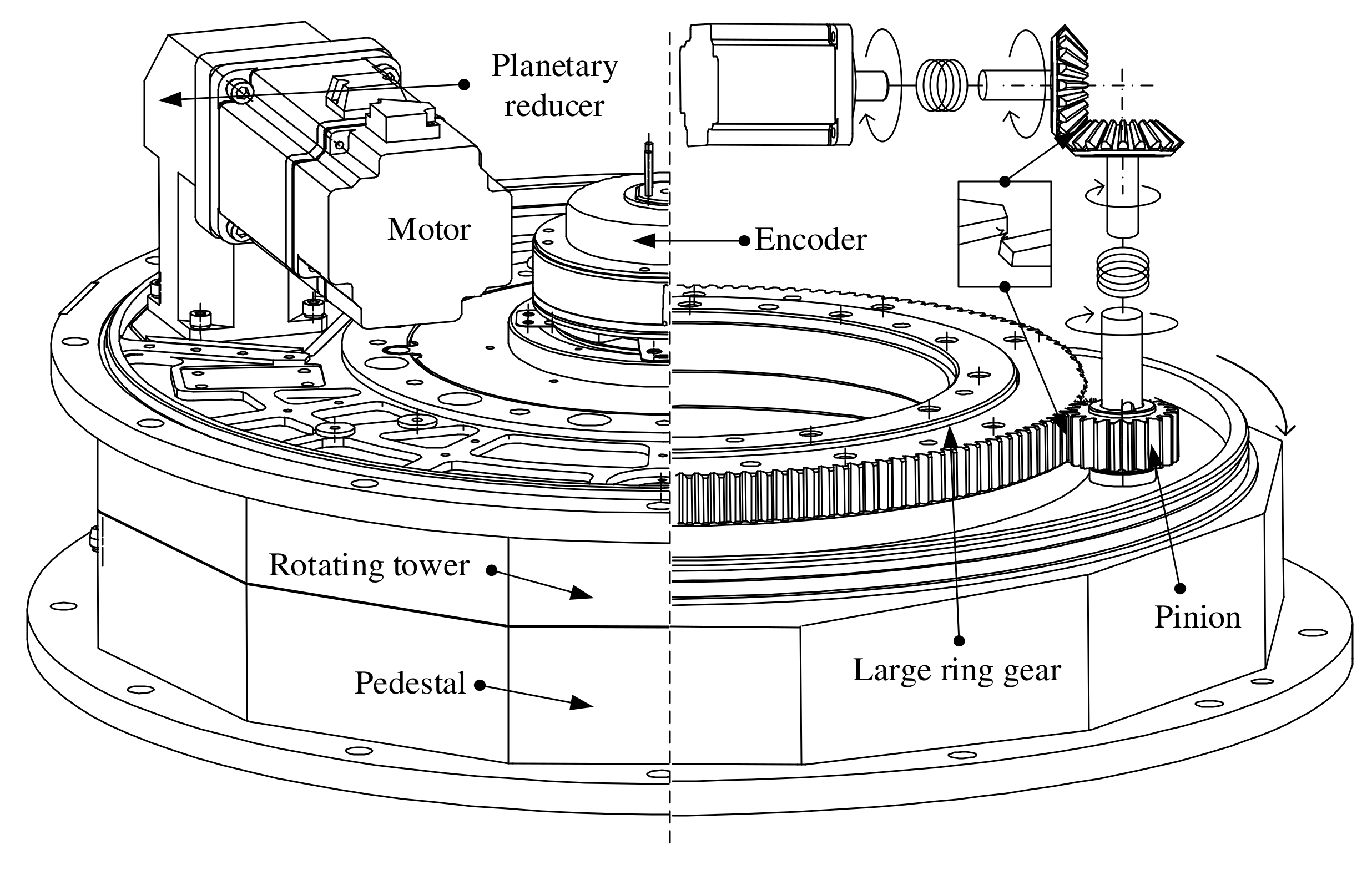
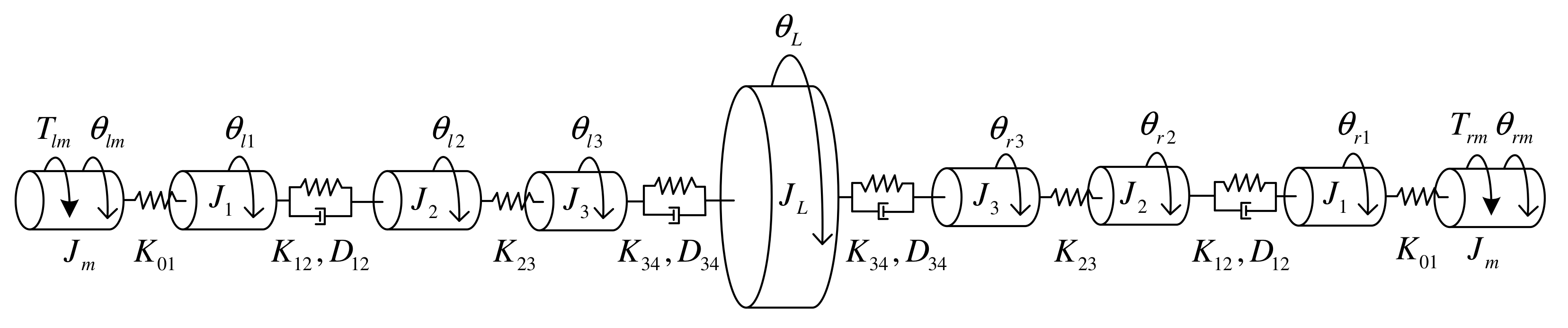
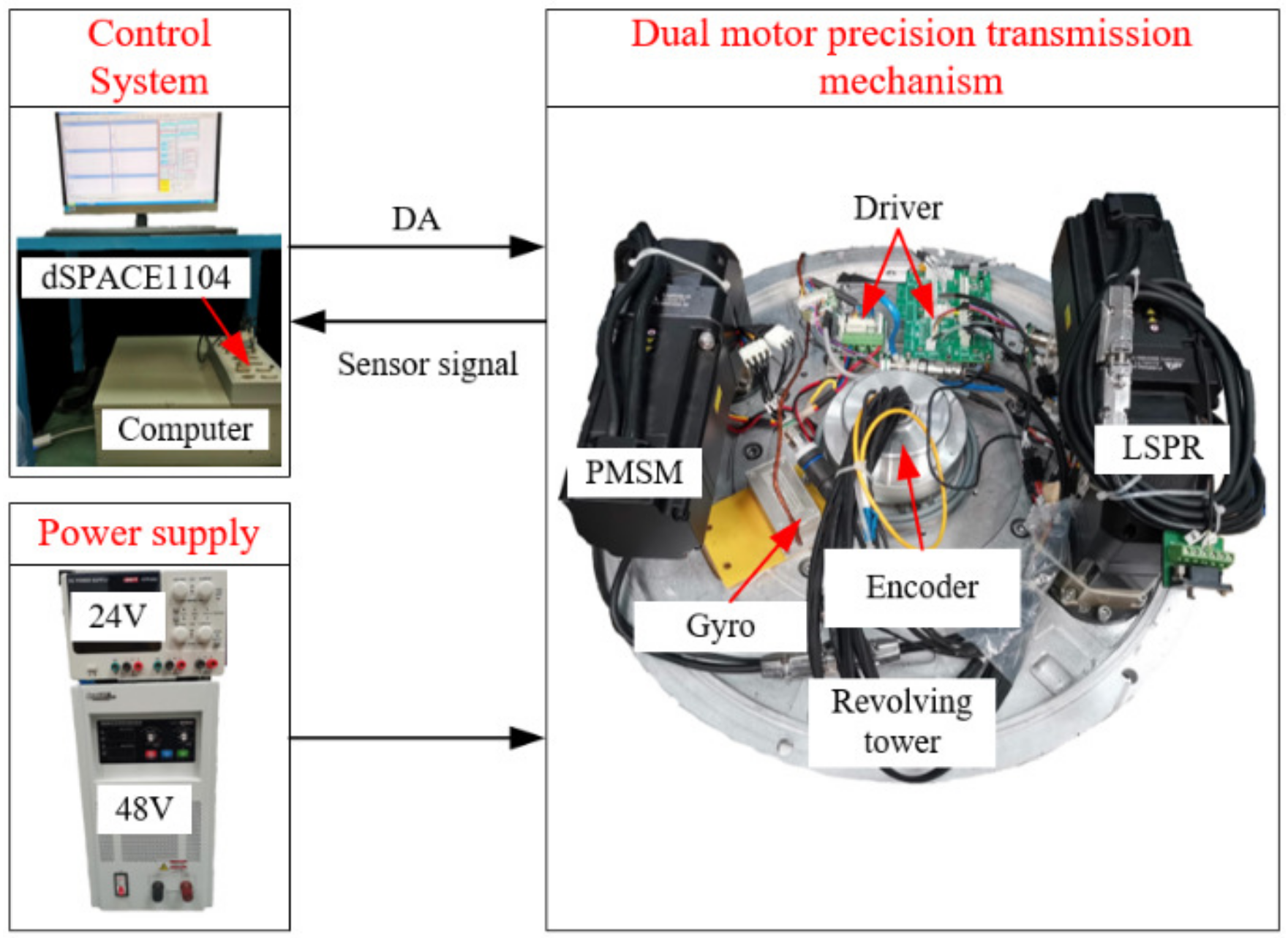
2.1. Overall Structure of the DMPTM
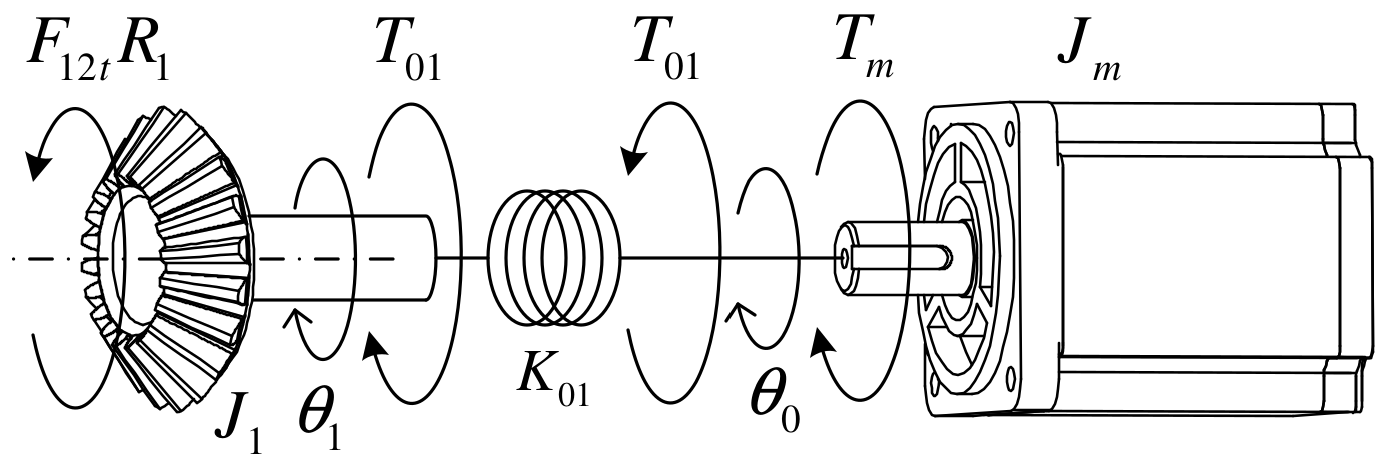
2.2. Motor and Driving Wheel of LSPR
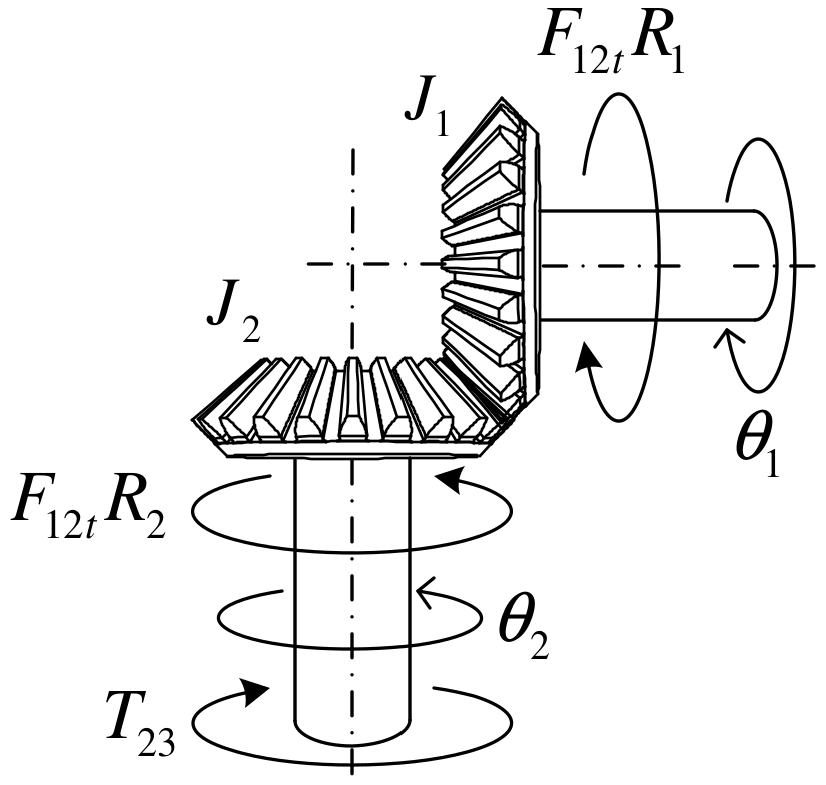
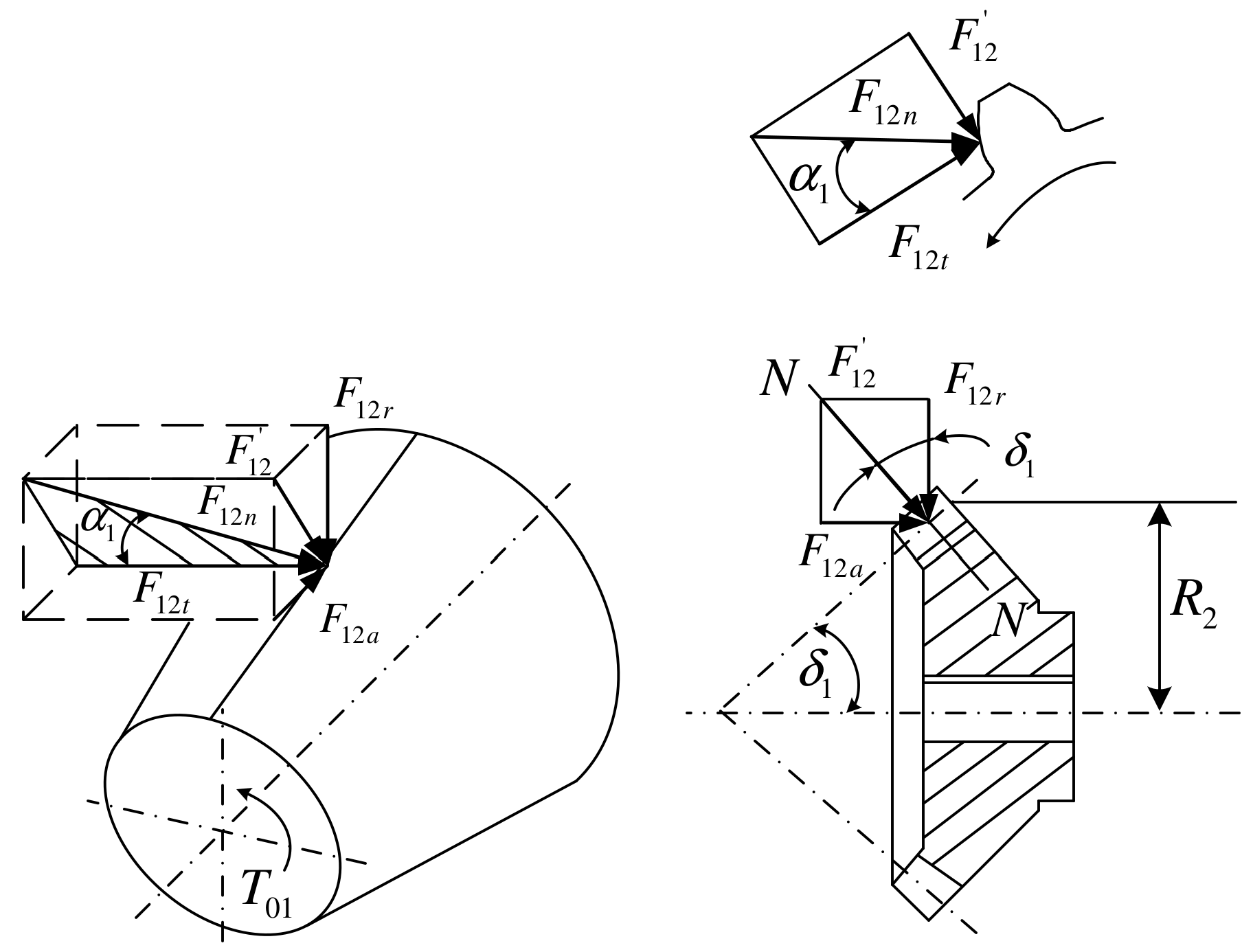
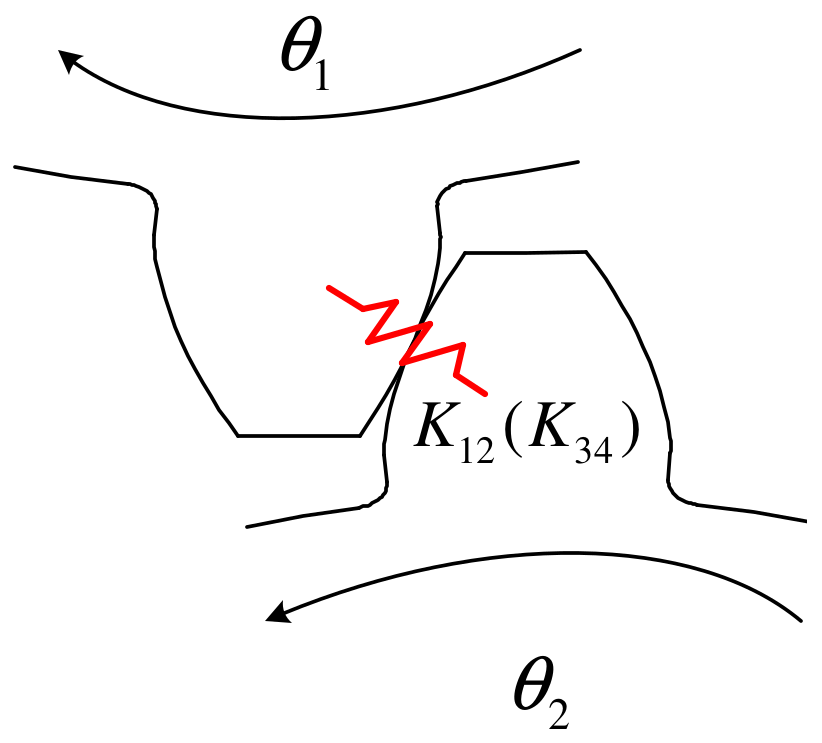
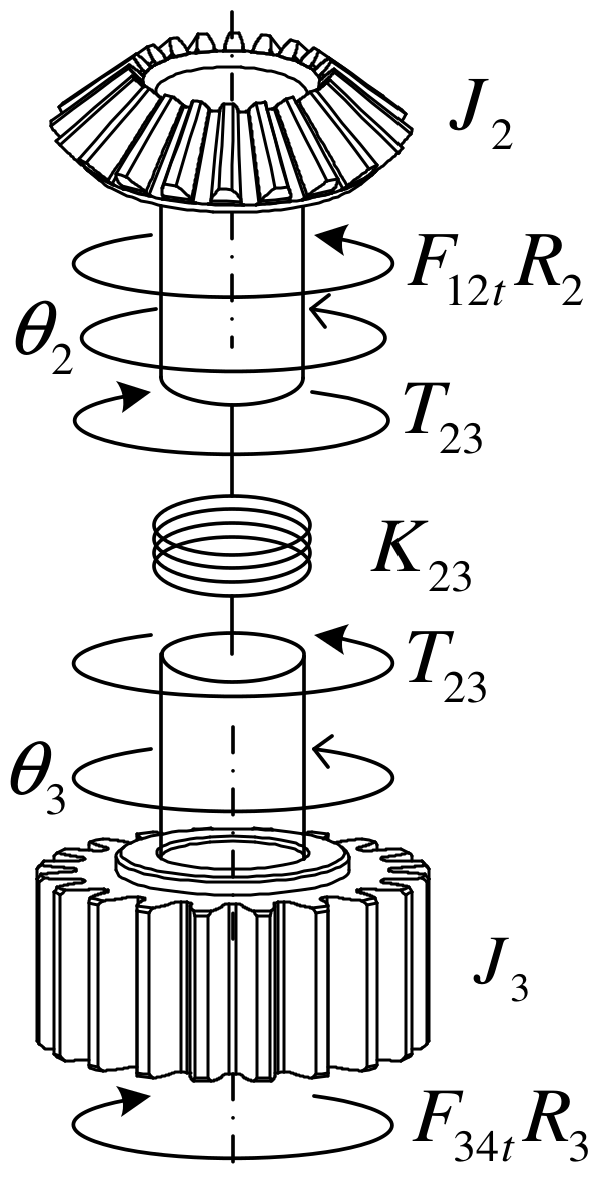
2.3. Internal Bevel Gear Drive of LSPR
2.4. Driven Wheel of LSPR and Pinion
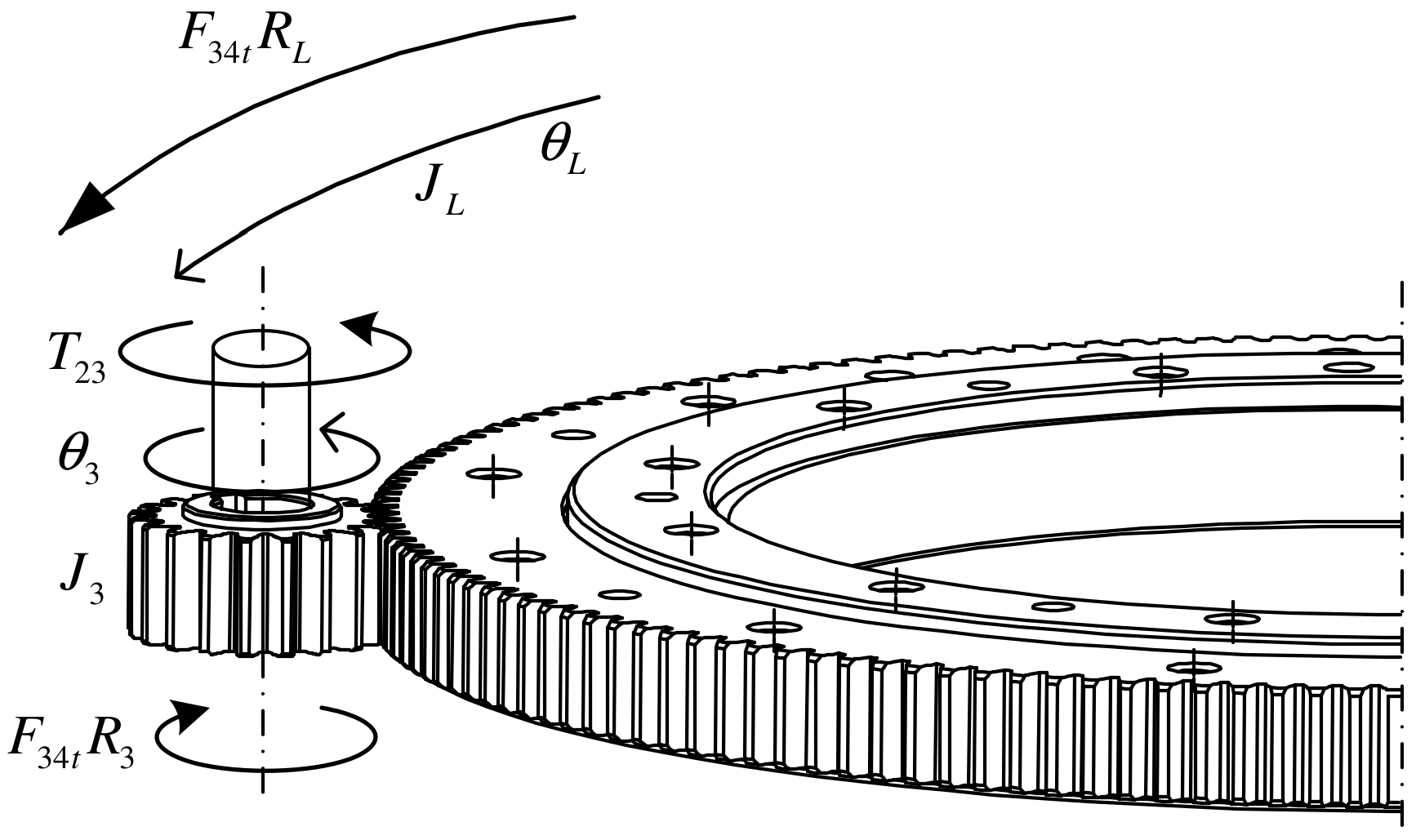
2.5. Pinions and LRG
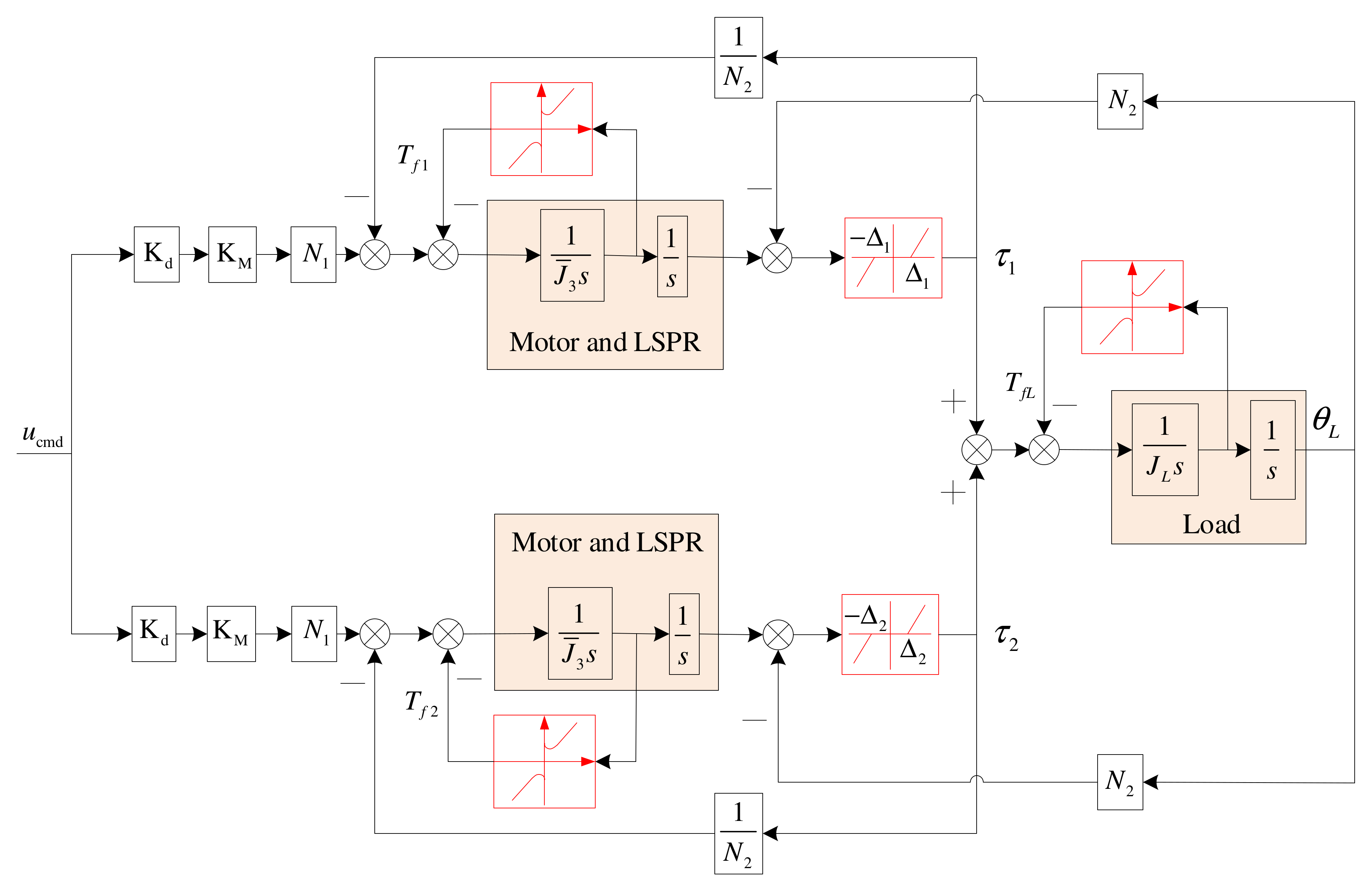
2.6. Overall Linear Model
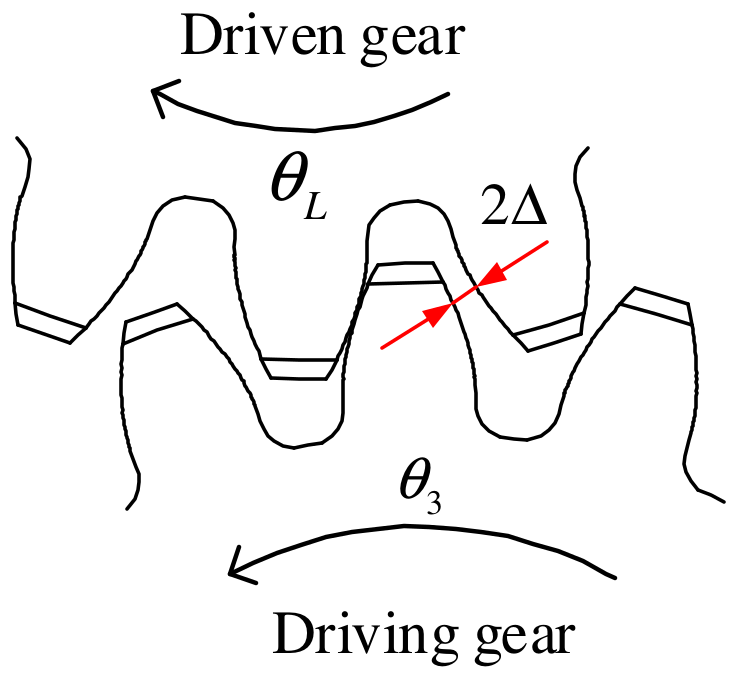
3. Analysis of Nonlinear Dynamics
3.1. Modified Dead-Zone Model
3.2. Stribeck Friction Model
3.3. Overall Dynamic Model
4. Model Validation
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Determination of Model Parameters
4.2.1. Inertia Parameter
4.2.2. Dead-Zone Model Parameters
4.2.3. Friction Model Parameters
4.3. Experimental Results
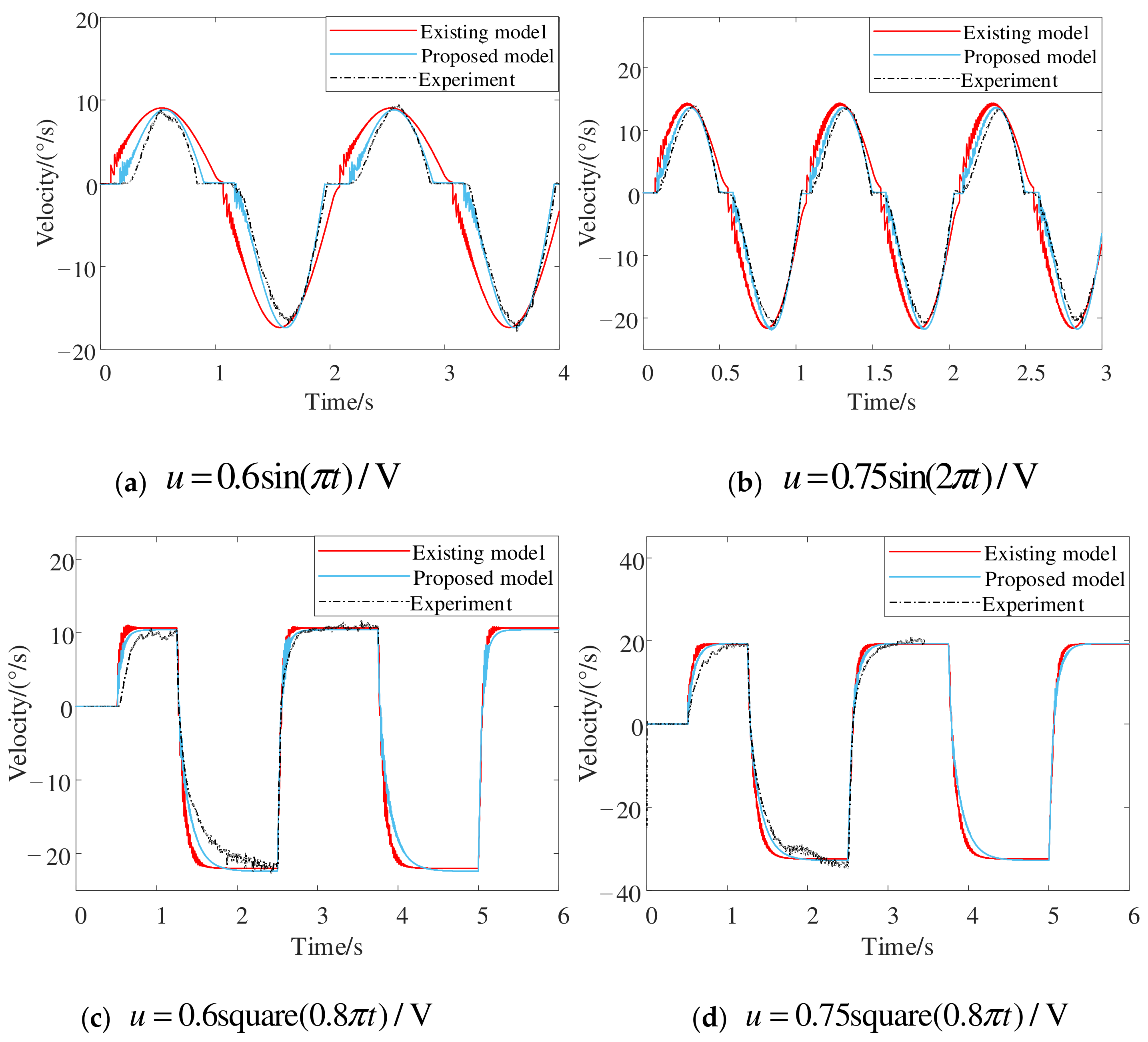
4.3.1. Open-Loop Time Response
4.3.2. Open-Loop Frequency Response
