Abstract
The problem of testing the equi-correlation coefficient of a standard symmetric multivariate normal distribution is considered. Constrained Bayesian and classical Bayes methods, using the maximum likelihood estimation and Stein’s approach, are examined. For the investigation of the obtained theoretical results and choosing the best among them, different practical examples are analyzed. The simulation results showed that the constrained Bayesian method (CBM) using Stein’s approach has the advantage of making decisions with higher reliability for testing hypotheses concerning the equi-correlation coefficient than the Bayes method. Also, the use of this approach with the probability distribution of linear combinations of chi-square random variables gives better results compared to that of using the integrated probability distributions in terms of providing both the necessary precisions as well as convenience of implementation in practice. Recommendations towards the use of the proposed methods for solving practical problems are given.
Keywords:
symmetric multivariate normal distribution; hypothesis; constrained Bayesian method; Bayes method; Stein’s approach MSC:
62F15; 62F03
1. Introduction
Symmetric multivariate normal distribution (SMND) is widely used in many applications of different spheres of human activities such as psychology, education, genetics, and so on [1]. It is also used extensively in statistical inference procedures, e.g., in analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the modeling of the error part [2]. A random vector has an SMND if its components have equal means, equal variances, and equal correlation coefficients between the pairs of the components. The last is called the equi-correlation coefficient [1,3,4,5,6]. A vector has a standard symmetric multivariate normal distribution (SSMND) when the components have zero mean and unit variances. The consideration of SSMND instead of SMND does not reduce generality when the means and variances are known. On the other hand, SSMND is interesting from several theoretical aspects [1] (p. 2): it is an invariant model which belongs to a curved exponential family [6,7], allows us to find a simple estimator of the correlation coefficient [8,9], and is amenable to the derivation of a small-sample optimal test for the correlation coefficient [1].
Extensive research on inference for the correlation coefficient in SMND exists, starting from the early 1940s [10] up to recent years [11,12,13,14]. In the majority of the works, the problem of finding estimators of the correlation coefficient was considered (see, e.g., [14,15,16,17,18]), compared to the testing problem [1,3,4,5,10]. The likelihood ratio test (LRT) for the general case of testing against and the locally most powerful test (LMPT) for testing against are presented in [1]. The LMPT is based on the best (minimum variance) natural unbiased estimator (BNUE) of . The beta-optimal test and the power envelope for testing vs. is considered in [5]. The relative performances of these tests are compared with a locally best test proposed in [1]. The analogous test of [1] for the symmetric multivariate normal distribution is constructed in [10] where it is shown that the proposed test is uniformly most powerful (invariant) even in the presence of a nuisance parameter, σ2.
In the present work, we for the first time consider the CBM for testing hypotheses vs. concerning the equi-correlation coefficient using the exact and asymptotical probability density functions (pdfs) of test statistics obtained in [1,18,19]. It allows us to make a decision with the restricted criteria of optimality on the desired levels, i.e., permits us to specify both the significance level and the power of the test, which is not achieved by the testing rules given in [1,3,4,5,10]. Along with the theoretical results, the results of the simulation are presented for the demonstration of the validity of the obtained results and the investigation of their properties.
The layout of the rest of this paper is as follows: A statement of the problem is given in Section 2. Approaches for handling directional hypotheses tests concerning the equi-correlation coefficient based on both the maximum ratio test and on Stein’s approach using CBM methodology are developed in Section 3. The general statement of the CBM of testing hypotheses is offered in Section 4, and the application of the CBM’s two possible statements to testing formulated hypotheses is given in Section 5 and Section 6. Statistical computations under concrete examples are presented in Section 7 followed by a discussion and brief conclusions included in Section 8 and Section 9.
2. The Problem Under Consideration
Consider first the problem of the testing of hypotheses concerning a specified value of the correlation coefficient of SMND.
Let the -dimensional random vector follow the -variate normal distribution with zero mean vector and a correlation matrix of the following structure:
where is an identity matrix and is a matrix of ones.
It is known [1] that
where
and the density function of for non-singular is the following:
, ; .
The support of , assures the non-singularity of the correlation matrix [4].
Let us introduce the Helmert orthogonal transformation on the uncorrelated multivariate normal vectors sequence , i.e., and is the Helmert matrix given as [2]
Then, each of are i.i.d. -dimensional random vectors with zero means and a diagonal correlation matrix
where are the eigenvalues of the correlation matrix , i.e., [4]. It is known that [6]
Let be i.i.d. observations, i.e., a random sample from , and introduce variables
where , .
The maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) of the correlation coefficient is [2,19]
The problem we want to solve can be formulated as follows: to test
or
on the basis of the sample . Here, is a -dimensional random vector with independent components each of which has zero mean and variances determined by (5).
The pdf of is
The joint pdf of the sample has the following form [1]:
where and are defined by (6).
3. Testing (2.8) Hypotheses
Let us transform hypotheses (8) into directional ones, i.e., instead of (8), consider the following hypotheses:
.
3.1. The Test Using Maximum Ratio Estimation of the Parameter
Consider testing the hypothesis
where is defined by (7).
We use the sample and the pdf (10) with the parameters and under the hypotheses and , respectively, i.e., pdfs at null and alternative hypotheses are determined by (10) using the values of and for null and alternative specifications, respectively.
The algorithm for making decisions is the following. Let us designate i.i.d. random vectors obtained by the Helmert orthogonal transformation of the sample , i.e., . On the basis of the first half of the vectors we compute the MLE of the parameter by (7), and on the basis of the second half of the sample , we test the hypotheses (12). The pdfs used for testing are the following: and determined by (10). When testing (12), the decision is made in favor of the alternative hypothesis, i.e., we accept if , otherwise .
3.2. Stein’s Approach
Stein’s method [20,21] integrates the density over using special measures to obtain the density of the maximum invariant statistic, which can then be used to analyze the problems, for example, to find the uniformly most powerful invariant test [22].
The integrated conditional pdfs of the sample are necessary in this case for the hypotheses under consideration, i.e., the following pdfs:
where is defined by (10) for the sample ; and are the densities of the parameter at the alternative specifications and , respectively.
Because at alternative hypotheses and the value of the parameter belongs to the intervals and , respectively, and no information is available about the preference of some values from these intervals, we use the uniform distributions of in the appropriate intervals, i.e., (14) and (15) pdfs transform in the following forms:
where and are computed by (6) for the sample .
