Rough Neutrosophic Digraphs with Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
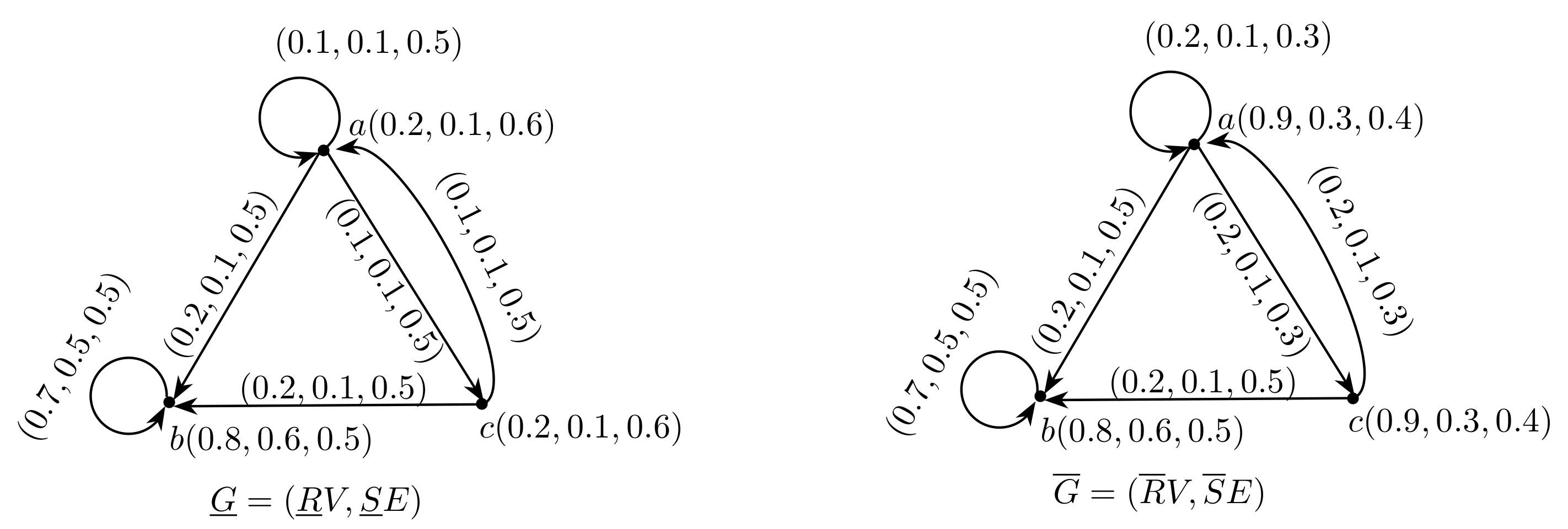
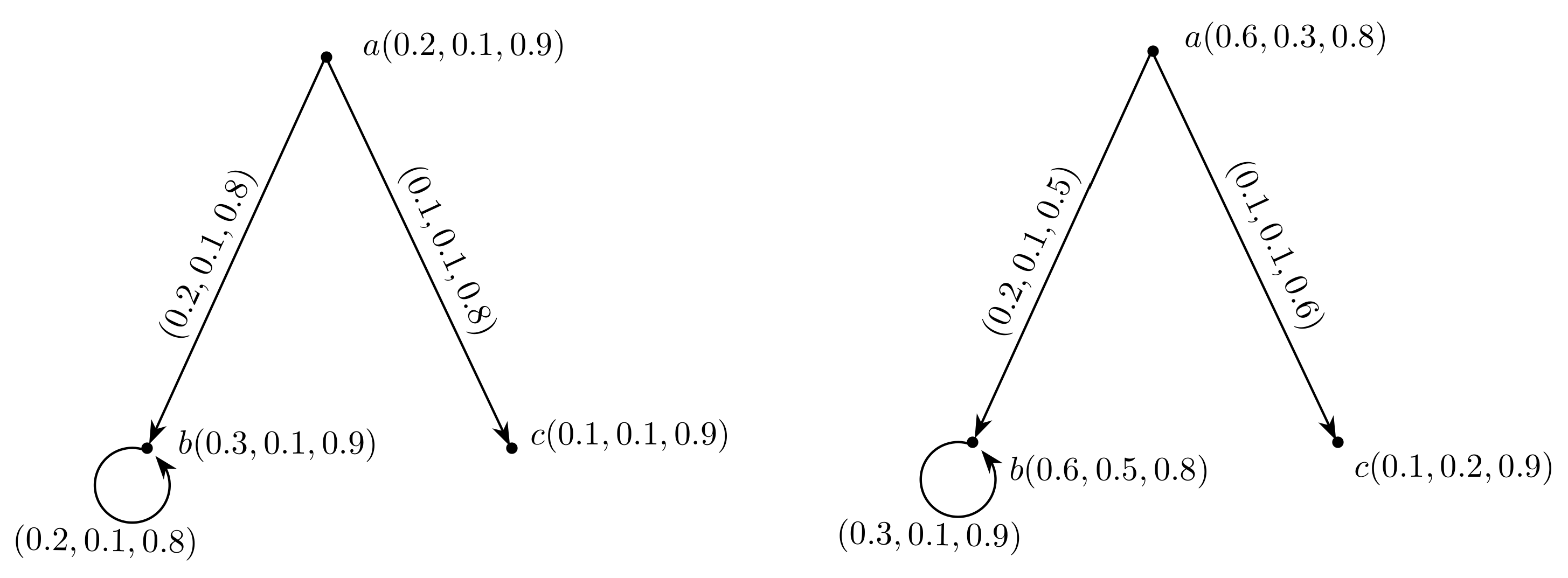
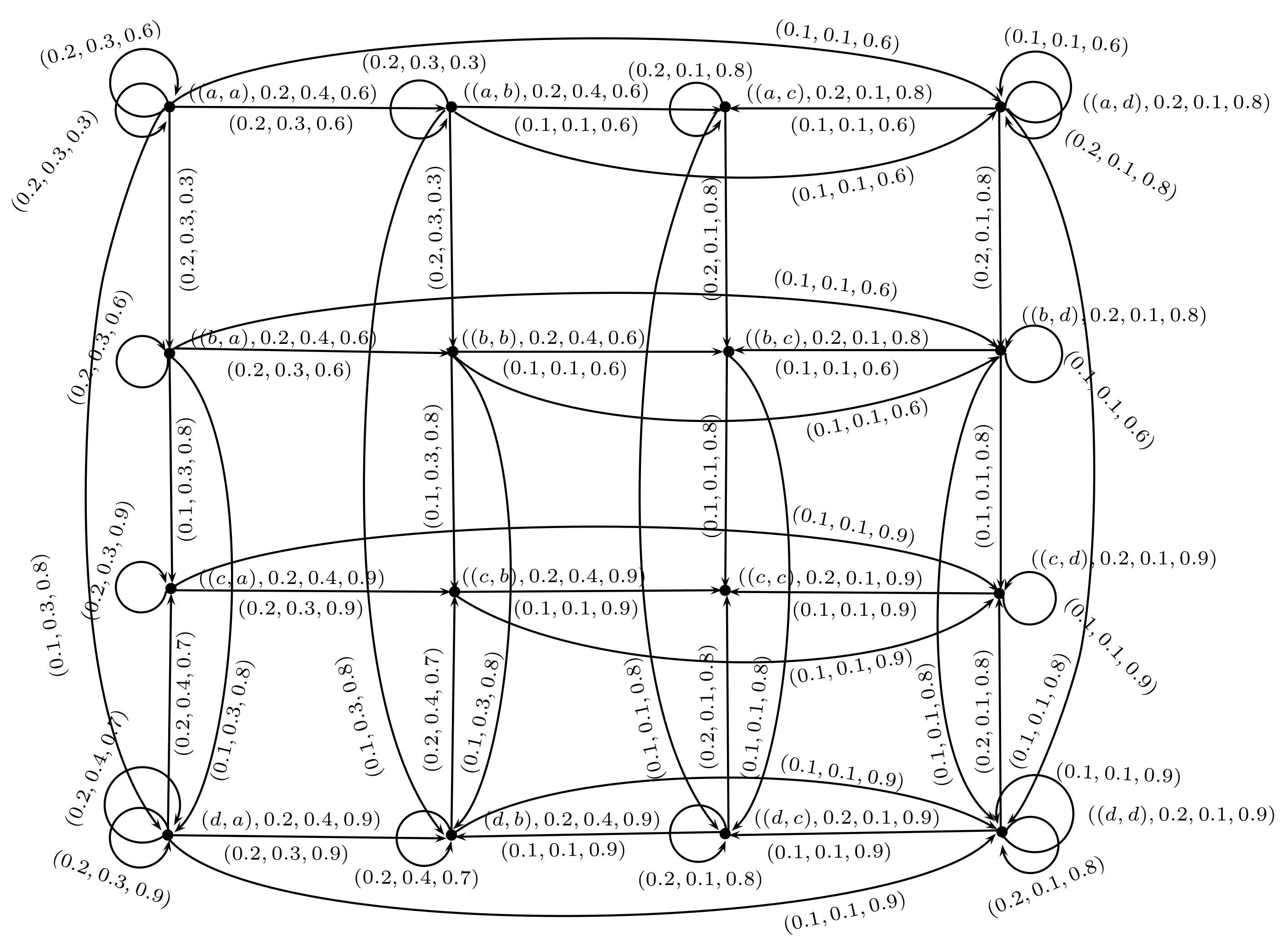
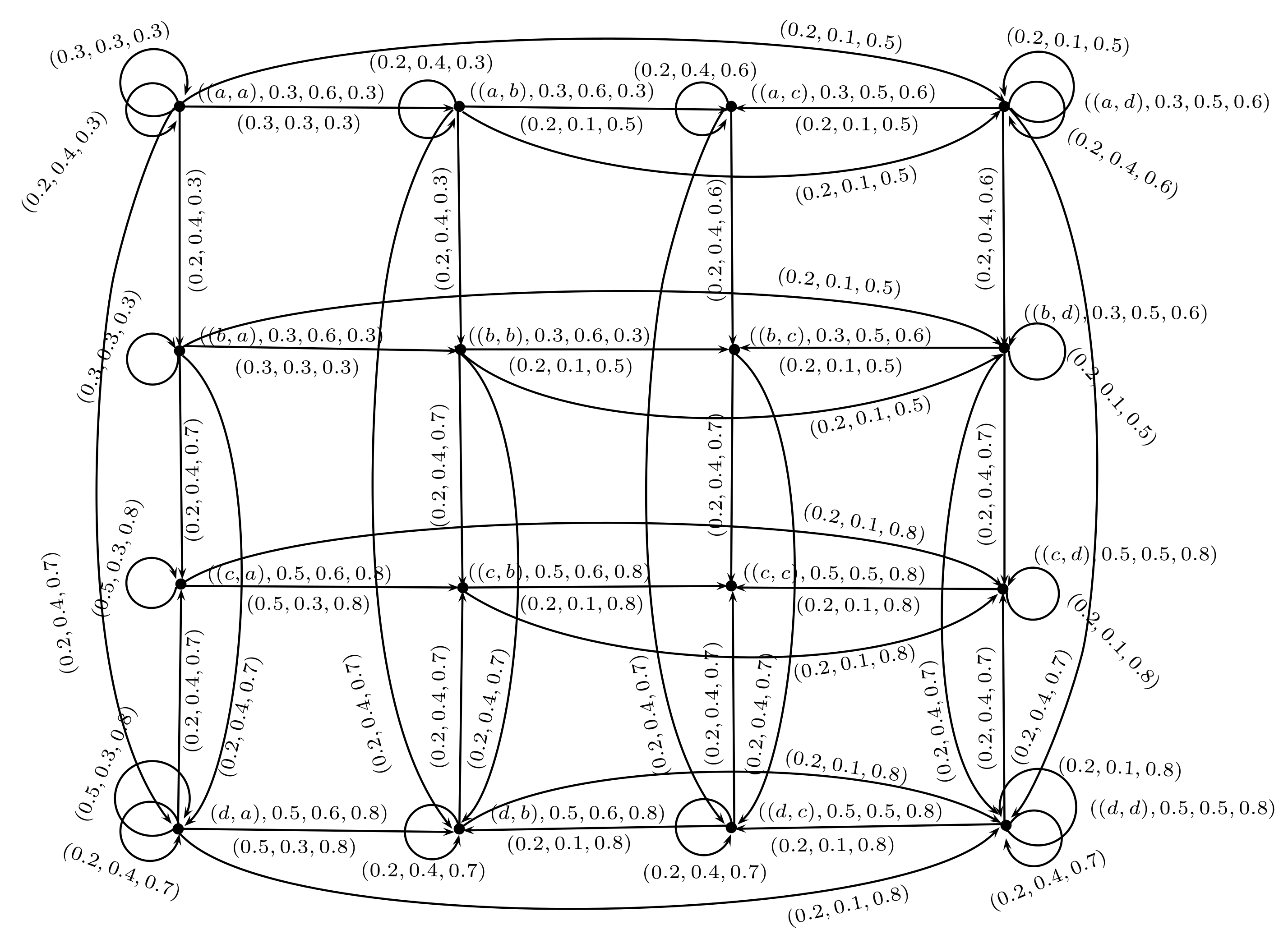
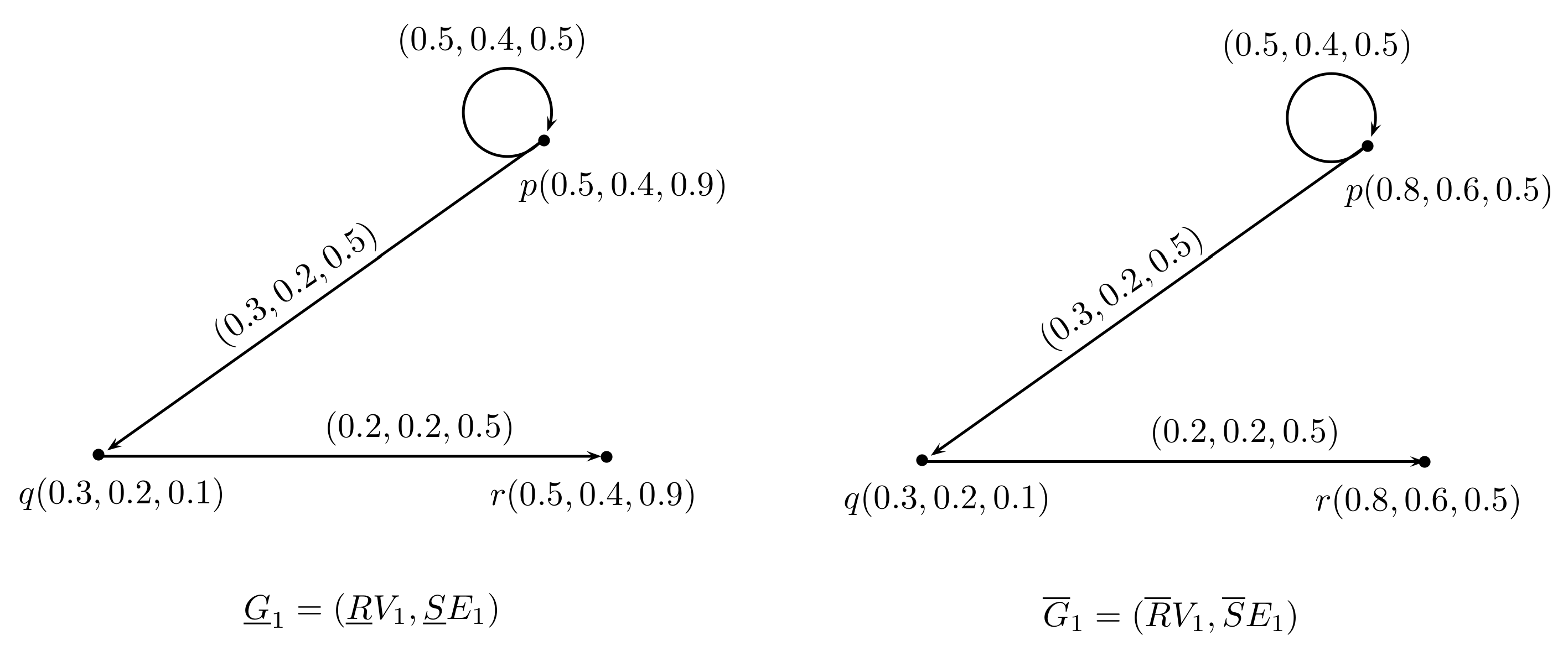
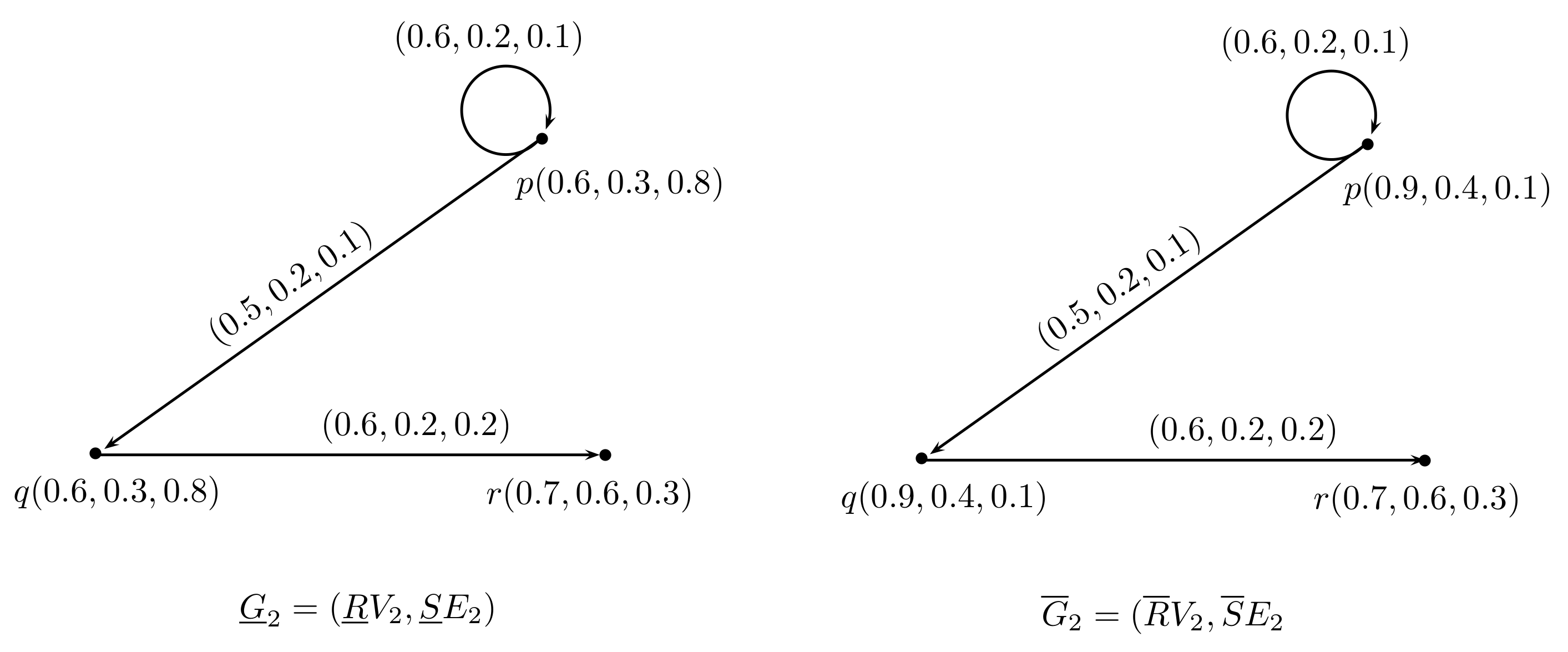
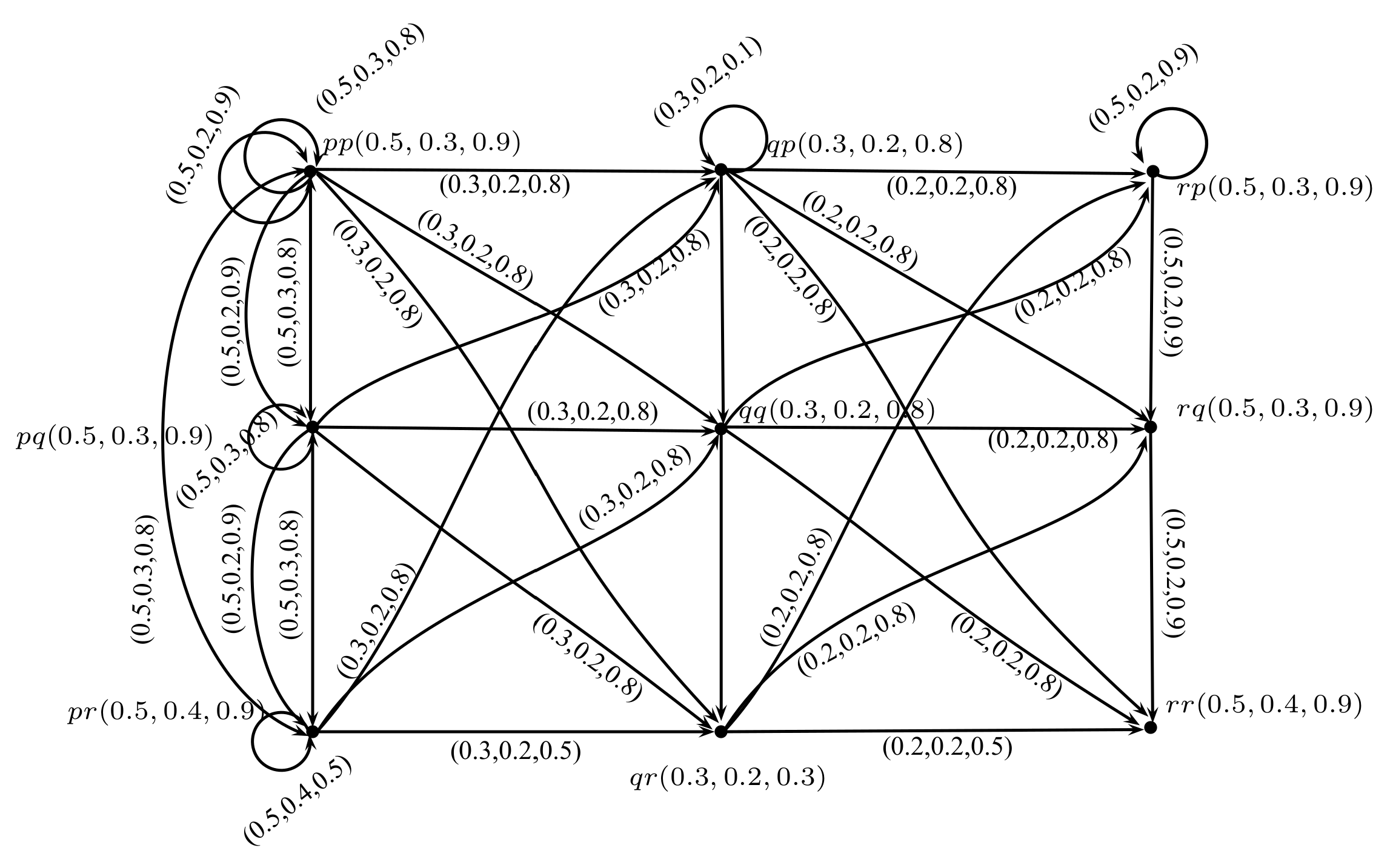
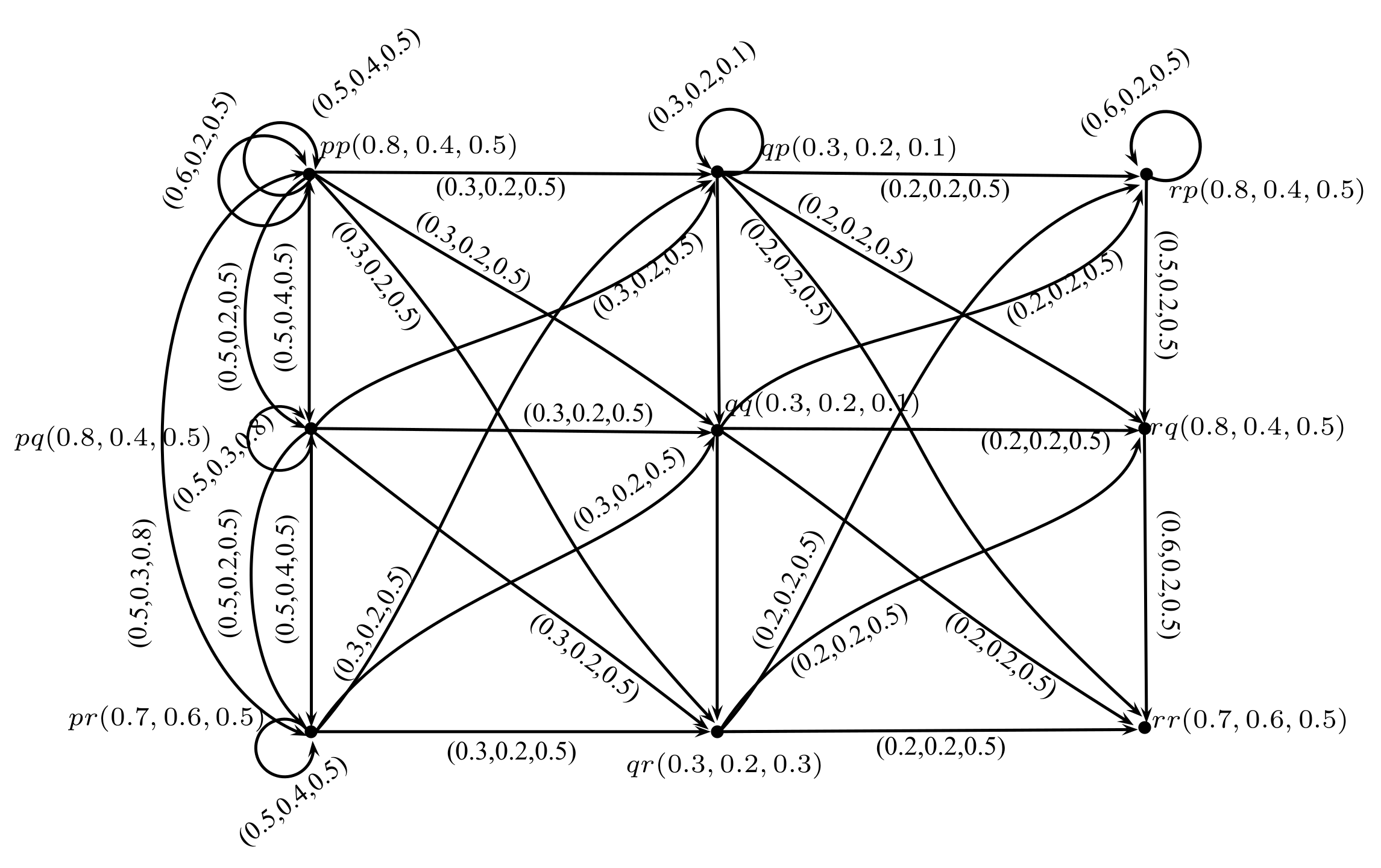
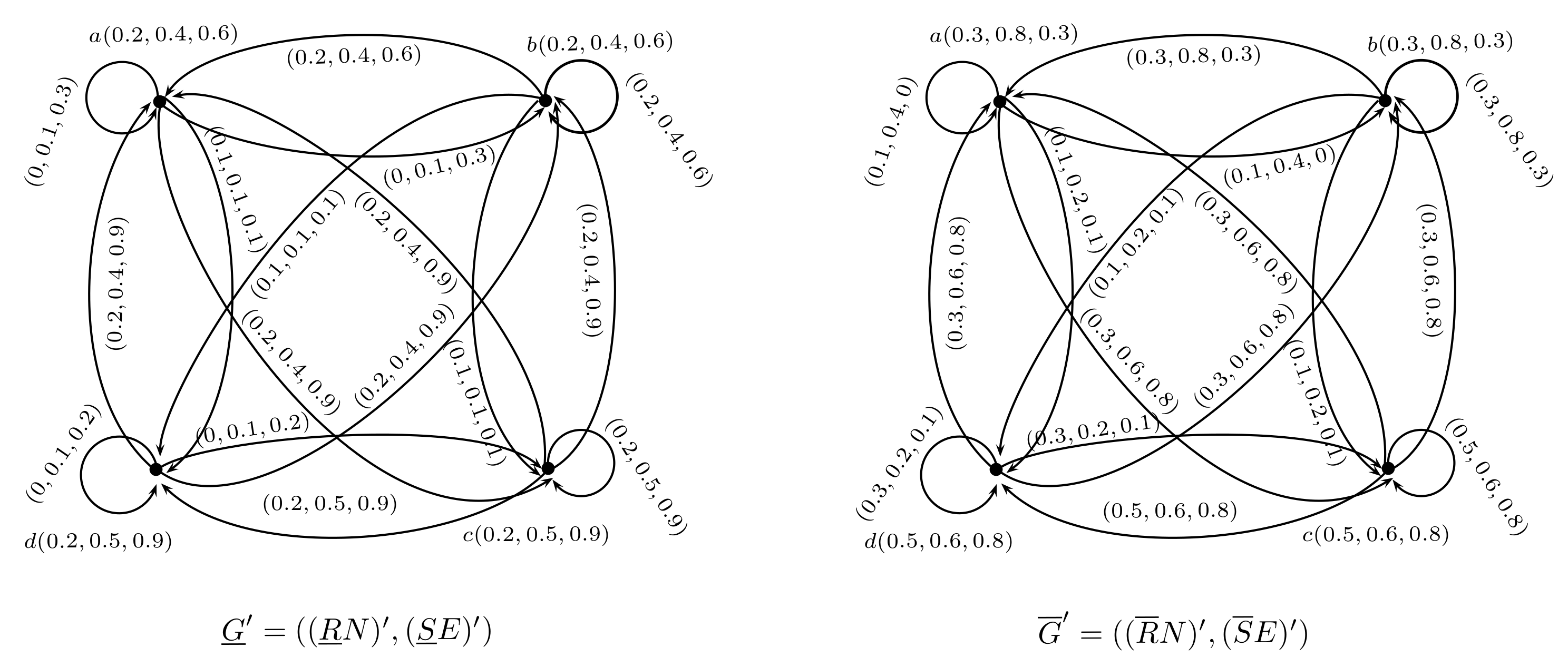
2. Rough Neutrosophic Digraphs
- (a)
- R is an equivalence relation on ;
- (b)
- S is an equivalence relation on ;
- (c)
- is a rough neutrosophic set on ;
- (d)
- is a rough neutrosophic relation on and
- (e)