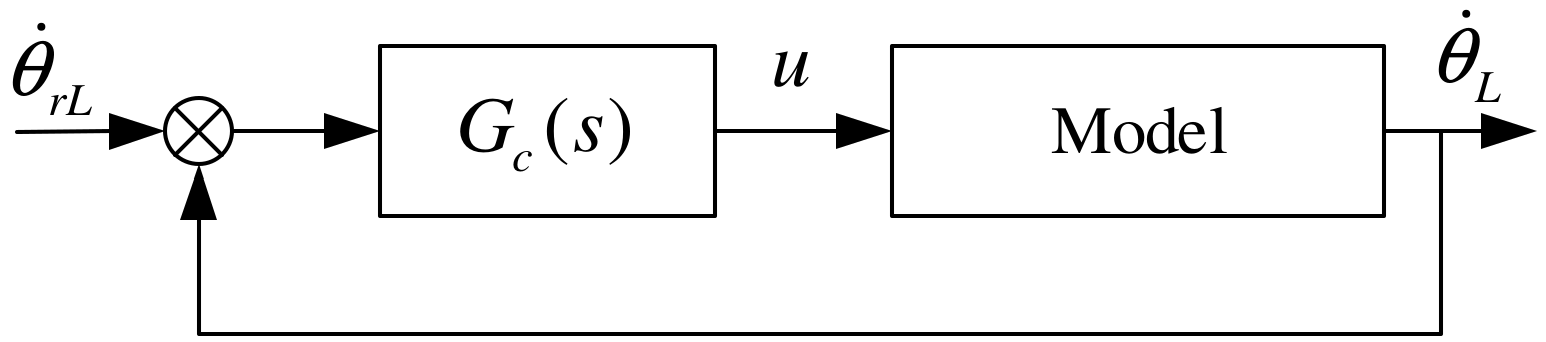
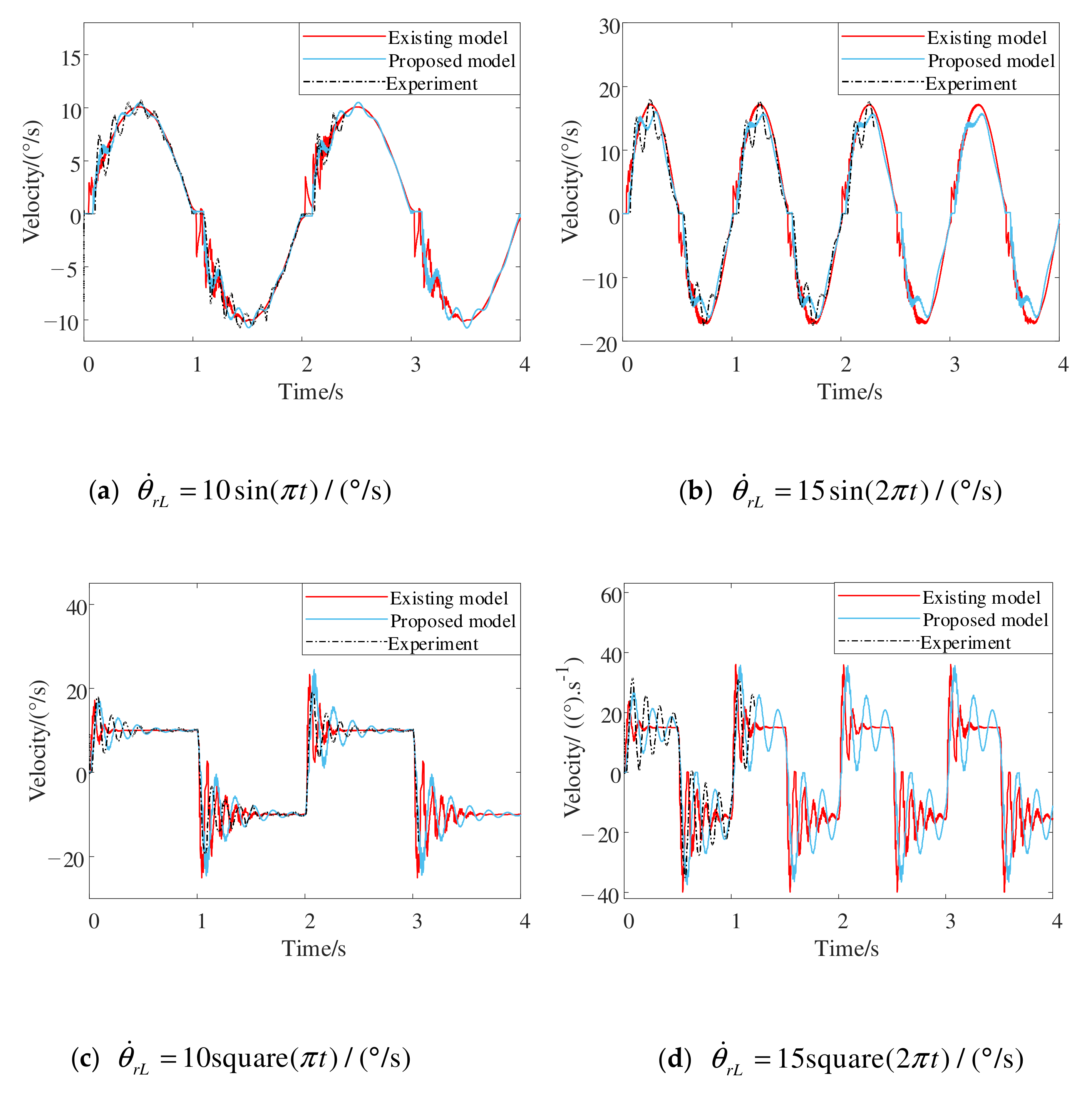
4.3.3. Closed-Loop Time Response
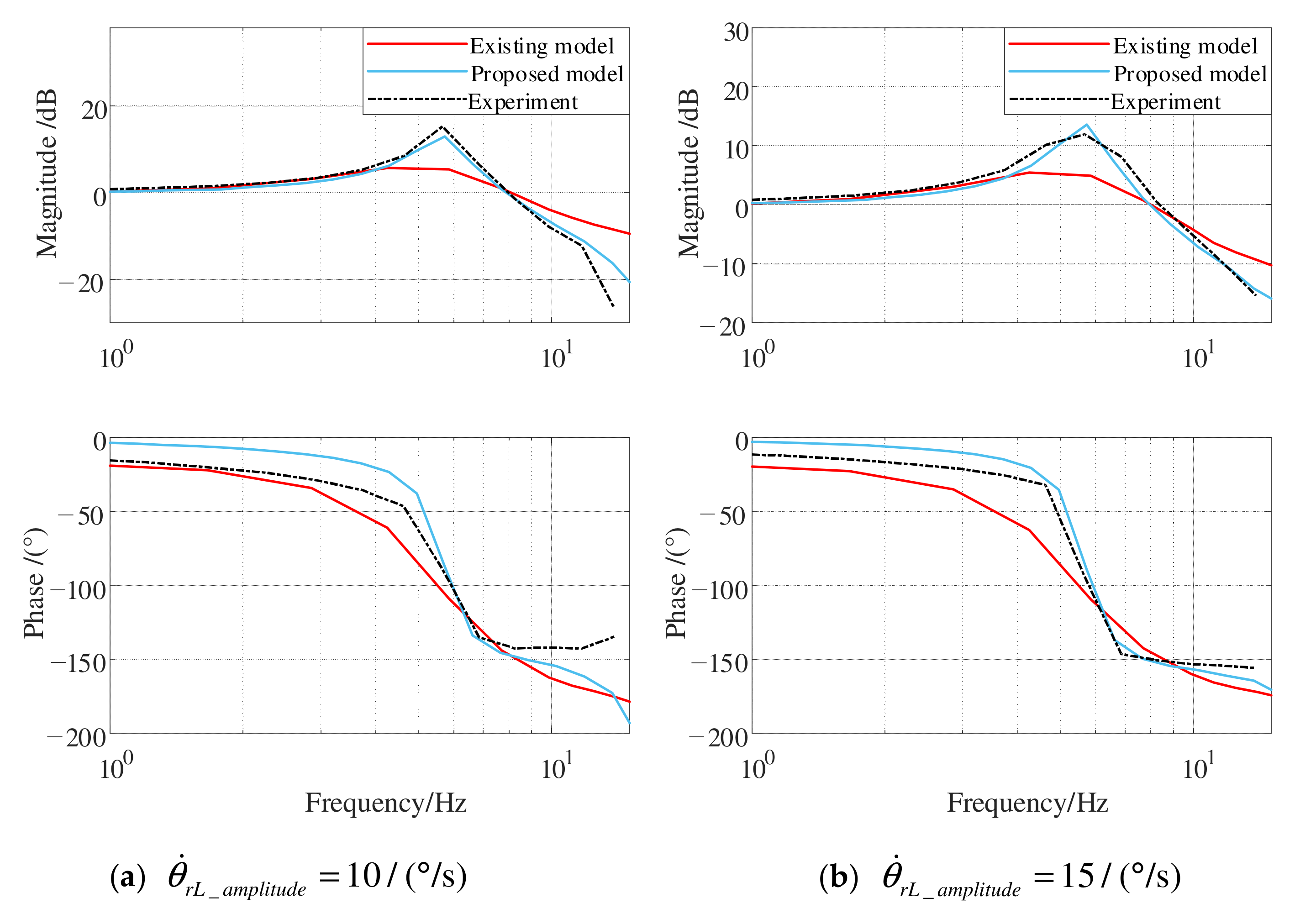
4.3.4. Closed-Loop Frequency Response
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jiang, X.; Fan, D.; Fan, S.; Xie, X.; Chen, N. High-Precision Gyro-Stabilized Control of a Gear-Driven Platform with a Floating Gear Tension Device. Front. Mech. Eng. 2021, 16, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konigseder, F.; Kemmetmuller, W.; Kugi, A. Attitude Estimation Using Redundant Inertial Measurement Units for the Control of a Camera Stabilization Platform. IEEE Trans. Contr. Syst. Technol. 2016, 24, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, R.; Zhao, L. A High Precision Compound Control Scheme Based on Non-Singular Terminal Sliding Mode and Extended State Observer for an Aerial Inertially Stabilized Platform. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2020, 18, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarskov, V.; Tunik, A.; Sushchenko, O. Design of Composite Feedback and Feedforward Control Law for Aircraft Inertially Stabilized Platforms. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8853928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedula, R.V.; Pagilla, P.R. Effect of Compliance and Backlash on the Output Speed of a Mechanical Transmission System. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2012, 134, 31010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlene, R.; Abderrazak, L. Study on the Influence of Backlash Phenomenon on Wind Turbine Power Using Bond Graph Approach. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W. Modeling and Analysis of Steady-State Vibration Induced by Backlash in Servo Rotary Table. Front. Mech. Eng. 2015, 10, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Zheng, W.; Hu, K.; Xu, D. Analysis and Suppression of Limit Cycle Oscillation for Transmission System With Backlash Nonlinearity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 9261–9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, D.; Zheng, W.; Lang, X. Shaft Torque Limiting Control Using Shaft Torque Compensator for Two-Inertia Elastic System With Backlash. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 2902–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Iwasaki, M.; Yu, J. Command Filtered Adaptive Backstepping Control for Dual-Motor Servo Systems With Torque Disturbance and Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Choi, Y. A New Actuator System Using Dual-Motors and a Planetary Gear. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 17, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ren, X.; Gao, X. Synchronization and Tracking Control for Multi-Motor Driving Servo Systems with Backlash and Friction. Int. J. Robust. Nonlinear Control 2016, 26, 2745–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ren, X.; Li, L. Synchronization and Tracking Control for Dual-motor Driving Servo Systems with Friction Compensation. Asian J. Control 2019, 21, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Y. Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control and High-Gain Nonlinearity Compensation for Dual-Motor Driving System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2020, 16, 4090–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Y. Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control Based Plant/Controller Co-Design of Dual-Motor Driving System. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2019, 50, 1847–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, R.; Peng, X. Survey of Nonlinear Vibration of Gear Transmission Systems. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2003, 56, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guesalaga, A. Modelling End-of-Roll Dynamics in Positioning Servos. Control Eng. Pract. 2004, 12, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzouki, R.; Cadiou, J.C. Estimation of Backlash Phenomenon in the Electromechanical Actuator. Control Eng. Pract. 2005, 13, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R.S.; Tenreiro Machado, J.A. Describing Function Analysis of Systems with Impacts and Backlash. Nonlinear Dyn. 2002, 29, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, F.B.; Machado, J.T. Describing Function of Two Masses with Backlash. Nonlinear Dyn. 2009, 56, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villwock, S.; Pacas, M. Time-Domain Identification Method for Detecting Mechanical Backlash in Electrical Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zuo, Z. Backstepping Control for Gear Transmission Servo Systems with Backlash Nonlinearity. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, X. Nonlinear Dynamics of a Spur Gear Pair with Time-Varying Stiffness and Backlash Based on Incremental Harmonic Balance Method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2006, 48, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranawetter, K.; Seeber, R.; Bauer, R.; Horn, M. A New Backlash and Gear Play Model with Friction. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics (ICM), Ilmenau, Germany, 18–20 March 2019; Volume 1, pp. 346–351. [Google Scholar]
- Kahraman, A.; Singh, R. Non-Linear Dynamics of a Spur Gear Pair. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 142, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkorkmaz, K.; Altintas, Y. High Speed CNC System Design. Part II: Modeling and Identification of Feed Drives. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2001, 41, 1487–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Symbol | Value | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (A∙V−1) | 3 | 20 | |