For testing hypotheses (11) and (12), using pdfs (10) and (13), (16), and (17), respectively, let us use the CBM—a brief introduction to it is given below [22,23].
4. Constrained Bayesian Method of Testing Hypotheses
Let be generated from , and the problem of interest is to test , , where , , are disjoint subsets with . The number of tested hypotheses is . Let the prior on be denoted by , where for each , is the a priori probability of hypothesis , and is a prior density with support ; denotes the marginal density of given , i.e., , and is the set of solutions, where , it being so that
is the decision function that associates each observation vector with a certain decision:
(notation: depending upon the choice of , there is a possibility that for more than one or for all ).
is the region of acceptance of the hypothesis , i.e., . It is obvious that is completely determined by the regions, i.e., .
Let us introduce the loss function which determines the value of the loss in the case where the sample has a probability distribution corresponding to hypothesis , but the decision is made wrongly. In the general case, the loss function consists of two components:
where is the loss for the incorrect acceptance of when is true and is the incorrect rejection of in favor of .
It is possible to formulate nine different statements of the CBM depending on what type of restriction is desired, determined by the aim of the specific problem to be solved [22,23].
For concreteness, let us introduce one of the possible statements, namely Task 1, as an example, for a demonstration of the specificity of the CBM. In this case, we have to minimize the averaged loss of the incorrectly accepted hypotheses
subject to the averaged loss of the incorrectly rejected hypotheses
where is some real number determining the level of the averaged loss of the incorrectly rejected hypotheses.
By solving problem (19) and (20), we have
where the Lagrange multiplier () is defined so that the equality holds in (20).
The acceptance regions (21) of the hypotheses differ from the classical cases where the observation space is divided into two complementary sub-spaces for acceptance and rejection regions. Here, the observation space contains the regions where decisions can be made as well as the regions where they cannot be made. This also gives us the opportunity to develop the corresponding sequential tests [22,23,24].
5. CBM for Testing Hypotheses in (3.1)
Let us consider the CBM for testing the hypotheses (11) with a stepwise loss function.
One of possible statements of the CBM, namely, the so-called Task 7, has the following form [22,23,24]:
subject to
where , , and are a priori probabilities of the appropriate hypotheses, , , is the probability of the acceptance of the hypothesis when the hypothesis is true, on the basis of , and and define the loss functions of incorrectly accepting and incorrectly rejecting the hypotheses given by
is a decision function, , , is the acceptance region of the hypothesis , and , , and are the specified levels of the averaged losses of the incorrect acceptances of the hypotheses , , and , respectively.
The solution of the problem (22) and (23) using undetermined Lagrange multipliers yields the acceptance regions for the hypotheses as follows:
where the Lagrange multipliers , , and are determined so that the equalities hold in the conditions (23).
In accordance with the theorems proven in [24], when the circumstances , () are satisfied, where , the conditions or are fulfilled. Here, the following criteria of optimality of arriving at the decisions are used: the mixed directional false discovery rate (), the summary type III error rate (), and the false acceptance rate (). They are determined by the following formulae:
Another possible statement of the CBM, namely, the so-called Task 2, has the following form [22,23,24]:
subject to
where , , and are specification levels in the considered statement.
The solution of the problem of (28) and (29) by the Lagrange method yields the following acceptance regions for the hypotheses:
where the Lagrange multipliers , , and are determined so that the equalities hold in the conditions (29).
Theorems are proven in [24] in accordance with which (30) decision regions ensure specified error rates of type I and type II, determined by the following ratios:
They also ensure the specification of the averaged loss of incorrectly accepted hypotheses and the averaged loss of incorrectly rejected hypotheses by the following ratios:
where
6. Evolution of CBM 2 for Testing (3.1) Hypotheses
6.1. Using the Maximum Ratio Estimation
Like (30), the hypotheses acceptance regions, testing (12) hypotheses using the CBM 2, have the following forms:
where the Lagrange multipliers and are determined from the following conditions [23]:
where and are the specified levels under and , respectively.
For the conditional pdfs of , we have (13) under and the following under :
Let us determine the Lagrange multipliers and in (33) of (34). The acceptance regions (33) of the hypotheses under the conditional densities (13) and (35), after simple transformations, take the forms
where
where
For the determination of the Lagrange multipliers and from the conditions (34), the computation of the probabilities and is essential. For this purpose, knowledge of the pdfs of the random variables
is necessary.
The properties of and are given in [1,4]:
The distribution function of a linear combination of chi-square random variables is considered in many works [24,25,26,27]. Below, we use the results of [26], in accordance with which the distribution function of , , from (40) is
where the formulae for the determination of the coefficients , , , and density are given in Appendix A.
Using (42), conditions (34) will be written as follows:
We solve the above with respect to the Lagrange multipliers and . Then, using the sample , we can make the decision depending on which of the conditions (33) is satisfied.
- Note 1. Because of the specificity on the acceptance regions of the hypotheses, in the CBM, they can be intersected or their union may not lead to the entire observation space. Thus, the situation can arise such that none of the (12) hypotheses are accepted on the basis of the sample . In this case, we enhance the sequential approach, i.e., we increase the sample size by one and test hypotheses (12). If a unique decision is not made on the basis of the sample , we again increase its size by one, i.e., we obtain the sample and so on until a unique decision is made.
- Note 2. The decision-making procedure can be purely sequential when we start testing (12) hypotheses for . Otherwise, it is combined: after the original testing approach, if on the basis of observations a simple decision is not made, we adopt the sequential approach and proceed as above until a decision is made.
Notes 1 and 2 concern the Stein’s approach too, which is described below.
6.2. Using the Stein’s Approach
We generate the sample vectors , , , where is a -variate normal distribution. As a result, we have , , where the components of the vectors are independent and are given by the ratios
Here, is a one-dimensional normal distribution with zero mean and a variance equal to . Depending on which of equation from (5.8) we solve, takes values
under , , or hypotheses, respectively.
Let us suppose that for the vectors , , condition is fulfilled times; then, we have
where and , , are defined by (30).
By changing in , we achieve the fulfilment of the condition
where is the desired accuracy of the solution of the Equation (29).
For the next generated value and already determined , , we test the conditions (30) using distribution densities
That particular hypothesis is accepted which belongs to the acceptance region corresponding to it. If the accepted hypothesis is , a decision is correct; otherwise, the decision is incorrect.