- is a neutrosophic digraph where and are lower and upper approximate neutrosophic digraphs of G such thatand
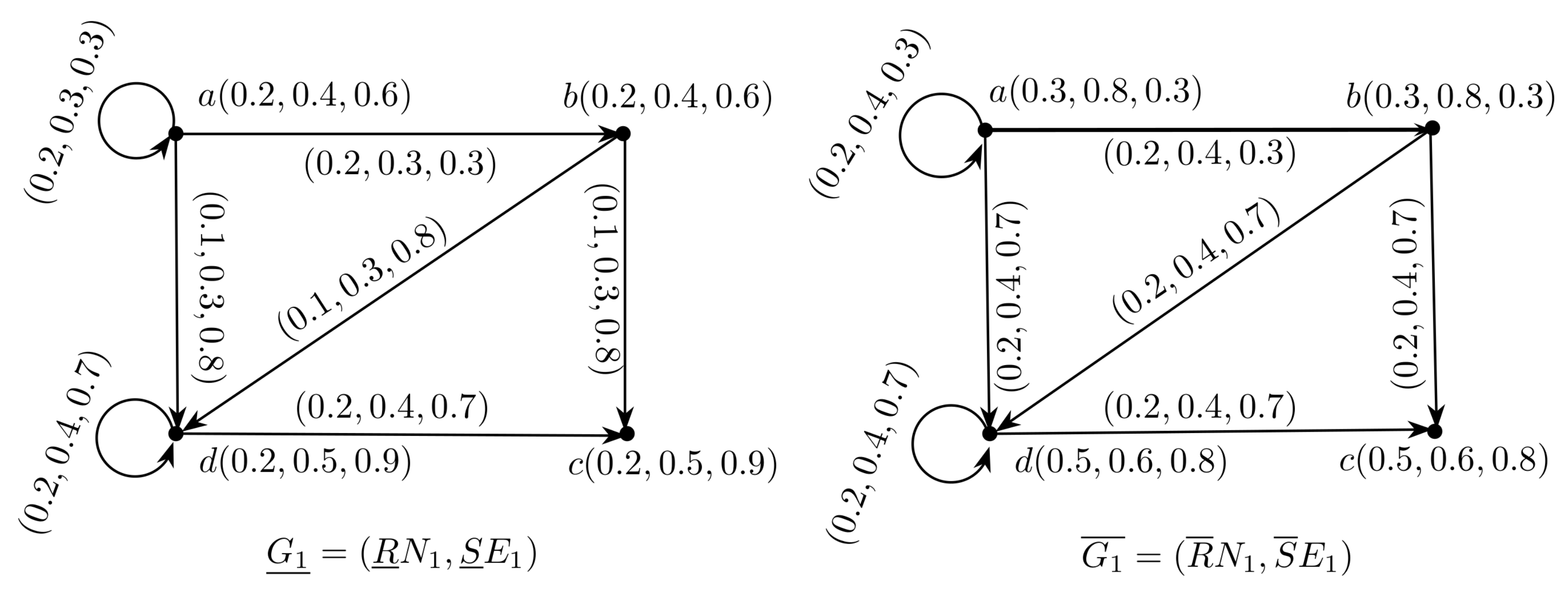
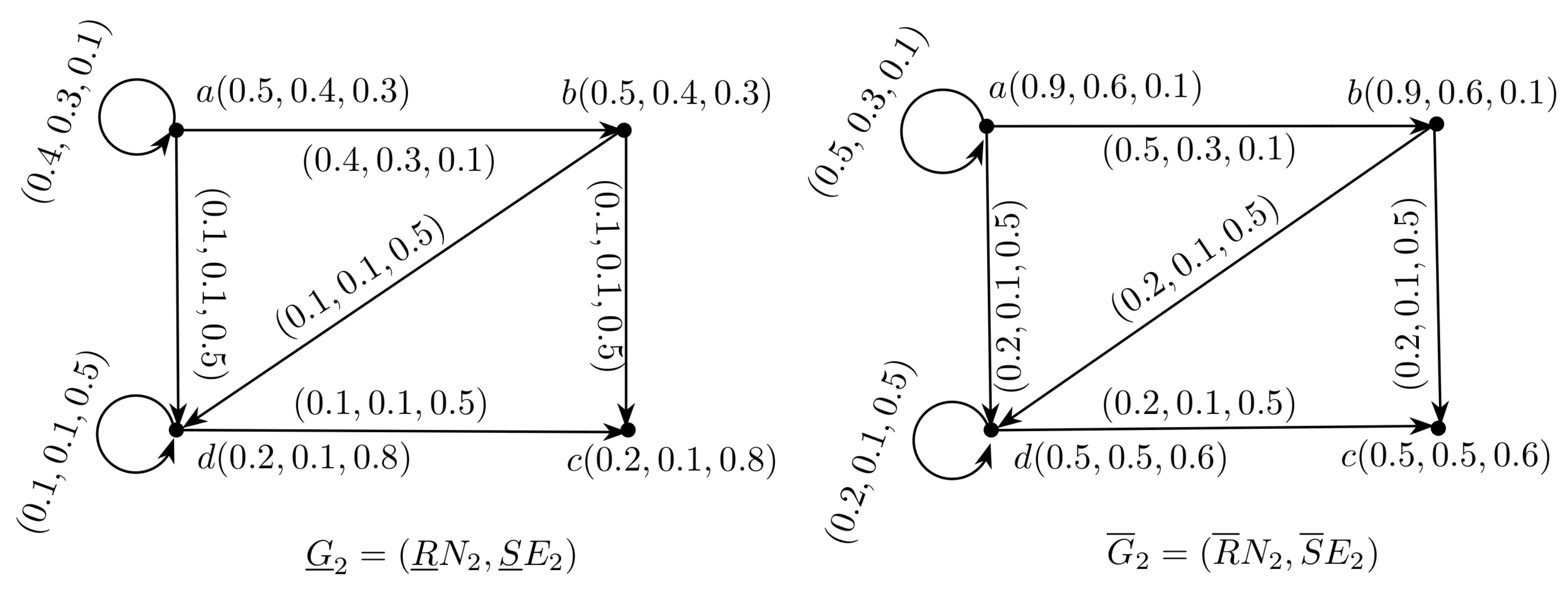
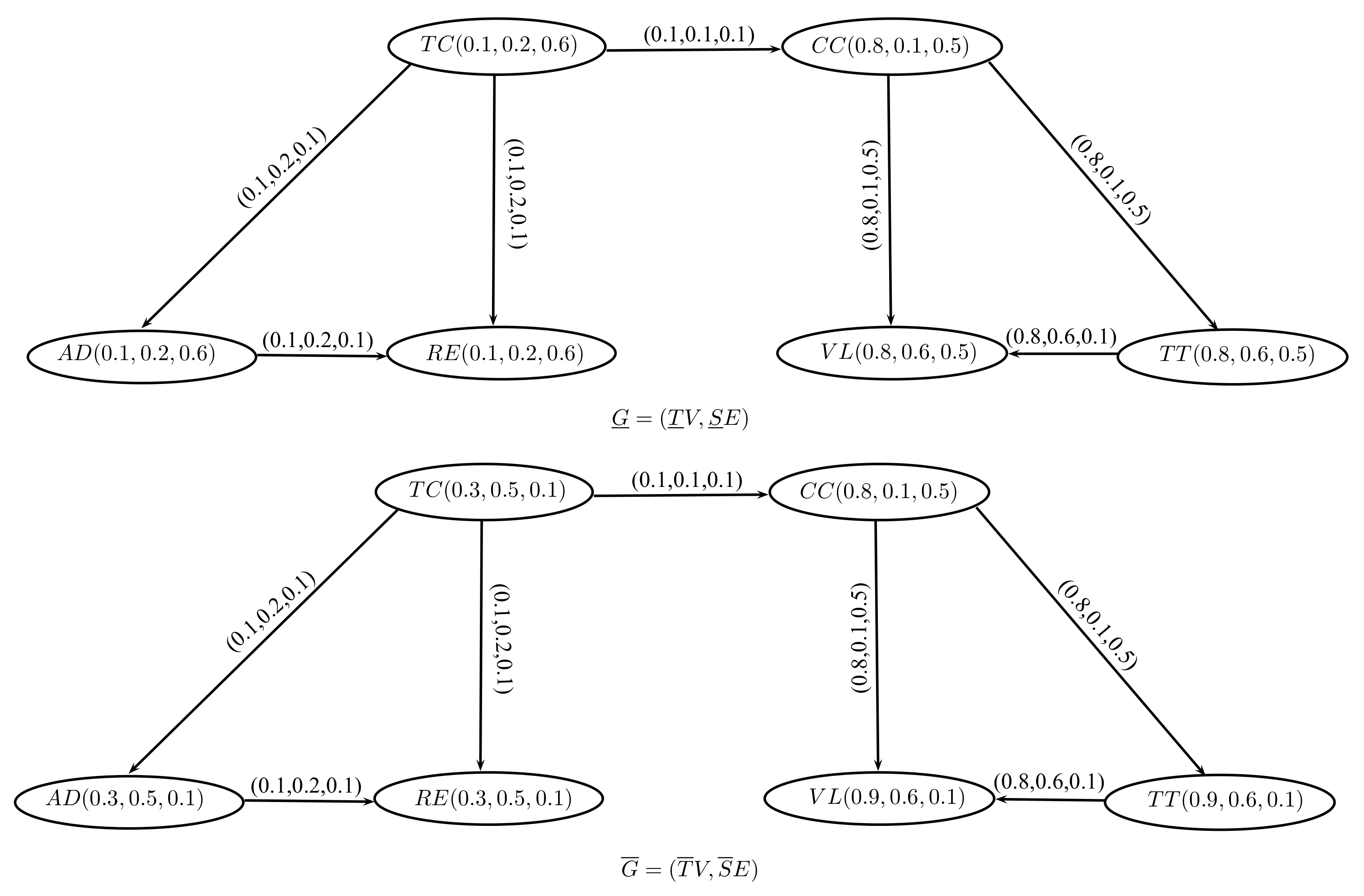
3. Application
| Algorithm 1 Calculation of Optimal decision |
|
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smarandache, F. A Unifying Field in Logics. Neutrosophy: Neutrosophic Probability, Set and Logic; American Research Press: Rehoboth, NM, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarandache, F. Neutrosophy Neutrosophic Probability, Set, and Logic; American Research Press: Rehoboth, NM, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Smarandache, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sunderraman, R. Single-valued