An Infeasibility Condition for Rank Reversal in the Analytic Hierarchy Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- A new option is added;
- (ii)
- An existing option is deleted;
- (iii)
- A new criterion is added;
- (iv)
- An existing criterion is deleted.
2. The Problem of Rank Reversal
2.1. The Belton–Gear Example
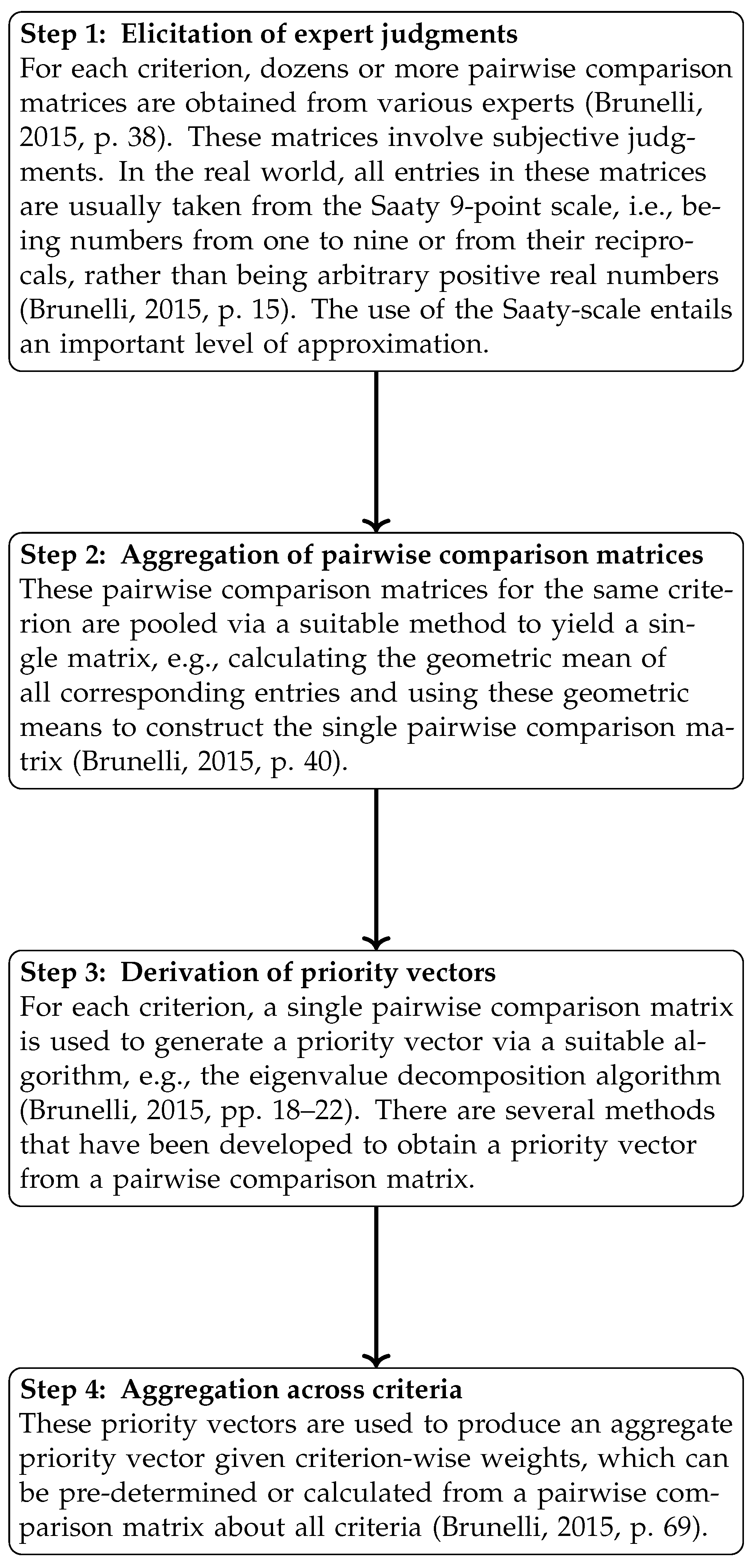
2.2. Four Steps Arising from the Usual AHP
3. The Option Set and Its Augmentation
4. The Infeasibility Condition
5. Illustration
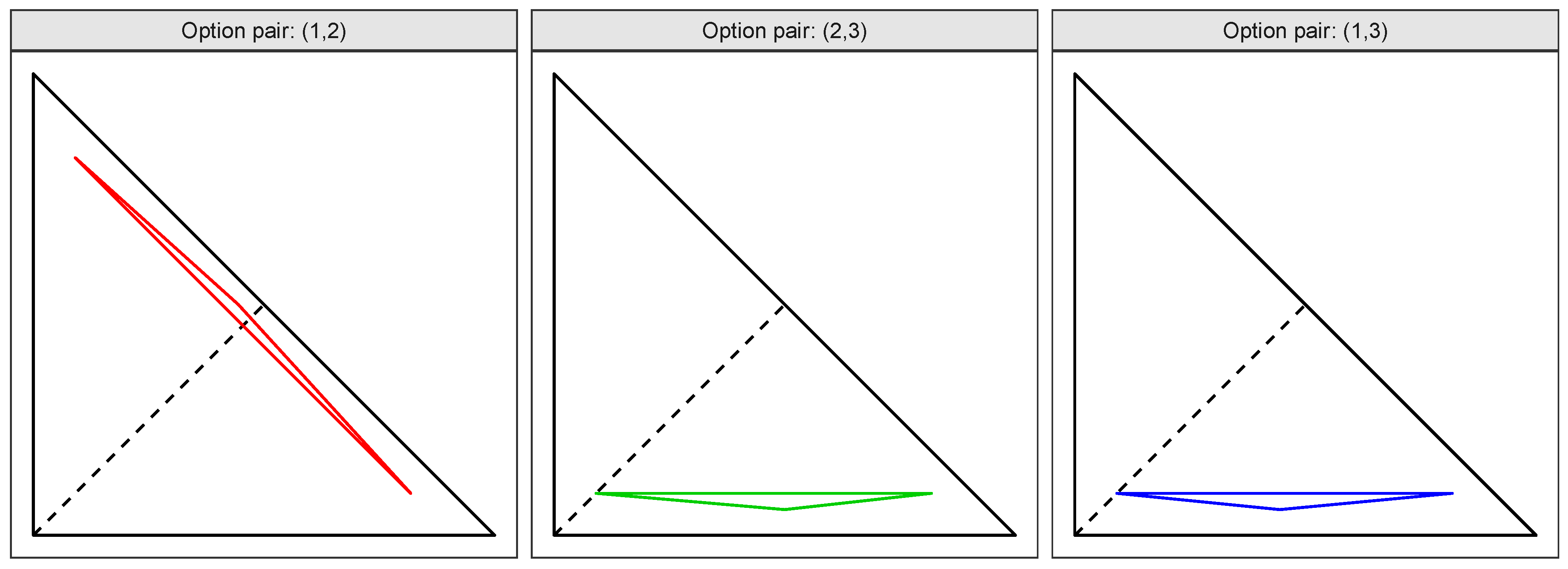
5.1. The Belton–Gear Example Revisited
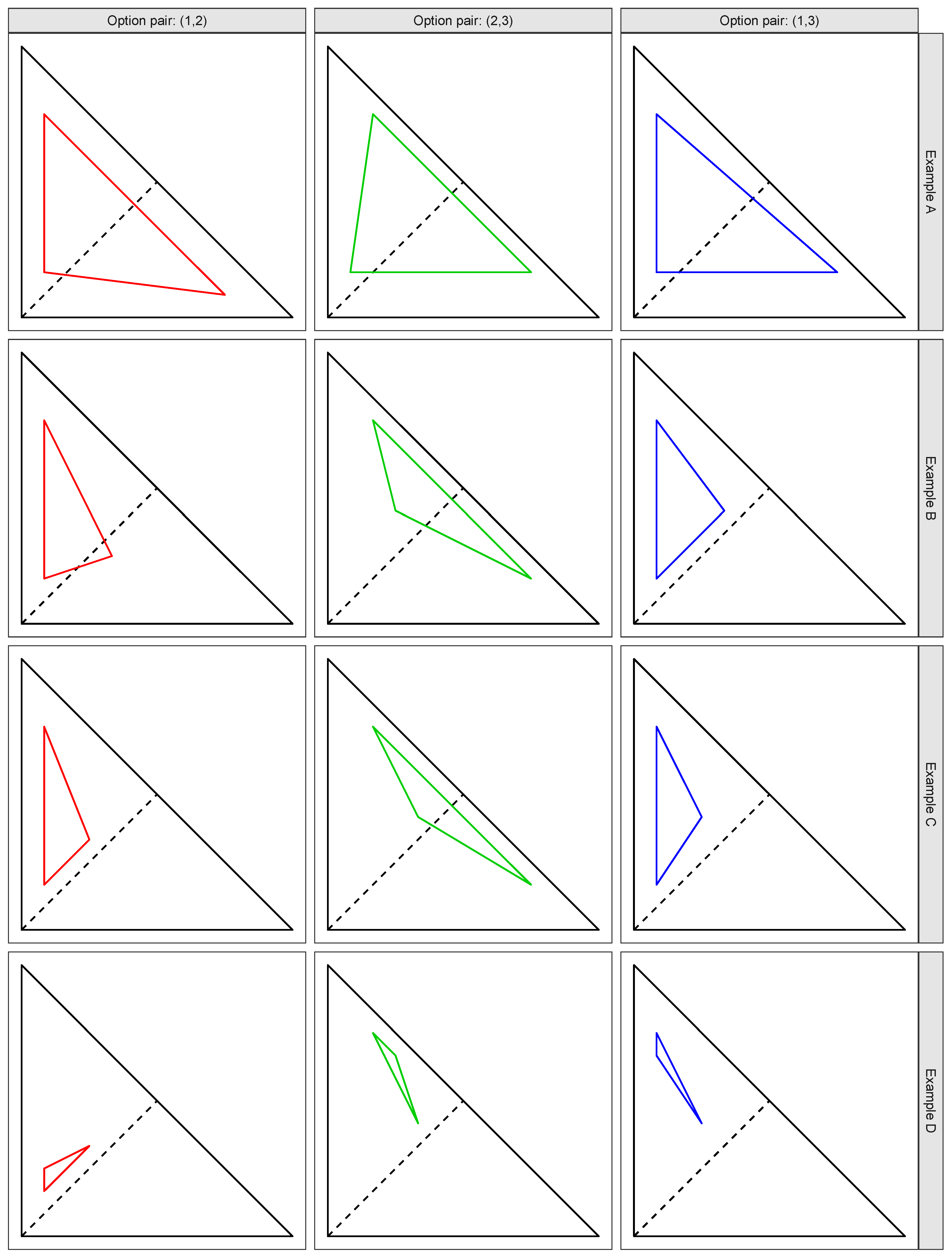
5.2. Four Synthetic Examples
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHP | Analytic Hierarchy Process |
| MCDM | Multi-Criteria Decision Making |
References
- Wolf, B.; Häring, A.-M.; Heß, J. Strategies towards evaluation beyond scientific impact: Pathways not only for agricultural research. Org. Farming 2015, 1, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaoui, G.; Yaagoubi, R.; Mastere, M. Integrating geospatial technologies and multi-criteria decision analysis for sustainable and resilient urban planning. Chall. Sustain. 2025, 13, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorka, P.; Buchuk, R.; Klymenko, M.; Saibert, F.; Petrushyn, A. The use of adaptive artificial intelligence learning models in decision support systems for smart regions. J. Res. Innov. Technol. 2025, 4, 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Terentieva, N.; Karpenko, V.; Yarova, N.; Shkvyria, N.; Pasko, M. Technological innovation in digital brand management: Leveraging artificial intelligence and immersive experiences. J. Res. Innov. Technol. 2025, 4, 201–223. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.-L.; Yoon, K. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications, a State-of-the-Art Survey; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, A.; Köppel, J. A multi-criteria approach for assessing the sustainability of small-scale cooking and sanitation technologies. Chall. Sustain. 