If none of the hypotheses are accepted, a new random vector is generated. Then, the conditions of (30) are tested using (10) (in which ) until one of the tested hypotheses is not accepted.
- Note 3. The fact that is asymptotically normally distributed when is shown in [19], i.e.,
On the basis of this fact, for a quite big , we can test the directional hypotheses (11) using the CBM for the following conditional distributions, instead of (13), (16), and (17):
For testing hypotheses (12) using the maximum ratio test, we have to use the following densities:
Here, is a normal distribution with a mathematical expectation and variance .
7. Computation Results
The CBM 2 for both the maximum ratio test and for Stein’s approach with the uniform distribution of the densities of the parameter at the alternative specifications and was obtained through MATLAB R2021b codes, both for making computations and the investigation of the theoretical results, which are given above. The CBM with the maximum likelihood estimation using both densities (13) and (35) or densities (52) gives very unreliable results due to the informational closeness of the null and alternative hypotheses. Therefore, the computational results for only the Stein’s approach for both the cases when the densities are given by formulae (13), (16), and (17) as well as when they are given by formulae (49), (50), and (51) are given below. The Bayes method when the distribution densities are given by the formulae (49), (50), and (51) gives very unreliable results. Therefore, its results for only the distribution densities of (13), (16), and (17) are given below.
For the implementation of the CBM 2 using the Stein’s approach for testing the hypotheses of (11) for the distributions (13), (16), and (17), the following algorithm was used:
- Estimation of the parameter is computed by (7) using the sample .
- The values of the Lagrange multipliers , , and are determined by solving equations (29) using densities (13), (16), and (17); necessary integrals are computed by the Monte Carlo method.
- The sample with the size distributed by one of the distributions (13), (16), and (17), depending on which hypothesis we test, is used for making a decision using (30) acceptance regions for the hypotheses.
The same algorithm was used for testing (11) hypotheses in the second case where the densities (13), (16), and (17) were changed by the densities (49), (50), and (51).
Example: The results of testing (11) hypotheses using the CBM 2 (acceptance regions for the hypotheses are (30) where Lagrange multipliers are defined from (29)) or Bayes rules (hypotheses acceptance regions are (30) where Lagrange multipliers are equal to 1) for making a decision are given in Appendix B and Appendix C. The following notations are used there: AN—averaged number of observations necessary for making a decision; —the size of the observation vector; —the number of observations for computing the parameter’s estimation; —the value of the correlation coefficient at hypothesis ; , , and —Lagrange multipliers under hypotheses , , and , respectively; , , and —restriction levels in (29) determining probabilities of correct decisions at , , and , respectively; —the number of generated random variables for computing probabilities of acceptance of hypothesis under hypothesis , i.e., for computing probabilities , ; and Averaged—averaged values of the appropriate variables obtained at different computations (runs of the program) for one scenario.
In all computations presented in Appendix B and Appendix C, the following values were used: ; ; a priori probabilities of hypotheses 1/3, 1/3, and 1/3; ; and the accuracy of the solution of Equation (29) is equal to 0.001.
8. Discussion
The results of the computation showed the following characteristics of the considered problem.
When using the (13), (16), and (17) distribution laws in the CBM 2, the following was observed:
- Distribution laws (13), (16), and (17) are very close to each other for hypotheses (11), as can be seen from the computed values of the divergences between hypotheses and from their graphical representations given in Figure A1 of Appendix D.
- The minimum divergence between testing hypotheses that can be discriminated with given reliability decreases with increasing the size of the random vector. This fact is seen in Table of Appendix E and in the graphs of Figure A1.
- The absolute value of the difference between correlation coefficients corresponding to the null and alternative hypotheses equal to 0.05, i.e., , is sufficient in the CBM for making the correct decision with a high reliability for .
- For the case , which is computed in Appendix B, must be no less than 0.18 or 0.20 in the CBM for different values of for testing hypotheses with given reliabilities (equal to 0.05). The Bayes method does not guarantee the reliability of a decision equal to 0.05 for some divergences (see Appendix B).
- The number of observations necessary for making a decision is equal to 51.
- The number of observations for computing the parameter’s estimation is equal to 50.
- The Bayes method uses fifty observations for computing the estimation of and only one additional observation for making a decision. In general, it gives worse results than the CBM 2 (see Appendix B).
- Conditions (31) and (32) are fulfilled for the CBM 2. This is violated for the Bayes method for some values of .
For the practical use of the presented method when the alternative values of the correlation coefficient are not known for testing hypotheses, we use Lagrange multipliers computed for a divergence equal to 0.18 between correlation coefficients. In this case, the necessary reliability of the decisions made when the divergence between the correlation coefficients of null and alternative hypotheses is greater than 0.18 is guaranteed. This is due to the fact that with the increase in the informational distance between the hypotheses, the errors of the decisions made decrease [28,29].
The probabilities of correct decisions for the different values of and for different divergences between correlations of null and alternative hypotheses when the Lagrange multipliers correspond to 0.18—to the minimal value of the divergence—are given in Appendix E.
The following was found using the (49), (50), and (51) distribution densities in the CBM 2:
- It is seen from the (49), (50), and (51) formulae that the distribution densities depend on and (the last is ML estimator of ). Therefore, the computed values of , , and are the same for all possible alternative hypotheses and when given , and correct decisions are made with identical reliability in all cases.
- Based on what has been stated above, in practical applications, we compute the Lagrange multipliers for given and for the minimal distance between the (11) testing hypotheses (for example, equal to 0.05) and use them to test the hypothesis versus any possible and hypotheses.
- The number of observations necessary for making a decision is equal to 26 in the considered case.
- The number of observations for computing the parameter’s estimation, i.e., for , is equal to 15 in the considered case.
- Conditions (31) and (32) are fulfilled.
Despite that the divergences between distribution densities (49), (50), and (51) are also very close to each other for the (11) hypotheses, the CBM 2 using Stein’s approach for these distributions gives better results than the use of distribution laws (13), (16), and (17). The superiority is in the number of used observations, providing necessary reliabilities, and also in the convenience of implementation in practical situations. The basic superiority of this case is that for testing the (11) hypotheses the knowledge of is not necessary. Only the knowledge of and the Lagrange multipliers computed for the values are required, i.e., in its practical use, for any possible values of and -s, corresponding to alternative hypotheses and such that , the Lagrange multipliers are computed and they are used in real testing processes when the exact values of are not known but . Theorems confirming the convergence of the testing algorithms for both the (13), (16), and (17) and (49), (50), and (51) distribution densities can be found in [24,29]. Also, as was mentioned above, the results in Table A1 clearly demonstrate that conditions (31) and (32) are fulfilled for both cases.