| (Nm∙A−1) | 0.13 | 165 | |
| (kg∙m2) | 2 × 10−4 | (Nm∙rad−1) | 3.6 × 104 |
| (kg∙m2) | 0.125 | (Nm∙deg−1∙s) | 1 |
| (kg∙m2) | 2.5 | (arcmin) | 14 |
| 25 | (arcmin) | 10 | |
| 8.25 |
| Friction of the LSPRs | Friction of the LRG | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Value | Symbol | Value |
| (Nm) | 2.5 | (Nm) | 23 |
| (Nm) | −2 | (Nm) | −20 |
| (Nm) | 2.8 | (Nm) | 20 |
| (Nm) | −1.8 | (Nm) | −17 |
| (°/s) | 2 | (Nm) | 1 |
| (Nm) | −2 | (Nm) | −1 |
| (Nm∙deg−1∙s) | 0.01 | (Nm∙deg−1∙s) | 1.2 |
| (Nm∙deg−1∙s) | 0.008 | (Nm∙deg−1∙s) | 1 |
| Experiments | Existing Model/% | Proposed Model/% | Improvement/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 94.13 | 99.41 | 5.61 | |
| 97.47 | 99.67 | 2.26 | |
| 99.14 | 99.68 | 0.54 | |
| 99.30 | 99.73 | 0.43 |
| Experiment | Existing Model/% | Proposed Model/% | Improvement/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 98.53 | 99.17 | 0.65 | |
| 98.13 | 98.66 | 0.54 | |
| 92.77 | 94.42 | 1.78 | |
| 82.75 | 83.70 | 1.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, J.; Xie, X.; Tan, R.; Chen, L.; Li, B.; Fan, D. An Elaborate Dynamic Model of the Dual-Motor Precision Transmission Mechanism for Performance Optimization. Machines 2022, 10, 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121181
Zheng J, Xie X, Tan R, Chen L, Li B, Fan D. An Elaborate Dynamic Model of the Dual-Motor Precision Transmission Mechanism for Performance Optimization. Machines. 2022; 10(12):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121181
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Jieji, Xin Xie, Ruoyu Tan, Lingyu Chen, Baoyu Li, and Dapeng Fan. 2022. "An Elaborate Dynamic Model of the Dual-Motor Precision Transmission Mechanism for Performance Optimization" Machines 10, no. 12: 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121181
APA StyleZheng, J., Xie, X., Tan, R., Chen, L., Li, B., & Fan, D. (2022). An Elaborate Dynamic Model of the Dual-Motor Precision Transmission Mechanism for Performance Optimization. Machines, 10(12), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121181