2018, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Bouraima, M.B.; Badi, I.; Stević, Ž.; Simic, V. A decision-making model for prioritizing low-carbon policies in climate change mitigation. Chall. Sustain. 2024, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J. Math. Psychol. 1977, 15, 234–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Zahir, S. A comprehensive literature review of the rank reversal phenomenon in the analytic hierarchy process. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 2013, 20, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, M. Introduction to the Analytic Hierarchy Process; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Liao, H.; De Baets, B. A simulation study on the probabilities of rank reversal, tie making, and tie breaking for multiple criteria decision-making methods. Omega 2024, 125, 103033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, E.; Yanase, J. The use of pairwise comparisons for decision making may lead to grossly inaccurate results. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 198, 110653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starczewski, T. Rounding errors in pairwise comparisons matrices by Monte Carlo analysis. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Mech. 2025, 24, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, V.; Gear, T. On a short-coming of Saaty’s method of analytic hierarchies. Omega 1983, 11, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoner, B.; Wedley, W.C. Ambiguous criteria weights in AHP: Consequences and solutions. Decis. Sci. 1989, 20, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoner, B.; Wedley, W.C.; Choo, E.U. A unified approach to AHP with linking pins. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1993, 64, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lootsma, F.A. Scale sensitivity in the multiplicative AHP and SMART. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 1993, 2, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzilai, J.; Golany, B. AHP rank reversal, normalization and aggregation rules. INFOR Inf. Syst. Oper. Res. 1994, 32, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzilai, J.; Lootsma, F.A. Power relations and group aggregation in the multiplicative AHP and SMART. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 1997, 6, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lootsma, F.A.; Barzilai, J. Response to the comments by Larichev, Korhonen and Vargas on ‘Power Relations and Group Aggregation in the Multiplicative AHP and SMART’. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 1997, 6, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, A. Short note on ‘On the Measurement of Preferences in the Analytic Hierarchy Process’. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 1997, 6, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, E. Two new cases of rank reversals when the AHP and some of its additive variants are used that do not occur with the multiplicative AHP. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 2001, 10, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, A.; Silva, A.P.D. On multiplicative priority rating methods for the AHP. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 145, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L.; Vargas, L.G. The legitimacy of rank reversal. Omega 1984, 12, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, V.; Gear, T. The legitimacy of rank reversal—A comment. Omega 1985, 13, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Yang, G. Discussion for the Belton-Gear normalization of analytic hierarchy process. IAENG Int. J. Appl. Math. 2025, 55, 553–564. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, L.G. Comments on Barzilai and Lootsma: Why the multiplicative AHP is invalid: A practical counterexample. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 1997, 6, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Wu, Z. Analytic hierarchy process rank reversals: Causes and solutions. Ann. Oper. Res. 2025, 346, 1785–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, R.F.F.; Ferreira, L. The rank reversal problem in multi-criteria decision making: A literature review. Pesqui. Oper. 2018, 38, 331–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Theory and Applications of the Analytic Network Process: Decision Making with Benefits, Opportunities, Costs, and Risks; RWS Publications: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, B. Classement et choix en présence de points de vue multiples. Rev. Fr. Inform. Rech. Oper. 1968, 2, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, J.P.; Vincke, P. Note—A Preference Ranking Organisation Method. Manag. Sci. 1985, 31, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareschal, B.; Brans, J.-P. Geometrical representations for MCDA. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1988, 34, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, J.; Mao, C. An Infeasibility Condition for Rank Reversal in the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Axioms 2025, 14, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14120860
Yan J, Mao C. An Infeasibility Condition for Rank Reversal in the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Axioms. 2025; 14(12):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14120860
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Junpeng, and Changxuan Mao. 2025. "An Infeasibility Condition for Rank Reversal in the Analytic Hierarchy Process" Axioms 14, no. 12: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14120860
APA StyleYan, J., & Mao, C. (2025). An Infeasibility Condition for Rank Reversal in the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Axioms, 14(12), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms14120860