Because the Bayes method yields very bad results when , for this case, the computation results of the Bayes method are not provided when the distributions are (49), (50), and (51).
- Note 4. Because the noted peculiarities remain in force for other possible values of , the computation results for only are given in Appendix C to conserve space.
It is worth separately noting the fact that the method proposed in this paper can achieve better results than other methods known to us for the considered problem [1,5,10]. For example, comparing the results given in Appendix C of this paper with the results of the beta-optimal methods given in Table 5 of [5] clearly shows the superiority of the proposed method. On the other hand, in [5] (see p. 87 “Summary”) it is mentioned that the beta-optimal methods outperform SenGupta’s test, but those are motivated differently.
9. Conclusions
Constrained Bayesian and classical Bayes methods, using the maximum likelihood estimation and Stein’s approach, for testing the equi-correlation coefficient of a standard symmetric multivariate normal distribution are developed and investigated. For the investigation of the obtained theoretical results and choosing the best among them, different practical examples are computed using computer codes developed in MATLAB R2021b. The simulation results showed that the CBM using Stein’s approach gives opportunities to make decisions with higher reliability for testing the (11) hypotheses than the Bayes method. Also, the CBM 2 using Stein’s approach with distribution densities (49), (50), and (51) gives better results in comparison with the (13), (16), and (17) densities in terms of the number of observations needed and providing the necessary reliabilities, as well the convenience of their implementations in practice. Recommendations and guidelines for the use of the proposed methods for solving practical problems are given.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K. and A.S.; methodology, K.K.; software, K.K.; validation, K.K. and A.S.; formal analysis, K.K. and A.S.; investigation, K.K.; resources, A.S.; data curation, K.K.; writing—original draft preparation, K.K.; writing—review and editing, A.S.; visualization, K.K.; supervision, A.S.; project administration, K.K.; funding acquisition, no funding. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All computations were made on the basis of simulated data, which can be repeated by any interested researcher based on the data described in Item 7.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. An Algorithm for Computation of (42) Distribution Function
The algorithm is developed on the basis of the results of [25].
Let us consider random variable
where
where and are determined by (37) and (39).
Then, the probability distribution function of is [25]
where
Appendix B. Stein’s and Bayes Methods Using Distributions (13), (16), and (17)
| (A). Hypothesis is true. The samples for making decisions are generated by (13) with the size . | ||||||||||||||||||||
50 | CBM | Bayes Method | ||||||||||||||||||
| AN | ||||||||||||||||||||
| −0.1 = 0.145 Averaged | (1) 51.0490 (2) 51.0569 (3) 51.0552 (4) 51.0520 (5) 51.0514 51.0529 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.9976 0.9974 0.9978 0.9966 0.9982 0.9975 | 0.0024 0.0014 0.0008 0.0009 0.0004 0.0012 | 0.3418/ 2.1034 × 10−14/ 0.2441 | 0.0008 0.0001 0.0004 0.0008 0.0001 0.00044 | 0.9850 0.9838 0.9864 0.9848 0.9828 0.9846 | 0.0142 0.0152 0.0132 0.0144 0.0162 0.01464 | ||||||||||||
| 0 = 0.18 Averaged | (1) 51.0052 (2) 51.0098 (3) 51.0092 (4) 51.0082 (5) 51.0083 51.00814 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.9582 0.9622 0.9590 0.9554 0.9568 0.95832 | 0.0418 0.0378 0.0410 0.0446 0.0432 0.04168 | 0.5310/ 0.0057/ 1.8768 | 0.0026 0.0022 0.0022 0.0018 0.0012 0.002 | 0.9782 0.9778 0.9786 0.9798 0.9792 0.97872 | 0.0192 0.0200 0.0192 0.0184 0.0196 0.01928 | ||||||||||||
| 0.1 = 0.18 Averaged | (1) 51 (2) 51.0053 (3) 51.0035 (4) 51.0027 (5) 51 51.0023 | 0.0056 0.0063 0.0042 0.0036 0.0074 0.00542 | 0.9534 0.9548 0.9522 0.9562 0.9550 0.95432 | 0.0410 0.0389 0.0436 0.0402 0.0376 0.04026 | 0.6836/ 2.9297/ 2.5635 | 0.0052 0.0034 0.0042 0.0040 0.0044 0.00424 | 0.9730 0.9728 0.9740 0.9746 0.9740 0.97368 | 0.0218 0.0238 0.0218 0.0214 0.0216 0.02208 | ||||||||||||