neutrosophic sets. Multispace Multistructure 2010, 4, 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J. Multicriteria decision-making method using the correlation coefficient under single-valued neutrosophic environment. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2013, 42, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Improved correlation coefficients of single valued neutrosophic sets and interval neutrosophic sets for multiple attribute decision making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 27, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak, Z. Rough sets. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 1982, 11, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.; Prade, H. Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 1990, 17, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, S.M. Group decision making based on Heronian aggregation operators of intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 2514–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broumi, S.; Smarandache, F.; Dhar, M. Rough neutrosophic sets. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2014, 3, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.L.; Zhang, C.L.; Guo, Z.L.; Liu, Y.L.; Liao, X. A hybrid model of single valued neutrosophic sets and rough sets: Single valued neutrosophic rough set model. Soft Comput. 2016, 21, 6253–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordeson, J.N.; Peng, C.S. Operations on fuzzy graphs. Inf. Sci. 1994, 79, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Shahzadi, S. Neutrosophic soft graphs with applicatin. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 32, 841–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Sarwar, M. Novel multiple criteria decision making methods based on bipolar neutrosophic sets and bipolar neutrosophic graphs. Ital. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2017, 38, 368–389. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, M.; Siddique, S. Neutrosophic competition graphs with applications. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 33, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Sitara, M. Interval-valued neutrosophic graph structures. Punjab Univ. J. Math. 2018, 50, 113–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zafer, F.; Akram, M. A novel decision-making method based on rough fuzzy information. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Pal, S.K. Roughness of a fuzzy set. Inf. Sci. 1996, 93, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, S.M.; Junlin, L. Some intuitionistic fuzzy interaction partitioned Bonferroni mean operators and their application to multi-attribute group decision making. Inf. Sci. 2017, 411, 98–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. Multiple attribute group decision making method based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy power Heronian aggregation operators. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 108, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, J.; Yu, Y. On the union and intersection operations of rough sets based on various approximation spaces. Inf. Sci. 2015, 292, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.L.; Yang, H.L. On single valued neutrosophic refined rough set model and its application. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 33, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayed, S.; Ishfaq, N.; Akram, M.; Smarandache, F. Rough Neutrosophic Digraphs with Application. Axioms 2018, 7, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms7010005
Sayed S, Ishfaq N, Akram M, Smarandache F. Rough Neutrosophic Digraphs with Application. Axioms. 2018; 7(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms7010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayed, Sidra, Nabeela Ishfaq, Muhammad Akram, and Florentin Smarandache. 2018. "Rough Neutrosophic Digraphs with Application" Axioms 7, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms7010005
APA StyleSayed, S., Ishfaq, N., Akram, M., & Smarandache, F. (2018). Rough Neutrosophic Digraphs with Application. Axioms, 7(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms7010005