| 0.3 = 0.2 Averaged | (1) 51.0185 (2) 51.0225 (3) 51.0211 (4) 51.0202 (5) 51.0197 51.0204 | 0.0091 0.0050 0.0073 0.0077 0.0256 0.01094 | 0.9724 0.9877 0.9864 0.9878 0.9712 0.9811 | 0.0185 0.0073 0.0063 0.0045 0.0032 0.00796 | 0.8240/ 7.8125/ 0.6773 | 0.0052 0.0050 0.0054 0.0074 0.0068 0.00596 | 0.9722 0.9718 0.9698 0.9656 0.9676 0.9694 | 0.0226 0.0232 0.0248 0.0270 0.0256 0.02464 | ||||||||||||
| 0.5 = 0.2 Averaged | (1) 51.0269 (2) 51.0338 (3) 51.0327 (4) 51.0317 (5) 51.0314 51.0313 | 0.0055 0.0036 0.0030 0.0020 0.0016 0.00314 | 0.9742 0.9759 0.9698 0.9710 0.9742 0.97302 | 0 1.746 × 10−7 1.2001 × 10−11 1.5429 × 10−4 4.1067 × 10−5 | 0.9277/ 3.9063/ 0.0134 | 0.0066 0.0040 0.0048 0.0062 0.0060 0.00552 | 0.9692 0.9690 0.9666 0.9704 0.9680 0.96864 | 0.0242 0.0270 0.0286 0.0234 0.0260 0.02584 | ||||||||||||
| 0.7 = 0.18 Averaged | (1) 51.0368 (2) 51.0401 (3) 51.0396 (4) 51.0380 (5) 51.0368 51.03826 | 0.0012 0.0008 0.0002 0.0003 0.0002 0.00054 | 0.9988 0.9992 0.9998 0.9997 0.9998 0.99946 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.8789/ 0.2365/ 8.7041 × 10−10 | 0.0024 0.0038 0.0026 0.0044 0.0040 0.00344 | 0.9728 0.9738 0.9714 0.9712 0.9686 0.97156 | 0.0248 0.0224 0.0260 0.0244 0.0274 0.025 | ||||||||||||
| (B). Hypothesis is true. The samples for making decisions are generated by (10) with for the size . | ||||||||||||||||||||
50 | CBM | Bayes Method | ||||||||||||||||||
| AN | ||||||||||||||||||||
| −0.1 = 0.145 Averaged | (1) 51.0502 (2) 51.0583 (3) 51.0567 (4) 51.0549 (5) 51.0549 51.055 | 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.3422/ 2.1684 × 10−14/ 0.2756 | 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||||||||
| 0 = 0.18 Averaged | (1) 51.0560 (2) 51.0613 (3) 51.0606 (4) 51.0589 (5) 51.0538 51.058 | 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.5127/ 0.0054/ 2.0142 | 1 0.9996 1 0.9998 1 0.99988 | 0 0.0004 0 0.0002 0 0.00012 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||||||||
| 0.1 = 0.18 Averaged | (1) 51 (2) 51 (3) 51.0053 (4) 51.0035 (5) 51.0027 51.0023 | 0.9549 0.9555 0.9544 0.9541 0.9544 0.95466 | 0.0451 0.0445 0.0456 0.0459 0.0456 0.04534 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.6592/ 2.9297/ 2.5635 | 0.8868 0.8910 0.8986 0.8900 0.8922 0.89172 | 0.1132 0.1090 0.1014 0.1100 0.1078 0.10828 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||||||||
| 0.3 = 0.2 Averaged | (1) 51 (2) 51 (3) 51 (4) 51.0059 (5) 51.0039 51.00196 | 0.9566 0.9568 0.9533 0.9533 0.9536 0.95472 | 0.0372 0.0378 0.0402 0.0467 0.0464 0.04166 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.8423/ 7.8164/ 0.6580 | 0.8018 0.8122 0.8080 0.8068 0.8098 0.80772 | 0.1982 0.1878 0.1920 0.1932 0.1902 0.19228 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||||||||
| 0.5 = 0.2 Averaged | (1) 51 (2) 51.0054 (3) 51.0036 (4) 51.0027 (5) 51.0022 51.00278 | 0.9585 0.9568 0.9565 0.9561 0.9564 0.95686 | 0.0415 0.0432 0.0435 0.0439 0.0436 0.03484 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.9766/ 4.0893/ 0.0153 | 0.8978 0.8988 0.8998 0.8924 0.8934 0.89644 | 0.1022 0.1012 0.1002 0.1076 0.1066 0.10356 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||||||||
| 0.7 = 0.18 Averaged | (1) 51.0206 (2) 51.0271 (3) 51.0256 (4) 51.0260 (5) 51.0249 51.02484 | 0.9884 0.9891 0.9894 0.9896 0.9894 0.98918 | 0.0116 0.0109 0.0106 0.0104 0.0106 0.01082 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.8286/ 0.2651/ 8.5265 × 10−10 | 0.9898 0.9860 0.9854 0.9876 0.9872 0.9872 | 0.0102 0.0140 0.0146 0.0124 0.0128 0.0128 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||||||||
| (C). Hypothesis is true. The samples for making decisions are generated by (10) with for the size . | ||||||||||||||||||||
50 | CBM | Bayes Method | ||||||||||||||||||
| AN | ||||||||||||||||||||
| −0.1 = 0.145 Averaged | (1) 51.0414 (2) 51.0408 (3) 51.0452 (4) 51.0434 (5) 51.0420 51.04256 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.0060 0.0058 0.0050 0.0050 0.0072 0.0058 | 0.9940 0.9942 0.9950 0.9950 0.9928 0.9942 | 0.3296/ 2.4293 × 10−14/ 0.2632 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.0202 0.0158 0.0180 0.0204 0.0196 0.0188 | 0.9798 0.9842 0.9820 0.9796 0.9804 0.9812 | ||||||||||||
| 0 = 0.18 Averaged | (1) 51.0038 (2) 51.0089 (3) 51.0069 (4) 51.0061 (5) 51 51.00514 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.0446 0.0469 0.0473 0.0467 0.0457 0.04624 | 0.9554 0.9531 0.9527 0.9533 0.9543 0.95376 | 0.4883/ 0.0057/ 1.9531 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.0970 0.0888 0.0914 0.0912 0.0874 0.09116 | 0.9030 0.9112 0.9086 0.9088 0.9126 0.90884 | ||||||||||||
| 0.1 = 0.2 Averaged | (1) 51.0004 (2) 51.0053 (3) 51.0037 (4) 51.0030 (5) 51.0025 51.00298 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.0474 0.0497 0.0442 0.0480 0.0488 0.04762 | 0.9526 0.9503 0.9558 0.9520 0.9512 0.95238 | 0.6348/ 0.7334/ 1.5869 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.0858 0.0870 0.0826 0.0734 0.0836 0.08248 | 0.9142 0.9130 0.9174 0.9266 0.9164 0.91752 | ||||||||||||
| 0.3 = 0.2 Averaged | (1) 51.0336 (2) 51.0336 (3) 51.0393 (4) 51.0372 (5) 51.0384 51.03642 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.0304 0.0284 0.0275 0.0289 0.0294 0.02892 | 0.9696 0.9716 0.9725 0.9711 0.9706 0.97108 | 0.8446/ 7.0801/ 0.6084 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.0404 0.0376 0.0348 0.0370 0.0382 0.0376 | 0.9596 0.9624 0.9652 0.9630 0.9618 0.9624 | ||||||||||||
| 0.5 = 0.18 Averaged | (1) 51.0734 (2) 51.0845 (3) 51.0790 (4) 51.0789 (5) 51.0781 51.07878 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0.0002 0.0006 0.0004 0.0003 0.0004 0.00038 | 0.9998 0.9996 0.9996 0.9997 0.9996 0.99966 | 0.8667/ 4.5166/ 0.0143 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0.0002 0 0.0004 0.0002 0.00016 | 1 0.9998 1 0.9996 0.9998 0.99984 | ||||||||||||
| 0.7 = 0.18 Averaged | (1) 51.0840 (2) 51.0911 (3) 51.0863 (4) 51.0860 (5) 51.0851 51.0865 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 0.7813/ 0.2518/ 7.9581 × 10−10 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 1 1 1 1 1 1 | ||||||||||||
Appendix C. Stein’s Method Using Distributions (49), (50), and (51)
| (A). Hypothesis is true. The samples for making decisions are generated by (see (49)) with the size . | ||||||||||
15 | CBM | |||||||||
| AN | ||||||||||
| = 0.05 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0506 (2) 26.0635 (3) 26.0563 (4) 26.0542 (5) 26.0540 6.05572 | 0.0071 0.0020 0.0017 0.0010 0.0016 0.00268 | 0.9810 0.9780 0.9770 0.9750 0.9710 0.9764 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 7.3590087890625/ 2.298583984375/ 0.58624267578125 | |||||
| = 0.10 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0618 (2) 26.0569 (3) 26.0538 (4) 26.0516 (5) 26.0512 26.05506 | 0.0036 0.0031 0.0010 0.0010 0.0012 0.00198 | 0.9730 0.9680 0.9820 0.9780 0.9750 0.9752 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||
| = 0.15 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0653 (2) 26.0592 (3) 26.0580 (4) 26.0596 (5) 26.0587 26.06016 | 0.0031 0.0014 0.0015 0.0004 0.0010 0.00148 | 0.9780 0.9779 0.9740 0.9790 0.9760 0.97698 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||
| = 0.20 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0565 (2) 26.0562 (3) 26.0567 (4) 26.0557 (5) 26.0556 26.05614 | 0.0007 0.0005 0.0006 0.0004 0.0004 0.00052 | 0.9800 0.9830 0.9760 0.9780 0.9780 0.9790 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||
| = 0.249 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0564 (2) 26.0556 (3) 26.0558 (4) 26.0559 (5) 26.0557 26.05588 | 0.0007 0.0002 0.0007 0.0006 0.0003 0.0005 | 0.9750 0.9780 0.9860 0.9680 0.9730 0.9760 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||
| —the number of observations distributed in accordance with , the arithmetic mean of which is used for making a decision. —the number of observations used for the computation of ML estimator . | ||||||||||
| (B). Hypothesis is true. The samples for making decisions are generated by (see (50)) with for the size . | ||||||||||
15 | CBM | |||||||||
| AN | ||||||||||
| = 0.05 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0530 (2) 26.0570 (3) 26.0497 (4) 26.0475 (5) 26.0476 26.05096 | 0.9960 0.9985 0.9957 0.9960 0.9960 0.99644 | 0.0040 0.0040 0.0050 0.0030 0.0040 0.0040 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 7.3590087890625/ 2.298583984375/ 0.58624267578125 | |||||
| = 0.10 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0397 (2) 26.0340 (3) 26.0298 (4) 26.0445 (5) 26.0560 26.0408 | 0.9967 0.9971 0.9975 1 1 0.99826 | 4.003 × 10−6 4.003 × 10−6 4.003 × 10−6 0 0 2.4018 × 10−6 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||
| = 0.15 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0297 (2) 26.0223 (3) 26.0178 (4) 26.0148 (5) 26.0127 26.01946 | 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | ||||||
| —the number of observations distributed in accordance with , , the arithmetic mean of which is used for making a decision. —the number of observations used for the computation of ML estimator . | ||||||||||
| (C). Hypothesis is true. The samples for making decisions are generated by (see (51)) with for the size . | ||||||||||
15 | CBM | |||||||||
| AN | ||||||||||
| = 0.05 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0126 (2) 26.0126 (3) 26.0125 (4) 26.0124 (5) 26.0123 26.01248 | 2.0298 × 10−5 2.8654 × 10−5 4.0069 × 10−5 5.5761 × 10−5 7.7157 × 10−5 4.43878 × 10−5 | 0.0390 0.0450 0.0470 0.0351 0.0410 0.04142 | 0.9945 0.9881 0.9789 0.9741 0.9686 0.98084 | 7.3590087890625/ 2.298583984375/ 0.58624267578125 | |||||
| = 0.10 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0274 (2) 26.0209 (3) 26.0168 (4) 26.0140 (5) 26.0119 26.0182 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 4.6000 × 10−8 4.6000 × 10−8 4.6000 × 10−8 4.6000 × 10−8 4.6000 × 10−8 4.6000 × 10−8 | 0.9516 0.9631 0.9704 0.9753 0.9789 0.96786 | ||||||
| = 0.15 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0367 (2) 26.0244 (3) 26.0183 (4) 26.0147 (5) 26.0122 6.02126 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 1.4000 × 10−5 1.4000 × 10−5 1.4000 × 10−5 1.4000 × 10−5 1.4000 × 10−5 1.4000 × 10−5 | 0.9930 0.9953 0.9965 0.9972 0.9977 0.99594 | ||||||
| = 0.20 25 Averaged | (1) 26.0440 (2) 26.0293 (3) 26.0220 (4) 26.0176 (5) 26.0147 6.02552 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 0 0 | 1 1 1 1 1 1 | ||||||
| —the number of observations distributed in accordance with , , the arithmetic mean of which is used for making a decision. —the number of observations used for the computation of ML estimator . | ||||||||||
Appendix D. The Kullback–Leibler Divergence Between the Distributions Corresponding to the Basic and Alternative Hypotheses
The formula for computing the Kullback–Leibler divergence [29] between the distributions corresponding to the basic and alternative hypotheses (11) has the following form:

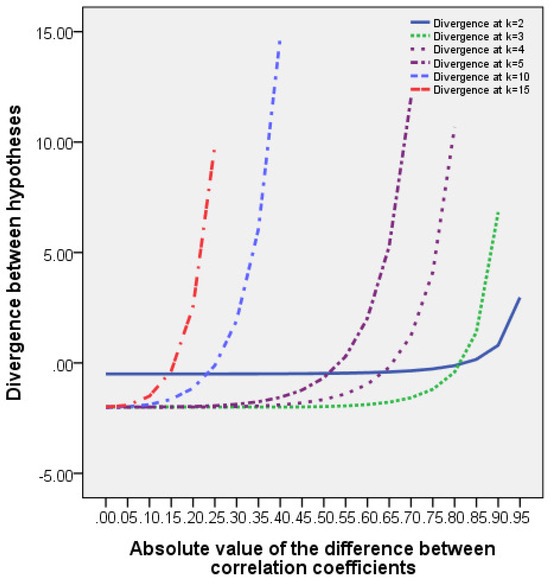
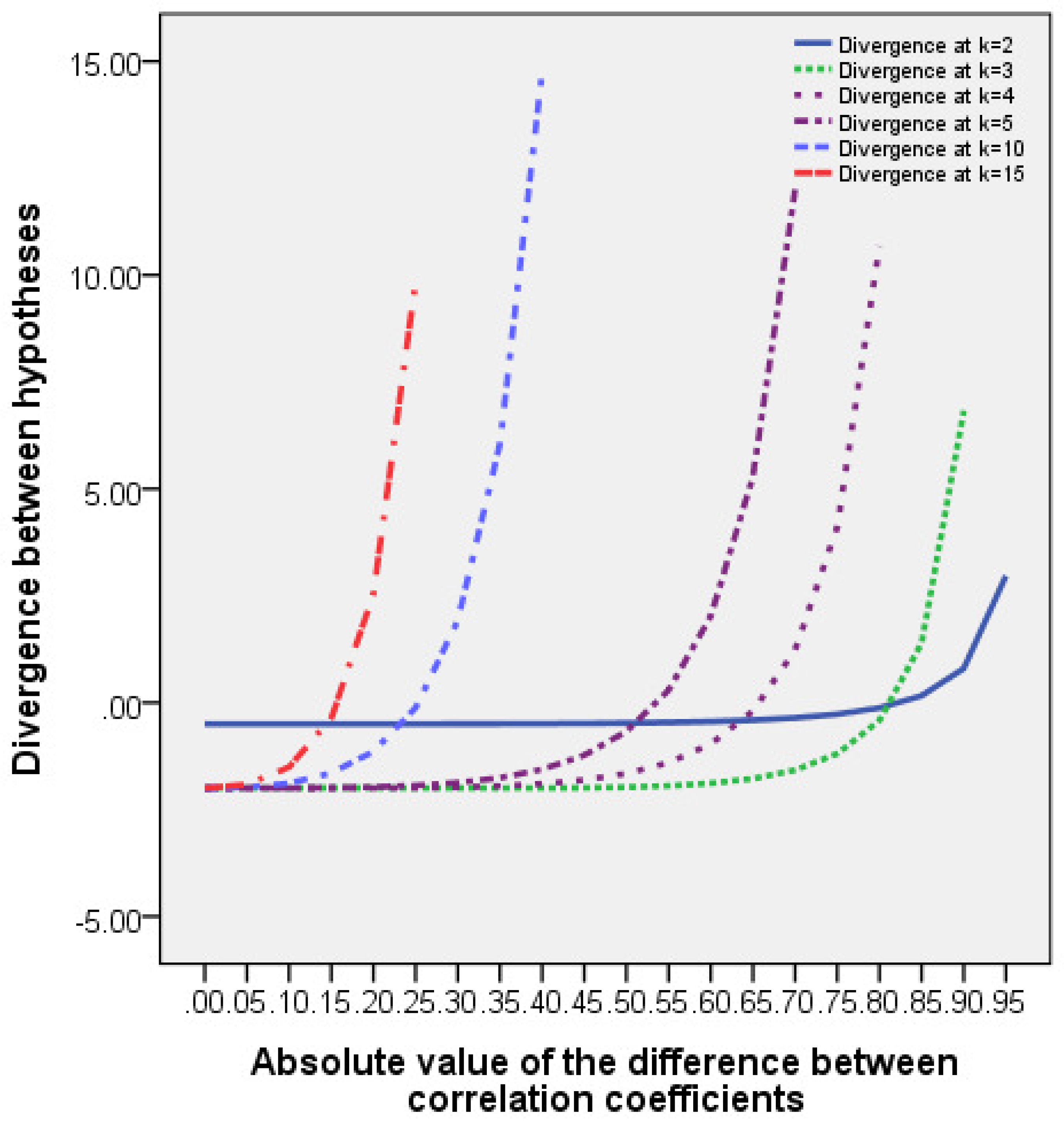

Table A1.
The Kullback–Leibler divergence between the considered distributions.
Table A1.
The Kullback–Leibler divergence between the considered distributions.
| Absolute Value of the Difference between Correlation Coefficients | Divergence between Hypotheses | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| —Dimension of the Random Vector | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
| 0 | −0.500000 | −2 | −2 | −2 | −2 | −2 |
| 0.05 | −0.499998 | −1.998452 | −1.999800 | −1.999868 | −1.978545 | −1.913498 |
| 0.10 | −0.499975 | −1.996207 | −1.999897 | −1.9981428 | −1.884038 | −1.508130 |
| 0.15 | −0.499870 | −1.994991 | −1.999923 | −1.991384 | −1.647123 | −0.361850 |
| 0.20 | −0.499578 | −1.995222 | −1.998287 | −1.974225 | −1.140647 | 2.5478240 |
| 0.25 | −0.498936 | −1.996664 | −1.992357 | −1.938667 | −0.118422 | 9.863595 |
| 0.30 | −0.497705 | −1.998624 | −1.978181 | −1.872546 | 1.921221 | 28.907530 |
| 0.35 | −0.495539 | −1.999952 | −1.949830 | −1.756739 | 6.057835 | 81.612806 |
| 0.40 | −0.491939 | −1.998882 | −1.898169 | −1.560040 | 14.7615462 | 239.804571 |
| 0.45 | −0.486178 | −1.992709 | −1.808639 | −1.229397 | 34.099183 | 764.261963 |
| 0.50 | −0.477174 | −1.977174 | −1.657081 | −0.670322 | 80.263477 | 2723.863943 |
| 0.55 | −0.463281 | −1.945327 | −1.401508 | 0.294955 | 200.982274 | 1.118287 × 104 |
| 0.60 | −0.441894 | −1.885285 | −0.964754 | 2.023792 | 554.973471 | 5.477538 × 104 |
| 0.65 | −0.408723 | −1.775568 | −0.194875 | 5.296226 | 1755.615892 | 3.355081 × 105 |
| 0.70 | −0.356280 | −1.574484 | 1.234836 | 12.003869 | 6677.652705 | 2.750979 × 106 |
| 0.75 | −0.270482 | −1.193147 | 4.113706 | 27.420558 | 32759.954823 | 3.3554421 × 107 |
| 0.80 | −0.121937 | −0.415705 | 10.684338 | 69.403428 | 2.325059 × 105 | 7.2660899 × 108 |
| 0.85 | 0.160835 | 1.394187 | 29.065156 | 218.913453 | 2.955932 × 106 | 3.8925993 × 1010 |
| 0.90 | 0.801213 | 6.830008 | 103.504803 | 1080.614380 | 1.086956 × 108 | 1.086957 × 1013 |
| 0.95 | 2.964254 | 36.955242 | 827.124043 | 16,658.959510 | 5.333333 × 1010 | 1.706667 × 1017 |

Figure A1.
Dependence of the divergence between hypotheses on the difference between correlation coefficients, i.e., on , for different -dimensions of the random vector.
Figure A1.
Dependence of the divergence between hypotheses on the difference between correlation coefficients, i.e., on , for different -dimensions of the random vector.

Appendix E. The Probabilities of Correct Decisions for the Different Values of and for the Different Divergences Between Correlations of Basic and Alternative Hypotheses When the Lagrange Multipliers Correspond to the Minimal Value of the Divergence Equal to 0.20
| Probabilities of correct decisions | |||||
| 0.20 | 0.9814/0.9724/0.9708 | 0.9732/0.9769/0.9998 | 0.145 | 0.9670/1 | 0.9776/1 |
| 0.25 | 0.9810/0.9760/0.9694 | 0.9842/0.9794/0.9999 | 0.146 | 0.9681/1 | 0.9754/1 |
| 0.30 | 0.9774/0.9774/0.9716 | 0.9892/0.9815/0.99993 | 0.147 | 0.9701/1 | 0.9792/1 |
| 0.35 | 0.9776/0.9762/0.9708 | 0.9919/0.9832/0.99995 | 0.148 | 0.9712/1 | 0.9794/1 |
| 0.40 | 0.9804/0.9766/0.9658 | 0.9935/0.9846/0.99996 | 0.149 | 0.9712/1 | 0.9752/1 |
| 0.45 | 0.9780/0.9760/0.9684 | 0.9946/0.9858/0.99997 | |||
| 0.50 | 0.9788/0.9760/0.9684 | 0.9953/0.9868/0.99997 | |||
References
- SenGupta, A. On Tests for Equi-correlation Coefficient of a Standard Symmetric Multivariate Normal Distribution. Aust. J. Stat. 1987, 29, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.K.; Mukhopadhyay, N. Two-stage fixed-width and bounded-width confidence interval estimation methodologies for the common correlation in an equi-correlated multivariate normal distribution. Seq. Anal. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SenGupta, A.; Pal, C. Locally Optimal Test for no Contamination in Standard Symmetric Multivariate Normal Mixtures. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 1991, 29, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SenGupta, A.; Pal, C. Optimal Tests for No Contamination in Symmetric Multivariate Normal Mixtures. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1993, 45, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.I.; King, M.L. A Beta-optimal Test of the Equicorrelation Coefficient. Aust. J. Stat. 1990, 32, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.R. Linear Statistical Inference and Its Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B. Defining the curvature of a statistical problem. Ann. Stat. 1975, 3, 1189–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderssen, S. Invariant normal models. Ann. Stat. 1976, 3, 132–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, A.R. Stepwise BAN estimators for exponential families with multivariate normal applications. J. Multivar. Anal. 1976, 6, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalanobis, P.C. A Sample Survey of the Acreage Under Jute in Bengal. Sankhya 1940, 4, 511–530. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, M.I. On optimal testing for the equality of Equi-correlation: An example of loss in power. Stat. Pap. 2000, 41, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, N.; De Silva, B.M. Sequential Methods and Their Applications; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zacks, S. The Exact Distributions of the Stopping Times and Their Functionals in Two-Stage and Sequential Fixed-Width Confidence Intervals of the Exponential Parameter. Seq. Anal. 2009, 28, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Mukhopadhyay, N. A General Sequential Fixed-Accuracy Confidence Interval Estimation Methodology for a Positive Parameter: Illustrations Using Health and Safety Data. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 2016, 68, 541–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, A.R. Simple BAN estimators of correlations for certain multivariate normal models with known variances. J. Amer. Stat. Assoc. 1978, 73, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.K.; Sen, P.K. Handbook of Sequential Analysis; Edited volume; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, M.; Mukhopadhyay, N.; Sen, P.K. Sequential Estimation; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- De, S.K.; Mukhopadhyay, N. Fixed Accuracy Interval Estimation of the Common Variance in an Equi-Correlated Normal Distribution. Seq. Anal. 2015, 34, 364–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacks, S.; Ramig, P.F. Confidence Intervals for the Common Variance of Equicorrelated Normal Random Variables. In Contributions to the Theory and Applications of Statistics, Volume in Honor of Herbert Solomon; Gelfand, A.E., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 511–544. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, S. Distributions of Maximal Invariants Using Quotient Measures. Ann. Stat. 1982, 10, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijsman, R.A. Cross-Sections of Orbits and Their Application to Densities of Maximal Invariants. In Proceedings of the 5th Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Berkeley, CA, USA, 21 June–18 July 1965 and 27 December 1965–7 January 1966; Volume 1, pp. 389–400. [Google Scholar]
- Kachiashvili, K.J. Constrained Bayesian Methods of Hypotheses Testing: A New Philosophy of Hypotheses Testing in Parallel and Sequential Experiments; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kachiashvili, K.J. Testing Statistical Hypotheses with Given Reliability; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kachiashvili, K.J.; Kachiashvili, J.K.; Prangishvili, I.A. CBM for Testing Multiple Hypotheses with Directional Alternatives in Sequential Experiments. Seq. Anal. 2020, 39, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleiss, J.L. On the Distribution of a Linear Combination of Independent Chi Squares. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. Theory Method 1971, 66, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, H.; Stephens, M.A. Distribution of a Sum of Weighted Chi-Square Variables. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. Theory Method 1977, 72, 881–885. [Google Scholar]
- Moschopoulos, P.G.; Canada, W.B. The distribution function of a linear Combination of Chi-Squares. Comput. Math. Appl. 1984, 10, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.A. On the Distribution of Linear Combinations of Chi-Square Random Variables. In Computational and Methodological Statistics and Biostatistics: Contemporary Essays in Advancement; Bekker, A., Chen, D., Ferreira, J., Eds.; Emerging Topics in Statistics and Biostatistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullback, S. Information Theory and Statistics; Mass. Peter Smith: Gloucester, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
